Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Immunofluorescence description | Immunofluorescence images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Tripathy A, Husain AN. Pneumocystis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumorpcp.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is a serious infection caused by the fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii in immunocompromised patients
Essential features
- One of the most common AIDS defining diseases in HIV infected patients
- Substantial mortality and morbidity
- Direct microscopic examination of bronchoalveolar lavage, sputum and lung biopsy are the gold standard methods of diagnosis
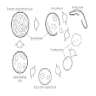
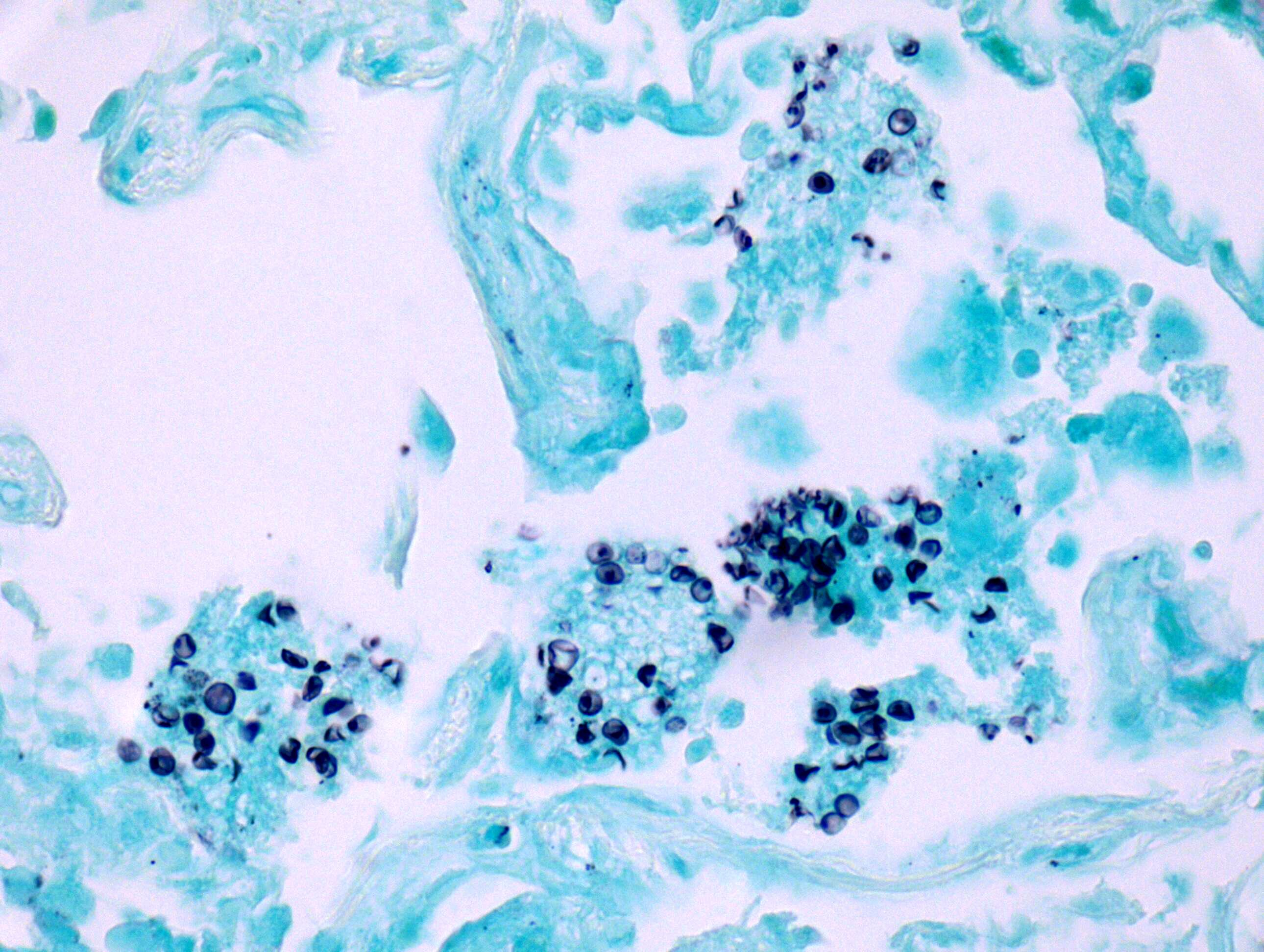
- Cup shaped organisms with a central dot-like density
Terminology
- Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)
- Formerly known as Pneumocystis carinii
ICD coding
- ICD-10: B59 - pneumocystosis
Epidemiology
- Incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia has declined substantially with widespread use of Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis and antiretroviral therapy
- Recent incidence among patients with AIDS in Western Europe and the United States is < 1 case per 100 person years
- Commonly seen in HIV and immunocompromised patients (hematologic malignancies followed by autoimmune diseases) (Int J Infect Dis 2022;121:172)
