Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Lott Limbach A. Odontogenic myxoma / fibromyxoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillamyxoma.html. Accessed September 23rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign odontogenic neoplasm resembling odontogenic ectomesenchyme
- Characterized by bland spindled to stellate cells in myxoid stroma
- Requires radiographic and clinical correlation to differentiate from a dental follicle / papilla
- References: Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, J Oral Surg 1975;33:523, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214, Oral Dis 2019;25:676
Essential features
- Stellate, spindle shaped, round cells arranged haphazardly in abundant, fibrillary myxoid / mucoid stroma with infiltration into surrounding bone
- Radiolucent lesion with thin, fine, coarse or wispy trabeculae of residual bone arranged perpendicular to one another (tennis racket or soap bubble appearance)
- Recurrence is common due to infiltrative nature of the neoplasm
Terminology
- Odontogenic myxoma
- Odontogenic fibromyxoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9320/0 - odontogenic myxoma
- ICD-10
- ICD-11
- 2E83.0 & XH48L4 - benign osteogenic tumors of bone or articular cartilage of skull or face & odontogenic myxoma
- 2E83.1 & XH48L4 - benign osteogenic tumors of bone or articular cartilage of lower jaw & odontogenic myxoma
Epidemiology
- Incidence is 0.5 - 17.7% of all odontogenic tumors of the jaw (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214, J Oral Pathol Med 2016;45:599)
- Wide age range but generally occurs in second and third decades (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
- More common in women but may vary by population (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214, Oral Dis 2019;25:676, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2007;104:101)
Sites
- More common in mandible (67%) than maxilla (33%) (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021)
- In both the mandible and maxilla, more common posteriorly (Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
Pathophysiology
- Not well described
- May originate from the primitive mesenchymal portion of a developing tooth or periodontal membrane (J Oral Surg 1975;33:523, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2007;104:101)
- May result from myxomatous degeneration of odontogenic fibroma (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2007;104:101)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Often asymptomatic, incidentally discovered by imaging (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2007;104:101)
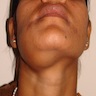
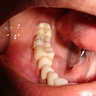
- Can present with slow growing swelling, rarely pain (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Oral Dis 2019;25:676)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is often made by radiographical evaluation and correlated clinical and pathologic findings (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
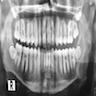
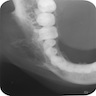
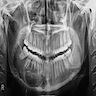
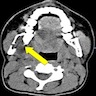
Radiology description
- Unilocular or multilocular radiolucency (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2007;104:101, Int J Dent 2021:2021:1093412)
- Variable margins from well defined and corticated to poorly defined scalloped (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021)
- Characteristic radiographic finding of thin, fine, coarse or wispy trabeculae of residual bone arranged perpendicular to one another (tennis racket or soap bubble appearance) (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Recurrence rates are variable, 10 - 43% and related to extent of excision (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
Case reports
- 14 year old boy with maxillary mass (BMJ Case Rep 2020;13:e234933)
- 18 year old man with maxillary mass (J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:ZD29)
- 22 year old woman with right mandibular mass (Head Neck Pathol 2018;12:44)
- 28 year old woman and 36 year old man both with maxillary masses (Contemp Clin Dent 2015;6:131)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is mainstay of treatment (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214, Oral Dis 2019;25:676, J Clin Exp Dent 2021;13:e637)
- Varies from curettage to surgical resection with 1 cm wide margin (Oral Dis 2019;25:676)
Clinical images
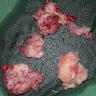
Gross description
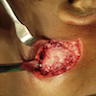
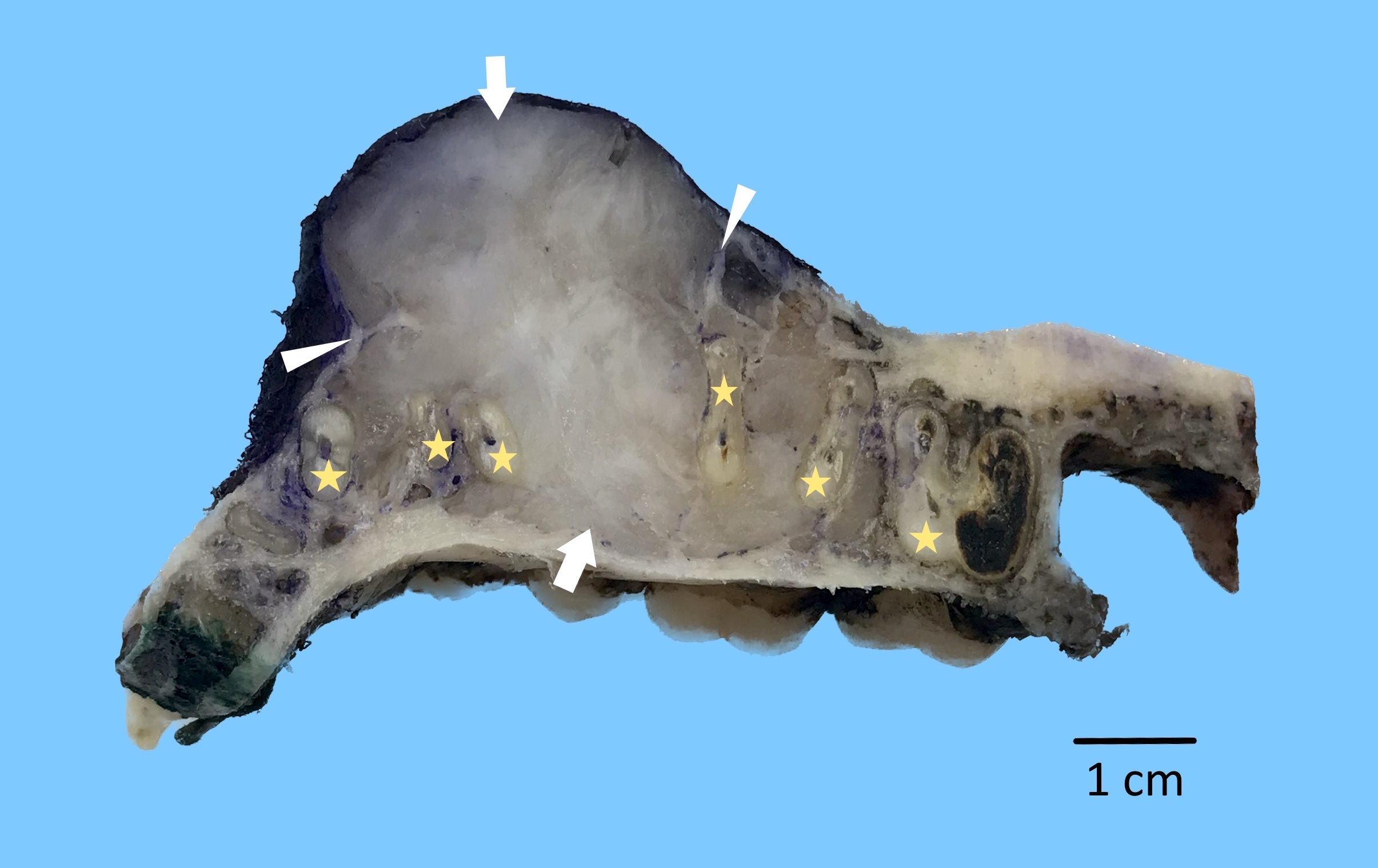
- Whitish gray gelatinous loose structure (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021)
Gross images
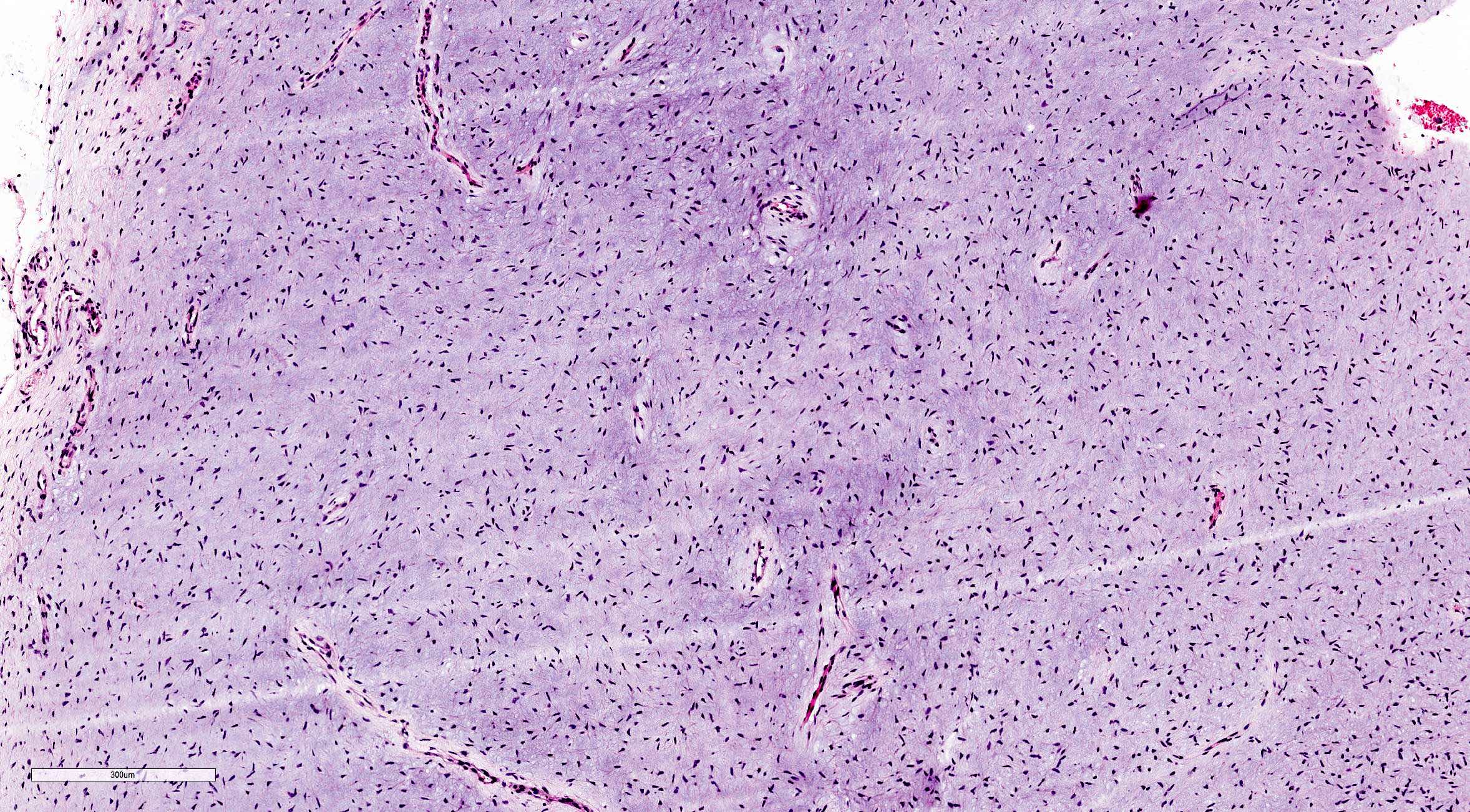
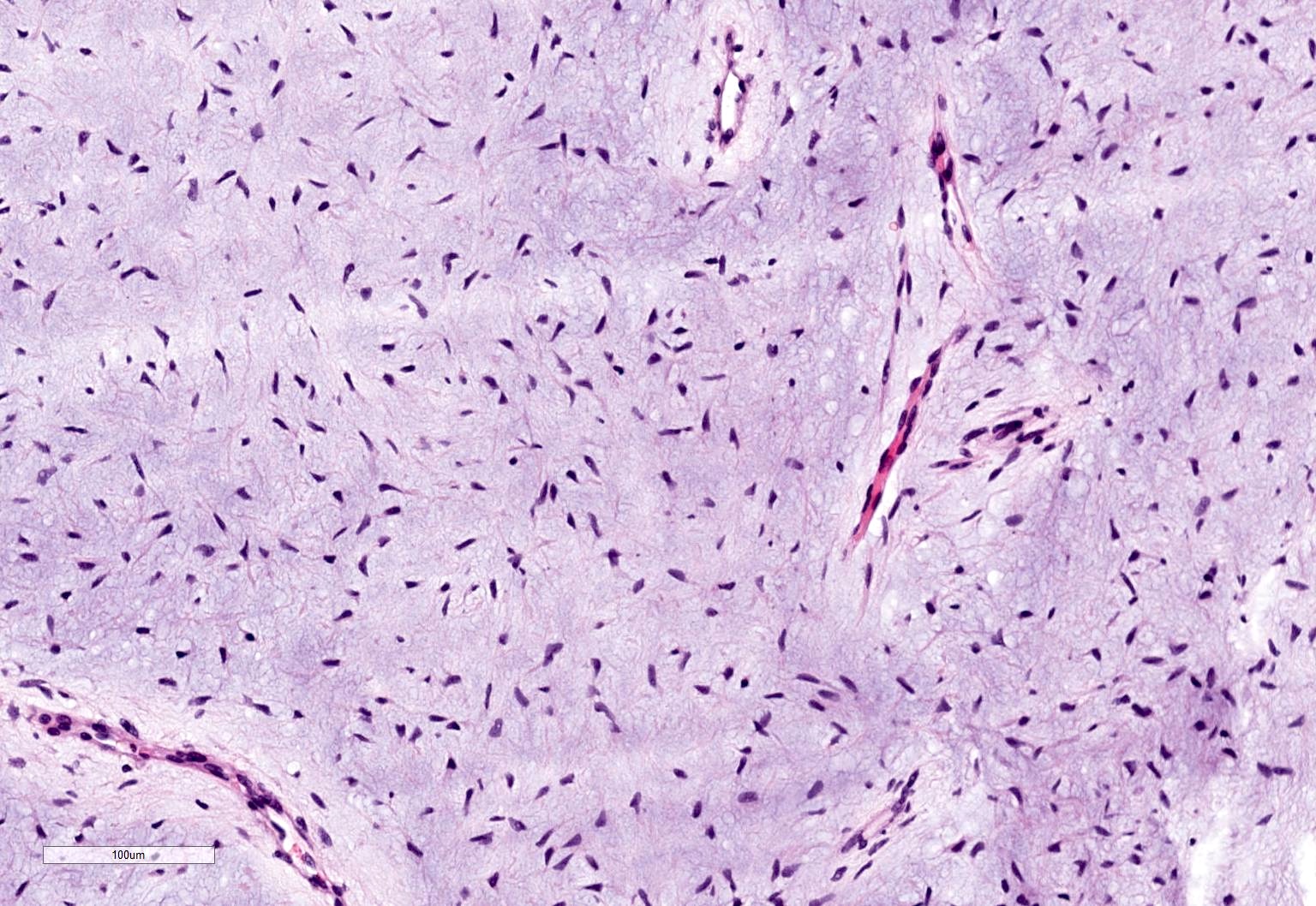
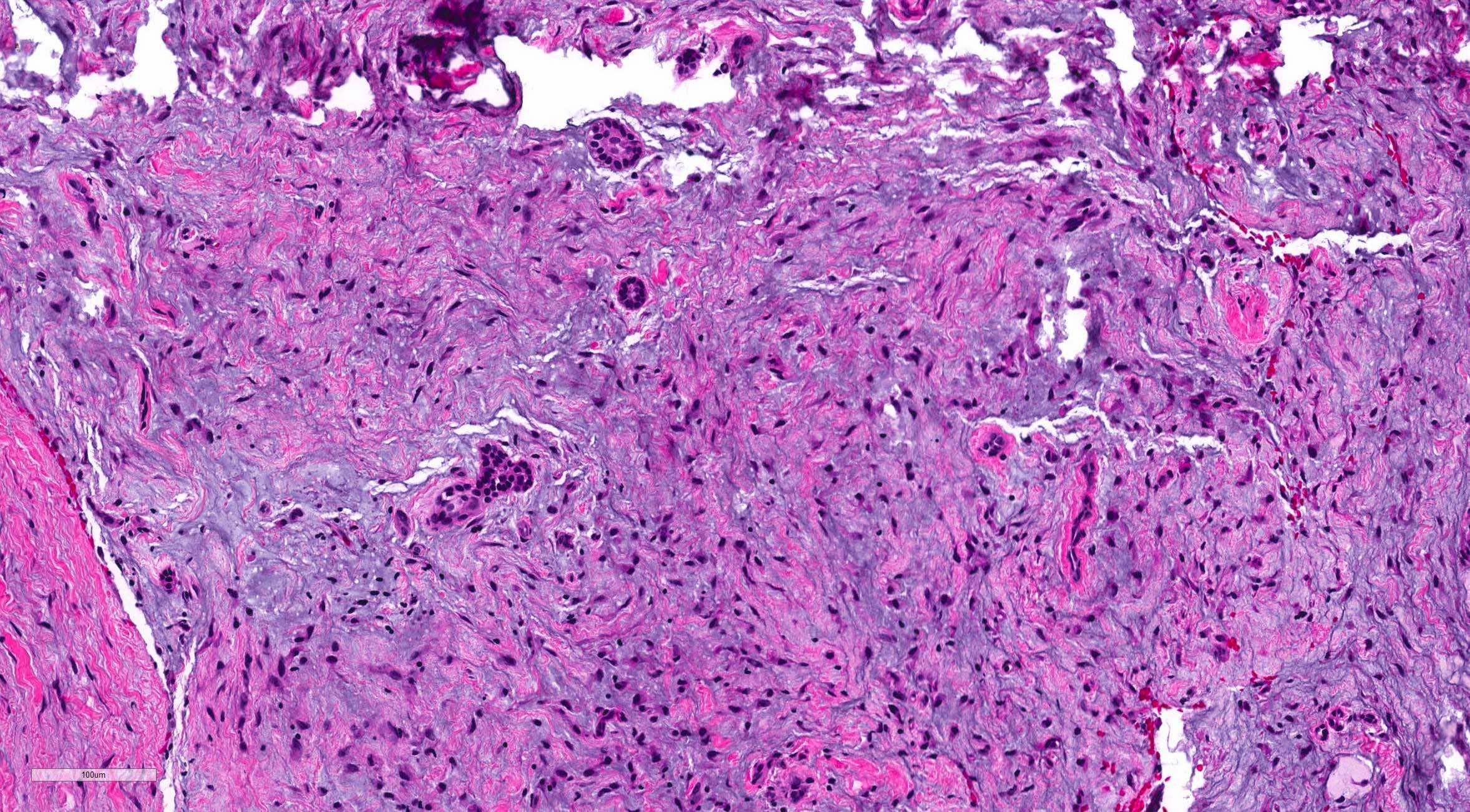
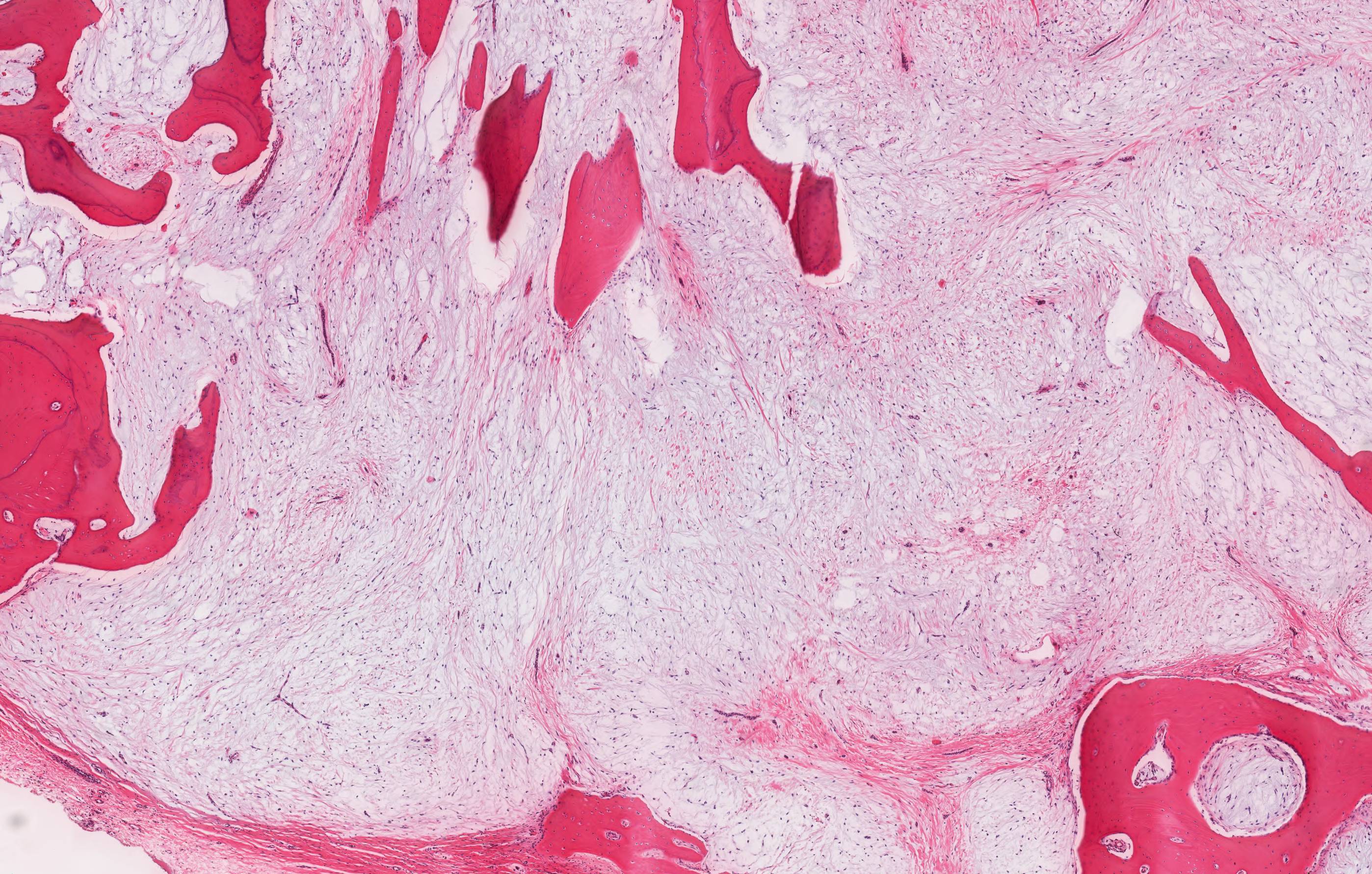
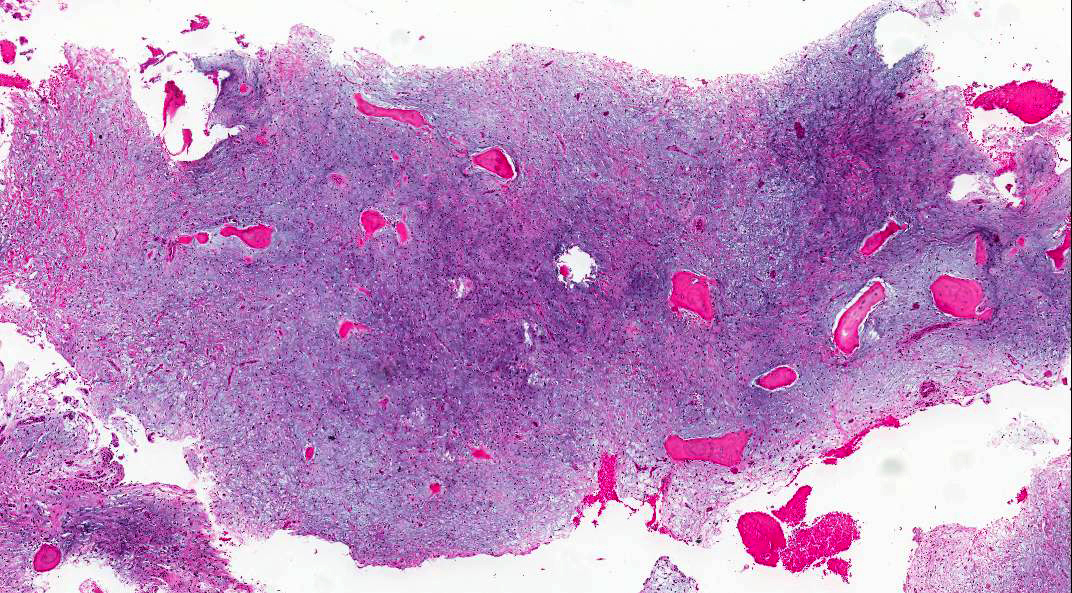
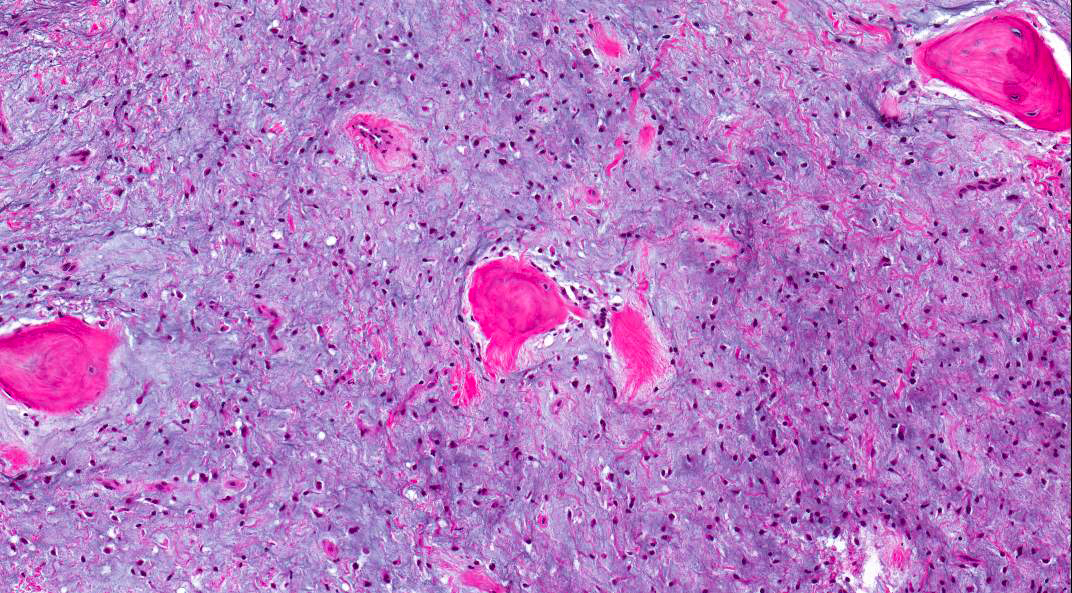
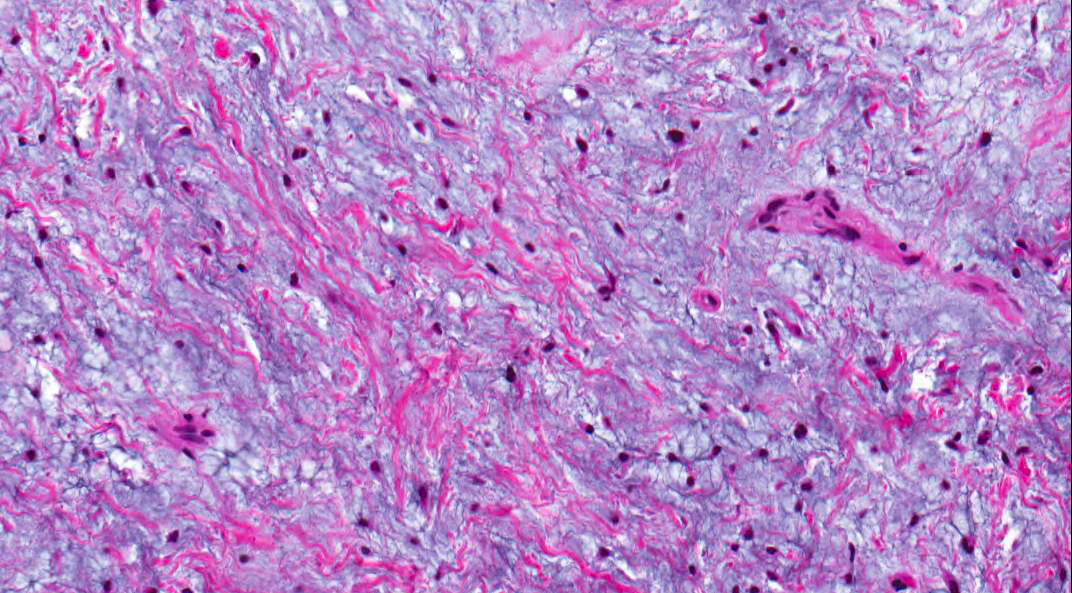
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Stellate, spindle shaped, round cells arranged haphazardly in abundant, fibrillary myxoid / mucoid stroma (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021)
- Infiltrates surrounding bone (Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
- Small islands of inactive odontogenic epithelial rests can be seen (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021)
- If abundant collagen is present, the term fibromyxoma is used (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:1021, Eur J Clin Invest 2020;50:e13214)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- SMA
- β catenin: nuclear positive staining is rarely reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:1301)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- MAPK / ERK pathway activation (Oral Oncol 2011;47:325)
Sample pathology report
- Mandible, segmental resection:
- Odontogenic myxoma
- Margins of excision negative
Differential diagnosis
- Dental papilla or dental follicle:
- Immature dental pulp or follicle from a developing tooth
- Often requires clinical and radiographic correlation to differentiate from myxoma
- Dental papillae may show a rim of odontoblasts
- Myxoid neurofibroma:
- S100 positive
- Chondromyxoid fibroma:
- Presence of chondroid / mature cartilaginous component
- Odontogenic fibroma:
- More cellular and fibrocollagenous
- Strands or islands of odontogenic epithelium more prominent
- Infantile sinonasal myxoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:1301):
- Short, intersecting fascicles of bland, stellate to spindle cells
- Prominent stromal vessels and variably myxoid to collagenous stroma
- Neoplastic cells exhibited bipolar to stellate, fibroblastic cytomorphology, with pale pink cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei and small, distinct nucleoli
- Pushing border rather than infiltrative growth
- No dystrophic calcifications
- No rests of odontogenic epithelium
- Mitotic index low (median < 1 per 10 HPF)
- Strong and diffuse nuclear β catenin in majority of cases, rare SMA positive
- Negative for S100 protein, CD34 and desmin
- Molecular level: most tumors harbor CTNNB1 mutations (D32Y, G34E, G34R and I35S) on exon 3 or APC alterations consistent with biallelic inactivation
- Combination of patient age, tumor site and strong and diffuse nuclear β catenin expression generally distinguished infantile sinonasal myxomas from odontogenic myxoma
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. Odontogenic myxoma. The image shows scant spindle cells in a myxoid background consistent with odontogenic myxoma. Answer B is incorrect because intraosseous mucoepidermoid carcinoma would have an epidermoid component and lack spindle cells. Answer A is incorrect because chondromyxoid fibroma contains cartilage (not seen in the image). Answer C is incorrect because odontogenic keratocyst is lined by a squamous type epithelium and lacks significant myxoid change.
Comment Here
Reference: Odontogenic myxoma / fibromyxoma
Comment Here
Reference: Odontogenic myxoma / fibromyxoma
Practice question #2
Odontogenic myxomas have been shown to have which of the following molecular alterations?
- BRAF mutations
- GNAS mutations
- KRAS mutations
- MAPK / ERK pathway activation
Practice answer #2
D. MAPK / ERK pathway activation. Odontogenic myxomas have been shown to have activation of the MAPK / ERK pathway. Answer A is incorrect because BRAF mutations can be seen in ameloblastomas. Answer B is incorrect because GNAS mutations are seen in fibrous dysplasia. Answer C is incorrect because KRAS mutations can be seen in adenomatoid odontogenic tumors.
Comment Here
Reference: Odontogenic myxoma / fibromyxoma
Comment Here
Reference: Odontogenic myxoma / fibromyxoma