Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative stainingCite this page: Pernick N. PAX2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainspax2.html. Accessed May 13th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Paired-box 2; nuclear transcription factor, structurally similar to PAX8 with virtually identical expression in nonneoplastic tissue
- Essential in embryonic development of Müllerian organs and hindbrain
- Suppressed through promoter methylation at later stages of embryonic development but is reactivated during carcinogenesis (J Cell Mol Med 2013;17:1048)
Clinical features
- PAX2 mutations are associated with kidney hypoplasia (J Am Soc Nephrol 2001;12:1769), including renal-coloboma syndrome (Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2013;17:786)
Uses by pathologists
- Nuclear stain
- Cervix: help distinguish benign cervical mesonephric and Müllerian glandular lesions (PAX2+) from endocervical adenocarcinoma, including minimal deviation adenocarcinoma (PAX2-, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:137)
- CNS: differentiate hemangioblastoma (PAX2-, PAX8-, inhibinA+) from metastatic renal cell carcinoma (PAX2+ or PAX8+, inhibin-, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:262) but hemangioblastoma is rarely PAX2+ (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:1953)
- GU: determine whether tumors are of renal, Müllerian or Wolffian duct origin
- Kidney: renal cell carcinoma - confirm diagnosis in cytology specimens (Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40:667)
- Uterus: may be helpful in diagnosis of EIN (usually negative, with background normal glands as internal positive control, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:678)
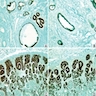
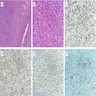
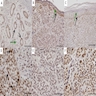
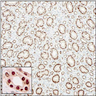
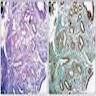
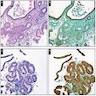
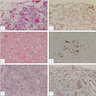
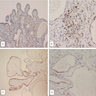
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Fallopian tube
- Prostate: epithelium of seminal vesicle and ejaculatory duct (Hum Pathol 2010;41:1145)
- Testis: rete testis
- Uterus: most epithelial cells of endocervix, endometrium (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1837)
Positive staining - disease
- Müllerian tumors: variable sensitivity but less than PAX8 (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1837)
- Cervix: mesonephric remnants and hyperplasia (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:137)
- CNS: medulloblastoma (Int J Oncol 2012;41:235)
- Fallopian tube: endosalpingiosis, paratubal cyst
- Kidney: renal cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1462), primary and metastatic renal tumors, although PAX8 is more sensitive (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:1541)
- Kidney: mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1264), Wilm tumor (epithelial and blastema components, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1186)
- Kidney: variable staining of B cell ALL and rhabdomyosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1186)
- Nephrogenic metaplasia / adenoma of GU tract (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:47, Mod Pathol 2006;19:356, Mod Pathol 2013;26:792)
- Urethra: clear cell adenocarcinoma
- Uterus: endometrial polyp, endometriosis
Negative staining
- Adenomatoid tumor
- Bladder: clear cell adenocarcinoma (usually)
- Kidney: angiomyolipoma with epithelial cysts and synovial sarcoma are negative but PAX2 and PAX8 often positive in epithelial cysts, likely due to entrapment and dilation of renal tubules (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1264)
- Kidney: carcinoid
- Kidney: Ewing / PNET, neuroblastoma, T ALL
- Mesothelioma (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:272)
- Testis: normal seminiferous tubules or interstitium; germ cell tumors, Leydig cell tumors, Sertoli cell tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1473)
- Uterus: usually (71%) loss of PAX2 staining