Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Yoda R, Cimino PJ. Hemangioblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorhemangioblastoma.html. Accessed September 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, slowly growing, highly vascular neoplasm containing neoplastic stromal cells which usually involves the cerebellum, brainstem or spinal cord
- Generally associated with loss or inactivation of the VHL gene, with frequent occurrence in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease (Am J Clin Pathol 1997;107:459)
Essential features
- Circumscribed, enhancing solid cystic mass, most frequently located in the cerebellum and observed as a cyst with enhancing mural nodule (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992;13:1343)
- Composed of neoplastic stromal cells with foamy cytoplasm within a background network of numerous small vessels
- Associated with loss of function of VHL, with frequent occurrence in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease (Am J Clin Pathol 1997;107:459)
- Other neoplasms associated with VHL may be histologic mimics (e.g. clear cell renal cell carcinoma, paraganglioma, pheochromocytoma)
- WHO grade 1
Terminology
- Hemangioblastoma
- Capillary hemangioblastoma (not recommended)
- Lindau tumor (not recommended)
- Angioblastoma (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9161/1 - hemangioblastoma
- ICD-10:
- D33.0 - benign neoplasm of brain, supratentorial
- D33.1 - benign neoplasm of brain, infratentorial
- D33.2 - benign neoplasm of brain, unspecified
- D33.3 - benign neoplasm of cranial nerves
- D33.4 - benign neoplasm of spinal cord
- D33.7 - benign neoplasm of other specified parts of central nervous system
- D33.9 - benign neoplasm of central nervous system, unspecified
- ICD-11:
Epidemiology
- 0.141 per 100,000 person years (Front Oncol 2020;10:570103)
- Cerebellar
- ~1 - 2% of primary CNS tumors (Surg Neurol 1977;7:79)
- ~7 - 12% of primary posterior fossa tumors (Surg Neurol 1977;7:79)
- Spinal
- ~2% of spinal tumors (Neuroepidemiology 2016;46:14)
- Genetics
- ~70% sporadic (J Neurosurg 1989;70:24, Neurosurgery 2001;48:55)
