Table of Contents
CD40 | CD41 | CD42a | CD42b | CD42c | CD42d | CD43 | CD44 and CD44R | CD45 (LCA) | CD45RA | CD45RB | CD45RC | CD45RO | CD46 | CD47 | CD47R | CD48 | CD49 | Diagrams / tables | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Pernick N. CD40-49. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd40.html. Accessed August 24th, 2025.
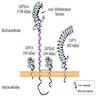
CD40
- Costimulatory protein found on antigen presenting cells, required for their activation
- Also called TNF receptor superfamily member 5; ligand is CD40L (CD154)
- Pathophysiology:
- Plays a central role in regulating cell mediated immunity and antibody mediated immunity
- Also mediates T cell dependent immunoglobulin class switching, memory cell development and germinal center formation
- Clinical features:
- Cardiovascular disease:
- May mediate inflammatory component of atherogenesis
- Variation of CD40 gene is associated with coronary artery calcification in diabetes (Am Heart J 2006;151:706)
- CD40 / CD40L signaling contributes to:
- Inflammatory and prothrombogenic responses and brain infarction induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion (Circulation 2005;111:1690)
- Acute cerebral ischemia (Stroke 2003;34:1412)
- CD40 mediated platelet activation may play a role in thrombosis, inflammation and atherosclerosis (Circ Res 2003;92:1041)
- Effects may be mediated by soluble form of CD40L (Ann Med 2011;43:331)
- Has role in pathogenesis of various autoimmune disorders (Semin Immunol 2009;21:293)
- Mutations may cause hyper IgM disease type 3 with opportunistic infections due to inability of B cells to undergo type switching and to defective T cell mediated immunity (OMIM: 606843 [Accessed 6 May 2021], Blood 2003;102:4099)
- CD40 - CD40L binding may cause microglial activation and contribute to Alzheimer's disease (CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2010;9:149)
- Epithelial CD40 may cause inflammatory disorders, generation of self tolerance and chronic rejection of allografts (Semin Immunol 2009;21:289)
- EBV LMP1 is a constitutively active functional mimic of CD40, utilizing TNFR associated factor adaptor proteins to induce signaling (J Biol Chem 2011;286:9948)
- Cardiovascular disease:
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Prognostic factors:
- Expression in > 50% of cells may have poor prognostic value in adult soft tissue sarcomas (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:2824)
- CD40+ diffuse large B cell lymphomas are associated with favorable survival (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:2824)
- Positive staining - normal:
- B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, mast cells, monocytes, platelets
- Also astrocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, Langerhans cells (in oral mucosa), microglia, nevus cells, pancreatic islet cells, prostatic acini, other epithelial cells (Diabetologia 2005;48:268)
- Positive staining - disease:
- Kaposi sarcoma (Am J Pathol 1996;148:1387)
- Melanoma (Am J Pathol 1996;149:1953)
- Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin lymphoma (70%) (Am J Pathol 1994;144:21)
- Most B cell lymphomas (70% of diffuse large B cell lymphoma), B-ALL (some)
- Carcinomas:
- Renal cell (Cell Immunol 2005;235:145)
- Squamous cell carcinoma of oral mucosa (J Oral Pathol Med 2006;35:268)
- Thyroid (Thyroid 2005;15:105)
- Negative staining: plasma cells, Gaucher cells, prostatic adenocarcinoma (Oncol Rep 2004;12:679)
- Reference: OMIM: 109535 [Accessed 6 May 2021]
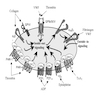
CD41
- Platelet glycoprotein IIb, important for platelet aggregation
- Also called platelet glycoprotein IIb, GPIIb, platelet fibrinogen receptor alpha subunit
- Pathophysiology:
- Gene encodes integrin alpha chain 2b, which undergoes post-translational cleavage to yield disulfide linked light and heavy chains which join with integrin beta3 (CD61) to form a fibronectin receptor expressed in platelets, which is crucial for platelet aggregation through binding of soluble fibrinogen
- GP IIb / IIIa is also a receptor for fibrinogen, plasminogen, prothrombin, thrombosponin, vitronectin and von Willebrand factor
- Recognizes the sequence R-G-D in a wide array of ligands
- Downregulated by factor XIII and calpain (J Biol Chem 2004;279:30697)
- Clinical features: mutations cause Glanzmann thrombasthenia, with a tendency to bleed for prolonged periods following injury (OMIM: 273800 [Accessed 6 May 2021])
- Uses by pathologists:
- Identify platelets or megakaryocytes (marker is specific)
- Isolate platelets (Cytometry A 2005;65:84)
- Confirm diagnosis of AML M7
- Diagnose Glanzmann thrombasthenia
- Positive staining - normal:
- Platelets, megakaryocytes, hematopoietic progenitor cells (erythroid, myeloid, megakaryocytes) (Br J Haematol 1999;105:1044, Development 2002;129:2003)
- Mast cells (Exp Hematol 2005;33:403)
- Positive staining - disease: AML M7, blasts in transient myeloproliferative disorder (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:204)
- Negative staining: AML M0 to M6
- References: OMIM: 607759 [Accessed 6 May 2021], J Clin Invest 2005;115:3363, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003;23:945
CD42a
- CD42a - d complex is receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin
- Also called platelet glycoprotein GPIX, GP9
- Absence of CD42 complex (mutations in CD42a - c) causes Bernard-Soulier syndrome (giant platelet syndrome), a bleeding disorder with thrombocytopenia, prolonged bleeding time and giant platelets (OMIM: 231200 [Accessed 6 May 2021])
- Pathophysiology:
- CD42a - d complex is receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin
- This complex mediates adhesion of platelets to subendothelial matrices that are exposed in damaged endothelium and amplifies platelet response to thrombin
- GP-IX (CD42a) is a small membrane protein glycoprotein that forms a noncovalent complex with GP-Ib (CD42b)
- Actual binding site of vWF and thrombin is on CD42b
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: platelets and megakaryocytes
- Negative staining: red blood cells, T cells
- Reference: OMIM: 173515 [Accessed 6 May 2021]
CD42b
- CD42a - d complex is receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin
- Also called platelet GPIb alpha, glycoprotein Ib alpha
- Mutations are associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome (giant platelet syndrome), a bleeding disorder with thrombocytopenia, prolonged bleeding time and giant platelets (OMIM: 231200 [Accessed 6 May 2021], Int J Hematol 2002;76:319)
- CD42b mutations also cause platelet type von Willebrand disease, which is known as pseudo von Willebrand disease (OMIM: 177820 [Accessed 6 May 2021])
- Reduced levels are associated with bleeding disorders in AML patients (Saudi Med J 2005;26:1095)
- Aspirin induces shedding of CD42d and CD42b from platelets (J Biol Chem 2005;280:39716)
- Various snake venoms induce platelet aggregation via CD42b, including:
- TVMA (but inhibits platelet aggregation) (Toxicon 2004;44:649, Xenotransplantation 2004;11:203)
- Alboluxin (Thromb Haemost 2002;87:692)
- Bilinexin (Thromb Haemost 2001;86:1277)
- CD42b physiology is part of bacterial virulence factors:
- Streptococcus sanguis, an oral bacteria causing infective endocarditis, adheres to platelets and platelet fibrin vegetations via CD42b (Br J Haematol 2005;129:101)
- Some strains of H. pylori induce platelet activation mediated by H. pylori bound vWF interacting with CD42b, which may promote peptic ulcer disease and H. pylori associated cardiovascular disease (Gastroenterology 2003;124:1846)
- Pathophysiology:
- CD42a - d complex (also called glycoprotein Ib-IX-V receptor) is the surface platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor on endothelium (particularly CD42b)
- Endothelial damage exposes vWF, which binds to platelets very quickly despite high shear pressures; this leads to platelet activation, then a change in the platelet GpIIb-IIIa receptor, which allows binding to surface bound fibrinogen and free fibrinogen; this leads to platelet crosslinking and aggregation
- Platelet activation apparently involves disruption of the macromolecular complex of GP-Ib with the platelet glycoprotein IX (GP-IX) and dissociation of GP-Ib from the actin binding protein
- GPIb alpha (CD42b) and GPIb beta (CD42c) form main part of VWF receptor
- CD42b also binds to thrombospondin-1, a glycoprotein in arteriosclerotic plaques, causing thrombus formation independent of von Willebrand factor (FASEB J 2003;17:1490)
- Platelet receptors are important in understanding thrombus formation (Haematologica 2009;94:700)
- Case reports: Bernard-Soulier disease variant (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:e214)
- Uses by pathologists: marker of megakaryocytes and platelets; diagnosis of AML M7; distinguish AML M7 (CD42b positive) from acute myelosis with myelofibrosis (usually CD42b negative) (Mod Pathol 2005;18:603)
- Positive staining - normal: platelets, megakaryocytes and megakaryoblasts
- Positive staining - disease: blasts in transient myeloproliferative disorder
- Reference: OMIM: 606672 [Accessed 6 May 2021]
CD42c
- CD42a - d complex is receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin
- Also called platelet GPIb beta, glycoprotein Ib beta
- Mutations are associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome (giant platelet syndrome), a bleeding disorder with thrombocytopenia, prolonged bleeding time and giant platelets (OMIM: 231200 [Accessed 6 May 2021], Int J Hematol 2002;76:319)
- Reduced levels are associated with bleeding disorders in AML patients (Saudi Med J 2005;26:1095)
- Pathophysiology:
- CD42a - d complex is receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin
- GPIb alpha (CD42b) and GPIb beta (CD42c) form main part of VWF receptor
- CD42c also amplifies the platelet response to thrombin during platelet activation where thrombin is involved
- Platelet activation apparently involves disruption of the macromolecular complex of GP-Ib with the platelet glycoprotein IX (GP-IX) and dissociation of GP-Ib from the actin binding protein
- Case reports: mutation in Bernard-Soulier syndrome patient (J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:217)
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: platelets and megakaryocytes; also endothelium, heart and brain (J Clin Invest 1994;93:2417)
- References: OMIM: 138720 [Accessed 6 May 2021], Thromb Haemost 2001;86:1238
CD42d
- CD42a - d complex is receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin
- Also called platelet GP V, GP5
- Aspirin induces shedding of CD42d and CD42b from platelets (J Biol Chem 2005;280:39716)
- CD42d is the predominant target antigen in gold-induced autoimmune thrombocytopenia (Blood 2002;100:344)
- Deficiency does not appear to cause Bernard-Soulier syndrome (Blood 1999;94:4112)
- Pathophysiology:
- Part of CD42a - d complex
- May activate residual platelets in thrombocytopenia regardless of its origin as immune thrombocytopenic purpura or thrombocytopenia of aplastic pancytopenia (J Natl Med Assoc 2008;100:86)
- Also involved in binding of thrombin (Blood 1997;89:4355)
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: platelets and megakaryocytes
- Reference: OMIM: 173511 [Accessed 6 May 2021]
CD43
- See CD43
CD44 and CD44R
- See CD44
CD45 (LCA)
- See CD45 (LCA)
CD45RA
- See CD45RA
CD45RB
- CD45 isoform generated by alternative mRNA splicing of exon 5, leading to change in the extracellular domain of the molecule (J Exp Med 1987;166:1548)
- Influx of CD4+, CD45RB high T cells is present in inflammatory bowel disease; may be important in pathogenesis as they produce more proinflammatory cytokines than CD4+ CD45RB low T cells (J Leukoc Biol 2004;75:1010)
- Pathophysiology:
- CD45 is a high molecular weight transmembrane protein with intrinsic tyrosine phosphatase activity
- CD45 is heavily glycosylated and expressed at high levels on nucleated hematopoietic cells
- CD45 isoforms, including CD45RB, are generated by alternative mRNA splicing of exons 4 (CD45RA), 5 (CD45RB) and 6 (CD45RC), leading to changes in the extracellular domain of the molecule
- Down regulated in memory cells
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: similar staining as CD45, except not expressed in Langerhans cells and some T cells; B cells, most T cells, monocytes, macrophages and granulocytes (weak)
- Positive staining - disease: most leukemias and lymphomas
- Negative staining: some T cells; Langerhans cells, platelets; plasma cell neoplasms, Reed-Sternberg cells, some lymphoblastic lymphomas and some anaplastic large cell lymphomas
CD45RC
- CD45 isoform generated by alternative mRNA splicing of exon 6, leading to change in the extracellular domain of the molecule (J Exp Med 1987;166:1548)
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type C; PTPRC gene
- CD45RC+ CD4+ cells and CD45RC- CD4+ T cells have different cytokine profiles (Th1-like and Th2-like respectively)
- CD45RC expression divides human T cells into functionally distinct subsets that are imbalanced in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis (AAV); this may be a preexisting immune abnormality involved in the etiology of AAV (PLoS One 2009;4:e5287)
- Pathophysiology:
- CD45 is a high molecular weight transmembrane protein with intrinsic tyrosine phosphatase activity
- CD45 is heavily glycosylated and expressed at high levels on nucleated hematopoietic cells
- CD45 isoforms, including CD45RC, are generated by alternative mRNA splicing of exons 4 (CD45RA), 5 (CD45RB) and 6 (CD45RC), leading to changes in the extracellular domain of the molecule
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal:
- Thymocytes, monocytes and dendritic cells
- High levels: B cells, NK and CD4+ T cells
- Intermediate levels: CD8+ T cells
- Negative staining: myeloid cells
- Reference: OMIM: 151460 [Accessed 7 May 2021]
CD45RO
- Marker of activated T cells
- Also called UCHL1, although this is also an abbreviation for ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1, a gene expressed in neurons and whose mutations are associated with Parkinson's disease
- Low density of intratumoral CD45RO+ cells was poor prognostic factor for non-metastasized esophageal adenocarcinoma (BMC Cancer 2010;10:608)
- Increased CD45RO+ T cell infiltrate is present in:
- Atherosclerosis (Am J Pathol 1992;140:907)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, MALT lymphoma (Am J Pathol 1997;151:1353)
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: interfollicular infiltrate (J Clin Pathol 2004;57:1258)
- Kikuchi’s disease, molar pregnancy (J Clin Pathol 1999;52:888)
- Ovarian carcinoma (Am J Pathol 1997;150:1723)
- Primary cutaneous neoplasms (Am J Pathol 1993;142:1556)
- Well nourished versus malnourished infected children (Clin Exp Immunol 2001;126:461)
- CD4+ CD45RO+ T cells are a major latent viral reservoir in HIV+ individuals (Am J Pathol 1992;140:15)
- Increased percentage of CD45RO+ peripheral blood T cells in patients with preeclampsia and psoriasis (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:889, Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med 2001;56:465)
- Pathophysiology:
- Most regulatory T cells in adults are CD45RO+; percentage increases with age (J Immunol 2010;184:4317)
- Ligand is CD22
- CD45RO+ T cells are more common than naïve T cells (CD45RA+) in inflammatory myopathies (Am J Pathol 1995;146:1178)
- Uses by pathologists: T cell marker for diagnosis and classification of lymphoma; identify T cell subsets (i.e. memory T cells)
- Positive staining - normal: memory and activated T cells, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages and cortical thymocytes; some B cells
- Positive staining - disease:
- T cell lymphomas (75%), including:
- Angiocentric and angioimmunoblastic (Hum Pathol 2005;36:784)
- Cutaneous T cell, hepatosplenic alpha beta and gamma delta and peripheral NOS (Am J Clin Pathol 2010;133:281)
- AML (25%), histiocytic sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1133)
- Myeloma (some, both on tumor cells and in infiltrate) (J Clin Pathol 1998;51:432)
- Some plasma cell neoplasms
- Also Candida albicans (Am J Clin Pathol 2000;113:59)
- T cell lymphomas (75%), including:
- Negative staining: B cells (most), NK cells; B cell lymphoma (most), carcinoma and autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (Am J Pathol 1998;153:1541)
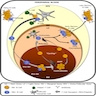
CD46
- Antigen which helps downregulate the immune system
- Also called membrane cofactor protein (MCP), trophoblast leukocyte common antigen
- Pathophysiology:
- Has multiple isoforms but unlike CD45, they don’t appear to have clinical significance
- Cofactor for proteolytic cleavage of C3b and C4b by factor I (J Immunol 2002;168:6298)
- Prevents inappropriate complement activation, especially via alternative pathway, by limiting formation and function of C3 convertases
- Induces regulatory T cells (Nature 2003;421:388)
- Suppresses immune function by secreting IL-10 and may prevent autoimmunity; various pathogens (see below) appear to exploit this property by binding to CD46 to induce an immunosuppressive phenotype
- Clinical features:
- Receptor for:
- Adenovirus (various serotypes) (J Virol 2005;79:7503)
- HHV-6 (Cell 1999;99:817, J Biol Chem 2003;278:25964)
- Measles virus (Cell 1993;75:295)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (J Cell Biol 2002;156:951)
- Streptococcus pyogenes (Infect Immun 2008;76:3951)
- Expression is often increased on tumor cells
- Homozygosity for specific alleles is a high risk factor for some types of recurrent pregnancy loss (Hum Reprod 2006;21:818)
- Mutations predispose to familial hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical type 2 (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003;100:12966)
- Receptor for:
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: all cells except erythrocytes and some bone marrow cells
- Negative staining: red blood cells
- References: OMIM: 120920 [Accessed 6 May 2021], Springer Semin Immunopathol 2005;27:345
CD47
- See CD47
CD47R
- May not be a current CD marker; information is based on older sources
- Designation for CDw149 which was deleted at the 7th HLDA Workshop (Tissue Antigens 2000;56:258)
- Poorly characterized, with little information available
- Also called Rh related antigen, MEM133
- Similar distribution as CD47 but dimmer
- Recognizes a clustered subset of CD47 (Tissue Antigens 2000;56:258)
- Positive staining: lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils (weak), eosinophils (weak) and platelets (weak)
- Negative staining: erythrocytes
CD48
- Activation associated cell surface glycoprotein active in lymphocytes
- Also called B lymphocyte activation marker blast 1
- Pathophysiology:
- Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored surface molecule that mediates T cell activation by binding to CD2 (J Immunol 2009;182:7672)
- Induces numerous effects in B and T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, mast cells and eosinophils, partly based on its interaction with 2B4 / CD244 (Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2011;43:25)
- Regulates NK cell effector function (Blood 2006;107:3181)
- Clinical features: mast cell response to M. tuberculosis is mediated by CD48 (J Immunol 2003;170:5590)
- No significant clinical uses for pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes (weak)
- Negative staining: platelets, fibroblasts, epithelium, endothelium; usually dendritic cells (J Immunol 2005;175:3690)
- Reference: OMIM: 109530 [Accessed 6 May 2021]
CD49
- See CD49
Diagrams / tables