Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Alexiev BA. Osteoblastoma, NOS. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/boneosteoblastoma.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Osteoblastoma is a locally aggressive bone forming tumor, morphologically similar to osteoid osteoma but with growth potential and generally > 2 cm in dimension
Essential features
- Bone forming tumor composed of trabeculae of woven bone rimmed by plump osteoblasts in a vascularized stroma
- Well defined tumor borders
- Absence of host bone permeation
- Radiology demonstration of a > 2 cm lesion
Terminology
- Acceptable: epithelioid osteoblastoma
- Not recommended: pseudomalignant osteoblastoma, aggressive osteoblastoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9200/1 - osteoblastoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2E83.Z & XH4316 - benign osteogenic tumor of unspecified site & osteoblastoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare, representing < 1% of primary bone tumors (J Surg Oncol 2008;98:179, Hum Pathol 1994;25:117)
- Affects mainly adolescents and young adults (mean age 20 years), with a male predominance (2.5:1) (StatPearls: Osteoblastoma [Accessed 8 July 2021])
Sites
- Predilection for the spine and sacrum (40 - 55%), most commonly involving the posterior elements of the spine (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1460)
- Other common sites of involvement include the maxillofacial region's osseous structures and the long bones, with a predilection for the lower extremity (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1976;126:321, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006;102:639)
- Any bone may be affected
Pathophysiology
- Expresses Runx2 and Osterix, transcription factors involved in osteoblastic differentiation (Hum Pathol 2010;41:1788)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Earliest symptom in most patients is nonspecific pain, characterized as a dull ache that is less severe at night than during the day (Neurosurg Focus 2016;41:E4)
- Pain is unlikely to be relieved by salicylates (PLoS One 2013;8:e74635)
- Tumors located in the spine can press on nerves; when this happens, patients usually develop neurological symptoms in the legs, such as numbness, weakness or pain (PLoS One 2013;8:e74635)
- Can produce beta hCG as a paraneoplastic manifestation (Skeletal Radiol 2017;46:1187)
Diagnosis
- In many cases, the diagnosis is suggested by the tumor location, size and appearance on Xray, computed tomography and magnetic resonance scans
- Definitive diagnosis usually requires a biopsy
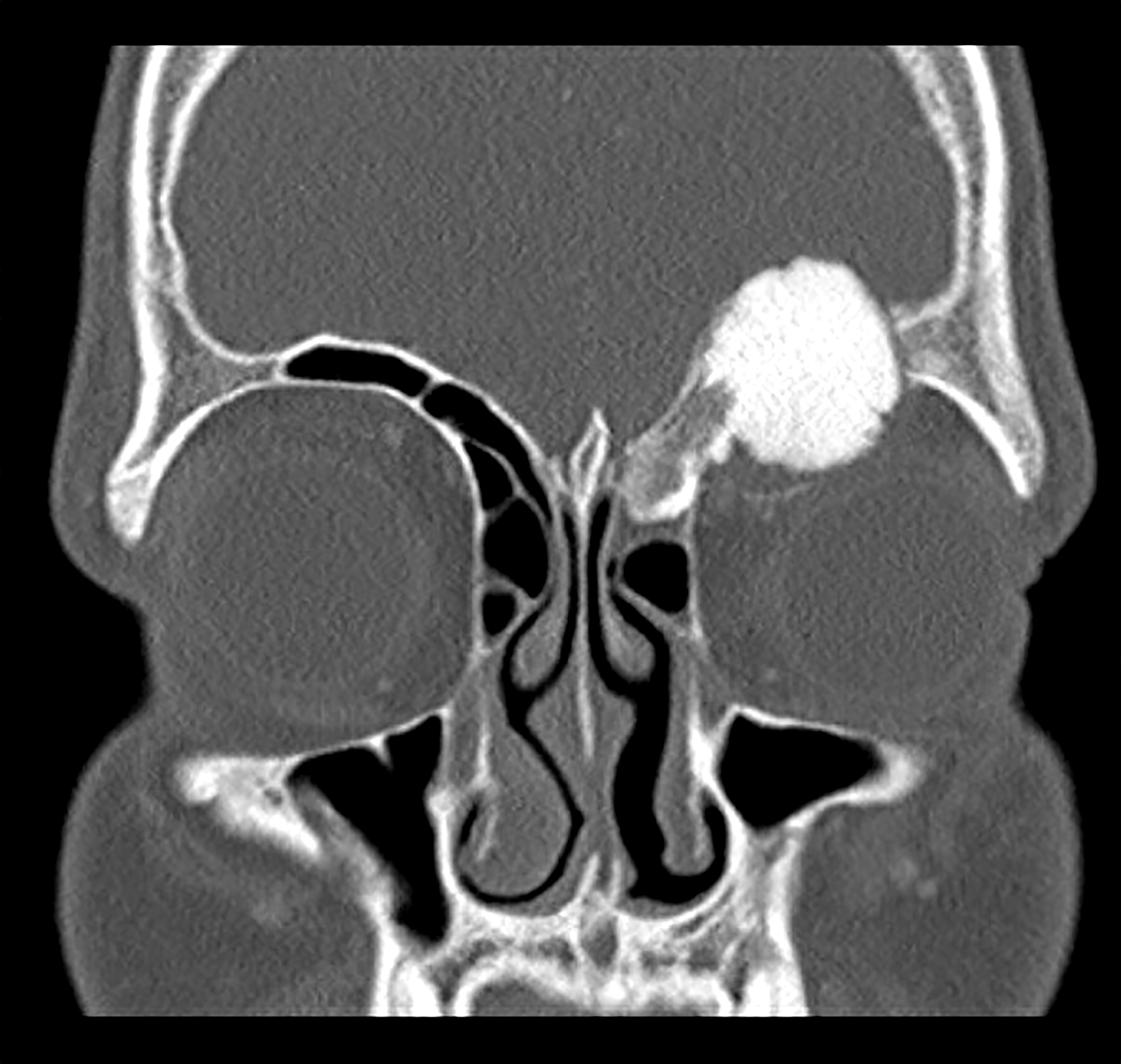
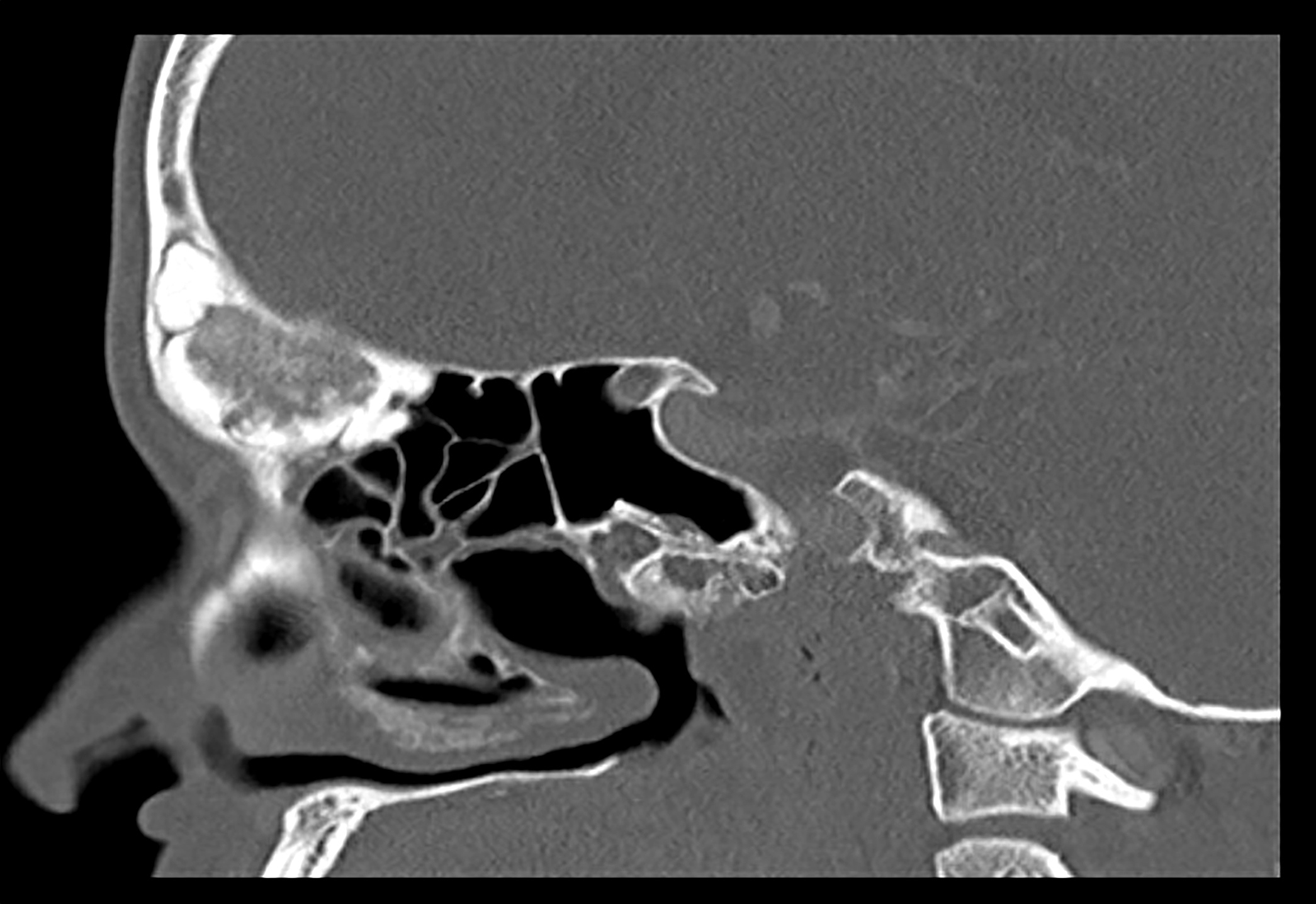
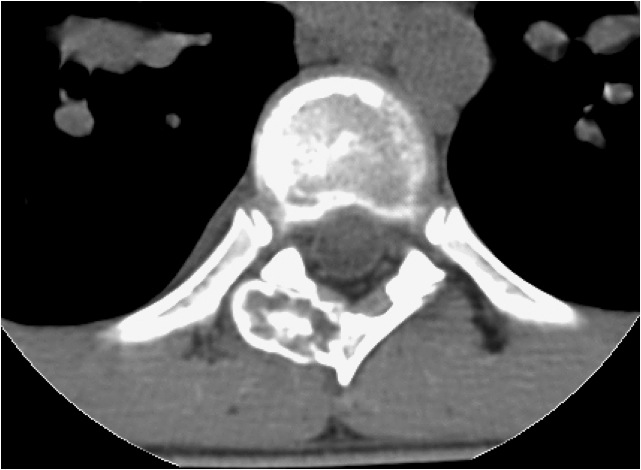
Radiology description
- Characteristic appearance on radiographs is a dense shell of bone surrounding the lesion, with some tumors resembling osteoid osteoma with a radiolucent nidus and surrounding sclerotic changes
- In some cases, the bony shell tends to be very thin, with expansion into adjacent soft issues (Neurosurg Focus 2016;41:E4, Eur Spine J 2015;24:1778)
- Cortical expansion and destruction are common radiographic findings (Hum Pathol 1994;25:117)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis is excellent, with most patients cured following the initial surgical treatment
- Local recurrence is a relatively common complication, with rates ranging from 15% to 25% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1460, J Surg Oncol 2008;98:179)
Case reports
- 19 year old man presented with a mass in the left maxillary sinus (Head Neck Pathol 2012;6:451)
- 24 year old man with a painless lump in the frontoparietal area (J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2013;66:270)
- 25 year old man with a tumor of the mandible (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2019;128:e16)
- 32 year old man with a mass of the sternum (Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 2010;68:55)
- 45 year old man with a bony nasal septum mass (J Laryngol Otol 2011;125:1062)
Treatment
- Primary treatment is surgery, either en bloc resection or curettage, with allograft or autograft (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002;397:394, J Pediatr Orthop 2004;24:319)
- There is no definite role for adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy (J Surg Oncol 2008;98:179)
- Imaging surveillance may be necessary due to the risk of local recurrence
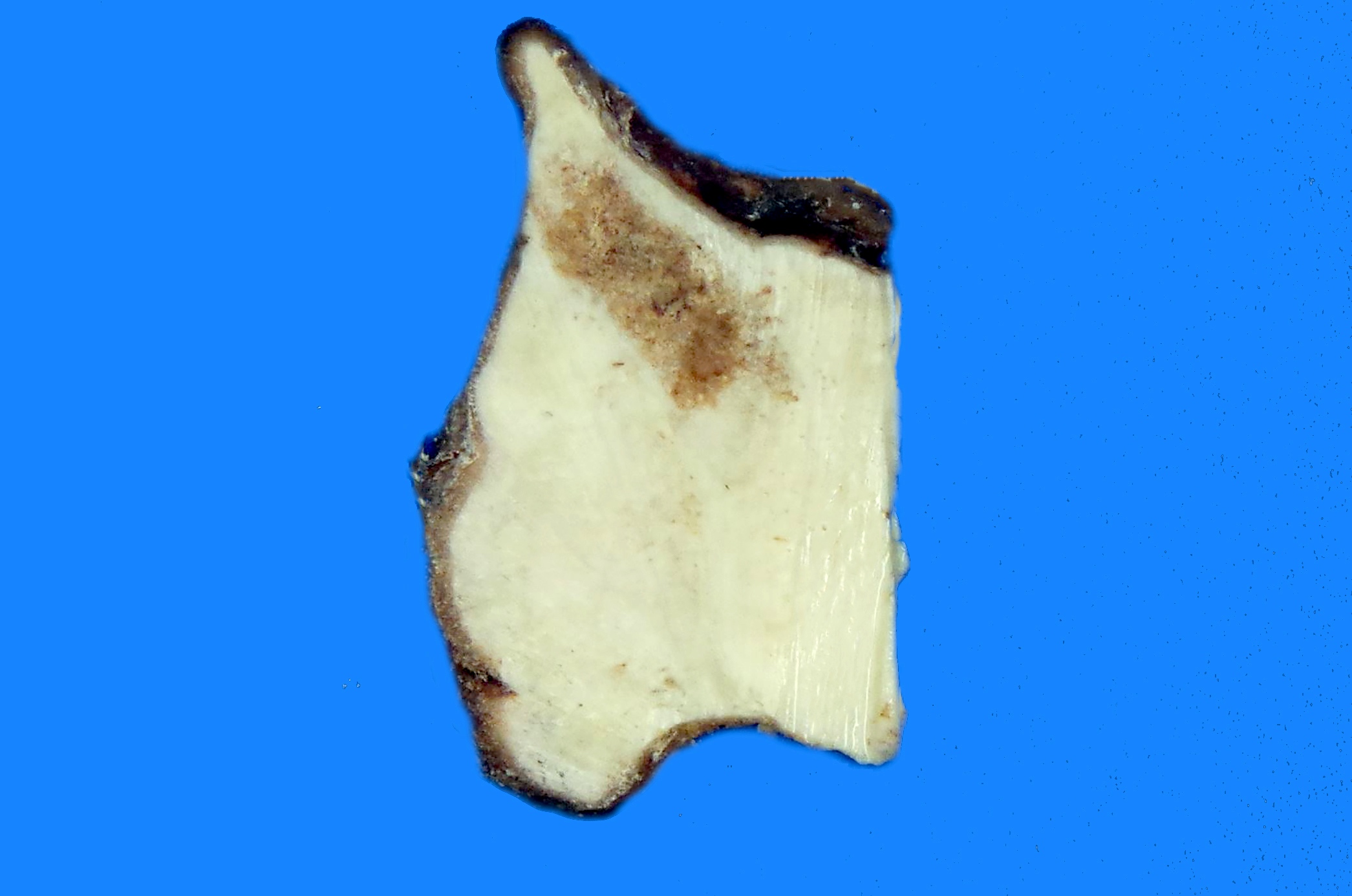
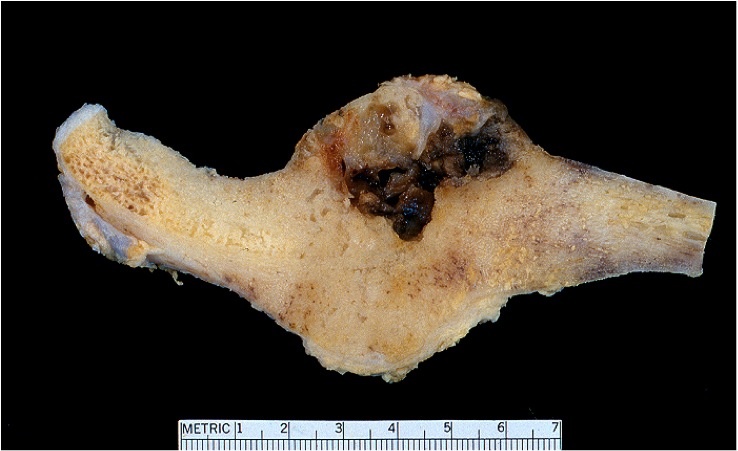
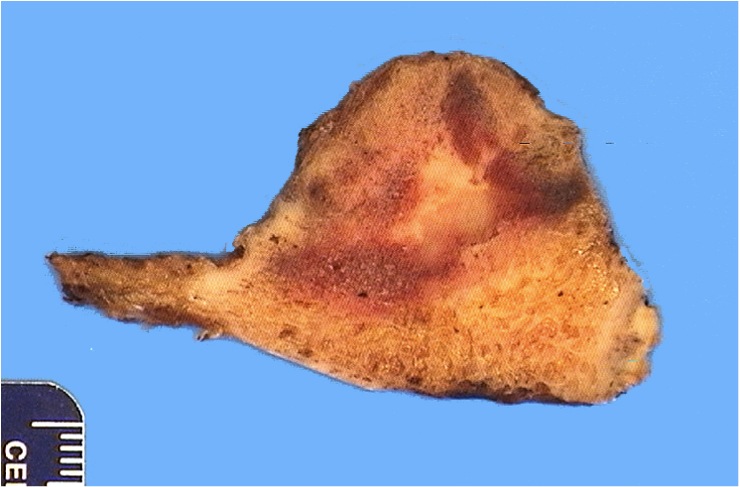
Gross description
- Tumor is usually round to oval with a thinned, expanded cortex, surrounding sclerosis and periosteal reaction (StatPearls: Osteoblastoma [Accessed 8 July 2021])
- Border between the tumor and medullary cavity is sharp
- Tumor has a pushing border against the endosteal cortical surface and trabecular bone of the marrow, consistent with its benign nature (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1460)
- There may be evidence of hemorrhage, cystic changes with blood filled spaces and reparative changes in lesions with secondary aneurysmal bone cysts or large lesions (Clin Imaging 2020;62:23)
Gross images
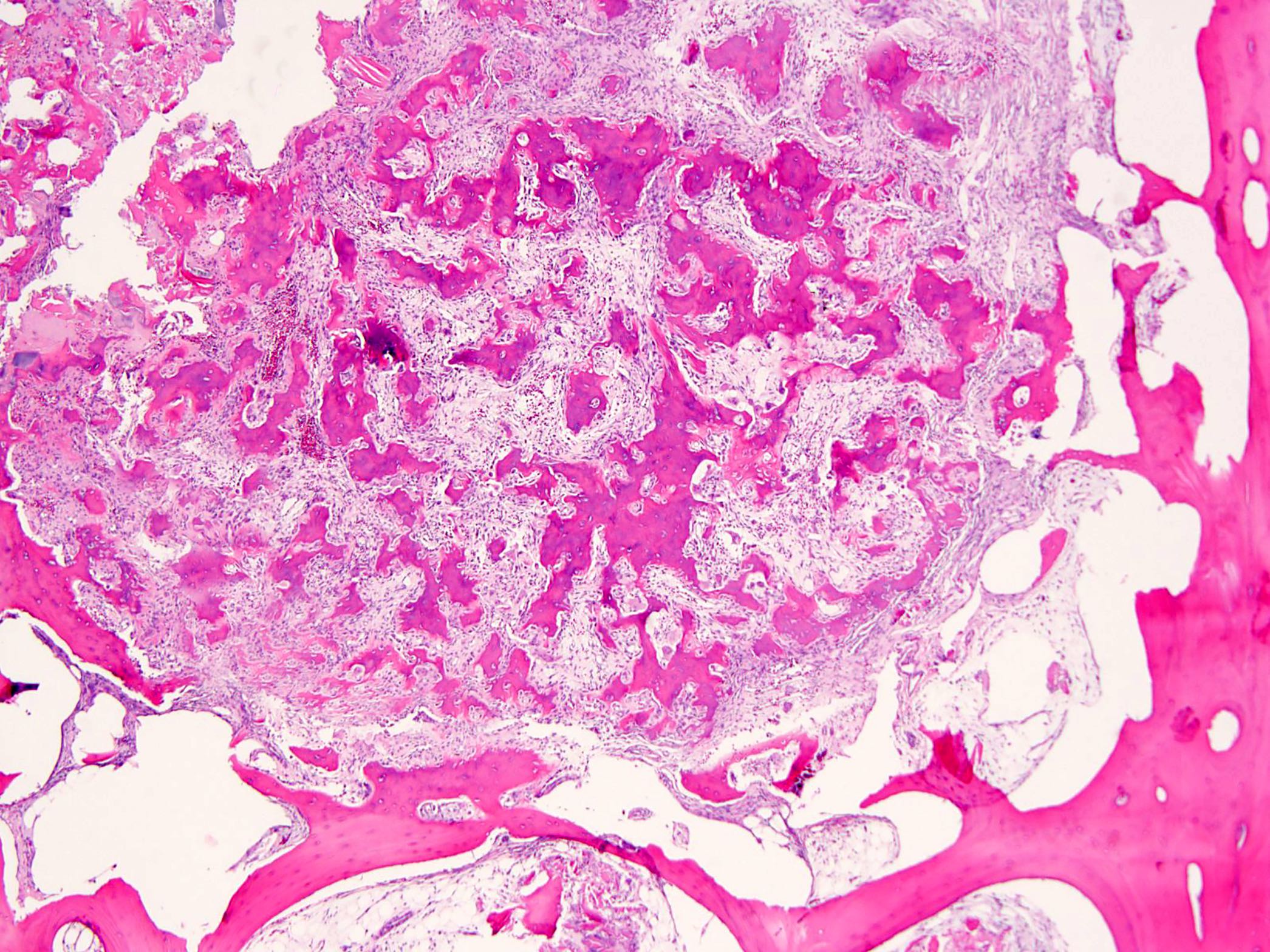
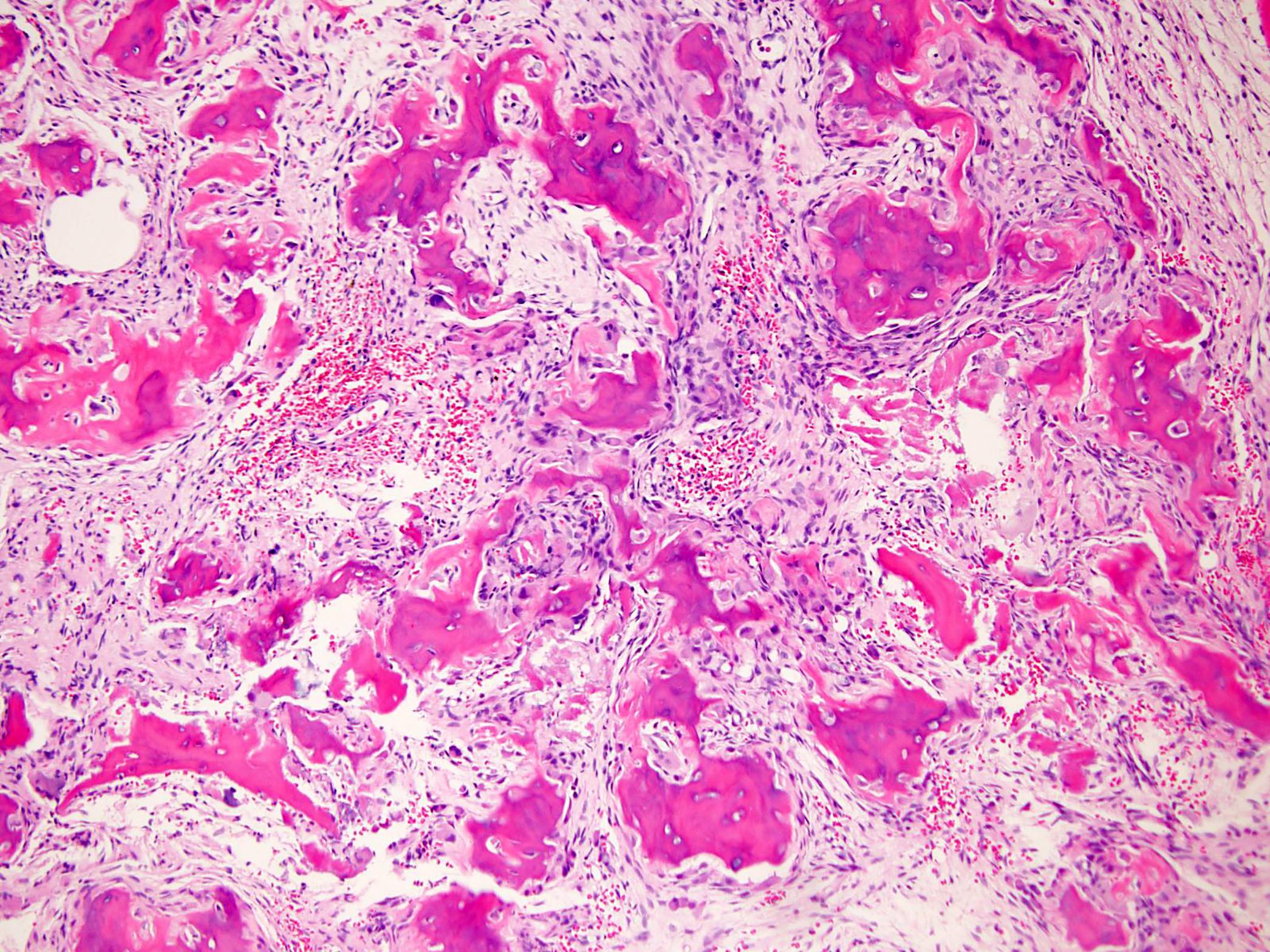
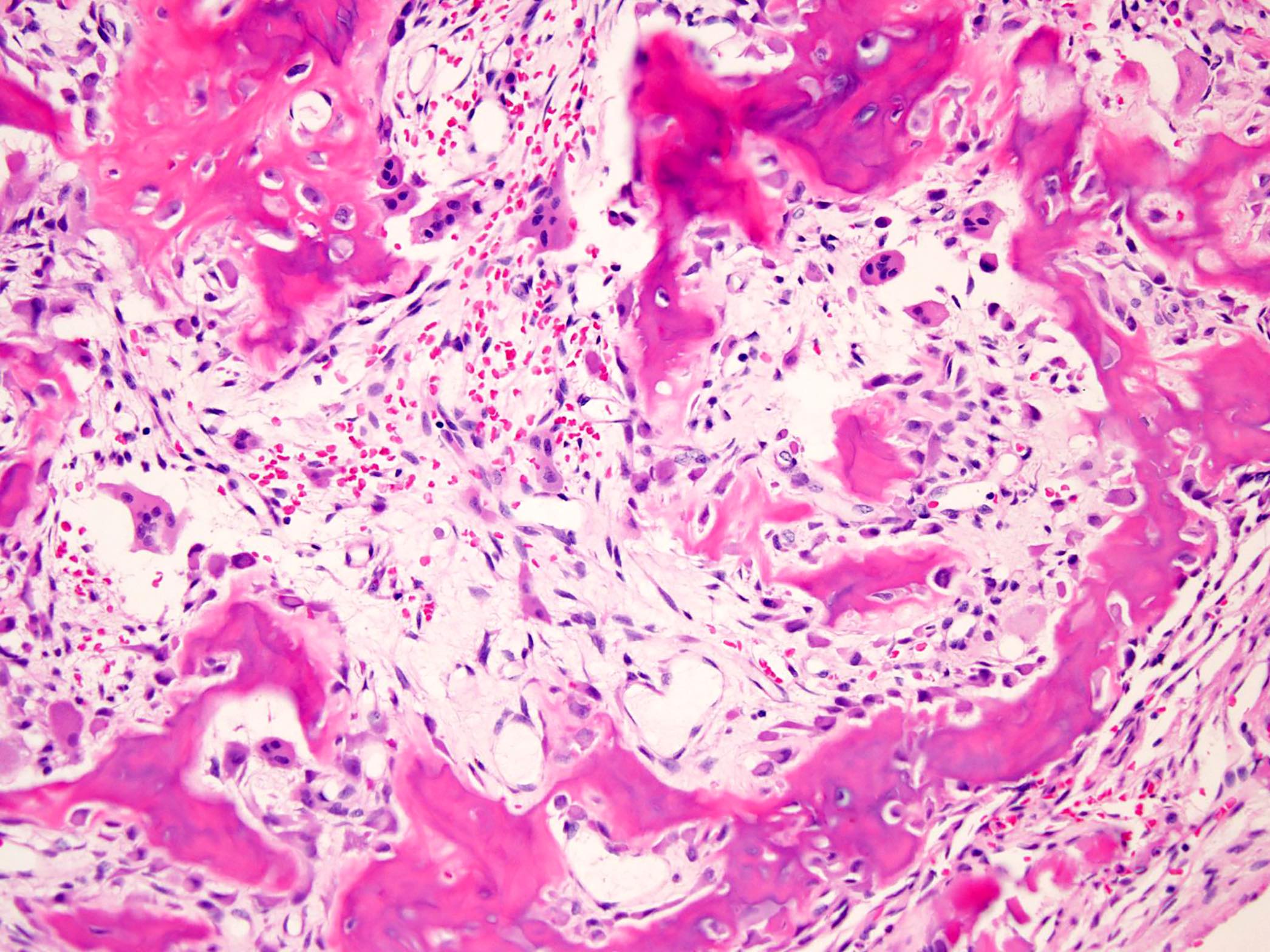
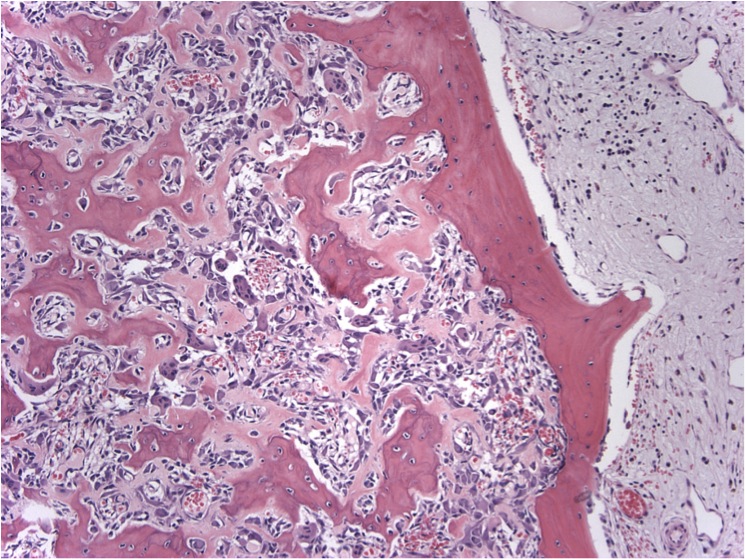
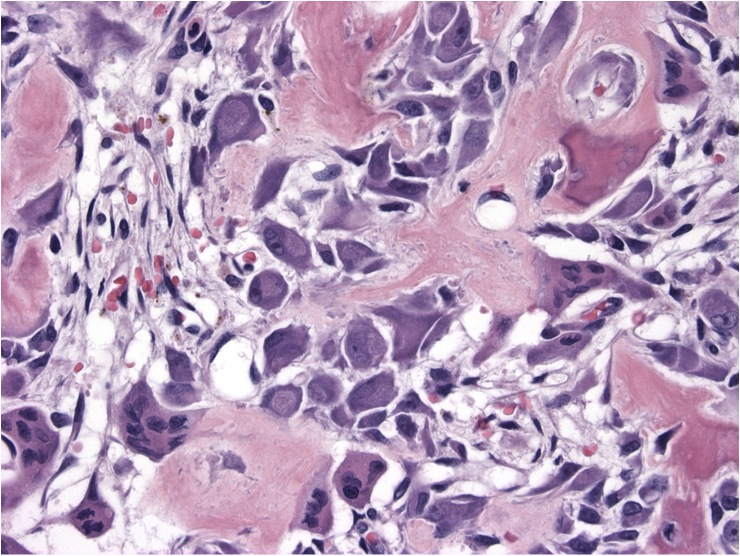
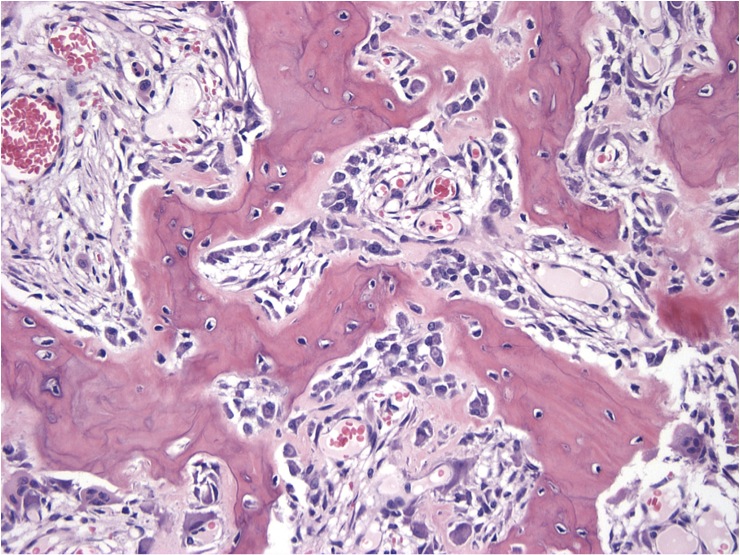
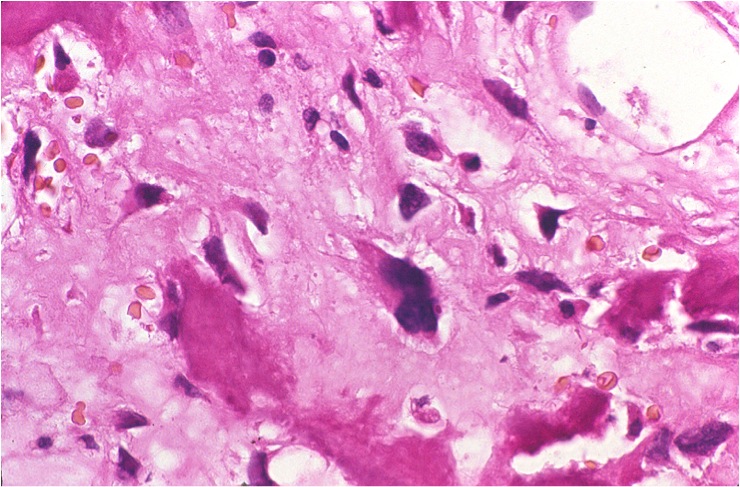
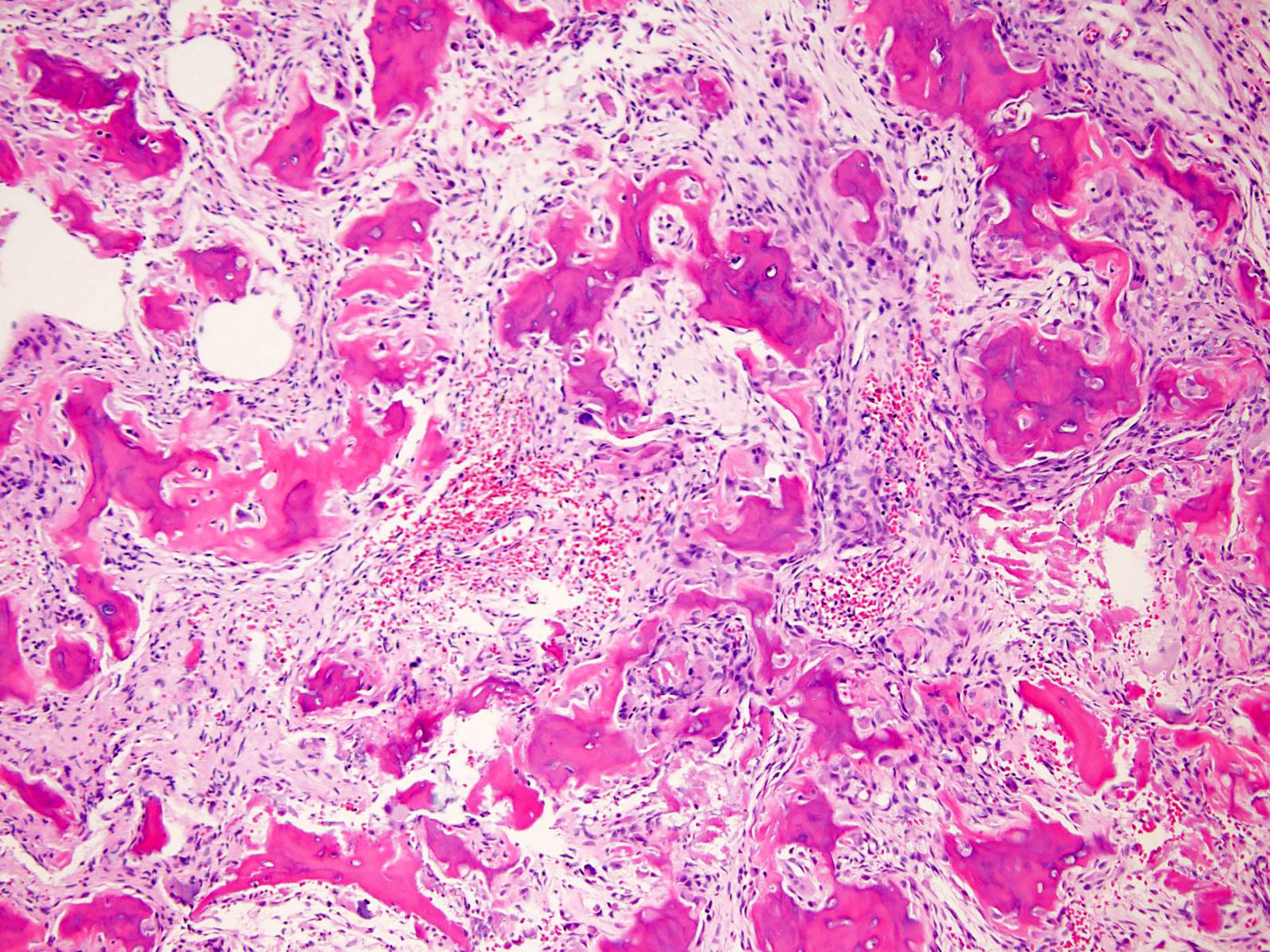
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Expansile, surrounded by a sclerotic rim, may or may not have a central sclerotic nidus (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1460)
- Composed of interanastomosing trabeculae of woven bone, set within loose edematous fibrovascular stroma, often with extravasated erythrocytes (StatPearls: Osteoblastoma [Accessed 8 July 2021])
- Tumors show a spectrum of bony maturational changes ranging from cords and clusters of activated osteoblasts associated with minimal osteoid to lace-like wispy osteoid to broad anastomosing trabeculae of woven bone to sclerotic sheets of woven bone (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1460)
- Osseous trabeculae are lined by a single layer of osteoblasts
- Diffusely scattered osteoclast type, multinucleated giant cells are often present
- Degenerative cytologic atypia characterized by cells with large degenerated nuclei and smudged chromatin may be present
- Secondary aneurysmal bone cysts can occur, most commonly in large or expanded lesions
- Rarely, one finds cartilage or chondro-osseous matrix within an osteoblastoma
- Mitotic rate may be high but atypical mitoses are not present
- Does not infiltrate or permeate pre-existing lamellar bone structures (StatPearls: Osteoblastoma [Accessed 8 July 2021])
- Epithelioid osteoblastoma is a rare variant characterized histologically by epithelioid osteoblasts and clinically by local recurrences if not completely excised (J Foot Ankle Surg 2020;59:1279)
- Sheets of pleomorphic epithelioid cells with eccentric nuclei and prominent nucleoli associated with eosinophilic amorphous osteoid and foci of calcification (Pathol Res Pract 2001;197:569, Head Neck Pathol 2011;5:165)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Borislav A. Alexiev, M.D. and David R. Lucas, M.D.
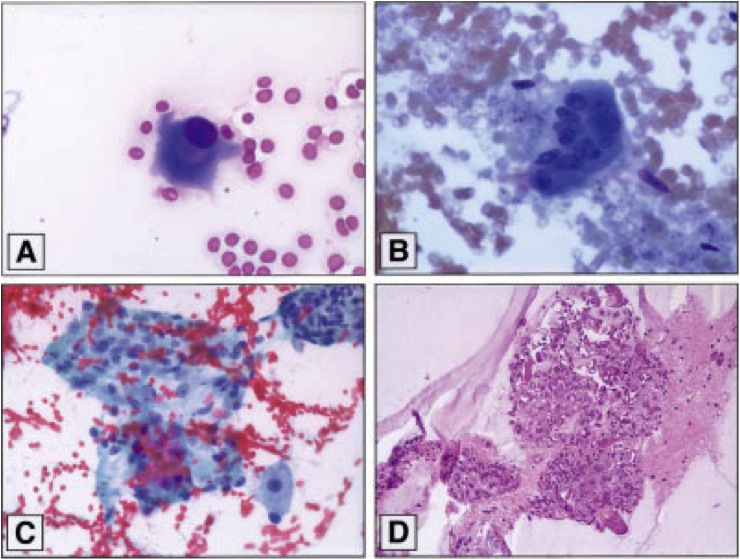
Cytology description
- Cellular smears with the presence of mononuclear and binucleated osteoblasts, along with scattered osteoclastic giant cells and uniform spindle cells entangled in myxoid stroma (Diagn Cytopathol 2015;43:218)
- No necrosis and no atypical mitosis are observed (Cytojournal 2018;15:20)
Immunofluorescence description
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization using split apart probes for FOS shows a segregated red and green signal (Virchows Arch 2020;476:455)
Positive stains
- Nuclear beta catenin staining (StatPearls: Osteoblastoma [Accessed 8 July 2021])
- FOS (Virchows Arch 2020;476:455)
- SATB2 (Histopathology 2013;63:36)
Negative stains
- Negative for H3F3A (G34W) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1059)
- Negative for epithelial (keratin AE1 / AE3) and melanoma (HMB45, MelanA, SOX10) markers
Electron microscopy description
- Osteoblasts in osteoblastoma resemble normal osteoblasts with few exceptions: irregular, indented nuclei and occasional mitochondria with curved cristae and electron lucent areas (Cancer 1977;39:2127)
- Ovoid or elongated osteoblasts with eccentric nuclei with irregular, indented nuclear membrane and condensed chromatin towards the periphery and abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum and well developed Golgi apparatus (Acta Pathol Jpn 1979;29:791)
- Osteocytes and osteoclasts resemble their normal counterparts
- Osteocytes with less prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum and well developed Golgi apparatus
- Osteoclasts with sparse rough endoplasmic reticulum and numerous mitochondria
- Osteoprogenitor cells in different stages of maturation
- Calcified matrix and osteoid
- Many blood vessels of varying caliber with osteoblasts in different stages of differentiation in the perivascular spaces
- Large numbers of red blood cells and few monocytoid cells and histiocytes
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Homo or hemizygous deletions in chromosome 22
- Losses of ZNRF3, KREMEN1 and NF2 (inhibitors of the Wnt / beta catenin pathway) (PLoS One 2013;8:e80725)
Sample pathology report
- Left frontal sinus mass, resection:
- Osteoblastoma (see comment)
- Comment: Radiology images demonstrate a calcified lobulated lesion centered in the mid left frontal sinus, 3.2 cm in greatest dimension. Histologically, the neoplasm is composed of interanastomosing trabeculae of woven bone, set within loose edematous fibrovascular stroma, with extravasated erythrocytes. The osseous trabeculae are lined by a single layer of osteoblasts. Diffusely scattered osteoclast type, multinucleated giant cells are present. The neoplasm is surrounded by a sclerotic rim. There is no infiltration of pre-existing lamellar bone structures. Rare mitotic figures and no necrosis are seen. Immunohistochemically, positive staining for FOS and nuclear beta catenin in lesional cells is present. Overall, the appearance on computed tomography and magnetic resonance scans, size (> 2 cm), morphological features and immunohistochemical profile support the diagnosis of osteoblastoma.
- The prognosis of osteoblastoma is excellent, with most patients cured following the initial surgical treatment. Local recurrence is a relatively common complication, with rates ranging from 15% to 25%.
Differential diagnosis
- Osteoid osteoma:
- Characteristically presents with dull aching pain, worse at night and often relieved with NSAIDS (Conn Med 2014;78:233)
- Most commonly found in long bone (Conn Med 2014;78:233)
- Size is an important differentiator between osteoblastomas and osteoid osteomas, with the former typically measuring > 2 cm in size (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020;21:240)
- Aneurysmal bone cyst:
- Because osteoblastoma can be very hemorrhagic and show secondary aneurysmal bone cyst changes and conversely, because primary aneurysmal bone cyst can show extensive reactive new bone production that resembles osteoblastoma, it can be challenging to tell them apart in some cases (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1460)
- Negative for FOS expression (Virchows Arch 2020;476:455)
- USP6 rearrangement (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:281)
- Giant cell tumor of bone:
- Negative for FOS expression (Virchows Arch 2020;476:455)
- H3F3A (G34W) nuclear immunoreactivity (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1059)
- Giant cell rich osteosarcoma:
- Neoplastic osteoblasts with marked nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli and atypical mitoses (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2020;24:S67)
- Abundant spindle cells with marked atypia arranged in a streaming or storiform pattern (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:9718)
- Numerous osteoclast-like giant cells
- Infiltration of pre-existing lamellar bone structures
- Negative for FOS expression (Virchows Arch 2020;476:455)
- Osteoblastoma-like osteosarcoma:
- Tumor permeation of the surrounding host tissue (Mod Pathol 1993;6:707)
- Lack of maturation toward the edges (Cancer 1985;55:416)
- Negative for FOS expression (Virchows Arch 2020;476:455)
- Osteoma with osteoblastoma-like features:
- In the frontoethmoid region, conspicuous osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity may be present
- Focally indistinguishable from osteoblastoma (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:503, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1587)
- Osteoma with osteoblastoma-like features has much more mature bone in the form of solid / compact (ivory osteoma) and dense cancellous (mature osteoma) bone (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1587)
- Outer contour of an osteoma has a smooth rounded surface, often lined by respiratory mucosa
- True osteoblastoma, by contrast, will form an expansile intramedullary or periosteal bone tumor with a radiolucent or partially calcified appearance, often with surrounding sclerosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1587)
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 31 year old man presented with an aggressive appearing thoracic spine lesion measuring 2.8 cm in greatest dimension. Hematoxylin eosin stains demonstrate interanastomosing trabeculae of woven bone, set within loose edematous fibrovascular stroma, with extravasated erythrocytes. There is a spectrum of bony maturational changes ranging from cords and clusters of activated osteoblasts associated with minimal osteoid to lace-like wispy osteoid to broad anastomosing trabeculae of woven bone to sclerotic sheets of woven bone. The osseous trabeculae are lined by a single layer of osteoblasts. Diffusely scattered osteoclast type, multinucleated giant cells are present. The neoplasm is surrounded by a sclerotic rim. There is no infiltration of pre-existing lamellar bone structures. Rare mitotic figures and no necrosis are seen. Immunohistochemical stains for FOS and beta catenin (nuclear) are positive in tumor cells, while all of the following are negative: keratin AE1 / AE3, H3F3A (G34W) and p53. The tumor is negative for USP6 rearrangement.
Which of the following is most likely the correct diagnosis?
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
- Giant cell tumor of bone
- Osteoblastoma
- Osteoid osteoma
- Osteosarcoma
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following is true about osteoblastoma?
- Osteoblastoma is more common in females
- Predilection for the spine and the sacrum (40 - 55%)
- Tumor is positive for H3F3A (G34W)
- Tumor permeation of the surrounding host tissue structures is frequently identified
- Tumors of the mandible are associated with a poor prognosis
Practice answer #2