Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | CPT coding | Sites | Radiology description | Case reports | Cytology description | Cytology images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2 | Practice question #3 | Practice answer #3Cite this page: Khan MYA, Shidham V. Nondiagnostic. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cytopathologylungnondiagnostic.html. Accessed August 21st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nondiagnostic / inadequate / insufficient specimen lacks sufficient material in quantity or quality for a reliable diagnosis
- They should lack any atypical cell / microorganism / acellular matrix that guides to a specific malignancy, benign diagnosis and any infectious cause (Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:399)
- Risk of malignancy is 40% for a nondiagnostic specimen (Layfield: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology System for Reporting Respiratory Cytology, 1st Edition, 2019)
- The term nondiagnostic is preferred to its synonymous terms: insufficient and inadequate
Essential features
- Lung cytopathology involves the assessment of specimens that can be categorized into
- Exfoliative cytology (sputum, bronchial brushing, bronchial wash and bronchoalveolar lavage [BAL])
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology (percutaneous transthoracic and endobronchial ultrasound guided [EBUS])
- Nondiagnostic result is reported when no malignant cells are seen or a specific benign diagnosis could not be made
- Most common causes are insufficient cellularity, cellular degeneration, poor preservation of cells and hemorrhagic samples (Layfield: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology System for Reporting Respiratory Cytology, 1st Edition, 2019)
- Bronchoalveolar lavage with fewer than 10 alveolar macrophages per 2 mm² using a high power field diameter of 0.5 mm, is considered inadequate (WHO Joint Editorial Board: WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2023)
| Adequacy criteria in respiratory cytology specimens | ||
| Sample type | Normal cellular components | Adequacy criteria |
| FNA |
|
|
| Bronchoalveolar lavage |
|
|
| Bronchial wash |
|
|
| Bronchial brush |
|
|
| Sputum |
|
|
CPT coding
Sites
- Lung
Radiology description
- Usually a mass-like lesion or ground glass opacity is seen on imaging
Case reports
- 31 year old man with esophageal bronchogenic cyst (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3111)
- Woman in her 50s presented with blood tinged sputum (Cytojournal 2019;16:23)
- 72 year old man with a subcarinal lesion (Cytojournal 2023;20:1)
- 73 year old man who received repeated chemotherapy for angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (Respirol Case Rep 2022;10:e0924)
- 76 year old woman who had a demonstrable solitary pulmonary nodule and 81 year old woman with a solitary nodule in the left lower lobe of the lung (BMC Pulm Med 2003;3:2)
Cytology description
| Cell type | Location | Cytologic features |
| Alveolar macrophages | Alveoli |
|
| Type II pneumocytes | Alveoli |
|
| Basal or reserve cells | Bronchi and bronchioles |
|
| Ciliated cells | Columnar cells (bronchi) and cuboidal cells (bronchioles) |
|
- Common causes of nondiagnostic sample include a mucopurulent exudate; cellular changes due to degeneration; or presence of laboratory artifacts (J Cytol 2013;30:241)
- Fine needle aspiration cytology
- Columnar cells with terminal bar and cilia are a common contamination in an EBUS FNA
- EBUS FNA should include reactive bronchial ciliated columnar cells or > 40 lymphocytes in the area of highest cellularity (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:434)
- Hyperchromatic crowded groups of basal / reserve cells are a potential pitfall in interpreting a specimen as atypical or suspicious
- Crush artifact of lymphocytes is a potential pitfall for small cell carcinoma
- Presence of a cytopathologist for rapid on site evaluation and expertise of the interventional radiologist or clinician has been shown to reduce nondiagnostic FNA samples (Ann Thorac Surg 2008;86:1104, Rev Port Pneumol (2006) 2015;21:253)
- Bronchial brushings usually show fragments of epithelial cells or tumor cells since the specimen is obtained under direct vision
- Absence of the tumor cells or poor fixation and air drying of the cells leading to swelling of nuclei and loss of chromatin detail is considered nondiagnostic
- A count of < 10 alveolar macrophages per 2 mm² using a high power field diameter of 0.5 mm is generally considered inadequate for a bronchoalveolar lavage
- Adequacy criteria in sputum samples is disputable; however, a high number of alveolar macrophages (no numerical cut off point has been defined), along with ciliated columnar bronchial cells and a recommended sufficient volume to produce at least 2 smears is considered adequate
- Several studies showed a decreased sensitivity of sputum sampling in the detection of diagnostic cells for patients affected by peripherally located lung masses (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:167)
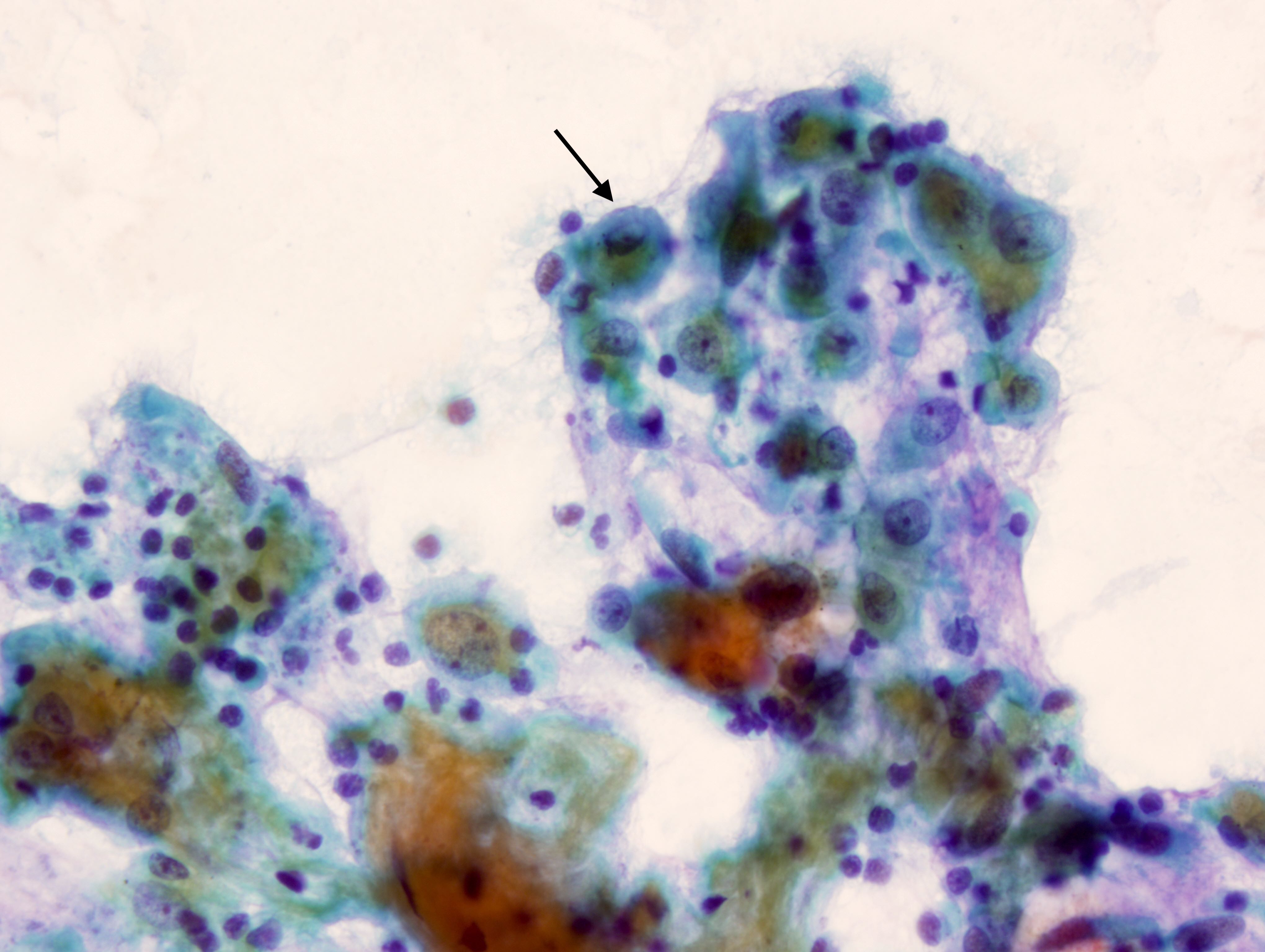
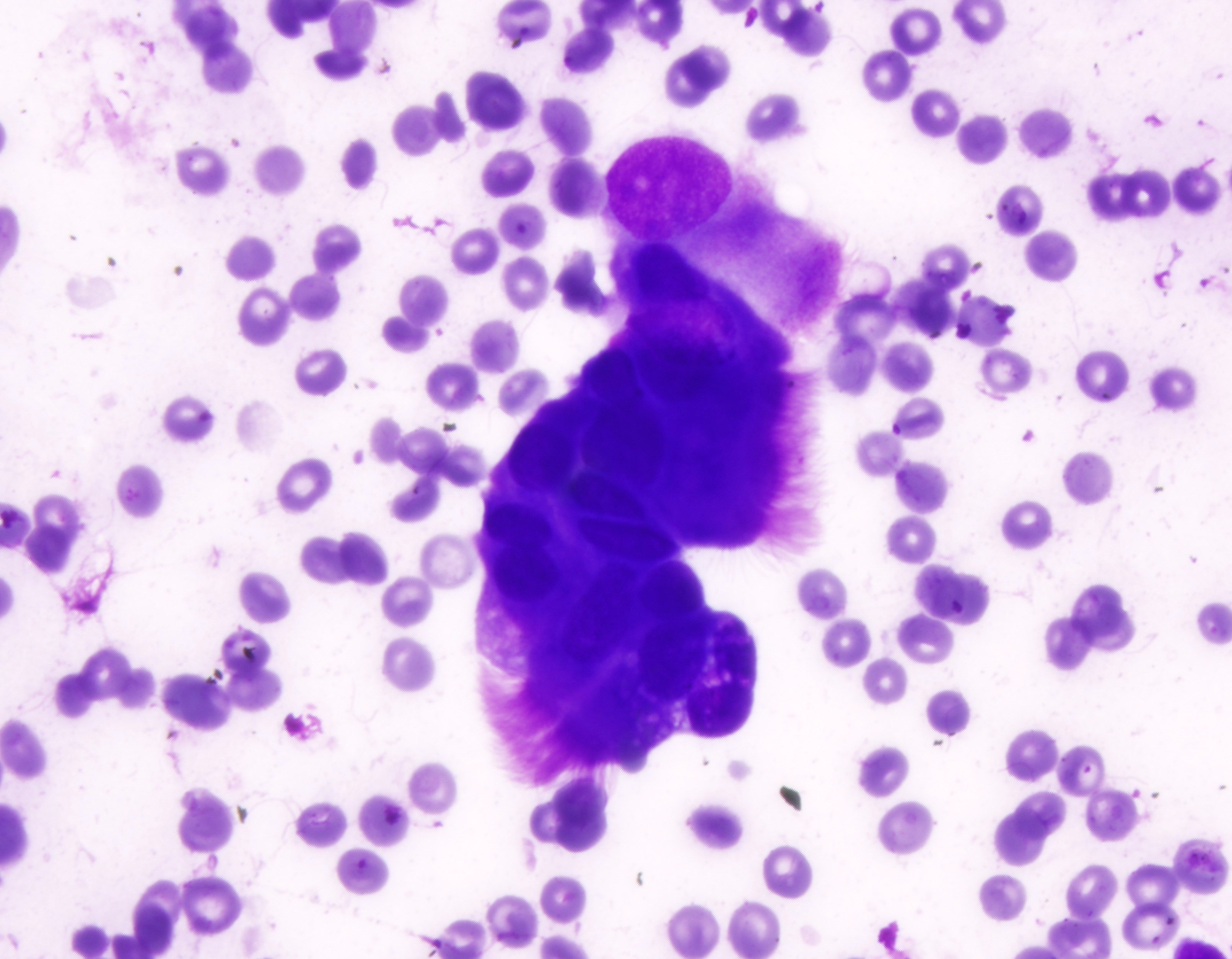
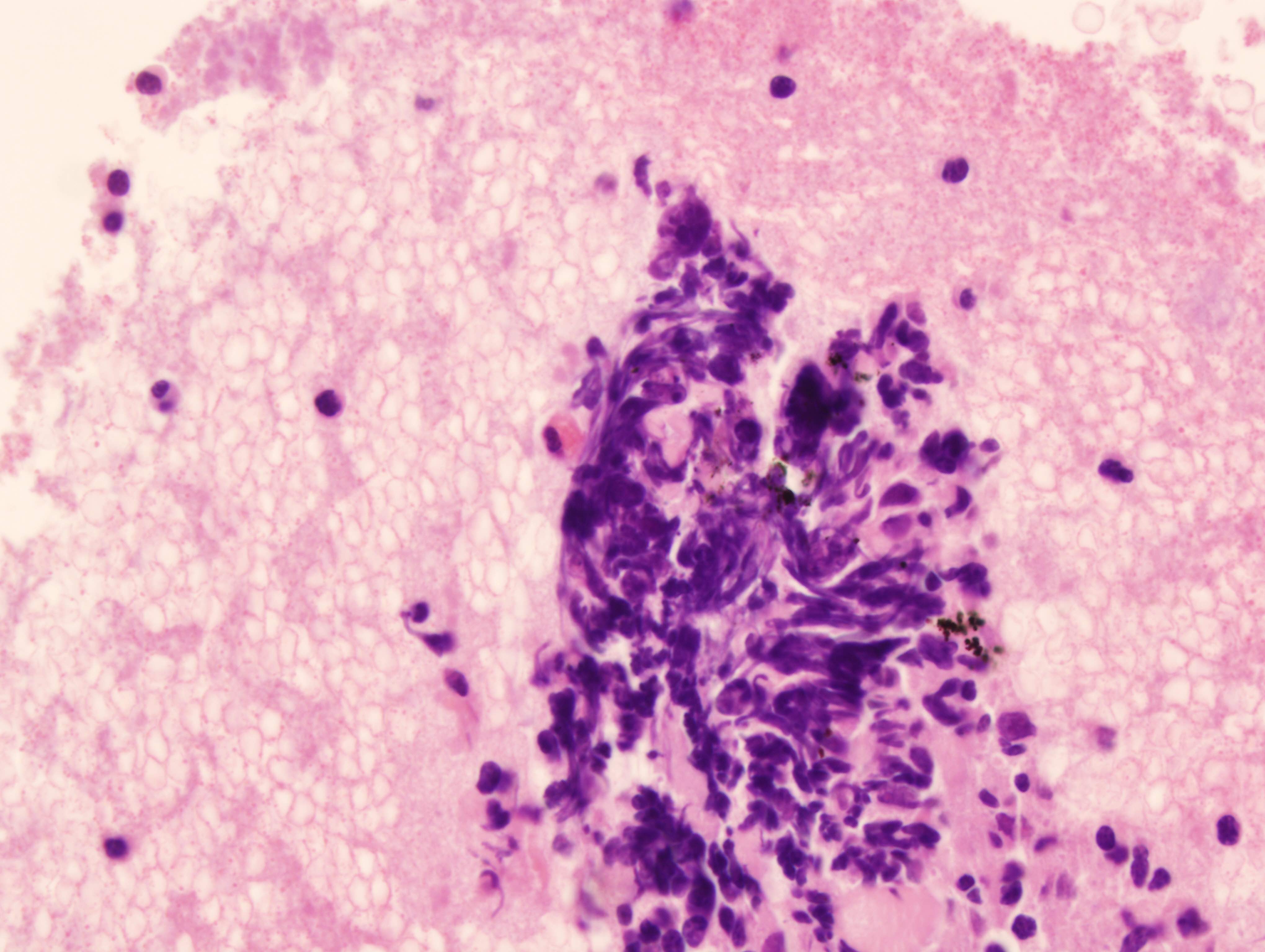
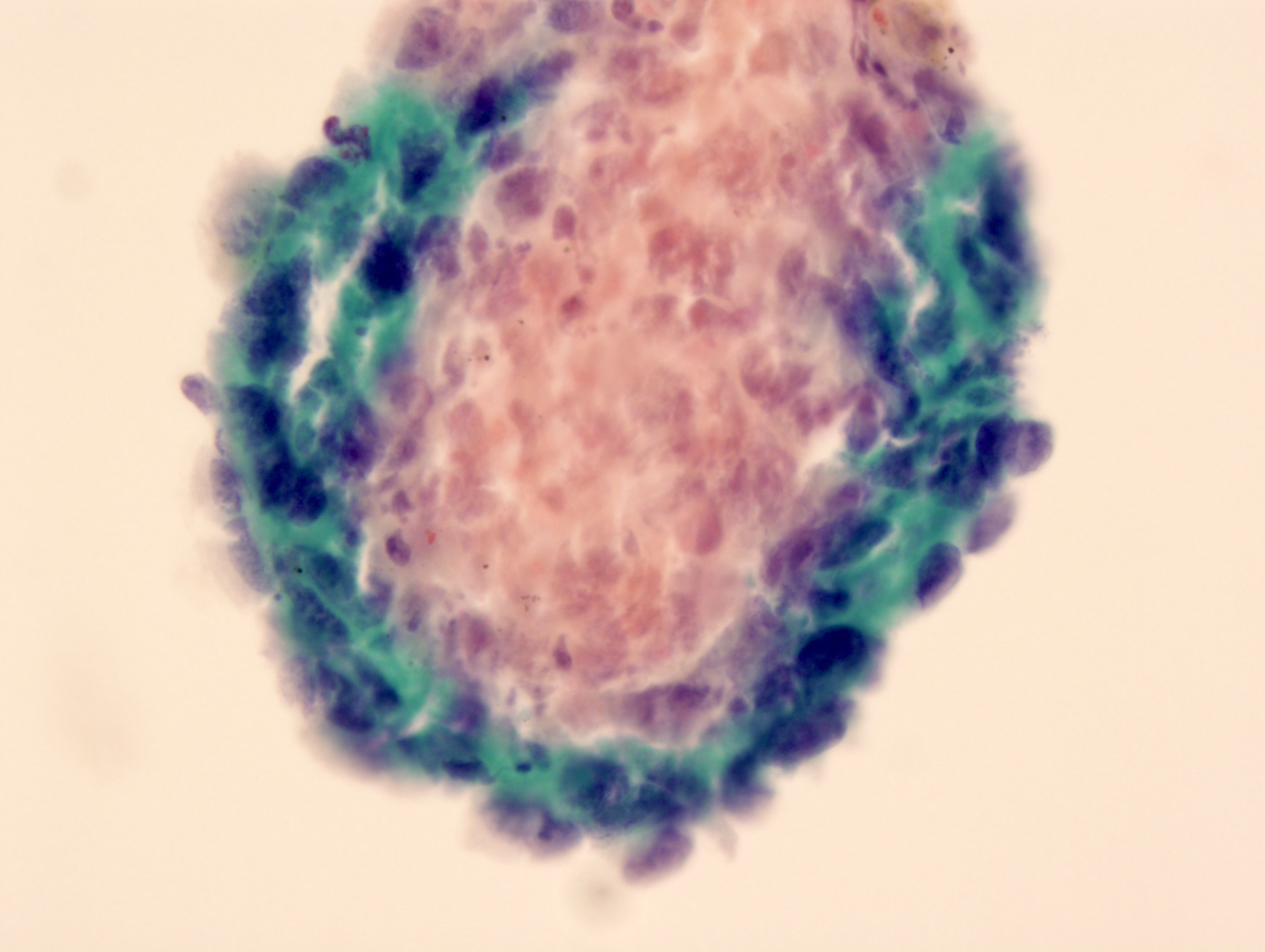
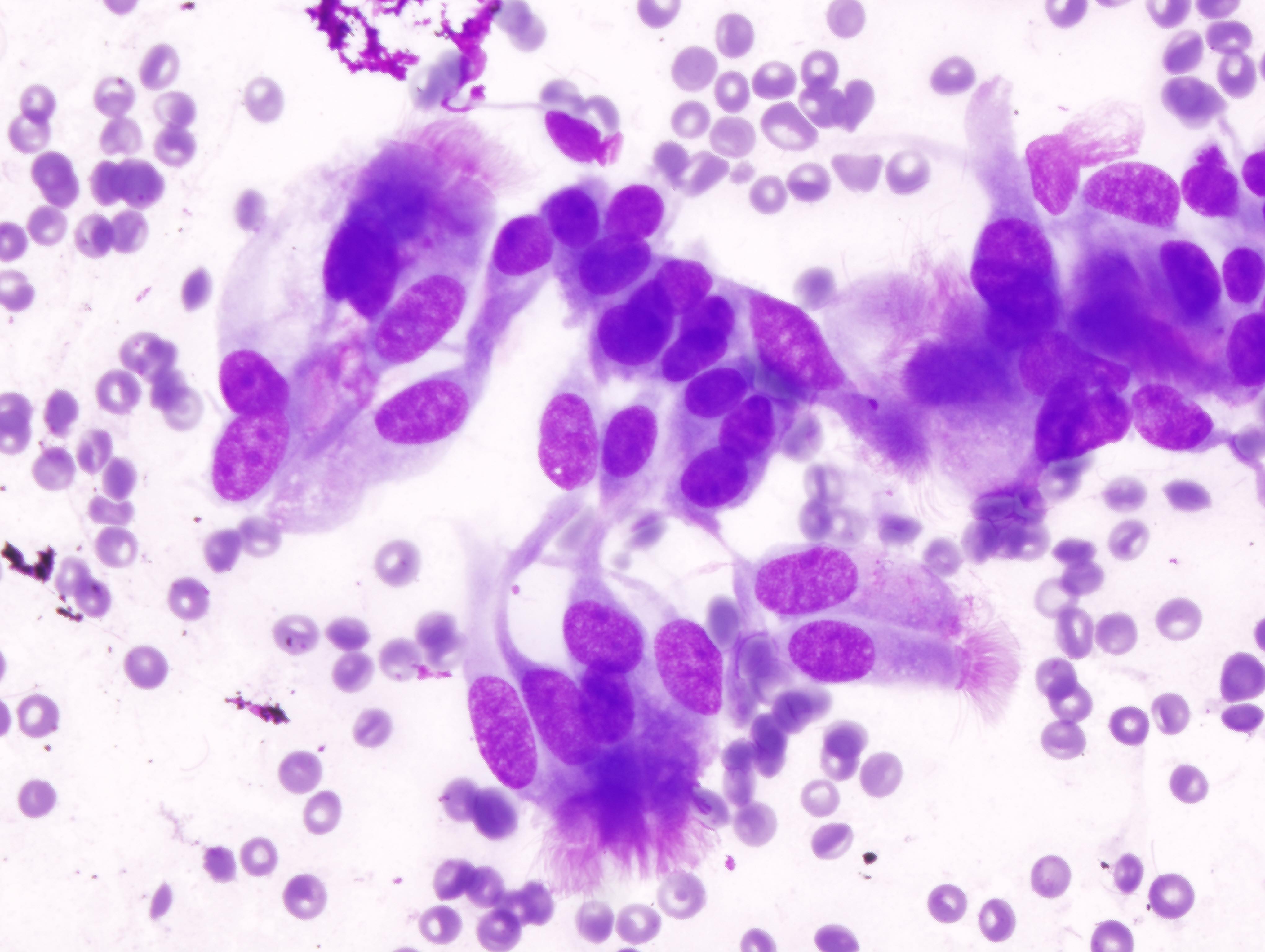
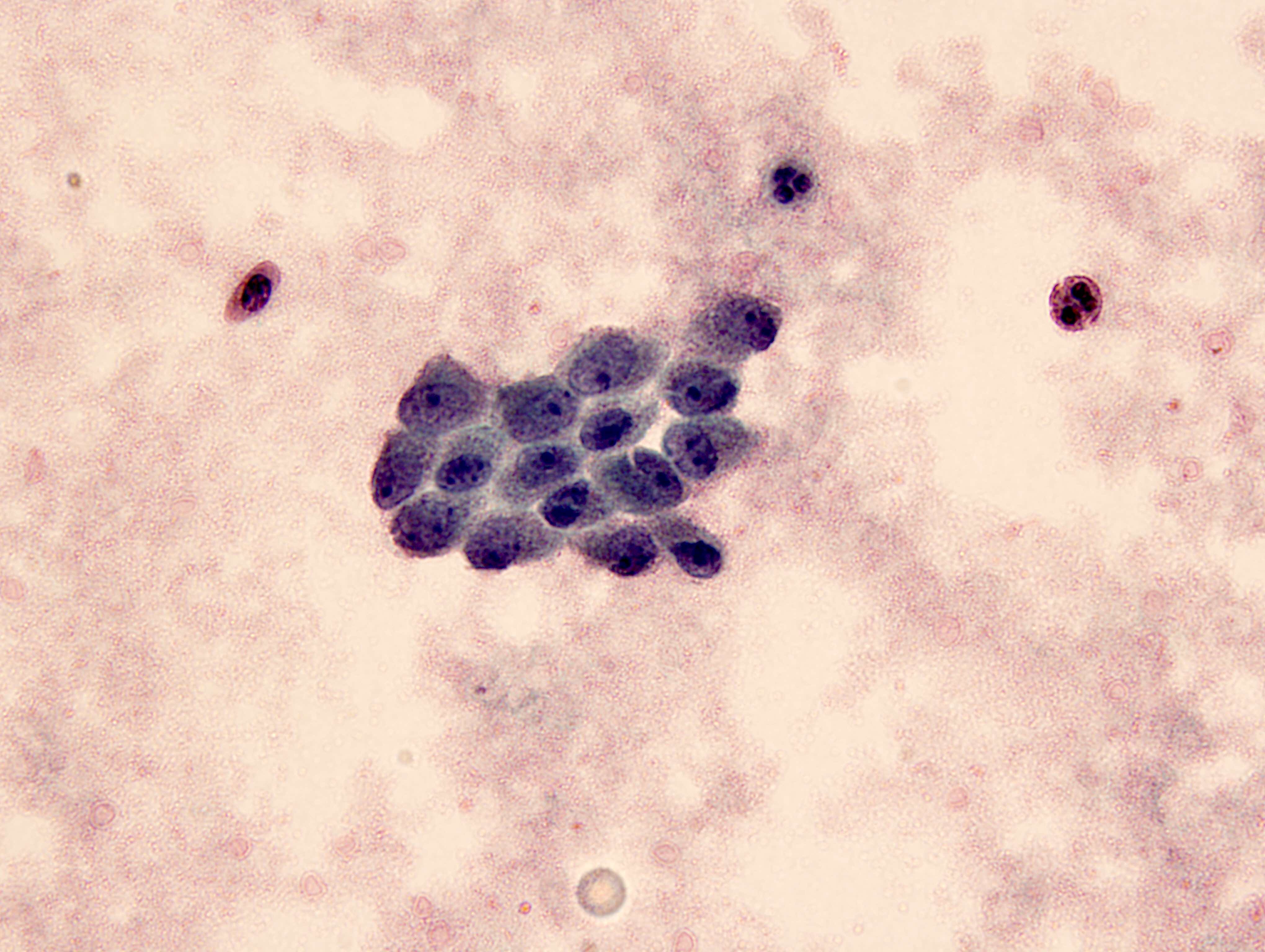
Cytology images
Videos
WHO reporting system for lung cytopathology
Adequacy criteria in EBUS FNA
Overview of lung cytopathology
Sample pathology report
- Lung, left, lower lobe, mass (2.0 cm, solid), endobronchial ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (with cell block):
- Specimen adequacy:
- Inadequate
- Cytopathologic interpretation / diagnosis:
- Nondiagnostic (see comment)
- Sample comments:
- Hemodiluted and hypocellular aspirates predominantly with bronchial mucosal contamination
- Tissue fragments are entrapped in blood clot and fibrin precluding cytologic evaluation
- Hypocellular specimen showing extensive crush artifact precluding cytologic evaluation of material present
- H&E stained sections of the cell block show few poorly preserved epithelial cells
- Specimen adequacy:
- Right lower lobe, bronchoalveolar lavage:
- Nondiagnostic: inadequate for evaluation due to nonrepresentative scant bronchial epithelial cells and absence of alveolar macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage
- Nondiagnostic: unsatisfactory for evaluation due to lack of pulmonary macrophages and poor preservation of cells
- Per IAC-IARC-WHO Cytopathology Reporting Systems, the report should always state "correlation with clinical and imaging findings is required"
Differential diagnosis
- Bronchogenic cyst:
- Shows predominance of degenerated cellular debris admixed with scattered fragments of cells showing ciliary tufts
- Carcinoid:
- Tumor cells are arranged in acini or pseudorosette structures, dispersed individual cells with monomorphic appearance
- Tumor cells reveal salt and pepper type chromatin, vesicular nuclei and inconspicuous or small nucleoli
- Pulmonary chondroma:
- Shows predominance of mature cartilage
- Clinicopathologic and radiology correlation is essential for accurate assessment of the specimen
Additional references
Practice question #1
Which of the following, when present in an EBUS FNA from a lung mass, is considered adequate?
- Aspergillus hyphae
- Goblet cells and alveolar macrophages
- Mucin
- Tufts of columnar epithelium with terminal bar and cilia
- Type 2 pneumocytes without atypia
Practice answer #1
A. Aspergillus hyphae. Aspergilloma is one of the causes of cavitary mass-like lesion in the lung. The presence of Aspergillus organisms explains the mass in the lung and is considered adequate for evaluation.
Answer B is incorrect because goblet cells and alveolar macrophages are part of the normal respiratory epithelial lining of the airways. Finding these in an EBUS FNA sample would likely indicate contamination with normal respiratory tract cells. These cells are not indicative of the characteristics of a lung mass and their presence would not help in evaluating the mass itself.
Answer C is incorrect because the presence of mucin in an EBUS FNA sample is generally not sufficient for evaluating a lung mass. Mucin can be present in various lung conditions but its presence alone does not provide specific information about the nature of the mass, whether it's benign or malignant or what type of mass it is.
Answer D is incorrect because in an EBUS FNA procedure, the goal is to obtain a sample that can be used to evaluate the nature and characteristics of a lung mass. The presence of respiratory epithelium, such as tufts of columnar epithelium with a terminal bar and cilia, is valuable because it indicates that the sample is from the lining of the airways. However, it does not explain the presence of a mass-like lesion.
Answer E is incorrect because type 2 pneumocytes are a type of lung cell responsible for producing surfactant and are not typically associated with the evaluation of lung masses. Finding these cells without atypia would suggest the presence of normal lung tissue but it doesn't provide information about the characteristics or pathology of the mass itself.
Comment Here
Reference: Lung - Nondiagnostic
Comment Here
Reference: Lung - Nondiagnostic
Practice question #2
Presence of which of the following cells in a percutaneous transthoracic FNA from a well circumscribed lung mass is a reason to consider the sample adequate?
- Alveolar macrophages
- Degenerated epithelial cells
- Neutrophils
- Red blood cells
- Superficial squamous cells
Practice answer #2
C. Neutrophils. Presence of increased number of neutrophils in a mass lesion may indicate an abscess. Neutrophils can be present in various lung conditions, and more clinical information is essential to make a definitive diagnosis.
Answer A is incorrect because alveolar macrophages are normal components of lung tissue and are not indicative of the nature of the lung mass. Their presence doesn't provide specific information about the mass.
Answer B is incorrect because in a percutaneous transthoracic FNA, the goal is to obtain a sample that can help diagnose and characterize the nature of a lung mass. While the presence of degenerated epithelial cells may indicate that the sample may be from a lung mass, a definitive diagnosis cannot be made just by the presence of degenerated epithelial cells.
Answer D is incorrect because the presence of red blood cells may suggest bleeding within the mass but doesn't, on its own, provide adequate information for characterizing the nature of the lung mass.
Answer E is incorrect because superficial squamous cells are typically part of the normal respiratory tract lining and may indicate contamination with normal cells rather than providing information about the nature of the mass.
Comment Here
Reference: Lung - Nondiagnostic
Comment Here
Reference: Lung - Nondiagnostic
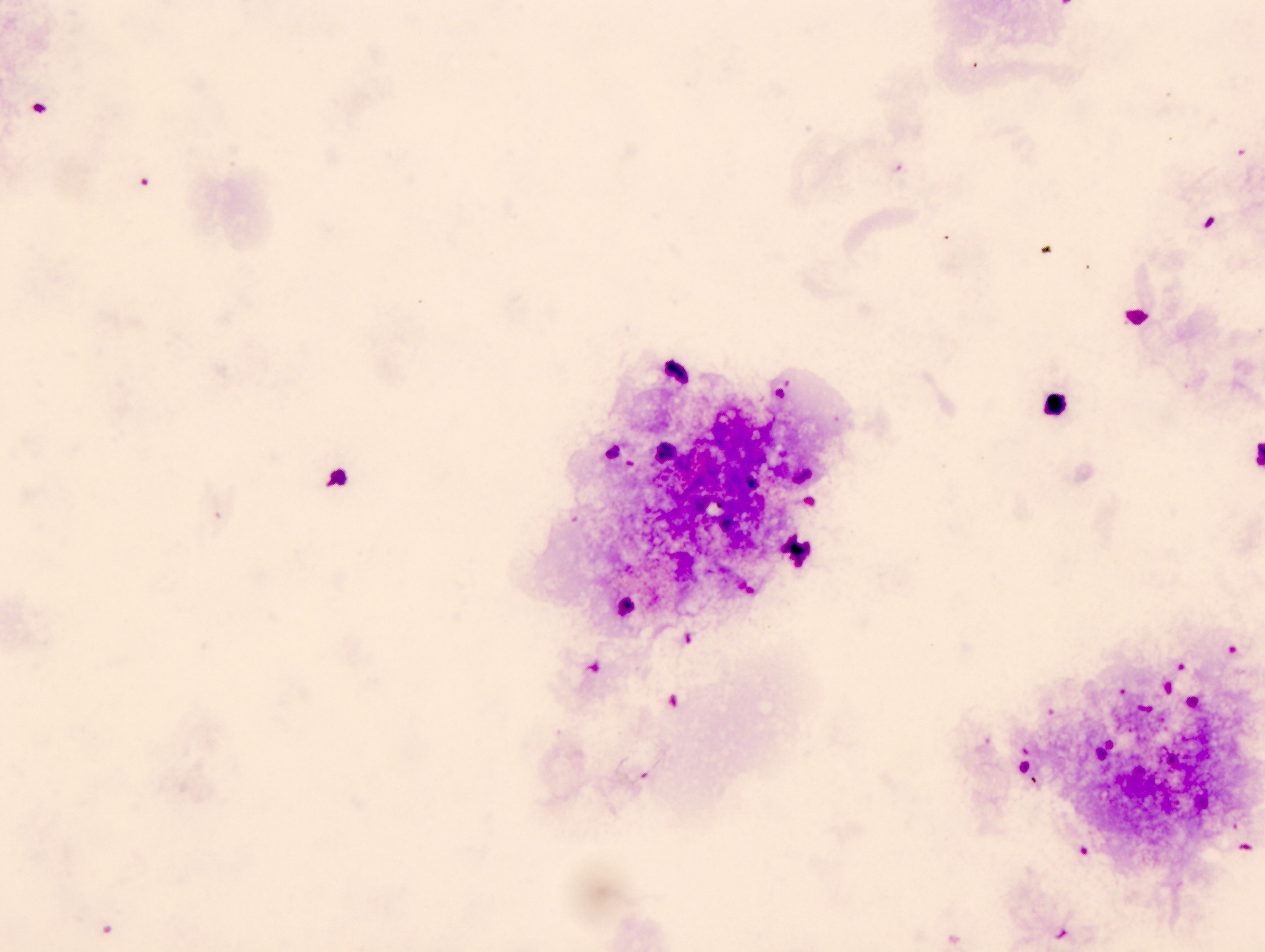
Practice question #3
Practice answer #3
C. Nondiagnostic. It is a nondiagnostic specimen due to the lack of alveolar macrophages. Other cells and material in this specimen, such as a few chronic inflammatory and mucin, may represent contamination.
Answer A is incorrect because this option is not likely as the specimen does not show the presence of atypical cells, which would typically be associated with malignancy.
Answer B is incorrect because while the specimen may not contain clear evidence of malignancy, it cannot be confidently classified as negative for malignancy due to the lack of alveolar macrophages and the nondiagnostic nature of the sample.
Answer D is incorrect because there is insufficient evidence in the specimen to conclude that it is positive for malignancy. The absence of alveolar macrophages and a clear lack of cancerous cells makes this an unlikely interpretation.
Answer E is incorrect because similar to the other options, this interpretation is not supported due to the lack of alveolar macrophages and the nondiagnostic nature of the specimen.
In summary, the provided picture of bronchioalveolar lavage (BAL) suggests that the sample is nondiagnostic due to the absence of alveolar macrophages and any atypical cell. Further testing or sampling may be needed to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Lung - Nondiagnostic
Comment Here
Reference: Lung - Nondiagnostic