Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Ludwig KS, Gonzalez RS. Dysplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderdysplasia.html. Accessed September 4th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Biliary intraepithelial neoplasia (BilIN) arising in the gallbladder
- Precursor lesion to gallbladder carcinoma with high risk of progression
Essential features
- Almost always found incidentally in cholecystectomy specimens
- Indicates an increased risk for carcinoma of the gallbladder and elsewhere in the biliary tract
- High grade dysplasia is found concurrently in 40 - 100% of patients with invasive carcinoma
- There remains a lack of consensus regarding the appropriate extent of grossing and histologic examination
Terminology
- Biliary intraepithelial neoplasia, low grade and high grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K82.9 - disease of gallbladder, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Rare; found incidentally in 1 - 5% of cholecystectomies (Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;37:7)
- Follows gallbladder carcinoma trends but with slightly younger age (early sixth decade) (J Surg Res 2014;189:17, Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;37:7)
- More common in women (F:M = 3:1) and in India, Chile, Mexico and Japan (Histopathology 2021;79:2, J Surg Res 2014;189:17)
- Incidence of gallbladder dysplasia in the United States appears comparatively low (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:386, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:374, Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;37:7)
- In Western countries, reportedly more common among native American, Hispanic and Asian populations (J Surg Res 2014;189:17, Histopathology 2021;79:2)
- Risk factors include anything leading to chronic inflammation (Histopathology 2021;79:2)
- Cholelithiasis (most common); patients may have larger gallstones (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:181)
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Chronic bacterial or parasitic infection (e.g., Salmonella typhi)
- Aflatoxin B1
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Porcelain gallbladder
- Pancreaticobiliary maljunction
Sites
- Fundus (most common) > body > neck (least common) (Hum Pathol 2018;82:87)
- Low grade dysplasia is usually focal
- Dysplasia is unlikely to cover > 20% of the gallbladder in patients without carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2018;82:87)
Pathophysiology
- Chronic inflammation leads to epithelial metaplasia (most commonly intestinal metaplasia), then low grade dysplasia, then high grade dysplasia and finally invasive carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:386, Hum Pathol 2018;82:87)
Clinical features
- Ranges from asymptomatic to vague, nonspecific signs and symptoms
- Clinical presentation can overlap with cholelithiasis / cholecystitis (Histopathology 2021;79:2)
- True neoplastic symptoms (right upper quadrant [RUQ] pain, fever, weight loss) rare in premalignant lesions
Diagnosis
- Almost always detected incidentally in cholecystectomy specimens or in the background of frankly invasive gallbladder carcinoma
- Finding incidental dysplasia in initial sections should prompt further careful assessment with additional sampling, though specific recommendations vary (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:374, HPB (Oxford) 2015;17:681, Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;37:7, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1668)
- Intestinal metaplasia: 4 additional sections (Am J Clin Pathol 2013;140:278)
- Low grade dysplasia: 4 additional sections (consider more in high risk patients or populations)
- High grade dysplasia: at least 4 additional sections but strongly consider submitting entire remaining gallbladder (high risk of malignancy elsewhere in gallbladder)
Radiology description
- Usually no findings
- US, CT or MRI can show nonspecific focal or diffuse gallbladder wall thickening or a space occupying lesion (Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;37:7)
Prognostic factors
- Increases risk for carcinoma of the gallbladder and elsewhere in the pancreatobiliary tract (J Gastrointest Surg 2019;23:686)
Case reports
- 36 year old woman with gallstone pancreatitis (BMJ Case Rep 2017;2017:bcr2016218994)
- 44 year old man with RUQ pain (Chin Clin Oncol 2019;8:34)
- 59 year old man with adenomyomatosis and gallbladder cancer (Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 2019;29:290)
- 61 year old woman with pancreatobiliary reflux (J Gastroenterol 2005;40:756)
Treatment
- Unlike gallbladder carcinoma, which likely necessitates further treatment, isolated gallbladder dysplasia is cured by cholecystectomy
- If cystic duct margin is involved, imaging and further surgery may be considered (HPB (Oxford) 2011;13:865)
Gross description
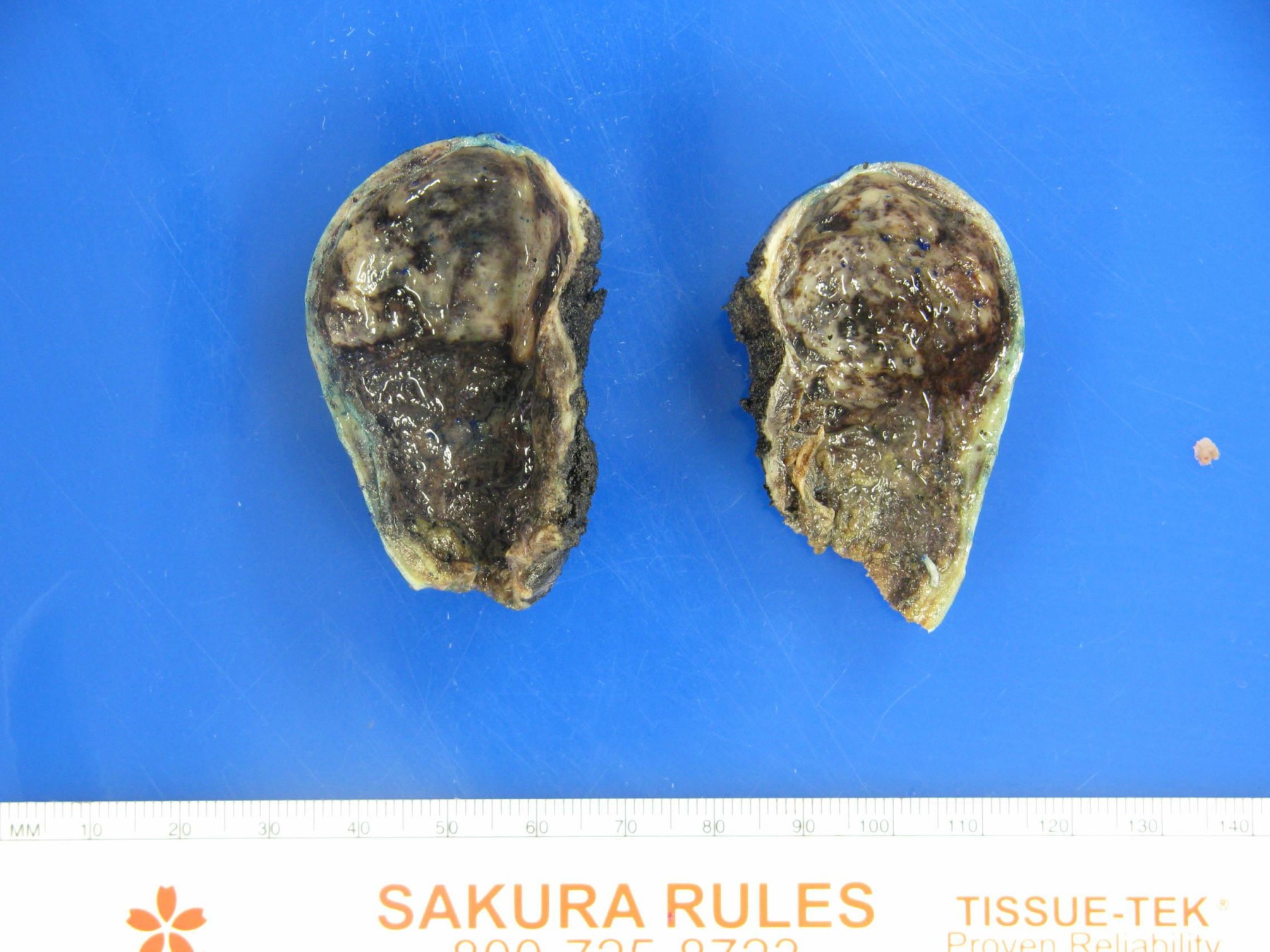
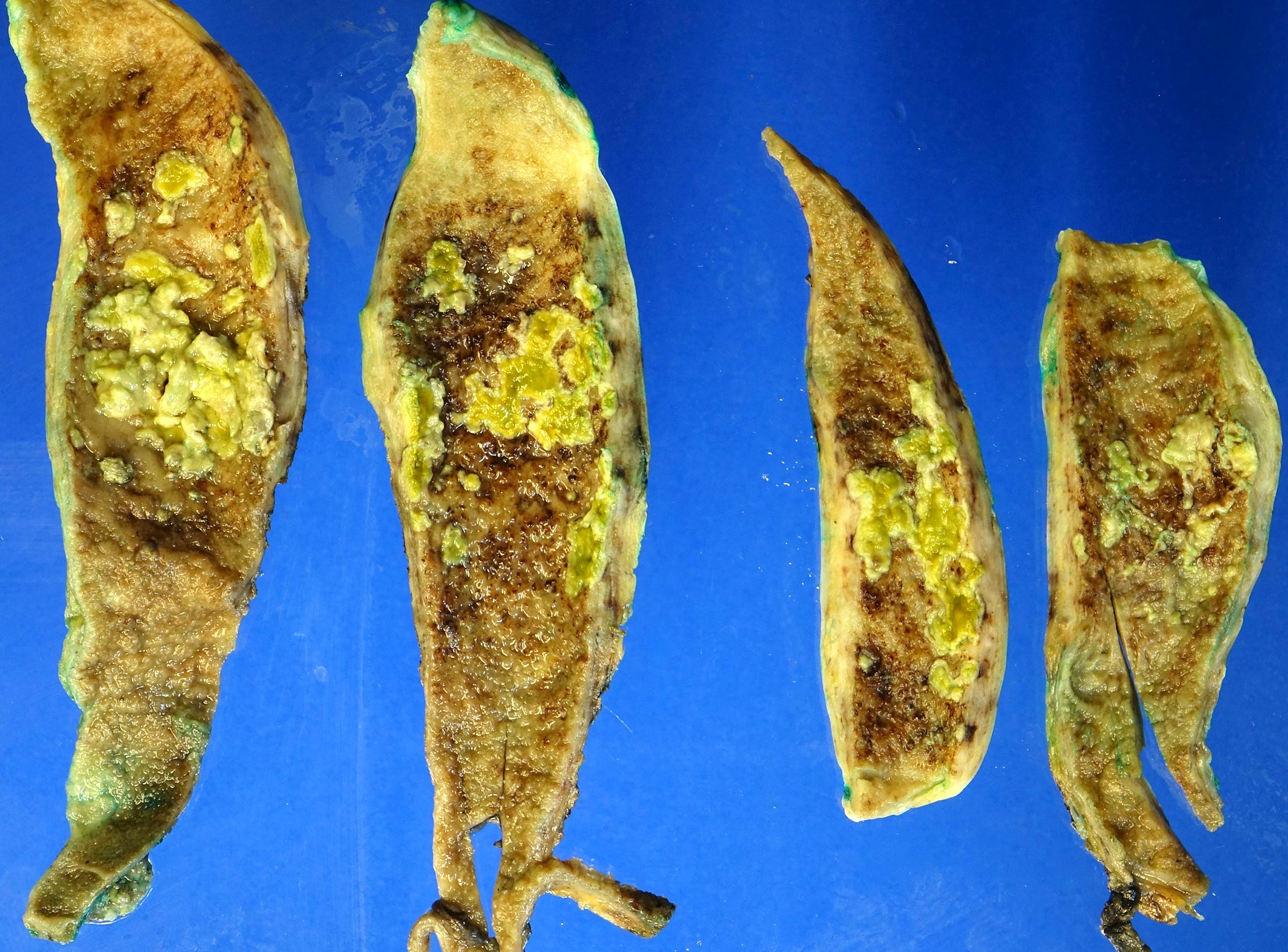
- Gallbladder almost always appears grossly normal (Hum Pathol 2018;82:87)
- Rarely shows nonspecific changes, such as a poorly defined area of mucosal thickening and induration (Ann Diagn Pathol 2018;37:7, Histopathology 2021;79:2)
Gross images
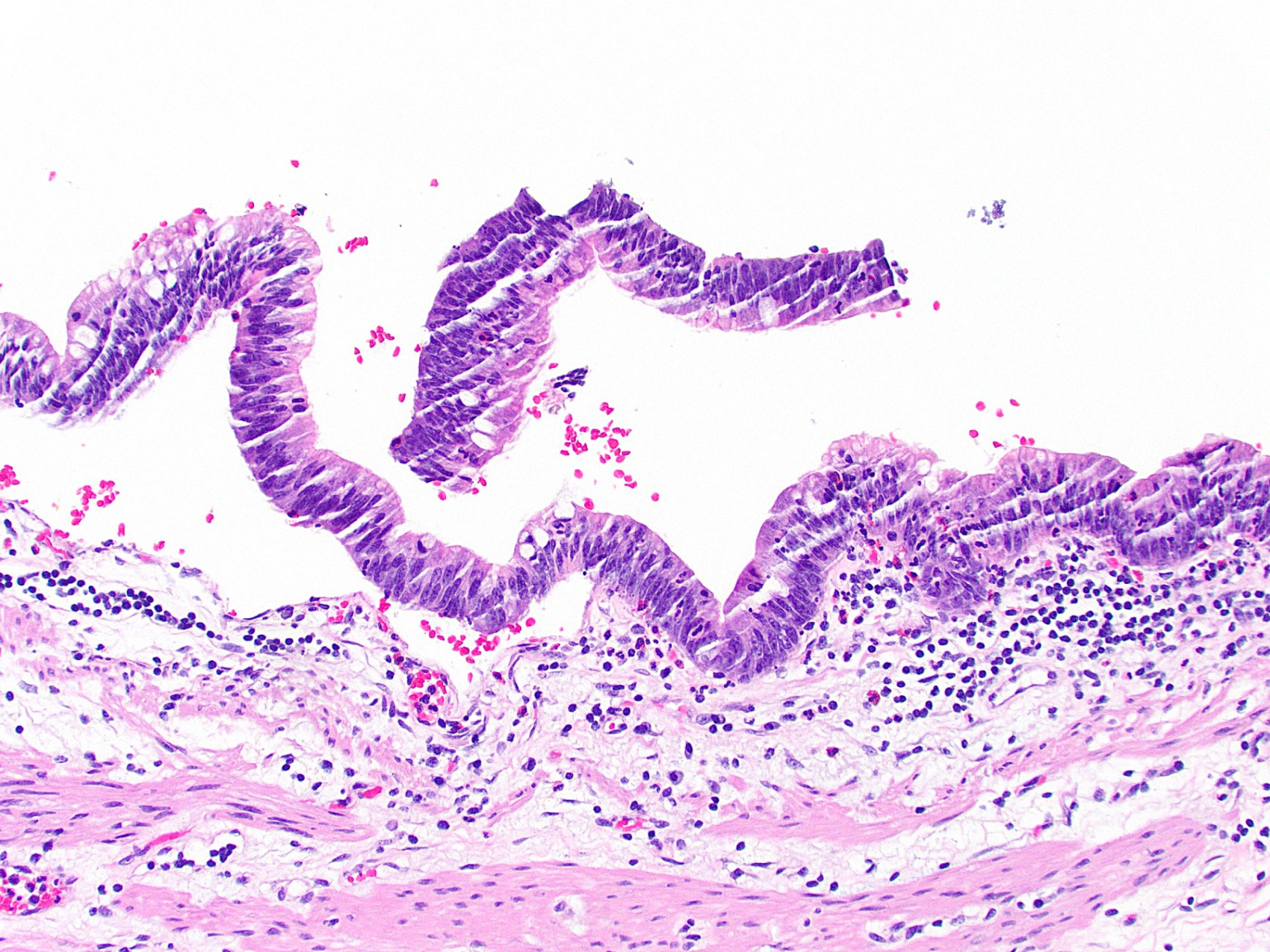
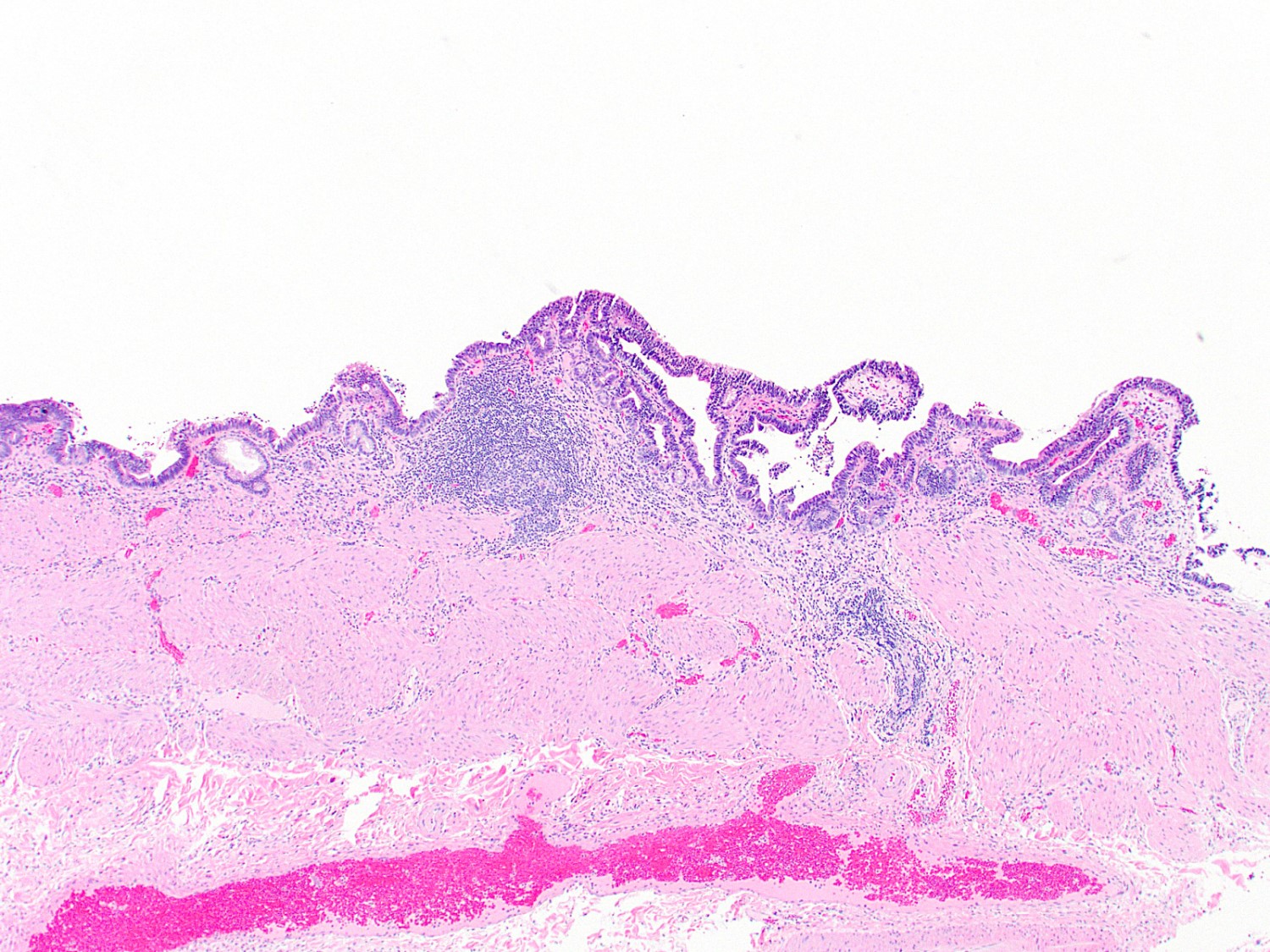
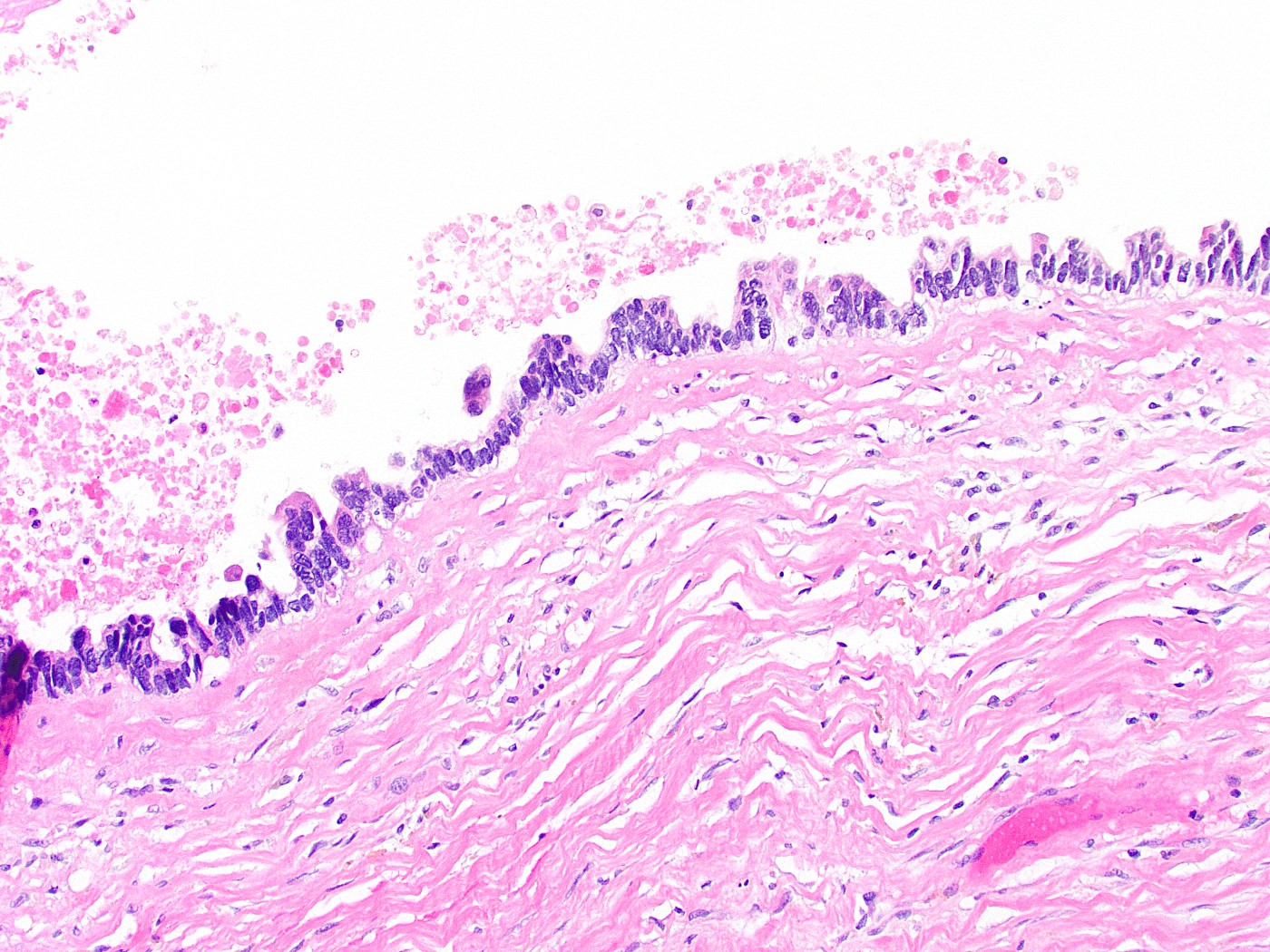
Microscopic (histologic) description
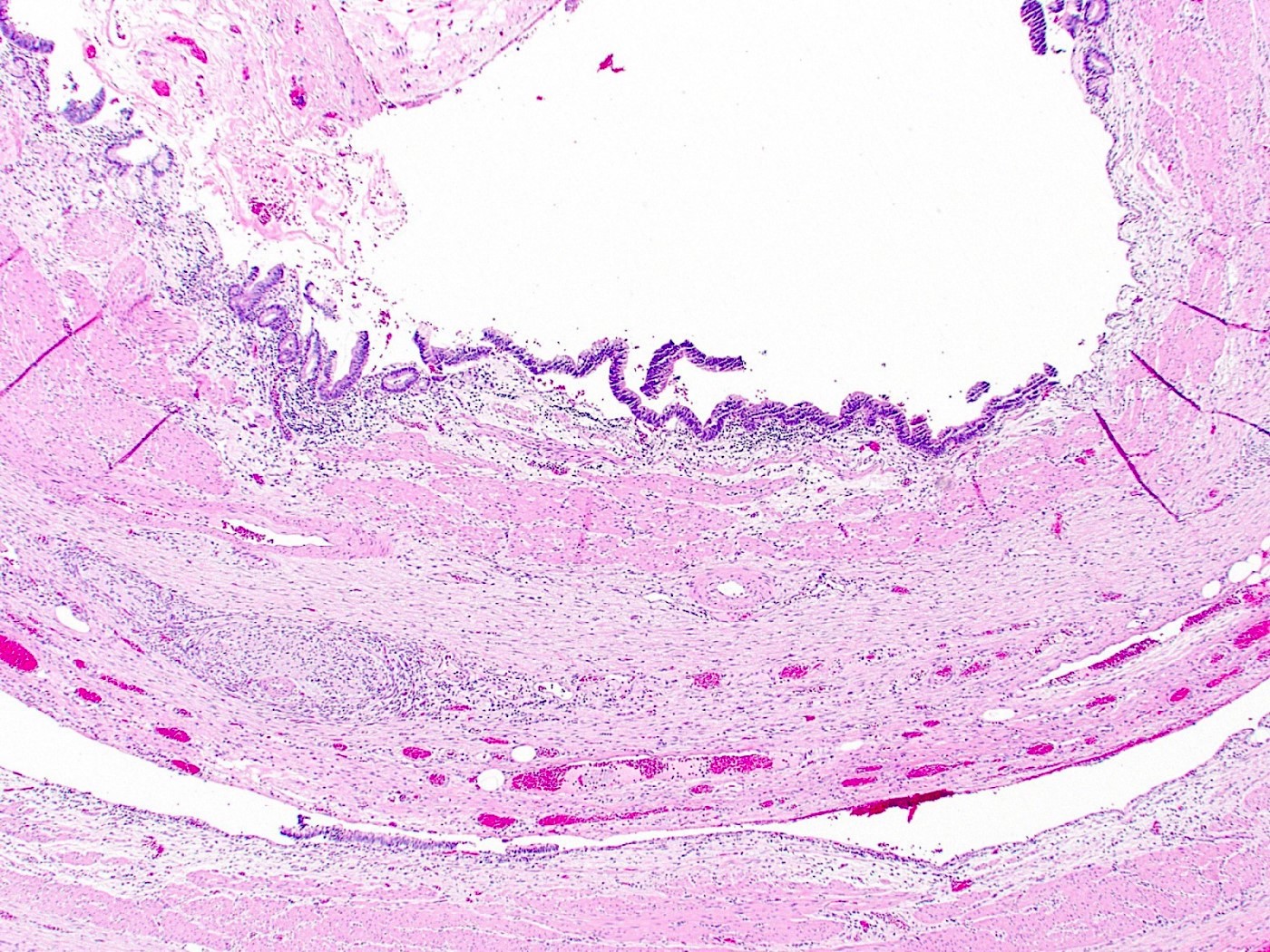
- Gallbladder dysplasia can be difficult to reproducibly define, in particular low grade dysplasia (Histopathology 2021;79:2)
- Low grade dysplasia
- Elongated (pencillate) hyperchromatic nuclei that may show pseudostratification but still maintain basal polarity, with moderate N:C ratios
- Mucosal surface often remains flat
- High grade dysplasia
- Markedly atypical nuclei with rounding, nucleoli and loss of polarity, with high N:C ratios and more complex surface architecture
- Low grade dysplasia often accompanies high grade dysplasia
- Intestinal metaplasia is often present in the background
- Neutrophils (acute inflammation) may be present in dysplastic epithelium, raising consideration for reactive atypia but erosion or ulceration is uncommon
- Interobserver variability exists for these diagnoses; strict diagnostic criteria have been proposed to address this (Mod Pathol 2007;20:701)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- May show p53 overexpression and increased Ki67 index (Hum Pathol 1996;27:360, Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 2007;111:734)
Videos
Gallbladder and bile duct pathology by Dr. Adsay
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Multifocal, flat, high grade dysplasia arising in chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis (see comment)
- Negative for invasive malignancy
- Cystic duct margin negative for dysplasia
- Comment: The entire gallbladder was submitted for microscopic examination.
Differential diagnosis
- Reactive atypia:
- Often occurs in the setting of prominent acute cholecystitis
- Nuclei have lower N:C ratios and less striking hyperchromasia
- Atypia may gradually transition into adjacent normal mucosa, rather than a clear cutoff
- Intestinal metaplasia:
- Defined by the presence of goblet cells
- Cells also show mild nuclear hyperchromasia and amphophilic cytoplasm
- Intracholecystic papillary tubular neoplasm:
- Dysplastic process that forms a discrete polypoid lesion, rather than remaining relatively flat
Practice question #1
A 72 year old woman presented to the emergency department with symptoms of cholecystitis and underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The gallbladder grossly looked normal but the one routine section submitted for histology showed the changes seen in the image above. What is the most appropriate next step in the workup of this case?
- Sign out the pathology report
- Submit 1 - 2 additional cassettes
- Submit the entire gallbladder
- Tell the surgeon the patient needs urgent hepatectomy
Practice answer #1
C. Submit the entire gallbladder. The image shows high grade dysplasia, which can be found incidentally in gallbladder specimens. It would be inappropriate to sign out the case without going back to the specimen. While recommendations vary, some experts suggest that discovery of high grade dysplasia means the entire gallbladder should be submitted for thorough histologic inspection to rule out invasive gallbladder carcinoma.
Answer A is incorrect because high grade dysplasia warrants further investigation so as to not miss a cancer diagnosis.
Answer B is incorrect because submitting 1 - 2 more sections errs on the insufficient side.
Answer D is incorrect because the patient does not necessarily need more surgery, though if carcinoma is found, definitive treatment may require additional surgery.
Comment Here
Reference: Gallbladder & extrahepatic bile ducts - Dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Gallbladder & extrahepatic bile ducts - Dysplasia
Practice question #2
Which of the following countries has the lowest incidence of gallbladder dysplasia and carcinoma?
- Chile
- India
- Japan
- United States
Practice answer #2
D. United States. Answer A - C are incorrect because Chile, India and Japan are all known to have a high incidence of gallbladder dysplasia and carcinoma, unlike the United States, which has a more standard incidence. In those countries, it may be prudent to submit additional sections from gallbladder specimens to rule out incidental dysplasia.
Comment Here
Reference: Gallbladder & extrahepatic bile ducts - Dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Gallbladder & extrahepatic bile ducts - Dysplasia