Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Albahra S, Hosler GA. Inverted follicular keratosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticinvertedfollicularkeratosis.html. Accessed September 14th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign tumor of the follicular infundibulum
Essential features
- Benign, endophytic follicular tumor with characteristic presence of squamous eddies
Terminology
- Inverted follicular keratosis (IFK)
Epidemiology
- More common in males and older individuals
- Multiple lesions may be associated with Cowden syndrome (Acta Derm Venereol 1976;56:337)
- Although this association may be as a result of its resemblance to trichilemmoma
Sites
- Most commonly on the head and neck (~90% of cases) but can also be found on extremities or trunk
- Predilection for cheeks and upper lip (Am J Dermatopathol 1983;5:467)
- Can involve eyelids (Am J Ophthalmol 1979;87:810)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown at this time
Etiology
- Regarded by some as a variant of seborrheic keratosis
Clinical features
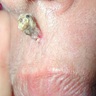
- Solitary flesh colored nodular or filiform lesion
- Typically 0.3 - 1 cm in diameter (J Cutan Pathol 1984;11:387)
Diagnosis
- Can be made on biopsy
Case reports
- 24 year old woman with a vulvar lesion (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2000;19:369)
- 55 year old woman with a keratotic lesion of the lip (Pan Afr Med J 2014;18:304)
- 63 year old man with a skin colored plaque on the eyelid (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2021;87:455)
Treatment
- Biopsy is usually curative
- Larger lesions treated by complete excision
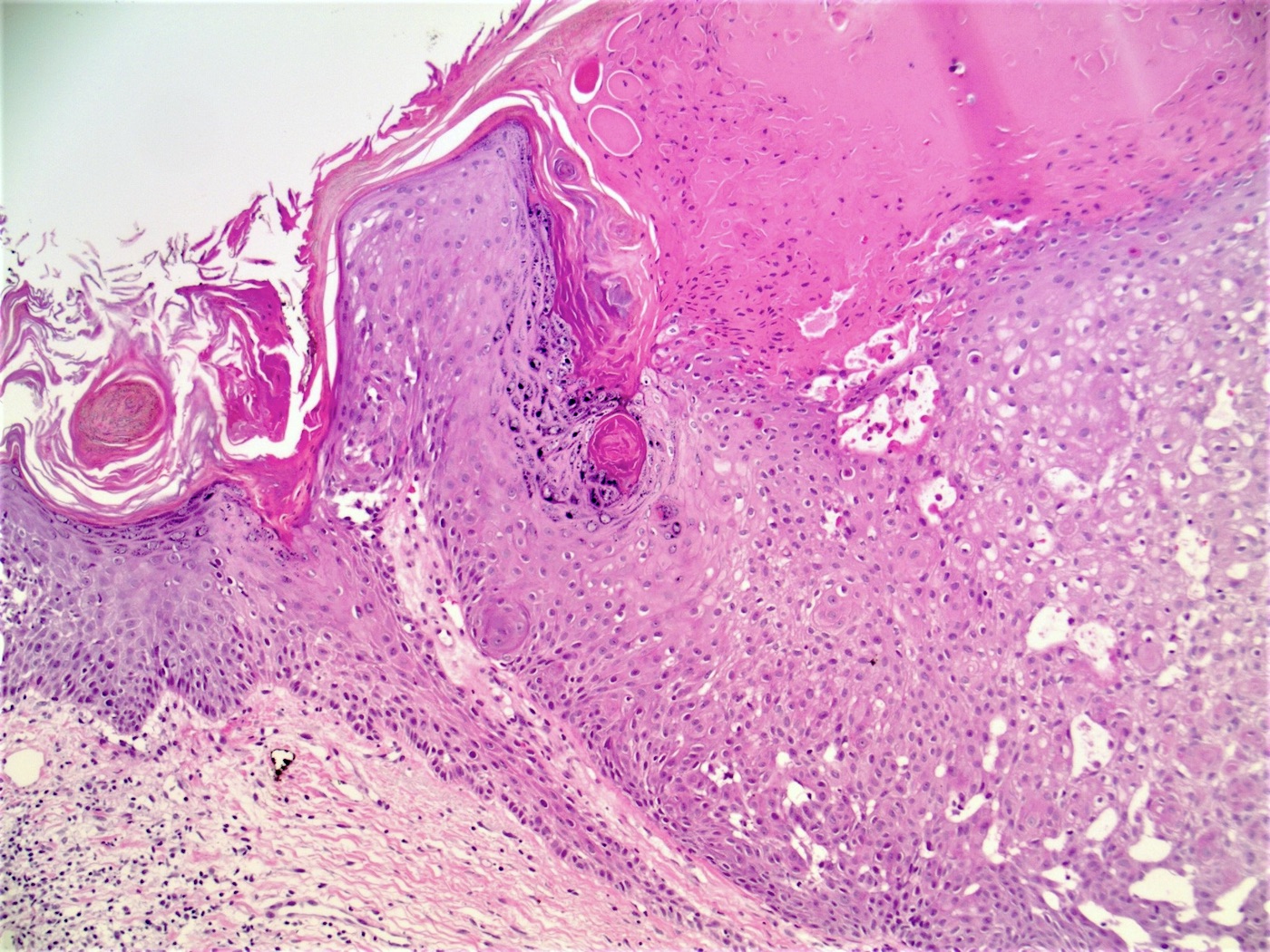
Microscopic (histologic) description
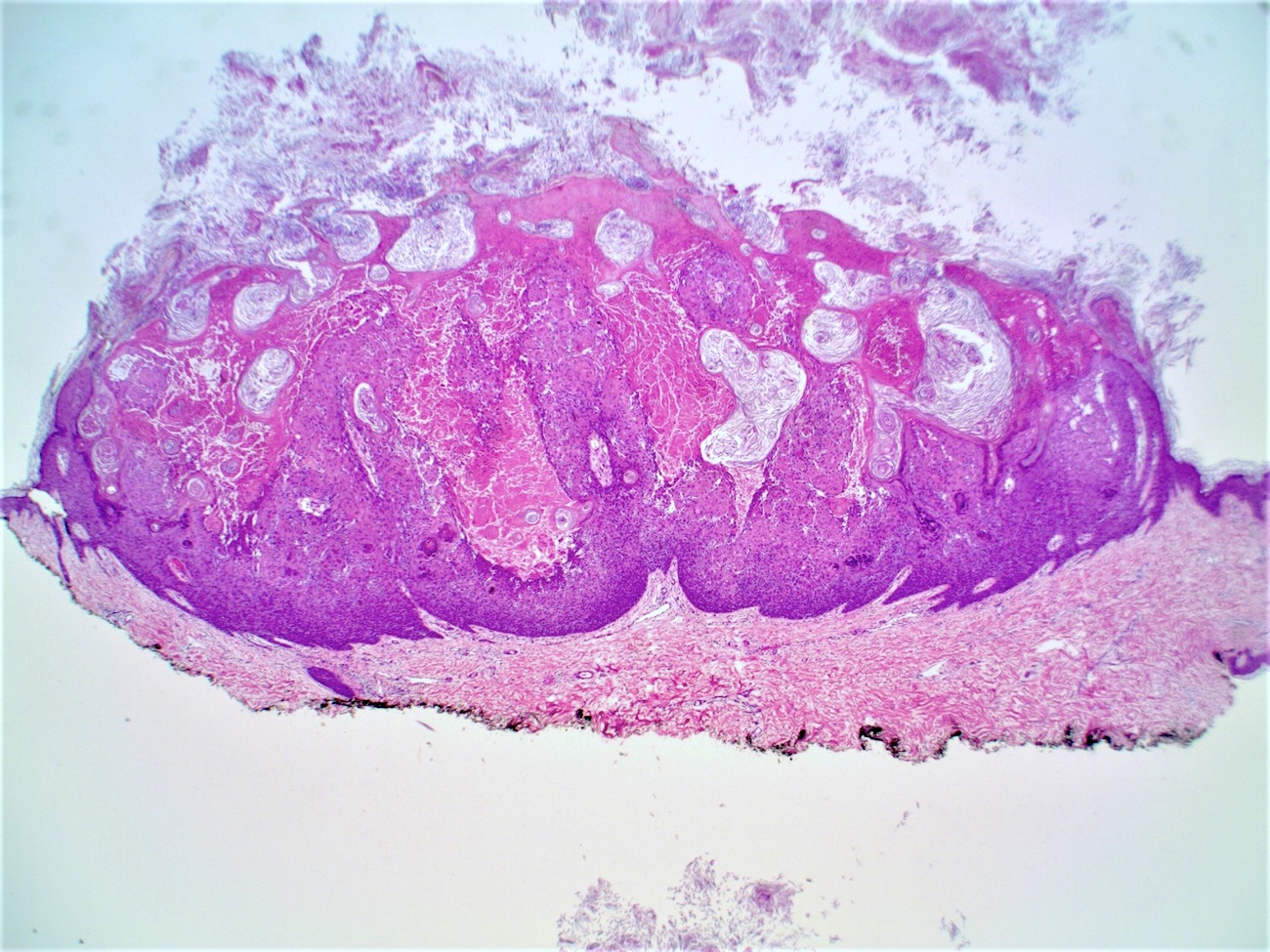
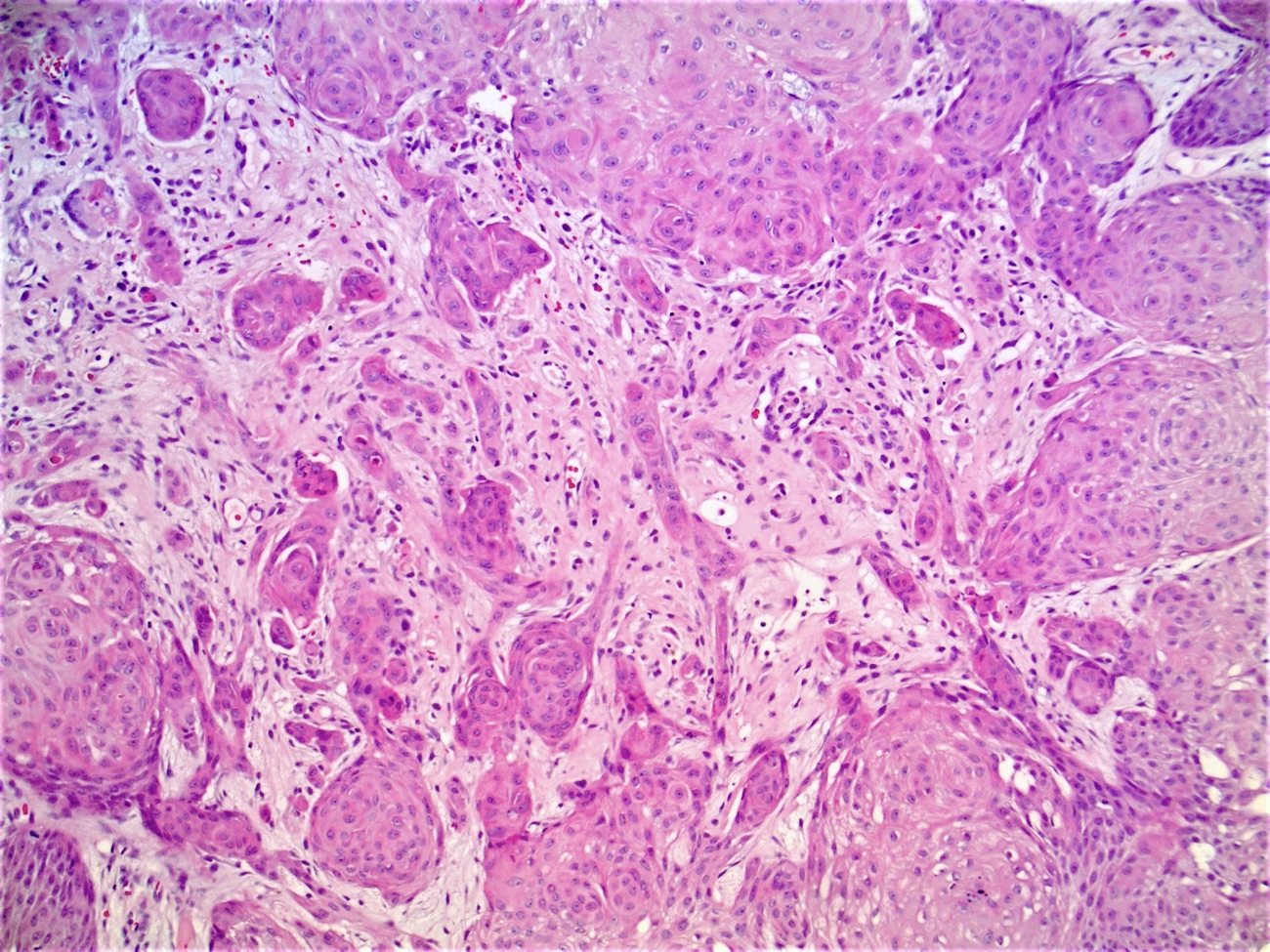
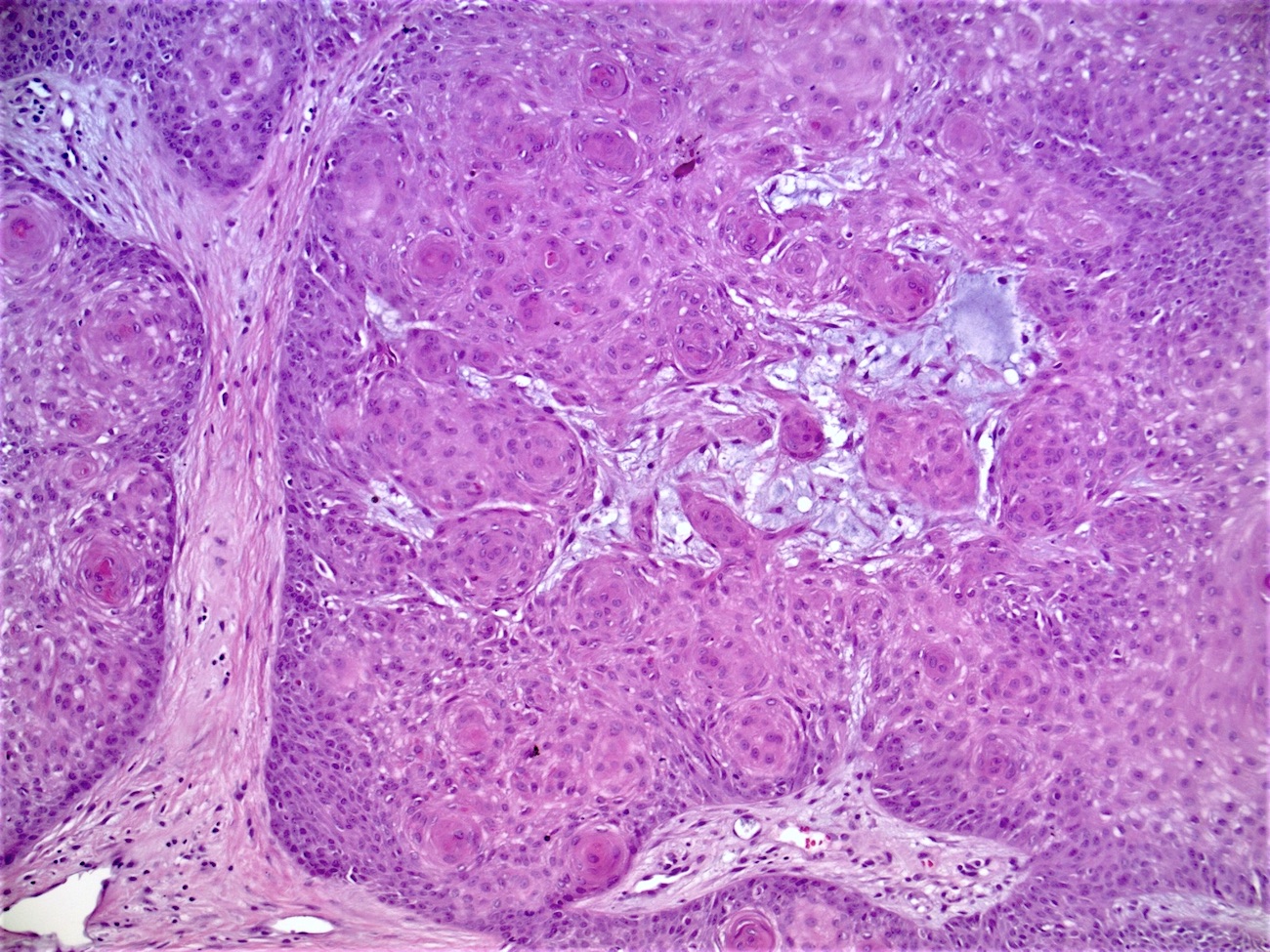
- Well circumscribed, endophytic tumor with large lobules or finger-like extensions that resemble expanded follicles
- Variable number of squamous eddies
- Occasional mitoses within peripheral basaloid cells
- Histologic variants have been described (J Cutan Pathol 1984;11:387):
- Papillomatous wart-like: exophytic with overlying hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis
- Keratoacanthoma-like: central exoendophytic mass
- Cystic type: irregular clefts within tumor and formation of small cysts
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- BCL2: positive dendritic cells are present in increased numbers in the suprabasal areas, compared to seborrheic keratosis (J Cutan Pathol 2006;33:498)
Videos
Inverted follicular keratosis:
5 minute pathology pearls
Inverted follicular keratosis with great squamous eddies
Sample pathology report
- Skin, upper cutaneous lip, shave biopsy:
- Inverted follicular keratosis
Differential diagnosis
- Irritated seborrheic keratosis:
- Presence of squamous eddies; however, lacks endophytic growth
- Tricholemmoma:
- Similar lobulated, endophytic architecture
- Clear glycogenated cells, palisaded basilar layer and thickened basement membrane
- Verruca vulgaris:
- More exophytic than endophytic with inward curving papillomatosis, coarse hypergranulosis and koilocytes
- Associated with human papillomavirus
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. These lesions are more commonly found on the head and neck. BCL2 has been found to be upregulated in the dendritic cells of IFK but not seborrheic keratosis. IFK is typically found on the head and neck of older men. Squamous eddies are a usual finding in IFK.
Comment Here
Reference: Inverted follicular keratosis
Comment Here
Reference: Inverted follicular keratosis
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2