Sites
- Lung and rarely extrapulmonary sites, which include lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, adrenal glands, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, thyroid gland, heart, pancreas, eyes, ears, lumina of blood vessels, perivascular involvement and lymphatic invasion (Arch Intern Med 1991;151:1205)
Pathophysiology
- Lung injury during infection is mostly due to host inflammatory response mediated by CD4+ T cells, alveolar macrophages, neutrophils and the soluble mediators
- Inflammatory response is primarily responsible for the damage of the alveolar capillary interface activity (N Engl J Med 2004;350:2487)
Etiology
- Immunocompromised conditions (e.g., cancer, HIV, transplant recipients on immunosuppressant therapies) (N Engl J Med 2004;350:2487)
Clinical features
- Symptoms include fever, nonproductive cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, fatigue and chills (Respiration 2018;96:52)
- These symptoms develop over several days to weeks
Diagnosis
- Sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage or lung biopsy
- Direct microscopic examination, polymerase chain reaction (PCR, highly sensitive but less specific), blood test to detect beta D glucan (Med Mycol 2020;58:1015)
- In direct microscopy, Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver (GMS) stain should be performed on tissue biopsy and lavage specimens; immunofluorescence may be performed
- Papanicolaou (Pap) and Romanowsky (Giemsa, Diff-Quik) barely stain the cyst wall of the organisms and infection can easily be missed
Laboratory
- Hypoxemia is the most characteristic laboratory abnormality
- Elevation of lactate dehydrogenase levels to > 500 mg/dL is common but also nonspecific
Radiology description
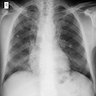
- Chest radiograph typically demonstrates diffuse, bilateral, symmetrical ground glass interstitial infiltrates emanating from the hila in a butterfly pattern (AIDS 1998;12:885)
- In early disease, a chest radiograph may be normal
- Atypical radiographic presentations also occur, e.g., nodules, blebs / cysts, asymmetric disease, upper lobe localization, intrathoracic adenopathy and pneumothorax
- Spontaneous pneumothorax in a patient with HIV infection should raise the suspicion of PCP
- Cavitation and pleural effusion are uncommon in the absence of other pulmonary pathogens or malignancy and their presence may indicate an alternative diagnosis or an additional pathology such as tuberculosis (TB), Kaposi sarcoma or bacterial pneumonia
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Treatment changes course of disease
Case reports
- 45 year old woman presented with dyspnea on exertion and significant weight loss within the preceding 4 months (BMC Infect Dis 2023;23:185)
- 50 year old man presented with hypoxia, 1 week history of pleuritic chest pain and fever (Turk Patoloji Derg 2020;1:246)
- 59 year old man presented with Pneumocystis jirovecii associated pneumonia and hypercalcemia due to ectopic production of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D, 6 years after renal transplantation (Acta Clin Belg 2021;76:75)
Treatment
- Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole
Gross description
- Lungs are heavy, firm and gray-brown
- There is fine porosity due to trapped pockets of air
- There may be small yellow indurated areas in the lung parenchyma and occasional emphysematous subpleural blebs (Can Med Assoc J 1969;100:846)
- Lung nodules with or without cavitation have been demonstrated in response to granulomatous inflammation (Thorax 2002;57:435)
Frozen section description
- Touch preparations with Giemsa stain of fresh frozen lung infected with Pneumocystis is preferred over histologic sections as morphologic features are more apparent in the former (Can Med Assoc J 1969;100:846)
Microscopic (histologic) description
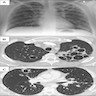
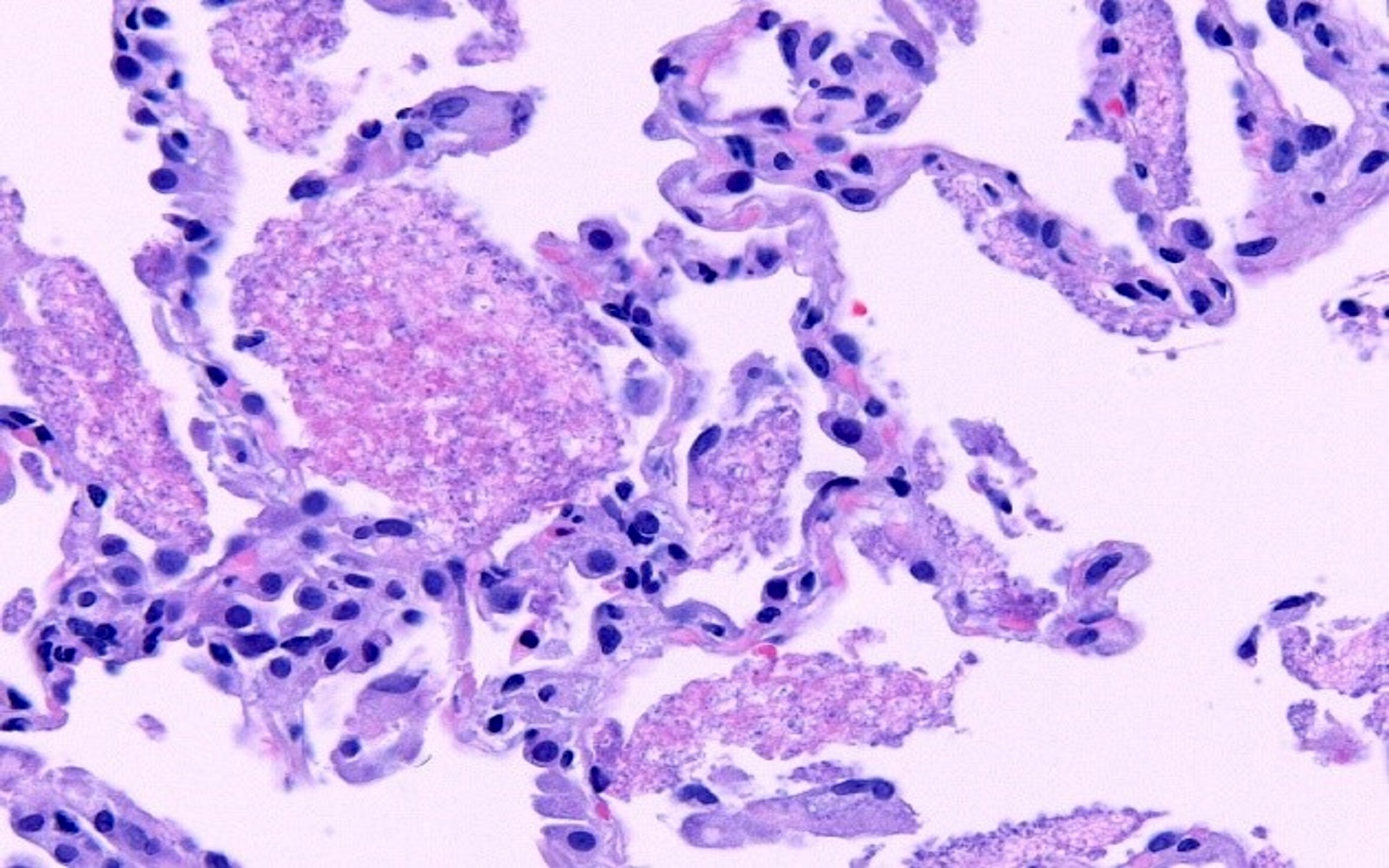
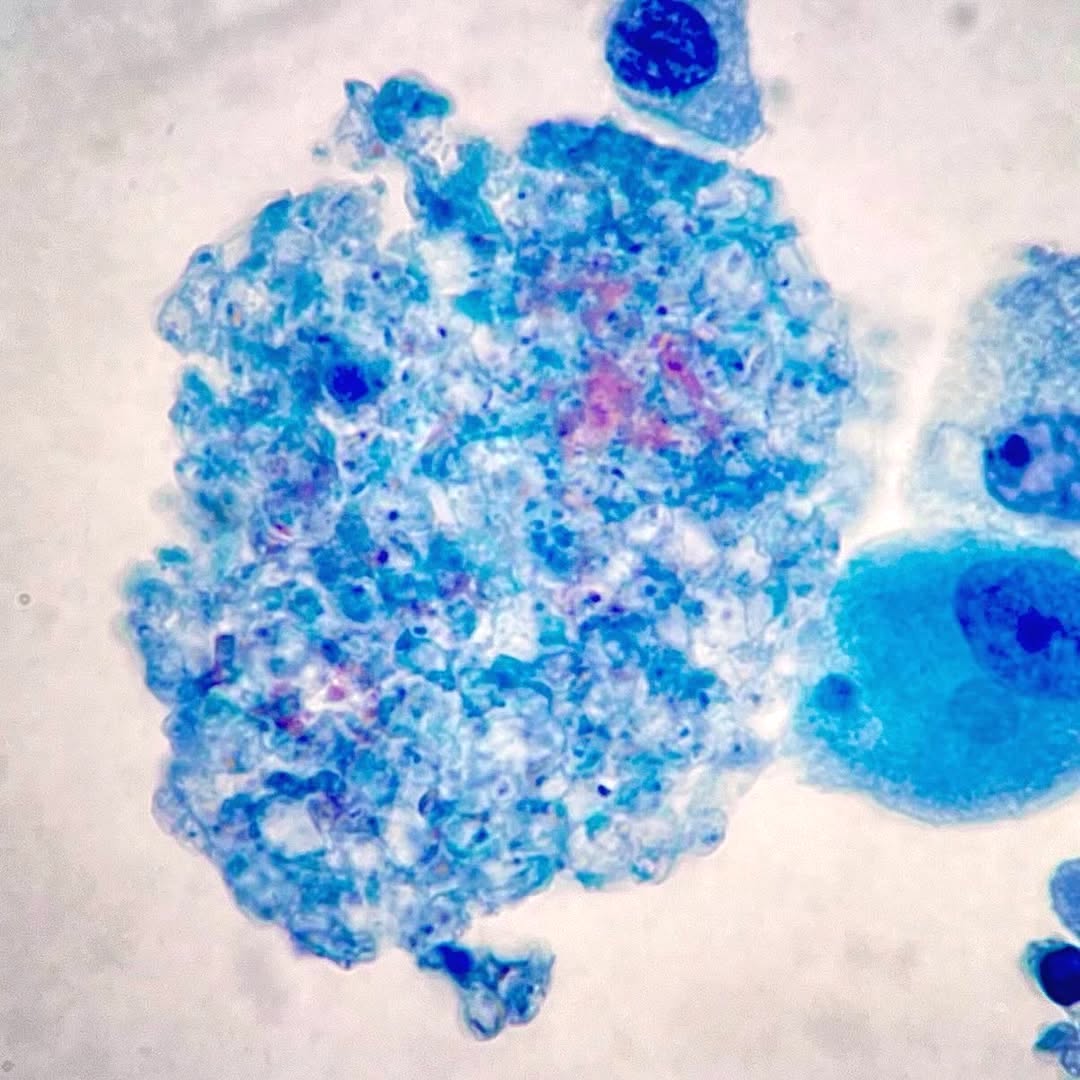
- Alveolar spaces filled with pink, foamy amorphous material composed of proliferating fungi and cell debris
- Pneumocystis organisms can be identified in the GMS (Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver) stained tissue sections within airspaces
- They are thin walled, oval, round and crescentic forms about the size of red blood cells (7 microns) (Can Med Assoc J 1969;100:846)
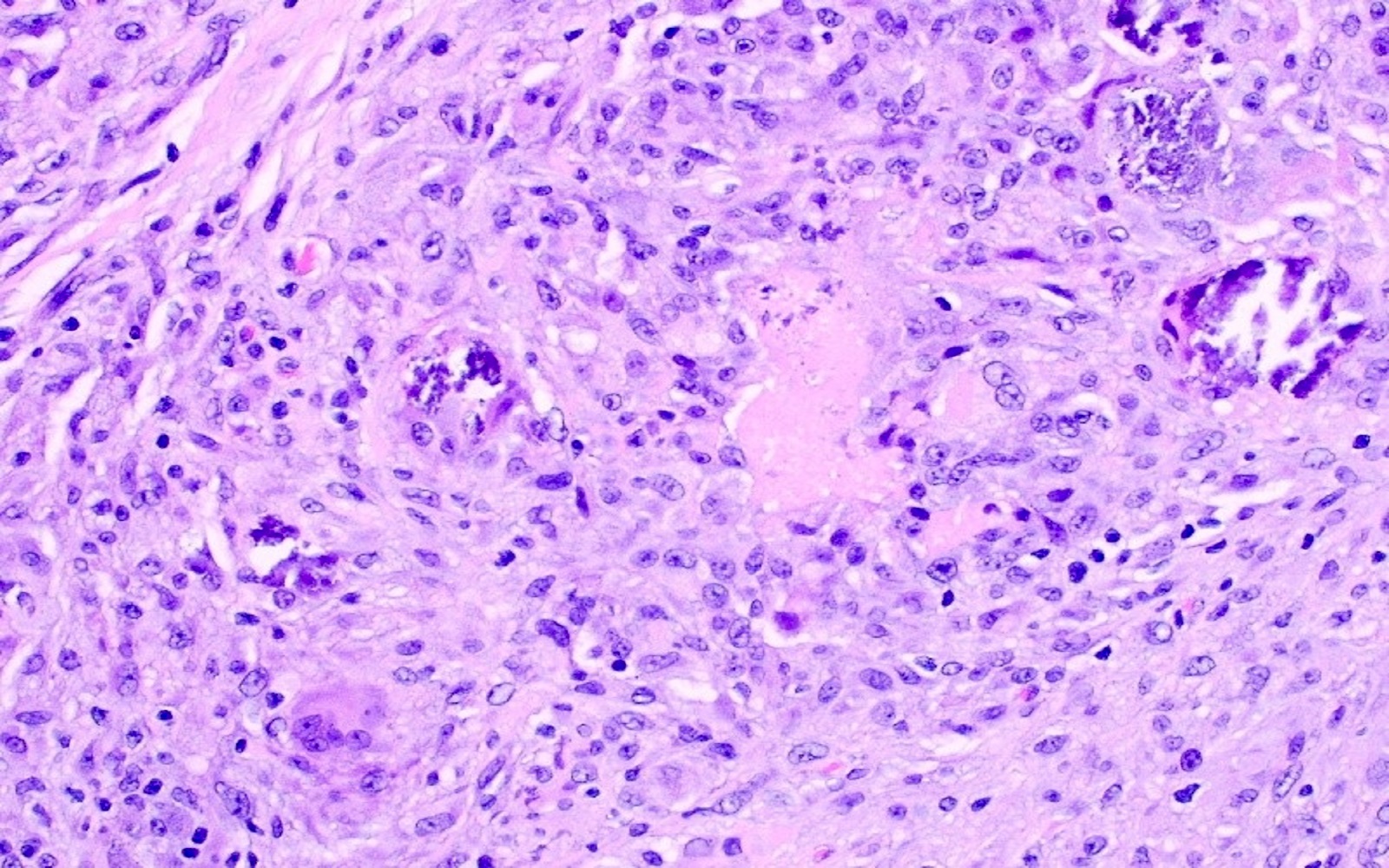
- Granulomas, although rare, are mostly necrotizing and multiple
- More than 1 infection, such as coexisting cytomegalovirus infection, may be present in these patients so it is important to look for other infectious organisms
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Characteristic morphological finding is round to oval and cup shaped dark black (GMS stain) cysts with central dot-like density
Immunofluorescence description
- Direct immunofluorescence testing on sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage specimens
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Periodic acid-Schiff stain
Electron microscopy description
- Trophic forms are 1 - 4 microns and have simple plasma membrane with filopodial projections (Clin Chest Med 2009;30:265)
- Cyst forms are 8 - 10 microns with rigid cell walls and up to 8 intracystic bodies (Clin Chest Med 2009;30:265)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Polymerase chain reaction is sensitive and rapid in detecting the presence of Pneumocystis jirovecii in bronchoalveolar lavage specimens (J Mycol Med 2022;32:101241)
Sample pathology report
- Lung, transbronchial biopsy:
- Organisms consistent with Pneumocystis jirovecii infection (see comment)
- Comment: Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver (fungal) stain is positive for organisms morphologically consistent with Pneumocystis jirovecii (control is appropriate).
Differential diagnosis
- Pneumocystis jirovecii lack budding and have a central dark dot-like density that is not seen in the following organisms: Candida, Histoplasma and Cryptococcus
- Alveolar proteinosis:
- Anti-GBM disease:
- Necrotizing, hemorrhagic, interstitial pneumonitis; associated with rapidly proliferative glomerulonephritis, linear immunoglobulin deposits on basement membranes of alveolar septal walls
- Also, intra-alveolar hemorrhage, septal thickening and hypertrophy, organization of blood in alveolar spaces
- Organizing pneumonia:
- Bronchiolar and alveolar plugs of loose fibrous tissue (Masson bodies)
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. Pneumocystis pneumonia. Pneumocystis jirovecii are round to oval and cup shaped GMS positive cysts, approximately the size of red blood cells, with a central dot. Answer C is incorrect because Cryptococcus is larger, usually 10 - 20 microns, budding and does not reveal a central dot with GMS stain. Answer A is incorrect because GMS is negative in alveolar proteinosis. Answer B is incorrect because Candida is larger, forms pseudohyphae and budding yeasts and does not reveal a central dot with GMS stain.
Comment Here
Reference: Pneumocystis
Comment Here
Reference: Pneumocystis
Practice question #2
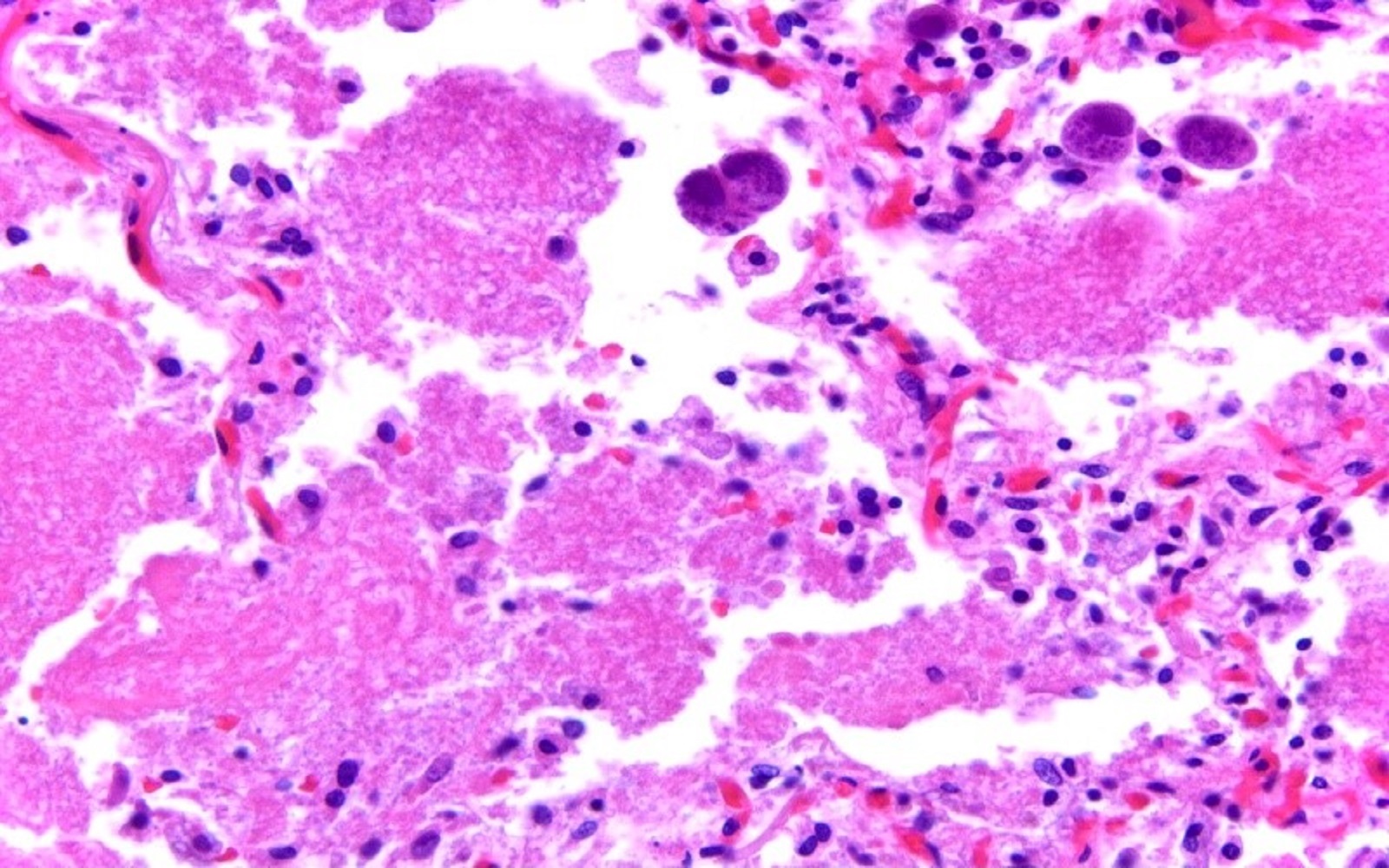
A 60 year old woman with dry cough, fever and shortness of breath revealed bilateral pulmonary nodules on imaging. Biopsy revealed features as shown in the figure above. What is the diagnosis?
- Blastomyces and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Cryptococcus neoformans and herpes virus
- Histoplasma capsulatum and adenovirus
- Pneumocystis pneumonia and cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Practice answer #2
D. Pneumocystis pneumonia and cytomegalovirus (CMV). The presence of intra-alveolar amorphous foamy material is characteristic of pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii. Enlarged cells with single intranuclear inclusion and multiple small intracytoplasmic inclusions are diagnostic for cytomegalovirus. Answers A, B and C are incorrect because intra-alveolar amorphous foamy material is rarely seen in Cryptococcus, Histoplasma and Blastomyces pulmonary infection. Adenovirus has smudged intranuclear inclusions. Herpes virus has glassy intranuclear inclusions and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes multinucleation with small intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions.
Comment Here
Reference: Pneumocystis
Comment Here
Reference: Pneumocystis