Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Nasri E, Reith JD. Osteoid osteoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/boneosteoidosteoma.html. Accessed September 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, bone forming tumor
- Usually small size (< 2 cm) and limited growth
Essential features
- Imaging: well demarcated, small central nidus, usually surrounded by zone of sclerosis
- Histology: bone forming tumor composed of woven bone with prominent osteoblastic rimming and a vascularized stroma
- Molecular: FOSB gene locus rearrangement (not necessary for diagnosis)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D16.20 - benign neoplasm of long bones of unspecified lower limb
Epidemiology
- 10 - 12% of all benign bone tumors; 2 - 3% of all primary bone tumors
- M:F = 2:1
- Rare familial occurrence reported (Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:416)
- More common in children and adolescents
Sites
- Broad skeletal distribution
- 50% occur in the long bones of the lower extremities
- Femoral neck is the single most frequent anatomic site
- Usually near the end of the diaphysis of long bones
- Less common in the long bones of upper extremities
- Bones of elbow are the most common site in upper extremity
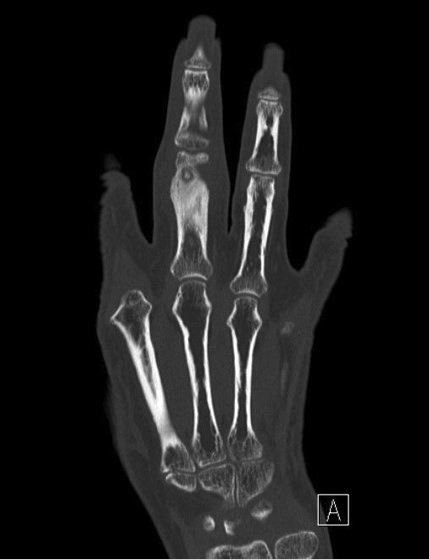
- Small bones of hands and feet and posterior elements of vertebral body
- Uncommon sites: flat bones, craniofacial bones
- 50% occur in the long bones of the lower extremities
- Preferential involvement of cortex (75%)
- Subperiosteal and intramedullary lesions are less common
- Reference: J Bone Oncol 2015;4:37
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Nocturnal pain, relieved by aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2011;19:678)
- Swelling and effusion of nearest joint in intracapsular osteoid osteomas
- Painful scoliosis in osteoid osteomas of spine (Neurosurg Focus 2003;15:E5)
- Osteoid osteomas in the small bones of the hands and feet may clinically mimic osteomyelitis
Diagnosis
- Requires correlation of clinical, radiographic and histologic findings
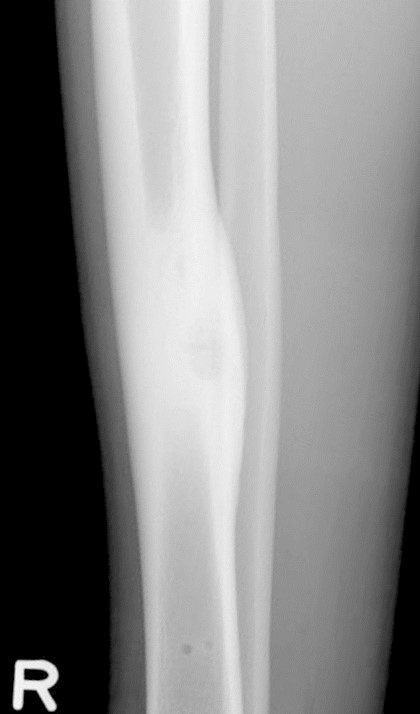
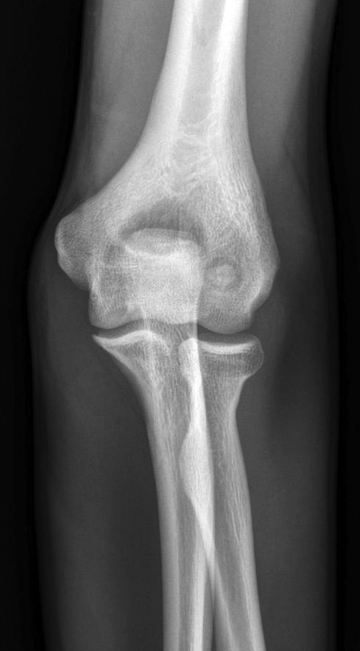
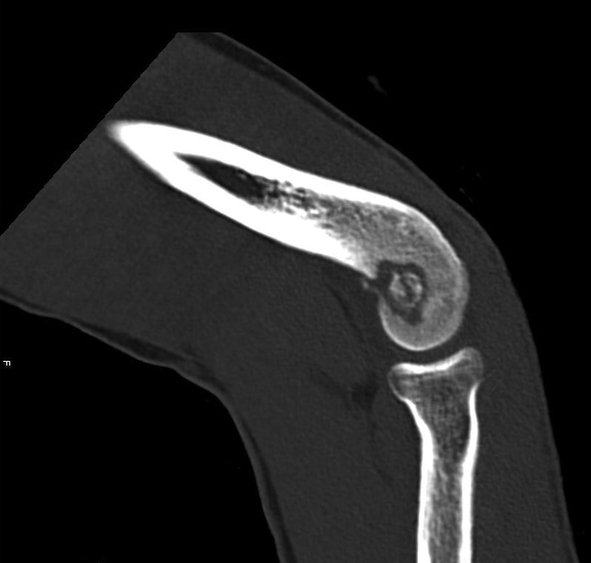
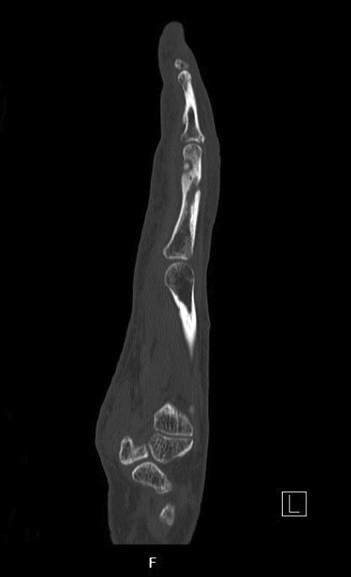
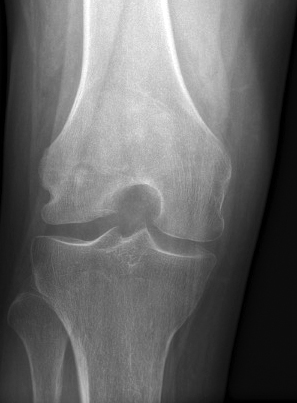
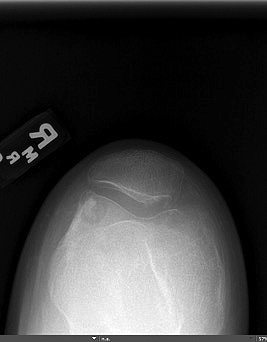
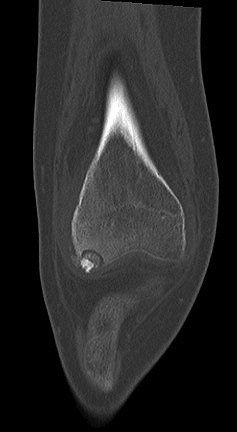
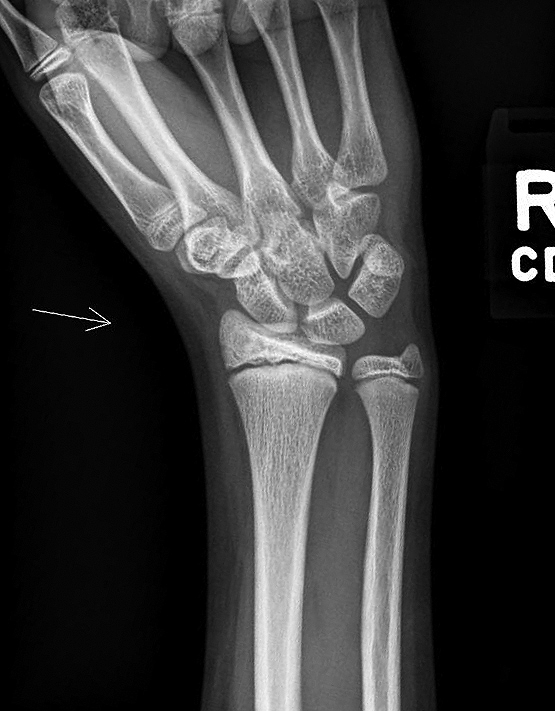
Radiology description
- Xray:
- Intracortical lesions have a nidus with a variable degree of mineralization and surrounding reactive osteosclerosis
- Intramedullary lesions may be more difficult to visualize on conventional radiography and often lack the surrounding sclerotic bone
- CT scan:
- Well defined oval to round nidus with low attenuation
- Reactive cortical sclerosis
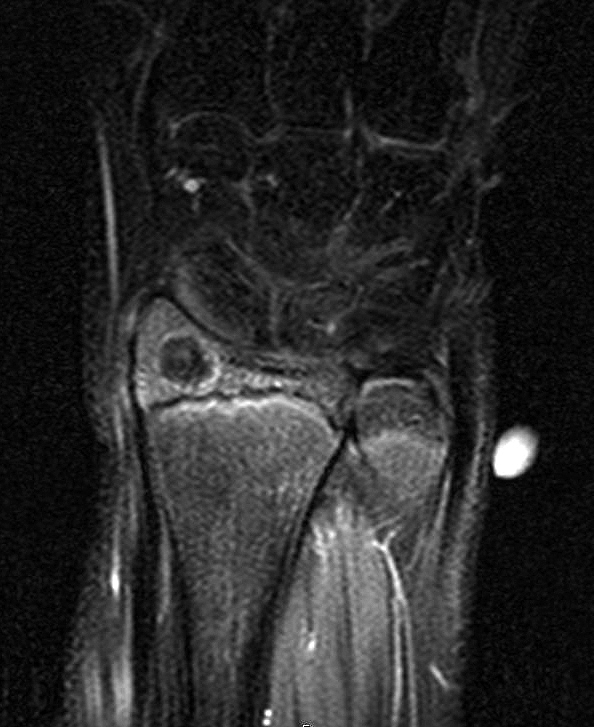
- MRI:
- Generally of limited value in the detection of a nidus, with the exception of intramedullary lesions
- Characteristics of nidus tissue (depending on the degree of mineralization):
- Low to intermediate signal intensity on T1 weighted images
- Variable signal intensity on T2 weighted images
- Target-like appearance of partially mineralized nidus
- Bone marrow edema and joint effusion
- Intracapsular lesions may be associated with marked synovitis, leading to an erroneous diagnosis of an inflammatory arthropathy
- Isotope scan:
- Zone of increased uptake corresponding to nidus and perilesional sclerosis
- Reference: Radiographics 2010;30:737
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis, with rare cases of recurrence (J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2011;19:678, Orthopade 2017;46:510)
Case reports
- 16 year old girl with polyostotic osteoid osteoma (Radiol Case Rep 2020;15:411)
- 22 year old man with hallux osteoid osteoma (Open Orthop J 2017;11:1066)
- 25 year old man with multifocal osteoid osteoma of tibia (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013201712)
- 29 year old woman and 29 year old man with osteoid osteoma of cervical spine (J Orthop Case Rep 2019;9:78)
- 39 year old man with multicentric, multifocal and recurrent osteoid osteoma of the hip (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2019;20:171)
- 41 year old woman with proximal phalanx osteoid osteoma (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2017;5:e1332)
Treatment
- NSAIDs
- CT guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (Radiology 2003;229:171)
- Symptomatic patients, nonresponsive to NSAIDs
- Outpatient
- Minimally invasive
- Curettage and resection (Orthopade 2017;46:510)
- Vertebral column
- Small bone of hands and feet
- Close relationship to peripheral nerves
- Recurrent lesions
- Reference: Acta Biomed 2018;89:175
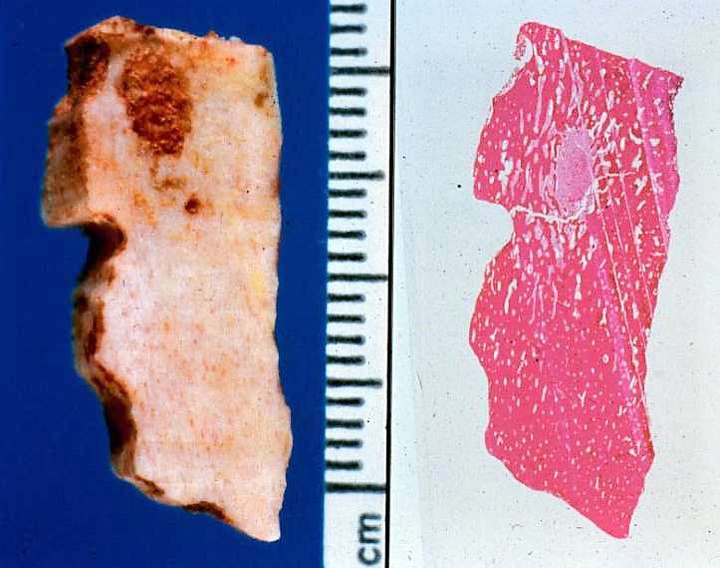
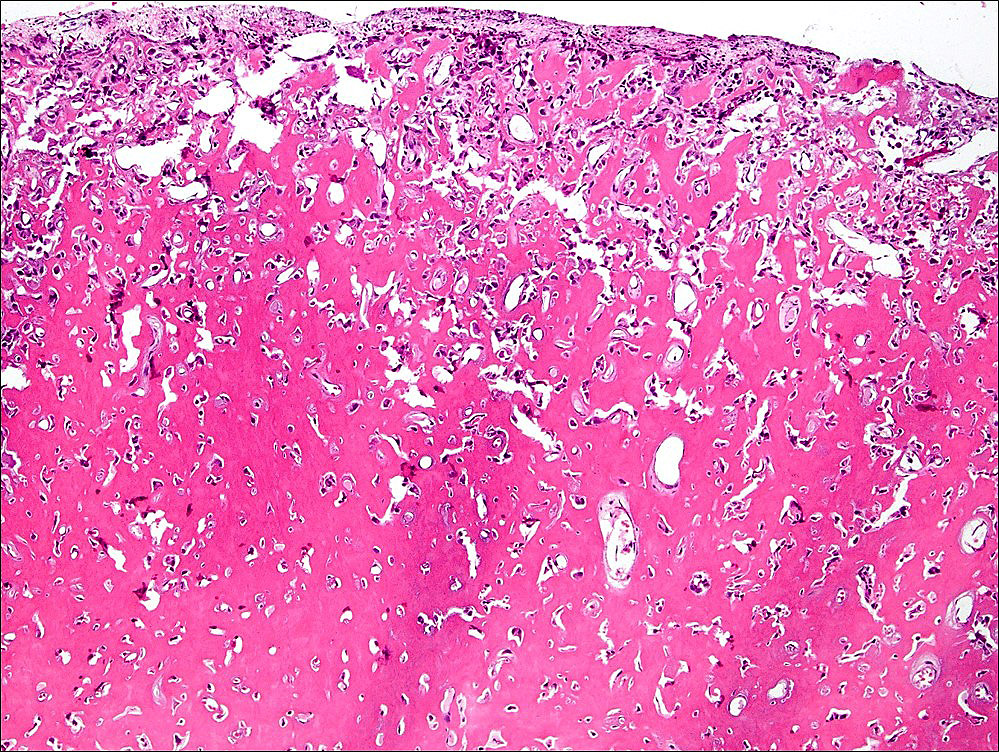
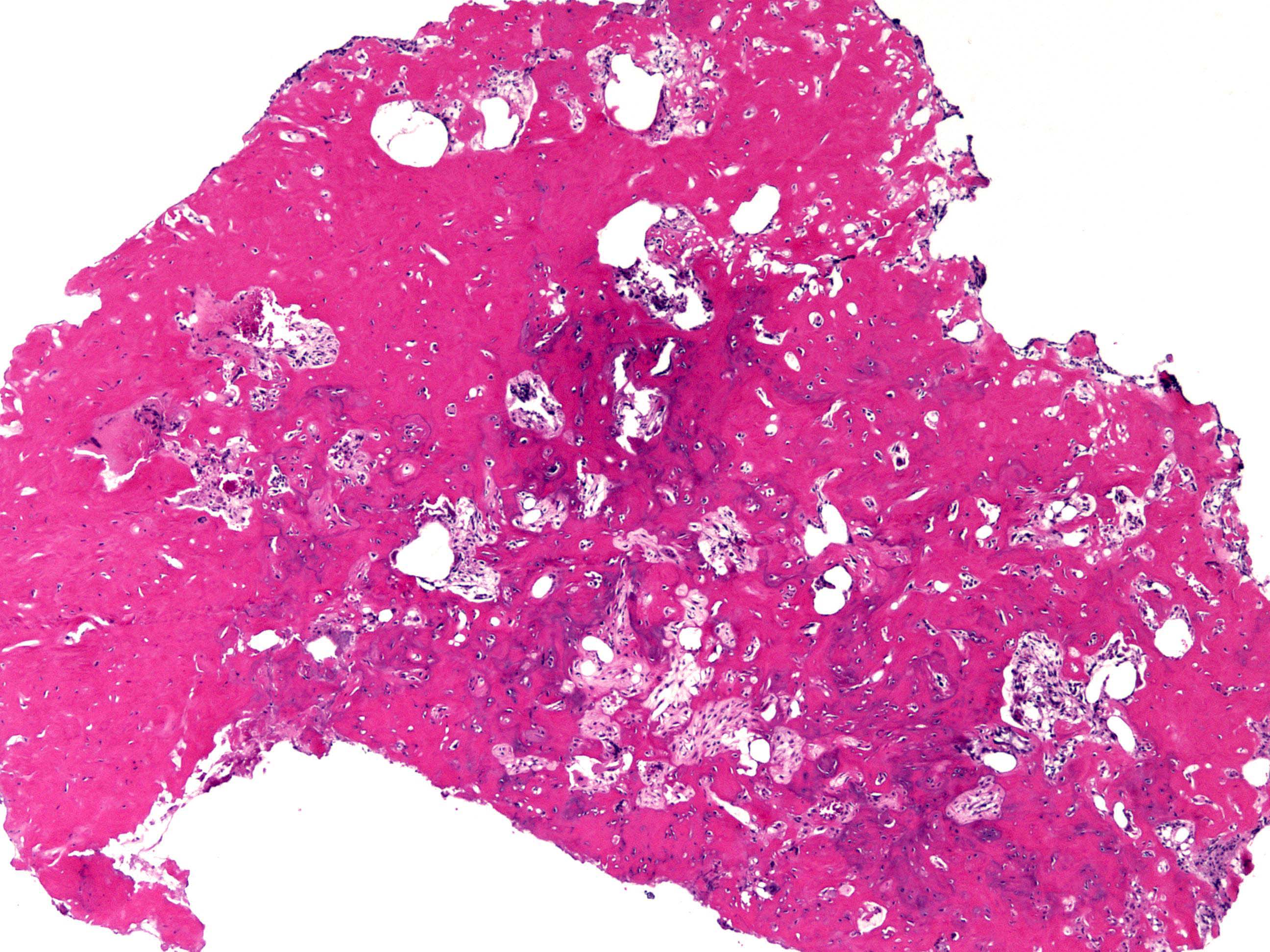
Gross description
- Oval red nidus is easily distinguishable from surrounding tissue
- Soft and friable to sclerotic nidus
- Surrounded by densely sclerotic reactive bone
Frozen section description
- Not usually performed
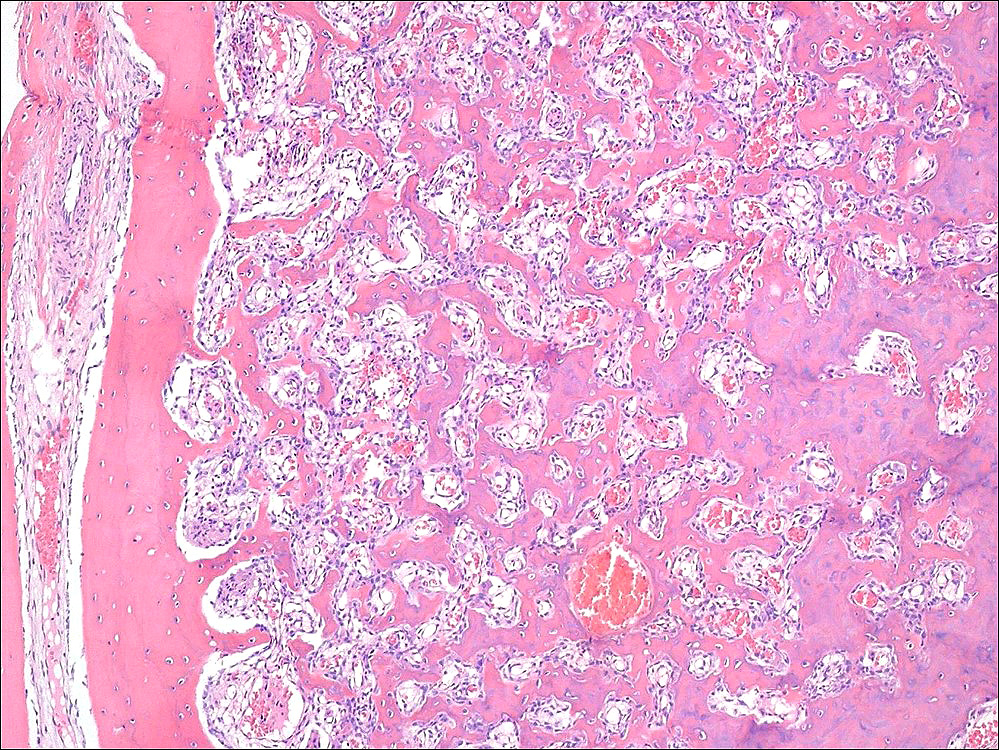
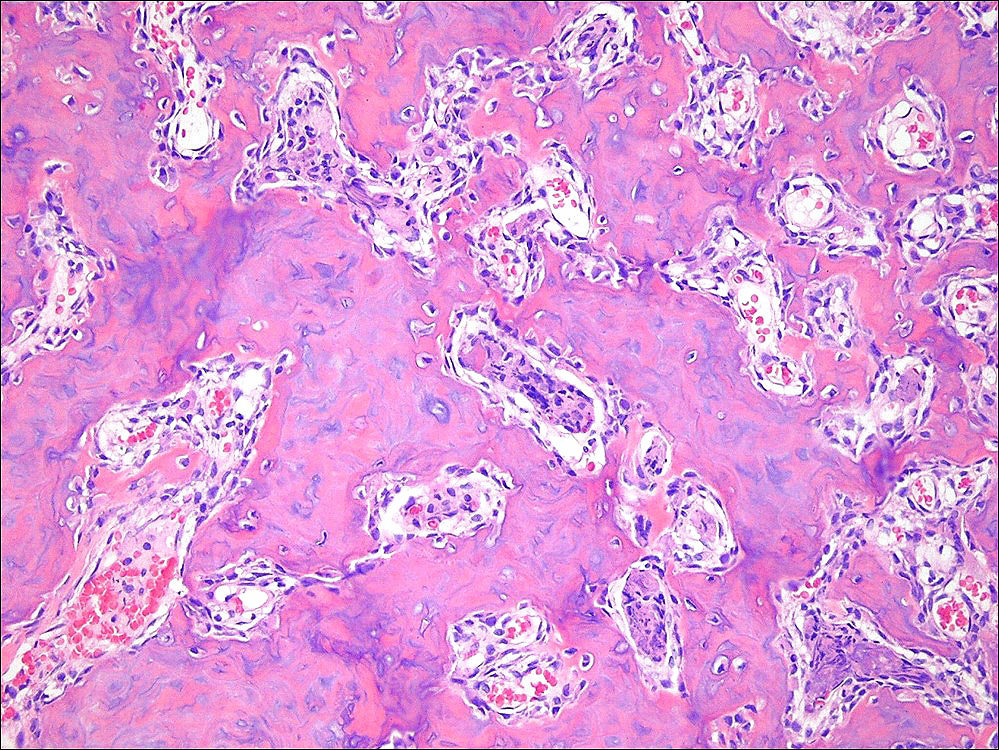
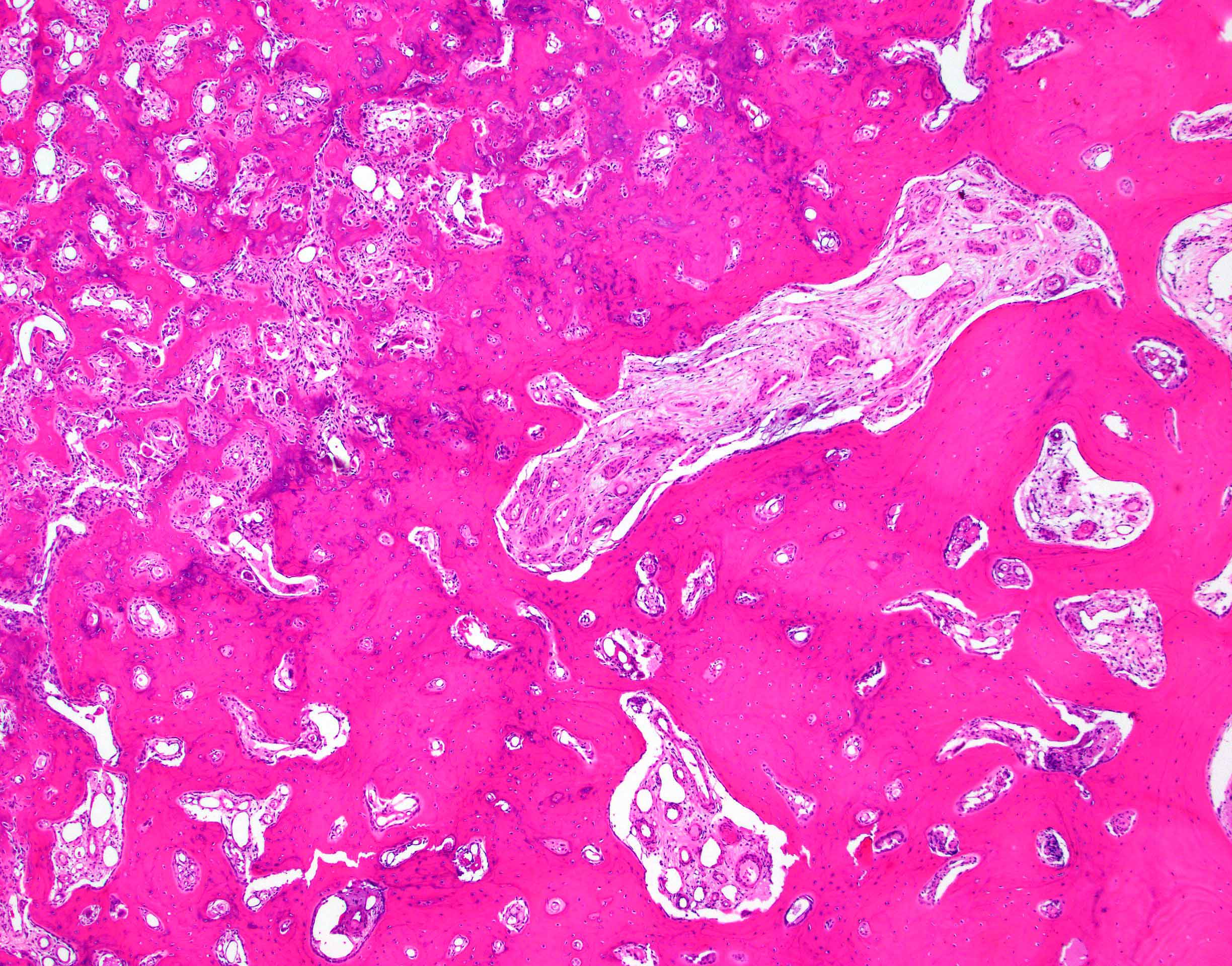
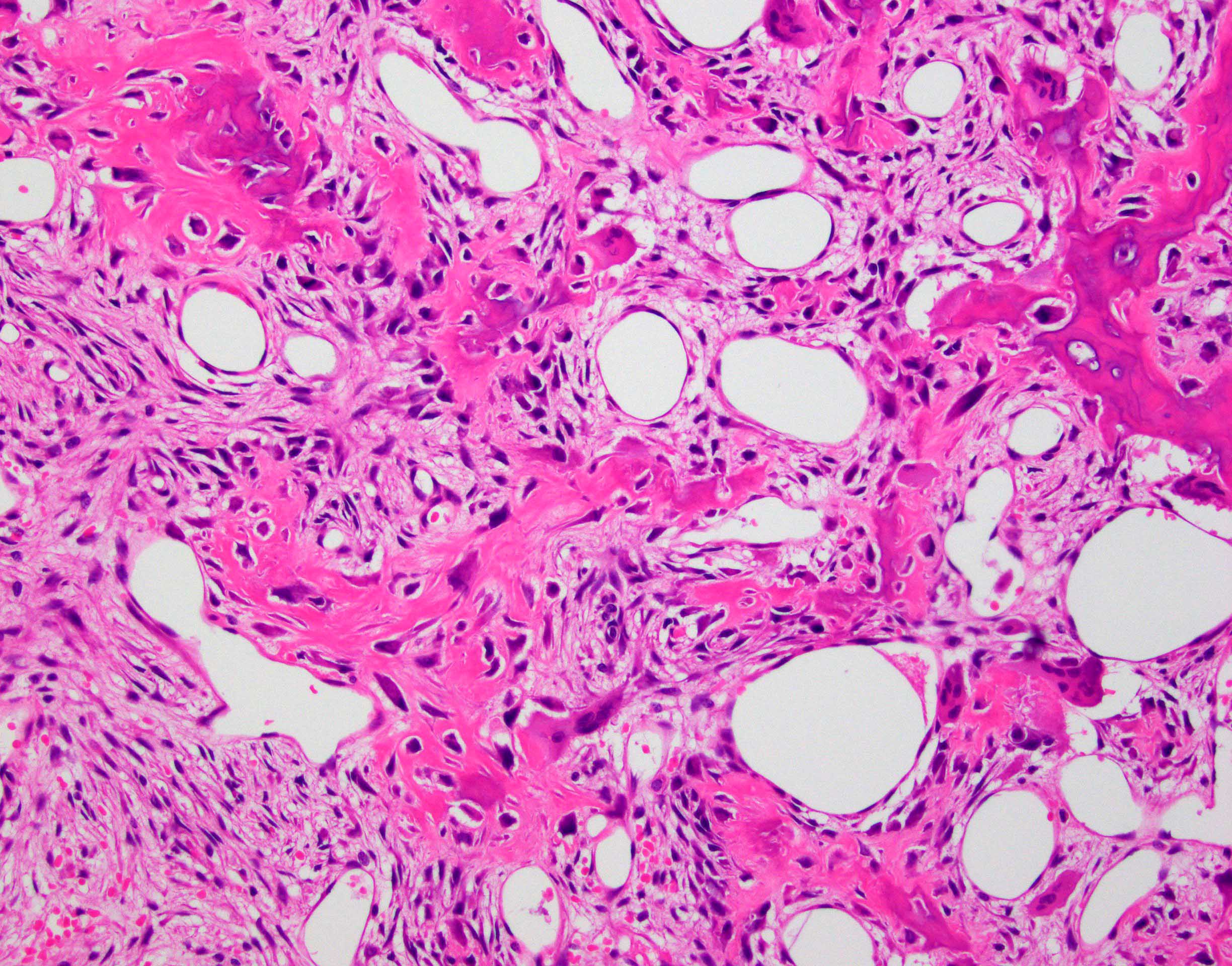
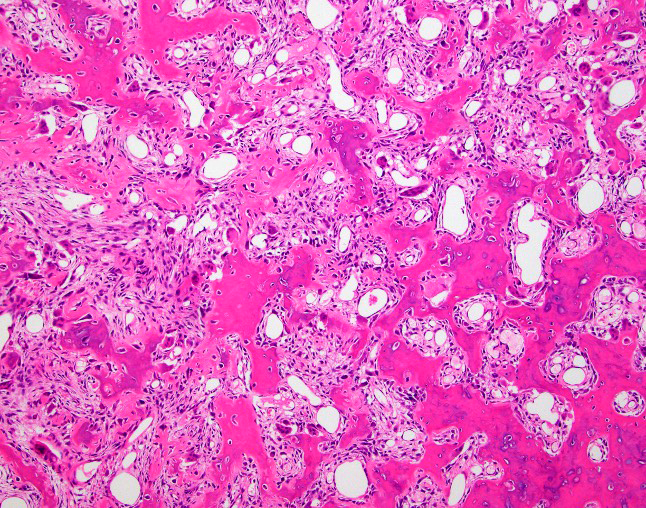
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nidus:
- Haphazard trabeculae of woven bone with prominent osteoblastic rimming
- Different thickness and mineralization level
- Disordered (Pagetic) cement lines in some cases
- Sheet-like osteoid deposition in some cases
- Densely sclerotic woven bone in some cases
- Haphazard trabeculae of woven bone with prominent osteoblastic rimming
- Surrounding bone:
- Thickened trabeculae of bone with adjacent loose fibrovascular stroma
- Reference: Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1661
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- cFOS in 73% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1661)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Rearrangement of AP1 transcription factor
- FOS (more common) gene on chromosome 14
- FOSB (less common) gene on chromosome 19
- Other tumors with FOSB gene rearrangement:
- Osteoblastoma
- Epithelioid hemangioma
- Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma
- Other tumors with FOSB gene rearrangement:
- References: Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1661, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019;58:88
Sample pathology report
- Mass, distal metaphysis, left tibia, biopsy:
- Osteoid osteoma
Differential diagnosis
- Osteoblastoma (J Clin Pathol 2013;66:768):
- Usually > 2 cm
- More likely to be locally aggressive
- Significant radiographic and morphologic overlap
- Osteomyelitis and intraosseous abscess (Brodie abscess) (Case Rep Orthop 2013;2013:234048):
- Most problematic in small bones of hands and feet
- Predominant inflammatory cells
- Stress fracture (Clin Nucl Med 2001;26:54):
- Lack of nidus
- Linear radiolucency oriented perpendicular to the cortex
Additional references
Practice question #1
Osteoid osteoma most likely shows rearrangement of which of the following genes?
- DDIT3
- EWSR1
- FOS / FOSB
- USP6
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2