23 July 2009 - Case #153
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
This case was contributed by Dr. Mowafak Hamodat, Eastern Health of Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, Canada.
Covance Expands Cytokeratin Antibody Portfolio
Covance's cytokeratin antibody portfolio now includes additional IVD labeled antibodies for IHC on formalin fixed paraffin embedded sections. The addition of these antibodies adds to Covance's growing portfolio of antibodies, detection chemistries and ancillaries for anatomic pathology.
Visit our website at www.covance.com to view our cytokeratin portfolio or call 800.223.0796 for more information.
Advertisement
Case #153
Clinical history:
A 34 year old woman presented with a history of indurated papular lesions on her hands and face. The lesions were red-blue and located around the nail folds, on the dorsum of the fingers and around the mucosal surface on her face.
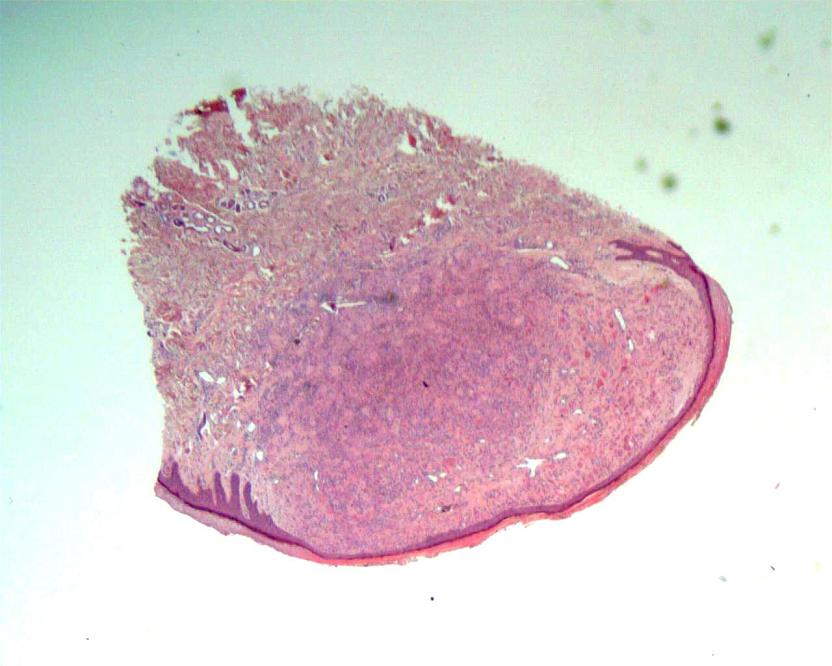
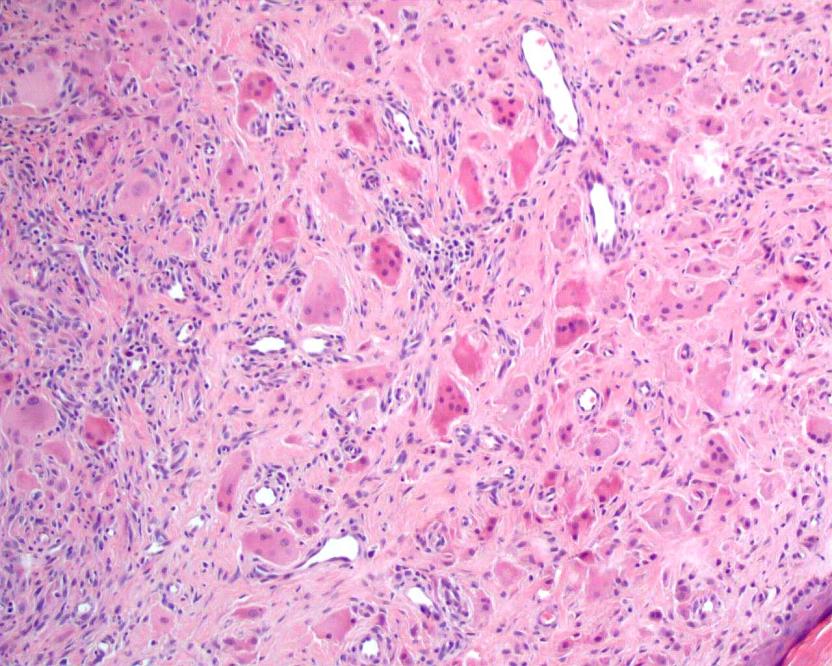
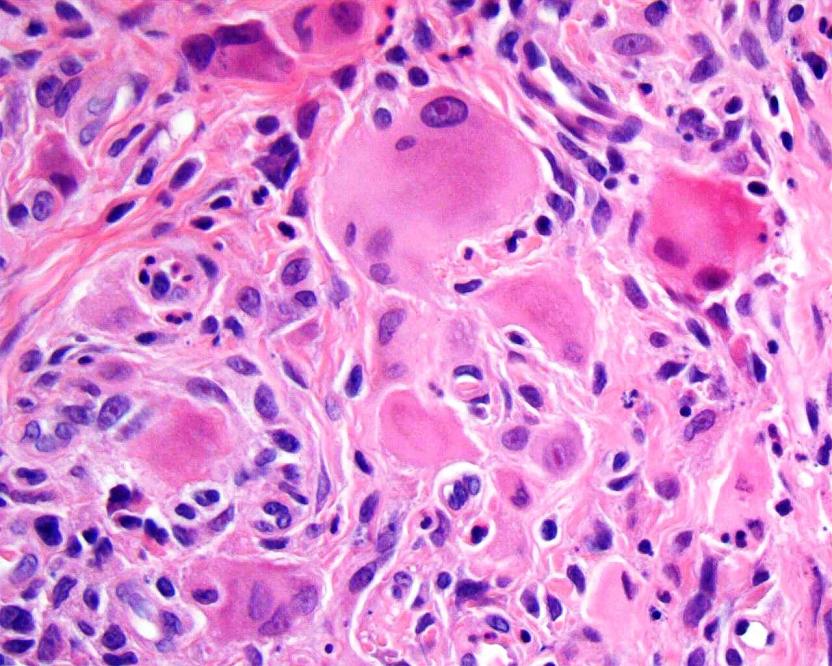
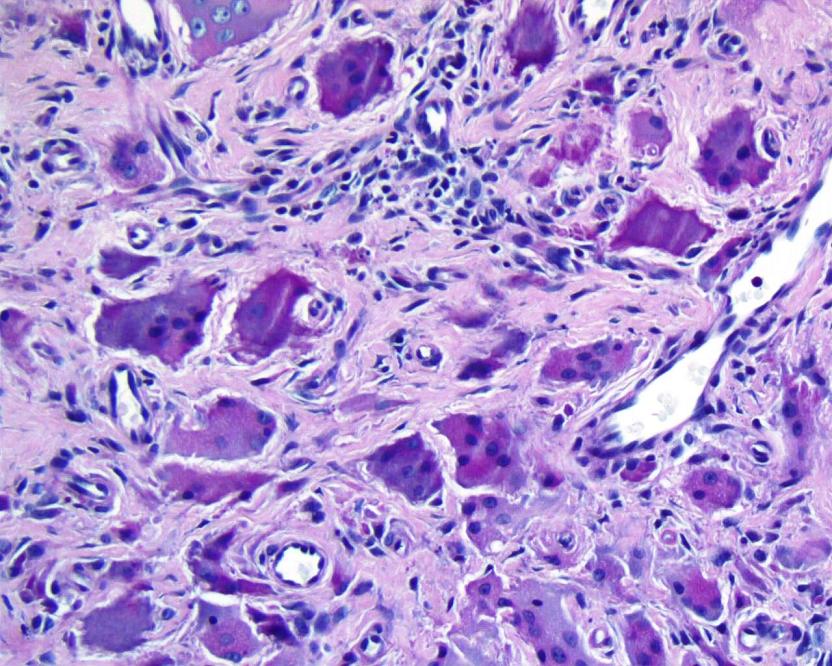
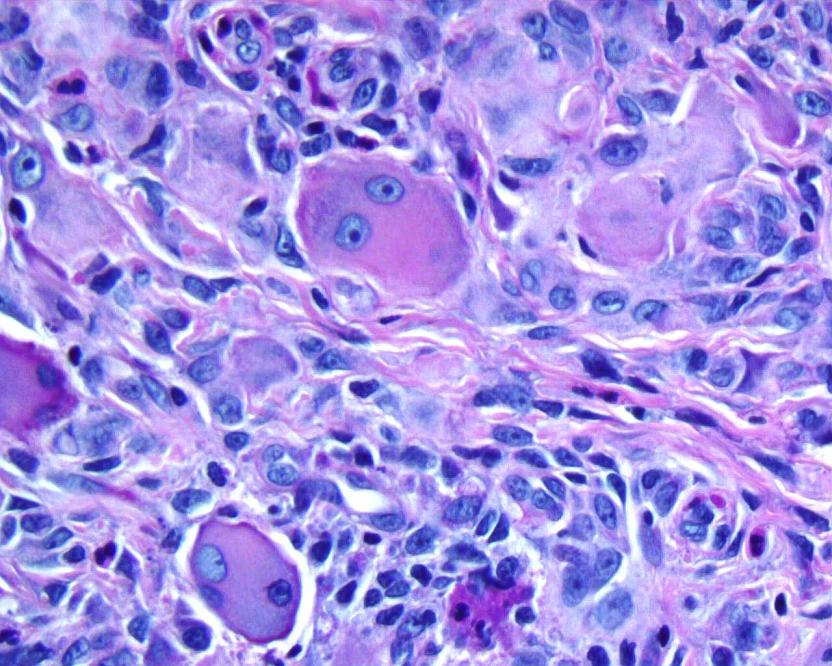
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis
Immunostains:
Discussion:
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH) is a rare disorder of histiocytes associated with destructive arthritis (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:687). In 28% of cases, it presents with a neoplasm and when malignancy is present, MRH precedes the development of cancer in 73% of cases (Med Pediatr Oncol 1985;13:273). MRH may be a paraneoplastic process or the association may be simply due to reporting bias (J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;39:864, eMedicine: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis [Accessed 29 April 2024]).
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis typically affects women 40 - 50 years but it has also been diagnosed in a 6 year old girl (J Rheumatol 1998;25:794). It is characterized by skin lesions on the hands, especially at the base of the nails (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:1102. Lesions may also appear on the face, ears, arms, scalp or mucosal surfaces. The lesions vary from small papules to lesions several centimeters across, and are usually skin colored, yellow or red-brown.
On histologic examination, there are prominent oncocytic histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells, which have eosinophilic, ground glass cytoplasm (Dermatology 2007;214:268, Clin Exp Dermatol 2004;29:373). The histiocytes and giant cells are positive for vimentin, CD68, CD45 and PAS, as well as CD163 and lysozyme. They are negative for S100, desmin, muscle specific actin and CD34 (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2001;15:524, Skinmed 2004;4:71). These findings are similar to those in solitary reticulohistiocytoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:521).
The differential diagnosis includes these other histiocytic disorders, which usually have a different clinical presentation:
There is no consistently reliable treatment, although TNF inhibitors, aminobisphosphonates and immunosuppressive drugs have been effective in individual cases but not consistently (Arch Dermatol 2008;144:1360, Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:3538, Dermatol Online J 2009;15:2, Ryumachi 1993;33:68).
References: Rheumatology 2008;47:1102, eMedicine: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis [Accessed 29 April 2024]
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
This case was contributed by Dr. Mowafak Hamodat, Eastern Health of Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, Canada.

Covance's cytokeratin antibody portfolio now includes additional IVD labeled antibodies for IHC on formalin fixed paraffin embedded sections. The addition of these antibodies adds to Covance's growing portfolio of antibodies, detection chemistries and ancillaries for anatomic pathology.
Visit our website at www.covance.com to view our cytokeratin portfolio or call 800.223.0796 for more information.
Case #153
Clinical history:
A 34 year old woman presented with a history of indurated papular lesions on her hands and face. The lesions were red-blue and located around the nail folds, on the dorsum of the fingers and around the mucosal surface on her face.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Click here for diagnosis and discussion:
Diagnosis: Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis
Immunostains:
Discussion:
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH) is a rare disorder of histiocytes associated with destructive arthritis (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:687). In 28% of cases, it presents with a neoplasm and when malignancy is present, MRH precedes the development of cancer in 73% of cases (Med Pediatr Oncol 1985;13:273). MRH may be a paraneoplastic process or the association may be simply due to reporting bias (J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;39:864, eMedicine: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis [Accessed 29 April 2024]).
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis typically affects women 40 - 50 years but it has also been diagnosed in a 6 year old girl (J Rheumatol 1998;25:794). It is characterized by skin lesions on the hands, especially at the base of the nails (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:1102. Lesions may also appear on the face, ears, arms, scalp or mucosal surfaces. The lesions vary from small papules to lesions several centimeters across, and are usually skin colored, yellow or red-brown.
On histologic examination, there are prominent oncocytic histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells, which have eosinophilic, ground glass cytoplasm (Dermatology 2007;214:268, Clin Exp Dermatol 2004;29:373). The histiocytes and giant cells are positive for vimentin, CD68, CD45 and PAS, as well as CD163 and lysozyme. They are negative for S100, desmin, muscle specific actin and CD34 (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2001;15:524, Skinmed 2004;4:71). These findings are similar to those in solitary reticulohistiocytoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:521).
The differential diagnosis includes these other histiocytic disorders, which usually have a different clinical presentation:
- Epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma: usually < 1 cm on extremities, usually no giant cells, primarily myofibroblastic, not histiocytic
- Epithelioid sarcoma: deep seated tumor with markedly atypical cells that form granuloma-like clusters with central necrosis; tumor cells are EMA+, keratin+, CD68-
- Granulomatous inflammation: well formed granulomas and prominent lymphocytes, no large epithelioid histiocytes with eosinophilic glassy cytoplasm
- Histiocytic sarcoma: typically forms a large mass of epithelioid histiocytes with significant nuclear atypia and mitotic activity
- Juvenile xanthogranuloma: usually children, has scattered Touton type histiocytic giant cells and numerous eosinophils but large epithelioid histiocytes are not prominent
- Rosai-Dorfman disease: associated with adenopathy; histiocytes are pleomorphic and S100+ and are associated with emperipolesis, B cells and plasma cells
There is no consistently reliable treatment, although TNF inhibitors, aminobisphosphonates and immunosuppressive drugs have been effective in individual cases but not consistently (Arch Dermatol 2008;144:1360, Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:3538, Dermatol Online J 2009;15:2, Ryumachi 1993;33:68).
References: Rheumatology 2008;47:1102, eMedicine: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis [Accessed 29 April 2024]