Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Bruehl F, Schürch CM. CD27. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd27.html. Accessed May 14th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF) family member expressed on T and B cells
Essential features
- CD27 is a costimulatory receptor of the TNF receptor superfamily expressed on lymphocytes
- CD27 is triggered by its unique ligand CD70, which is expressed on immune cells and often in cancers
- Soluble CD27 can be measured in serum and is an indicator of the CD70 - CD27 interaction in vivo
- CD27 deficiency should be considered in patients with immunodeficiencies
- CD27 staining in flow cytometry can help detect immunodeficiencies
Terminology
- Also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 7 (TNFRSF7)
Pathophysiology
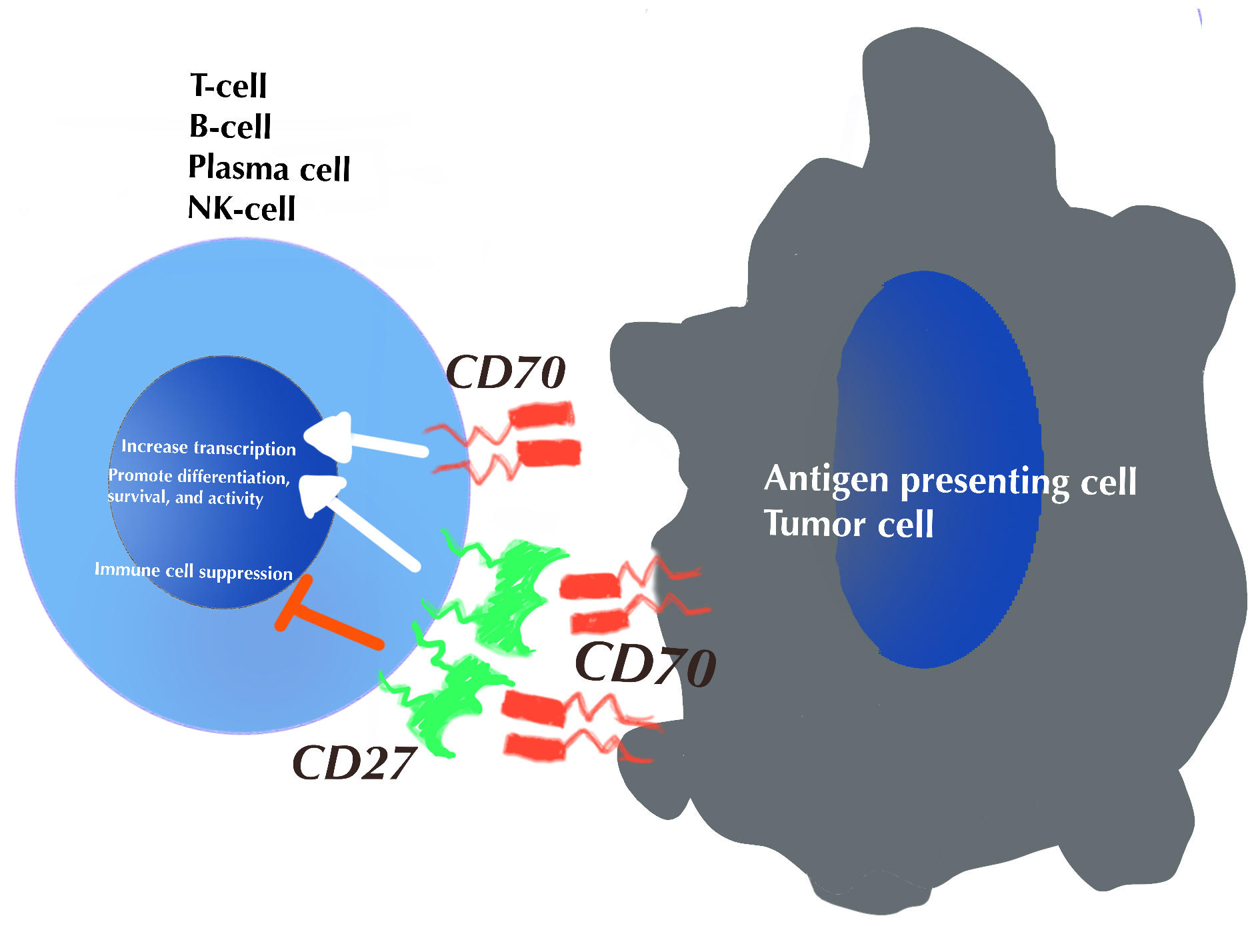
- CD27 is the receptor for its ligand CD70 (Int Immunol 1994;6:477)
- CD70 expression is tightly controlled in human tissues but often overexpressed in cancers (Pharmacol Ther 2015;155:1)
- CD27 is variably expressed on B, T and NK cells (J Immunol 1987;139:1589)
- CD27 is a costimulatory receptor (Int Immunol 1995;7:551)
- On T cells, CD27 activates NFκB and promotes cell survival, antigen receptor mediated proliferation and immune function (Curr Opin Immunol 2005;17:275)
- On B cells, CD27 augments Ig class switching and promotes plasma cell differentiation (Blood 2010;115:3051, Blood 1998;91:173)
- On NK cells, CD27 stimulates interferon gamma secretion (J Immunol 2000;164:1741)
- CD27 high and low NK cells represent functionally distinct subsets (J Immunol 2006;176:1517)
- On hematologic progenitor cells and leukemic stem cells, CD27 leads to Wnt pathway activation and promotes cell growth (J Clin Invest 2012;122:624)
- CD27 stimulation can lead to immune cell suppression depending on the duration and timing of signaling (Immunol Rev 2009;229:216)
- CD27 signaling increases the numbers of regulatory T cells and may promote tumor growth (Cancer Res 2012;72:3664)
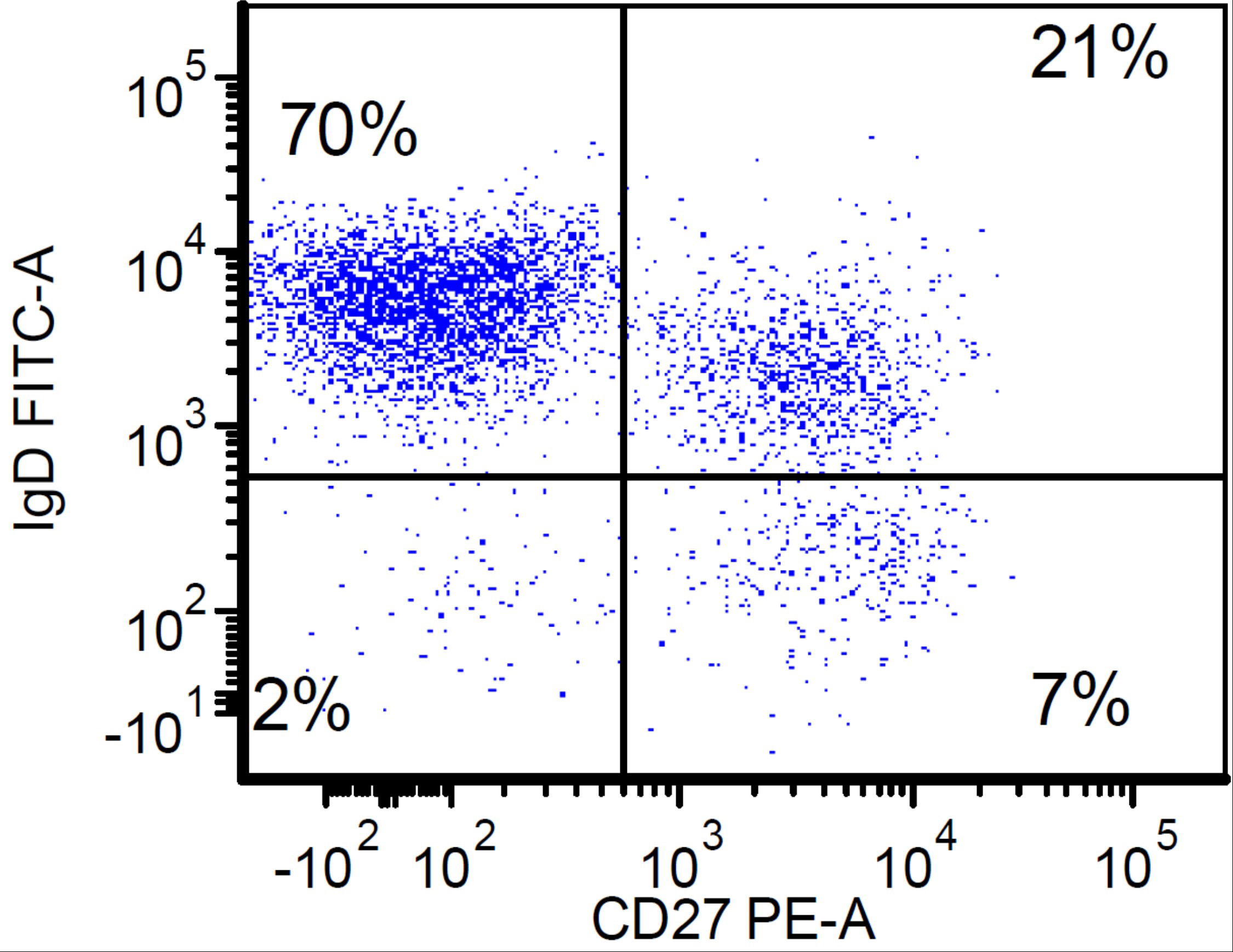
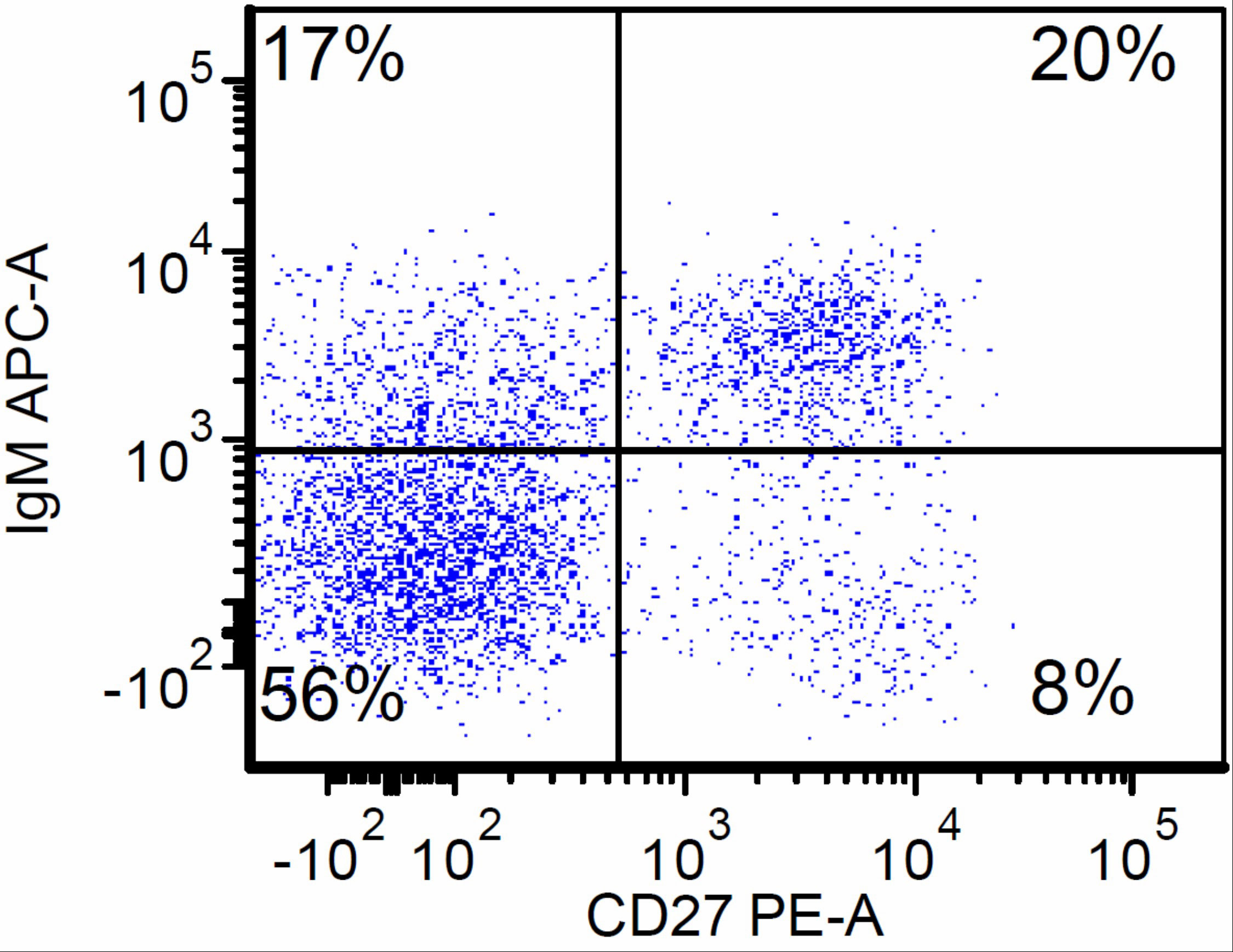
- CD27 is a marker for IgG class switched memory (CD27+ IgD- IgM-) versus naïve B cells (CD27- IgD+ IgM+) (J Exp Med 1998;188:1679)
- Triggering of CD27 by CD70 leads to shedding of soluble CD27 from cells by a protease (J Immunol 1991;147:29)
- Soluble CD27 can be measured in serum and reflects the extent of CD27 / CD70 interactions in vivo (J Exp Med 2017;214:359)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Soluble CD27 has been explored as a promising marker of immune function and disease status in a range of infectious, immunologic and oncologic settings (J Immunol 2013;190:6250)
- Immunology
- CD27 deficiency can be seen in many cases of common variable immune deficiency (Blood 2002;99:1544)
- CD27 deficiency should be considered in all patients with hypogammaglobulinemia or unusually severe causes of EBV infection to allow for individualized treatment (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;129:787, Haematologica 2013;98:473)
- CD27 expression on lymphocytes is increased in patients with diffuse and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (Intractable Rare Dis Res 2020;9:99)
- High serum levels of soluble CD27 and increased CD27 negative memory B cells are associated with disease severity in systemic lupus erythematosus (Clin Rheumatol 1995;14:293, J Immunol 2007;178:6624)
- Oncology
- CD27 signaling can enhance T cell proliferation and differentiation to effector and memory T cells (ESMO Open 2020;4:e000629)
- CD27 is being investigated as a therapeutic target for hematolymphoid malignancies and solid tumors (Blood Adv 2020;4:1917, J Clin Oncol 2017;35:2028)
- Its agonistic antibody, varlilumab, is being studied as a potential immune modulator for cancer patients (ESMO Open 2020;4:e000629)
- CAR T cells costimulated with CD27 signaling have improved survival and enhanced function in vitro and in vivo (Blood 2012;119:696)
Interpretation
- Membranous staining
Uses by pathologists
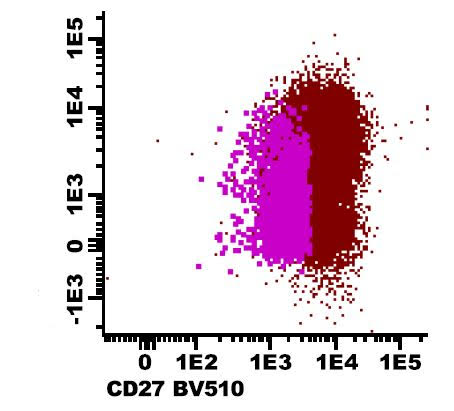
- CD27 dim expression detected by flow cytometry is a marker of atypical plasma cells (see Diagrams / tables) (Br J Haematol 2022;196:1175)
- B cell phenotyping for evaluation of immunodeficiency syndromes and immune competence analysis by flow cytometry
- T cell phenotyping for evaluation of immunodeficiency syndromes and immune competence analysis by flow cytometry
Prognostic factors
- Solid tumors
- CD27 positive tumor infiltrating lymphocytes predict inferior survival in renal cell carcinoma (Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:889)
- CD27 negative tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with an improved survival in high grade serous ovarian carcinoma (Clin Cancer Res 2012;18:3281)
- CD27 negative tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with an improved survival in hepatocellular carcinoma (Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:5994)
- Hematolymphoid neoplasms
- Soluble CD27 is an independent unfavorable prognostic marker in acute myeloid leukemia (J Exp Med 2017;214:359)
- CD27 is highly expressed in high risk B cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and associated with decreased survival (Blood Cancer J 2017;7:e575)
- Loss of CD27 expression indicates poor prognosis in multiple myeloma (Clin Immunol 2020;213:108363)
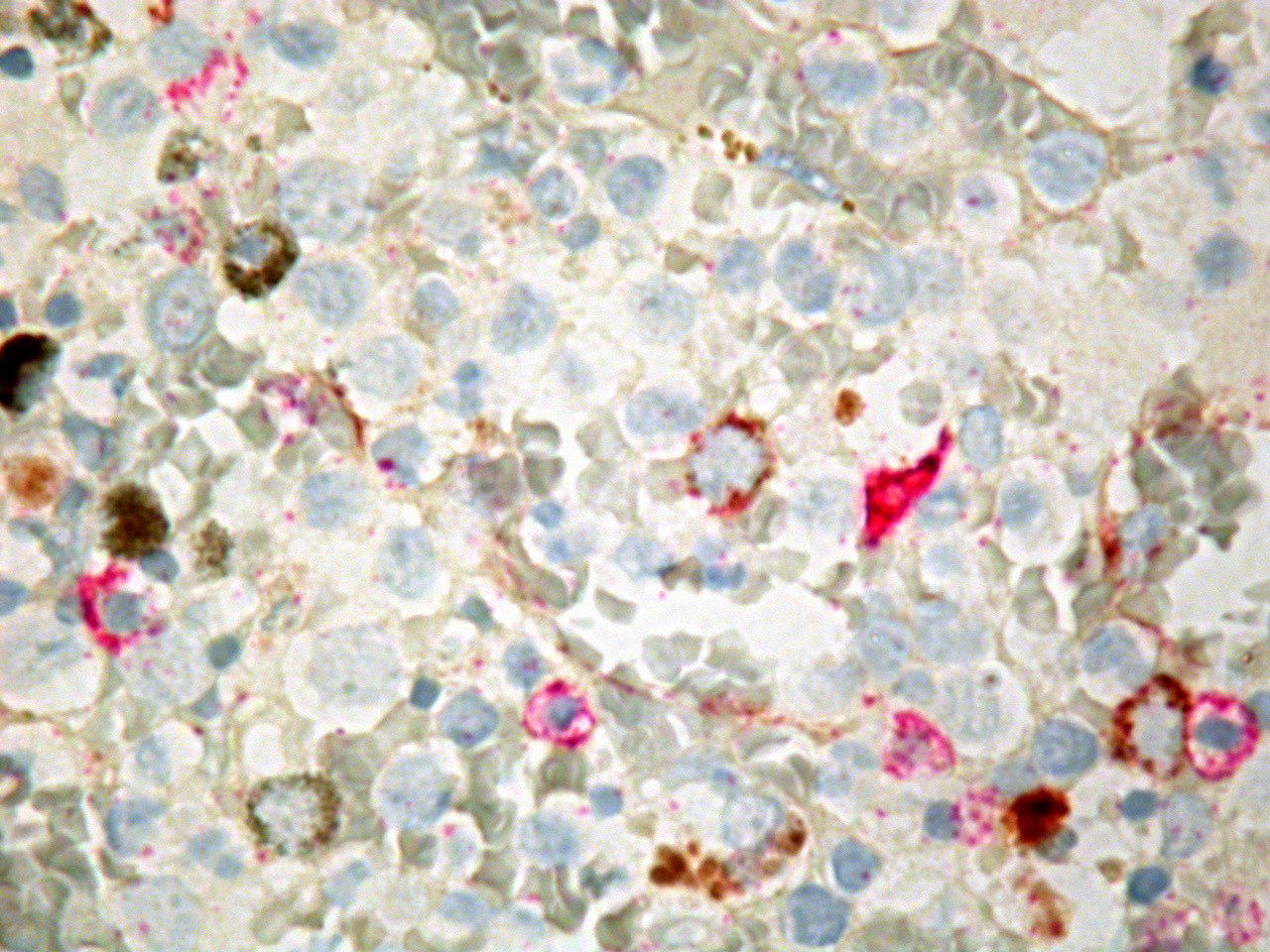
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Immune cells (see Pathophysiology)
Positive staining - disease
- Myeloma (heterogeneous expression) (Br J Haematol 2006;132:168, Br J Haematol 2003;121:36)Â
- Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma (100%, 17/17) (Am J Clin Pathol 2010;133:592)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (100%, 18/18) (Blood 1995;85:3556)
- Mantle cell lymphoma (100%, 15/15) (Leuk Lymphoma 2002;43:1855)
- Burkitt lymphoma (100%, 6/6) (Leuk Lymphoma 2002;43:1855)
- Pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Leuk Lymphoma 2002;43:1855, Exp Hematol 2005;33:1500)
- CD27 positive hairy cell leukemia, Japanese variant (Virchows Arch 2016;468:375)
- Chronic myeloid leukemia, CD34 positive blasts (J Clin Invest 2012;122:624)
Negative staining
- Oncology
- Hairy cell leukemia (Haematologica 2005;90:266)
- Splenic diffuse red pulp lymphoma (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2016;16:S166)
- Immunology
- Chronic active EBV infection associated with CD27 deficiency (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;136:703)
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- CD27 expression (based on mRNA detection by PCR) is higher in mycosis fungoides skin lesions than in healthy controls (Ital J Dermatol Venerol 2022;157:275)
Sample pathology report
- Peripheral blood, flow cytometry, quantitative B cell phenotyping analysis:
- Abnormal (see comment)
- Comment: A decrease of class switched memory B cells (CD19 positive, CD27 positive, IgM negative, IgD negative) is consistent with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Switched memory B cells are quantitatively decreased in relation to marginal zone B cells (CD19 positive, CD27 positive, IgM positive, IgD negative). This result is consistent with but not diagnostic of CVID. Quantitative B cell phenotyping is helpful for the classification and prognosis of CVID and should be considered in the context of clinical and other immunological and laboratory findings. Decreased class switched memory B cells may also be seen in some autoimmune diseases, secondary to certain medications and in patients with other hereditary syndromes.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. CD70, the ligand of CD27, is often overexpressed in cancer. CD70 is overexpressed in many cancers and the CD27 / CD70 immune axis is utilized by cancers to escape immune surveillance (Oncoimmunology 2012;1:1604). The expression of CD27 in lymphoid and myeloid progenitor cells is tightly controlled. The expression pattern of CD27 is predominantly membranous. Clinical uses include immunophenotypic evaluation of plasma cell neoplasms and analysis of lymphocytes in patients with immunodeficiency syndromes.
Comment Here
Reference: CD27
Comment Here
Reference: CD27