Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Arfa AS, Younes IE, Zhang L. FGFR1 rearrangement. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/myeloproliferativeFGFR1.html. Accessed May 14th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Pluripotent, hematopoietic, stem cell driven malignancy that may present as myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), T or B lymphoblastic lymphoma leukemia (T-ALL, B-ALL) or mixed phenotypic acute leukemia (MPAL)
Essential features
- MPN or myelodysplastic syndrome / myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS / MPN) with prominent eosinophilia, with or without lymphocytosis or neutrophilia
- Alternatively, AML or T-ALL or B-ALL or MPAL with eosinophilia in peripheral blood or bone marrow
- Presence of t(8:13)(p11.2;q12) or a variant of translocation leading to FGFR rearrangement in a myeloid progenitor, a lymphoblast or both
Terminology
- Hematopoietic stem cell neoplasm with FGFR1 abnormalities
- Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasm with FGFR1 abnormalities
- 8p11 stem cell leukemia / lymphoma syndrome
- 8p11 myeloproliferative syndrome
- 8p11 stem cell syndrome
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D47.7 - other specified neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue
Epidemiology
- M:F = 1.5:1 (Arkh Patol 2019;81:59)
- Age range of 3 - 84 years; median age of 32 years (Arkh Patol 2019;81:59)
Sites
- Bone marrow, peripheral blood, liver, spleen and lymph nodes
Pathophysiology
- FGFR1 gene rearrangement affects the pluripotent stem cells, which could differentiate to myeloid or lymphoid neoplasm
- Most cases present with chronic phase then may transform to acute blast phase; however, some cases may represent as de novo acute proliferation
Etiology
- Etiologic factors have not been identified
Diagrams / tables
Cytogenetics and molecular genetics reported in myeloid / lymphoid neoplasms with FGFR1 rearrangement
| t(8;13)(p11.2;q12.1) | ZMYM2-FGFR1, previously ZNF198-FGFR1 |
| t(8;9)(p11.2;q33.2) | CNTRL-FGFR1, previously CEP110-FGFR1 |
| t(6;8)(q27;p11.2) | FGFR10P-FGFR1 |
| t(8;22)(p11.2;q11.2) | BCR-FGFR1 |
| t(7;8)(q33;p11.2) | TRIM24-FGFR1 |
| t(8;17)(p11.2;q11.2) | MY018A-FGFR1 |
| t(8;19)(p11.2;q13.3) | HERVK-FGFR1 |
| ins(12;8)(p11.2;p11.2;p22) | FGFR10P2-FGFR1 |
| t(1;8)(q31.1;p11.2) | TPR-FGFR1 |
| t(2;8)(q13;p11.2) | RANBP2-FGFR1 |
| t(2;8)(q37.3;p11.2) | LRRFIP1-FGFR1 |
| t(7;8)(q22.1;p11.2) | CUX1-FGFR1 |
| t(8;12)(p11.2;q15) | CPSF6-FGFR1 |
- FGFR1 rearrangement has also been found in association with t(8;12)(p11.2;q15) and t(8;17)(p11.2;q25) but suspected involvement of FGFR1 in t(8;11)(p11.1-p11.2;p15) was not confirmed
- Additional cytogenetic abnormalities have been reported, of which trisomy 21 is the most common secondary chromosomal abnormality
Clinical features
- Lymphadenopathy, mediastinal mass or organomegaly
- Myeloproliferative features
- AML-like features or myeloid sarcoma
- Systemic symptoms (e.g., fever, weight loss and night sweats)
Diagnosis
- Cases usually present as chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL), atypical chronic myeloid leukemia (aCML) or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), the latter are usually with eosinophilia
- Overall, ~90% of chronic phase patients have peripheral blood or bone marrow clonal eosinophilia (including those with acute transformation), neutrophilia and occasionally monocytosis
- De novo AML or de novo T-ALL with or without eosinophilia
- Some cases show subsequent transformation to T-ALL, B-ALL, MPAL or AML (including myeloid sarcoma)
- Basophilia is not typical but may be seen in cases with BCR-FGFR1 fusion, t(1;8)(q31.1;p11.2) and TPR-FGFR, t(1;8)(q25;p11.2)
- Polycythemia vera has been reported in 5 cases with t(6;8) / FGFR10P-FGFR1 fusion (Hematol J 2004;5:534)
- Some patients primarily present as B-ALL or MPAL with t(8;13)
- T-ALL characteristically shows eosinophilic infiltration within the lymphoma, which can point toward this diagnosis
Laboratory
- Leukocytosis and sometimes anemia or thrombocytopenia
- Often presenting with eosinophilia but may show normal eosinophil count
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognosis, even for patients presenting in the chronic phase due to the high incidence of transformation
Case reports
- 34 year old woman with no subjective symptoms diagnosed with T lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL) with ZNF198-FGFR1 or ZMYM2-FGFR1; bone marrow (BM) aspirate and biopsy showed hypercellularity with hypereosinophilia (Hematology 2018;23:470)
- 48 year old Japanese man with peripheral leukocytosis, diagnosed with B-ALL with BCR-FGFR1 gene rearrangement (Bone Marrow Transplant 2019;54:326)
- 66 year old man had clinical features that resembled CML; however, bone marrow cytogenetic and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) studies showed t(8;22)(p11;q11) and BCR-FGFR1 fusion gene (Case Rep Hematol 2018;2018:5724960)
Treatment
- In several cases, interferon has induced a cytogenetic response
- Intensive chemotherapy with regimens such as hyper-CVAD for T or B cell lymphoblastic lymphoma, followed by early allogeneic transplantation, is recommended
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation should be considered, even for patients who present in the chronic phase
- Optional targeted therapy:
- Midostaurin (PKC412) for a patient with ZNF198 / ZMYM2-FGFR1 fusion (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2015;10:351, Haematologica 2010;95:696)
- Ponatinib has partial activity against the FGFR1 tyrosine kinase, which is reported effective in a patient with BCR-FGFR1 positive trilineage T / B / myeloid mixed phenotype acute leukemia (Med Res Rev 2014;34:280)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- B-ALL with FGFR1 rearrangement:
- Peripheral blood smear (PBS): shows left shifted granulocytosis with eosinophilia
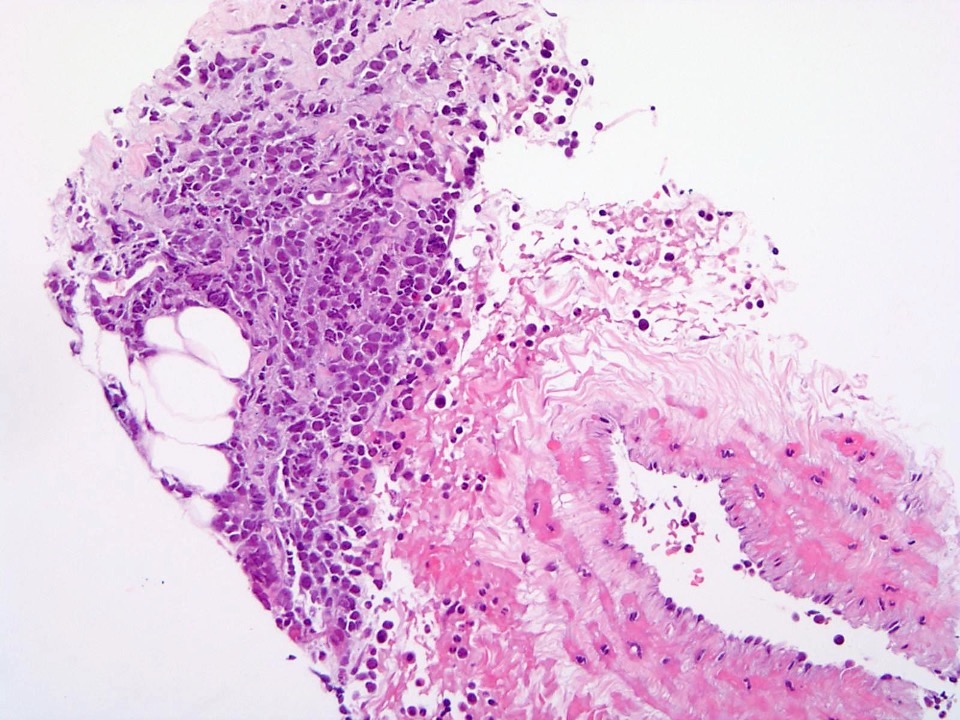
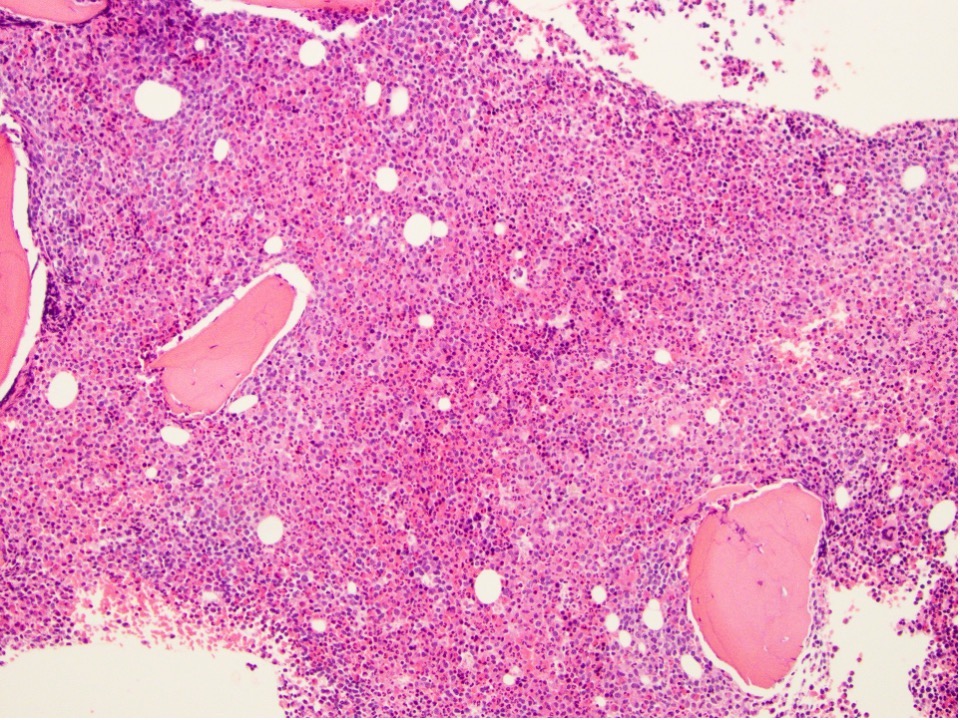
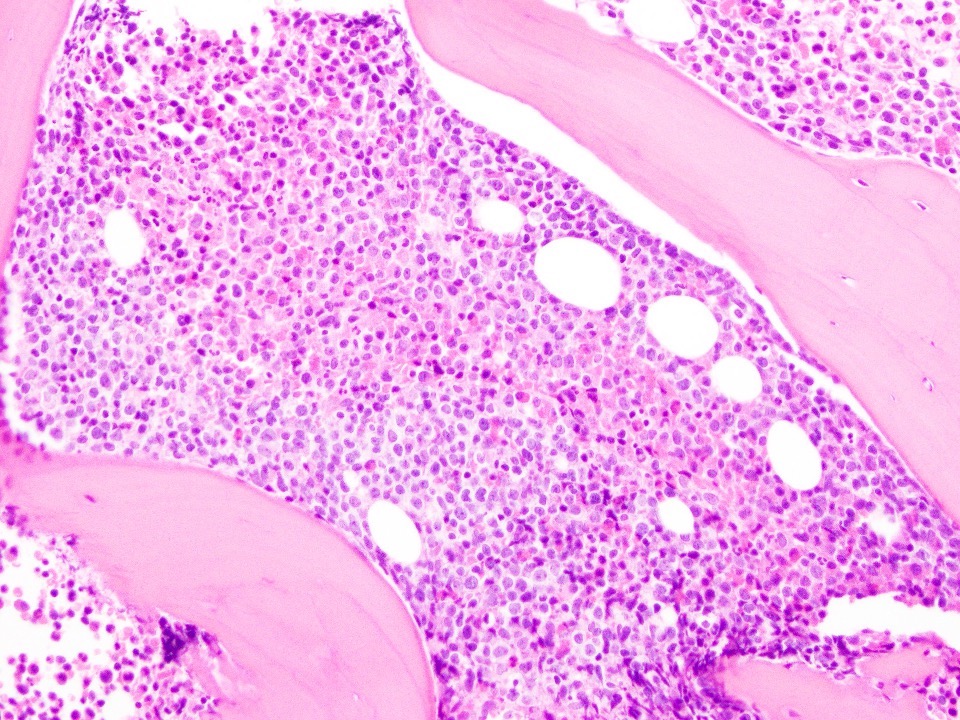
- Bone marrow biopsy:
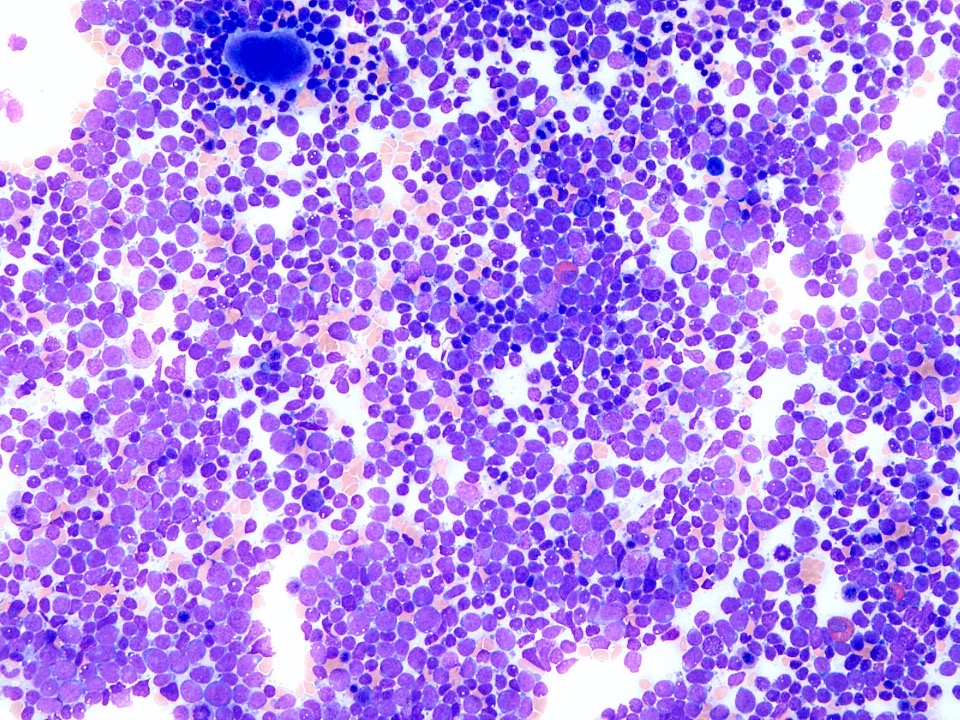
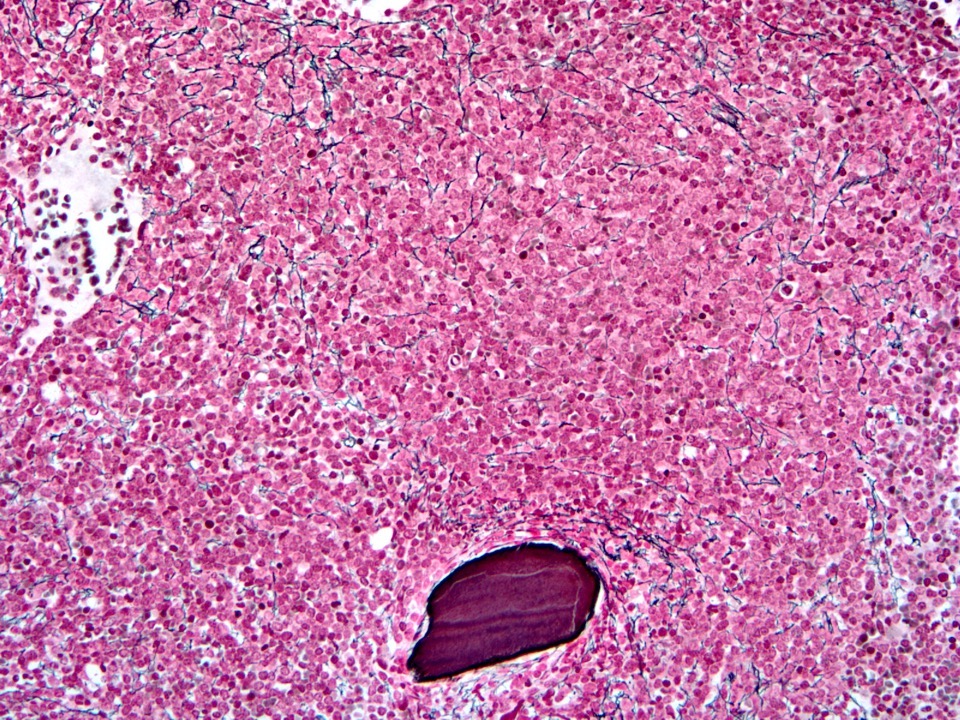
- Low power: hypercellular marrow (75%) with involvement by myeloid / lymphoid neoplasm
- High power: abnormal immature B cell proliferation indicates B lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma
- Aspirate smear:
- Granulocytic hyperplasia with increased eosinophils (10%)
- Immature lymphoid cells are increased, approximately 15% (hemodiluted aspirate)
- Megakaryocytes are present and show normal morphology
- Erythroid precursors show normoblastic maturation
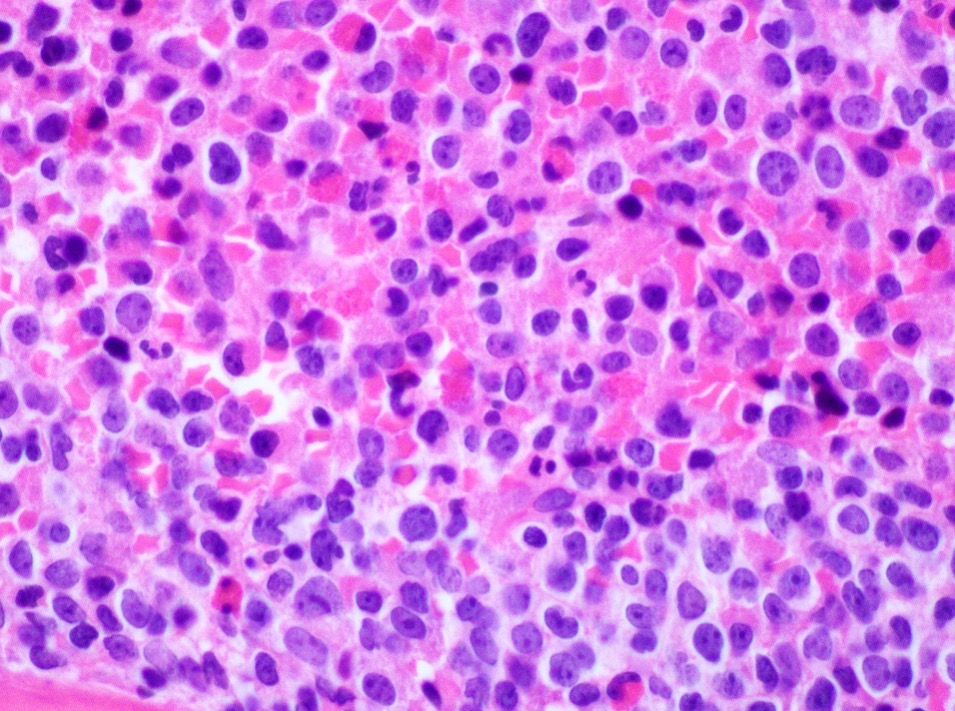
- AML with FGFR1 rearrangement:
- PBS: leukocytosis with increased blast count (> 20%), with eosinophilia (20%) and normocytic anemia with thrombocytopenia
- Bone marrow biopsy:
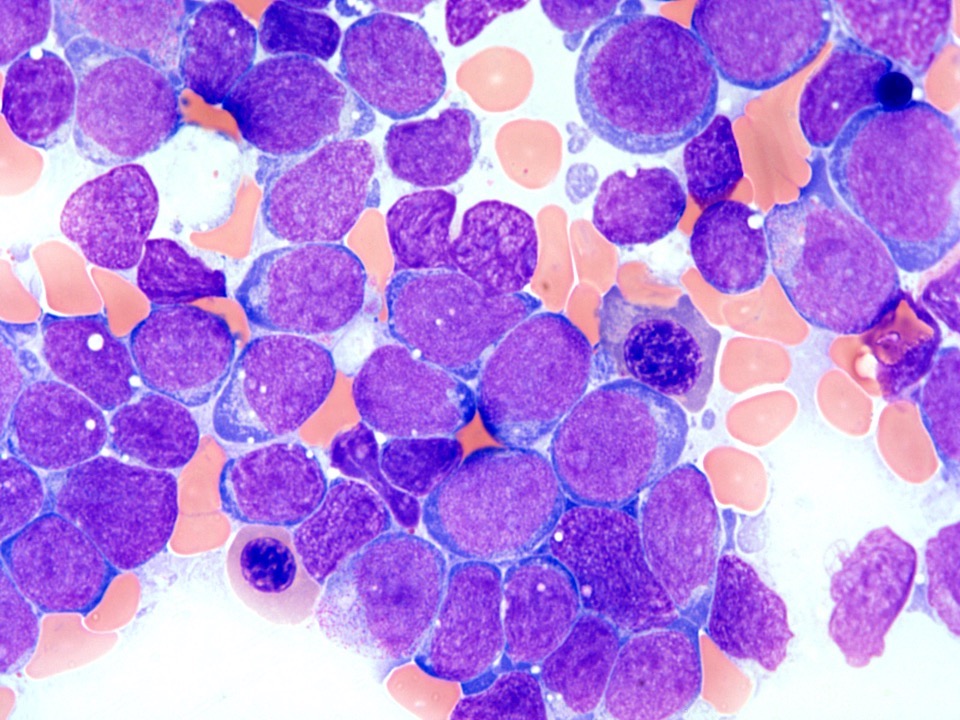
- Hypercellular marrow (80%) with involvement by sheets of blasts > 40%, which stains positive for CD34 and MPO
- Reticulin fibrosis is mildly increased (1/3)
- Aspirate smear: hypercellularity and diffuse infiltration by myeloblasts
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) with FGFR1 rearrangement:
- PBS: leukocytosis with eosinophilia and normocytic anemia with thrombocytopenia
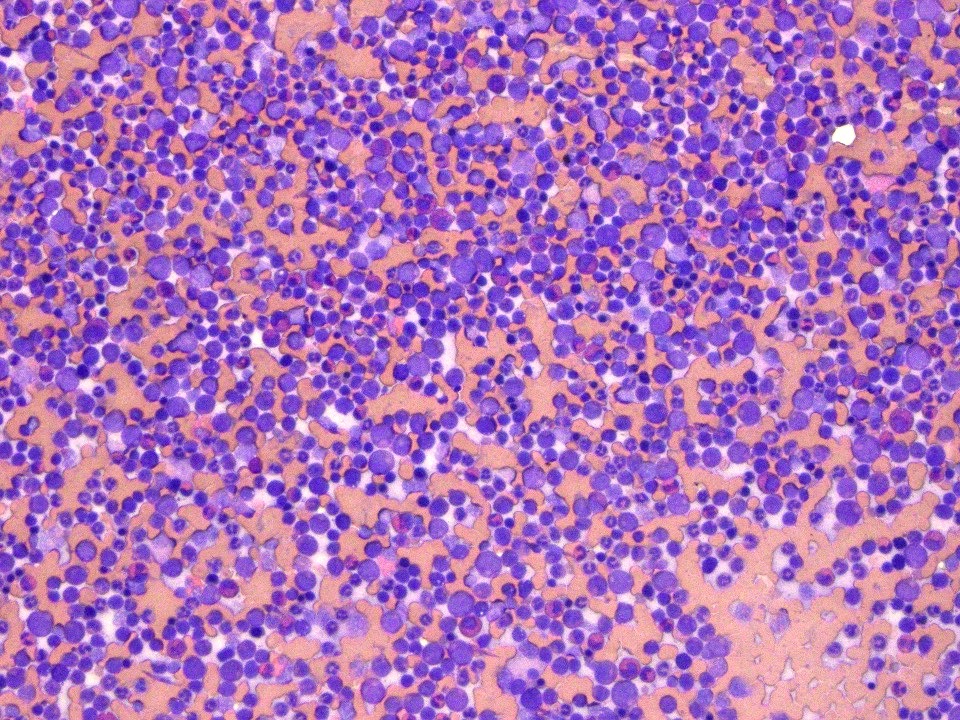
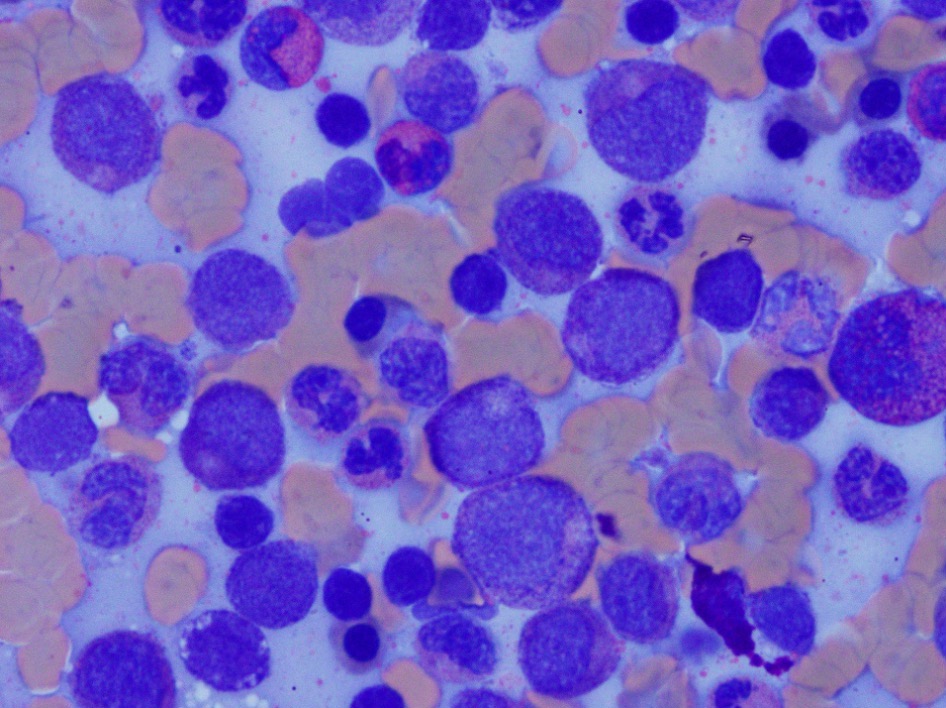
- Bone marrow biopsy: hypercellular marrow (80%) with left shifted maturation of the granulocyte lineage with increased eosinophils (which may be seen in clusters)
- Aspirate smear: hypercellularity with left shifted maturation of the granulocytes and eosinophilia
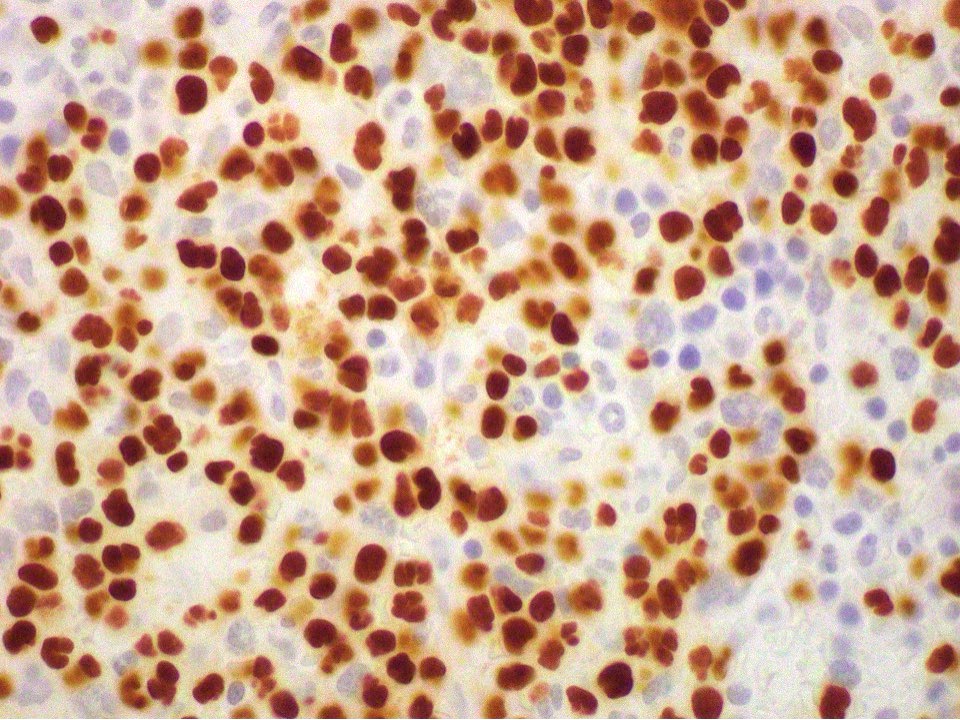
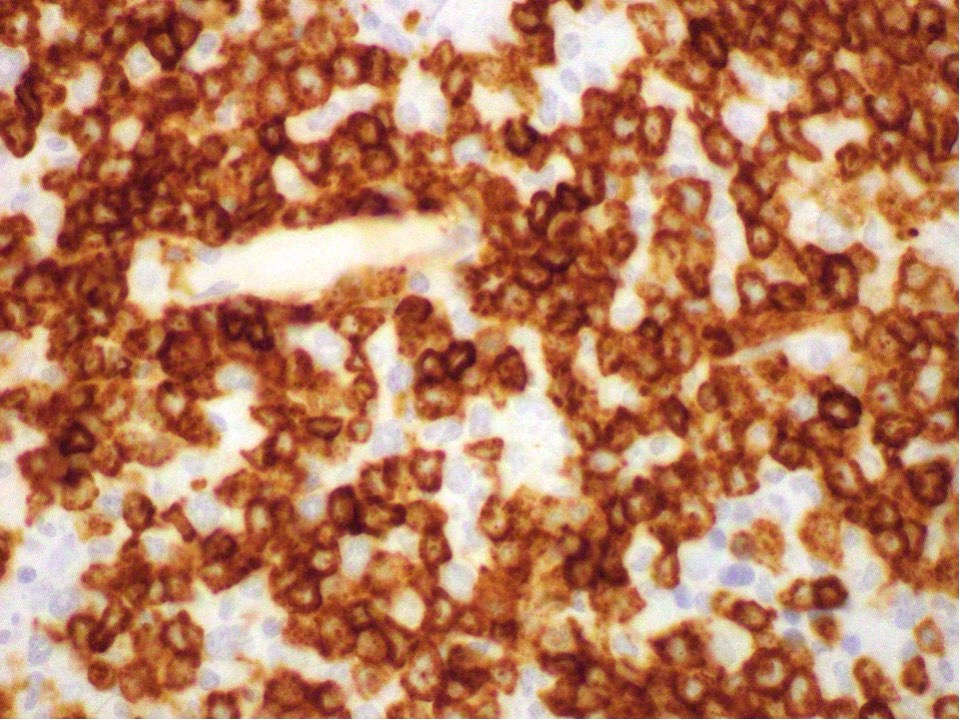
Microscopic (histologic) images
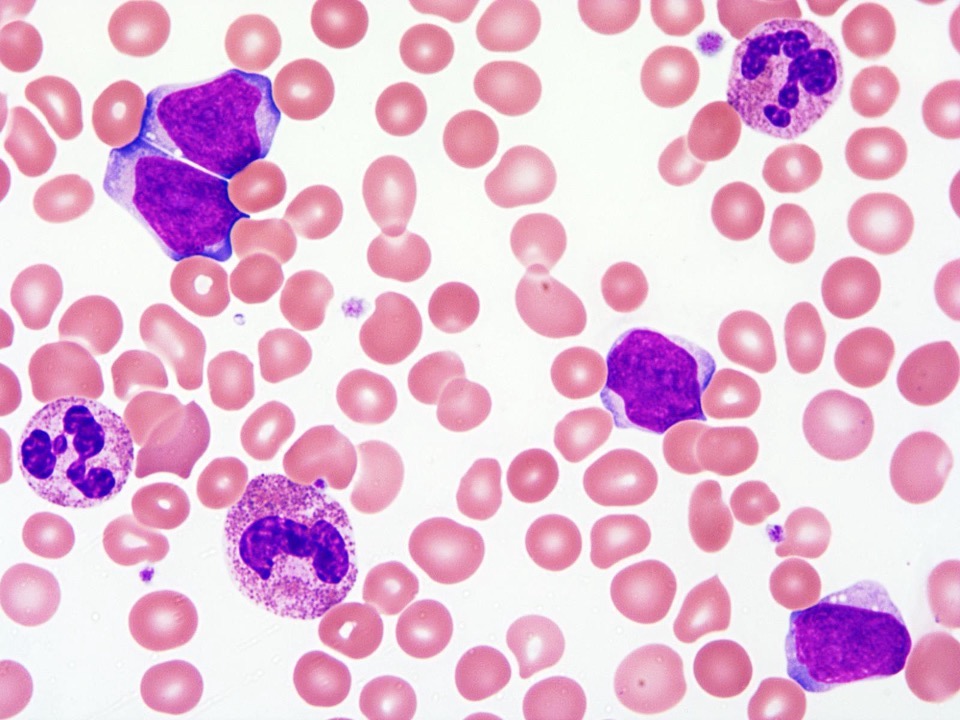
Peripheral smear description
- B-ALL with FGFR1 rearrangement:
- Left shifted leukocytosis with eosinophilia; normocytic normochromic red cell morphology and adequate reticulocytosis
- Anemia or thrombocytopenia is present, occasional monocytosis
- AML with FGFR1 rearrangement:
- Normocytic normochromic red cell morphology with adequate reticulocytosis; left shifted leukocytosis with increased blast cells and eosinophilia
Positive stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- FISH test with FGFR1 break apart probe: 1 red, 1 green and 1 fusion signal pattern indicates positive FGFR1 gene rearrangement detected in 72.5% of cells
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Peripheral blood:
- Left shifted granulocytosis with eosinophilia
- Bone marrow, right posterior iliac crest, aspirate and biopsy:
- Hypercellular marrow (75%) with involvement by myeloid / lymphoid neoplasm with FGFR1 rearrangement (see comment)
- Decreased stainable storage iron
- Comment: The concurrent flow cytometry identified immature abnormal B cell population. Immunohistochemical stains are performed on the current bone marrow core biopsy shows 30 - 40% PAX5+, TdT+, CD34+ subset immature B cells. FISH study reveals 64.5% cells with FGFR1 rearrangement. The patient's previous outside bone marrow biopsy showed abnormal karyotype with t(8:13)(p11.2;q12.1).
- The abnormal immature B cell proliferation indicates B lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma. With the clinical presentation of left shifted leukocytosis, monocytosis, eosinophilia and FGFR1 rearrangement, the findings are consistent with a myeloid / lymphoid neoplasm with FGFR1 rearrangement. Please correlate with pending FoundationOne Heme analysis, reported separately.
- Microscopic description:
- Peripheral blood smear:
- Cytopenias: not present
- Red cell morphology: normocytic normochromic
- Reticulocytosis: adequate
- Other findings: left shifted leukocytosis with monocytosis and eosinophilia
- Aspirate smear:
- Adequacy: adequate
- Significant findings: There is granulocytic hyperplasia with increased eosinophils (20%). Immature lymphoid cells are increased, approximately 15%. Megakaryocytes show normal morphology. Erythroid precursors show normal maturation.
- Clot section and core biopsy:
- The clot section (A) and the core biopsy (B) are flaccid in B plus fix (BBC) fixative. The core biopsy (B) is decalcified and formical (formic acid, formalin diet and EDTA). On level of the clot section (A) and core biopsy (B) are stained with PAS to evaluate myeloid maturation and more accurately estimate and M:E ratio. One level of the clot section (A) and core biopsy (B) is each stained with Prussian blue to evaluate iron stores and the average value reported. One level of the colon biopsy (B) is stained with reticulin stain to evaluate marrow fibrosis.
- Bony trabeculae: unremarkable
- Cellularity: 75%
- Megakaryocytes: adequate in number with normal morphology
- Estimated M:E ratio: 3 - 4:1
- Iron stores: decreased
- Reticulin fibrosis: normal
- Significant findings: hypercellular marrow with increased eosinophils and increased immature mononuclear cells
- Immunohistochemical stains are performed on the core biopsy with adequate controls. PAX5 and TdT highlight markedly increased to scattered and aggregates of immature B cells, overall 30 - 40%. Majority of this immature B cells are also positive for CD34. Spectrin stains mildly decreased erythroid precursor. CD61 highlights megakaryocytes.
- Peripheral blood smear:
Differential diagnosis
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome:
- Sustained eosinophilia (> 1.5 x 109/L) for at least 6 months with other reactive processes excluded with induced tissue damage, other reactive processes excluded
- Exclude cytokine related lymphoid variant hypereosinophilia
- Increased eosinophils with either no dysplastic features or no increase in blast cells in the bone marrow
- No lymphoid or myeloid neoplasms (e.g., MDS / MPNs, MPNs, systemic mastocytosis or AML)
- No cytogenetic or molecular alteration is identified
- No FGFR, PDGFRA, PDGFRB rearrangement, PCM1-JAK2, BCR-ABL1, ETV6-JAK2 or BCR-JAK2 fusions
- No inv(16)(p13.1q22), t(16;16)(p13.1q22) or t(8;21)(q22;q22.1)
- Reactive eosinophilia:
- Occurs secondary to allergies, drugs, infection, skin diseases, asthma, adrenal insufficiency, gastrointestinal eosinophilia
- Peripheral blood shows increased eosinophils (may be with abnormal forms)
- No evidence of FGFR1 rearrangement or active mutation or other cytogenetic / molecular abnormalities
- Systemic macrocytosis with eosinophilia:
- Major diagnostic criteria: multifocal infiltrates of mast cells (≥ 15 mast cells in aggregates) + 1 minor criterion or 4 minor criteria
- Minor criteria:
- Bone marrow shows eosinophilia with variable dysplastic features
- No FGFR1 rearrangement
- Chronic eosinophilic leukemia, NOS:
- Sustained eosinophilia (> 1.5 x 109/L) with other reactive processes excluded
- < 20% blasts in peripheral blood or bone marrow
- No inv(16)(p13.1q22), t(16;16)(p13.1q22), t(8;21)(q22;q22.1)
- Bone marrow aspirate is hypercellular with abundant eosinophils and eosinophilic precursors with dysplastic features
- Clonal cytogenetic (e.g., +8, -20q) or molecular genetic abnormalities (e.g., TET2, ASXL1 and DNMT3A); if no clonal abnormalities are found, then blast count must be > 2% in peripheral blood or > 5% in bone marrow aspirate
- No PDGFRA, PDGFRB, FGFR rearrangement, BCR-ABL1, PCM1-JAK2, ETV6-JAK2 or BCR-JAK2 fusions
- No lymphoid or myeloid neoplasms (e.g., MDS / MPN, MPNs, systemic mastocytosis or AML) are identified
- Idiopathic hypereosinophilia:
- Sustained eosinophilia (> 1.5 x 109/L) for at least 6 months with no tissue damages
- No reactive causes, lymphoid or myeloid neoplasms are identified
- Increased eosinophils with no dysplastic features or no increase in blasts in the bone marrow
- No molecular alteration is identified and no PDGFRA, PDGFRB, FGFR rearrangement, BCR-ABL1, PCM1-JAK2, ETV6-JAK2 or BCR-JAK2 fusions
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What is the most common partner for FGFR1 in myeloid / lymphoid neoplasms with FGFR1 rearrangement?
- BCR
- CNTRL
- FGFR10P
- ZMYM2
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following molecular aberration is associated with basophilia in myeloid / lymphoid neoplasms with FGFR1 rearrangement?
- BCR-FGFR1 fusion, t(1;8)(q31.1;p11.2)
- CPSF6-FGFR1 fusion, t(8;12)(p11.2;q15)
- CUX1-FGFR1 fusion, t(7;8)(q22.1;p11.2)
- FGFR10P-FGFR1 fusion, t(6;8)
Board review style answer #2