Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Clinical features | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Pyogenic granuloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorpyogenicgranuloma.html. Accessed September 4th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign capillary hemangioma forming a colonic polyp
Essential features
- Very rare
- Can cause rectal bleeding
Terminology
- Also called lobular capillary hemangioma
Sites
- Usually occurs in skin or oral cavity; gastrointestinal tract cases are very rare
Clinical features
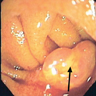
- Presents clinically as rectal bleeding and anemia
Case reports
- 18 month old girl and 5 year old girl with rectal bleeding (J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006;43:119)
- 62 year old woman with rectal bleeding (Ann Diagn Pathol 2005;9:106)
Clinical images
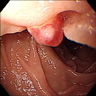
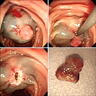
Gross description
- Pedunculated or sessile polyp
- May appear black and necrotic
Microscopic (histologic) description
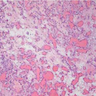
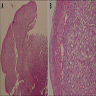
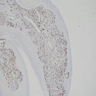
- Lobular arrangement of capillaries within edematous, inflamed stroma
- Endothelial cells often swollen
- Often shows surface ulceration; sometimes shows mitotic figures
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Vascular markers, such as CD34 (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1054)
Sample pathology report
- Transverse colon, polypectomy:
- Small focus of benign lobular vascular proliferation, most consistent with pyogenic granuloma
Differential diagnosis
- Bacillary angiomatosis:
- Warthin-Starry stain positive
- Granulation tissue:
- Lacks a lobular arrangement
- Inflammatory polyp:
- Lacks a lobular arrangement
- Kaposi sarcoma:
- Positive for HHV8
Practice question #1
A 21 year old man presents to his physician, complaining of hematochezia. Colonoscopy shows a small, pedunculated polyp. Microscopically, the polyp is mostly composed of inflammation and small blood vessels. Which of the following findings would favor a diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma?
- Dilated, ectatic crypts
- Lobular architecture
- Positivity for HHV8
- Surface adenomatous change
- Viral cytopathic effect
Practice answer #1