- ~30% familial with VHL syndrome (J Neurosurg 1989;70:24, Neurosurgery 2001;48:55)
- Mean age at presentation (J Neurosurg 1989;70:24)
- Sporadic ~47 yrs
- VHL ~29 yrs
- Sex: M:F = 1 - 1.25:1 (Neuroepidemiology 2016;46:14, Front Oncol 2020;10:570103)
Sites
- Occur throughout the central nervous system
- Common: cerebellum > brainstem > spinal cord (Front Oncol 2020;10:570103)
- Rare: cerebrum, peripheral nervous system (J Neurosurg 2014;120:1055)
- VHL syndrome - multiple hemangioblastomas (Neurosurgery 2001;48:55, J Neurosurg 2014;120:1055)
Pathophysiology
- VHL loss of function implicated in most cases
- Normal VHL protein (pVHL)
- Regulates cell cycle (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:993)
- Regulates cellular hypoxia signaling via the HIF (hypoxia inducible factor) complex, which under hypoxic conditions leads to enhanced levels of growth factors (e.g. vascular endothelial factor, platelet derived growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha) (Nat Rev Cancer 2015;15:55)
- Pseudohypoxia hypothesis
- Loss of function of VHL → loss of regulation of HIF complex → increased expression of growth factors in absence of hypoxia → increased angiogenesis and tumor growth (Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;24:957)
- VHL syndrome (Eur J Hum Genet 2011;19:617)
- Autosomal dominant tumor predisposition syndrome resulting from inactivating germline mutation in the VHL tumor suppressor gene
- Biallelic VHL inactivation
- Normal VHL protein (pVHL)
Etiology
- Sporadic: up to 78% of sporadic cases with VHL loss of function (J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:644, Cancer Res 1998;58:504, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2014;2:167)
- Familial (VHL syndrome): ~60% of VHL disease patients develop hemangioblastoma (J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:758)
Clinical features
- Symptoms
- General
- Increased intracranial pressure / hydrocephalus (J Neurosurg 2008;108:210)
- Secondary polycythemia due to erythropoietin production (Neurosurgery 2013;72:930, Blood 1998;92:3388, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992;13:1343)
- Hemorrhage (World Neurosurg 2015;83:1180.e13, Neurosurgery 2005;57:71, Neurosurg Rev 2010;33:11)
- Cerebellar
- Dysmetria, ataxia (J Neurosurg 2008;108:210)
- Spinal
- Pain, hypesthesia, incontinence (Neurosurgery 2001;49:321, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22:206)
- VHL syndrome sites of involvement (Eur J Hum Genet 2011;19:617)
- CNS: hemangioblastoma
- Retina: hemangioblastoma
- Head / neck: paraganglioma
- Kidney: clear cell renal cell carcinoma, cysts
- Adrenal: pheochromocytoma
- Pancreas: neuroendocrine islet cell tumor, cysts
- Inner ear: endolymphatic sac tumor
- Epididymis: papillary cystadenoma
- Broad ligament: cystadenoma
- General
Diagnosis
- Based on histologic and immunophenotypic features (Acta Neuropathol 2013;125:333)
- Clinical history of VHL syndrome or evidence of genetic alterations leading to VHL inactivation is supportive
Laboratory
- Secondary polycythemia (~5 - 40% of cases) (Neurosurgery 2013;72:930, Blood 1998;92:3388, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992;13:1343)
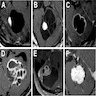
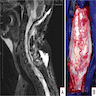
Radiology description
- General
- Well demarcated enhancing mass ranging from solid to cystic, frequently presenting as a cyst with an enhancing mural nodule (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992;13:1343)
- Spinal cord tumors often associated with syrinx (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1989;152:1087)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Nodule: T1 hypointense to isointense, T2 hyperintense (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992;13:1343)
- Serpentine flow voids in the nodular portion (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992;13:1343)
- Often abuts the pia (Cancer Imaging 2012;12:237)
- Cyst wall rarely enhances (Cancer Imaging 2012;12:237)
- Computed tomography
- Mural nodule is isodense to the brain on noncontrast scans (J Comput Assist Tomogr 1982;6:912)
- Calcification usually absent (J Comput Assist Tomogr 1982;6:912)
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis with complete surgical resection (Childs Nerv Syst 2020;36:2537, JAMA Neurol 2018;75:620, J Neurosurg 2008;108:210)
