Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Elbendary A, Hong SA. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderxanthogranulomatous.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Unusual histologic variant of chronic cholecystitis
- Infiltration of foamy histiocytes and fibrosis in the background of chronic active inflammation
Essential features
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (XGC), in clinical and radiologic findings, can frequently mimic gallbladder cancer
- Pathologic findings are quite characteristic with foamy histiocytes, fibrosis and chronic active inflammation; when XGC is confused with gallbladder cancer, frozen examination can be useful in excluding malignancy
Epidemiology
- 0.7 - 10% of examined resected gallbladders (Gastroenterol Res Pract 2014;2014:253645)
- Usually ages 60 - 70; rarely children and young adults (World J Radiol 2016;8:183)
- Typically associated with gallstones (Lancet 1988;2:931)
Pathophysiology
- Increased intraluminal pressure due to obstruction of bile flow (various etiologies: gallstone, cancer, etc.) ⇢ rupture of Rokinstanky-Aschoff sinuses ⇢ bile spillage ⇢ inflammatory reaction (Gastroenterol Res Pract 2014;2014:253645, World J Radiol 2016;8:183)
Etiology
- Gallstones
Clinical features
- Patients' symptoms manifest as acute cholecystitis
Diagnosis
- XGC is usually diagnosed with histopathologic examination
- Radiologic imaging, including computed tomography, ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging, can be helpful but are limited for diagnosis
Case reports
- 15 year old boy with abdominal pain (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;14:A29)
- 63 year old woman with suspected gallbladder tumor (Int J Surg Case Rep 2014;5:138)
- 64 year old man with multiple liver abscesses (J Surg Case Rep 2018;2018:rjy337)
Treatment
- Cholecystectomy
Gross description
- Irregular thickening of the gallbladder wall with multiple yellow nodules
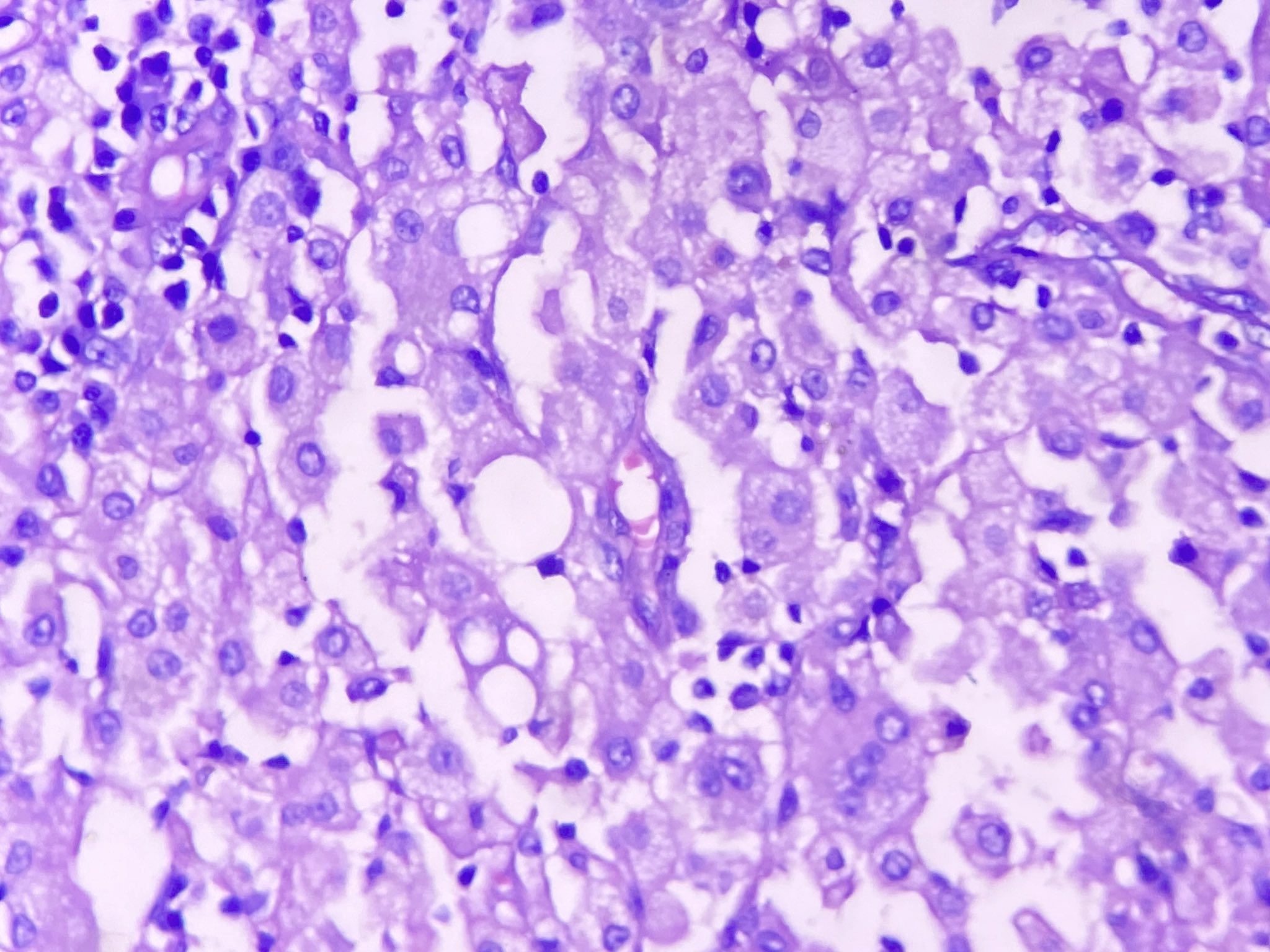
Microscopic (histologic) description
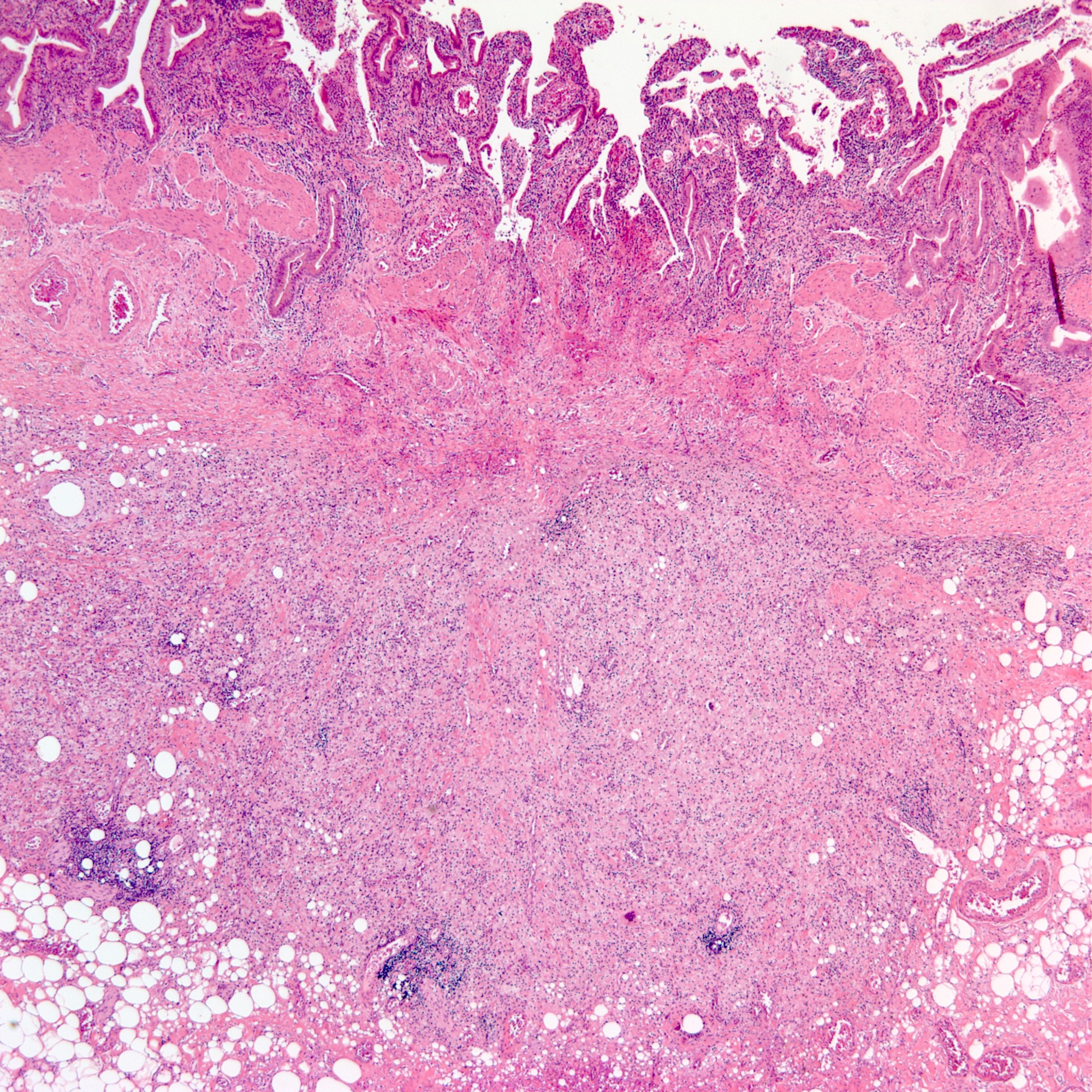
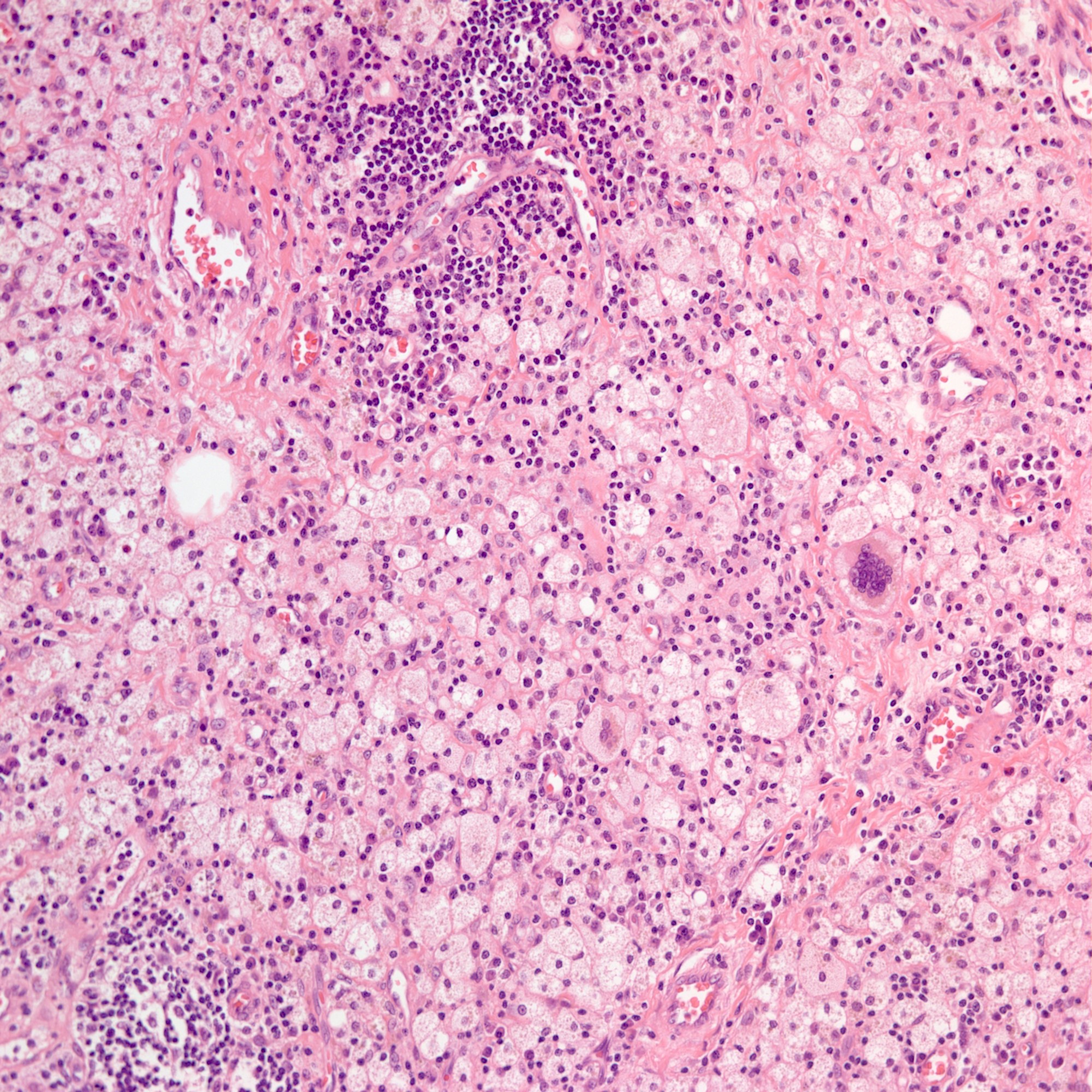
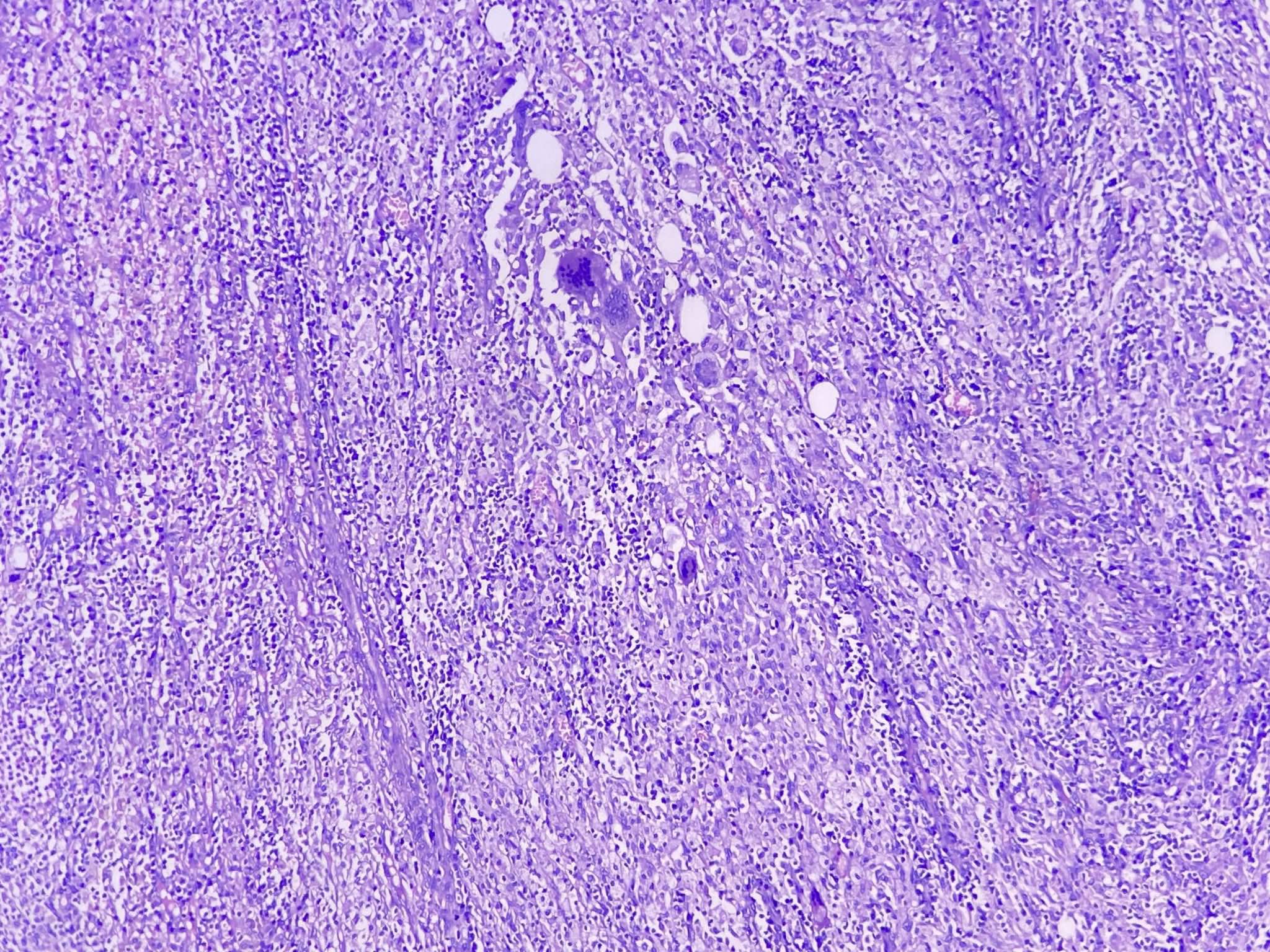
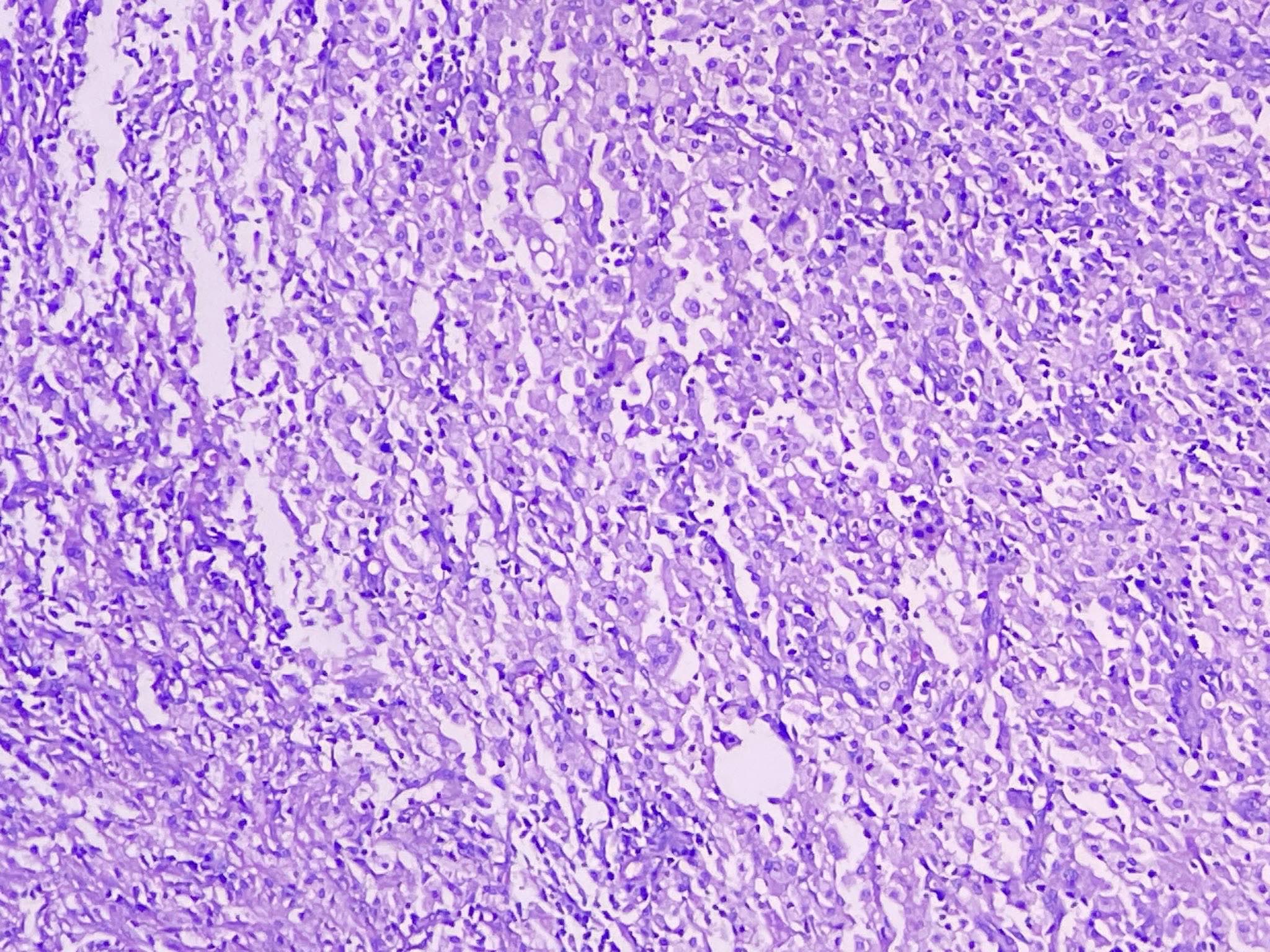
- Round to spindled shaped, lipid laden macrophages, giant cells and proliferative fibrosis in the background of chronic active inflammation (lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils and eosinophils)
- Transmural inflammation, mural and extramural inflammatory nodule
- Small foci of xanthomatous inflammation associated with chronic cholecystitis cannot be qualified as XGC
- Reference: World J Radiol 2016;8:183
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Amira Elbendary, M.B.B.Ch., M.Sc., Soon Auck Hong, M.D., Ph.D. and @riturajbaral on Twitter
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Cytokeratin may be needed to exclude carcinoma of the gallbladder
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Differential diagnosis
- Gallbladder adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell features:
- Cytokeratin staining is helpful
- Malakoplakia:
- Histiocytes with Michaelis-Gutmann bodies that are positive for PAS and von Kossa stains (Odze: Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas, 3rd Edition, 2014)
Practice question #1
In a resected gallbladder, histopathologic examination showed sheets of histiocytes in the gallbladder. PAS staining demonstrated intracytoplasmic granules in histiocytes. What is the best diagnosis?
- Hemophagocytosis
- Malakoplakia
- Rosai-Dorfmann disease
- Signet ring cell carcinoma
- Xathogranulomatous cholecystitis
Practice answer #1
B. Malakoplakia. Malakoplakia is rare but can occur in the gallbladder. The histologic findings are very similar to those of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis; however, histiocytes in malakoplakia are typically positive for PAS, while those in xanthogranulomoatus cholecystitis are negative.
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Practice question #2
A 63 year old patient visited the hospital with upper quadrant abdominal pain. Gallbladder cancer was strongly suspected in preoperative computed tomography. After the operation, histologic examination showed the findings in the image above. What is the best diagnosis?
- Acute emphysematous cholecystitis
- IgG4 related cholecystitis
- Mycobacterial infection
- Signet ring cell carcinoma
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Practice answer #2
E. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis is a rare variant of cholecystitis. It frequently mimics gallbladder malignancy according to radiologic examination. Histopathologic examination shows round to spindled shaped, lipid laden macrophages, giant cells and proliferative fibrosis in the background of chronic active inflammation (lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils and eosinophils).
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis