Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Wilham M, Dehner CA. Digital myxoid cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticdigitalmyxoidcyst.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Typically solitary cystic nodules found on the dorsal portion of phalanges
- Resemble either ganglion cysts or mucinosis depending on the variant
Essential features
- Benign pseudocyst associated with the dorsum of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint
- Most often found in women and those of older age, particularly with osteoarthritis
- Lined by fibrous spindle cells with random orientation
- Contents consist mostly of mucin with scattered fibroblasts
- Can be treated conservatively but recurrence rate is high without a full surgical excision
Terminology
- Digital mucoid cyst
- Digital mucous cyst
- Digital myxoid pseudocyst
Epidemiology
- Similar risk factors to ganglion cysts: prior trauma, arthritis, female sex at birth and older age (DynaMedex: Ganglion Cysts [Accessed 29 August 2024])
- Some sources suggest that ganglion cysts are almost 3 times more likely to affect women (StatPearls: Digital Mucous Cyst [Accessed 29 August 2024])
Sites
- Phalanges, frequently involving the distal interphalangeal joint
- May involve the nail bed
Pathophysiology
- Unclear at this time
- Thought to be a one way outpouching of synovial fluid that cannot flow back into the joint (Dermatol Clin 2021;39:281)
- Other proposed mechanisms include degeneration of local soft tissue (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:65)
Etiology
- Unknown at this time
Clinical features
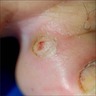
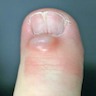
- Typically presents as a solitary, slow growing mass in close proximity to the distal interphalangeal joint
- Round and either firm or fluctuant
- Overlying skin may be thin or thick
- Transilluminates
- Associated with osteoarthritis (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:65)
Diagnosis
- Largely based on history and exam
- Diagnostic procedure can include workup for arthritis using Xrays
Radiology description
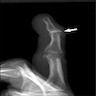
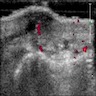
- Evidence of swelling / cystic space
- Osteoarthritis findings, including joint space narrowing or osteophytes (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2018;115:269)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Digital myxoid cysts are benign and can be treated conservatively
- Recurrence rates change depending on treatment
- Aspiration is the least invasive but has recurrence rates as high as 50% (StatPearls: Digital Mucous Cyst [Accessed 29 August 2024])
- Joint arthrodesis minimizes recurrence (J Hand Surg Am 2010;35:828)
Case reports
- 59 year old woman with early signs of osteoarthritis presented with multiple nodules (Int J Dermatol 2020;59:e242)
- 61 year old woman with osteoarthritis (Acta Med Port 2022;35:591)
- 62 year old man with coexisting digital myxoid cyst and epidermal inclusion cyst (Ann Dermatol 2008;20:67)
Treatment
- Conservative management in patients without disruptive symptoms
- Patients may elect for more invasive treatment for pain control or esthetics
- Surgical in the form of aspiration or full excision (Ann Dermatol 2017;29:69)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Tan, multilobulated, translucent cyst
- Cyst content is a viscous, clear to tan fluid (StatPearls: Digital Mucous Cyst [Accessed 29 August 2024])
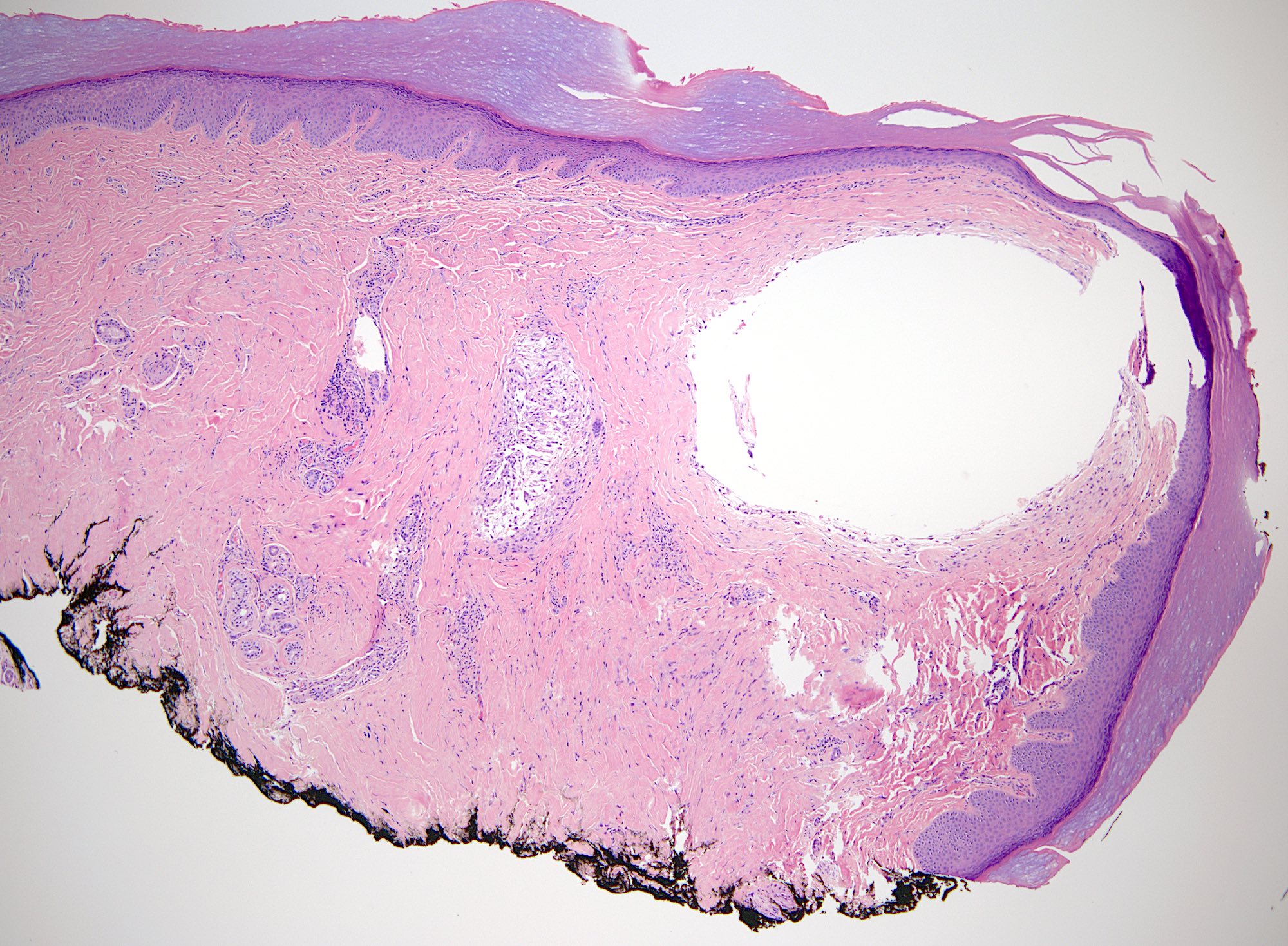
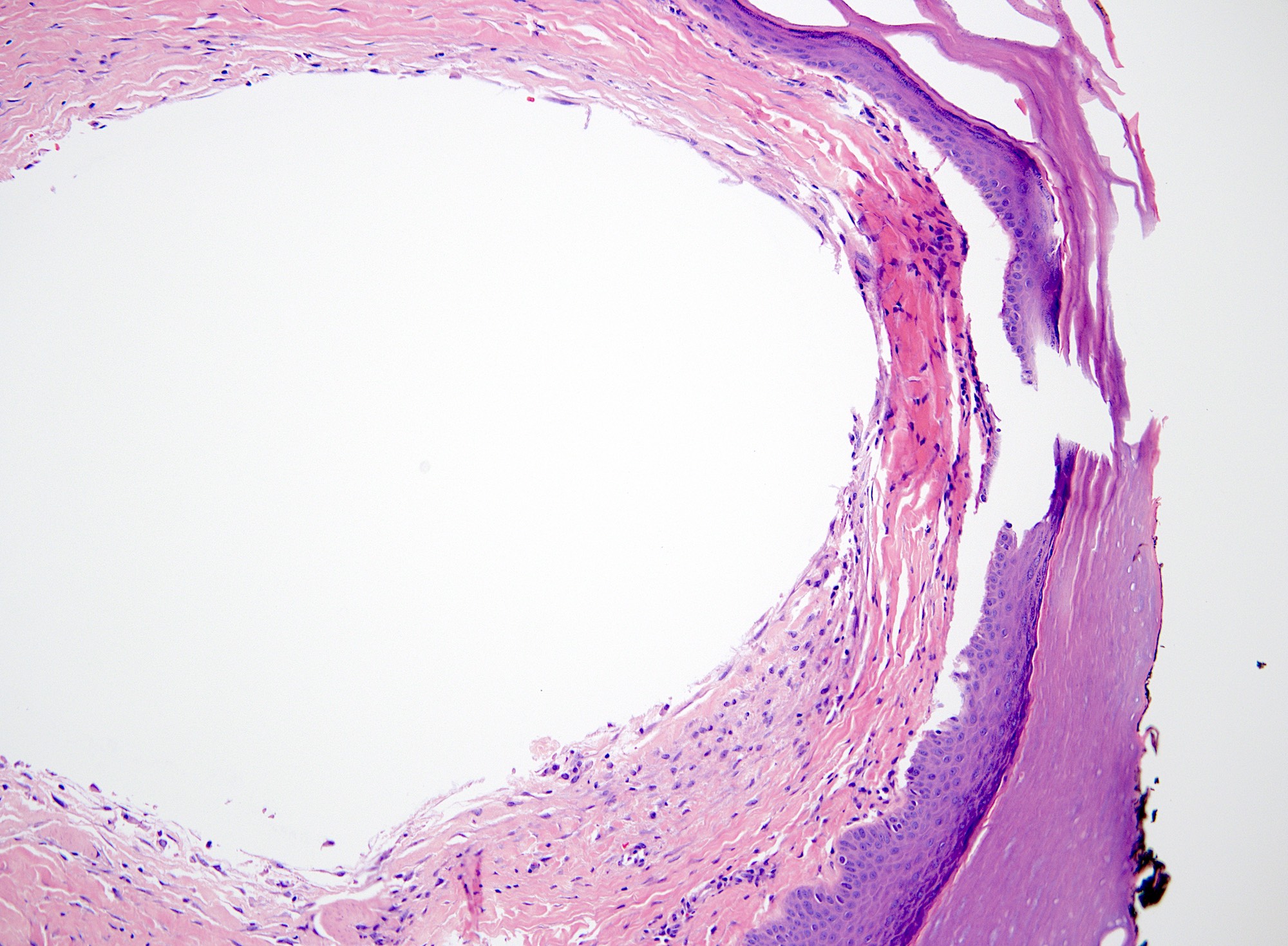
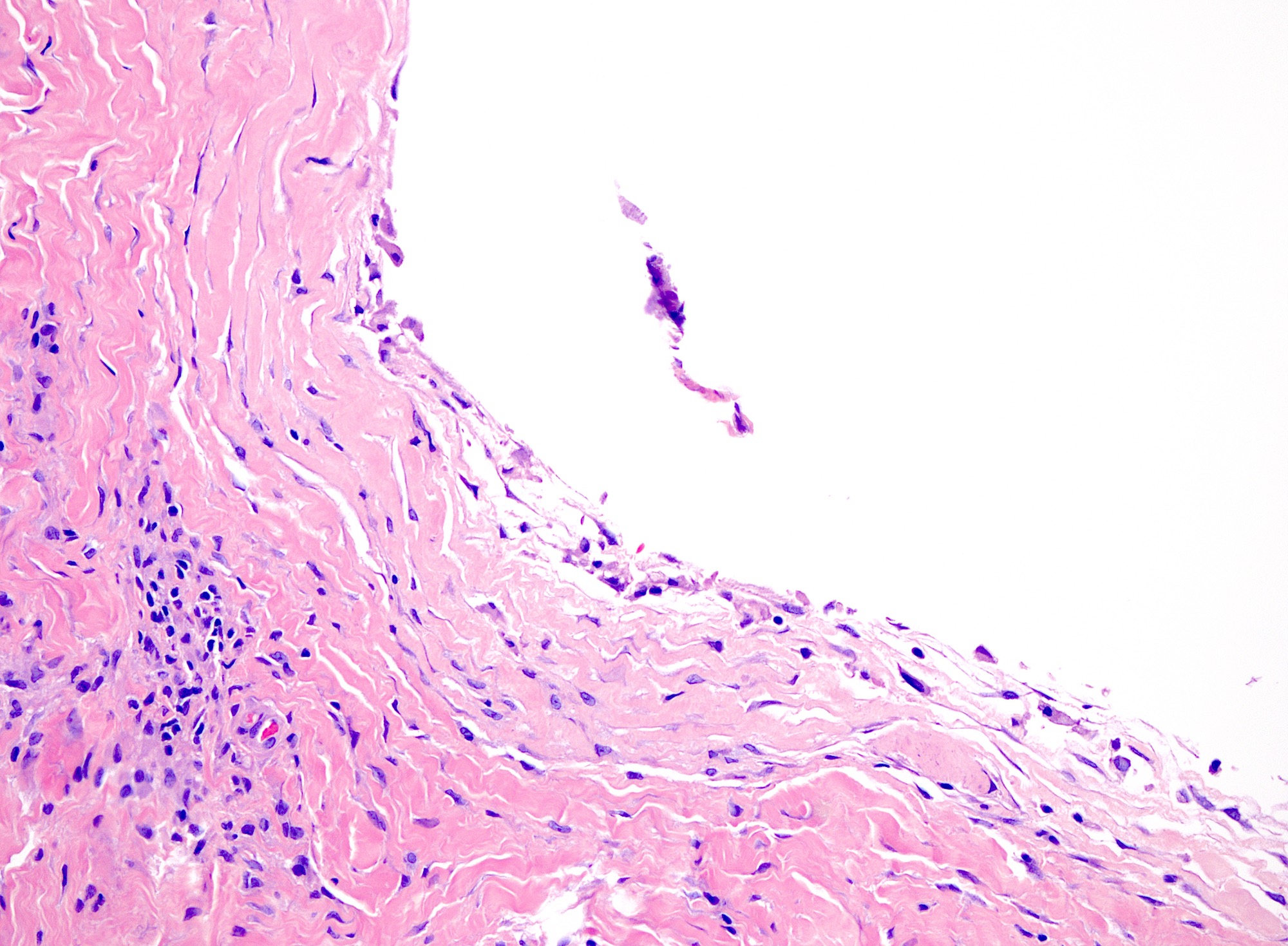
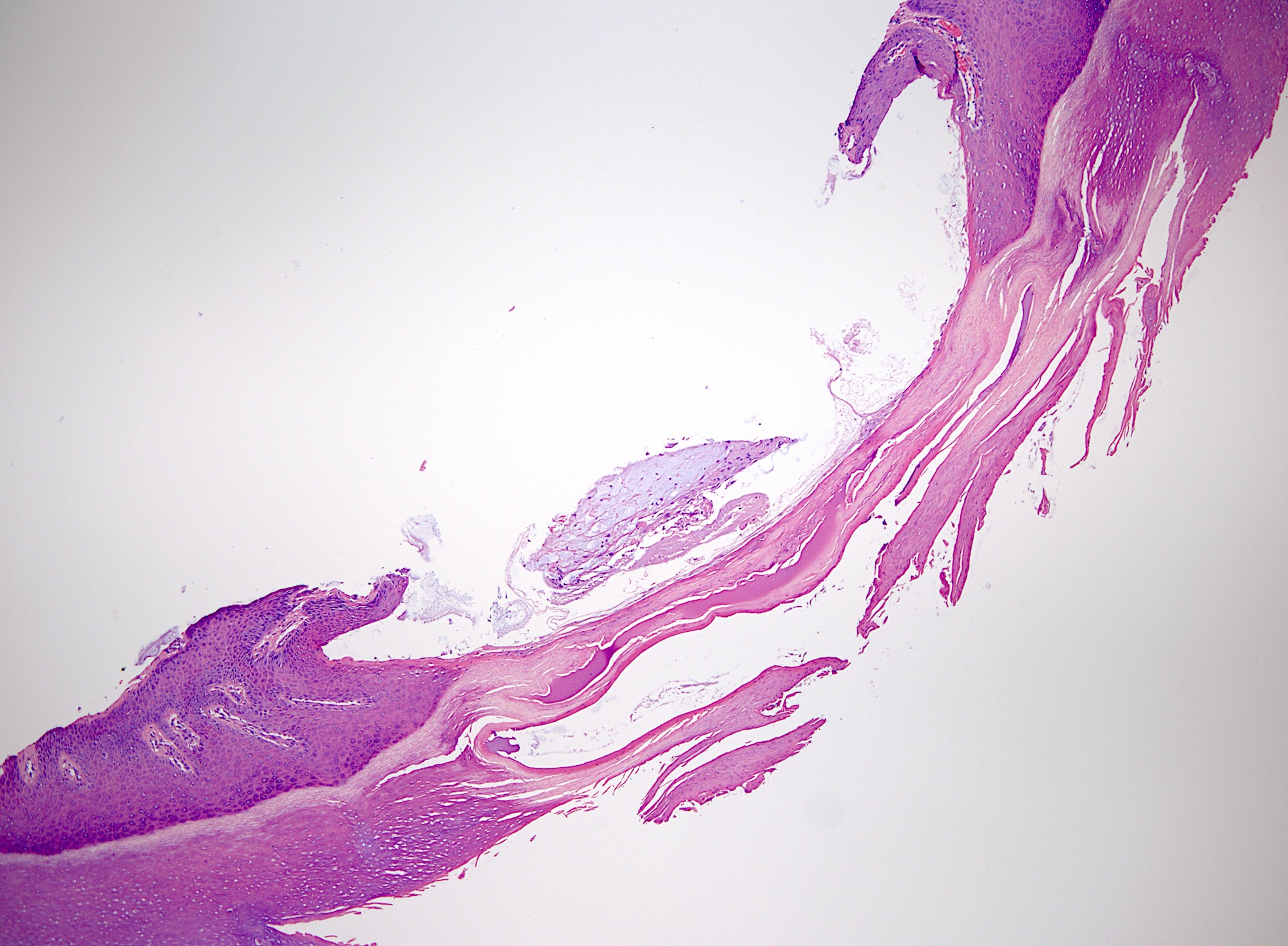
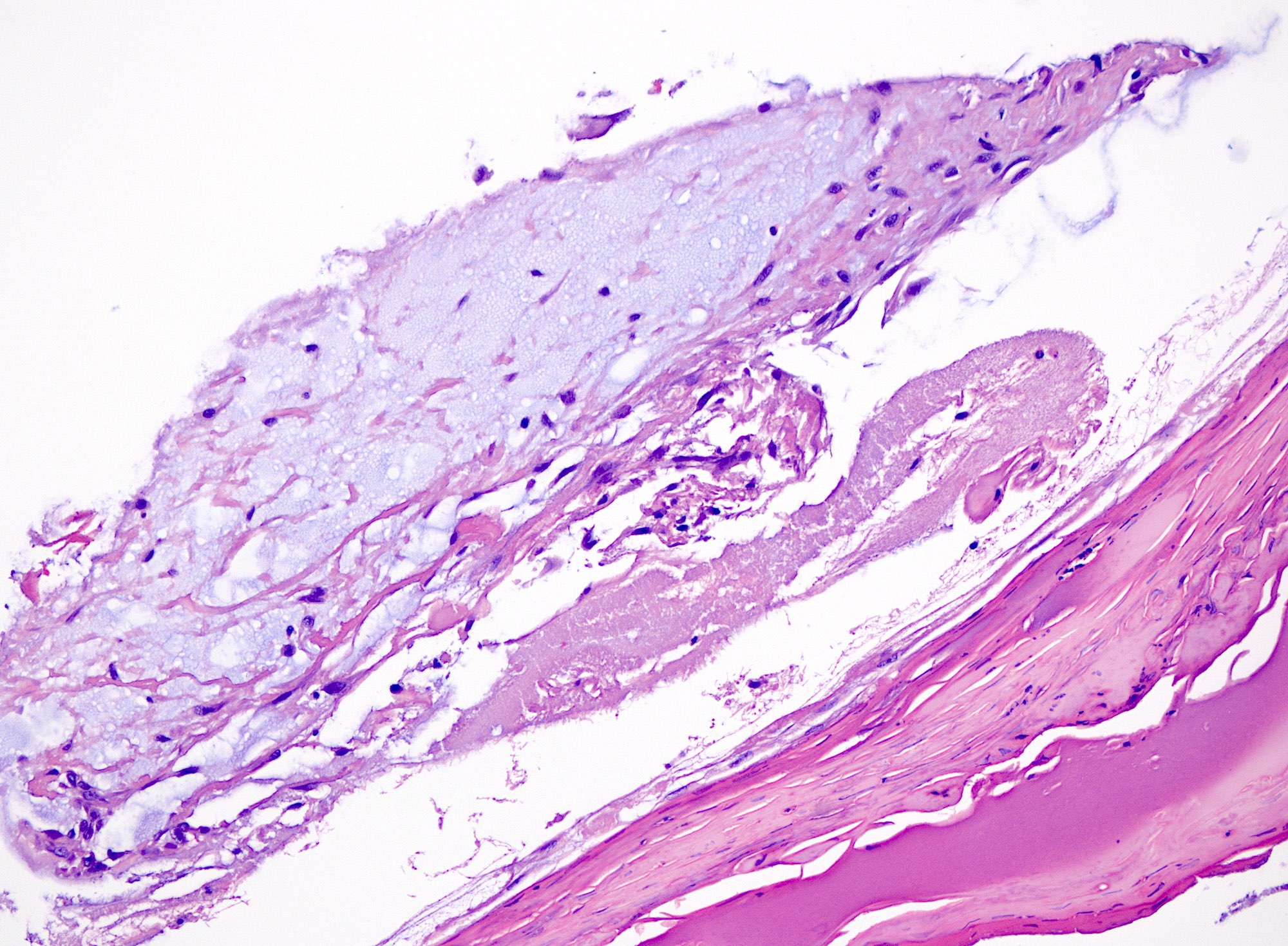
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Myxomatous or mucinosis-like variant has dermal mucin with fibrous stroma
- Ganglion-like variant has fibrous lining around a mucinous cystic structure
- Fibrous wall composed of randomly oriented layered collagen fibers
- Cystic contents mostly acellular, possibly containing fibroblasts or mesenchymal cells
- Lumen may appear empty (StatPearls: Digital Mucous Cyst [Accessed 29 August 2024])
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Alcian blue, colloidal iron and toluidine blue stain the mucinous cyst contents
Videos
Digital myxoid cysts versus ganglion cysts
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, right dorsal third finger, excision:
- Digital myxoid cyst (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a dermal based pseudocyst-like opening filled with mucinous secretions. The overall findings are consistent with a digital myxoid cyst.
Differential diagnosis
- Ganglion cyst:
- Found elsewhere in the body; digital myxoid cysts are exclusively found on phalanges
- Myxomatous variant can have intradermal mucin
- Focal cutaneous mucinosis:
- Does not form a pseudocyst
- Mucin deposition is more diffuse than in the myxomatous variant
- Myxoma:
- Deeper
- More diffuse
- Higher cellularity
- Synovial cyst:
- Lined by true epithelium or synovium
- Arises from either joints or tendon sheaths
Practice question #1
A 67 year old woman presents with a solitary, well circumscribed mass on the dorsal side of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint of her fourth finger. The mass has grown slowly over the past year and is associated with mild pain. Histologic evaluation of the lesion after excision is shown above. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Dermatofibroma
- Digital myxoid cyst
- Focal cutaneous mucinosis
- Lipoma
- Synovial cyst
Practice answer #1
B. Digital myxoid cyst. A pseudocystic structure filled with mucin and scattered fibroblasts and associated with the DIP joint in an older female is most likely a digital myxoid cyst, a benign finding.
Answer C is incorrect because focal cutaneous mucinosis does not typically present as a solitary, well circumscribed mass clinically and it would not appear as a cystic structure histologically.
Answer A is incorrect because dermatofibromas, while possibly resembling digital myxoid cysts in some aspects clinically, would also not typically appear as cystic structures histologically.
Answer D is incorrect because on histology, lipomas are collections of adipocytes rather than mucinous structures. Additionally, they rarely occur on phalanges.
Answer E is incorrect because synovial cysts, while possibly having similar contents as digital myxoid cysts, have true cyst linings, either of synovium or epithelium.
Comment Here
Reference: Digital myxoid cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Digital myxoid cyst
Practice question #2
Which of the following conditions is most strongly associated with digital myxoid cysts?
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Osteoarthritis
- Smoking
- Tuberous sclerosis
Practice answer #2
C. Osteoarthritis. Digital myxoid cysts are strongly associated with osteoarthritis. Other factors that predispose a person to be affected include female sex, prior trauma to the area and age. Answers A, B, D and E are incorrect because they are factors that have not been shown to have a strong relation to digital myxoid cysts.
Comment Here
Reference: Digital myxoid cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Digital myxoid cyst