- Outcome better in sporadic cases than in VHL syndrome cases (Brain Tumor Pathol 2000;17:111)
Case reports
- 41 year old man with a family history of VHL syndrome and a synonymous VHL mutation (BMC Med Genet 2020;21:42)
- 42 year old man with cerebellopontine angle tumor (Surg Neurol Int 2017;8:264)
- 54 year old woman with a past medical history of VHL syndrome and bilateral clear cell renal cell carcinoma found to have an enhancing intramedullary mass at C6 / C7 (J Clin Neurosci 2015;22:215)
- 63 year old man with suspected posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm (World Neurosurg 2019;122:165)
Treatment
- Surgical resection - standard of care (JAMA Neurol 2018;75:620)
- Stereotactic radiosurgery may provide some control for unresectable tumors but data on safety and long term efficacy is limited (J Neurosurg 2015;122:1469, Neuro Oncol 2010;12:80)
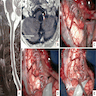
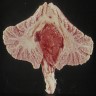
Gross description
- Solid or cystic with mural nodule (J Neurosurg 2003;98:82)
- Well circumscribed and pseudoencapsulated
- Highly vascular
- Red with yellow / orange cut surface regions attributed to lipid content
Gross images
Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images
Microscopic (histologic) description
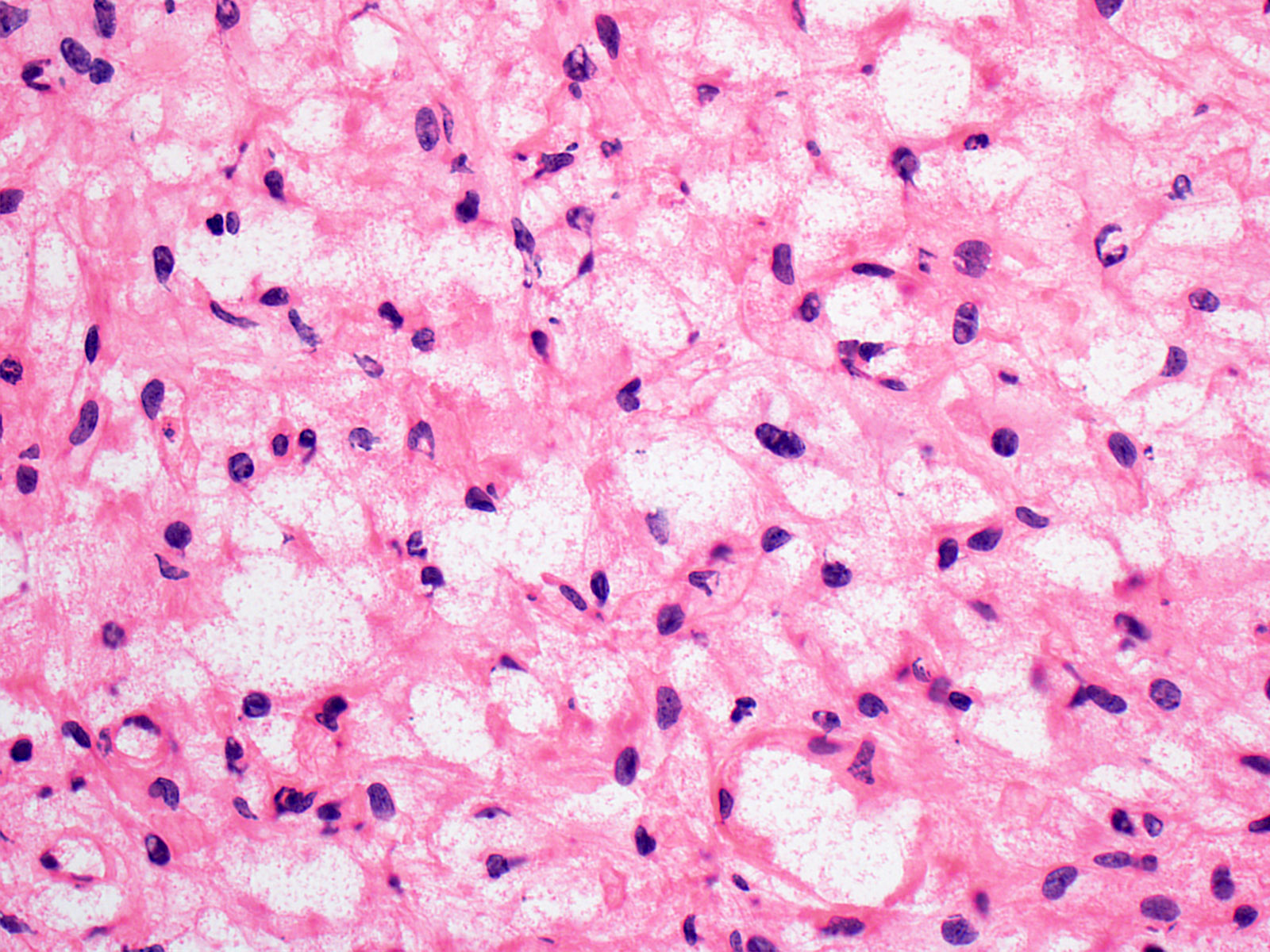
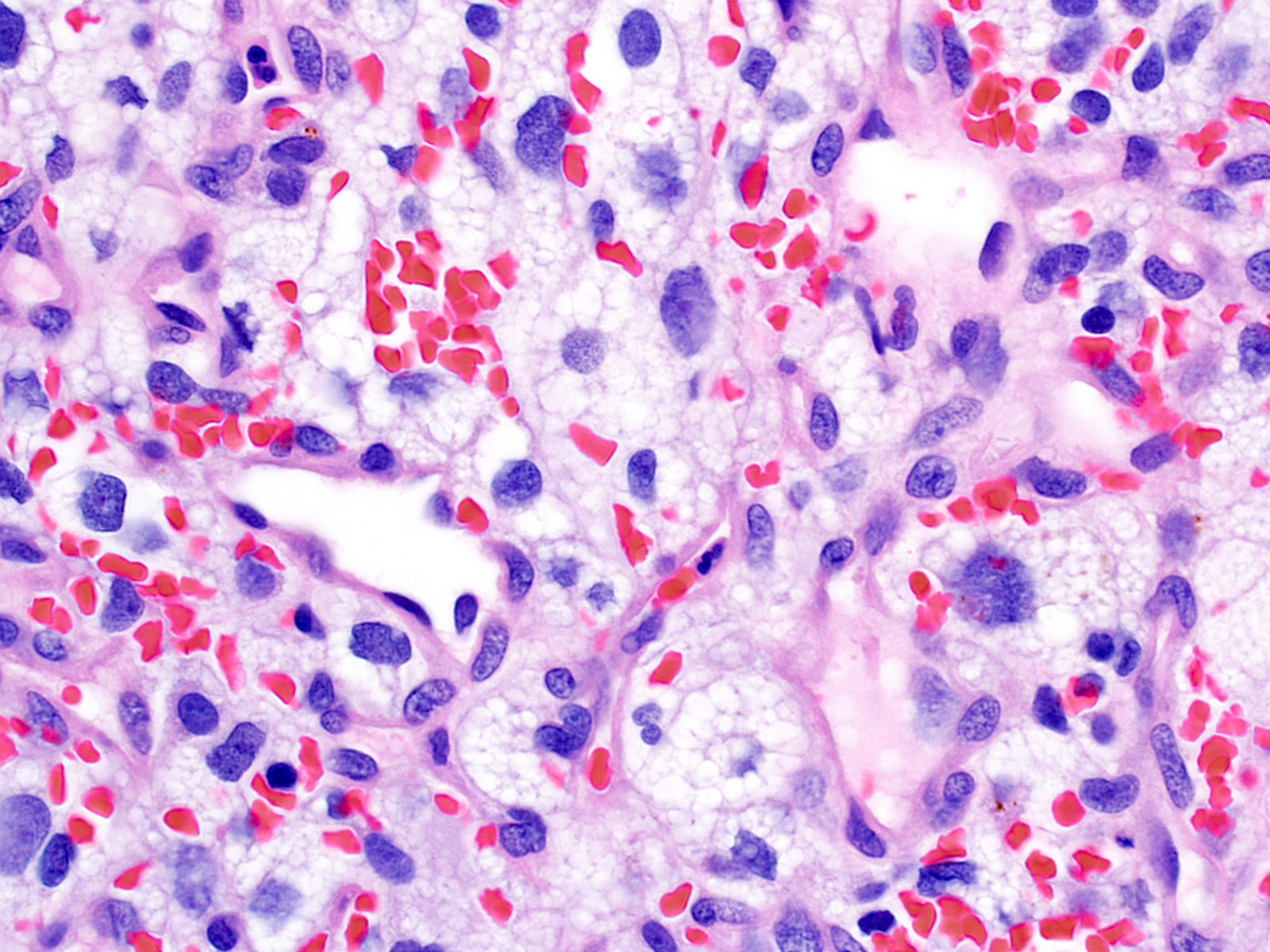
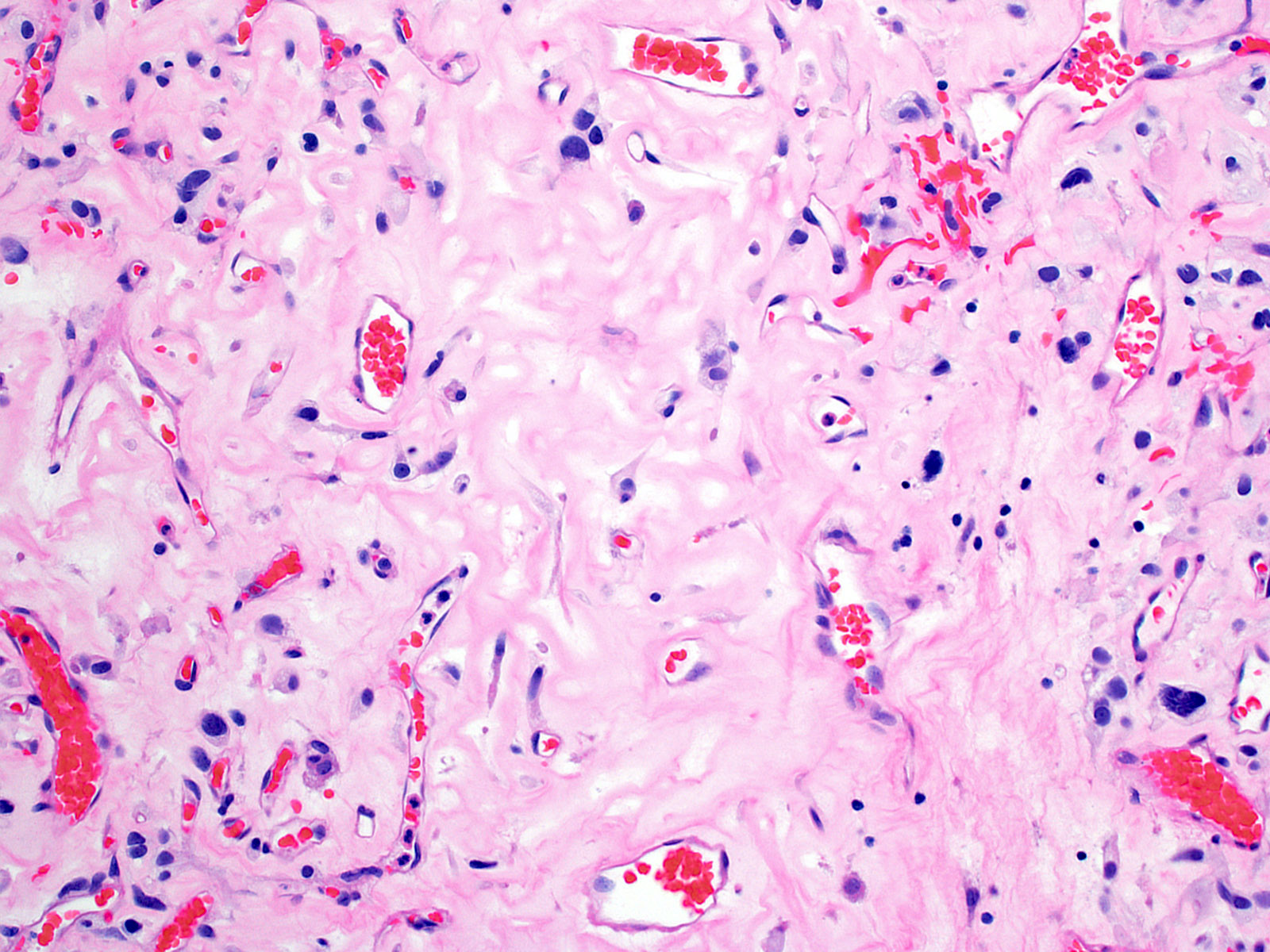
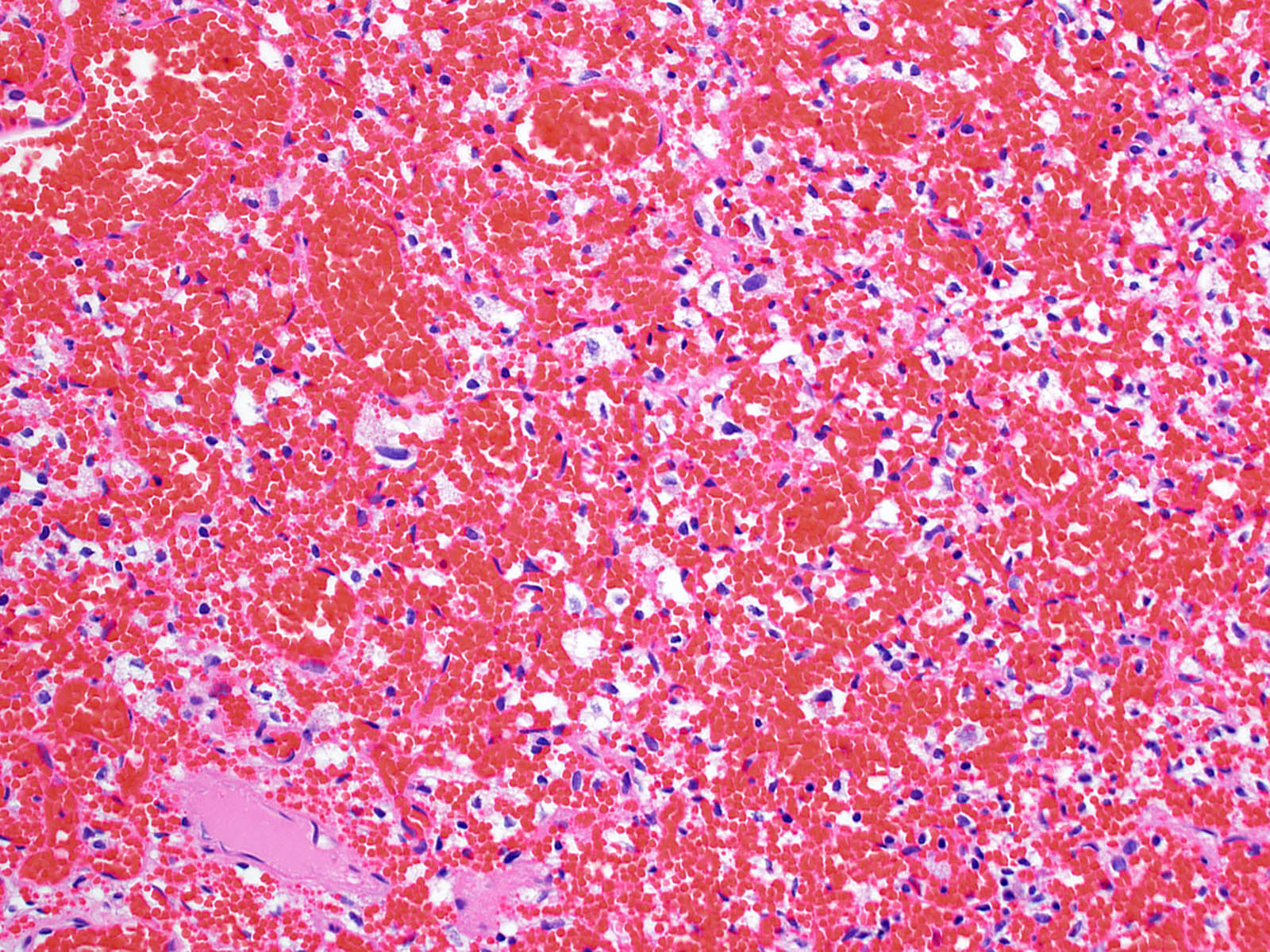
- Architecture (Acta Neuropathol 2013;125:333)
- Composed of neoplastic stromal cells arranged between numerous small vessels
- Compact, generally noninfiltrative growth with variable lobularity
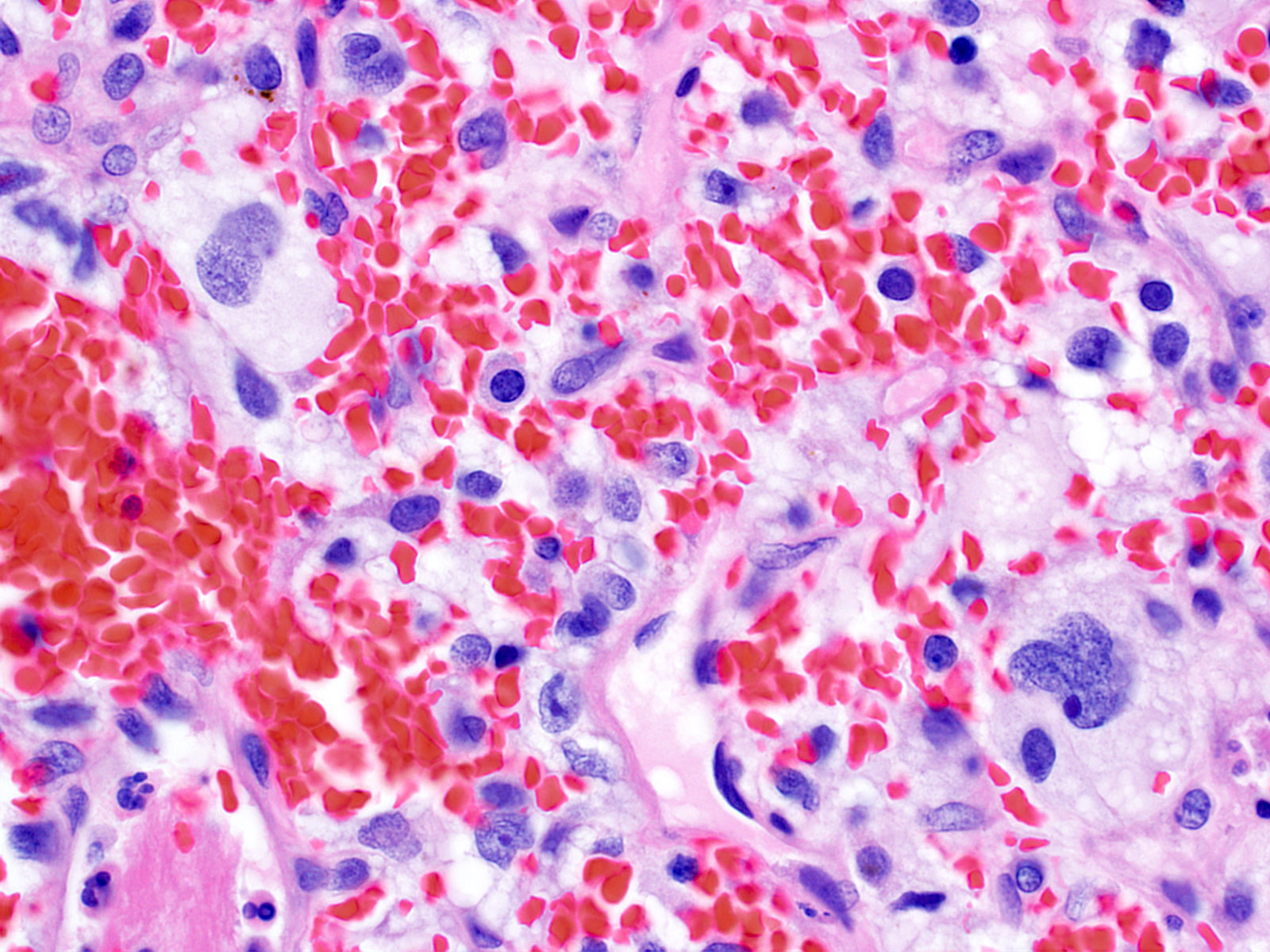
- Stromal component
- Mild nuclear pleomorphism with degenerative atypia
- Clear, foamy cytoplasm with lipid containing vacuoles
- Rare hyaline globules
- Vascular component
- Numerous thin walled vessels
- Well demarcated border with neoplasm
- Other findings
- Mitotic figures rare to absent
- Intratumoral hemorrhage
- Mast cells
- Cyst-like spaces
- Adjacent parenchyma may have piloid gliosis with Rosenthal fibers
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis (~15%) (Neurosurgery 1991;29:34)
- Histologic variants
- Reticular (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2005;31:618)
- Capillaries > stromal cells
- More common
- Cellular (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2005;31:618)
- Stroma cells > capillaries
- Less common
- Reticular (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2005;31:618)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Generally resistant to smear (squash preparation), resulting in larger tissue clumps
- Successful cytologic smear preparations include the following (Acta Cytol 1998;42:1104):
- Cytoplasm
- Foamy
- Indistinct cytoplasmic borders
- Nuclei
- Mildly pleomorphic
- Hyperchromatic, speckled chromatin
- Nuclear grooves
- Hemosiderin
- Clumping of cohesive cells often obscures cytologic features
- Cytoplasm
Positive stains
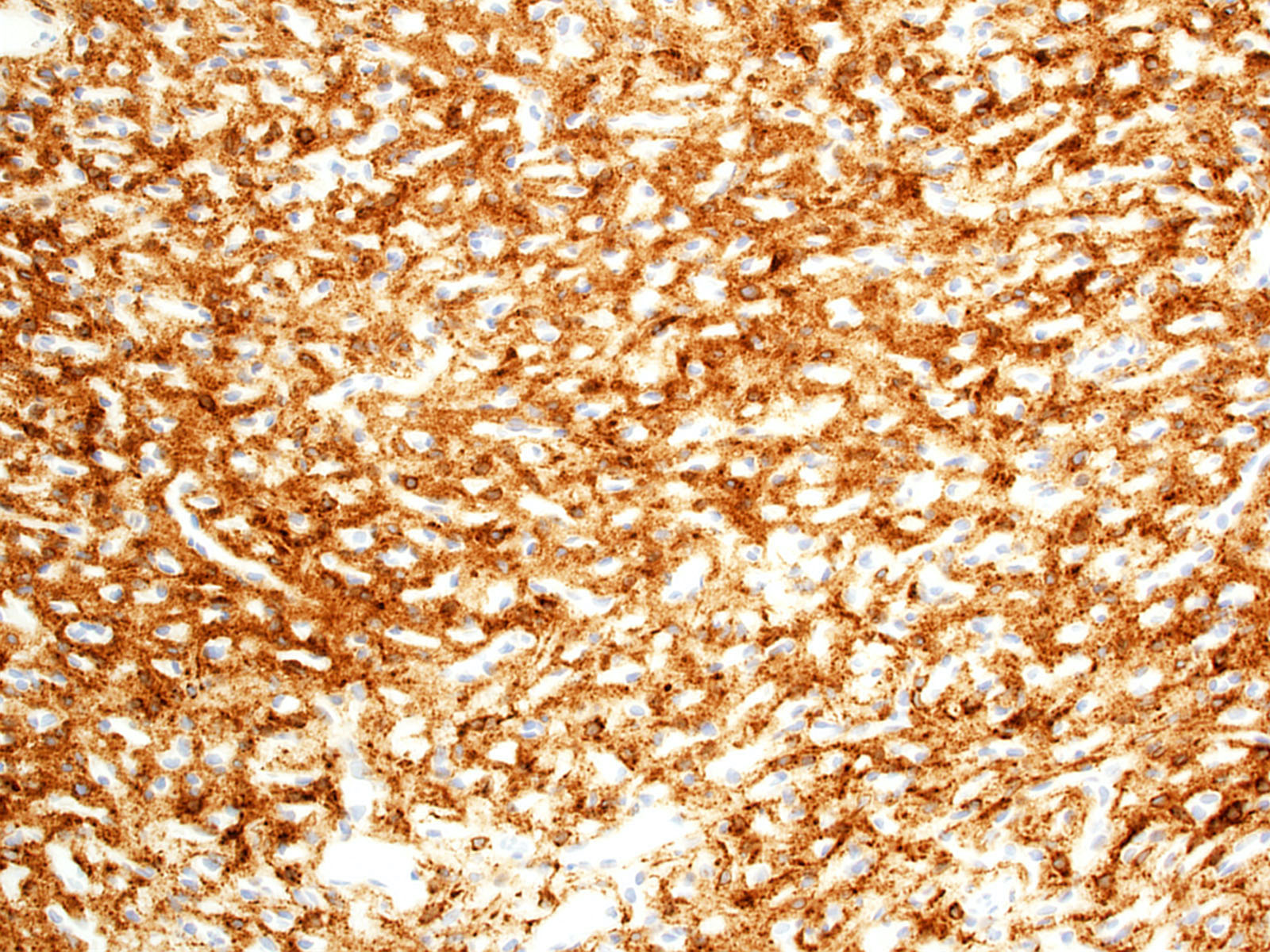
- Stromal cells
- Inhibin alpha (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:262, Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1152, Neuropathology 2010;30:580, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051)
- N-CAM1 (CD56) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:641)
- S100 (100%; scattered positive cells) (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:207)
- Carbonic anhydrase IX & XII (Neuro Oncol 2005;7:465)
- Brachyury (91% cytoplasmic) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1052)
- Vimentin (86 - 100%) (Mod Pathol 1989;2:638)
- Aquaporin 1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051)
- TFE3 (Am J Transl Res 2020;12:4498)
- Oil red O (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:641)
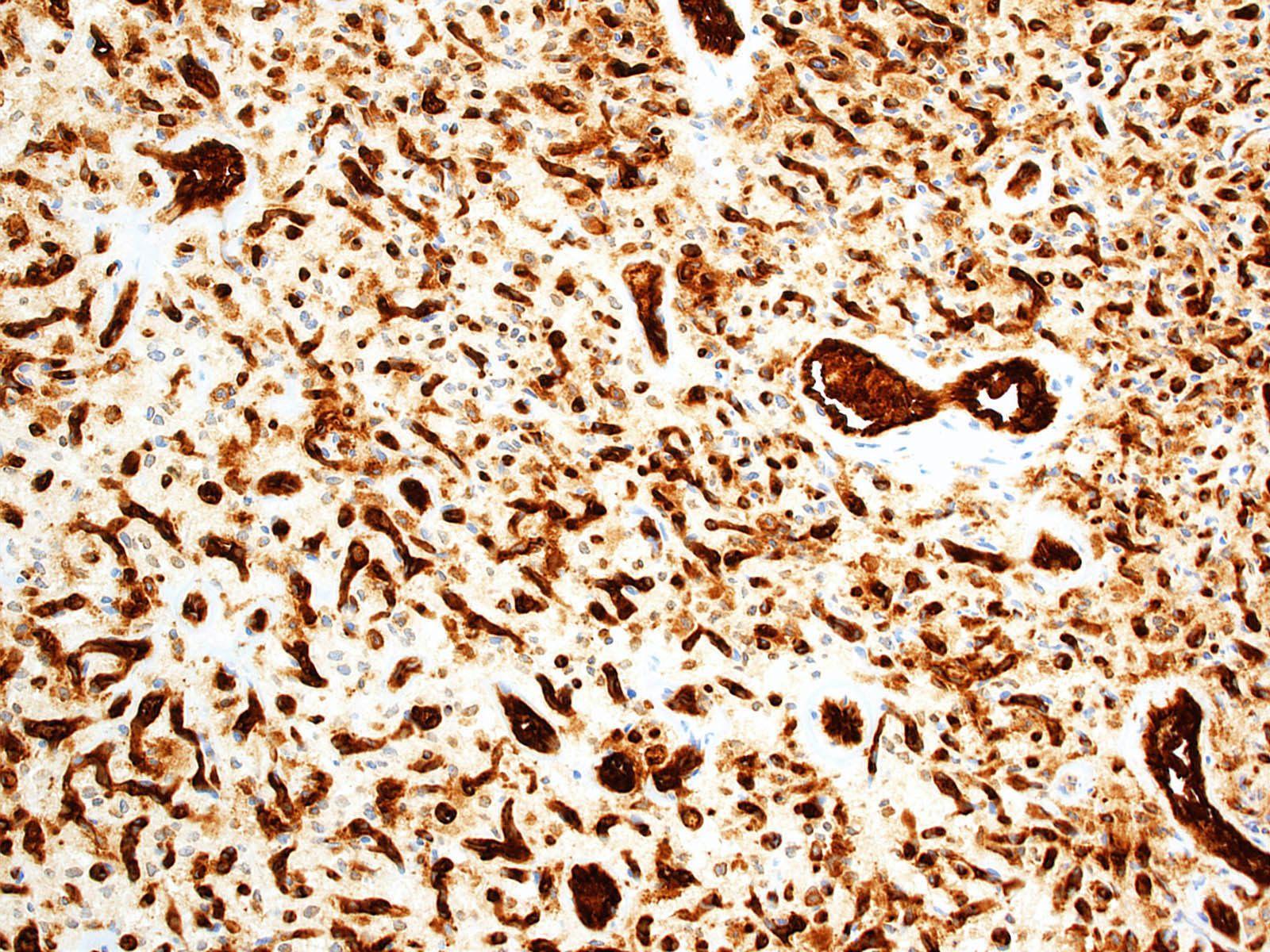
- Vascular cells
- Endothelial cell markers (e.g. CD31, CD34) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:641)
- Reticulin (highlights vessel walls)
Negative stains
- AE1 / AE3 (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051)
- CAM5.2 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:641)
- RCC marker (Neuropathology 2010;30:580)
- PAX8 (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:262)
- PAX2 (5%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:262)
- CD10 (0 - 12%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051, Neuropathology 2010;30:580)
- EMA (0 - 36%; membranous or diffuse cytoplasmic) (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:207, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051)
- NSE (33%) (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:207)
- GFAP (18%; scattered individual cells) (Histol Histopathol 1996;11:1049)
Electron microscopy description
- Lipid droplet containing stromal cells seen between capillaries (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002;61:1027)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- VHL syndrome
- Biallelic inactivation of VHL (J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:644)
- Sporadic
- Up to 78% of cases show loss / inactivation of VHL (J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:644, Cancer Res 1998;58:504, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2014;2:167, Neuro Oncol 2017;19:1228)
- Distinctive epigenetic classifying signature can be determined by genome wide DNA methylation array profiling (Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:181)
- MicroRNA (miRNA) patterns include elevated miRNA-9 and decreased miRNA-200a (Brain Pathol 2012;22:522)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Hemangioblastoma MRI
Hemangioblastoma histopathology
Sample pathology report
- Brain, cerebellum, excision:
- Hemangioblastoma, WHO grade 1
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
- Anaplasia, prominent nucleoli
- Mitotic activity
- Necrosis
- Usually lacks foamy / vacuolated cytoplasm
- Positive for AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2, EMA, CD10, PAX2, PAX8, RCC marker (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:641, Mod Pathol 2005;18:788, Neuropathology 2010;30:580, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:377)
- Negative for inhibin alpha, brachyury, N-CAM1 (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289, Mod Pathol 2005;18:788, Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1152, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:641, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1052)
- Meningioma (clear cell, microcystic, angiomatous subtypes):
- Usually positive for EMA (weak, patchy cytoplasmic), PR, SSTR2A (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Negative for inhibin alpha, brachyury (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1052)
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Positive for nuclear STAT6 (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Negative for inhibin alpha (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Glioma:
- Smear shows fibrillary processes, less cohesion
- Ependymoma:
- Perivascular pseudorosettes, ependymal rosettes and canals
- Positive for GFAP (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:25)
- EMA may show paranuclear dot-like or ring-like staining (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:25)
- Pilocytic astrocytoma:
- Biphasic appearance
- Compact fibrillar portions with Rosenthal fibers
- Loose microcystic portions with eosinophilic granular bodies
- Generally positive for GFAP, Olig2 (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:43, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2004;63:499)
- MAPK pathway activating genetic alterations (e.g. KIAA1549-BRAF fusion) (Nat Genet 2013;45:602)
- Biphasic appearance
- Diffuse glioma:
- Neoplastic glioma cells infiltrate background brain parenchyma (single cell infiltration, entrapped axons and neurons)
- Generally positive for GFAP, Olig2 (Acta Neuropathol 1986;72:15, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2004;63:499)
- Paraganglioma:
- Smear demonstrates individual cells
- Neuroendocrine cytologic features with uniform, round nuclei
- Zellballen architecture
- Diffusely positive for synaptophysin, chromogranin (J Clin Med 2018;7:280)
- Sustentacular cells positive for S100 (J Clin Med 2018;7:280)
- Capillary angioma / hemangioma:
- Lobular architecture
- Absence of extravascular stromal cells
