Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Thuzar M, Yeh YA. Dysplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderdysplasia.html. Accessed September 22nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Preneoplastic urothelial lesion that consists of cytological and architectural atypia that does not meet the criteria of a urothelial carcinoma in situ
Essential features
- Flat urothelial lesions with normal thickness but may be increased or decreased (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155)
- No maturation in basal and intermediate cell layers; umbrella cells are usually present
- Mild degree of loss of polarity (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155)
- Slight nuclear enlargement with variation in nuclear size and shape, hyperchromasia but not to the severity of urothelial carcinoma in situ
- Some authors report a lack of reproducible criteria to distinguish from atypia of unknown significance (Histopathology 2019;74:68)
Terminology
- Urothelial dysplasia
- Urothelial atypia, cannot exclude dysplasia
- Dysplasia / atypia of unknown significance (AUS)
- Low grade urothelial neoplasia (regarded as obsolete)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Commonly occurs in patients with urothelial carcinoma in situ and invasive urothelial carcinoma
- M:F = ~2.6:1 (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:443)
Sites
- Urinary bladder (most common in posterior wall), urinary tract (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:443)
Pathophysiology
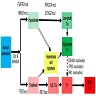
- Deletion of chromosome 9 occurs in early step of tumorigenesis
- TP53 mutation is involved in the development of urothelial dysplasia
- Dysplasia may progress to carcinoma in situ after loss of RB1 (Cancers (Basel) 2018;10:100)
Etiology
