Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Poorly differentiated variant (including osteoclast rich giant cells). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderundifferentiatedosteoclast.html. Accessed August 29th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Extremely rare variant of high-grade urothelial carcinoma with an aggressive behavior and poor outcome
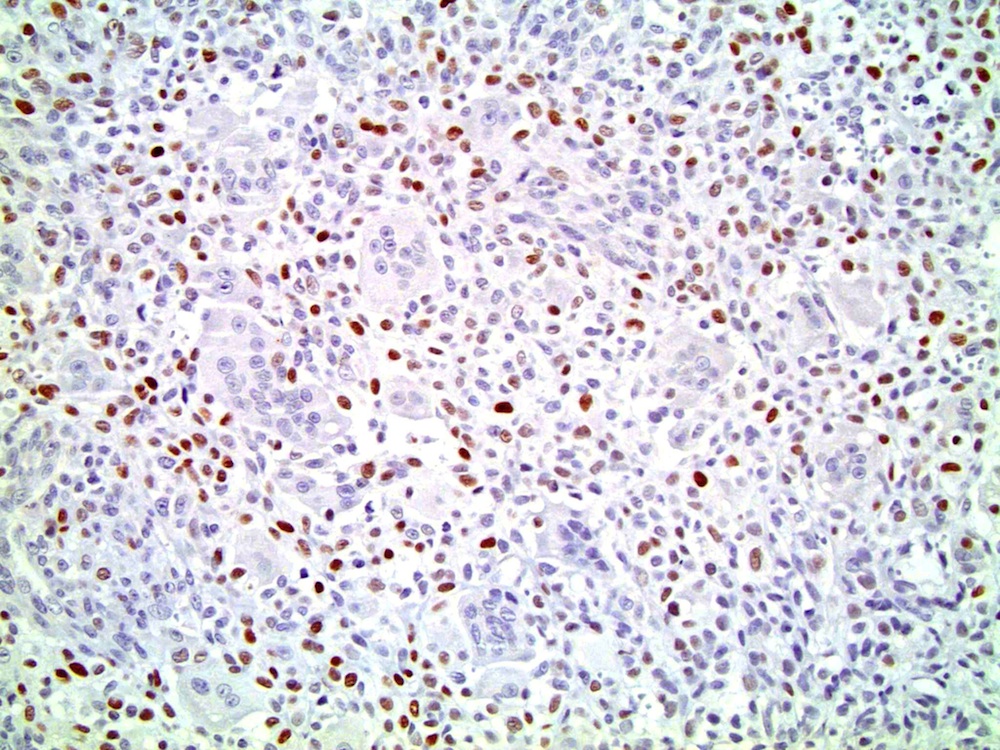
- Composed of a mixture of undifferentiated mononuclear carcinoma cells and osteoclast-like reactive giant cells (Mod Pathol 2006;19:161)
Epidemiology
- Mostly men in their 7th to 9th decade of life
Clinical features
- Usually gross hematuria, may present with flank pain, renal colic and dysuria
Case reports
- 63 year old man with gross hematuria (Diagn Cytopathol 2010;38:364)
- 69 year old man with bladder biopsy for gross hematuria (Case of the Week #339)
- 74 year old man (Cytojournal 2010;7:18)
- 76 year old man with tumor of distal ureter (Korean J Urol 2011;52:68)
Microscopic (histologic) description
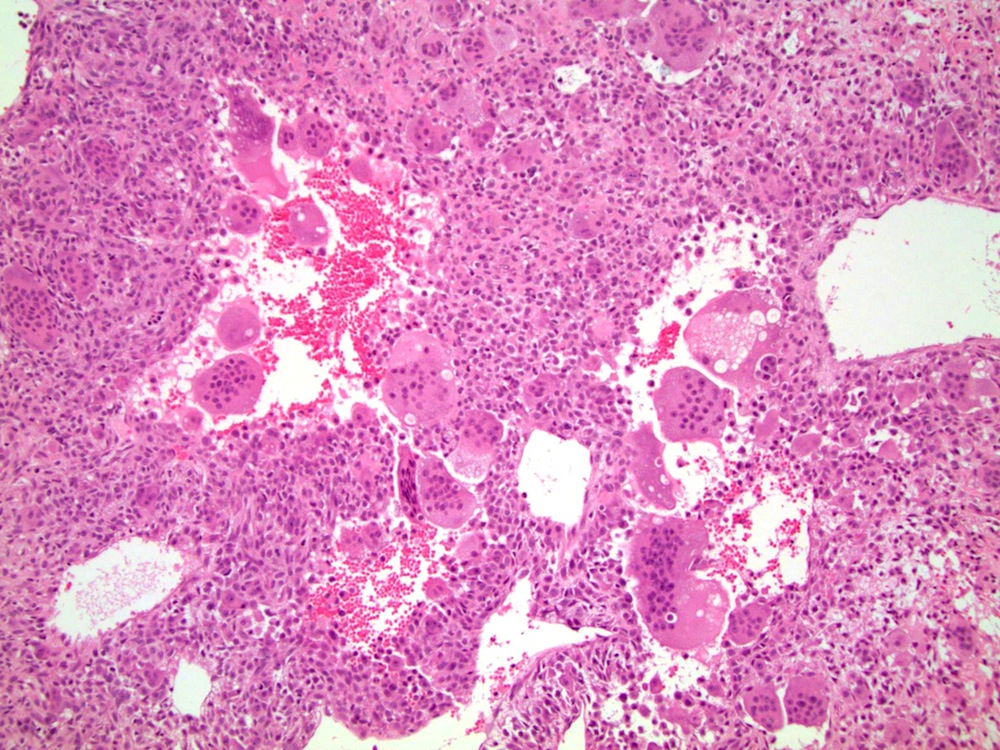
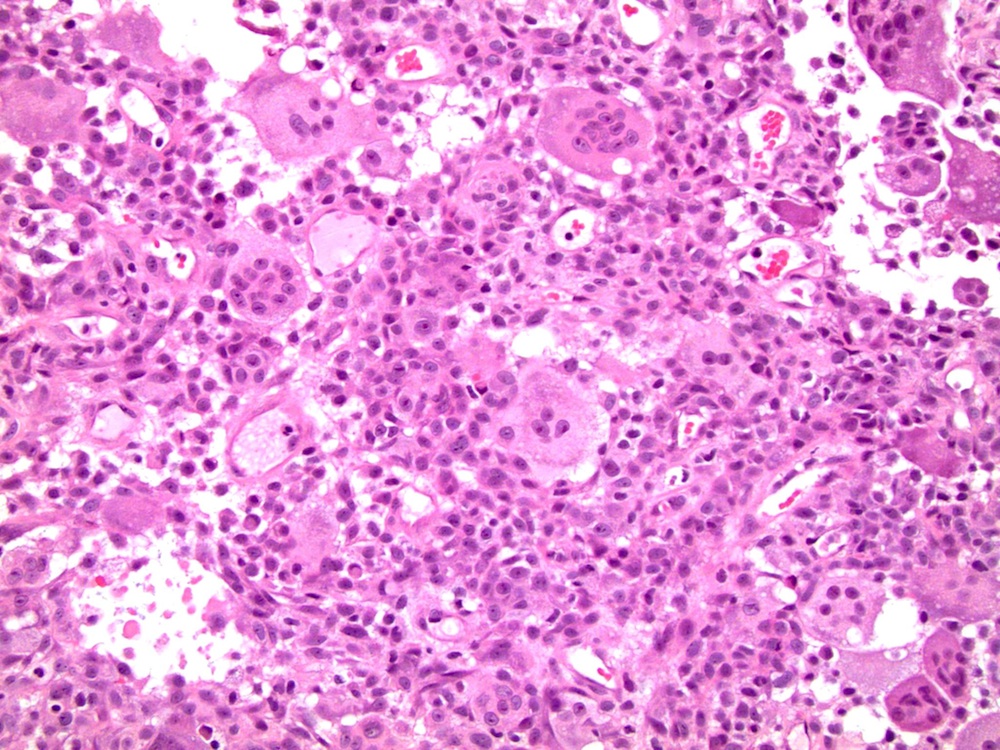
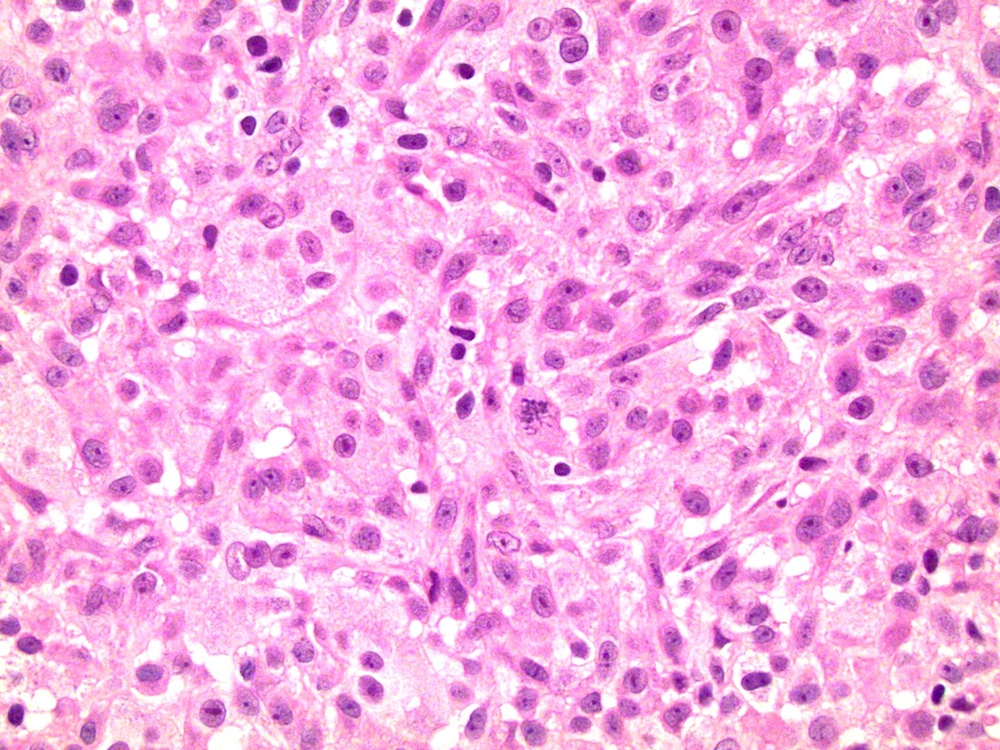
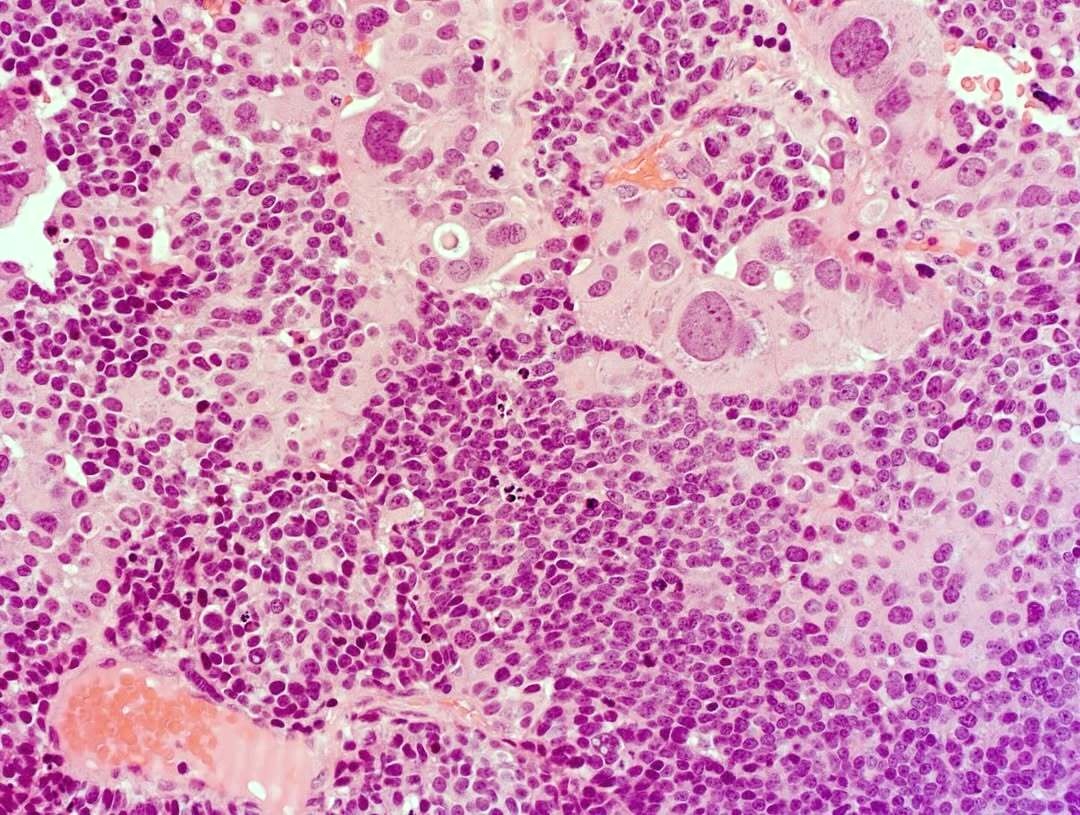
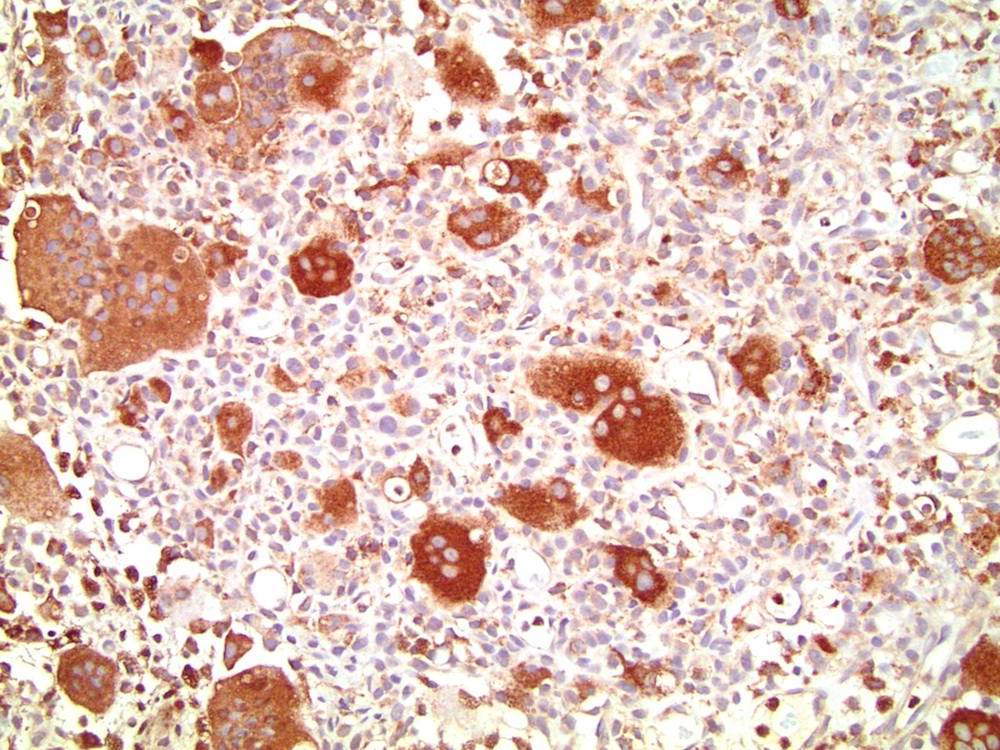
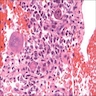
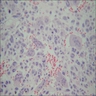
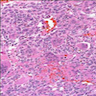
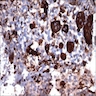
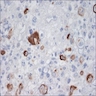
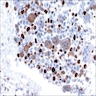
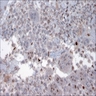
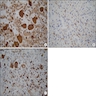
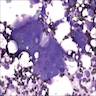
- Composed of a mixture of mononuclear malignant epithelial cells and multinucleated osteoclast-like reactive giant cells
- Mononuclear cells have abundant cytoplasm, round to oval vesicular nuclei, mild atypia and variable mitotic activity
- The giant cells are morphologically and immunohistochemically identical to osteoclasts and are regarded as being of histiocytic origin; are cytologically bland, may exhibit phagocytic activity but no mitotic activity; are generally evenly distributed among mononuclear cells but may condense around hemorrhagic foci
Microscopic (histologic) images
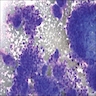
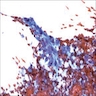
Positive stains
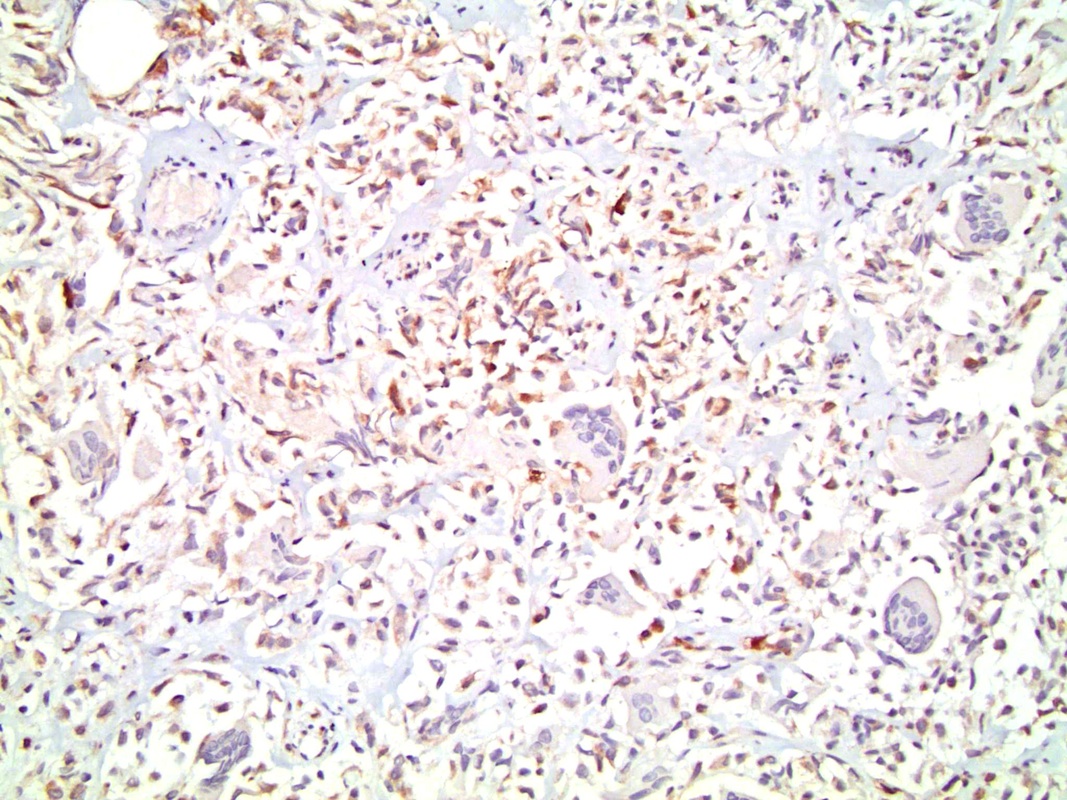
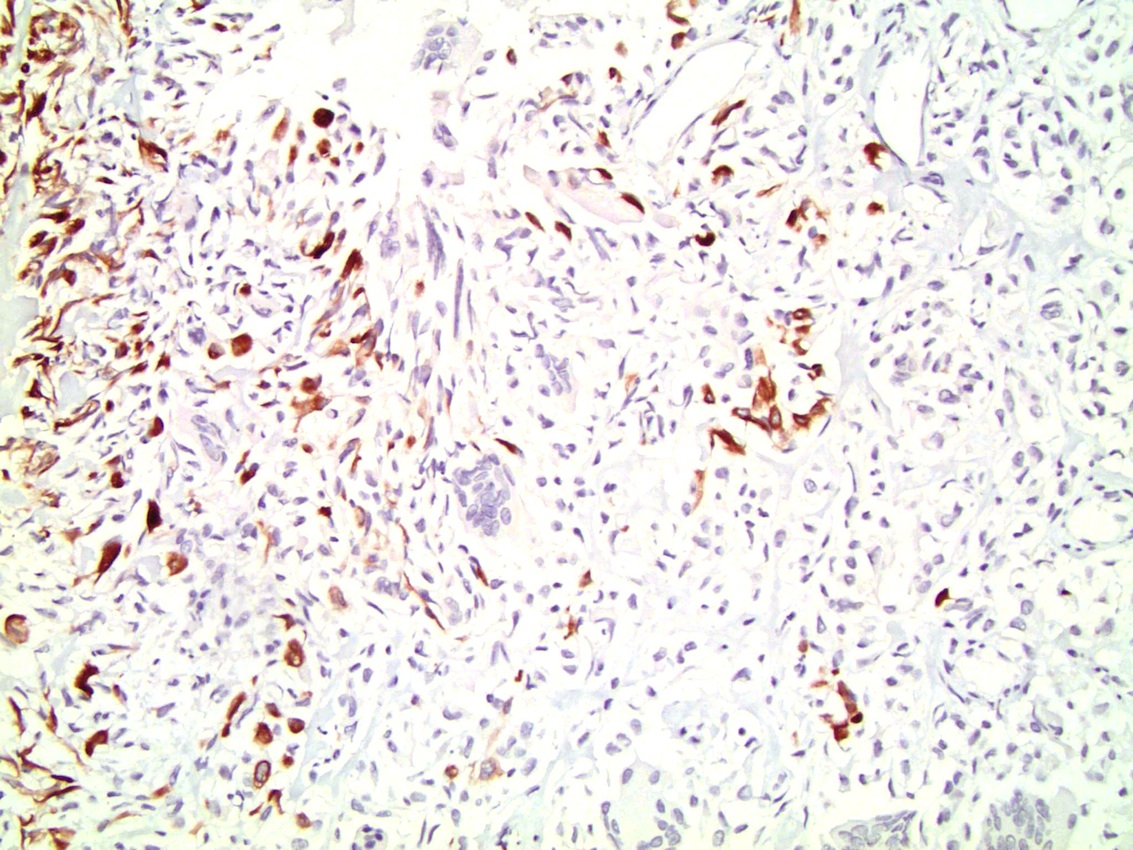
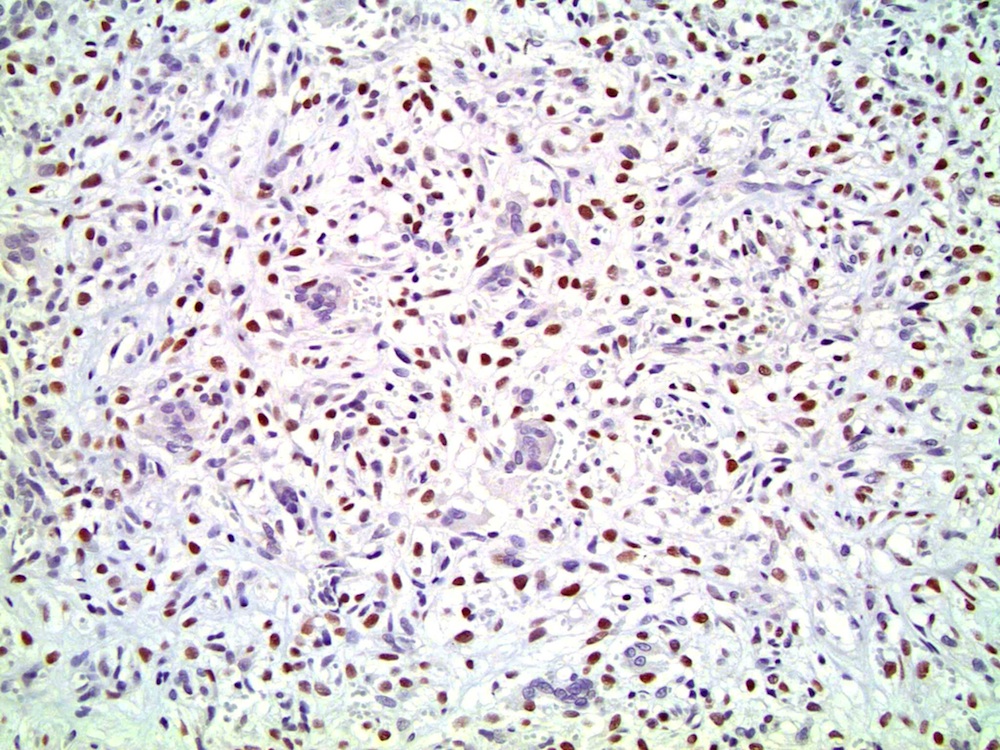
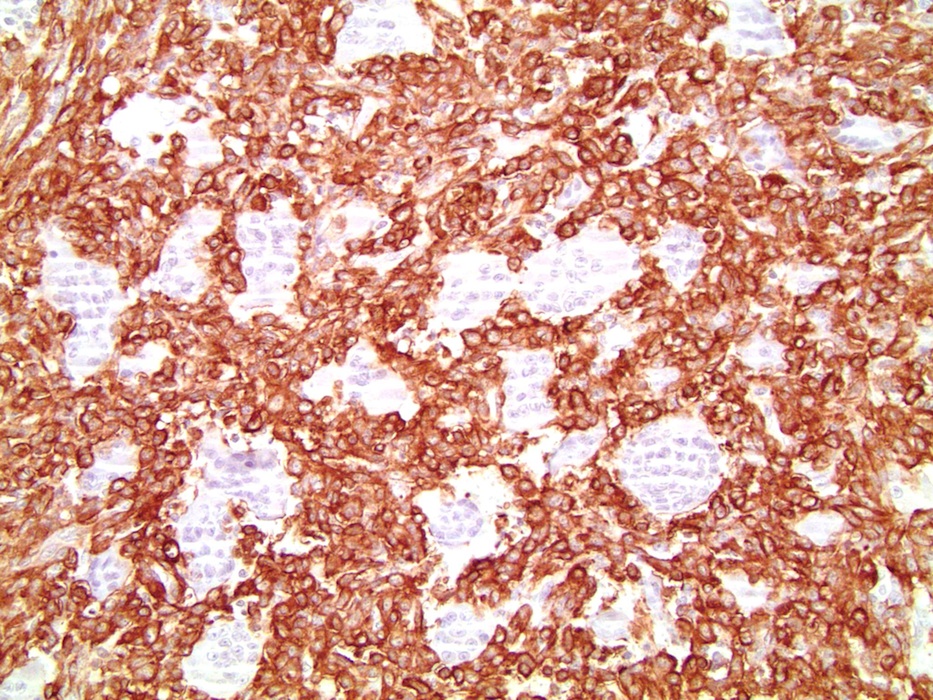
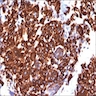
- Mononuclear cells: cytokeratin+, EMA+, vimentin+, Ki67+ , p53+
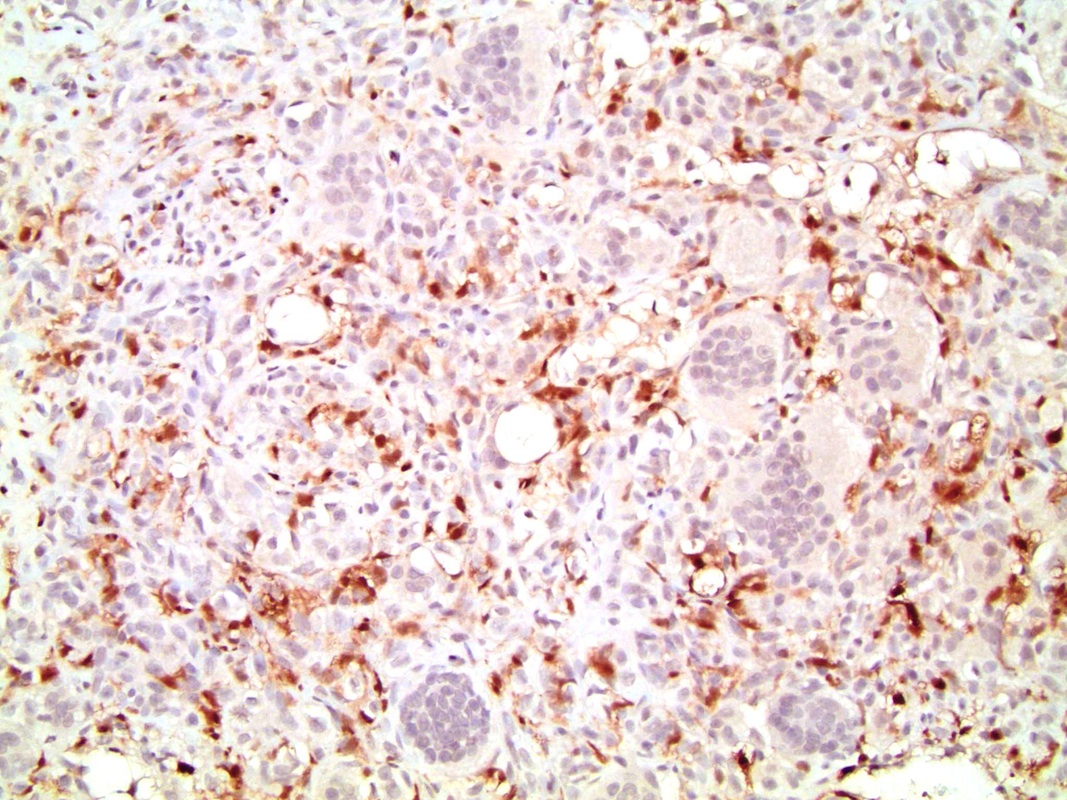
- Giant cells: CD68+, alpha-1 antitrypsin+, acid phosphatase+, vimentin+, CD51+, CD54+; cytokeratin-, EMA-, Ki67-, p53-
Differential diagnosis
- Giant cell carcinoma: obvious malignant bizarre giant cells, mitotic activity, invasion, positive staining for epithelial markers
- Foreign-body type giant cell reaction: inflammatory infiltrate, no atypia, no invasion