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 47 year old man presents with ataxia. MRI reveals a solitary cerebellar cyst with an enhancing mural nodule. A representative histologic photo of the surgical specimen is shown. On immunohistochemical stains, stromal cells are negative for AE1 / AE3 and PAX8. Which of the following IHC stains is most likely to be positive in stromal cells?
- CAM5.2
- CD31
- Inhibin alpha
- PAX2
- RCC marker
Practice answer #1
C. Inhibin alpha is positive in hemangioblastoma stromal cells. CAM5.2 (answer A) is negative in hemangioblastoma and positive in epithelial neoplasms. CD31 (answer B) is negative in hemangioblastoma stromal cells and positive in vascular endothelial cells. PAX2 (answer D) is negative in hemangioblastoma and positive in renal cell carcinoma. RCC marker (answer E) is negative in hemangioblastoma and positive in renal cell carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma
Practice question #2
A 32 year old woman is found to have multiple enhancing intra-axial mixed solid cystic masses in the cerebellum and spinal cord as well as numerous bilateral renal cysts and a renal mass. A biopsy of a cerebellar mass is shown. A germline mutation is most likely to be present in which gene?
- FLCN
- NF2
- PKD1
- TSC1
- VHL
Practice answer #2
E. VHL. Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome manifestations may include multiple hemangioblastomas, renal cysts and renal cell carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma
- FLCN - Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (increased risk of renal cysts and tumors; no CNS involvement)
- NF2 - neurofibromatosis type 2 (increased risk of various lesions primarily affecting the nervous system, including schwannoma, meningioma, ependymoma; no renal involvement)
- PKD1 - autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (associated with bilateral renal cysts and berry aneurysms; no other CNS involvement)
- TSC1 - tuberous sclerosis (renal manifestations may include angiomyolipoma and cysts; CNS manifestations may include cortical tubers and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma; no known association with hemangioblastoma)
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma