Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Roychowdhury M. Ki67. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainski67.html. Accessed September 24th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Marker of cell proliferation first described in 1983 (Int J Cancer 1983;31:13)
- Labile, nonhistone nuclear protein expressed in G1, S, G2 and M phases of cell cycle, then rapidly catabolized at end of M phase and not detectable in G0 and early G1 cells (J Cell Physiol 2000;182:311)
Essential features
- Marker of cell proliferation
- Nuclear stain; cytoplasmic staining is disregarded
- Used to help differentiate between benign versus malignant and increasingly used to grade various tumors (e.g. neuroendocrine tumors, pituitary tumor, schwannoma, meningioma, sarcoma, etc.) or dysplasia (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, anal intraepithelial neoplasia, dysplasia arising in Barrett, etc.)
- Used to determine prognosis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer and chordoma
Terminology
- MIB1 (MIB1 is the IgG1 antibody against Ki67 for formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue)
Pathophysiology
- MIB1 is a monoclonal antibody raised against a recombinant part of the Ki67 antigen
- Both MIB1 and polyclonal anti-Ki67 antibody recognize the Ki67 antigen in fixed material
Clinical features
- In general, increased in most malignant and inflammatory conditions but degree may differ
- Used to grade various tumors, distinguish between differential diagnosis and predict prognosis
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining
- Percentage of nuclei with positive staining in tumor cells is scored
- For dysplasia, thickness of epithelium / location of cells showing positive Ki67 staining is graded
Uses by pathologists
- Nuclear stain; cytoplasmic staining is disregarded
- Ki67 nuclear expression is proportional to the mitotic count but reveals more proliferating tumor cells than the latter
- Percentage of positive cells is usually calculated in hot spot regions with highest staining
- Distinguish benign / nonneoplastic and malignant / neoplastic lesions:
- Anus / cervix: HSIL (Ki67+) versus atrophy or normal (Ki67-) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1449)
