Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Hamasha R, Gonzalez RS. Cholesterolosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladdercholesterolosis.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Accumulation of lipids (triglycerides, cholesterol precursors and cholesterol esters) within subepithelial macrophages in the lamina propria of the gallbladder (J Ultrasound 2021;24:131)
- Can be focal, diffuse or polypoid (also known as cholesterol polyps) (Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 2003;49:217)
- Second most common histopathological finding in resected gallbladders (most common being chronic cholecystitis) (JSLS 2020;24:e2020.00052, Rev Col Bras Cir 2020;46:e20192279)
Essential features
- Due to accumulation of lipids in macrophages in the lamina propria
- Demographic: females, high BMI
- Focal, diffuse or polypoid (polypoid cholesterolosis = cholesterol polyps)
- Gross feature: focal or diffuse flat yellowish dots on the lining of the gallbladder
- When diffuse, resembles a strawberry, hence the name strawberry gallbladder
- Microscopic features: subepithelial lipid laden macrophages in the lamina propria and inside villi
Terminology
- Also known as strawberry gallbladder
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Seen in 10 - 30% of cholecystectomies (Rev Col Bras Cir 2020;46:e20192279, Cureus 2020;12:e9627)
- Occurs in female patients 75% of the time (Niger J Clin Pract 2019;22:1002)
- Associated with high BMI (Niger J Clin Pract 2019;22:1002)
Sites
- Gallbladder
Pathophysiology
- Bile is supersaturated with cholesterol in both cholesterolosis and gallstone disease, perhaps due to excess bile production
- Patients who are unable to fully solubilize cholesterol will form cholesterol gallstones
- Patients who are able to keep cholesterol fully solubilized may have increased mucosal cholesterol uptake and develop cholesterolosis (J Clin Pathol 1987;40:524)
- This likely occurs in patients with increased acyl-CoA cholesterol ester acyltransferase activity in gallbladder mucosa (Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:1518)
- The enzyme causes increased synthesis of cholesterol esters, which accumulate in mucosal macrophages (Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:1518)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic (J Ultrasound 2021;24:131, Semin Gastrointest Dis 2003;14:178)
- Noninflammatory (is usually an isolated finding) (Rev Col Bras Cir 2020;46:e20192279)
- No malignant potential (Rev Col Bras Cir 2020;46:e20192279)
Diagnosis
- Incidentally found during abdominal sonography (appears as a pseudopolyp; see Radiology description for details) or diagnosed on histopathology of surgical specimens (J Ultrasound 2021;24:131)
- Microscopic examination provides the definitive diagnosis
Laboratory
- Serum cholesterol may be normal or elevated
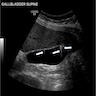
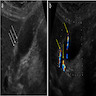
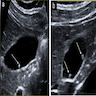
Radiology description
- Ultrasound cannot reliably detect cholesterolosis (Semin Gastrointest Dis 2003;14:178)
- Cholesterolosis may form pseudopolyps that appear as single or multiple hyperechoic parietal foci generating comet tail artifacts (J Ultrasound 2021;24:131)
Radiology images
Case reports
- 22 year old pregnant woman with persistent abdominal pain and vomiting (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e227826)
- 55 year old woman with acute pancreatitis (Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2018;31:324)
- 78 year old woman with a cholesterol polyp with osseous metaplasia (Cureus 2020;12:e12357)
Treatment
- Cholecystectomy (Saudi Med J 2004;25:1226)
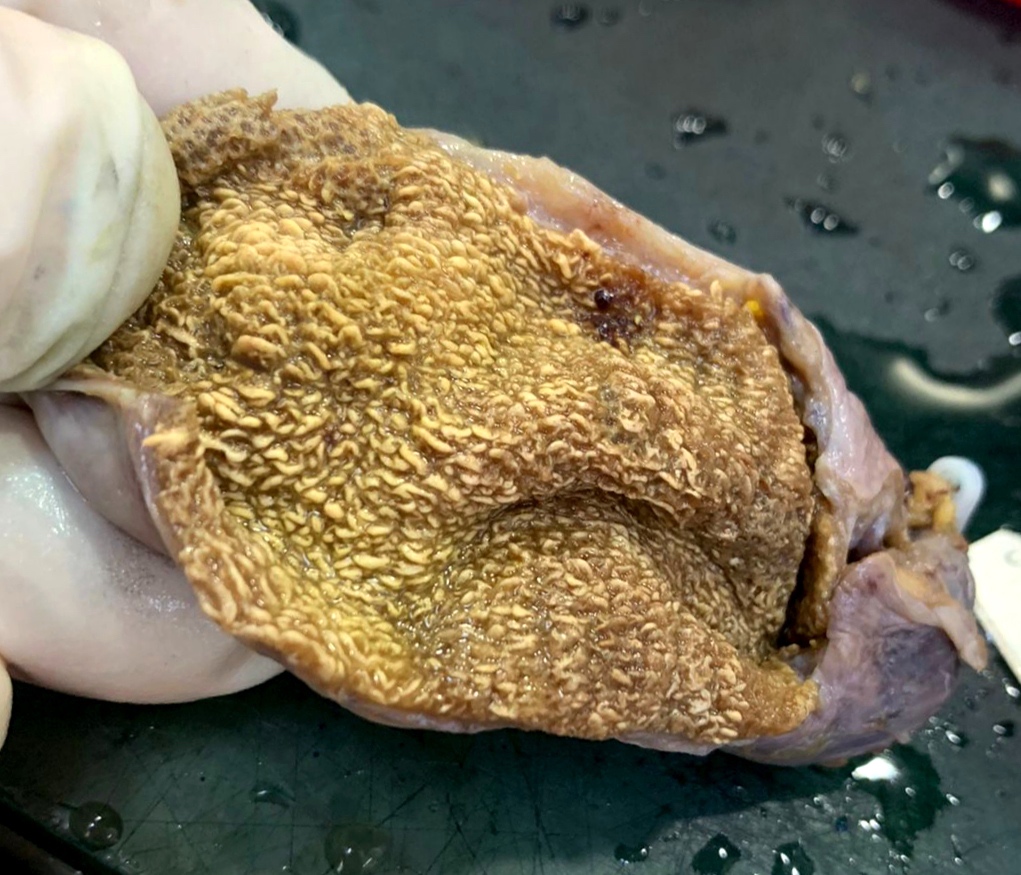
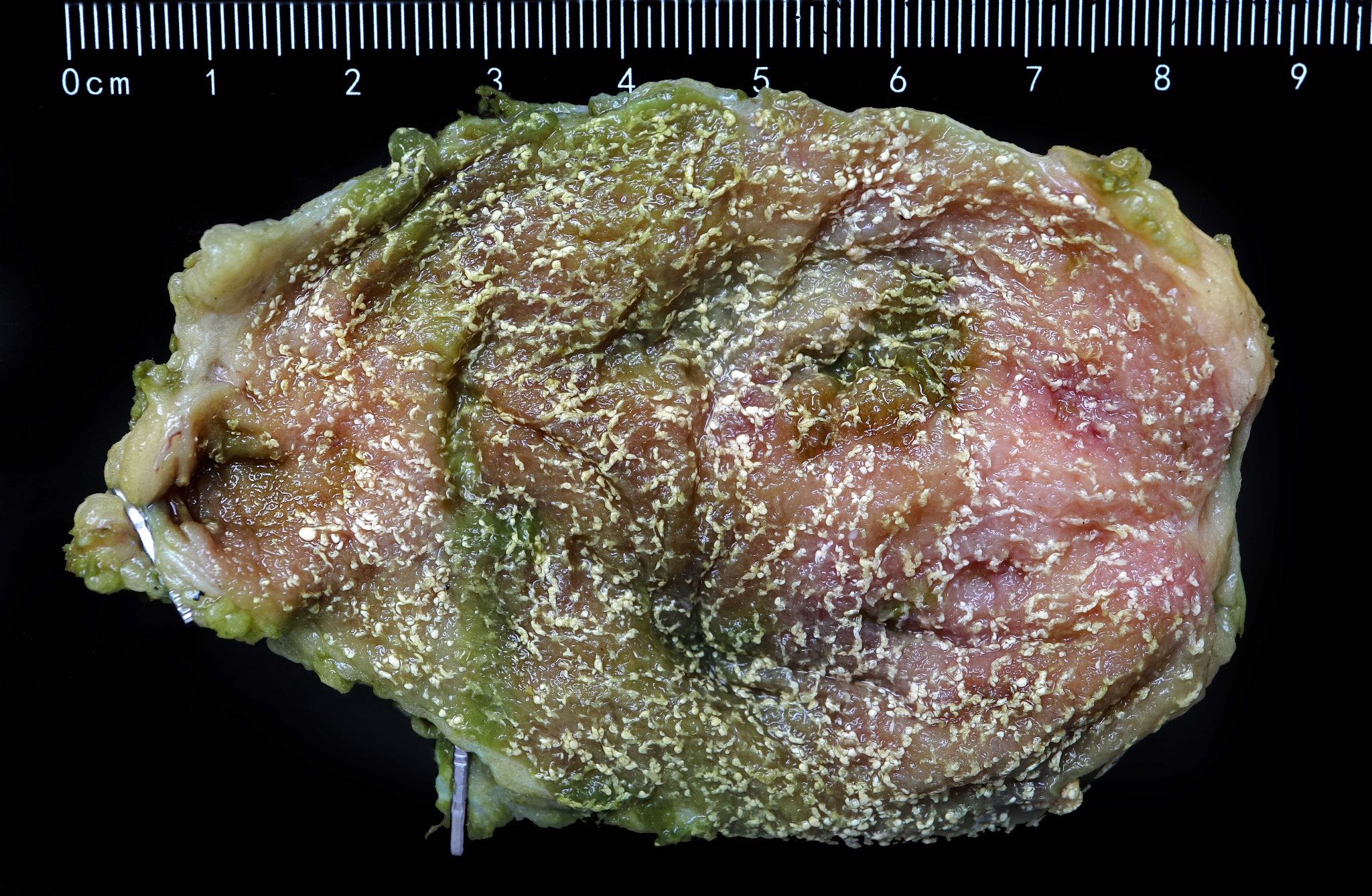
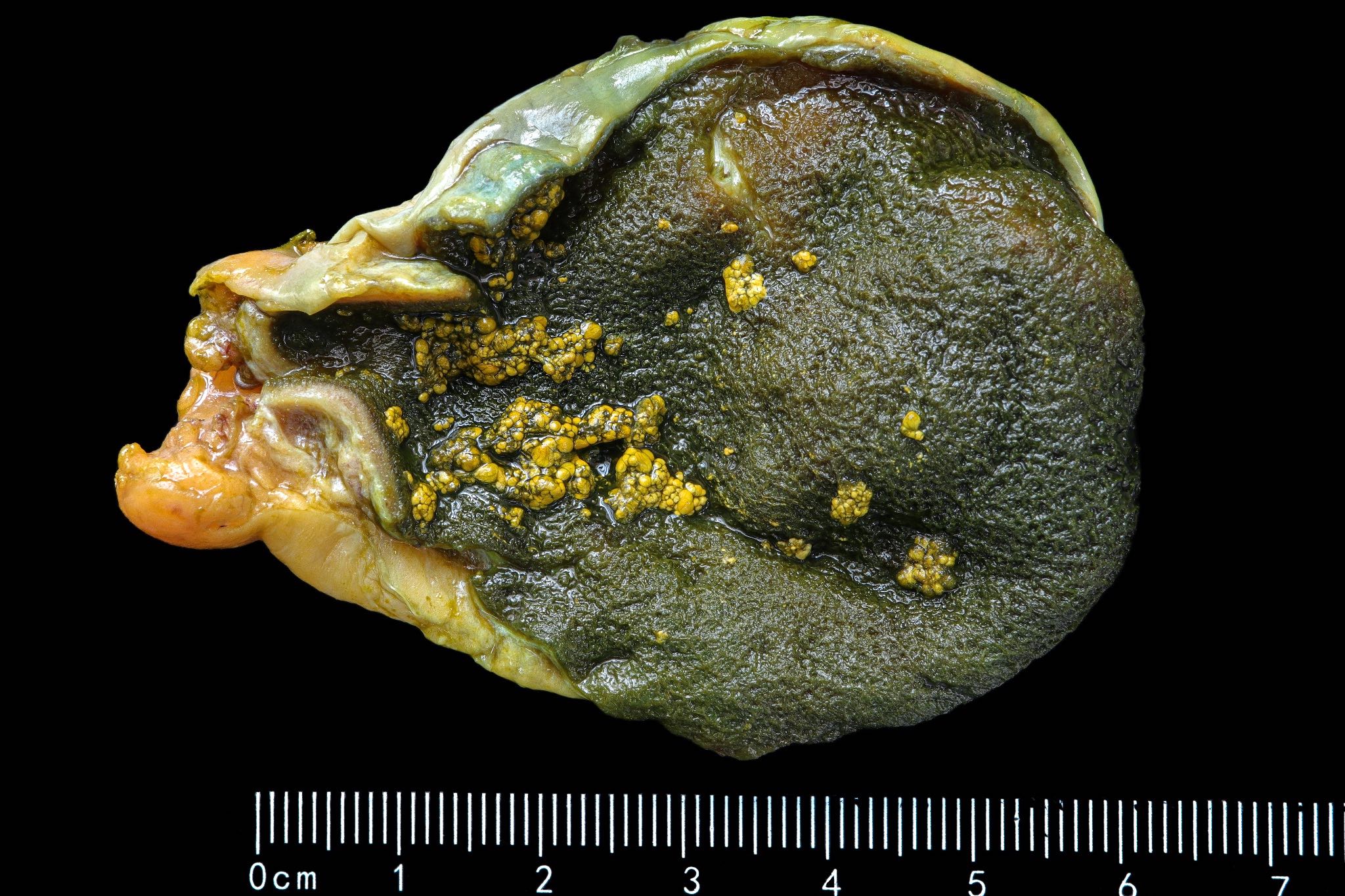
Gross description
- Diffuse or focal flat yellow dots on the lining of the gallbladder
- In the diffuse form, the dots on the mucosa / lining resemble a strawberry (J Hepatol 2004;40:8)
Gross images
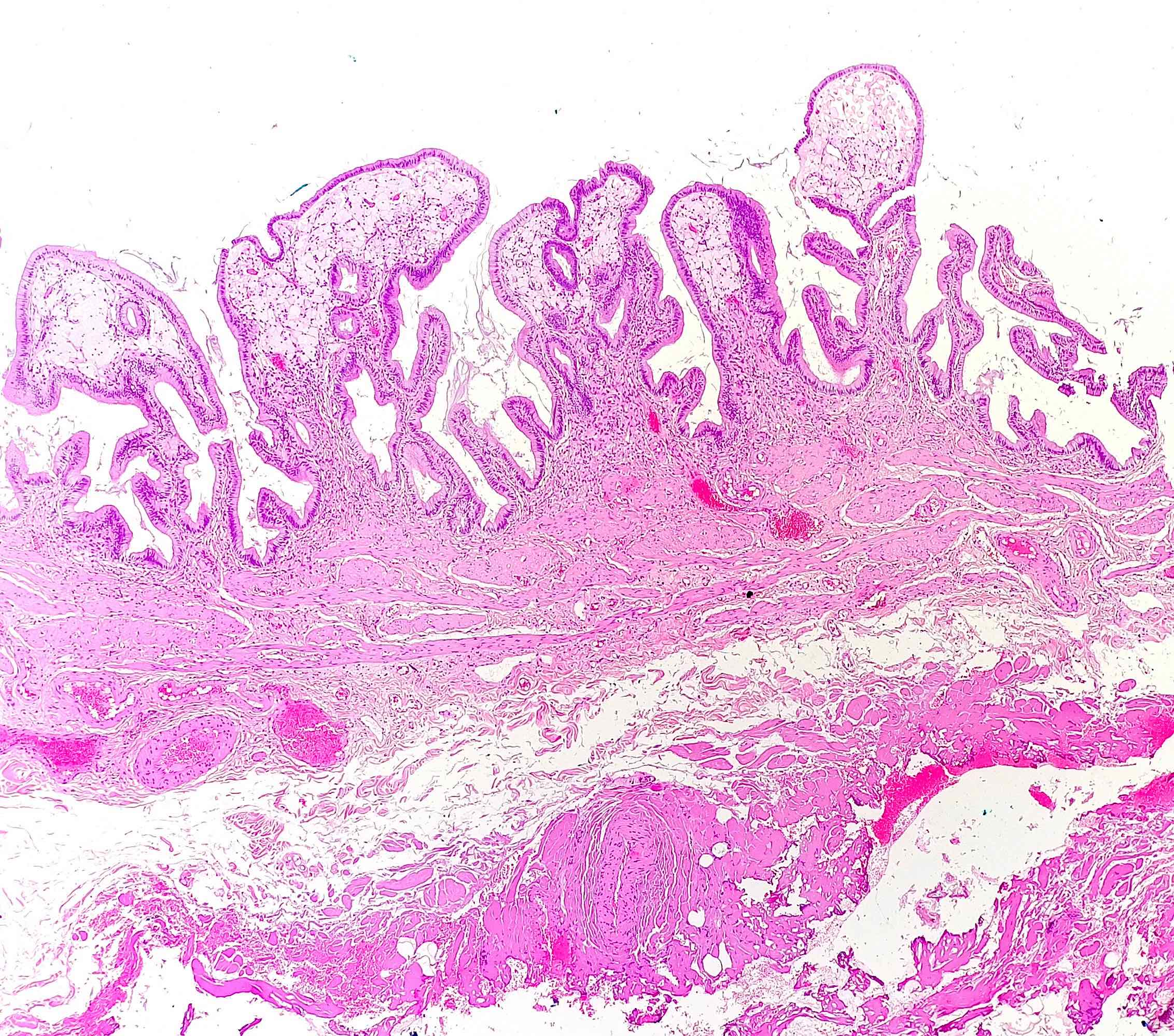
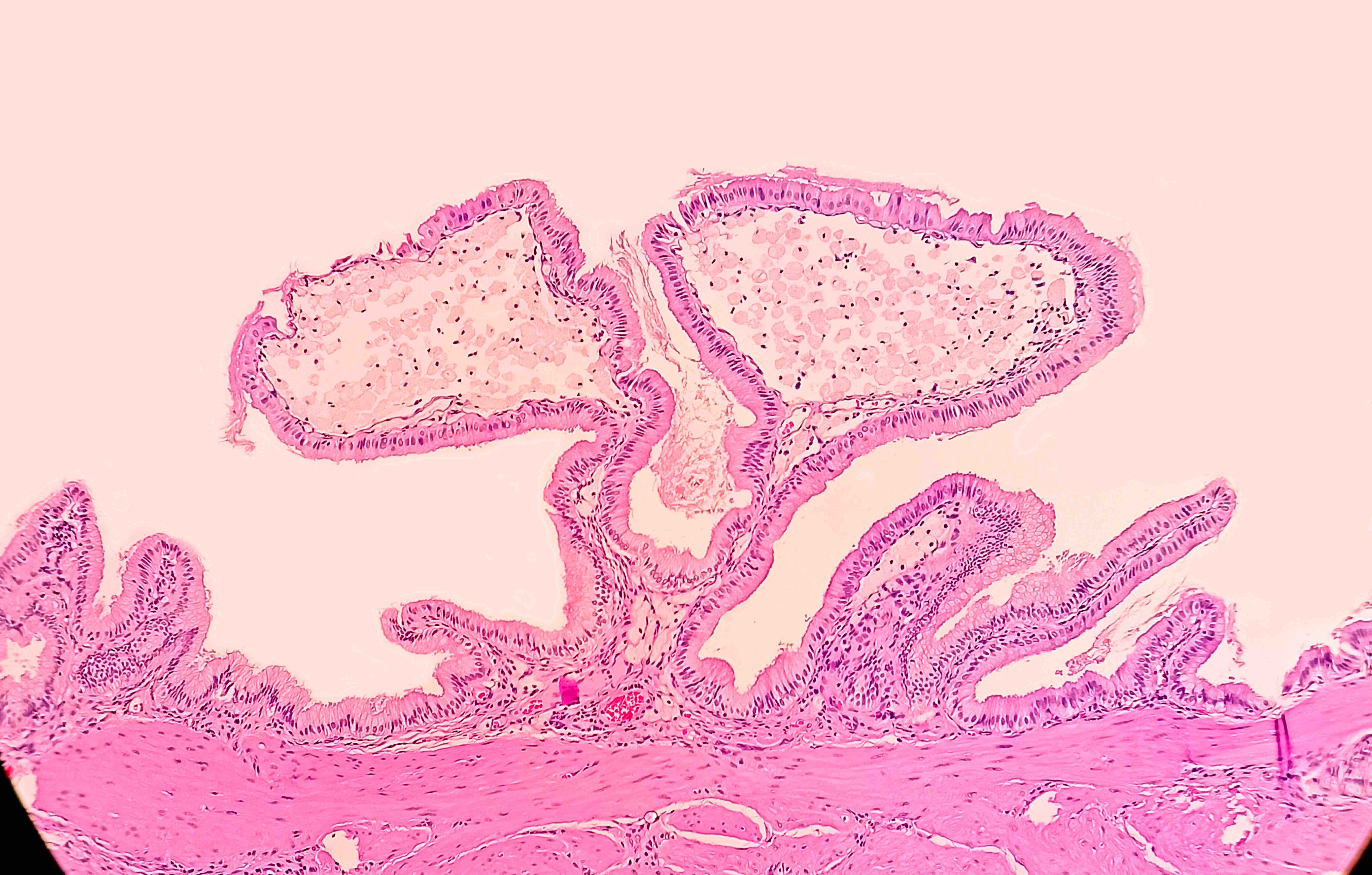
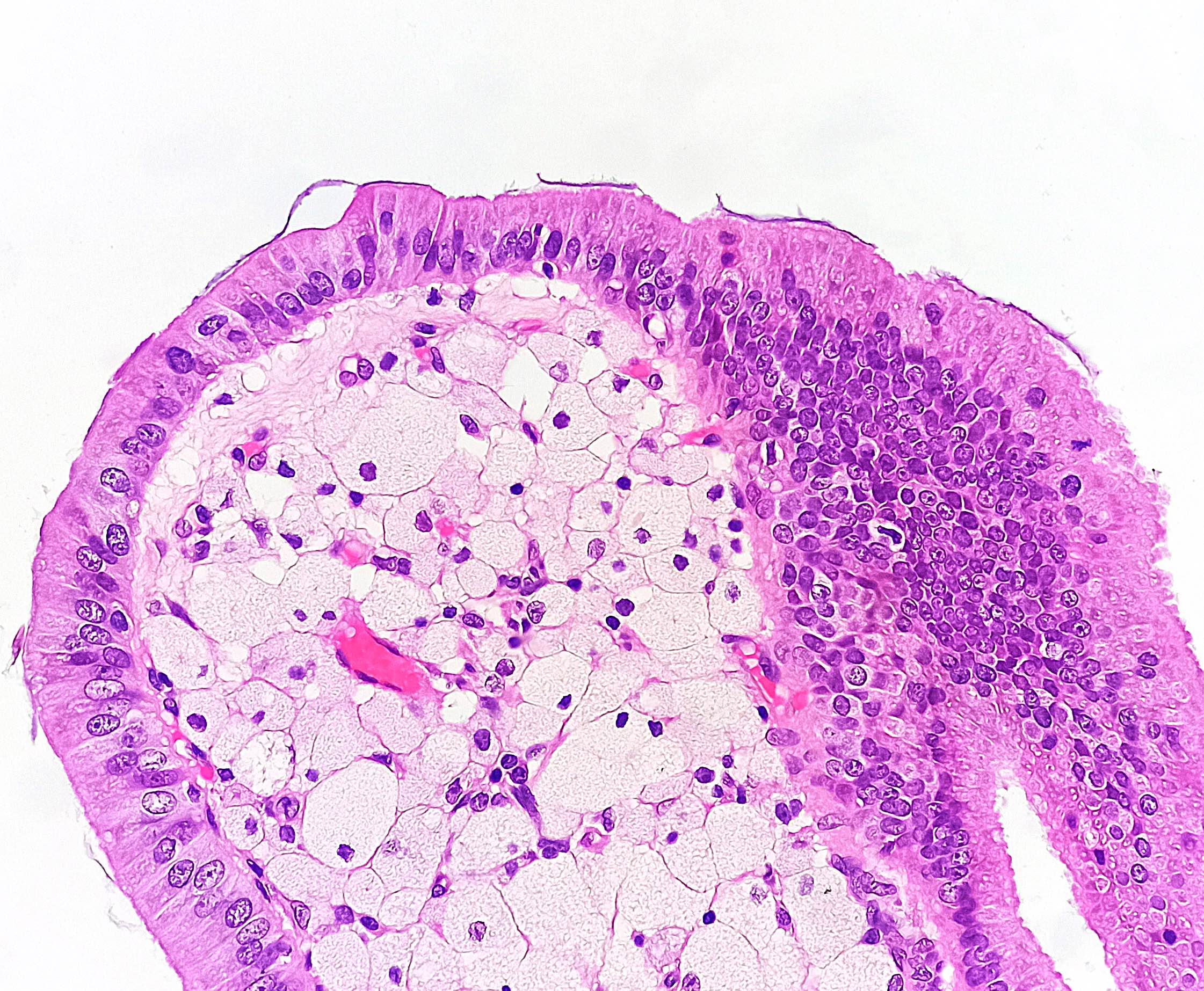
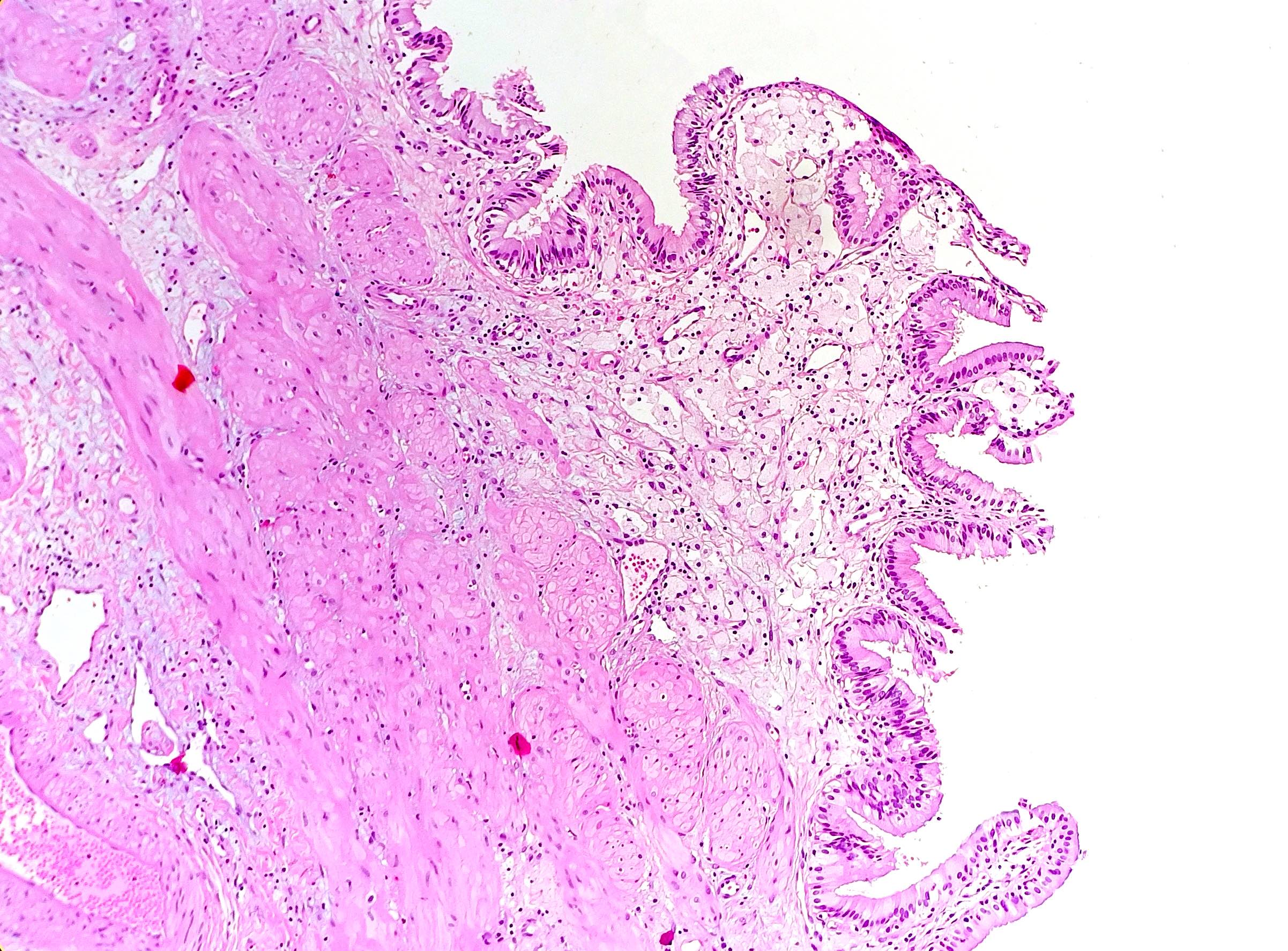
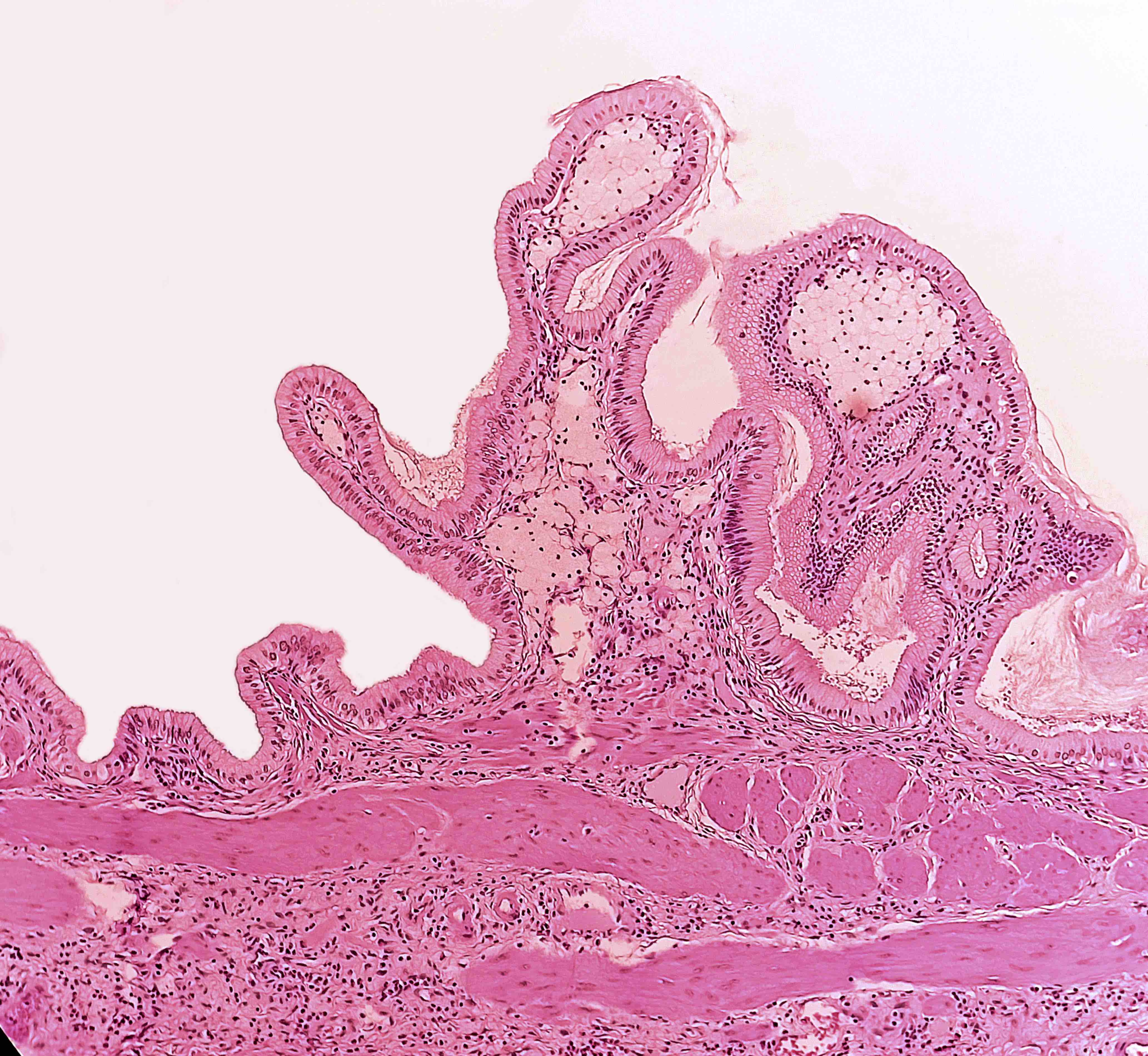
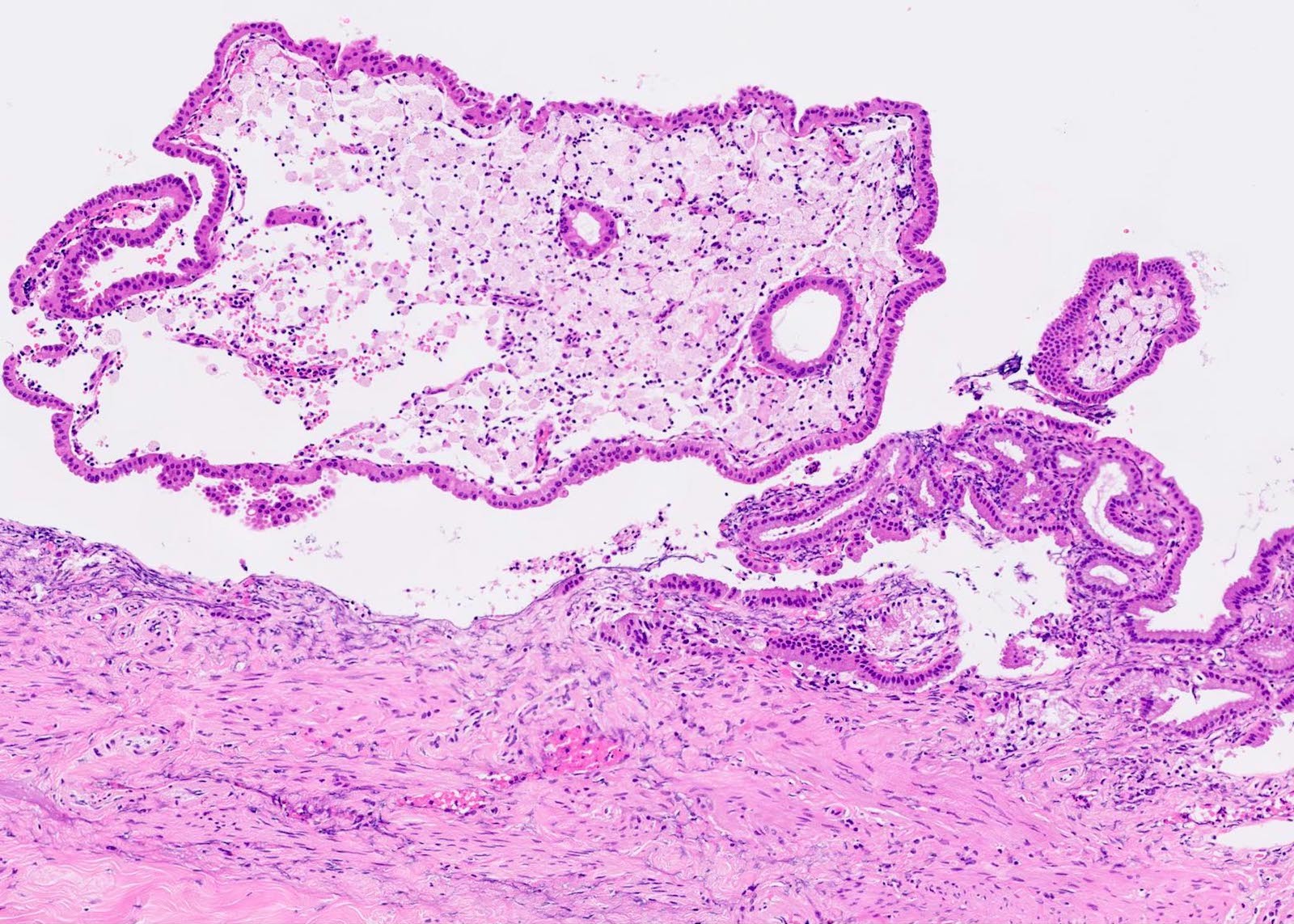
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Foamy lipid laden macrophages expanding the lamina propria
- Mucosal villous hyperplasia and hypertrophy (Semin Gastrointest Dis 2003;14:178, Cureus 2020;12:e9627)
- Usually isolated, with no signs of inflammation
- When cholesterolosis is not an isolated finding, most common association would be chronic cholecystitis (Rev Col Bras Cir 2020;46:e20192279)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Reem Hamasha, M.D., Faris Alshammas, M.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and Jijgee Munkhdelger, M.D., Ph.D.
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Chronic cholecystitis and cholesterolosis
Differential diagnosis
- Cholesterol polyp:
- Essentially a variant of cholesterolosis that forms a distinct polyp
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis:
- A variant of chronic cholecystitis, with lipid laden macrophages and acute and chronic inflammatory cells in the wall of the gallbladder (World J Radiol 2016;8:183)
- Hyperplastic polyp:
- Poorly defined benign entity characterized by mucosal hyperplasia including elongated villi, sometimes with metaplastic changes but never with dysplasia; macrophages are not part of this process
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
C. The patient is female. Cholesterolosis tends to occur in overweight female patients. It is generally asymptomatic and has no risk of progression to malignancy.
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterolosis
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterolosis
Practice question #2
Which of the following is the most likely pathophysiologic cause of gallbladder cholesterolosis?
- Increased synthesis and deposition of cholesterol esters
- Infiltration of macrophages due to subclinical infection
- Mucosal irritation due to longstanding inflammation
- Slow degradation and absorption of gallstones
Practice answer #2
A. Increased synthesis and deposition of cholesterol esters. Cholesterolosis appears to occur when excess bile is converted to cholesterol esters via acyl-CoA cholesterol ester acyltransferase. The esters are then stored in mucosal macrophages. Choleliths, inflammation and infection do not play a role in the development of cholesterolosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterolosis
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterolosis