Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Stojanov IJ. Leukoplakia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityleukoplakia.html. Accessed August 19th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Hyperkeratotic (white) plaque / patch of mucosa exhibiting clonality and representing precursor lesion to squamous cell carcinoma
- Approximately 40% of leukoplakias exhibit keratinizing dysplasia (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2014;118:713)
- Remaining exhibit hyperkeratosis / parakeratosis characterized genomically by KMT2C, TP53, TIAM1 or other mutations (Oral Dis 2019;25:1707)
- Term leukoplakia / leukoplakic also used descriptively in clinical setting to denote any white lesion without a readily apparent diagnosis
- Such use may skew understanding of leukoplakia biology / behavior due to preponderance of frictional / reactive keratoses in oral cavity, which are not always recognizable clinically but have no malignant potential (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:423)
- Defined by WHO as a white plaque of questionable risk having excluded (other) known diseases or disorders that carry no increased risk for cancer (J Oral Pathol Med 2007;36:575)
- Leukoplakia may occur throughout the upper aerodigestive tract
Essential features
- Hyperkeratotic (white) plaque / patch of mucosa exhibiting clonality and representing precursor lesion to squamous cell carcinoma
- Approximately 40% of leukoplakias exhibit keratinizing dysplasia; the remainder are characterized by hyperkeratosis alone
- Annual malignant transformation rate is 3% and most strongly predicted by presence of dysplasia on biopsy; increasing duration, increasing size and nonhomogenous appearance also associated with malignant transformation
- Leukoplakia exhibiting hyperkeratosis that is not frictional / reactive exhibits a malignant transformation rate of approximately 5%, similar to that of mild epithelial dysplasia
- Histologic appearance of leukoplakia indistinguishable from proliferative (verrucous) leukoplakia and requires clinical correlation
- Surgical excision reduces risk of malignant transformation approximately 3 times
Terminology
- Leukoplasia, erythroleukoplakia, erythroplakia
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K13.21 - Leukoplakia of oral mucosa, including tongue
Epidemiology
- Worldwide prevalence approximately 0.5% (Oral Oncol 2003;39:770, Oral Oncol 2009;45:317)
- Characteristically a disease of older males (M:F = 3:1)
Sites
- May present on any mucosal surface
- Associated with highest incidences of malignant transformation when occurring on ventrolateral tongue or floor of mouth (Oral Oncol 2009;45:317)
Pathophysiology
- Leukoplakia exhibiting keratinizing dysplasia characterized by genomic alterations including TP53 mutations and loss of heterozygosity at 3p and 9p (Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2012;5:1081)
- Leukoplakia exhibiting hyperkeratosis alone characterized by genomic alterations including KMT2C, TP53 and TIAM1 mutations (Oral Dis 2019;25:1707)
- Genetic progression model of head and neck cancer not well worked out, particularly with regards to early precursor lesions (Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:347)
Etiology
- Associated with smoking / smokeless tobacco, alcohol and areca nut (betel quid) use
- HPV associated with only a very small percentage of cases (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1646)
Clinical features
- Hyperkeratosis on mucosal sites not amenable to frictional / factitial trauma, particularly when sharply demarcated, considered clinically concerning (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017;75:723)
- Biopsy proven leukoplakia may clinically appear homogenous or nonhomogenous (Oral Oncol 2009;45:317)
- Homogenous leukoplakia: uniformly thin or thick hyperkeratosis, frequently sharply demarcated
- Nonhomogenous leukoplakia: irregular texture with fissuring, nodular / verrucous components or erythematous components (erythroleukoplakia)
- Proliferative (verrucous) leukoplakia: uncommon and significantly more aggressive (60 - 100% malignant transformation rate) disease characterized by multifocal oral mucosal involvement and a predilection for middle aged / elderly females with no / minimal history of tobacco or alcohol exposure (Oral Dis 2018;24:749)
- Best considered a separate disease on the basis of differing demographic / clinical presentation, biologic behavior and patient management considerations
Diagnosis
- Biopsy required for diagnosis and risk stratification
- Leukoplakia with dysplasia readily diagnosed on basis of conventional histopathologic features of epithelial dysplasia (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:423)
- Leukoplakia without dysplasia requires clinicopathologic correlation and exclusion of frictional / factitial features as identified clinically or histopathologically
Prognostic factors
- Annual malignant transformation rate 3% (Oral Oncol 1998;34:270)
- Presence of epithelial dysplasia most significant risk factor for malignant transformation (Oral Oncol 2009;45:317, Mod Pathol 2017;30:S112)
- Severe epithelial dysplasia: 28.4% risk
- Moderate epithelial dysplasia: 22.5% risk
- Mild epithelial dysplasia: 5.7% risk
- Hyperkeratosis: 4.9% risk
- Reported overall malignant transformation rates of 0.36 - 34% difficult to interpret due to historical inclusion of frictional / reactive keratoses in leukoplakia cohorts and variability in followup duration (J Oral Pathol Med 2016;45:155)
- Length of duration, increasing size and nonhomogenous appearance associated with increased risk of malignant transformation
Case reports
- 21 year old man with amalgam associated leukoplakia (J Oral Sci 2016;58:445)
- 59 and 66 year old men with tongue leukoplakia and squamous cell carcinoma (Mol Med Rep 2017;16:6780)
- 75 year old man with tongue lesion (Cleve Clin J Med 2020;87:133)
Treatment
- Surgical excision results in 3 times reduction in risk of malignant transformation (Head Neck 2009;31:1600)
- Leukoplakia with high grade (moderate / severe) dysplasia should be excised whenever possible
- Close clinical observation may be appropriate for extensive leukoplakia or patients with comorbidities but otherwise appears to have a limited role when conservative surgical management is possible (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017;75:723)
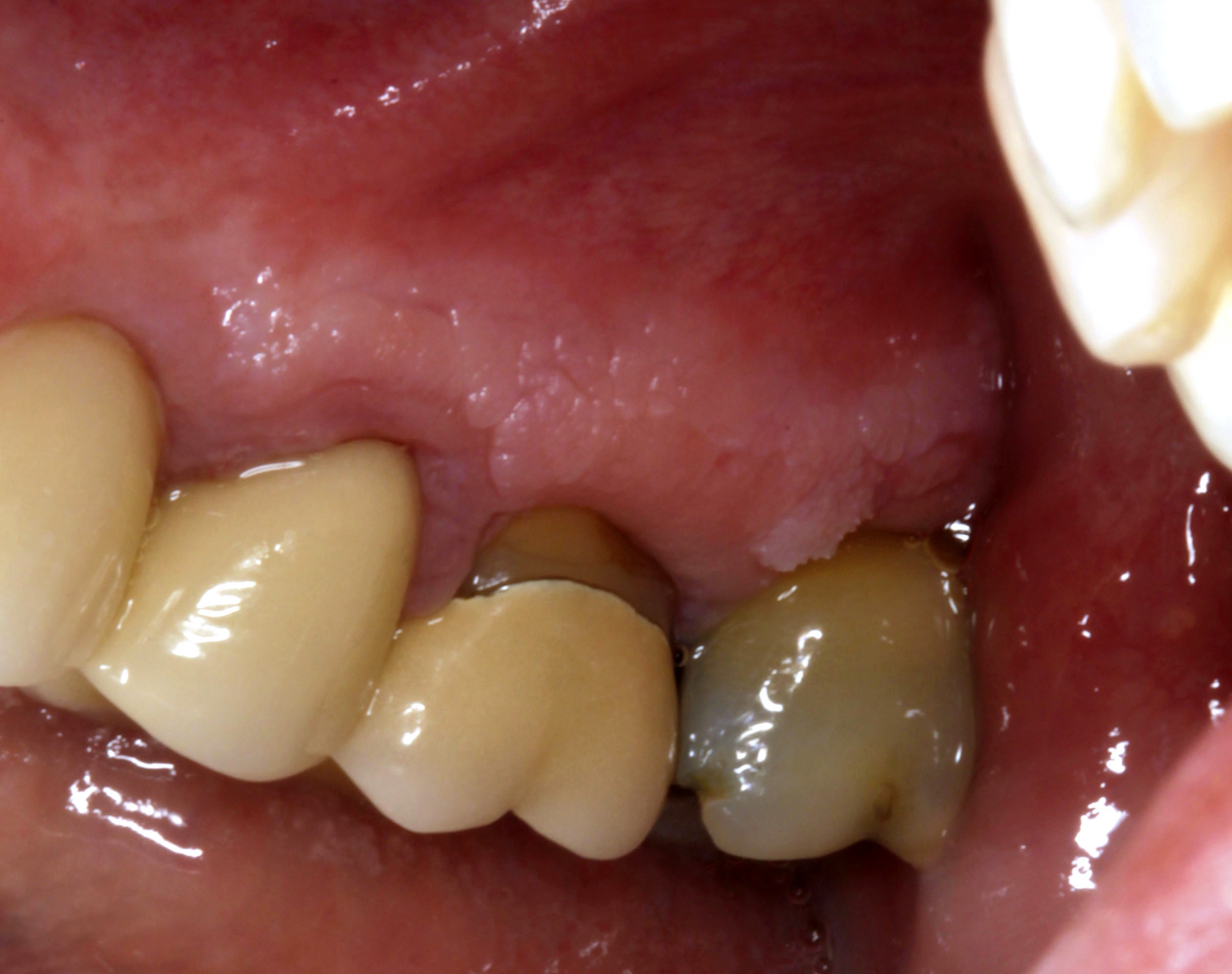
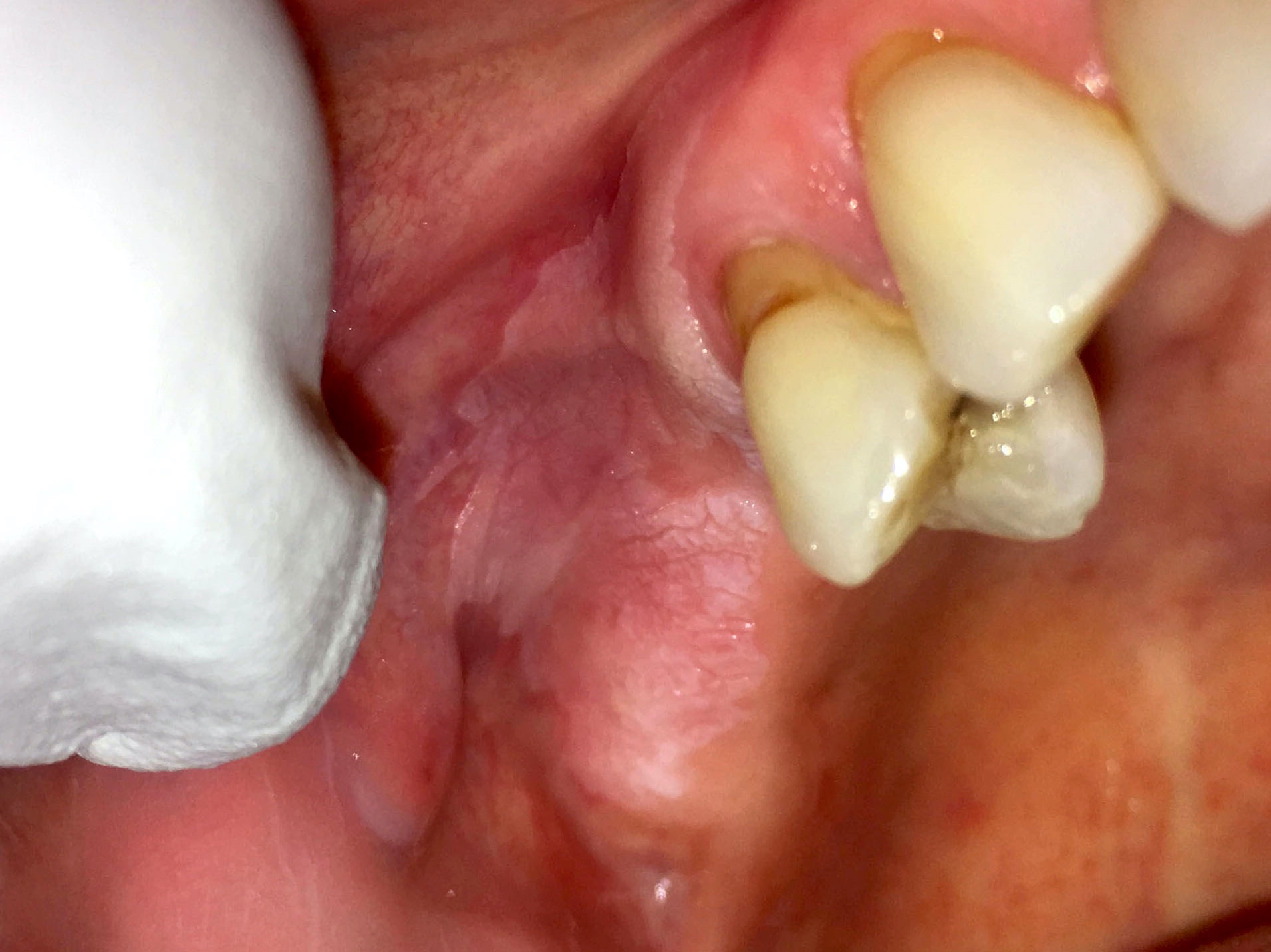
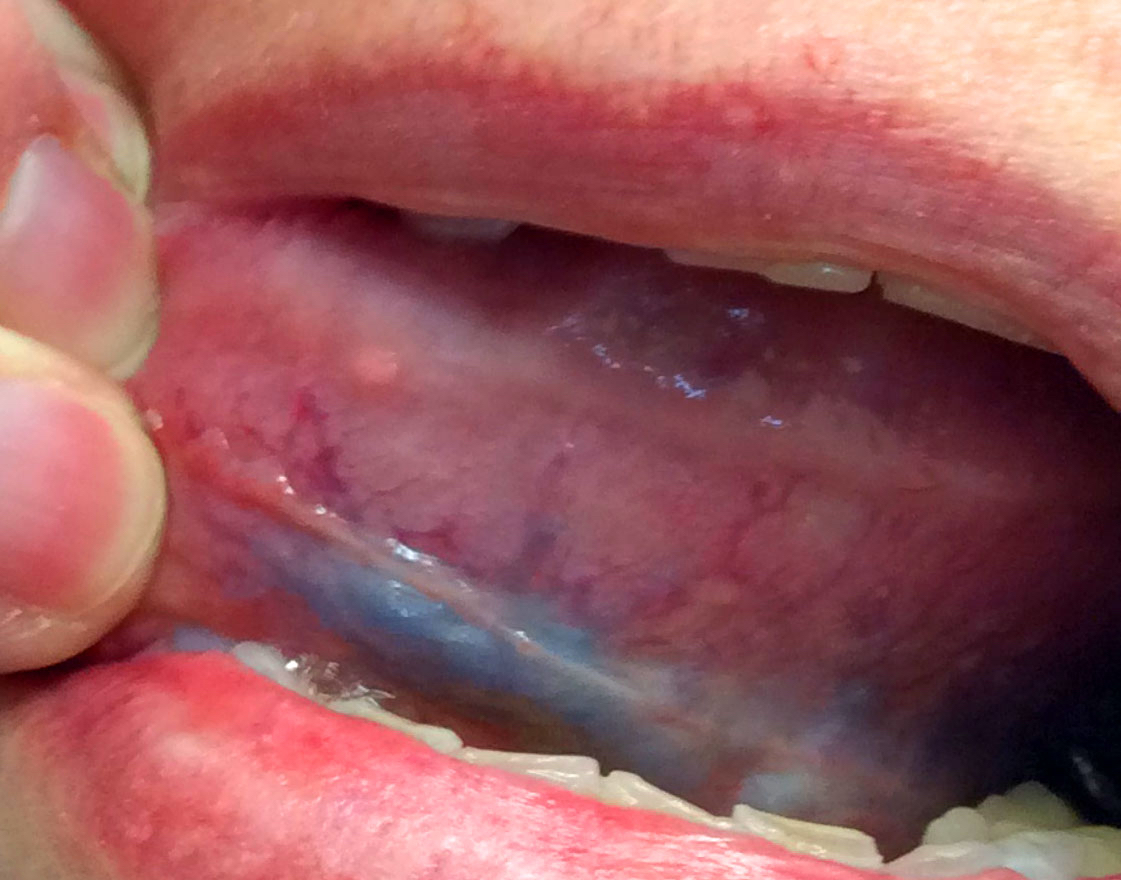
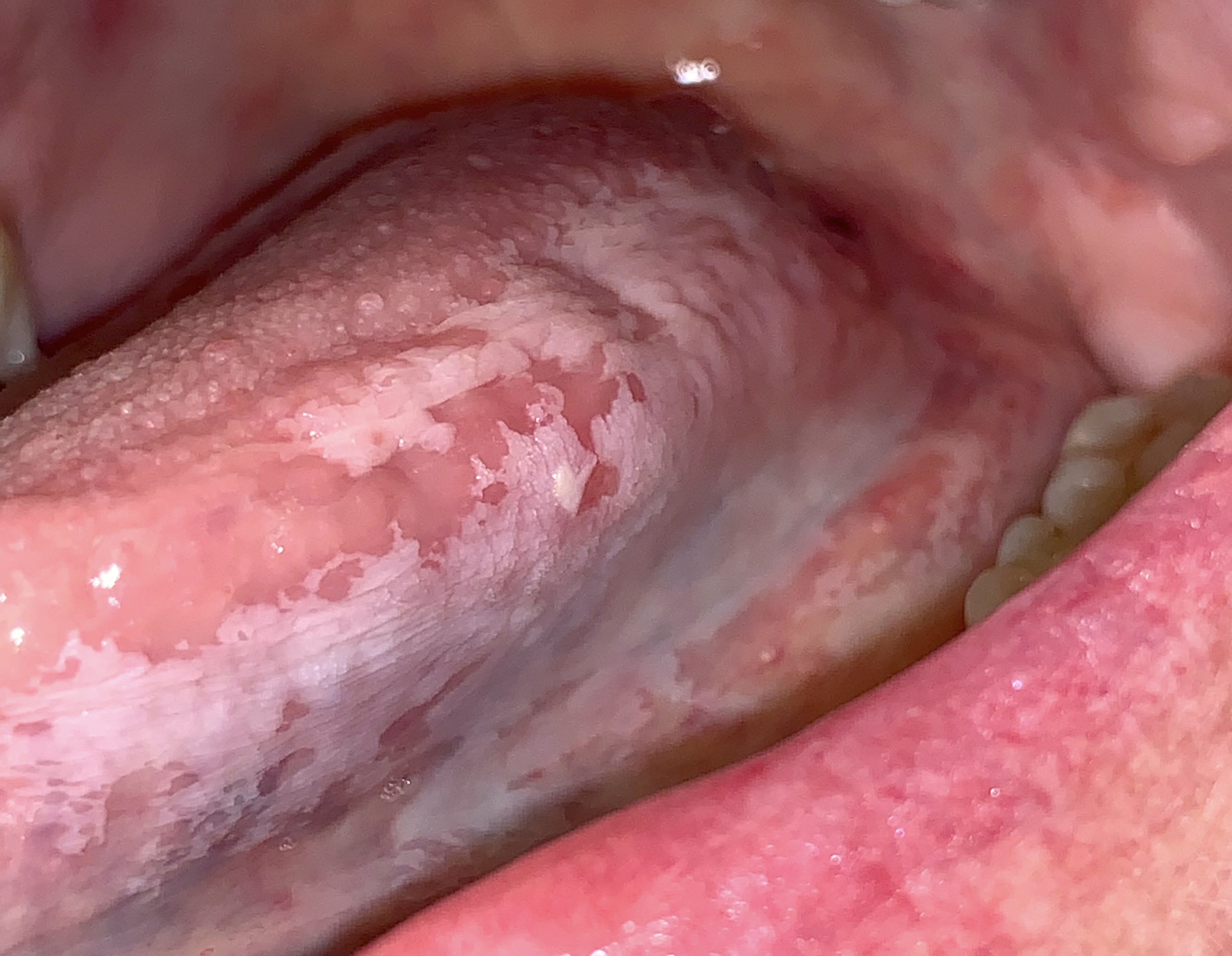
Clinical images
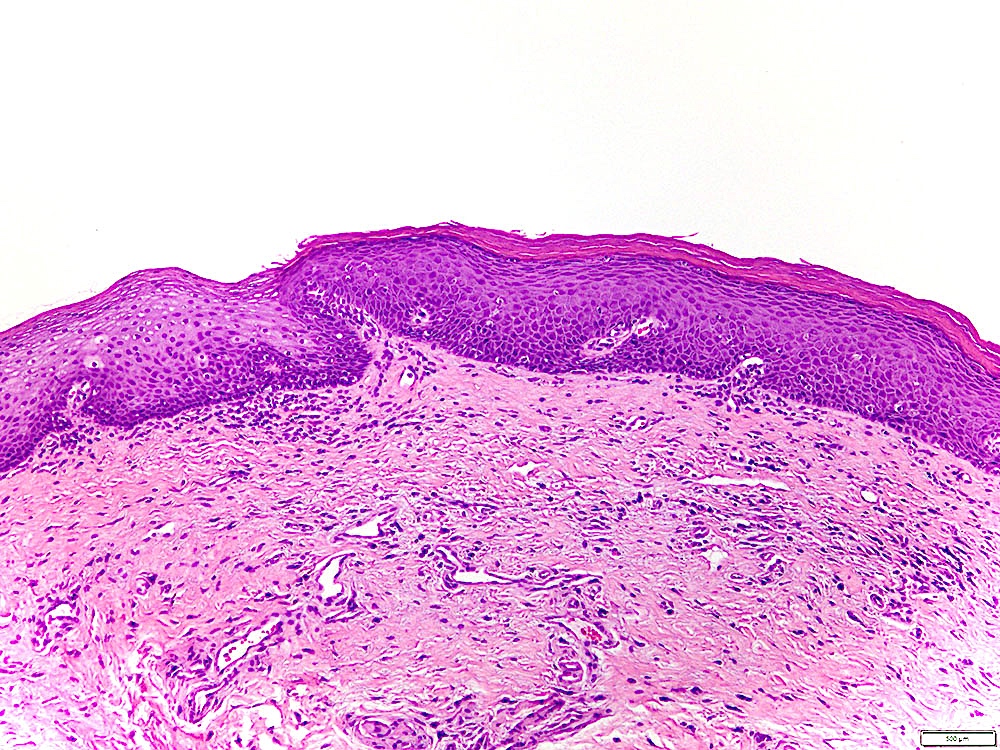
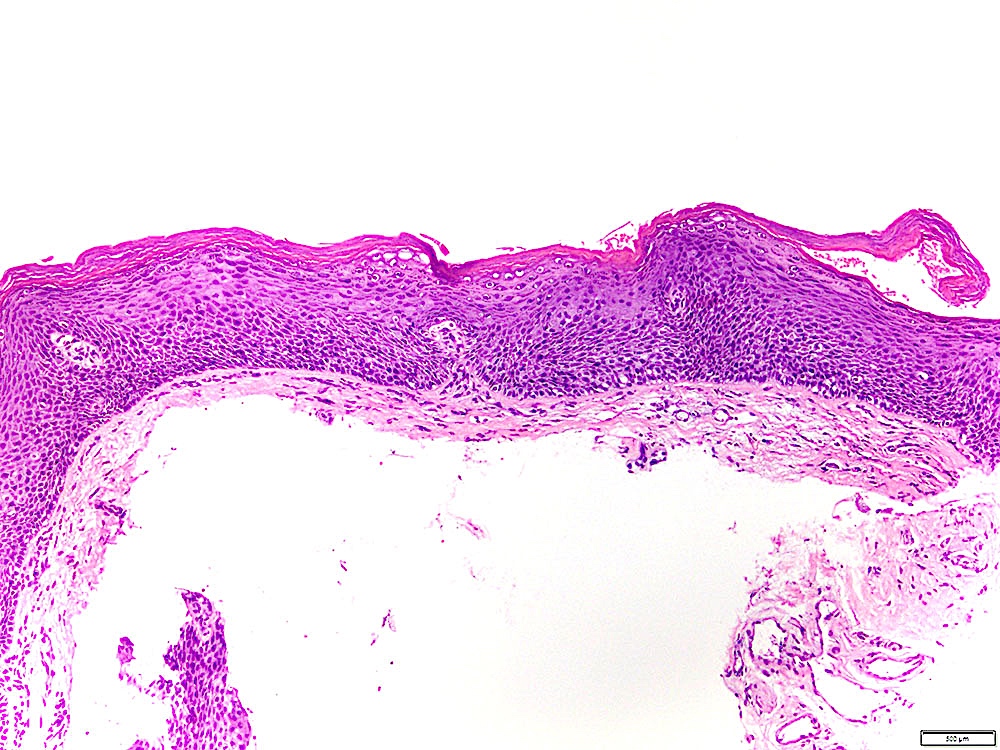
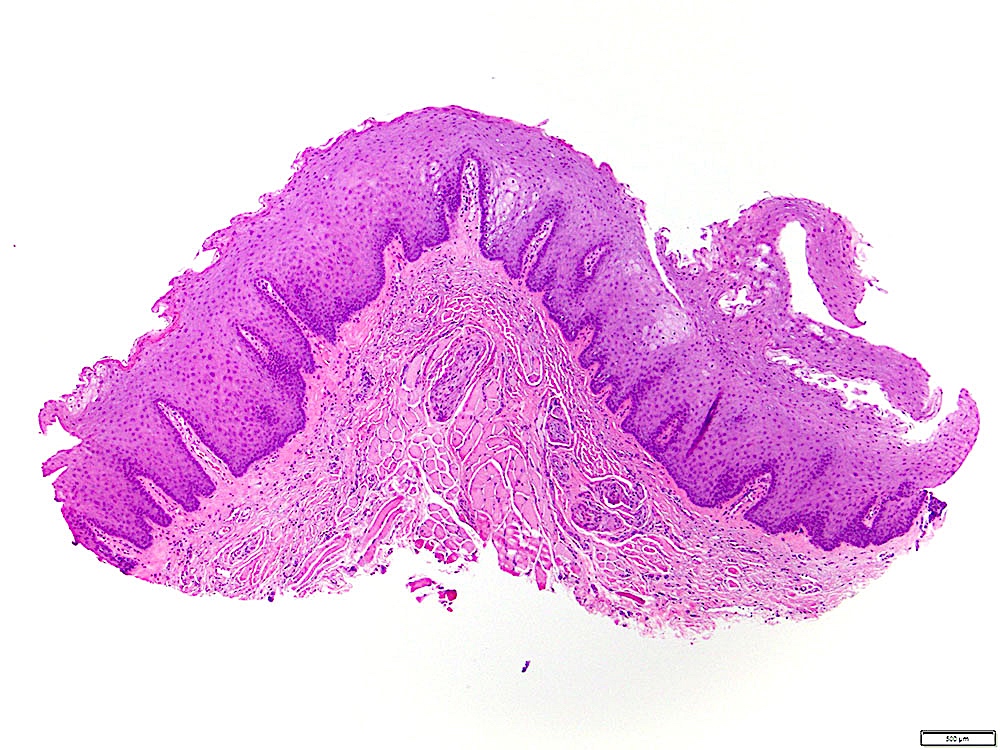
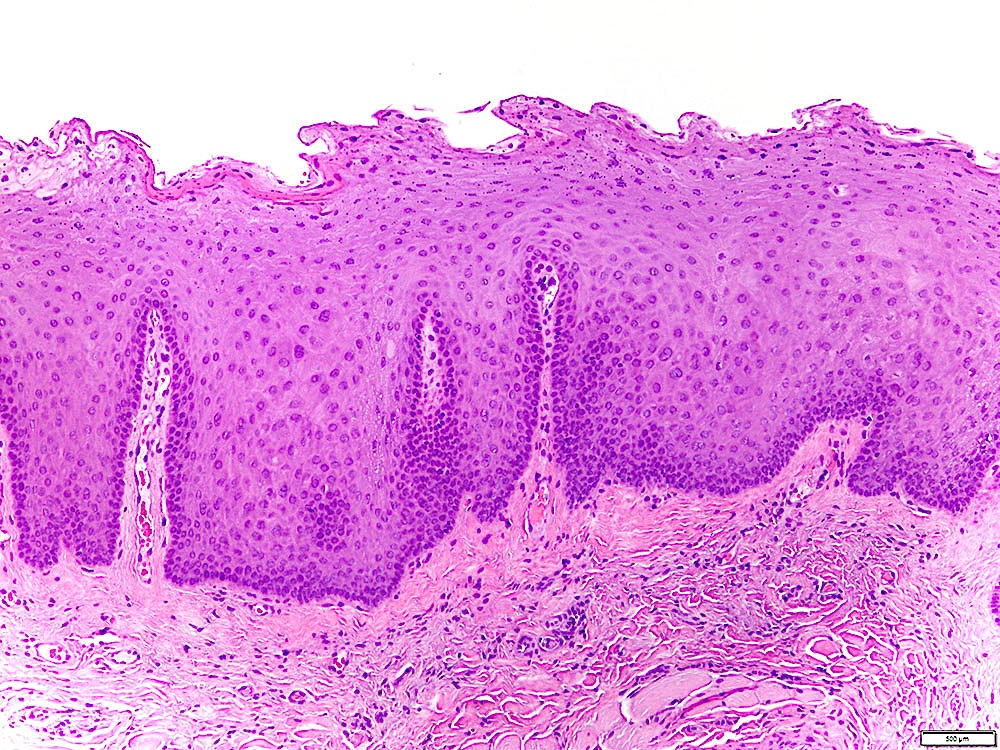
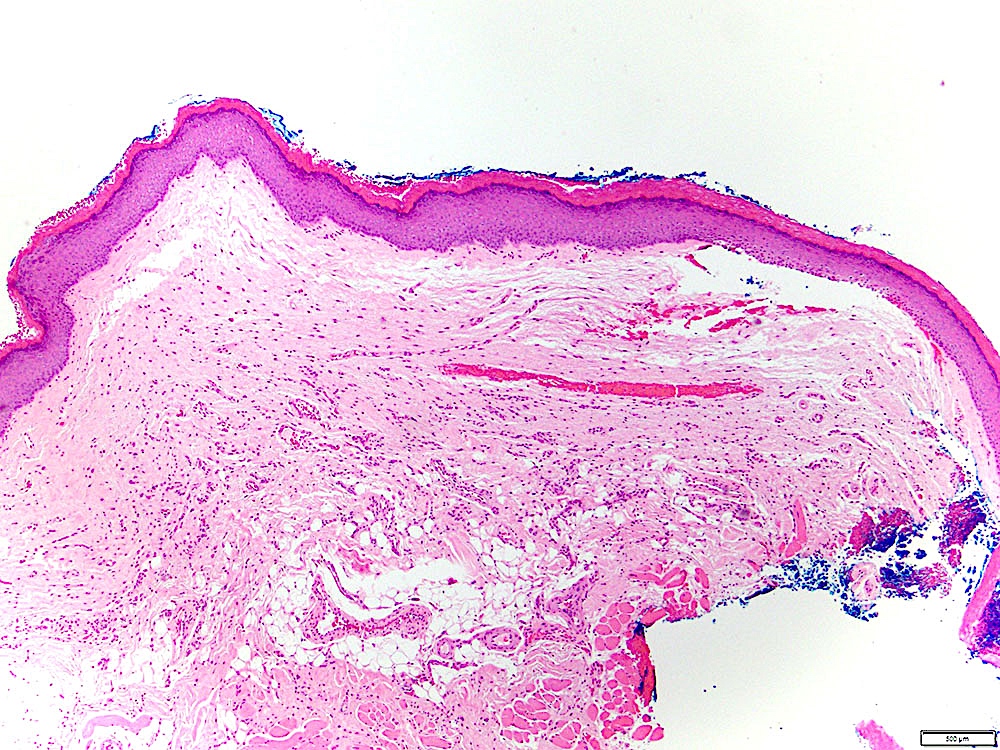
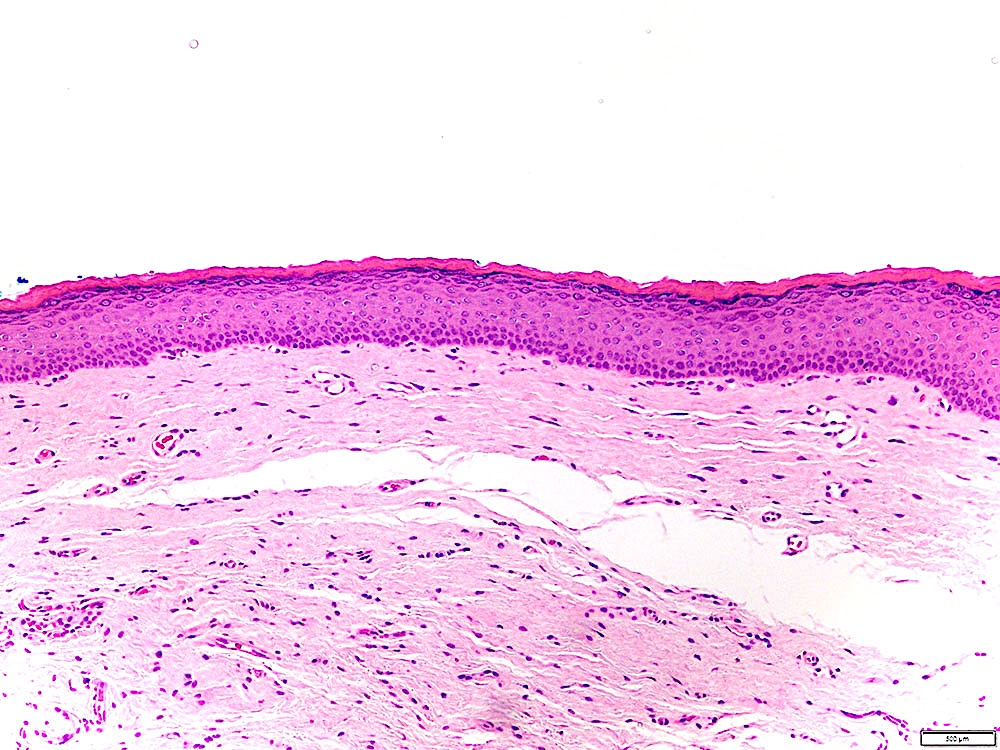
Microscopic (histologic) description
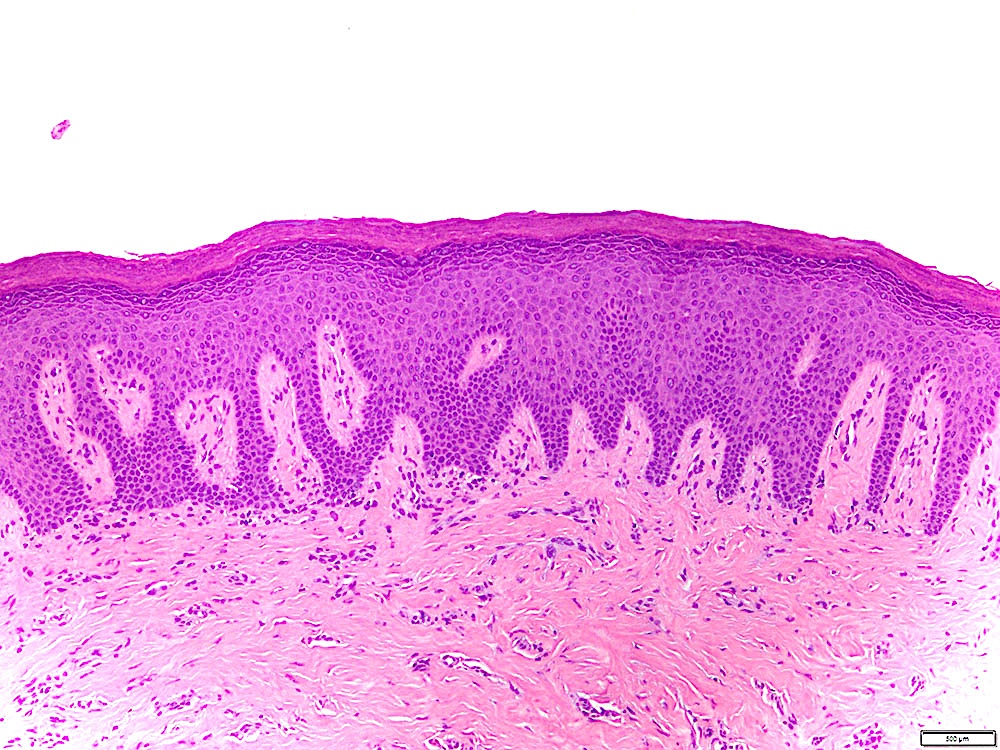
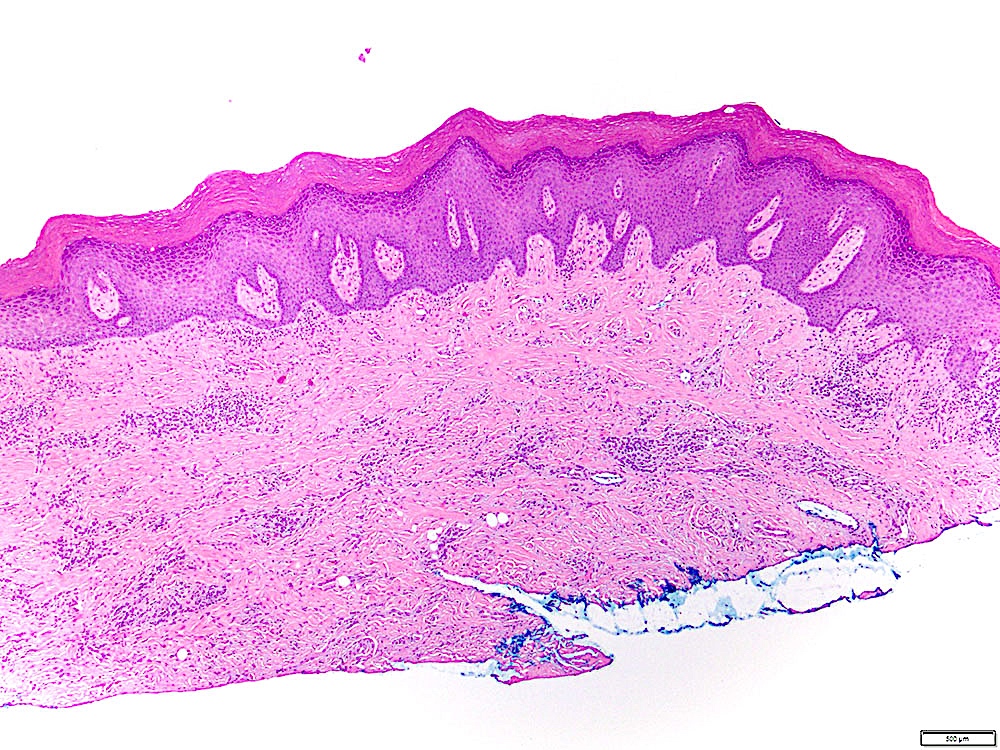
- Leukoplakia with dysplasia exhibits characteristic architectural and cytological features of keratinizing dysplasia
- Features include hyperkeratosis / parakeratosis, epithelial atrophy or hyperplasia with bulbous rete ridges, basal cell hyperplasia with nuclear hyperchromasia or increased nuclear cytoplasmic ratio, variable suprabasal or atypical mitoses, dyskeratosis or glassy cytoplasm, dyscohesion
- Approximately 33% of dysplasias are characterized by an inflammatory infiltrate and should not be misdiagnosed as lichen planus (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2014;117:511)
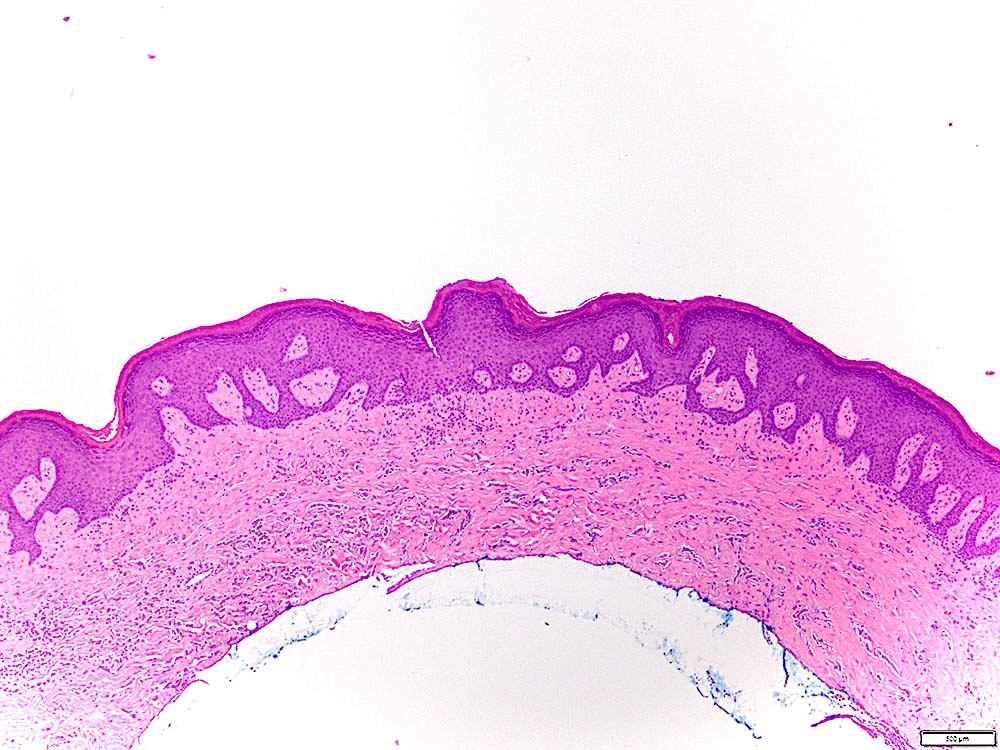
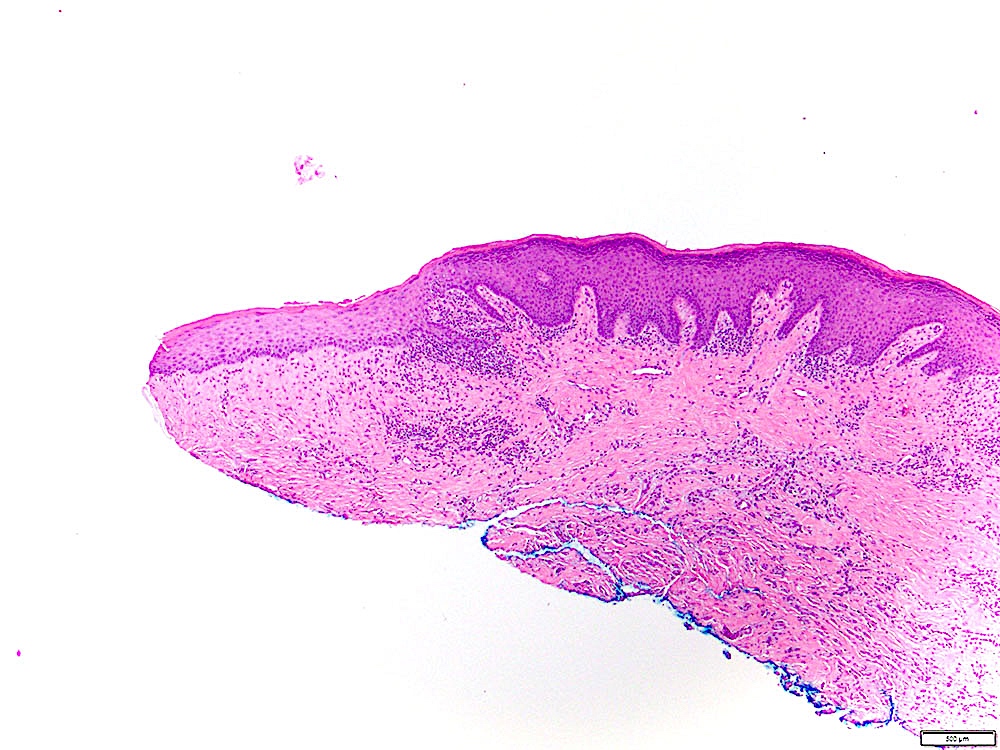
- Leukoplakia without dysplasia exhibits hyperkeratosis with no histologic features of a frictional / reactive process but is otherwise less well characterized
- Histologic features include (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:423):
- Compact hyperkeratosis with hypergranulosis
- Subtle verrucoid architecture
- Epithelial atrophy or hyperplasia
- If the periphery of the leukoplakia is sampled, hyperkeratosis will appear sharply demarcated
- Histologic features include (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:423):
- Some leukoplakias without dysplasia may exhibit prominent verrucous architecture and be reported as verrucous hyperplasia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Ivan J. Stojanov, D.M.D., M.M.Sc.
Cytology description
- Currently limited role for cytology:
- Difficulty sampling adequate tissue in unanaesthetized patients
- Epithelial atypia, if present, difficult to classify as reactive or dysplastic in absence of architectural features
- Patterns of keratinization cannot be assessed
- Oral cavity sites readily amenable to incisional biopsy
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- See Pathophysiology
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Mandible, gingiva, incisional biopsy:
- Hyperkeratosis, epithelial atrophy and mild chronic inflammation, not reactive (see comment)
- Comment: The hyperkeratosis exhibits no features of a frictional / reactive process and resembles the surface keratinization commonly seen in epithelial dysplasias. Cytologic atypia is minimal / absent in this specimen but leukoplakia without dysplasia (hyperkeratosis that is not reactive) has malignant transformation rates of approximately 5%, similar to that of leukoplakia with mild dysplasia. The findings are consistent with the clinically observed leukoplakia, which in approximately 60% of cases presents without dysplasia. If the clinical context is appropriate, proliferative (verrucous) leukoplakia may also be considered.
Differential diagnosis
- Benign alveolar ridge keratosis:
- Histologic features similar to lichen simplex chronicus
- Epithelial hyperplasia with verrucous / undulating surface and wedge shaped hypergranulosis
- Compact hyperkeratosis that tapers towards the edges and is not sharply demarcated
- Elongated rete ridges, occasionally confluent at tips
- No epithelial atypia
- Fibrosis and sparse chronic inflammation
- Chronic frictional / factitial keratosis:
- Shaggy / macerated parakeratosis with superficial bacterial colonization
- Epithelial hyperplasia with keratinocyte edema but no epithelial atypia
- Variable fibrosis, acute and chronic inflammation and leukocyte exocytosis
- Lichen planus / lichenoid mucositis:
- Squamatization / degeneration of the basal cell layer with Civatte bodies (dyskeratotic keratinocytes)
- Band-like lymphoplasmahistiocytic infiltrate in the superficial lamina propria with leukocyte exocytosis and spongiosis
- Proliferative (verrucous) leukoplakia:
- Characterized clinically by multifocal leukoplakia
- Gingival involvement common
- Predilection for middle aged / elderly females and with no / minimal tobacco or alcohol exposure
- Reason for this association is unclear
- Indistinguishable histologically from leukoplakia
- Verrucous epithelial architecture common but not necessarily present
- Characterized clinically by multifocal leukoplakia
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Which of the following is true regarding leukoplakia without dysplasia?
- It can be readily recognized by histologic features of a frictional / reactive process
- It can undergo malignant transformation
- It is usually associated with HPV infection
- It is diagnostic of proliferative (verrucous) leukoplakia
- It is rarely encountered in leukoplakia biopsies
Practice answer #2