Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Salibindla D, Sharma D. Candida. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophaguscandidaesophagitis.html. Accessed August 26th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Candida albicans, which can be locally invasive, is the most prevalent cause of infectious esophagitis
- Other common fungal species relevant to infectious esophagitis are C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, C. krusei and C. parapsilosis
Essential features
- Candida esophagitis is one of the most common types of esophagitis in immunosuppressed individuals
- Histological features include acute inflammation, intraepithelial neutrophilic abscesses and epithelial edema; parakeratosis most prominent in the superficial epithelial layers with yeast forms and pseudohyphae
- Treated with antifungals, often with good prognosis
Terminology
- Esophageal candidiasis, Candida esophagitis or esophageal moniliasis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Incidence rates ranging from 0.32% to 5.2% in the general population
- Increased prevalence in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive patients
- M = F (Gastroenterology Res 2018;11:195)
- Risk factors
- HIV
- Diabetes mellitus
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Medications such as antibiotics and corticosteroids
- Achalasia cardia
- Pregnancy
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPI) (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:200)
- Smoking
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Malignancy
Sites
- Can be diffuse or localized in esophagus (StatPearls: Esophageal Candidiasis [Accessed 27 November 2023])
Pathophysiology
- Due to impaired cell mediated immunity, the esophageal epithelial layer is susceptible to infection
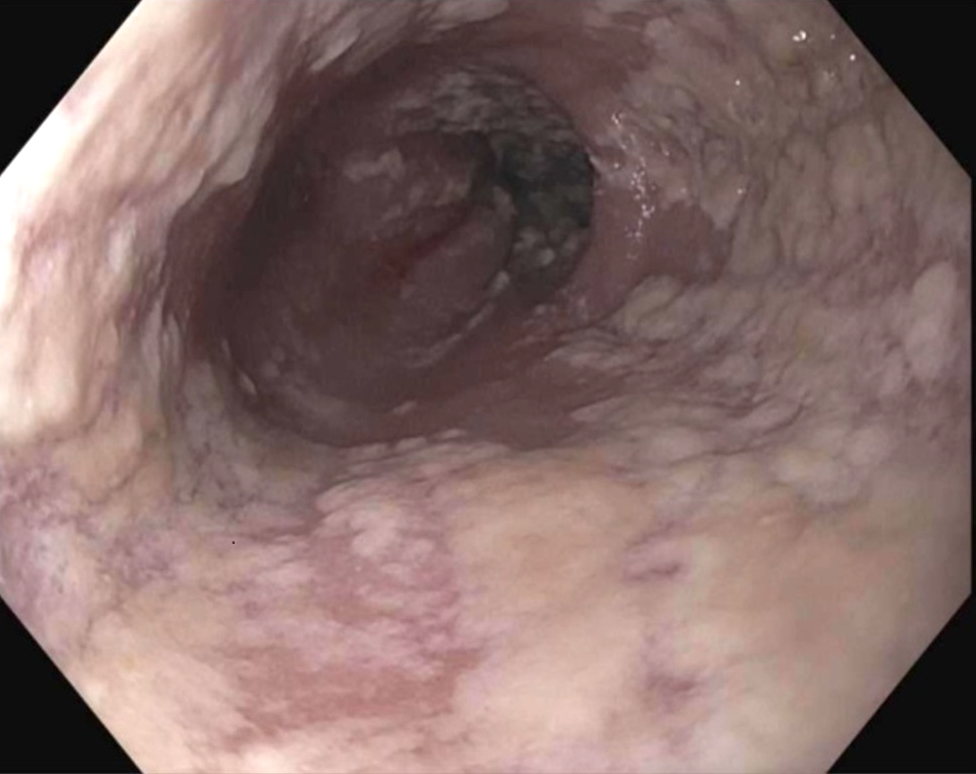
- Candida colonizes, proliferates and adheres to the esophageal mucosa, forming white-yellow plaques
- Reference: Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019:2019:3585136
Etiology
- Candida albicans
- Candida tropicalis
- Candida glabrata
- Candida krusei
- Candida parapsilosis
- Reference: Clin Infect Dis 2016;62:e1
Clinical features
- Typical symptoms include dysphagia, odynophagia and retrosternal pain
- Less commonly, abdominal pain, heartburn, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and weight loss (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:33)
- Plaques can be seen on upper endoscopy and do not wash from the mucosa with water irrigation
- May coexist with herpes or cytomegalovirus (CMV) esophagitis, oral thrush, esophageal intramural pseudodiverticulosis
Diagnosis
- Gold standard for the diagnosis is through histological examination
- Biopsy or brushing of the esophageal mucosa is taken during endoscopy
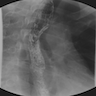
Radiology description
- Esophagogram
- On double contrast studies, discrete longitudinally oriented linear or irregular plaque-like lesions separated by normal mucosa with small (< 1 cm) punctuate, round or oval ulcers
- In advanced cases, the esophagus may have a grossly irregular or shaggy appearance as a result of innumerable plaques and pseudomembranes, with trapping of barium between the lesions
- Cobblestone appearance may be visible (Radiology 2005;237:414)
- Patients with scleroderma or achalasia may develop a foamy esophagus
Prognostic factors
- Poorer prognosis in the elderly (Dis Esophagus 2006;19:189)
- Esophageal obstruction, perforation and tracheoesophageal or aortoesophageal fistula formation are other rare but potentially life threatening complications
Case reports
- 29 year old Black woman, status post-deceased donor kidney transplant, with difficulty and pain in swallowing (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e230410)
- 36 year old man with esophageal stricture due to esophageal candidiasis (ACG Case Rep J 2021;8:e00603)
- 74 year old man with 3 day course of dysphagia (Cureus 2022;14:e24312)
- 80 year old woman with nausea, vomiting and appetite loss (JGH Open 2022;6:512)
Treatment
- Usually 2 - 3 week course of fluconazole (UpToDate: Esophageal Candidiasis in Adults [Accessed 16 November 2023])
- Treatment should continue for 1 - 2 weeks after resolution of symptoms
- Voriconazole is FDA approved for children at least 12 years of age
- Resolution of the radiographic findings sometimes lags behind the clinical recovery, so follow up barium studies may still be abnormal in patients who are asymptomatic
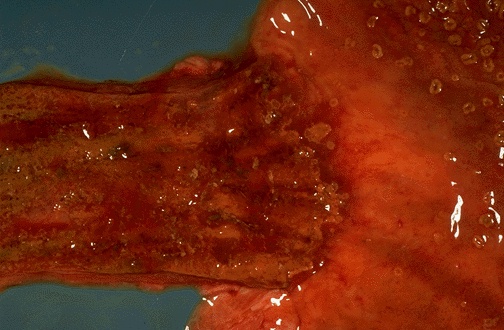
Gross description
- White or yellow patches measuring < 1 cm
- Resemble cottage cheese
- Reference: Prz Gastroenterol 2013;8:333
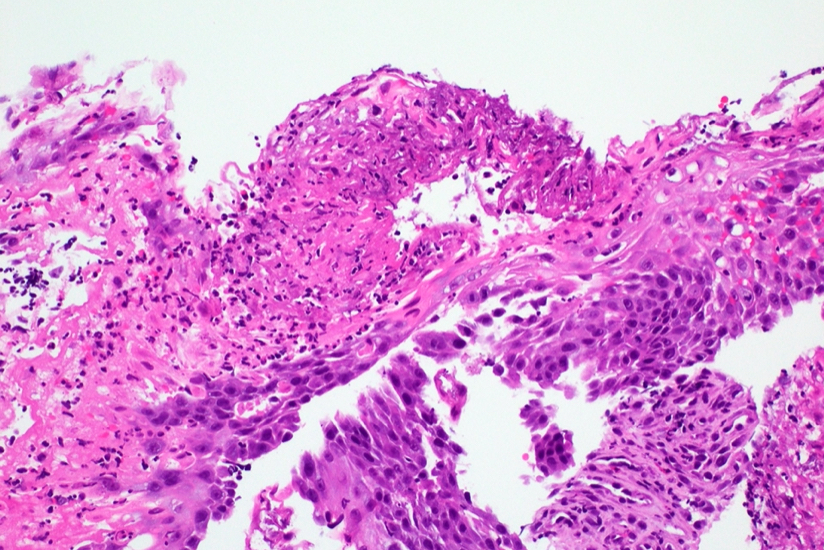
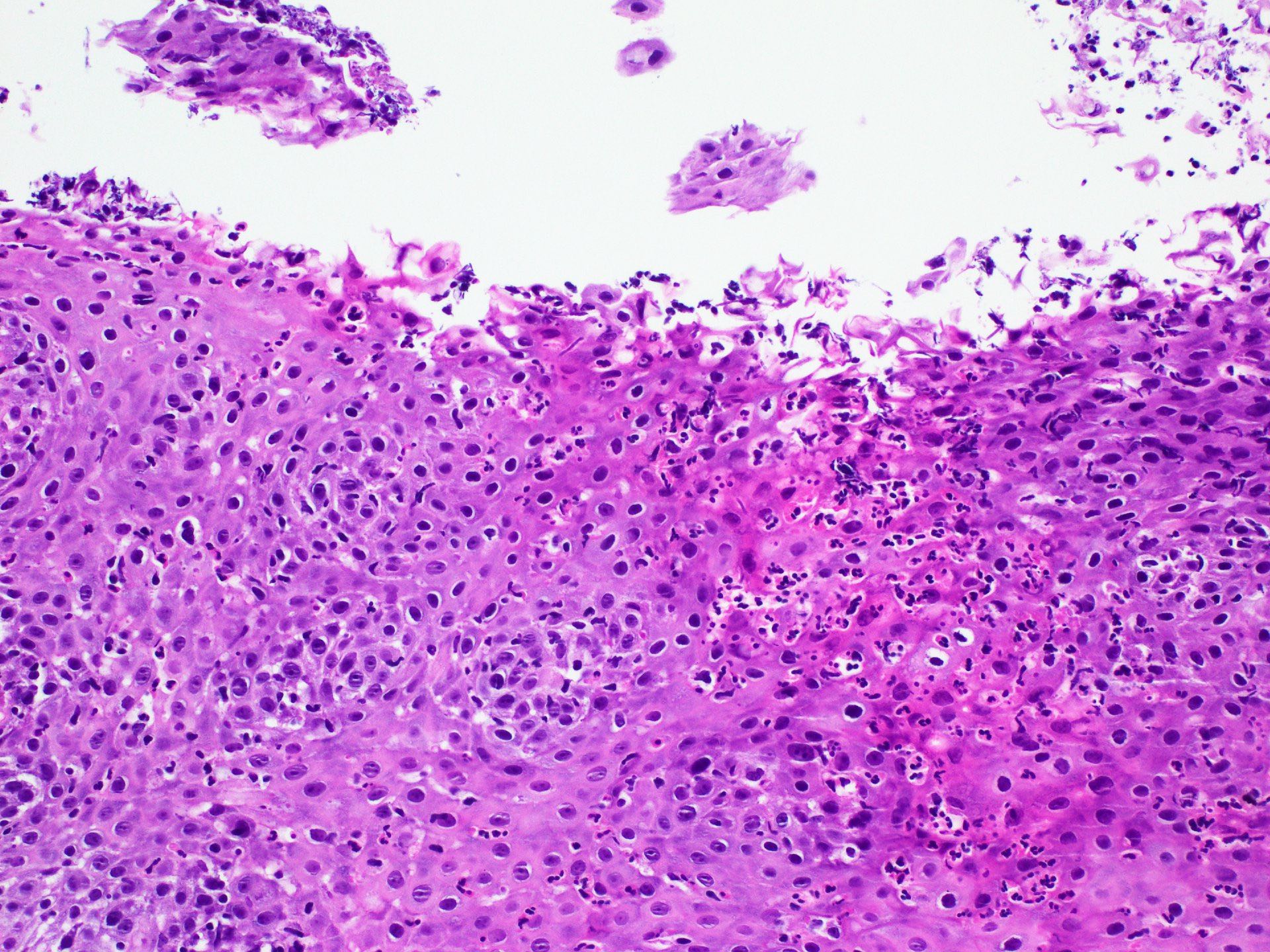
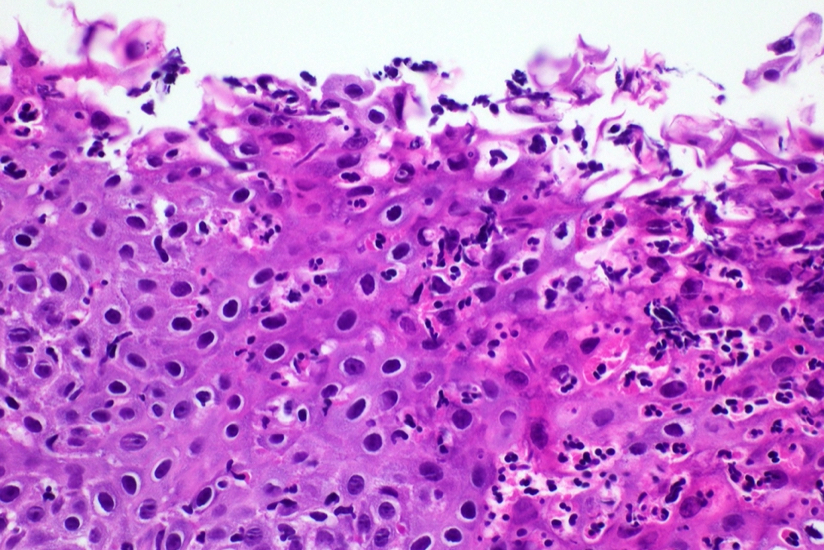
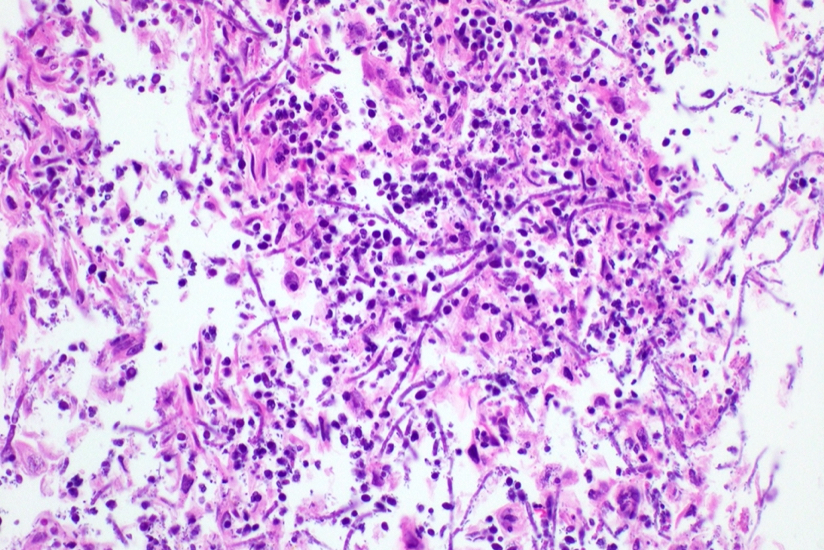
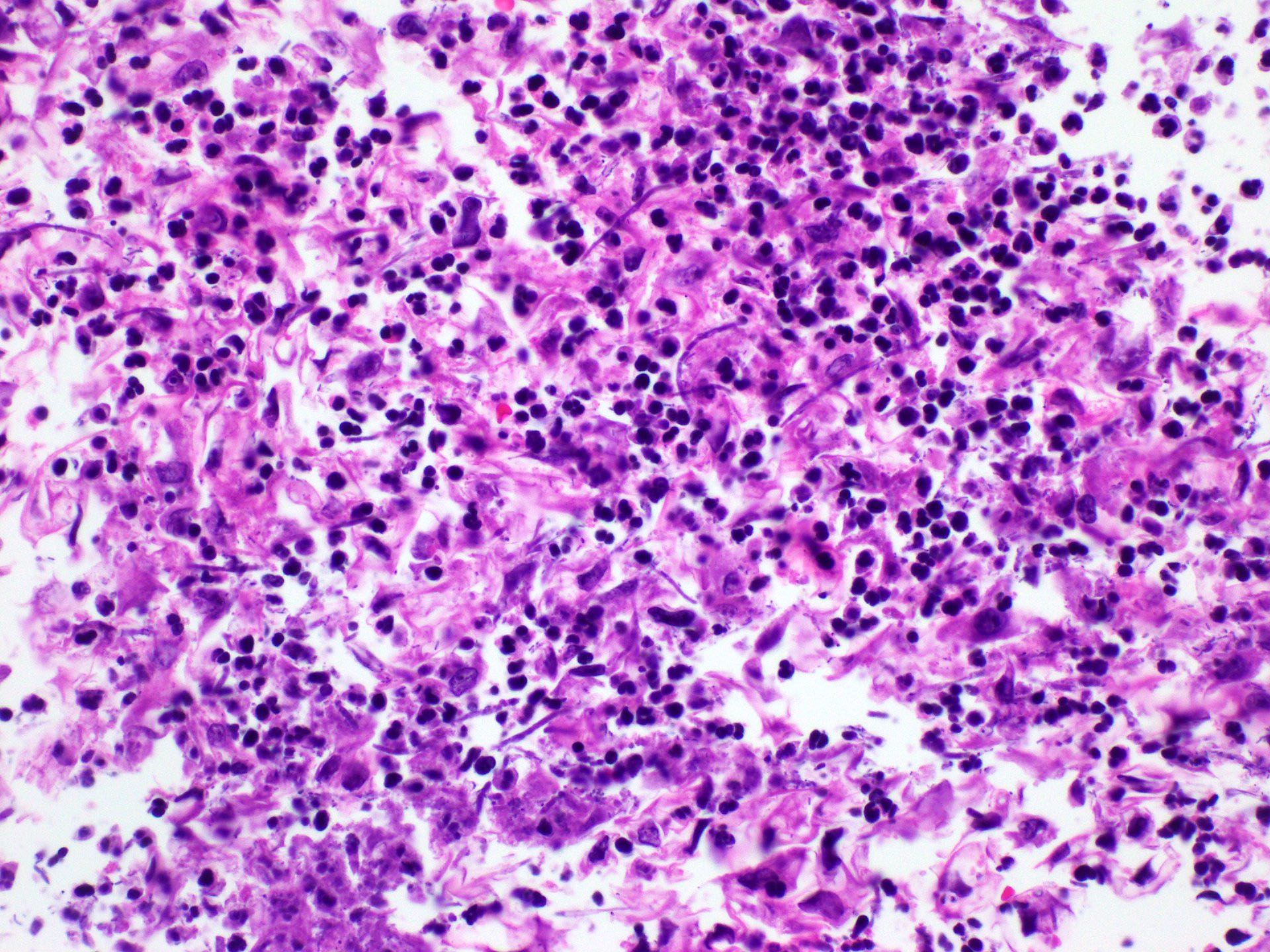
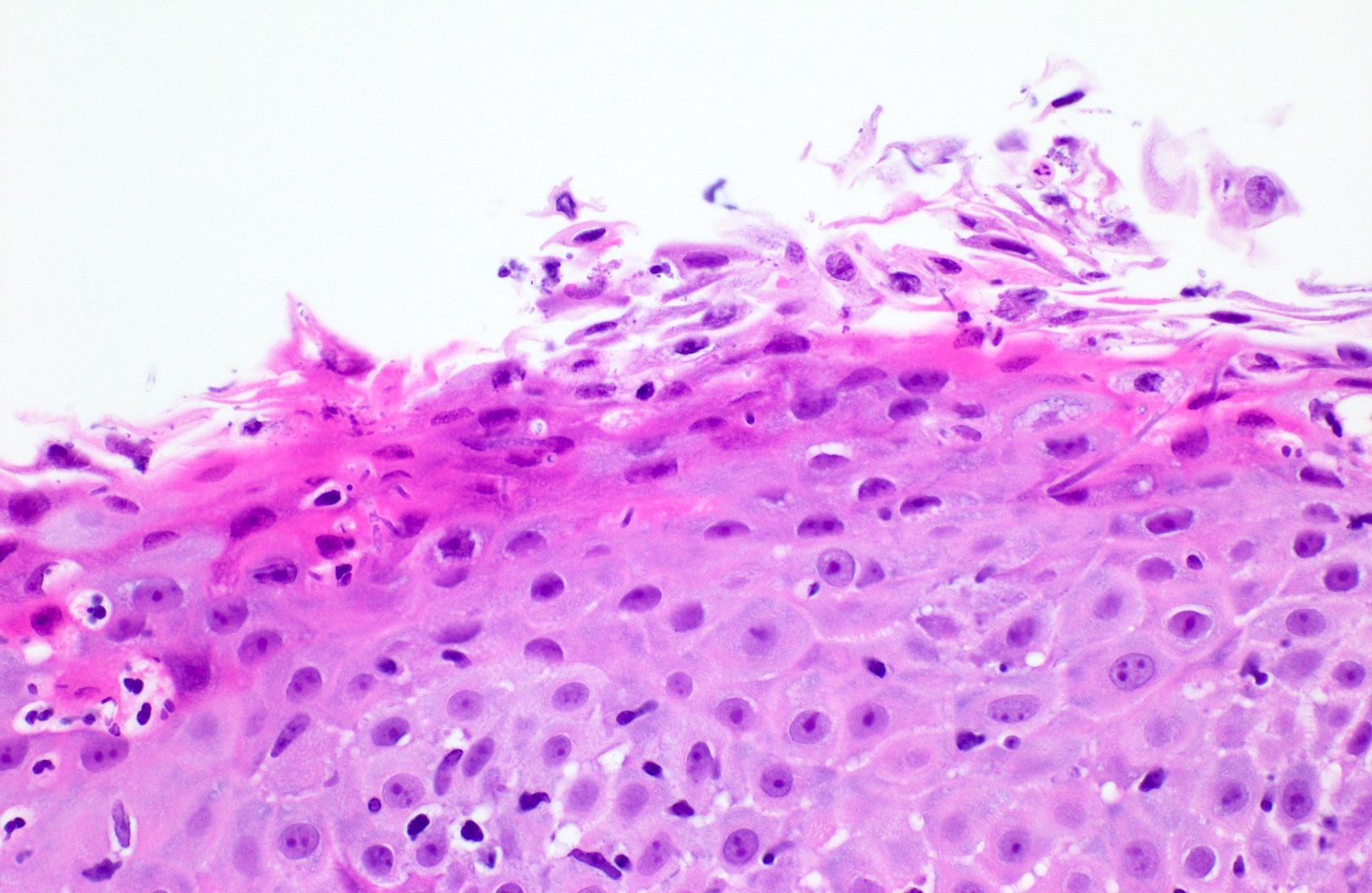
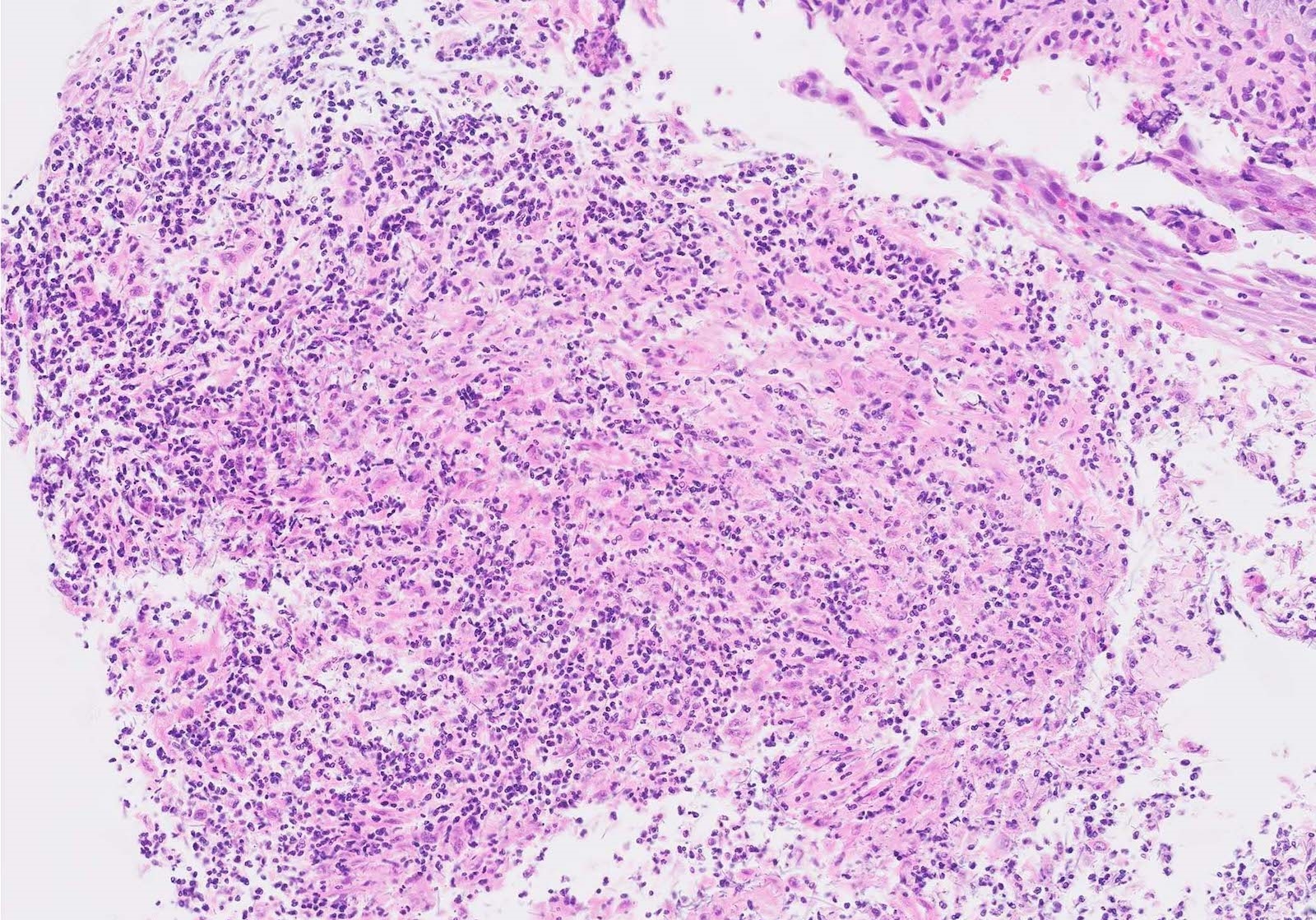
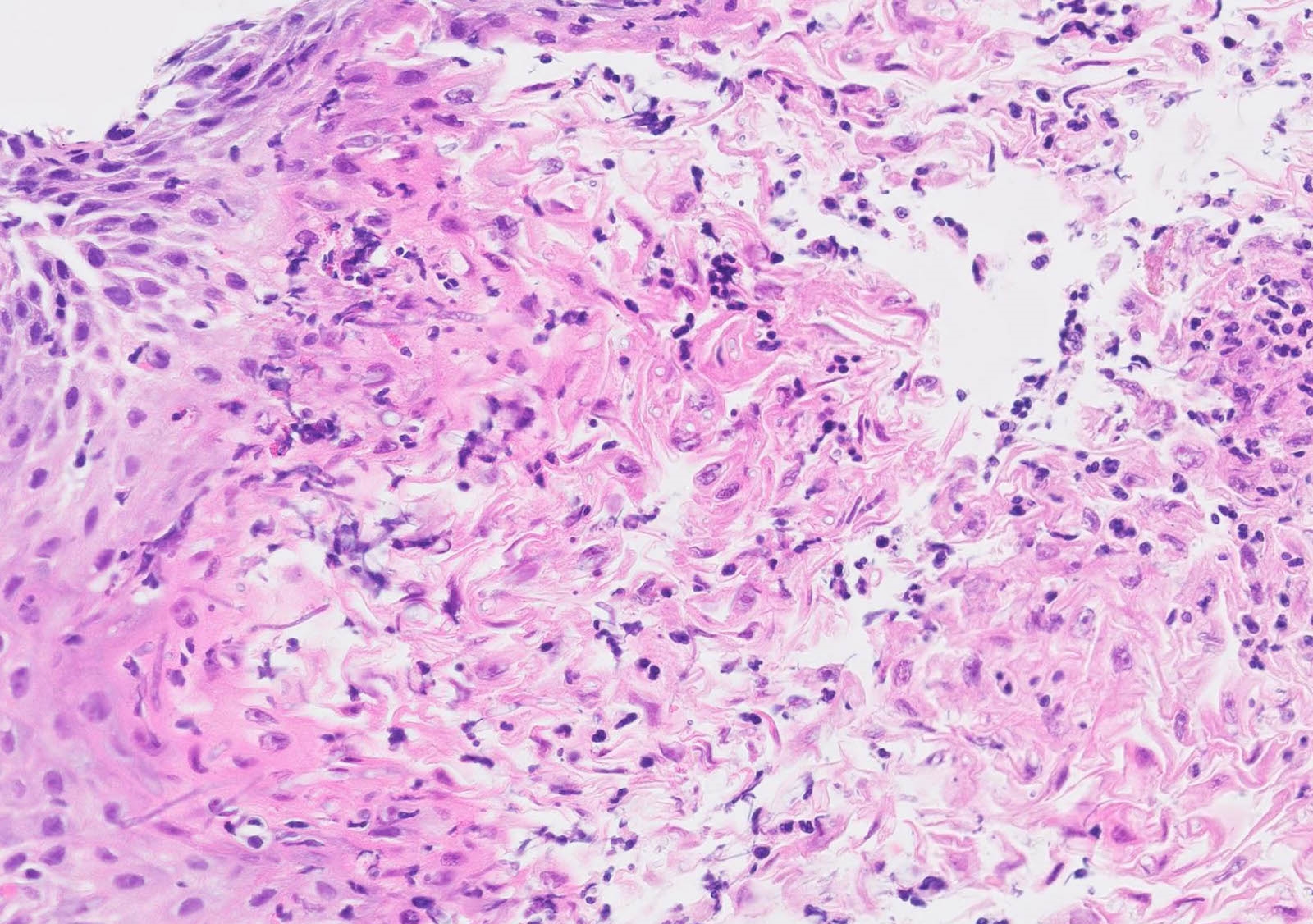
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Erosive esophagitis pattern of injury with acute inflammation, intraepithelial neutrophilic abscesses and epithelial edema most prominent in the superficial epithelial layers
- Reactive changes including basal zone hyperplasia, parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis are frequently associated
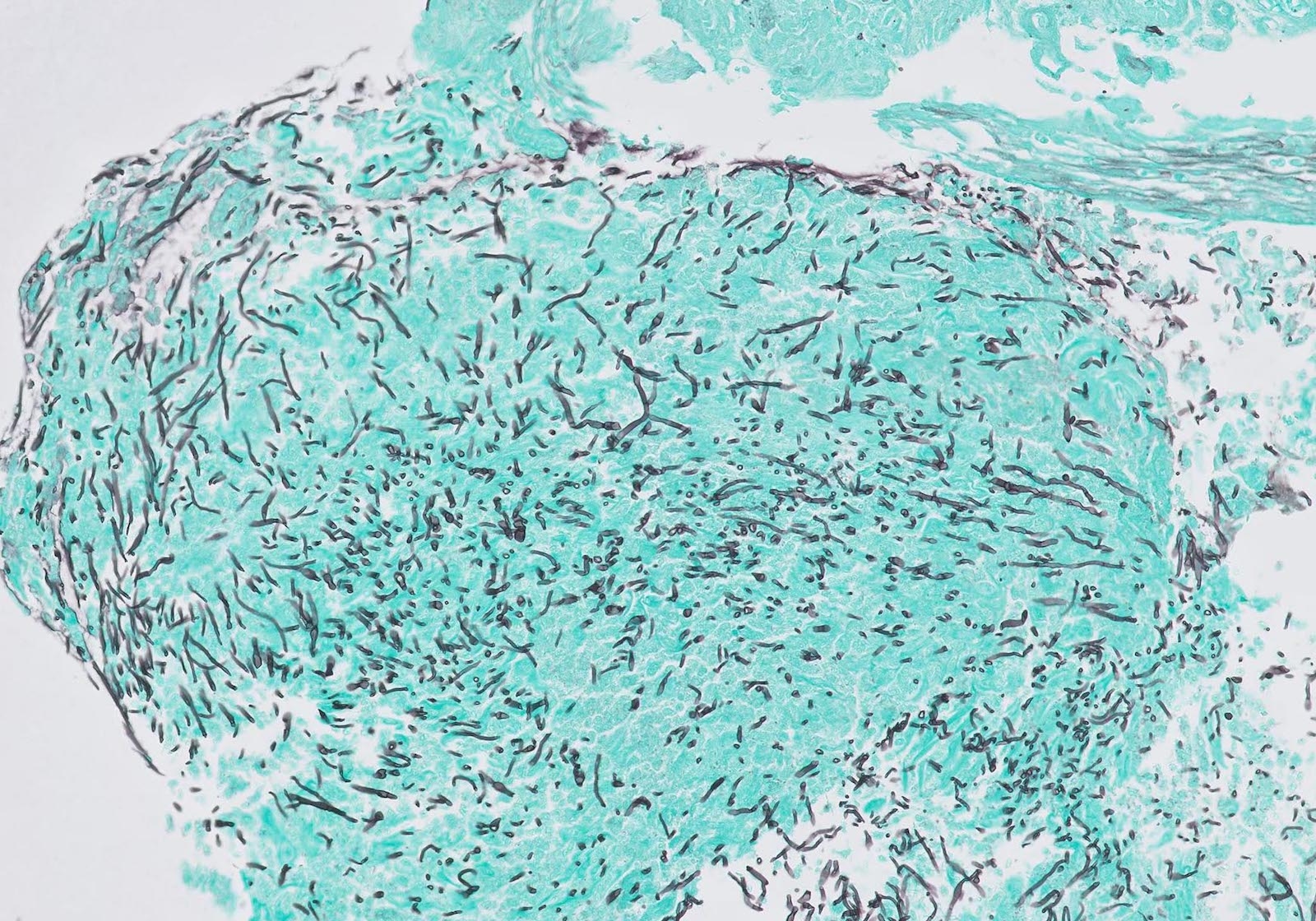
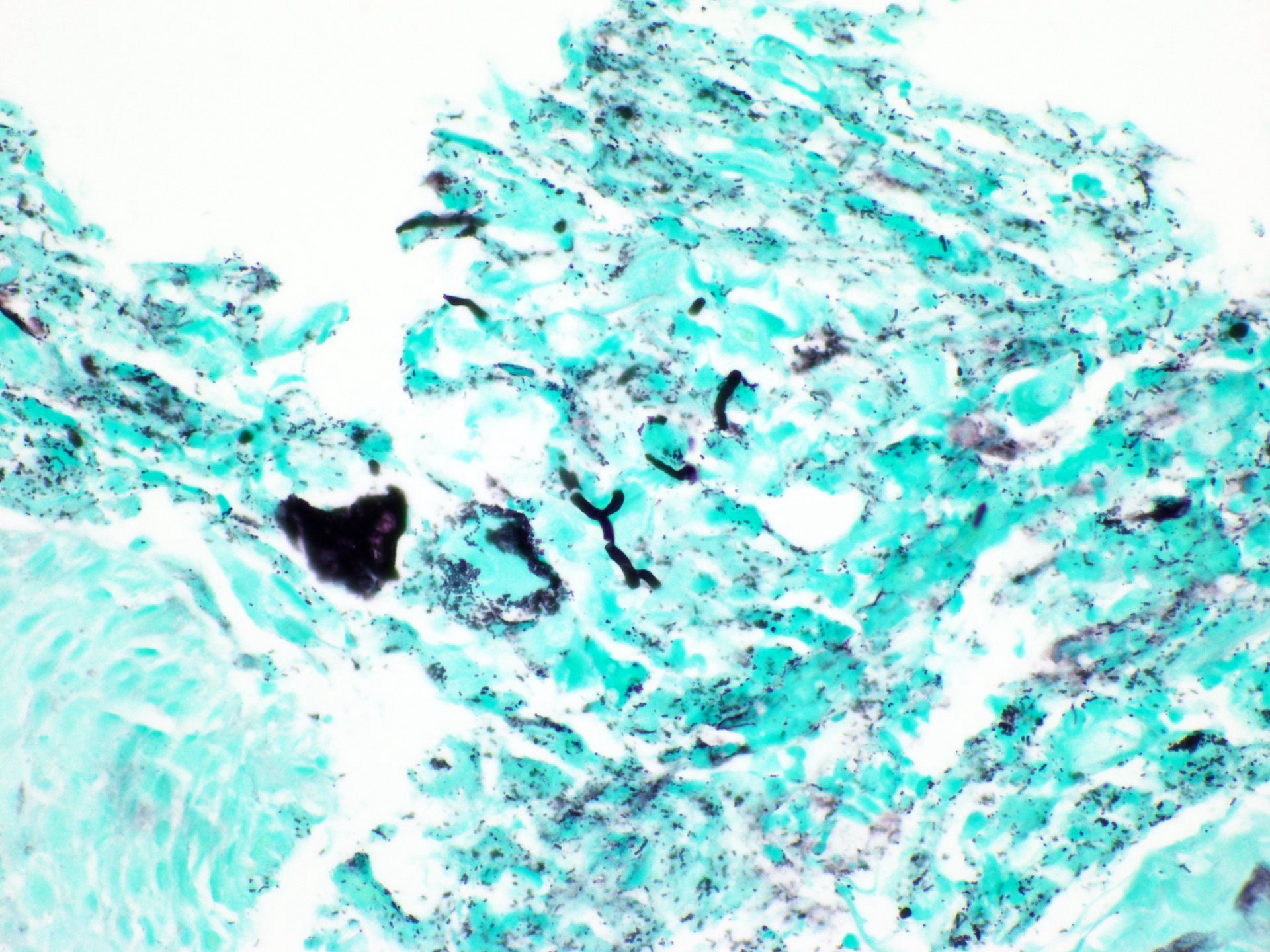
- 2 forms: yeast cells (often identified on Grocott methenamine silver stain [GMS]) and pseudohyphae
- Fungal elements are usually identified within the squamous debris, fibrinopurulent exudate or necrotic debris
- HIV patients may have invasion into muscularis propria and adventitia if untreated (Mycoses 1997;40:81)
- Histologic clues to esophageal candidiasis
- Hyper pink parakeratosis
- Shish kebab: pseudohyphae piercing through and skewer shed squames (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:33)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Divya Sharma, M.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and Jijgee Munkhdelger, M.D., Ph.D.
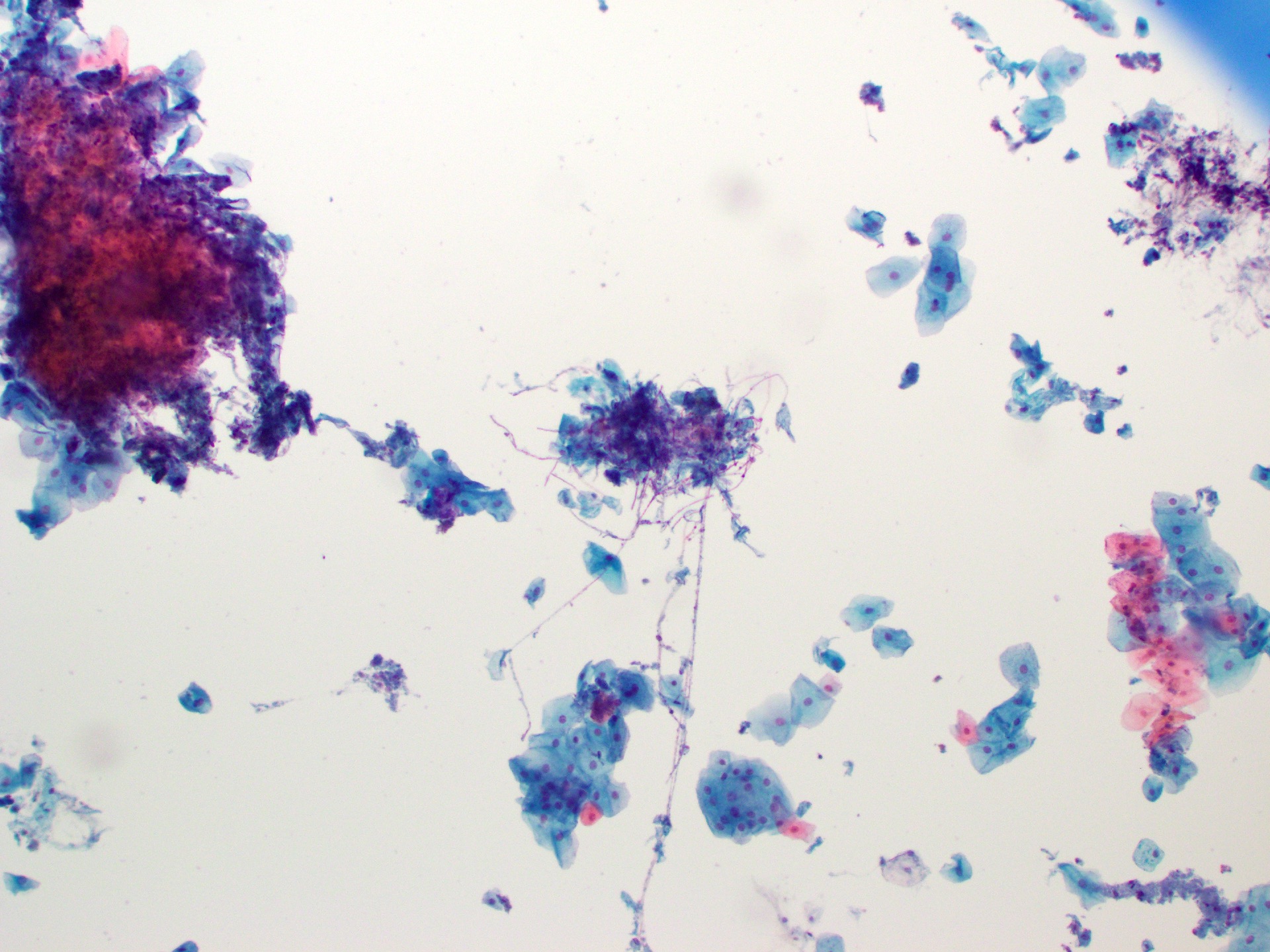
Cytology description
- Tiny budding yeast may form pseudohyphae with constrictions between adjacent cells
Videos
Candida esophagitis
Sample pathology report
- Esophagus, biopsy:
- Candida esophagitis
- Negative for intramucosal eosinophilia, dysplasia or malignancy
Differential diagnosis
- CMV esophagitis:
- More commonly presents as a single, isolated and deep, large ulcer rather than multiple small, shallow ulcerations as in herpes simplex virus (HSV) esophagitis
- Intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions are more common in mesenchymal and endothelial cells than epithelial cells
- Positive CMV IHC stain
- Negative HSV IHC stain
- Herpes esophagitis:
- Herpes zoster / varicella:
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 46 year old man with a history of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) presented with odynophagia. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) showed white-yellow mucosal plaques in the esophagus. The figure above is from an esophagus biopsy. Which of the following could be the causative agent?
- Candida
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Iron pills
Practice answer #1
A. Candida. This patient's history and the EGD findings of the esophagus suggest Candida esophagitis. His history of HIV is an underlying risk factor. The biopsy of the esophagus shows scattered neutrophils with fungal elements including pseudohyphae, supporting the above entity. Answer B is incorrect because pseudohyphae and yeast cells, as shown on the biopsy, are diagnostic for Candida esophagitis. Answer C is incorrect because while HSV esophagitis can affect both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, it is considerably more common in those with compromised immune function. In such cases, these viral infections typically present as ulcerative lesions in the esophagus rather than plaques. To confirm the presence of cytomegalovirus and HSV, it is advisable to perform biopsies of the ulcers. Answer D is incorrect as there was no polarizable crystalline material identified.
Comment Here
Reference: Candida
Comment Here
Reference: Candida
Practice question #2
Which of the following gross examination findings is consistent with Candida esophagitis?
- Bleeding varices
- Sloughing of the mucosa
- Ulcer in the mid esophagus
- Yellow-white mucosal plaques
Practice answer #2
D. Yellow-white mucosal plaques. Yellow-white plaques, which bleed upon removal, are consistent with Candida esophagitis. Answer C is incorrect as cytomegalovirus (CMV) / herpes simplex virus (HSV) are frequently associated with ulcers. Answer B is incorrect because sloughing of the mucosa can be seen in esophagitis dessecans superficialis. Answer A is incorrect because bleeding varices are associated with portal hypertension.
Comment Here
Reference: Candida
Comment Here
Reference: Candida