Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Lengyel K, Hanley K. Polycystic ovary disease. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarypco.html. Accessed September 6th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a clinicopathologic syndrome comprising polycystic ovaries and characteristic clinical features
- Polycystic ovaries resembling PCOS may be seen in prepubertal period or puberty without clinical manifestations
Essential features
- Most common cause of anovulatory infertility
- Presents with a variety of clinical and radiologic findings
- Grossly enlarged, multicystic ovaries, although may not be enlarged in adolescent patients
- Microscopically: ovaries with multiple cysts, hyperthecosis and atretic follicles
- Associated with endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial neoplasia
Terminology
- Formerly called Stein-Leventhal syndrome
Epidemiology
- Affects 4 - 12% of women in the U.S., usually of teenage or childbearing ages (Clin Med Res 2004;2:13)
Pathophysiology
- Development of insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovary disease is not fully understood
- Familial clustering of cases has been observed, strongly suggesting a genetic basis for polycystic ovary disease; however, no specific genetic abnormality has been shown to be the sole culprit in the development of polycystic ovary disease
Clinical features
- Presents with menstrual disorders (from amenorrhea to menorrhagia) and infertility
- Can cause acne, obesity, hirsutism, insulin resistance and diabetes
- 3 different diagnostic criteria:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) (1990): androgen excess, oligoovulation and exclusion of other entities that cause polycystic ovaries
- European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology / American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ESHRE / ASRM) in Rotterdam (2003) (2 of 3 present):
- Oligoovulation or anovulation
- Excess androgen activity (clinical or biochemical signs)
- Polycystic ovaries present (by ultrasound) but no other endocrine disorders
- Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (AE-PCOS) Society criteria (2006):
- Hyperandrogenism and any 1 or 2 of:
- Ovulatory dysfunction
- Polycystic ovarian morphology (PCOM)
- Hyperandrogenism and any 1 or 2 of:
- 90% of endometrial cancers arise in a background of chronic estrogen stimulation
- Obesity (associated with PCOS), which encourages the conversion of androstenedione to estrone in adipose tissue via aromatase activity, is strongly associated with this subset of endometrial tumors
- Reference: Crum: Diagnostic Gynecologic and Obstetric Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2017
Diagnosis
- Clinical symptoms:
- Oligo or anovulation
- Androgen excess (hirsutism, acne)
- Radiologic findings:
- Ultrasound is gold standard
- MRI may be used but is not generally indicated
- Reference: Crum: Diagnostic Gynecologic and Obstetric Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2017
Radiology description
- Transvaginal ultrasound:
- Increased ovarian volume with size > 10 mL
- Presence of at least 12 follicles that are between 2 and 9 mm in a single ovary (Hum Reprod 2003;18:598)
- Peripheral distribution of multiple follicles, giving a string of pearls appearance
Case reports
- 18 year old woman with hirsutism and oligomenorrhea (Gynecol Endocrinol 2013;29:273)
- 31 year old woman with polycystic ovary syndrome and increasing ovarian cyst size (Medicine (Baltimore) 2021;100:e28261)
- 32 year old woman with a few year history of hirsutism, menstrual disorders and T1DM (Endocr J 2016;63:193)
Treatment
- Lifestyle modifications, weight loss
- Treatment of hirsutism and insulin resistance
- Infertility:
- Letrozole (aromatase inhibitors) is associated with increased ovulation rate to clomiphene citrate (N Engl J Med 2014;371:119)
- Ovarian drilling puncture of small follicles with electrocautery, although effectiveness has been questioned (Hum Reprod 2002;17:2851, Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;3:CD001122)
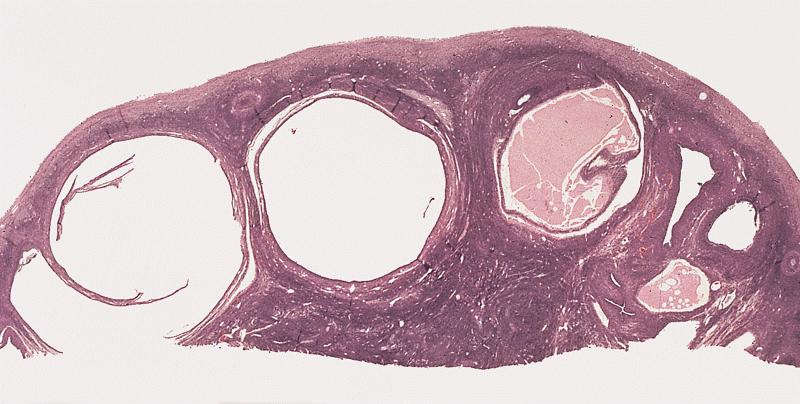
Gross description
- Enlarged ovaries, with numerous subcortical cysts (cysts may be immature follicles)
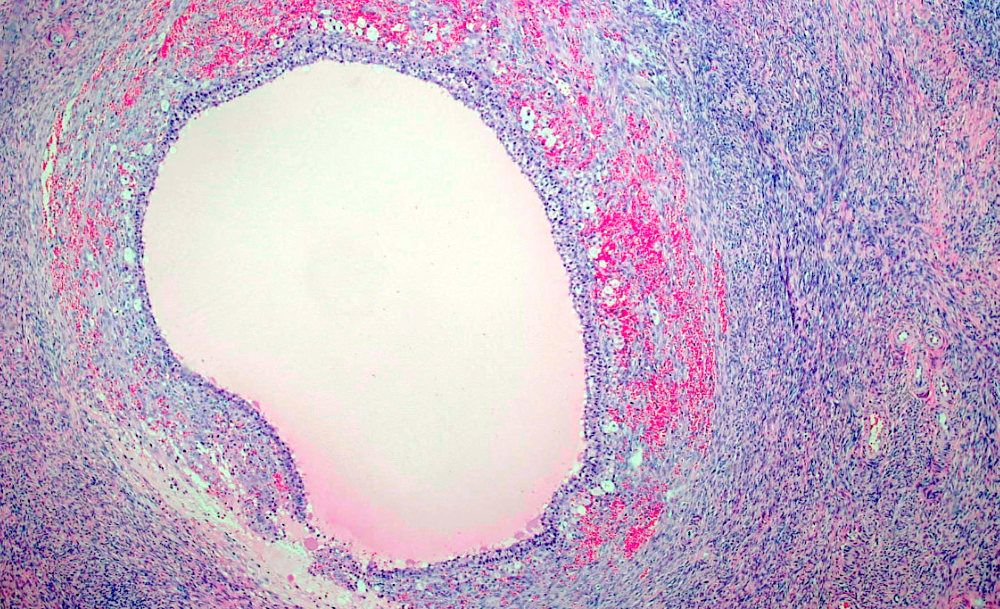
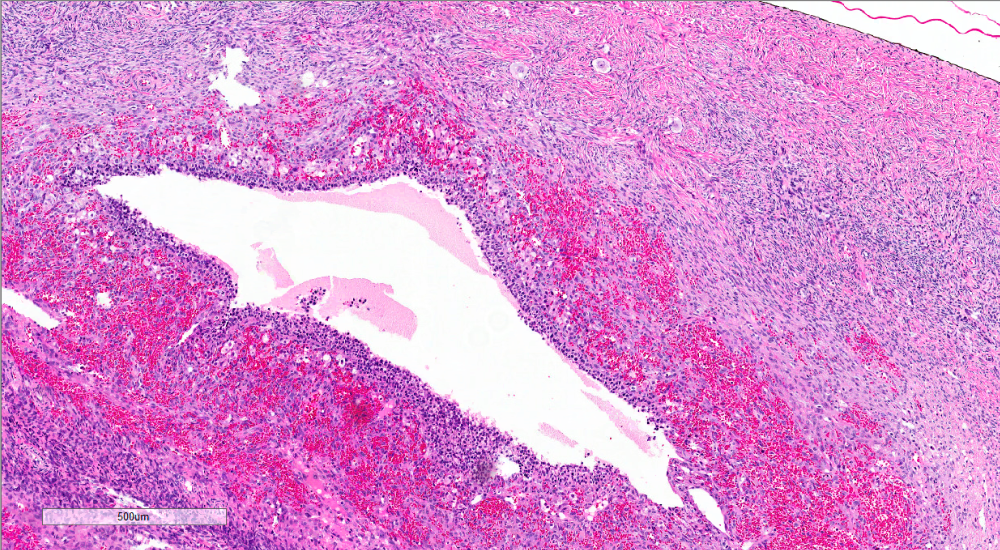
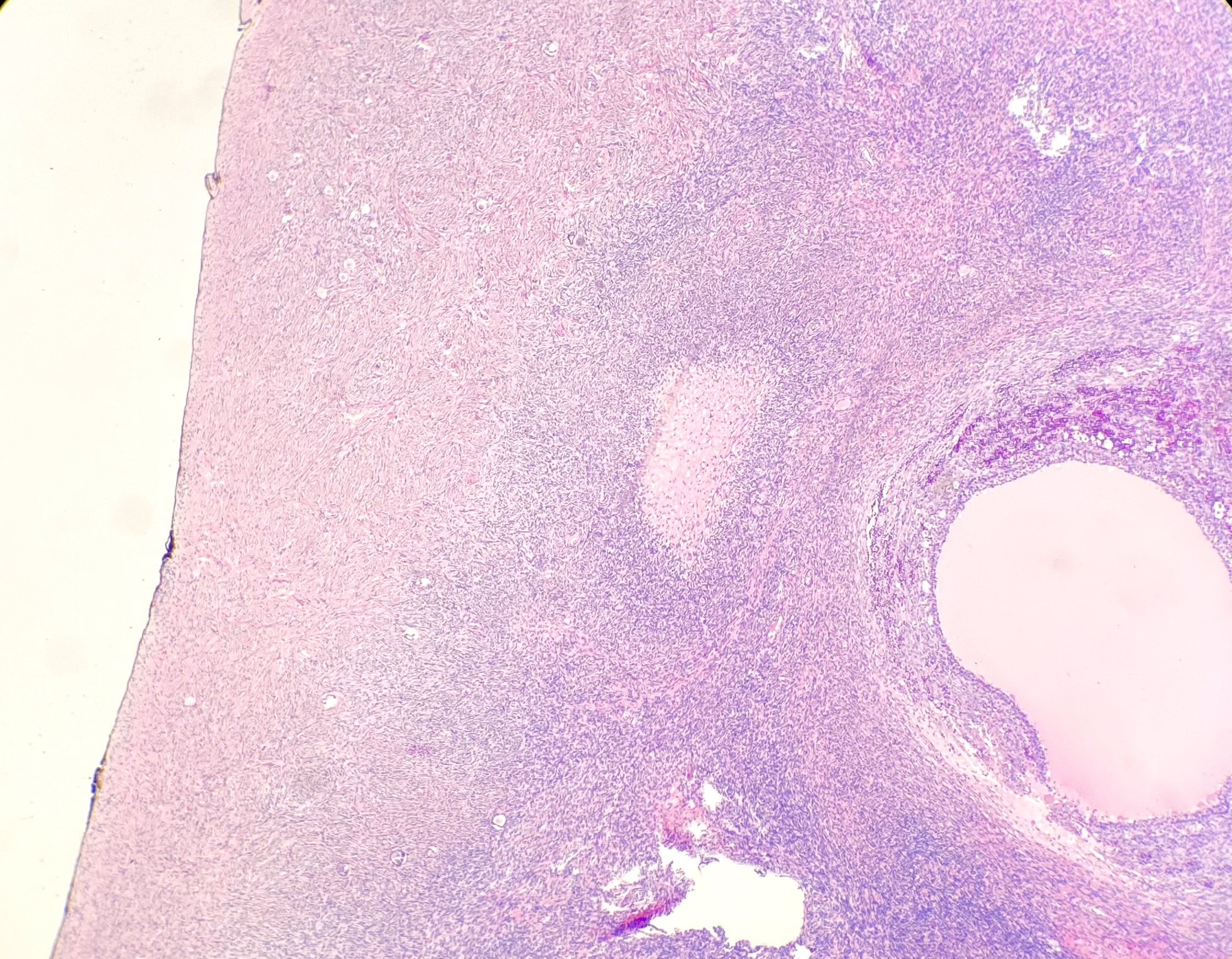
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Increased ovarian size, including thickness of cortical and subcortical stroma
- Thickened collagenized tunica
- Normal numbers of primordial follicles
- Twice the expected number of ripening and atretic follicles
- Multiple cystic follicles (1 - 2 mm) with luteinized theca layer (theca lutein hyperplasia)
- Reference: Crum: Diagnostic Gynecologic and Obstetric Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2017
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Ovary, left, oophorectomy:
- Benign ovary with collagenized tunica, theca lutein hyperplasia of cystic follicles and atretic follicles with residual theca lutein hyperplasia, consistent with polycystic ovary
Differential diagnosis
- Endocrine disorders:
- Androgen secreting tumors:
- Symptoms of hirsutism, acne, deepening of voice
- Laboratory results: high blood testosterone, DHEA sulfate levels and urine 17 ketosteroids
- Exogenous androgen:
- Laboratory results: high blood testosterone
- Cushing syndrome:
- Adrenal adenoma (ACTH independent Cushing syndrome)
- Symptoms include male pattern baldness, clitoromegaly and deepening of voice
- High cortisol levels, low ACTH level
- Nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia:
- Due to either 21 hydroxylase deficiency (most common), 11β hydroxylase deficiency or 3β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency
- Most common biochemical abnormality is adrenal androgen excess
- Measure 17 hydroxyprogesterone, serum cortisol, serum androstenedione
- Analysis of CYP21A2 gene, which encodes 21 hydroxylase, may be used to confirm diagnosis of nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (Hum Reprod Update 2017;23:580)
- Primary ovarian failure:
- Characterized by high levels of gonadotropins, particularly FSH
- Exceptions are prepubertal age or menopausal transition
- Characterized by high levels of gonadotropins, particularly FSH
- Androgen secreting tumors:
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 34 year old woman presents with years of irregular menstrual cycles and infertility. On physical examination, she's noted to have hirsutism, central obesity (BMI of 35) and acne. Her bloodwork is noted to have elevated total testosterone and an abnormal glucose tolerance test (GTT). What is she at increased risk of?
- Cardiovascular disease
- Endometrial hyperplasia / adenocarcinoma
- Hypothyroidism
- Primary ovarian failure
Practice answer #1
B. Endometrial hyperplasia / adenocarcinoma. The vignette describes a patient presenting with polycystic ovary disease (reproductive age woman with hirsutism and infertility). She had biochemical changes indicating polycystic ovary disease, such as elevated testosterone and an abnormal glucose tolerance test suggesting insulin resistance. She is at increased risk for endometrial hyperplasia / adenocarcinoma due to frequent anovulation.
Comment Here
Reference: Polycystic ovary disease
Comment Here
Reference: Polycystic ovary disease
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
C. Fibrotic ovarian cortex. Polycystic ovary syndrome has multiple histologic hallmarks, one of which is the fibrotic ovarian cortex / collagenized tunica. The other features include twice the expected ripening and atretic follicles, multiple cystic follicles with luteinized theca layer (theca lutein hyperplasia).
Comment Here
Reference: Polycystic ovary disease
Comment Here
Reference: Polycystic ovary disease