- Dysplasia harbors initial chromosome 9 deletion followed by TP53 mutation (Cancers (Basel) 2018;10:100)
- TERT promoter mutation, chromosome 9 deletion and TP53 mutations are much less frequent than in carcinoma in situ (Mod Pathol 2023;36:100120)
- HRAS mutations associated with Costello syndrome (71% uroepithelial dysplasia) (Clin Genet 2022;101:454)
Clinical features
- Often asymptomatic
- Hematuria, irritative voiding symptoms (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:443)
Diagnosis
- Fluorescence cystoscopy (98% sensitivity, 42.9% specificity) (J Endourol 2001;15:753, J Transl Med 2010;8:122)
- Bladder biopsy or transurethral resection of bladder tumor followed by histopathological studies
- Some studies suggest utility of IHC triple panel in diagnosis of dysplasia: CD44- (loss of expression), CK20+ (full thickness), p53 variable (wild type) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2018;26:180)
Prognostic factors
- Significant risk for progressing to urothelial carcinoma in situ and invasive urothelial carcinoma (19% of cases with follow up intervals ranging from 6 months to 8 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:443)
Treatment
- No standard treatment merely for urothelial dysplasia (Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 2000;205:116)
- Surgical excision for locally advanced disease
- More frequent patient follow up with cystoscopy, biopsy, urine cytology, UroVysion, molecular testing, etc. (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:443)
Gross description
- Usually unremarkable; mucosal inflammation or erythema may be present
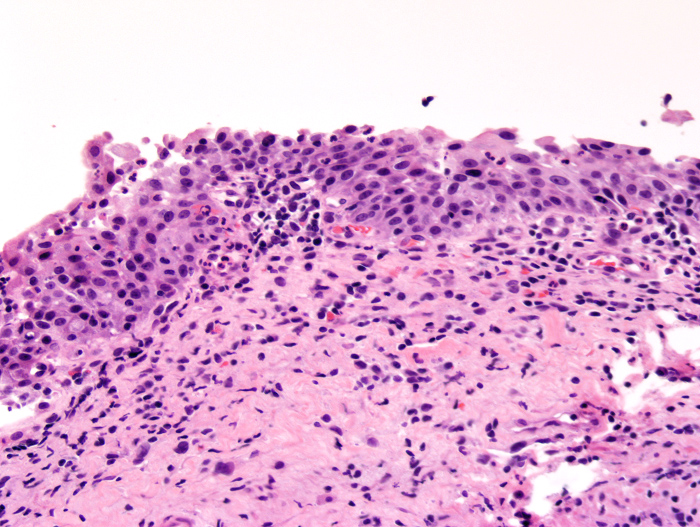
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Flat urothelial lesions with normal thickness but may be increased or decreased (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155)
- No maturation in basal and intermediate cell layers; umbrella cells are usually present
- Mild degree of loss of polarity (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155)
- Slight nuclear enlargement with variation in nuclear size and shape, hyperchromasia but not to the severity of urothelial carcinoma in situ
- Early low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma for flat dysplasia with foci of early papillary formation (Adv Anat Pathol 2021;28:179)
- Some authors report a lack of reproducible criteria to distinguish from atypia of unknown significance (Histopathology 2019;74:68)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Mild irregular nuclear membranes and fine or coarse chromatin
- Nuclear enlargement with slightly increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (> 0.5) (Rosenthal: The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology, 1st Edition, 2016)
- Small or invisible nucleoli
- Cytology correlated to biopsy to distinguish dysplasia from carcinoma in situ
Positive stains
- CK20 can be strongly positive in urothelium below umbrella cells (Pathol Int 2005;55:248, Mod Pathol 2022;35:1296)
- p53 can be diffusely positive in up to 80% of cases (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155, Mod Pathol 2003;16:187)
Negative stains
- CD44 can be negative (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- UroVysion fluorescence in situ hybridization (J Clin Pathol 2008;61:272)
- Polysomy (at least 1 of the chromosomes 3, 7, 17) in half of dysplasia cases and in > 90% of urothelial carcinomas in situ and invasive bladder carcinomas versus 17% of urothelial hyperplasia, reactive atypia and normal urothelium
Sample pathology report
- Urinary bladder, posterior wall lesion, biopsy:
- Urothelial mucosa with urothelial dysplasia (see comment)
- Comment: The bladder lesion biopsy shows urothelial mucosa with slightly increased cell layers. There is loss of polarity. Nuclear crowding with nucleomegaly and hyperchromasis is noted. However, the degree of nuclear atypia is less severe than that of carcinoma in situ. These changes are consistent with urothelial dysplasia.
Differential diagnosis
- Normal urothelium (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155):
- Normal thickness of urothelium (4 - 7 cell layers in a contracted bladder)
- Maintains cellular polarity, maturation from basal to superficial cell layer
- Absence of cellular atypia or mitotic activities
- Urothelial hyperplasia (Mod Pathol 2022;35:1296):
- Marked thickening of urothelium (> 7 cell layers)
- Maintains cellular polarity
- Absence of cellular atypia or mitotic activities
- Flat urothelial lesion with reactive atypia (Hum Pathol 2010;41:155):
- Nuclear enlargement (< 5x, usually 2 - 3x lymphocyte size) with prominent nucleoli
- Delicate nuclear chromatin
- Maintains cellular polarity
- Acute or chronic inflammation (intraurothelial inflammatory cells)
- Increased mitotic activity may be present
- Radiation related atypia with enlarged cells with dark, smudgy chromatin and vacuolated cytoplasm
- Flat urothelial lesion with atypia of unknown significance (Mod Pathol 2022;35:1296):
- Urothelial atypia with inflammation
- Degree of atypia more severe than reactive atypia but less severe than carcinoma in situ
- Challenging differential diagnosis; some authors report a lack of reproducible criteria to distinguish atypia of unknown significance from urothelial dysplasia (Histopathology 2019;74:68)
- Urothelial carcinoma in situ (Pathology 2021;53:86):
- Loss of cellular polarity
- Marked nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia and pleomorphism
Additional references
Practice question #1
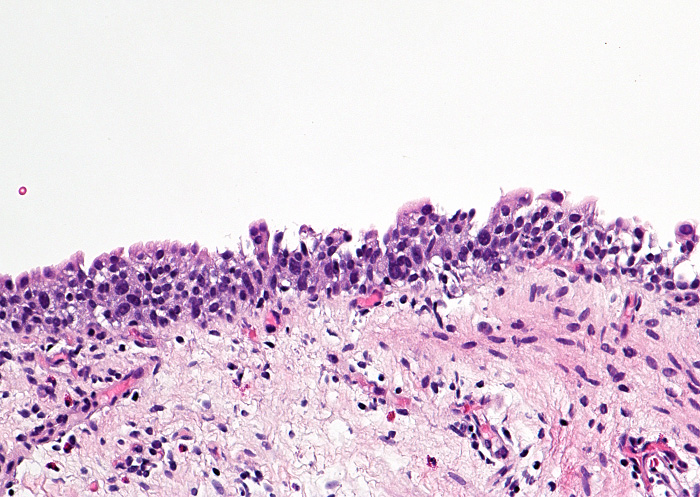
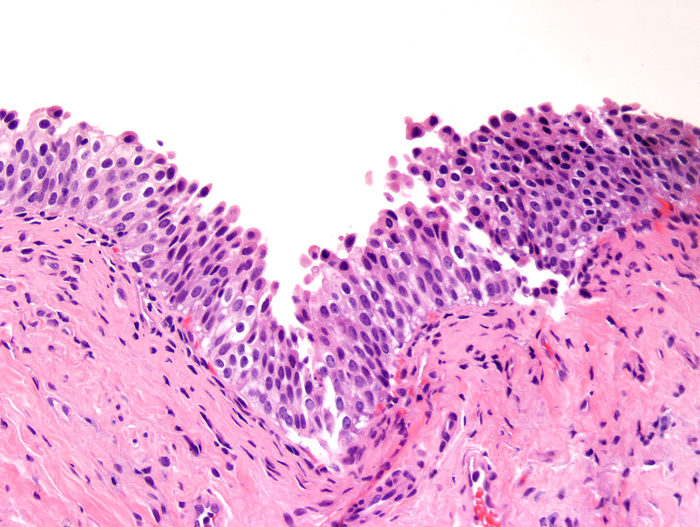
A 65 year old man presented with hematuria and urinary urgency. Cystoscopic examination showed a 1 cm erythematous lesion in the posterior wall. Biopsy of the lesion was performed. The photomicrograph is shown above. What is the diagnosis?
- High grade urothelial carcinoma
- Low grade urothelial carcinoma
- Normal urothelium
- Urothelial carcinoma in situ
- Urothelial dysplasia
Practice answer #1
E. Urothelial dysplasia. Urothelial dysplasia is characterized by variable thickness of urothelium with slightly enlarged nuclei and variable hyperchromasia but these do not reach the threshold of urothelial carcinoma in situ. Answer C is incorrect because there is hyperplasia and atypia. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because the enlarged nuclei and variable hyperchromasia fall short of urothelial carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia
Practice question #2
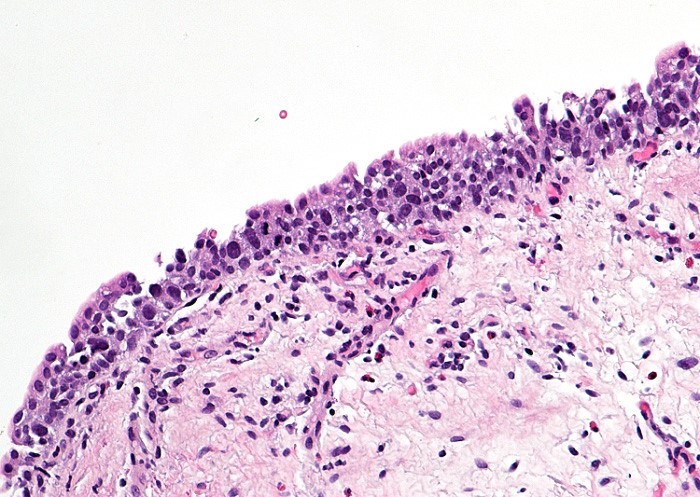
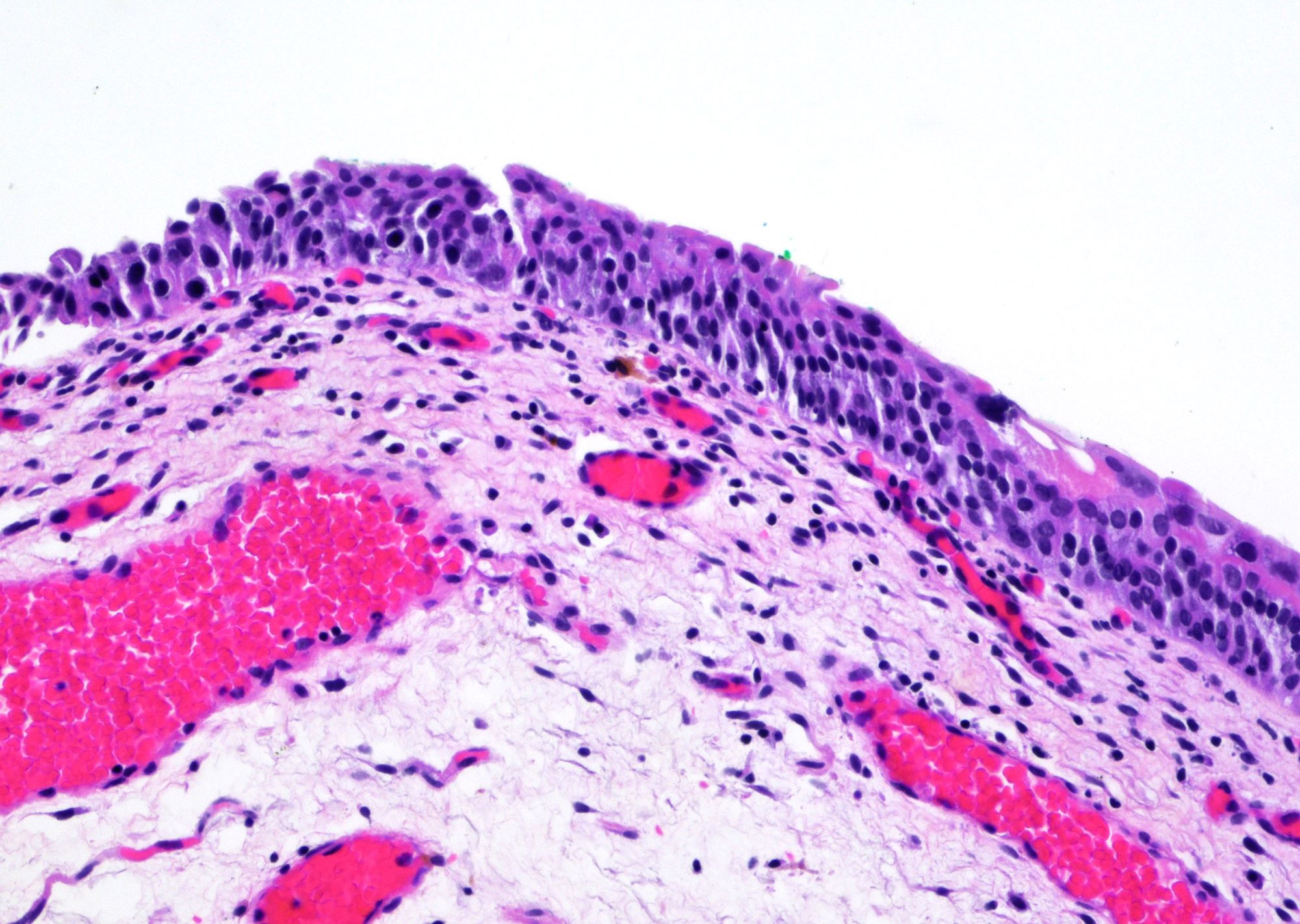
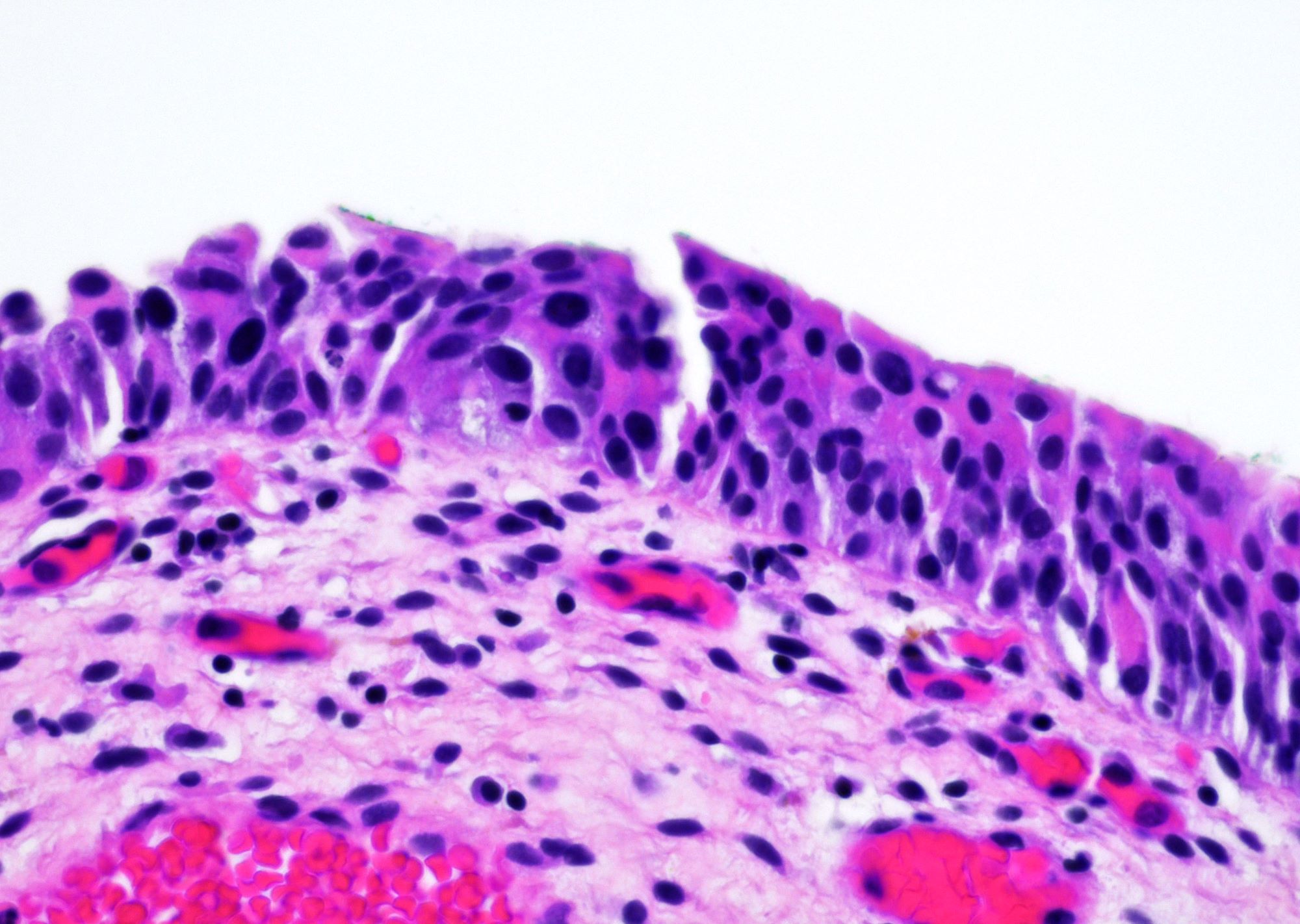
A 72 year old man presented with hematuria and dysuria. Cystoscopic examination showed a 1.5 cm erythematous lesion in the right lateral wall. Biopsy of the lesion was performed. The photomicrograph is shown above. What is the diagnosis?
- High grade urothelial carcinoma
- Low grade urothelial carcinoma
- Normal urothelium
- Urothelial carcinoma in situ
- Urothelial dysplasia
Practice answer #2
E. Urothelial dysplasia. The urothelium shows hyperplasia with some enlarged urothelial cells and hyperchromasia but the degree is less severe than that of a carcinoma in situ. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because their degree of dysplasia is greater than that of urothelial dysplasia. Answer C is incorrect because the lesion shows urothelial hyperplasia and cellular atypia.
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia