Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Alkhateeb KJ, Salih ZT. HSIL / CIN II / CIN III. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cervixhsilciniii.html. Accessed September 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Precancerous squamous proliferative lesion with full thickness nuclear atypia and varying degrees of cytoplasmic maturation
- Driven by high risk (HR) HPV subtypes
Essential features
- High risk (HR) HPV driven precancerous lesion (HPV 16 most common)
- CIN II: superficial cytoplasmic maturation; high rate of regression
- CIN III: marked full thickness atypia and loss of maturation; carries highest risk of progression to invasive squamous cell carcinoma
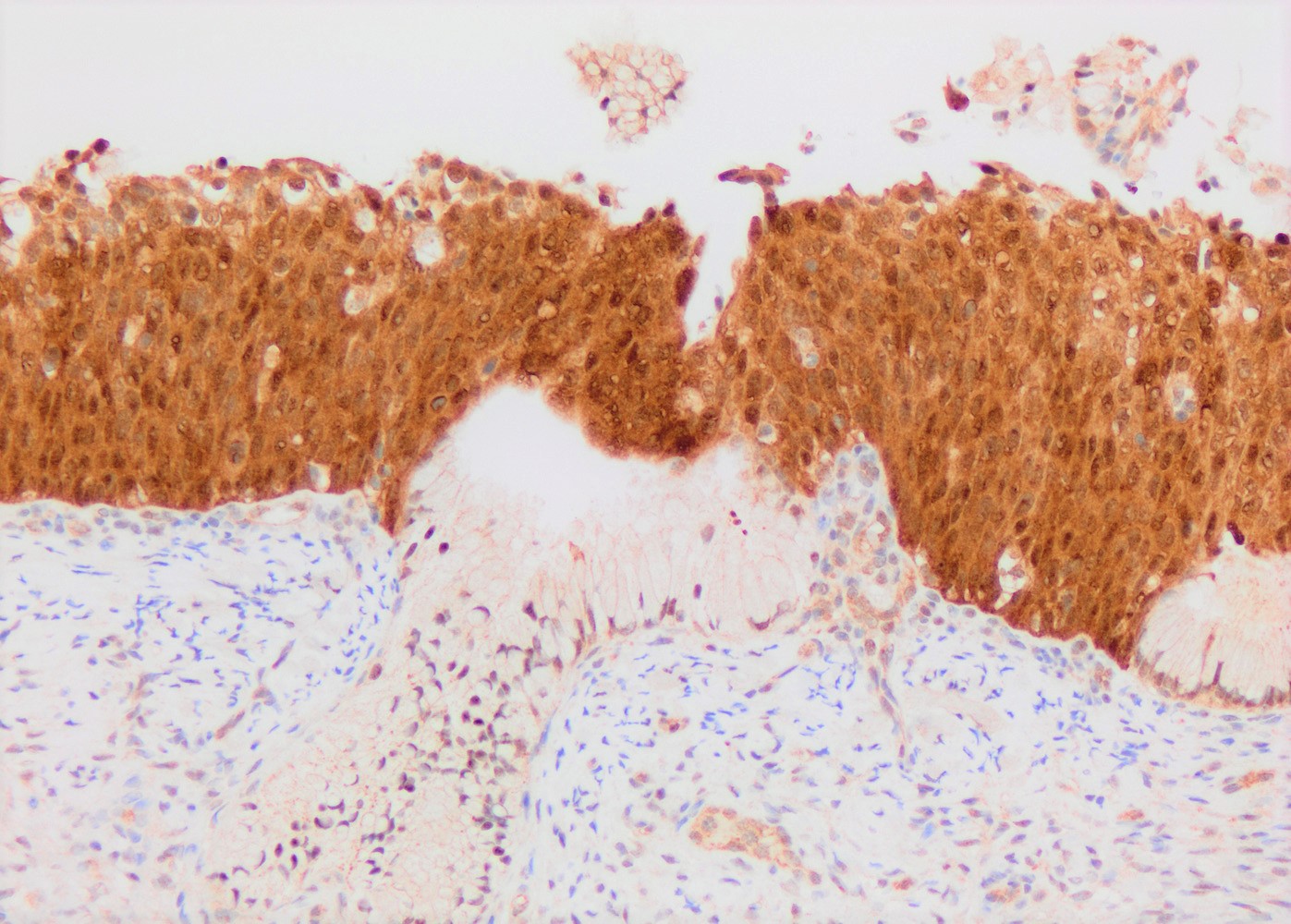
- p16: diffuse and strong nuclear and cytoplasmic reactivity (block type staining); improper use / interpretation may lead to overdiagnosis of HSIL
- Surgical excision is the treatment of choice, except during pregnancy or CIN II in females < 25 years old
Terminology
- Two tier grading is preferred: low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) / high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)
- HSIL may be subdivided into cervical intraepithelial neoplasia II (CIN II) and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia III (CIN III), particularly in young women (significantly higher regression rate in the former)
- CIN II: cytoplasmic maturation in the upper third of mucosa
- CIN III: diffuse basal / parabasal type, no maturation difference across all layers
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Reproductive age women
- Estimated prevalence: 0.5 - 1% (in high income countries)
- HSIL typically occurs at an older age compared with LSIL
- Risk factors: HIV infection, immunosuppression, cigarette smoking
Sites
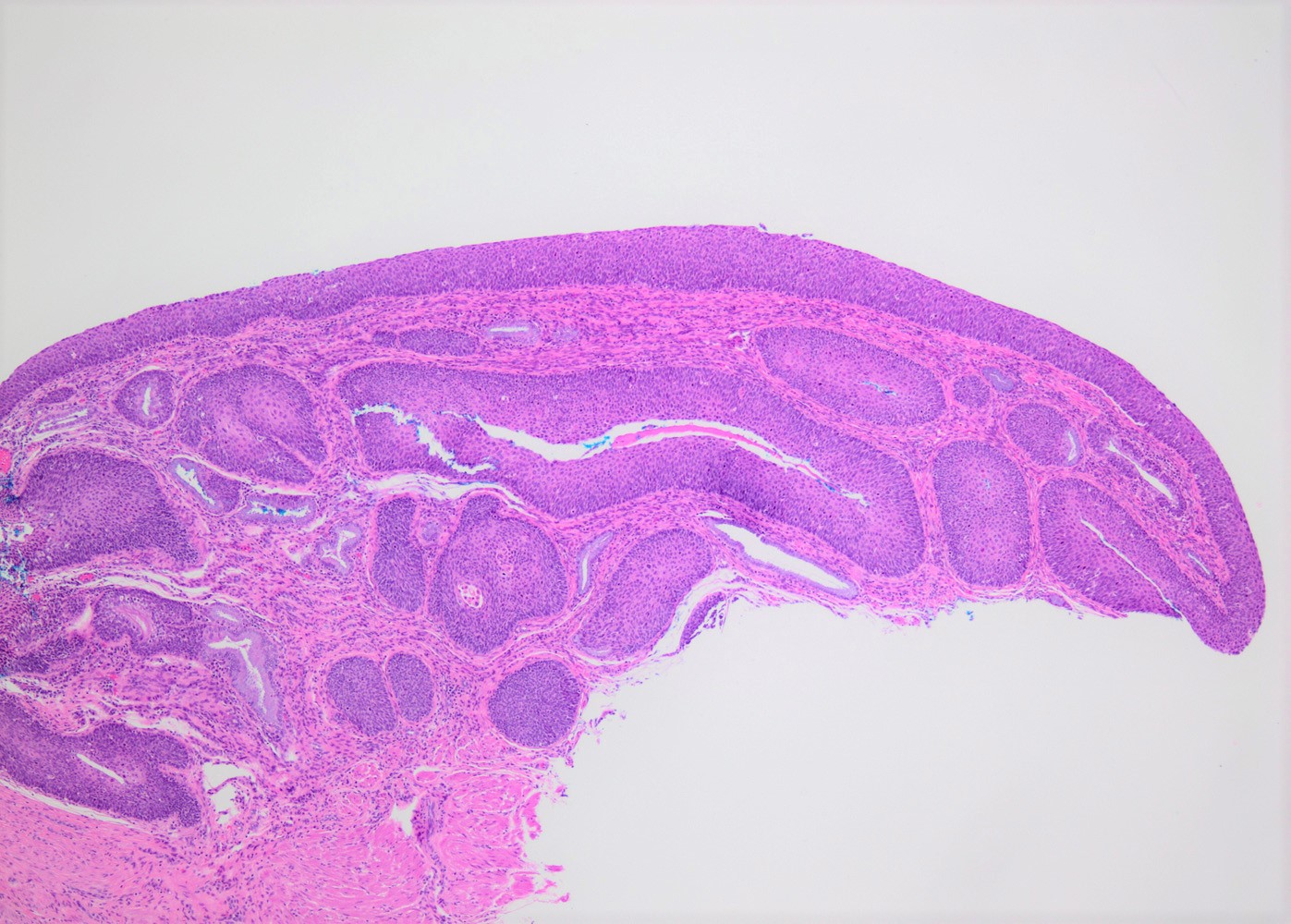
- Predominantly at transformation zone
- Occurs in squamocolumnar junctional cells or even in columnar epithelium (Int J Cancer 2015;137:2520)
Pathophysiology
- High risk HPV driven clonal proliferation of epithelial cells
- Viral E6 protein binds to p53 tumor suppressor protein, inducing its degradation
- Viral E7 protein inactivates retinoblastoma protein (Rb), leading to cell cycle progression
- Viral E7 protein function ultimately triggers upregulation of CDKN2A tumor suppressor gene, causing marked accumulation and overexpression of p16 (Am J Pathol 1998;153:1741)
- Extracellular E7 affects endothelial cells by increasing production of IL6 and IL8, promoting progression to invasive carcinoma (J Natl Cancer Inst 2001;93:1843)
Etiology
- Caused by high risk HPV subtypes
- Most common high risk HPV subtypes by descending frequency: 16, 18, 45, 31, 33, 52, 58 and 35 (N Engl J Med 2003;348:518)
- Subtypes 16 and 18 cause 50 - 60% of all HSIL (Gynecol Oncol 2006;103:21)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic disease of women of reproductive age
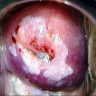
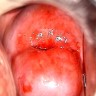
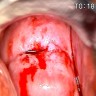
- Colposcopy - leukoplakia, acetowhite epithelium, mosaics, vascular changes
Diagnosis
- Cytology / Pap test
- Cervical biopsy
- Reference: Nucci: Gynecologic Pathology - A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series, 2nd Edition, 2020
Prognostic factors
- CIN II shows high spontaneous regression rate (42% and 50% at 12 and 24 months, respectively), particularly in young women (< 30 years) (BMJ 2018;360:k499)
- CIN II progression risk to CIN III or worse increases with time (from 5% at 3 months to 24% at 36 months) (BMJ 2018;360:k499)
- CIN III confers highest risk for progression to invasive squamous cell carcinoma (up to 31% if untreated) and lowest rate of spontaneous regression (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1993;12:186, J Clin Pathol 2011;64:303)
- Risk of HSIL after 2 consecutive high risk HPV+ tests = 17% (BMJ 2009;339:b2569)
- Increases to 41% with 2 previous HPV 16+ tests
Case reports
- 33 year old woman with CIN II following Gardasil vaccination (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e230366)
- 34 year old woman with CIN III coinfected with HPV 16 and 18 (J Korean Med Sci 1993;8:162)
- 50 year old HIV positive woman with multiple preinvasive and invasive HPV related anogenital tract lesions (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e5948)
Treatment
- Per the 2019 American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) guidelines (J Low Genit Tract Dis 2020;24:102):
- Treatment generally recommended for CIN II / CIN III or unspecified HSIL, except during pregnancy
- Patients < 25 years with CIN II: colposcopy and cytology at 6 month intervals is preferred over excision
- Often treated with local excision (BMJ 2005;331:1183)
- Treatment potentially increases risk of second trimester miscarriage and preterm birth (Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;2015:CD008478, Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;11:CD012847)
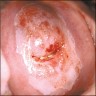
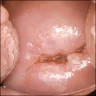
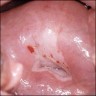
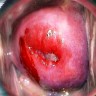
Clinical images
Gross description
- Predominantly flat lesions
- Hard to identify without acetic acid application
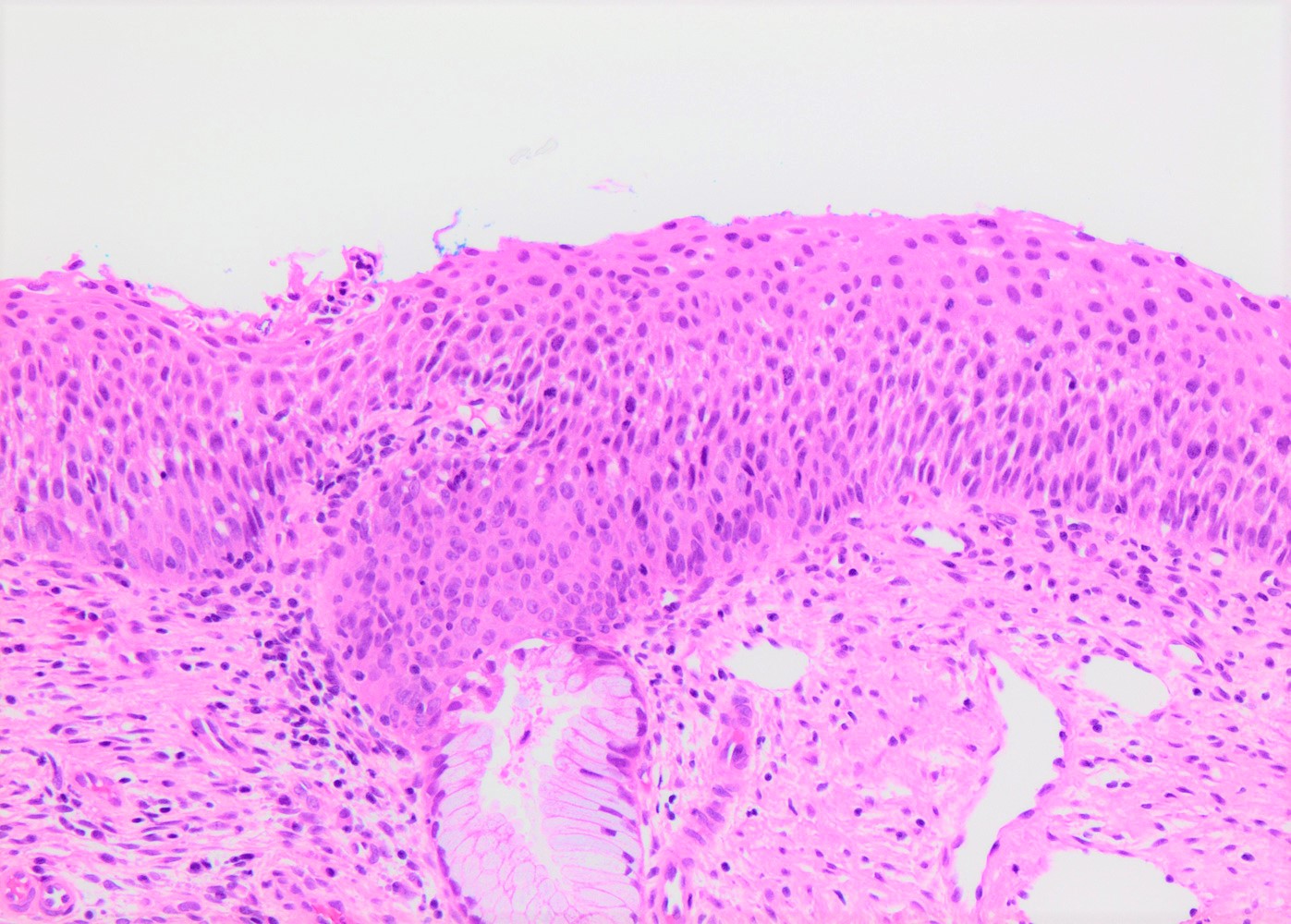
Microscopic (histologic) description
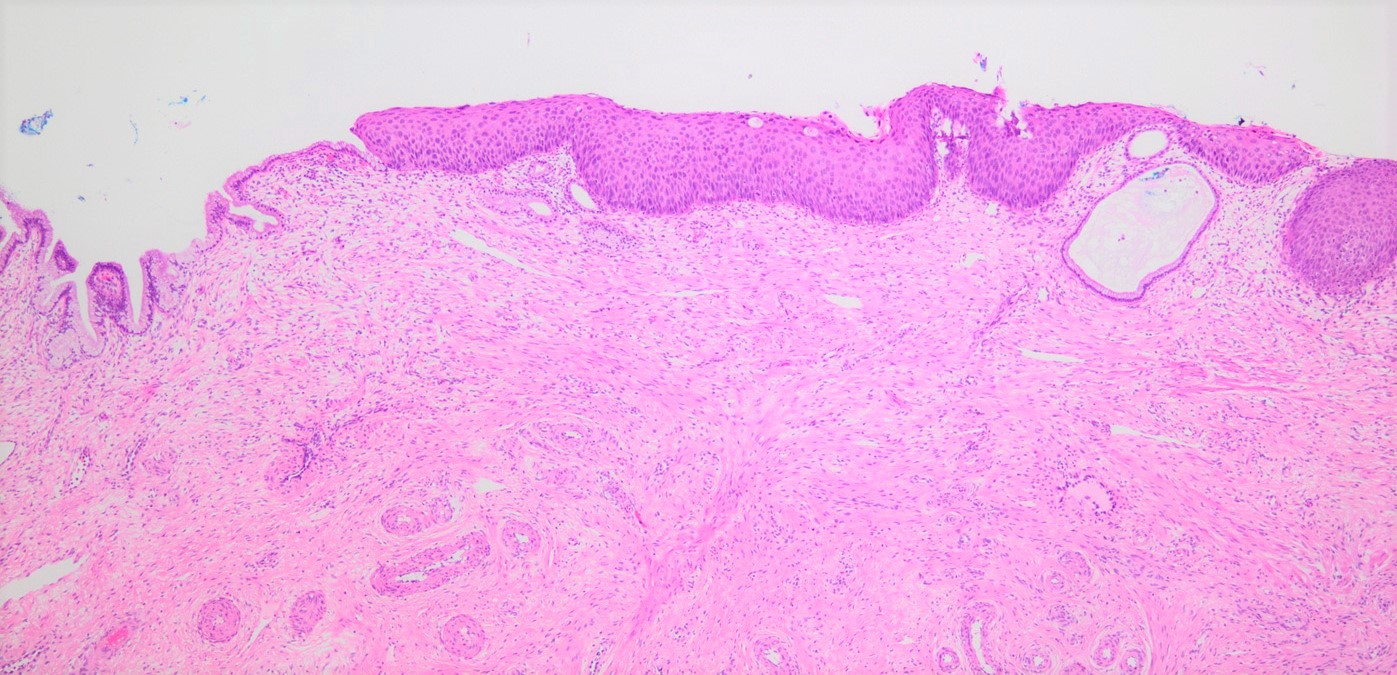
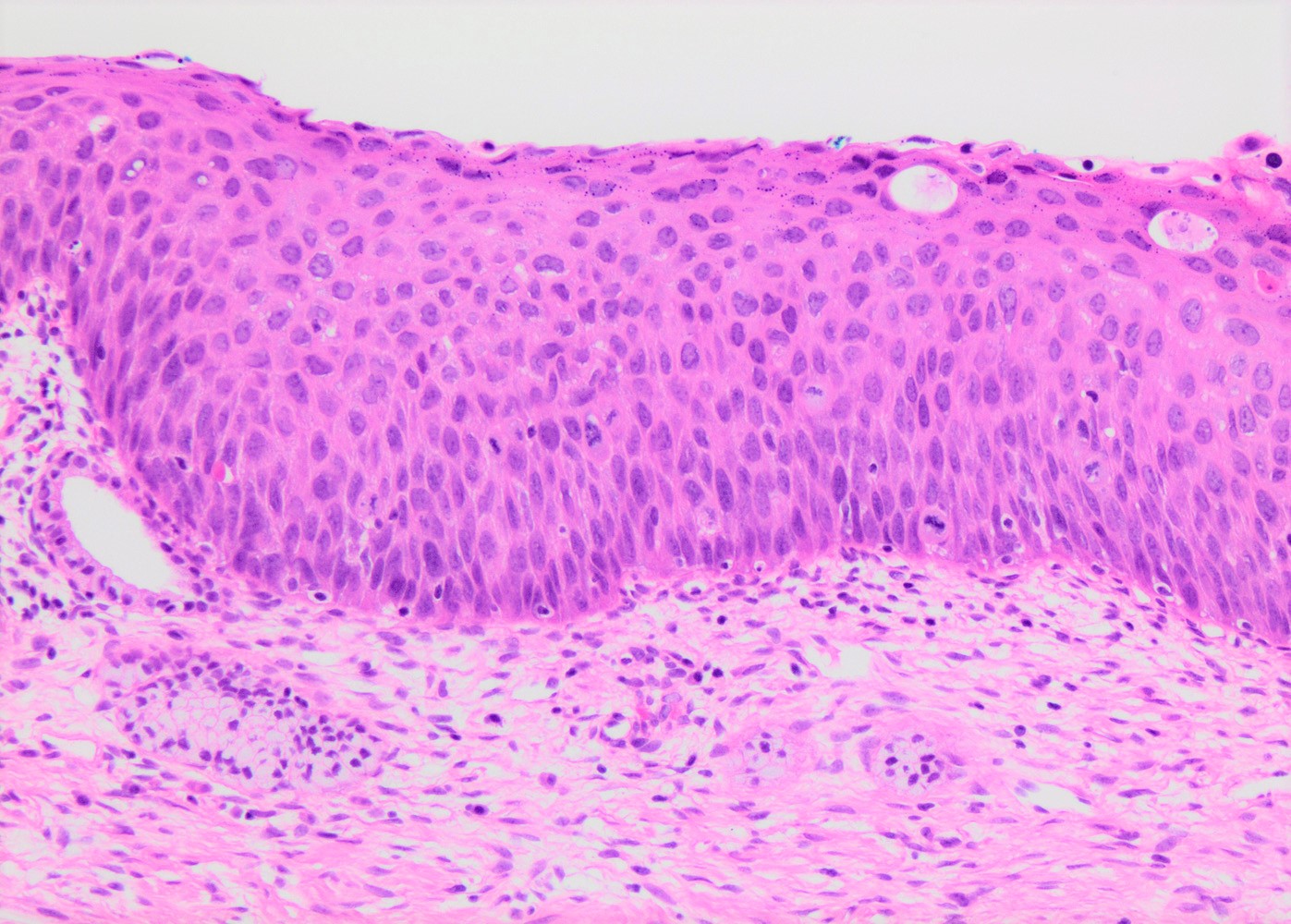
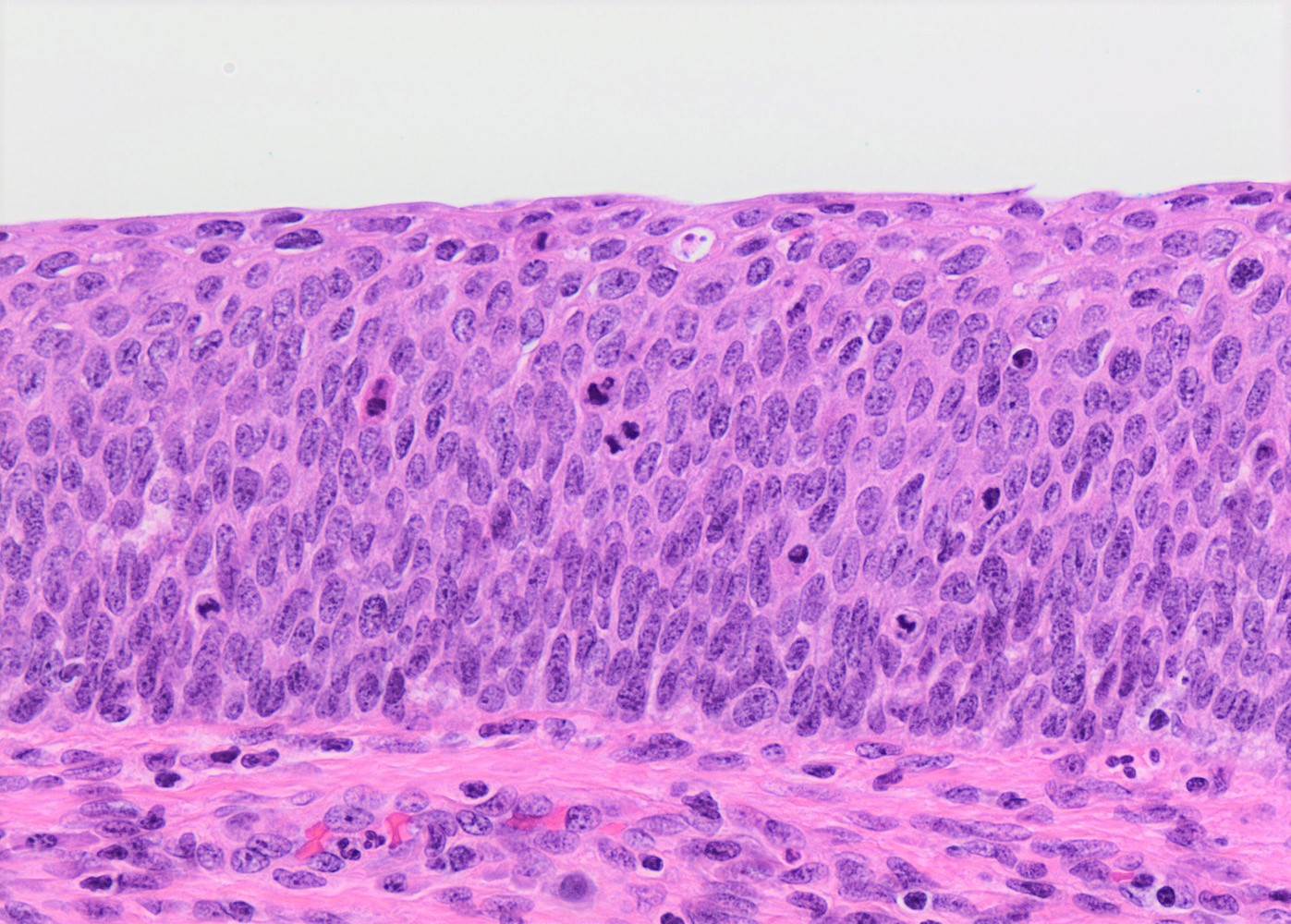
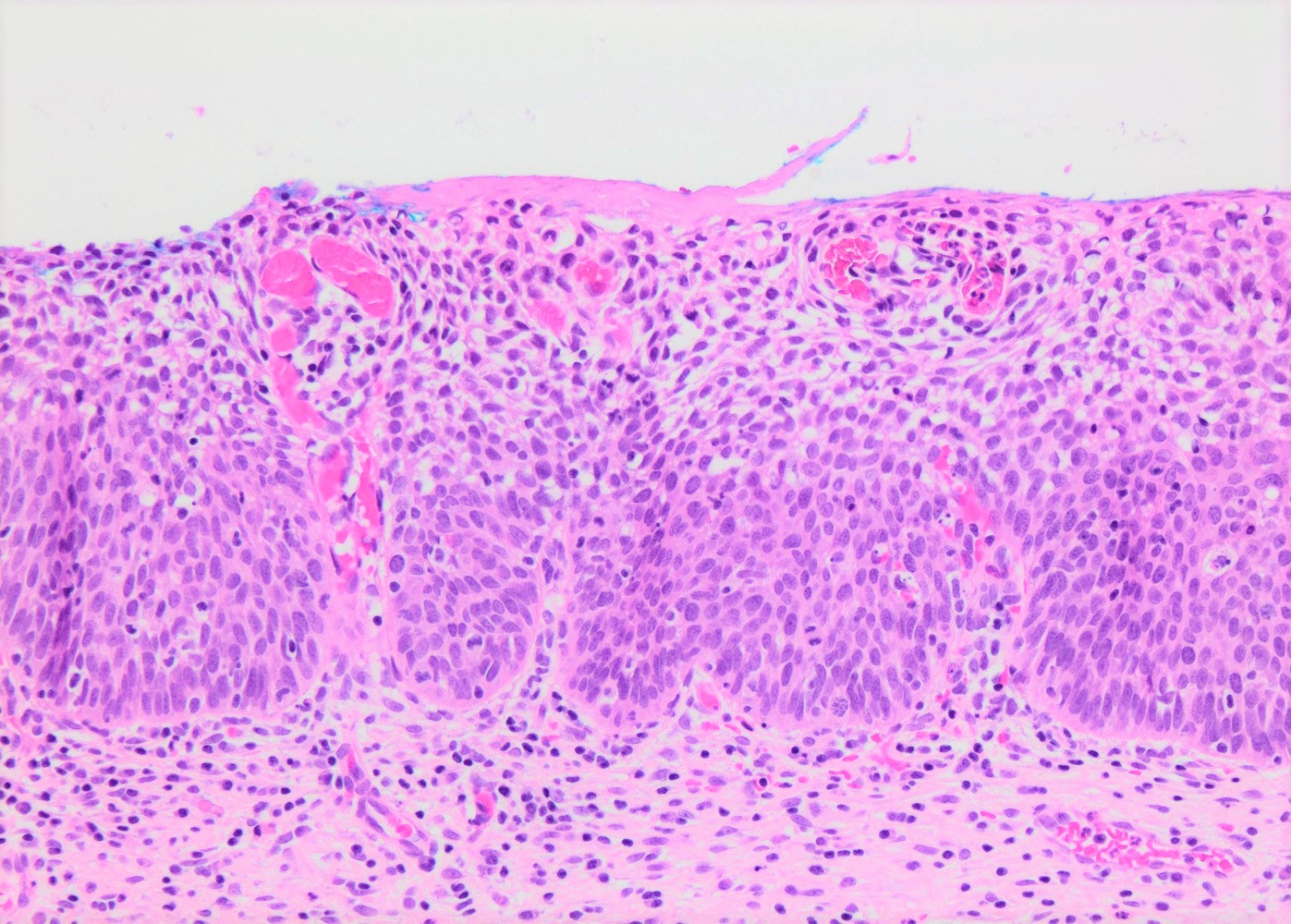
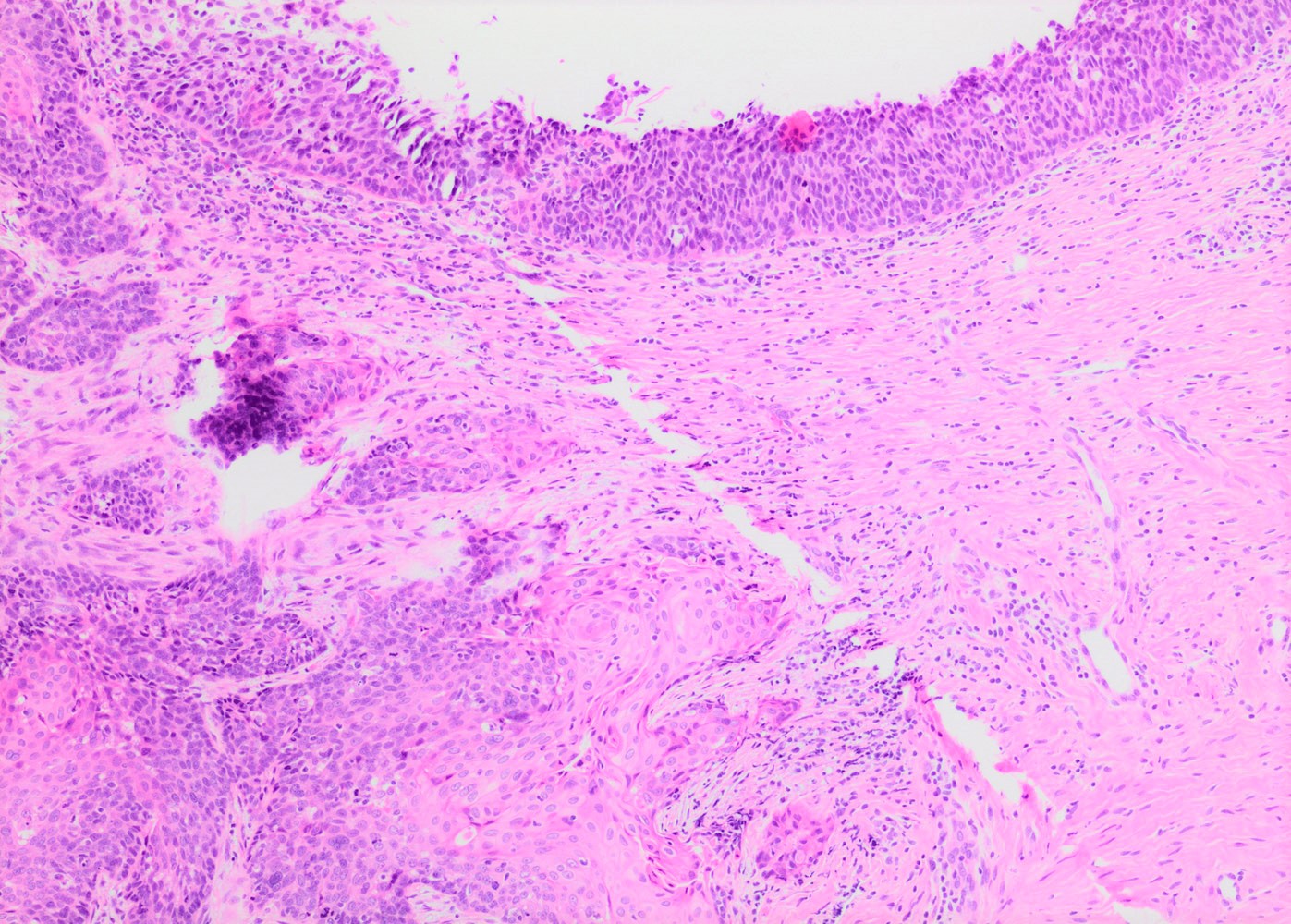
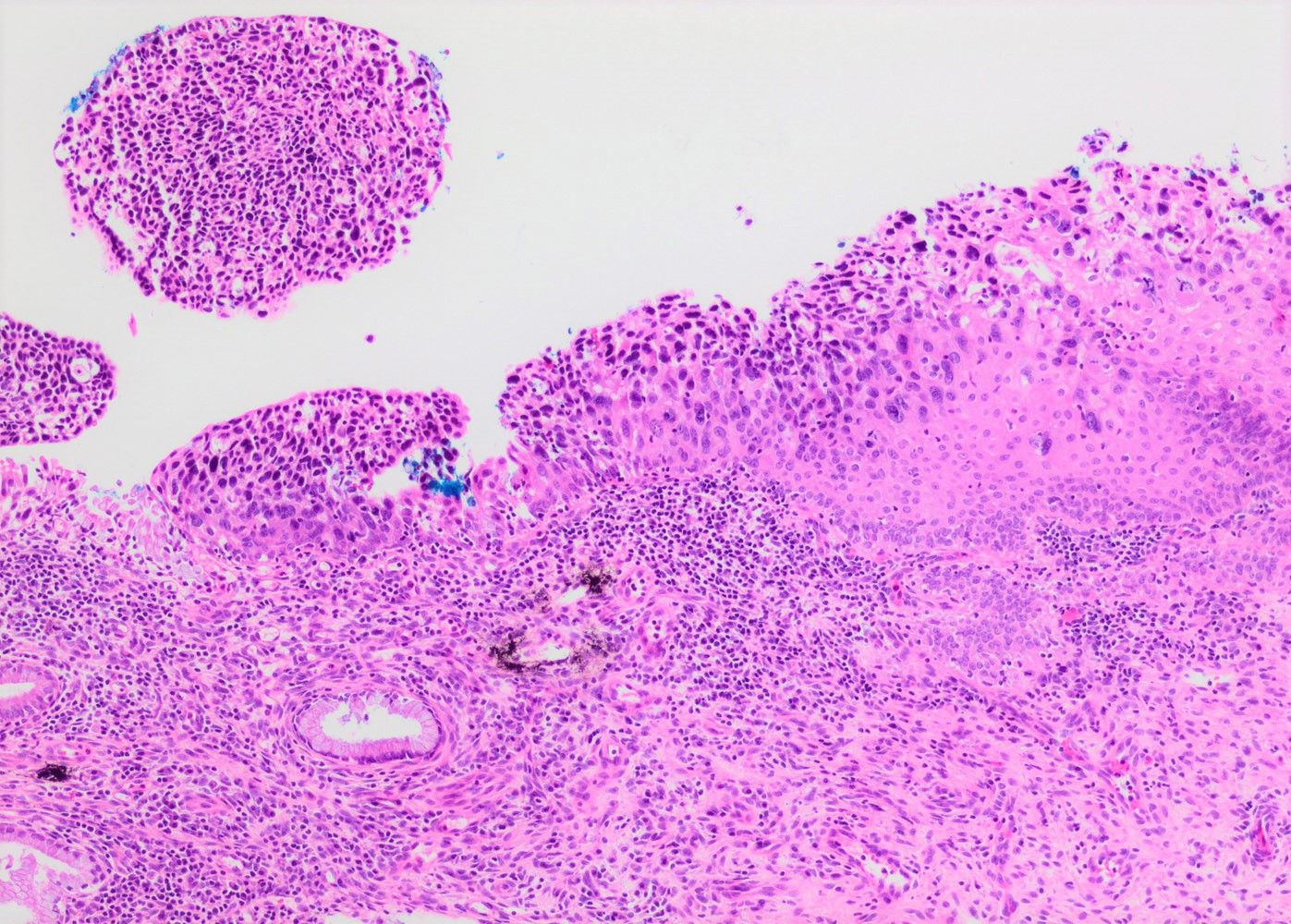
- Conventional / classic pattern: full thickness nuclear abnormalities (hyperchromasia, coarse chromatin, irregular nuclear contours and inconspicuous nucleoli), high N/C ratio in at least lower two - thirds of epithelium
- CIN II: cytoplasmic maturation in the upper third of mucosa
- CIN III: full thickness basal / parabasal type, no maturation difference across layers
- Increased mitotic activity with atypical mitoses
- Other patterns:
- Thin HSIL: < 10 cells thick; can mimic atrophy; usually focal and coexists with conventional HSIL (Histopathology 2019;75:405, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2017;36:71)
- Keratinizing HSIL: superficial keratinization without koilocytosis
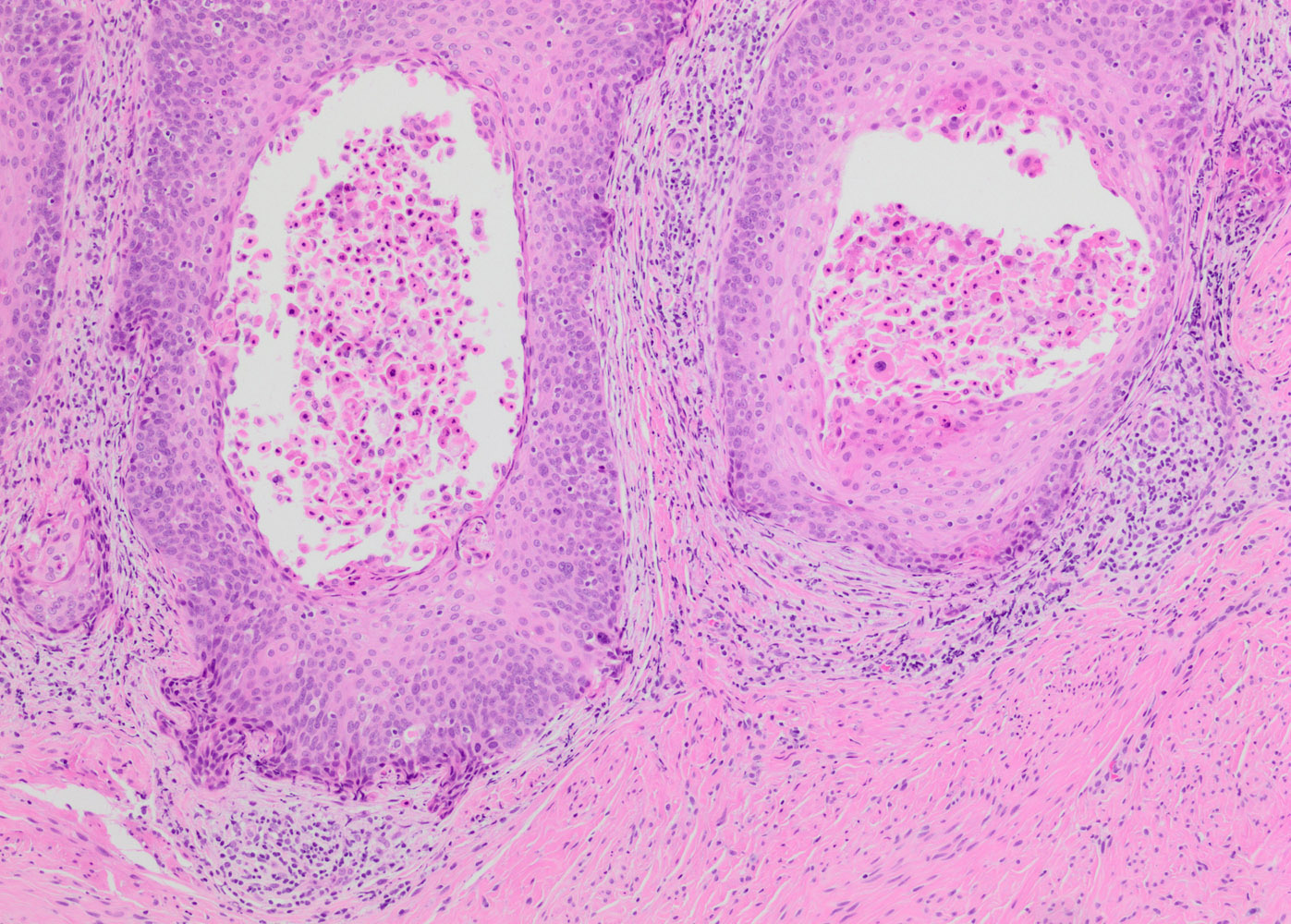
- Papillary HSIL: lining endocervical papillae
- Pleomorphic HSIL: focal bizarre nuclear changes / multinucleation (Pathology 2017;49:465)
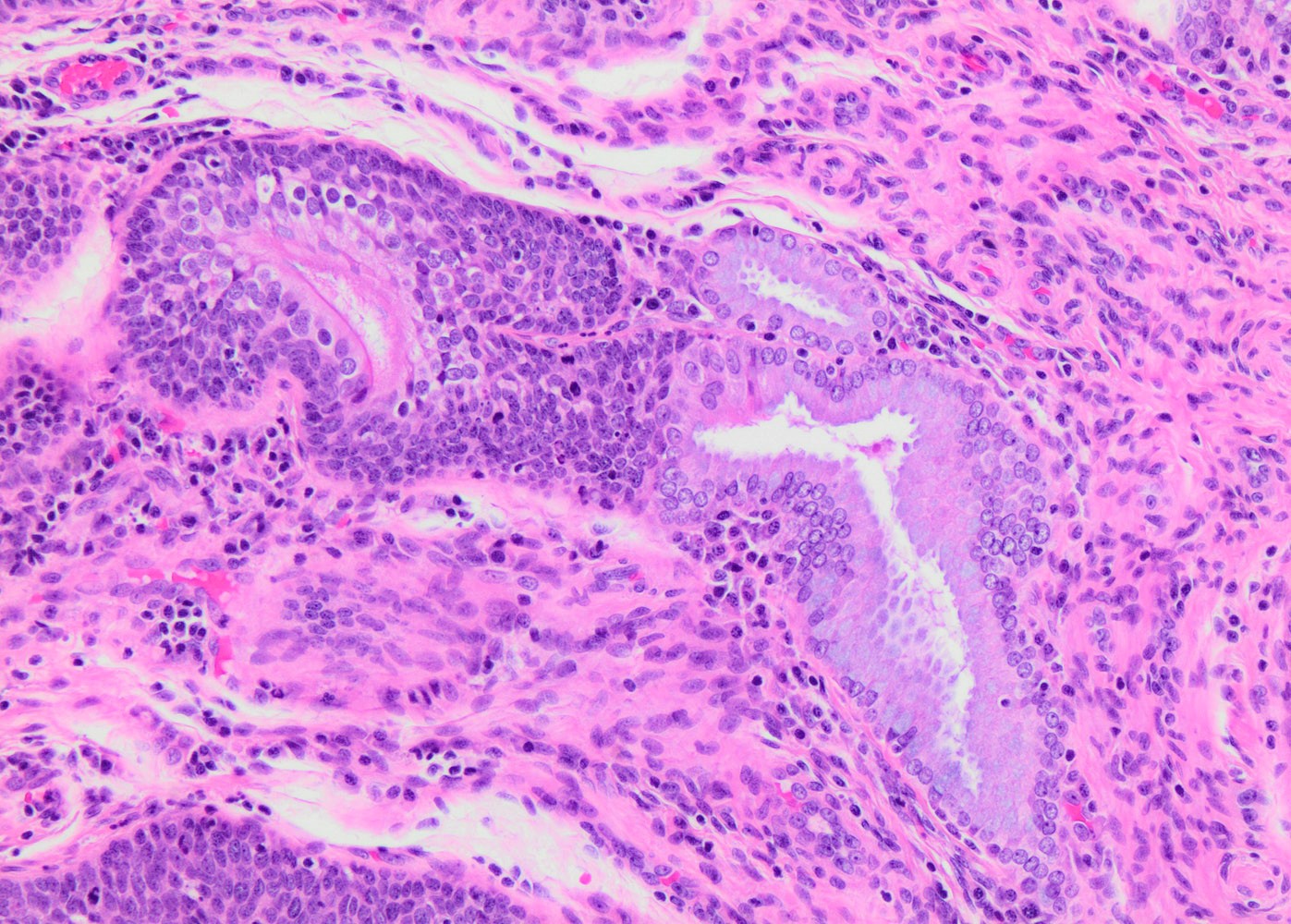
- May present as small metaplastic type cells mimicking immature metaplastic epithelium (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2007;26:180, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:470)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Khaled J. Alkhateeb, M.B.B.S.
Virtual slides
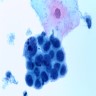
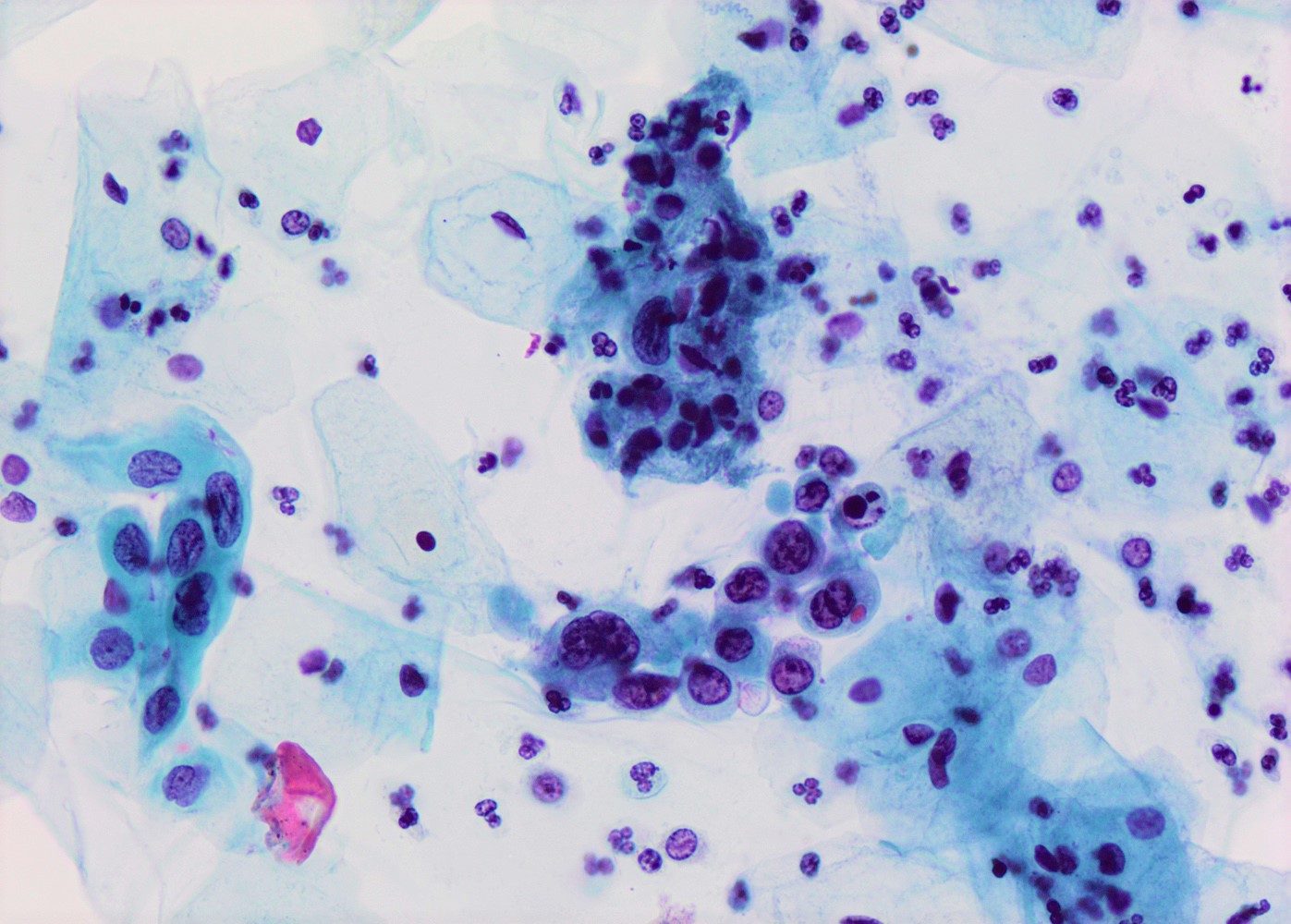
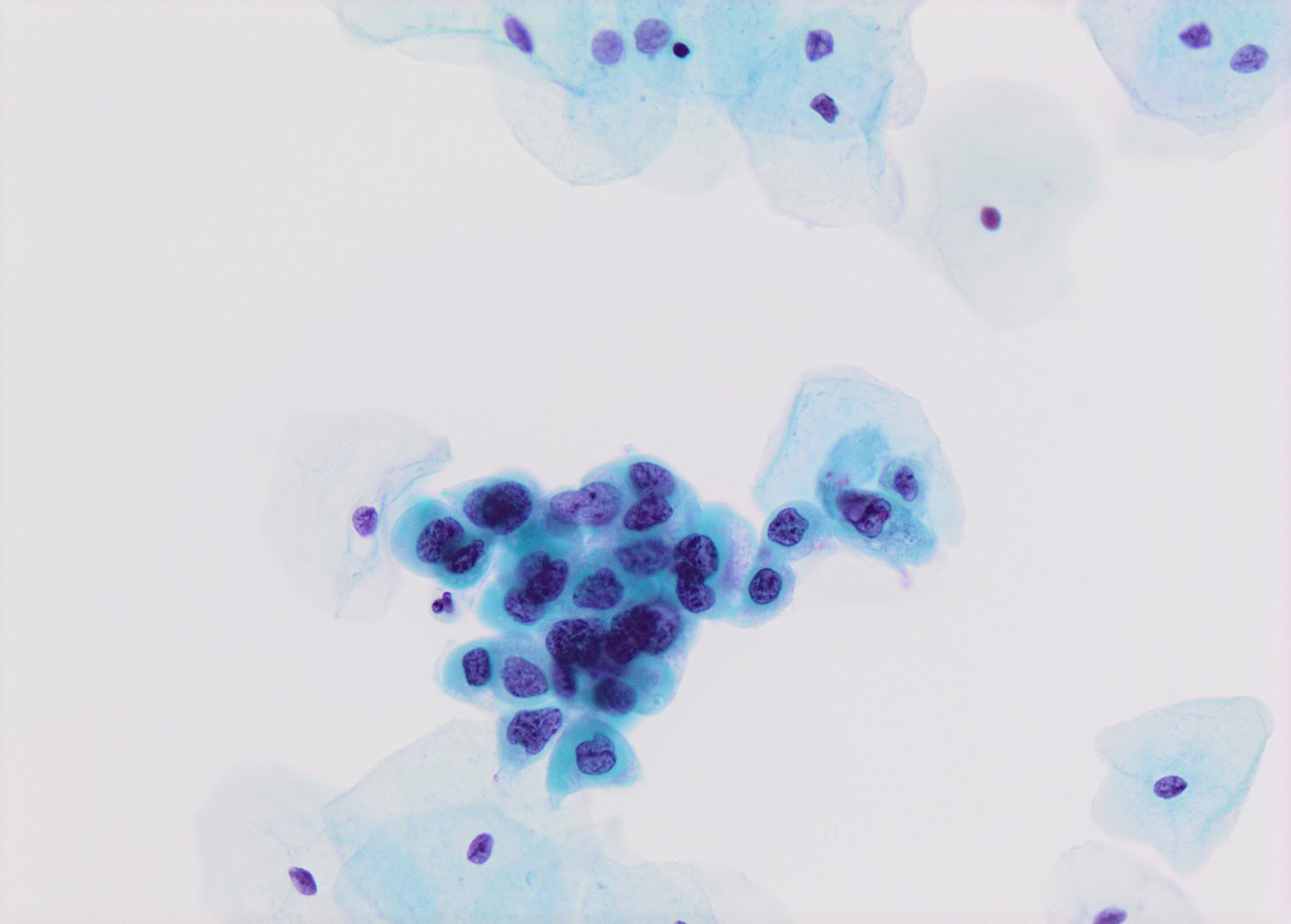
Cytology description
- High nuclear to cytoplasmic (N/C) ratio, nuclear enlargement (usually threefold), hyperchromasia, coarse chromatin, nuclear membrane irregularities and inconspicuous nucleoli
- Arranged as syncytium / hyperchromatic crowded groups or single cells
- Additional information available at: HSIL cytology
- References: Nucci: Gynecologic Pathology - A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series, 2nd Edition, 2020
Cytology images
Positive stains
- p16: strong and diffuse block staining, continuous nuclear or nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in the basal layer of dysplastic epithelium with upward extension involving at least one - third of the epithelium; extension into the upper half of epithelium is not required
- Lower anogenital squamous terminology (LAST) project recommends p16 IHC in the following contexts (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:1266):
- Distinguish HSIL from mimickers (e.g. atrophy, immature metaplasia)
- Distinguish morphologically equivocal LSIL / CIN I versus CIN II
- Professional disagreement on diagnosis when HSIL is in consideration
- Biopsies showing ≤ LSIL in patients at high risk for missed HSIL based on prior Pap / HPV testing results
- Improper use of p16 IHC may lead to overdiagnosis of HSIL (Hum Pathol 2016;55:51)
- Lower anogenital squamous terminology (LAST) project recommends p16 IHC in the following contexts (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:1266):
- Ki67: increased proliferation index compared with LSIL (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:723)
- BAG3: promising marker with expression shown to directly correlate with the degree of dysplasia (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2020;99:99)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HPV RNA in situ hybridization (ISH): assays detect E6 / E7 oncoproteins of majority of HR and LR-HPV subtypes
- High sensitivity and specificity for the detection of HPV in formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue (PLoS One 2014;9:e91142, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:607)
- Typical staining patterns (PLoS One 2014;9:e91142, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:192):
- Productive / proliferative pattern: abundant dense superficial epithelial nuclear staining as well as basal epithelial multiple dot-like cytoplasmic and nuclear staining; seen more commonly in LSIL / CIN I lesions
- Transformative / nonproliferative pattern: strong and diffuse multiple dot-like cytoplasmic / nuclear staining; absent / rare dense superficial nuclear staining; seen more commonly in CIN III lesions
- CIN II lesions commonly show a combination of productive / transformative staining, patterns
- More utility in distinguishing LSIL / CIN I from its mimics (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:192)
Sample pathology report
- Cervix, cone biopsy:
- High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion / cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 3 (HSIL / CIN III), extending into endocervical glands
- Surgical resection margins are negative for squamous intraepithelial lesion.
- No invasive carcinoma identified.
Differential diagnosis
- Atrophy:
- High N/C ratio, fine chromatin, no significant nuclear irregularities
- Absent / rare mitotic figures
- Ki67: absent / minimal staining
- Atypia of repair:
- Atypical cells may extend up to middle layer
- Superficial maturation and retention of cellular polarity in the more basal layers compared to HSIL
- Prominent nucleoli, no coarse chromatin
- Radiation changes:
- Cytomegaly with maintenance of low N/C ratio
- Immature squamous metaplasia:
- No loss of organization / polarity
- Uniform nuclei with fine chromatin
- Columnar cells may be present on surface
- No abnormal mitotic figures
- Transitional metaplasia:
- Postmenopausal women
- Upper layer shows horizontal orientation
- Oval nuclei with irregular contours, nuclear grooves and fine chromatin
- Invasive squamous cell carcinoma:
- May be difficult to distinguish from HSIL with complete replacement of endocervical glands or when dysplastic epithelium is displaced into stroma during prior surgical procedure
- HSIL involving endocervical glands shows smooth contours without desmoplastic stromal reaction or paradoxical maturation
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 32 year old woman presented after 2 consecutive Pap tests revealing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS). Colposcopic exam was unsatisfactory. Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) was performed and showed the histologic findings in the image above. What immunohistochemical study and staining pattern combination would be expected in this lesion?
- CK20: diffuse cytoplasmic immunoreactivity
- p16: diffuse block type nuclear and cytoplasmic immunoreactivity
- p16: scattered nuclear immunoreactivity
- p53: diffuse nuclear immunoreactivity
Practice answer #1
B. p16: diffuse block type nuclear and cytoplasmic immunoreactivity
Comment Here
Reference: HSIL / CIN II / CIN III
Comment Here
Reference: HSIL / CIN II / CIN III
Practice question #2
What is the most common HPV subtype in cervical HSIL?
- HPV 6
- HPV 16
- HPV 18
- HPV 58
Practice answer #2