- Esophagus: Barrett metaplasia versus dysplasia (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;153:695)
- Colonic polyp with cautery artifact: distinguish adenoma (Ki67+) from nonadenomatous polyp (Ki67-) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1089)
- Lymph node, sentinel node biopsy: distinguish melanoma (Ki67+) from nevus cells (Ki67-) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1351)
- Uterus: clear cell carcinoma (Ki67+) versus Arias-Stella reaction (Ki67-) (Am J Case Rep 2012;13:271, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:223)
- Placenta: distinguish hyperplasia of intermediate trophoblast (Ki67+) from exaggerated placental site (Ki67-) (Hum Pathol 1999;30:687)
- Adrenocortical tumors: distinguish benign and malignant (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1612)
- Schwannoma versus atypical schwannoma (J Laryngol Otol 2019;133:205)
- Grading:
- Invasive breast carcinoma: component of grading in addition to tubule formation and nuclear pleomorphism (Eur J Breast Health 2019;15:256, Sci Rep 2020;10:7648)
- Breast phyllodes tumor: distinguish benign, borderline, malignant (low grade / high grade) (Mod Pathol 2001;14:185)
- Gastrointestinal tract: grade well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors
- Sarcoma: component of grading in addition to necrosis and differentiation (World J Surg Oncol 2016;14:110, APMIS 1994;102:915)
- Grading of lung neuroendocrine tumors (as a complementary tool to mitotic count, however, not yet officially a part of grading system) (Chin Med J (Engl) 2019;132:551, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1523)
- Grading of meningioma (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e18644, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1995;137:174)
- Grading of astrocytoma in separating grade 2 from grade 3 (J Cancer Res Ther 2014;10:641, ResearchGate: Expression of Ki-67 in Low-Grade and High-Grade Astrocytomas [Accessed 23 February 2021])
- Poor prognostic factor (high levels) in many tumors:
- Breast carcinoma (part of prognostic marker panel along with ER, PR and HER2 / neu) (Cancer Biol Med 2016;13:496, J Natl Cancer Inst 2020 Dec 28 [Epub ahead of print])
- Bladder papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (Cancer 2002;95:784)
- Chordoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1170)
Prognostic factors
- High Ki67 proliferative index used as an adverse prognostic marker for breast cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, chordoma
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Percentage of nuclei with positive staining in tumor cells are scored
- < 10%: low
- 10 - 20%: borderline
- Used in surrogate immunohistochemical classification for gene expression profile based intrinsic breast cancer subtypes (low: luminal A; high: luminal B; higher: HER2; highest: basal-like) (Hoda: Rosen's Diagnosis of Breast Pathology by Needle Core Biopsy, 4th Edition, 2017)
- May assist in distinguishing benign from malignant breast phyllodes tumor; may correlate with tumor grade and adverse prognosis in malignant phyllodes tumor (Mod Pathol 2001;14:185, Breast J 2002;8:38, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:1516)
- Grading for neuroendocrine tumors of tubular gastrointestinal tract and pancreas (low grade: < 3%; intermediate grade: 3 - 20%; high grade: > 20%)
- Please note that there is a small subgroup of well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors that show > 20% Ki67 and are thus categorized as grade 3
- These tumors show prognosis intermediate between conventional grade 2 tumors and poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas and are less chemosensitive than neuroendocrine carcinomas (Amin: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th Edition, 2018)
- Useful in histological grading of soft tissue sarcomas (World J Surg Oncol 2016;14:110)
- Useful in grading of meningiomas and predicting risk of recurrence (J Clin Diagn Res 2016;10:EC15, Cureus 2017;9:e1820)
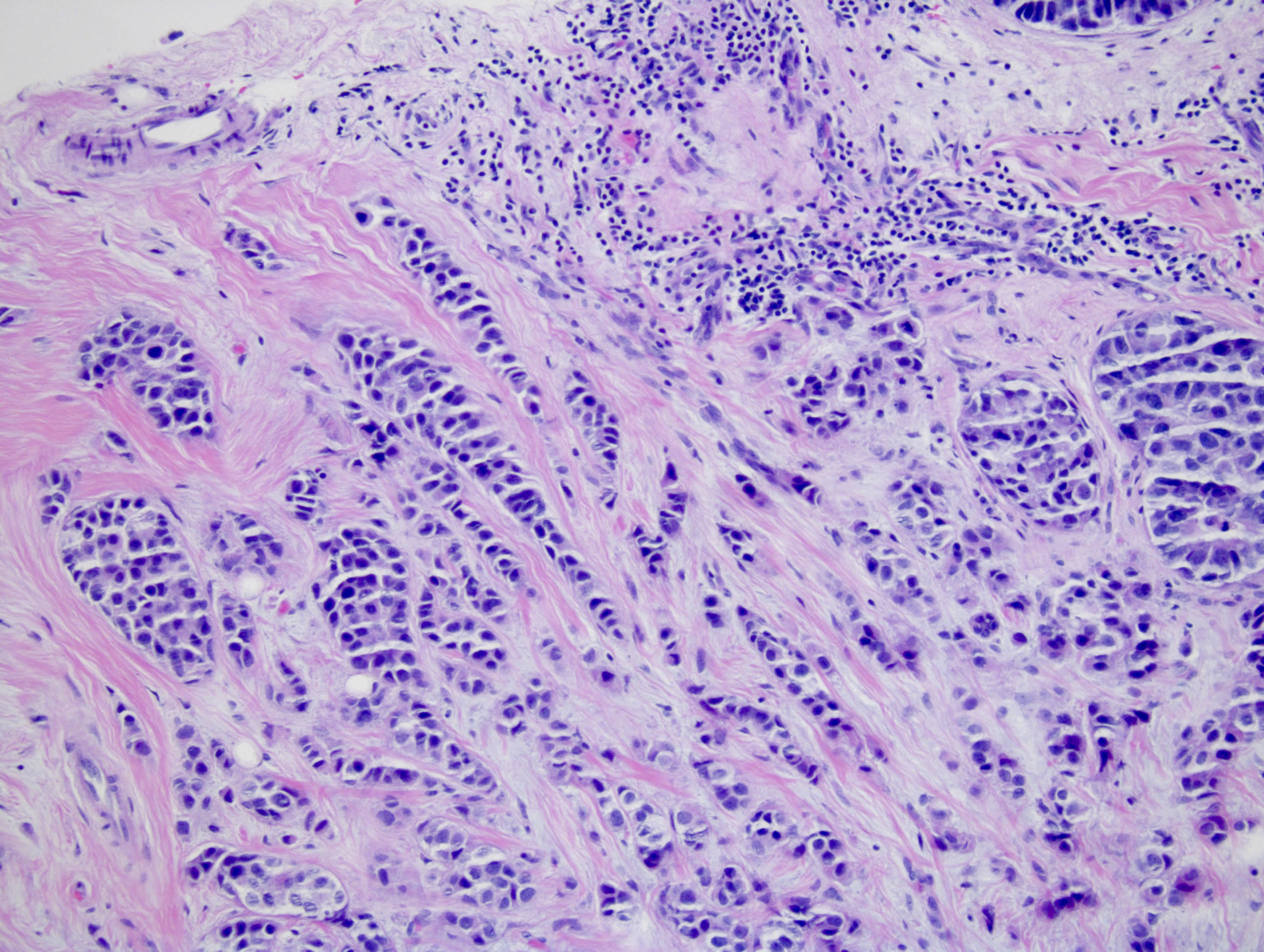
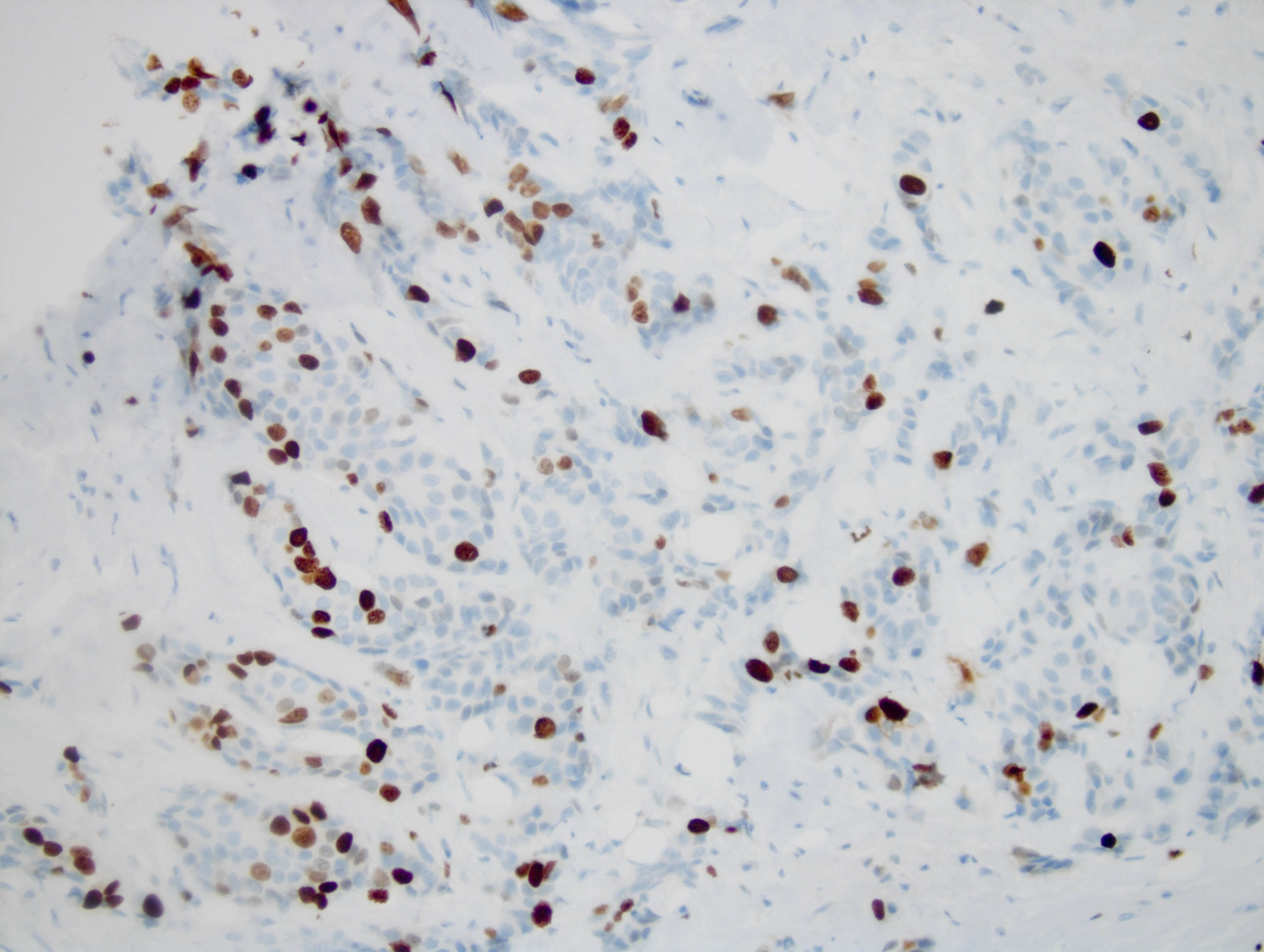
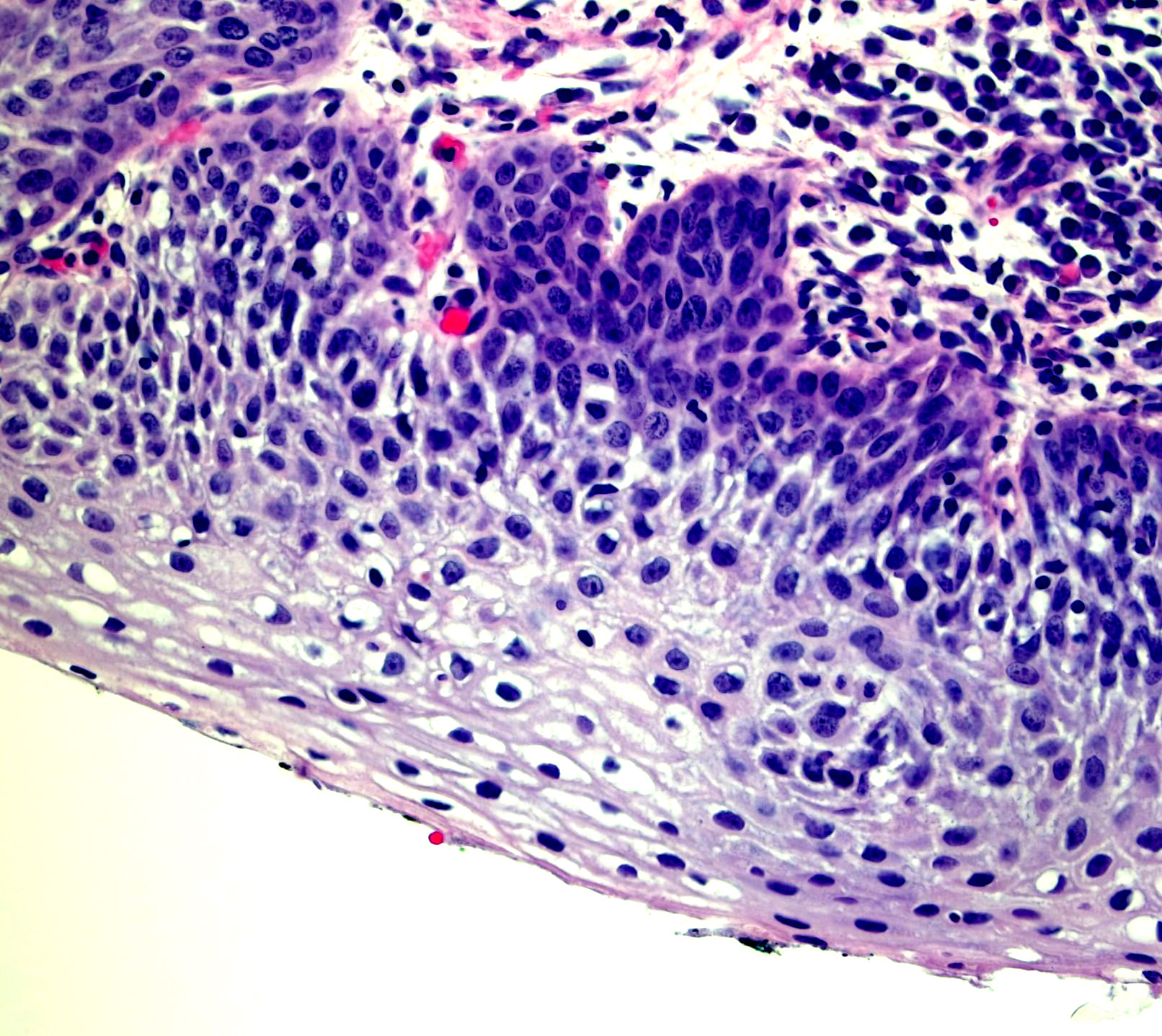
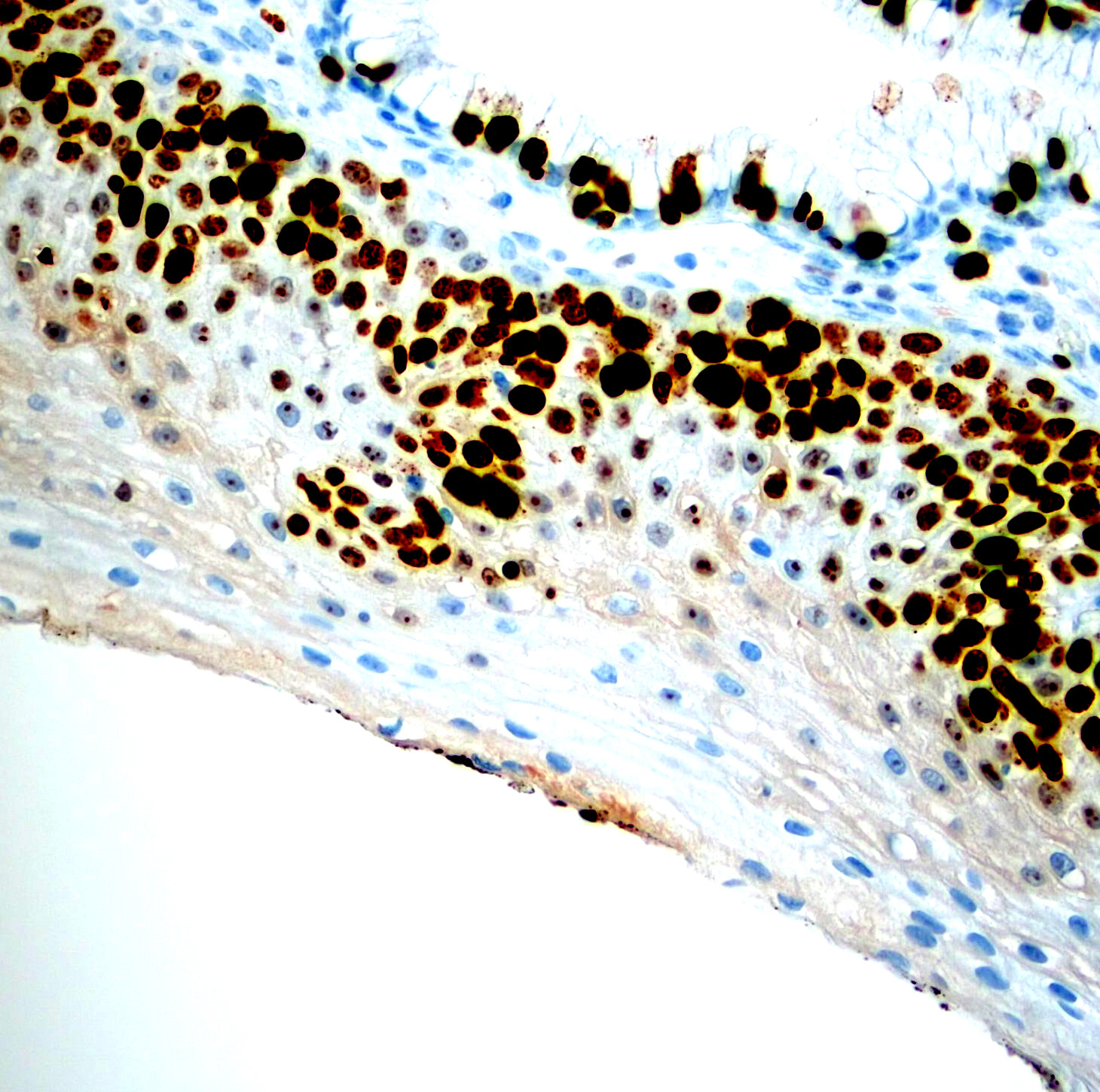
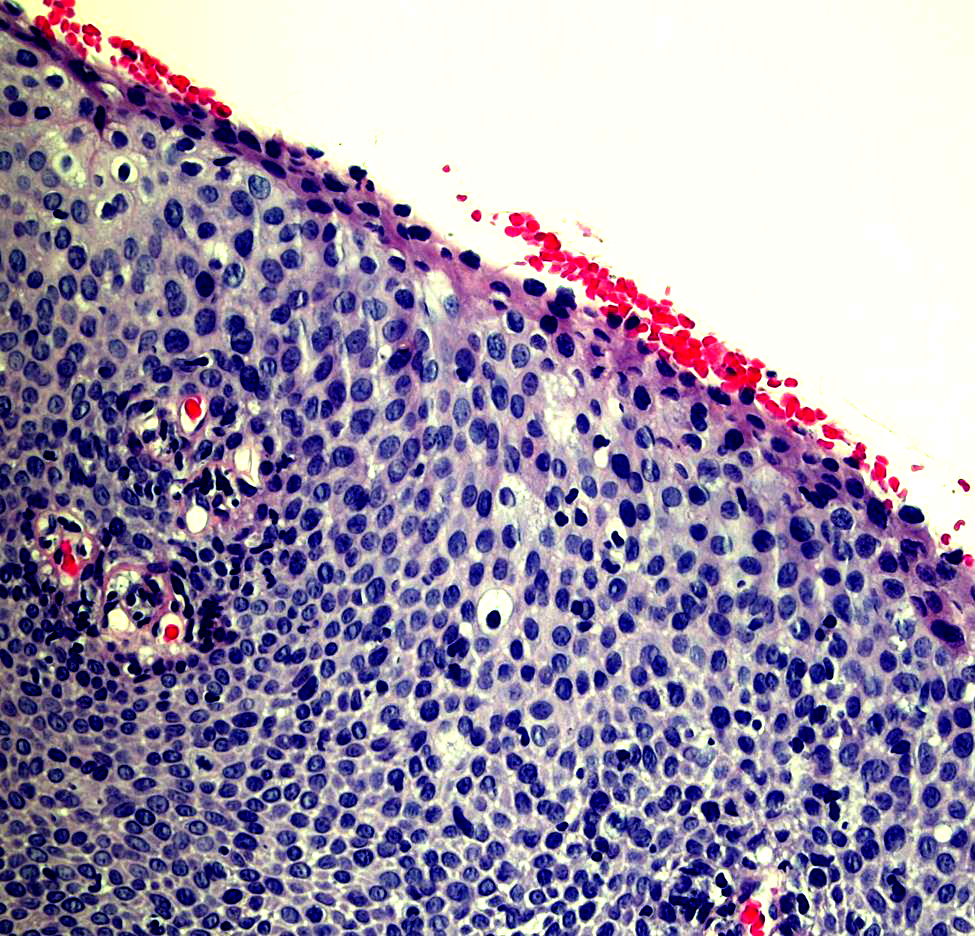
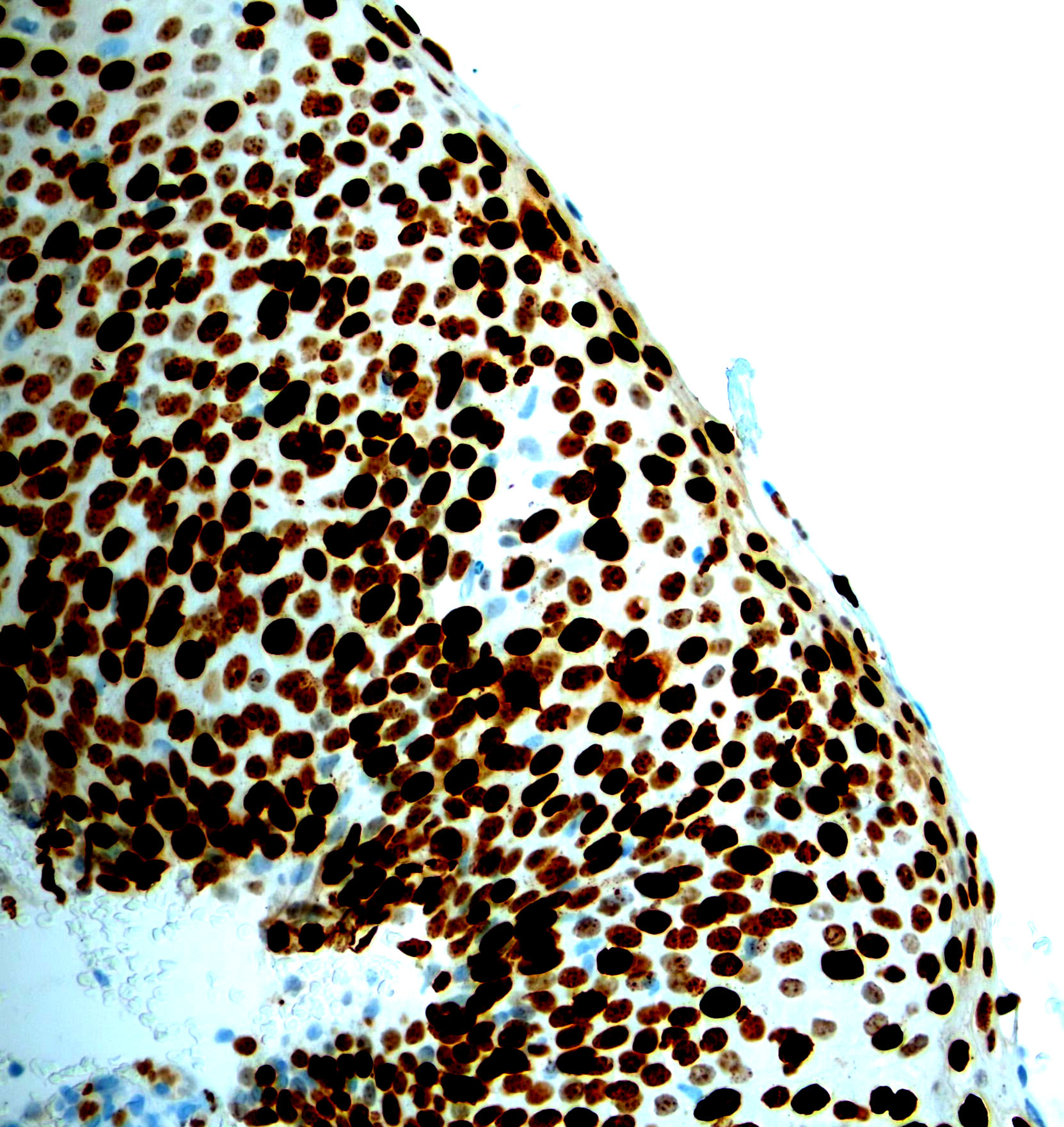
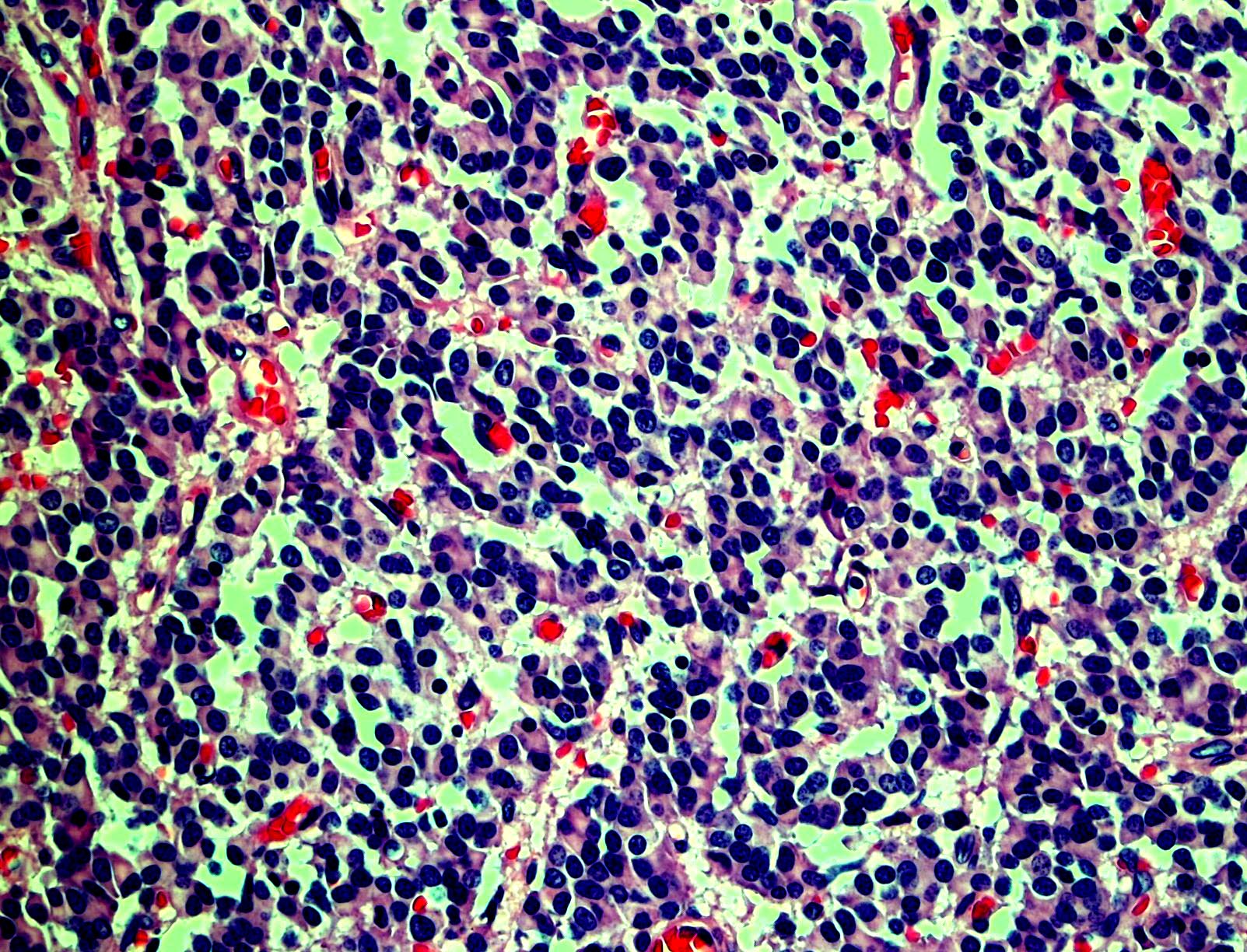
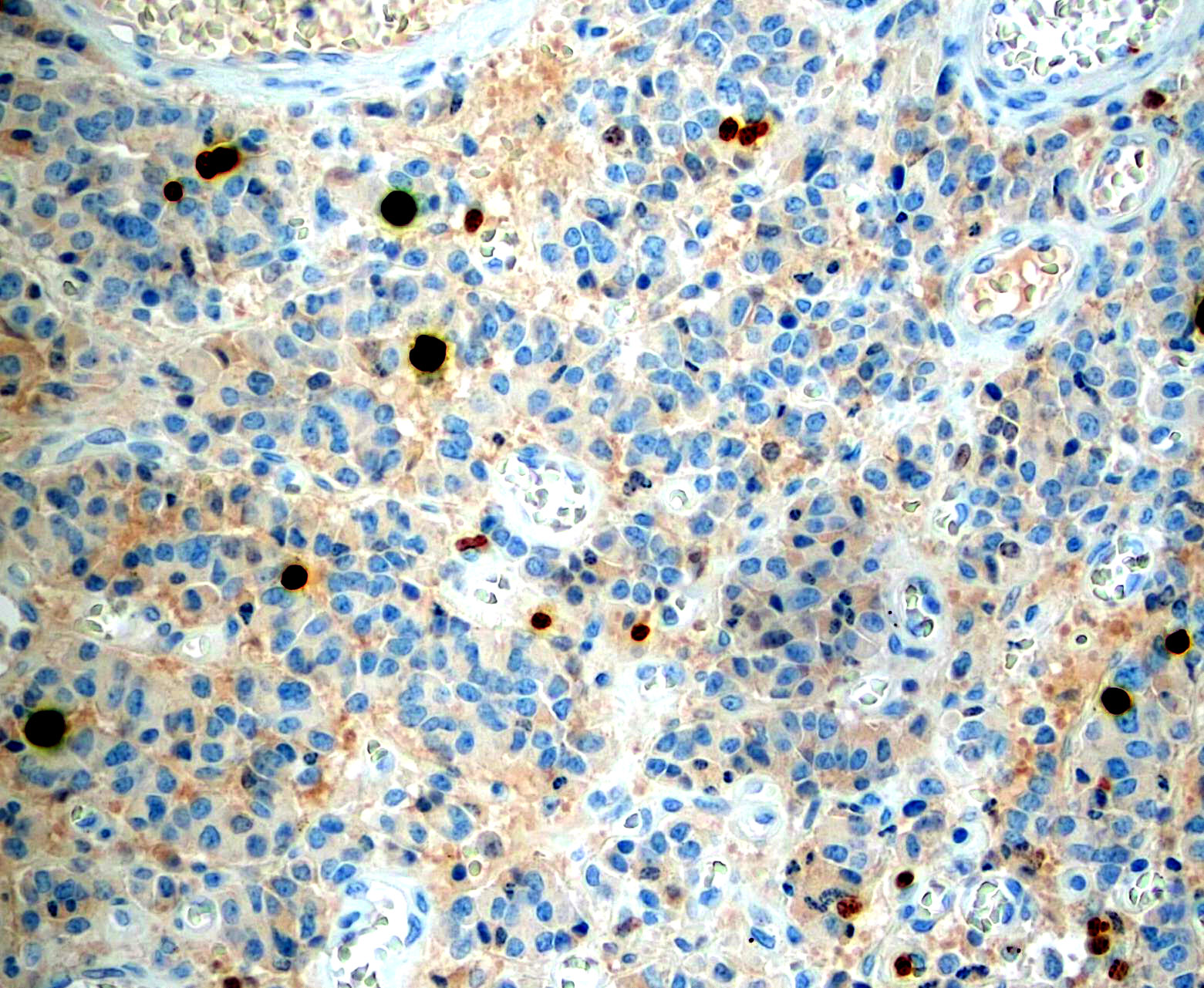
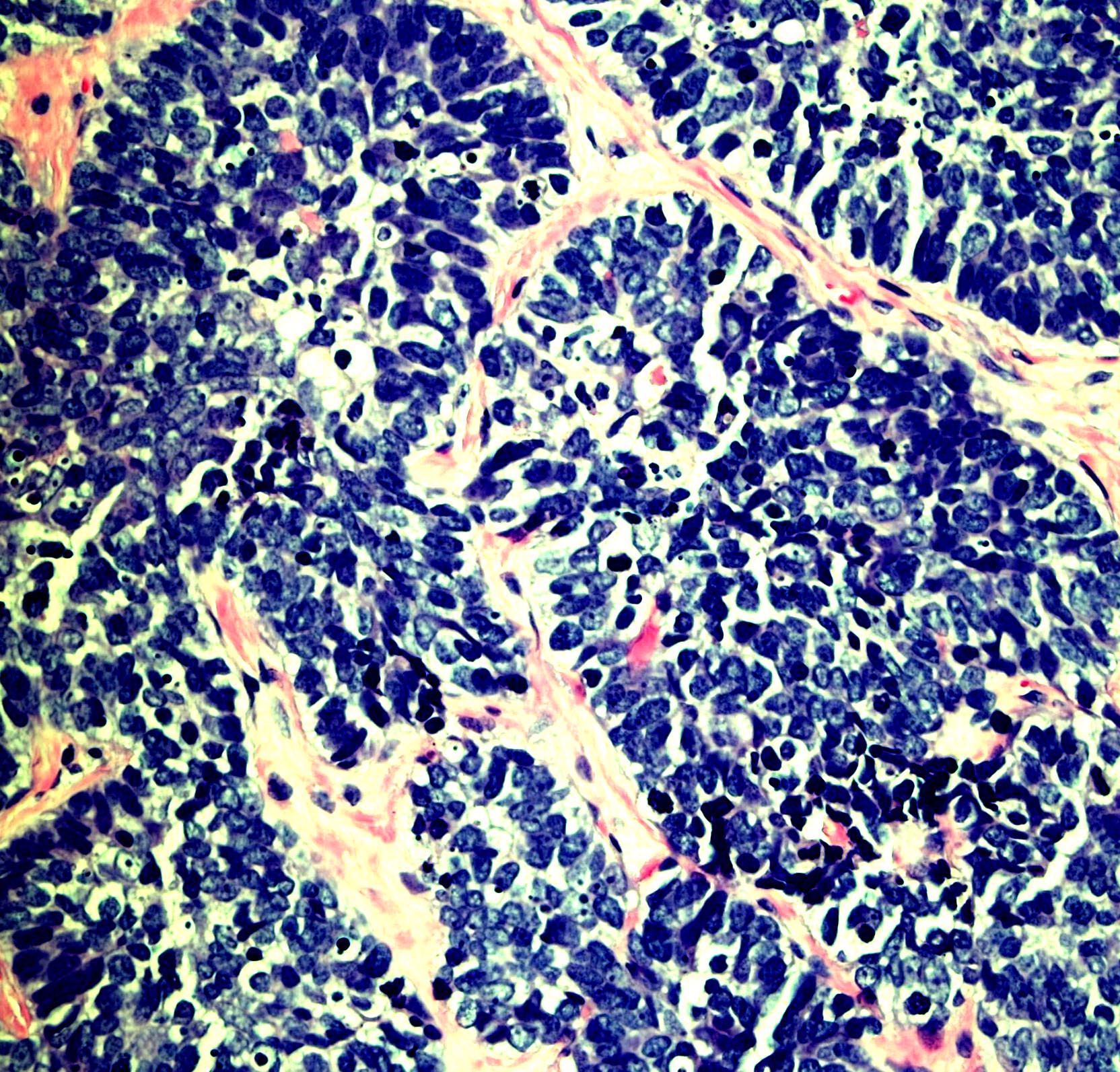
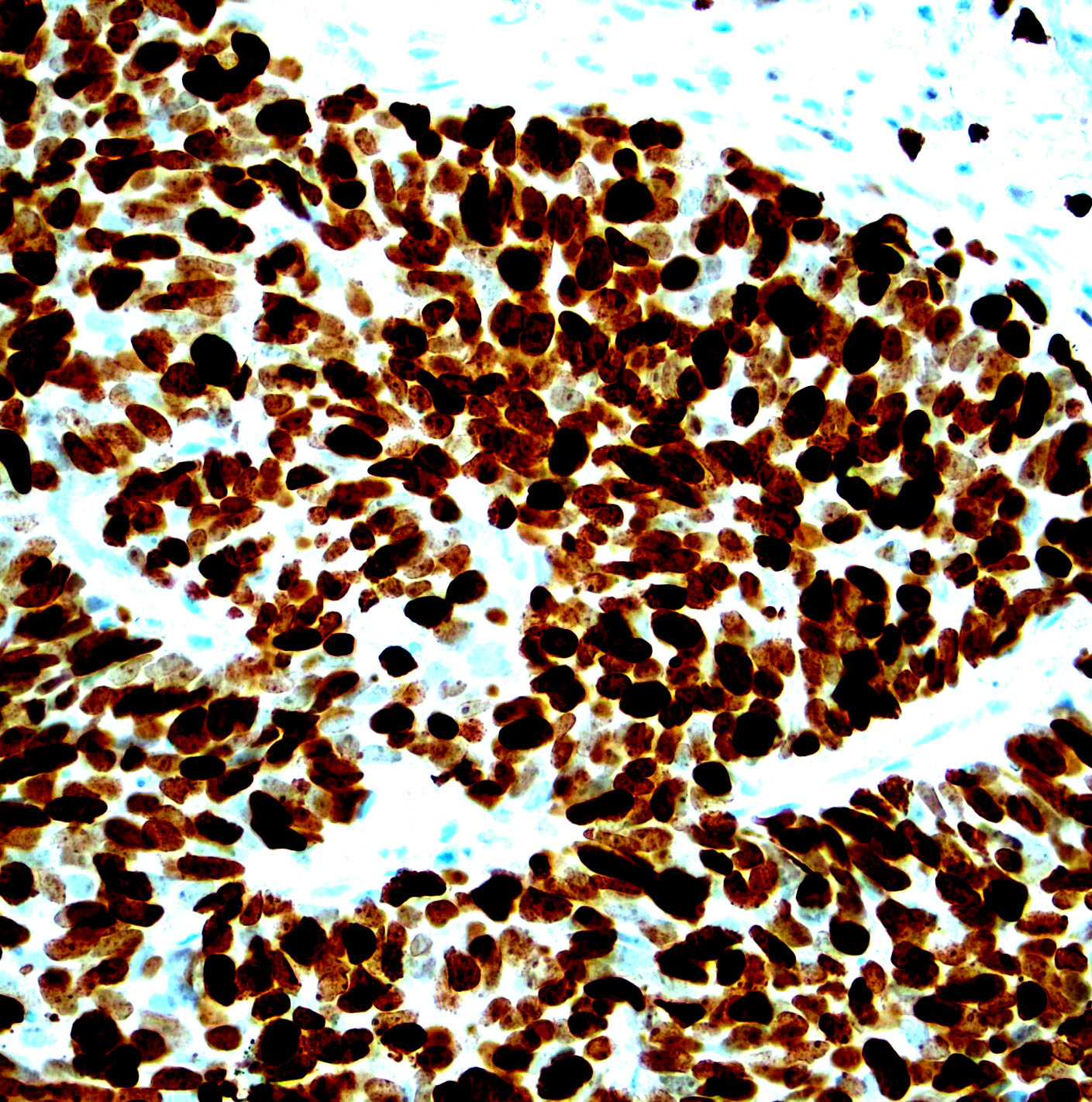
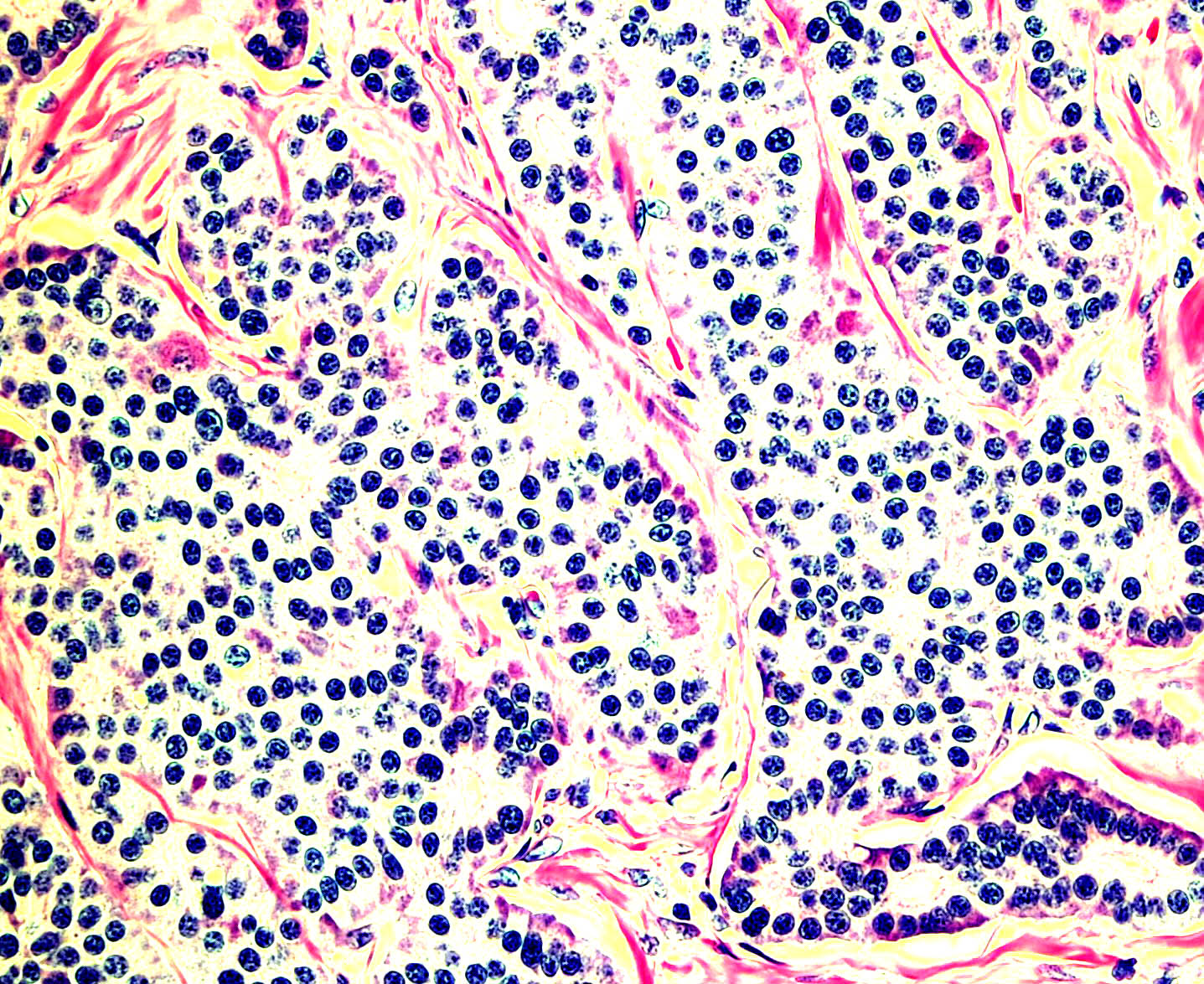
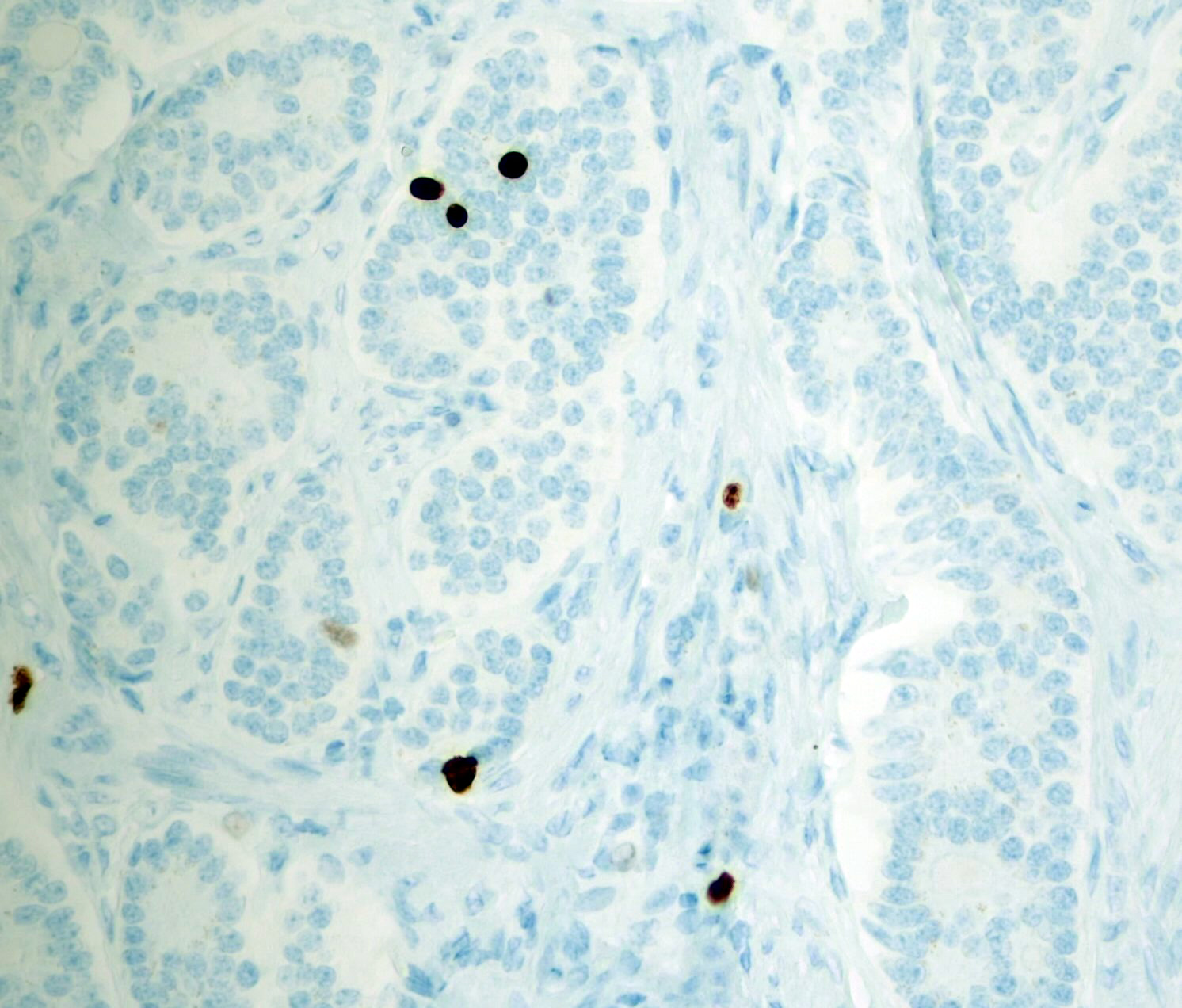
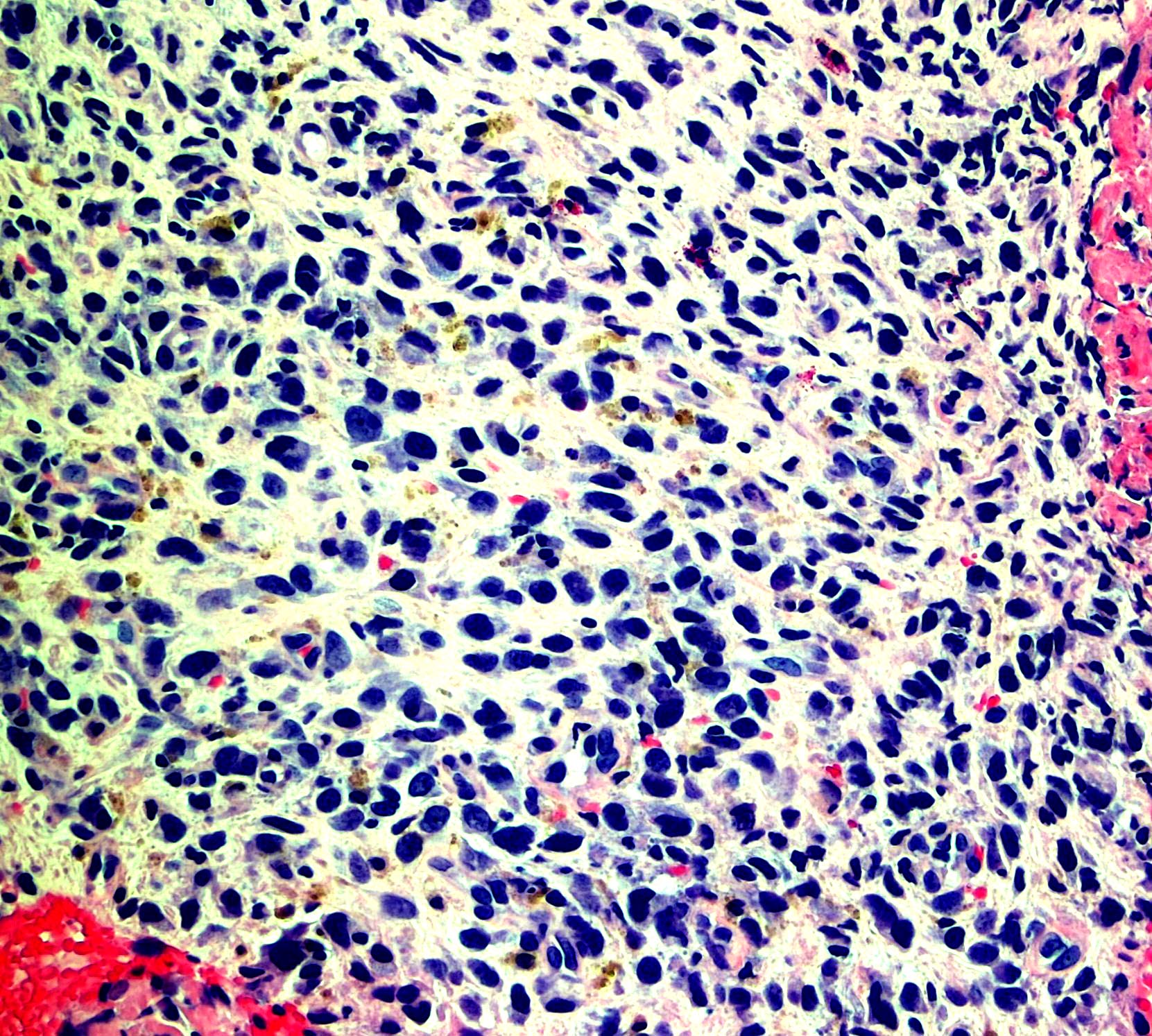
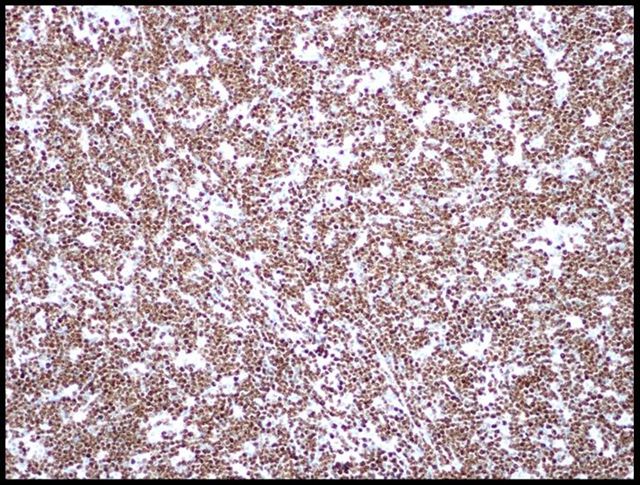
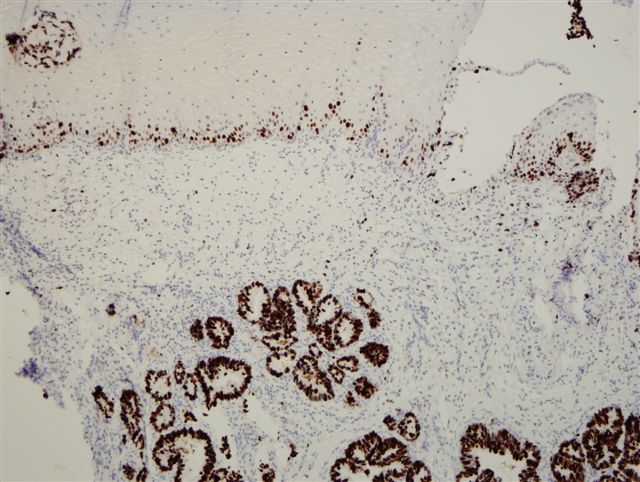
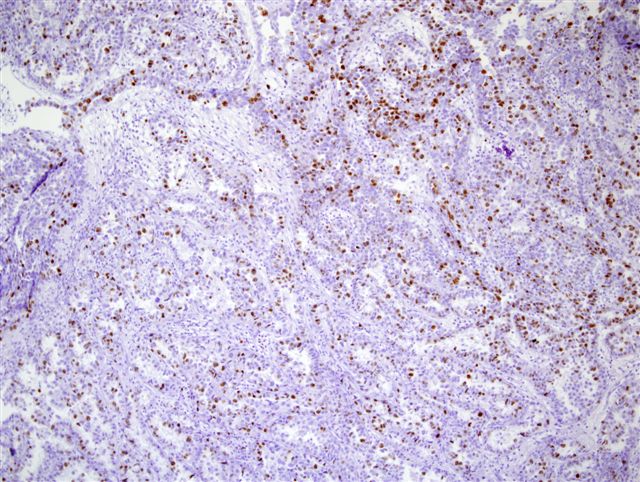
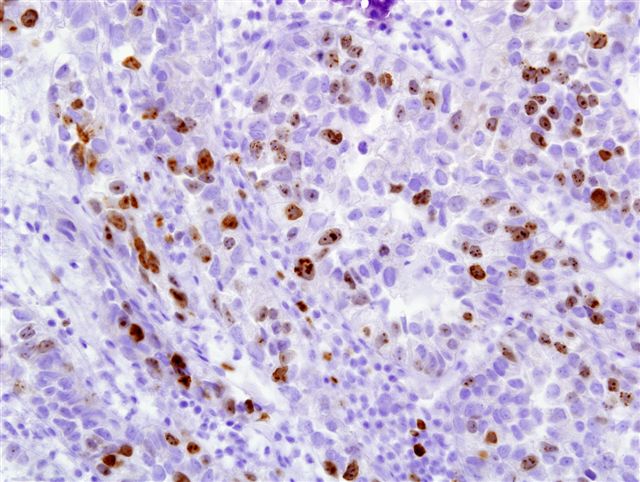
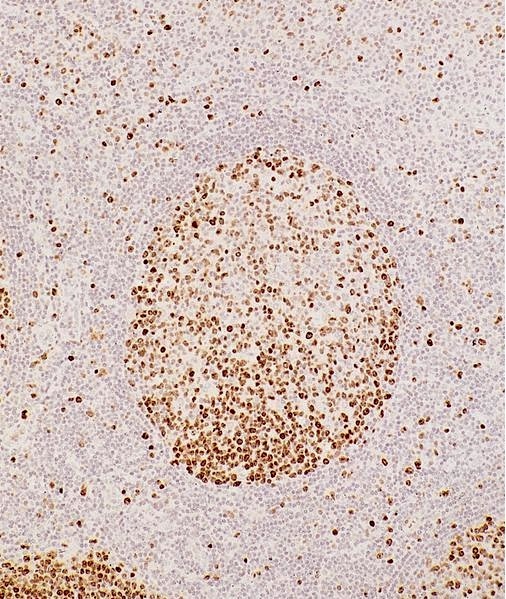
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Monika Roychowdhury, M.D., Kaveh Naemi, D.O., Cases #238, #237, #202, #194, AFIP images and Leica Microsystems
Positive staining - normal
- Most tissues have baseline positive staining 0 - 1% as a very low proliferative index
Positive staining - disease
- Cervical / anal dysplasia (mild dysplasia: lower 33% of epithelium shows increased Ki67 staining; moderate dysplasia: 66% of epithelium shows increased Ki67 staining; severe dysplasia / CIS: full thickness of epithelium shows increased Ki67 staining)
- Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (low grade: < 3%; intermediate grade: 3 - 20%; high grade: > 20%)
- Lung neuroendocrine tumors (typical carcinoid: up to 5%; atypical carcinoid: up to 20 - 25%; large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: 40 - 80%; small cell lung carcinoma: 50 - 100%) (Transl Lung Cancer Res 2017;6:513)
- Meningioma: Ki67 (not a diagnostic criterion but is usually > 4% and goes up to 20% depending on grade - I, II or III)
- Astrocytoma (astrocytoma: < 4%; anaplastic astrocytoma: 5 - 10%; glioblastoma: 15 - 20%) (Pathol Oncol Res 2006;12:143)
- Bladder cancer prognosis (PLoS One 2016;11:e0158891)
- Breast cancer prognosis, higher percentage associated with worse prognosis (cutoffs < 10%, 10 - 25%, > 25%) (Eur J Breast Health 2019;15:256)
Sample pathology report
- Stomach, resection:
- Well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor, 1.5 cm, surgical margins negative (see synoptic report)
- Ki67 labeling index < 3%
- Lung, right upper lobe, biopsy:
- High grade neuroendocrine carcinoma, small cell carcinoma
- Ki67 proliferative index > 90%
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 54 year old woman recently received the diagnosis of invasive ductal carcinoma for a right breast mass. Which of the prognostic markers below, if more than 30%, suggests aggressive behavior of the tumor?
- ER
- Ki67
- PR
- p63
Practice answer #1