Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: van der Kwast T. Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostatesmallcell.html. Accessed September 18th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate is a rare entity that may be pure or more commonly admixed with conventional acinar adenocarcinoma
- Its microscopic features are indistinguishable from small cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of other body sites
Essential features
- De novo small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate is very rare and may be associated with conventional acinar adenocarcinoma (mixed carcinoma)
- Dismal prognosis in spite of initial response to platinum based therapy
- Diagnosis can be made on microscopic features alone, immunostaining for neuroendocrine markers is auxiliary
- Must be distinguished from International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) / World Health Organization (WHO) grade group 5 prostate adenocarcinoma because of clinical implications and different metastatic pattern
Terminology
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate (recommended)
- Poorly differentiated small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate
- Small cell undifferentiated carcinoma of the prostate (not recommended)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare occurrence of de novo small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate
- Association with conventional acinar adenocarcinoma in over 50% of cases (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2021;19:e193)
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate more common in patients with metastatic disease subsequent to androgen receptor axis targeted therapy for conventional acinar adenocarcinoma (treatment emergent or treatment related small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma)
Sites
- Prostate
- Metastatic sites (bone, lymph nodes, liver, brain, other)
Pathophysiology
- Transdifferentiation of acinar adenocarcinoma acquiring stem cell properties and neuroendocrine features most likely underlies the development of a prostatic small cell carcinoma
- Shared TP53 gene mutation and TMPRS2::ERG fusion in mixed small cell and conventional acinar adenocarcinomas point at a clonal derivation of a common precursor cell (Prostate 2009;69:603, Mod Pathol 2011;24:1120)
Etiology
- No known etiology of de novo small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
Clinical features
- Urinary outflow obstruction is a first local symptom of small cell carcinoma of the prostate (Semin Oncol 2007;34:22)
- Bone metastatic disease or metastases to lymph nodes or to visceral sites (liver, brain, etc.) are often the first clinical manifestation
- Paraneoplastic syndrome (e.g., Cushing syndrome due to ectopic ACTH production, inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone or hypercalcemia due to excessive parathyroid hormone production), similar to small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of other organ sites
- Elevated serum chromogranin A or neuron specific enolase (NSE) in case of metastatic disease, while serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) remains low
Diagnosis
- Prostate biopsy, transurethral resections of the prostate or prostatectomy specimens as well as biopsies of metastatic foci
- Essential features: specific high grade cytonuclear features, including high N:C ratio, hyperchromatic nuclei, nuclear molding and high mitotic rate / MIB1 score of > 50%
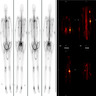
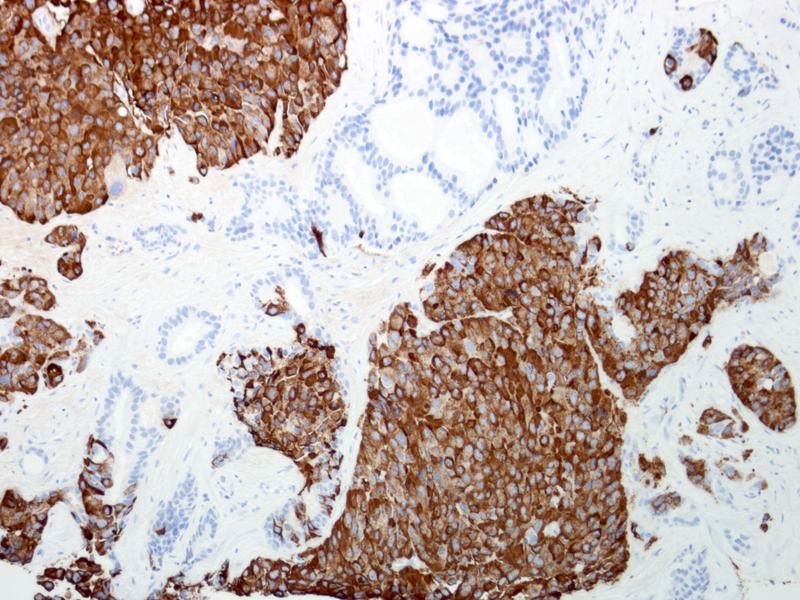
- Desirable: positive immunostaining for neuroendocrine markers (synaptophysin, INSM1, chromogranin A) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:756)
Laboratory
- Elevated serum chromogranin, low PSA
Radiology description
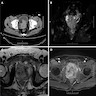
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of prostate shows prostate cancer with invasion of seminal vesicles and pelvic lymph node metastasis (World J Clin Cases 2022;10:1630)
- Whole body scan positive for multiple bone metastases (World J Clin Cases 2022;10:1630)
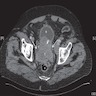
- Pelvic CT with contrast shows carcinoma involving both ureters (Indian J Urol 2012;28:89)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Dismal prognosis, median survival of 10 - 18 months; mixed adenocarcinoma / small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma has slightly longer survival (Nat Rev Urol 2014;11:213)
- Increased risk of lytic bone lesions, presence of visceral metastases, including brain metastasis
- Unresponsive to hormonal therapy
- Rapid progression after initial response to chemotherapy
Case reports
- 48 year old man with small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate completely negative for neuroendocrine markers (World J Clin Cases 2022;10:1630)
- 55 year old White man with mixed acinar adenocarcinoma (Gleason score 4 + 3 = 7) and small cell carcinoma (Prostate 2009;69:603)
- 61 year old man who presented with neck swelling (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa117)
- 63 year old Black man who initially presented to the hospital with an elevated PSA level of 9.41 ng/mL (Cureus 2020;12:e7074)
- 79 year old Caucasian man presented with acute urinary retention (Indian J Urol 2012;28:89)
Treatment
- Platinum based chemotherapy
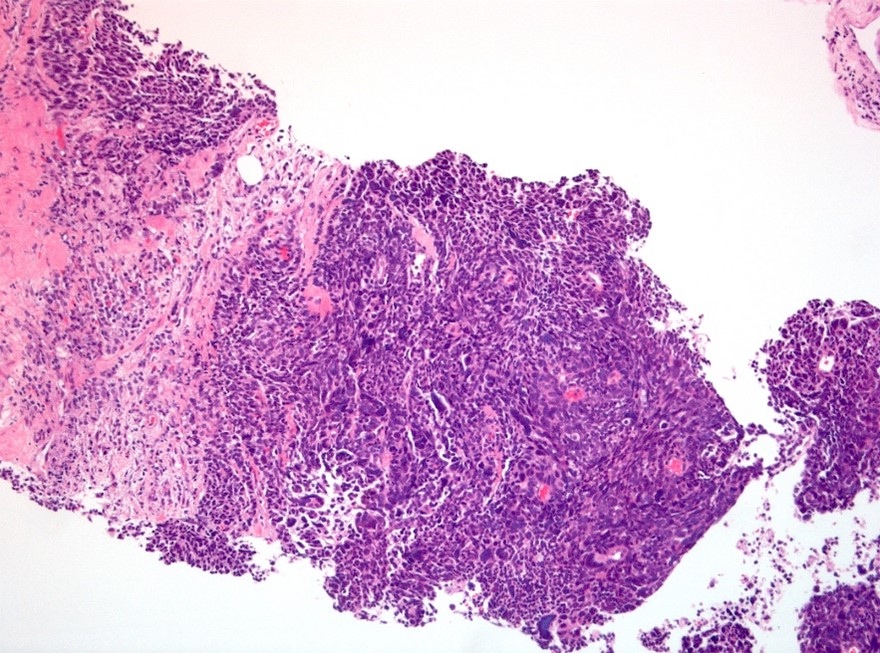
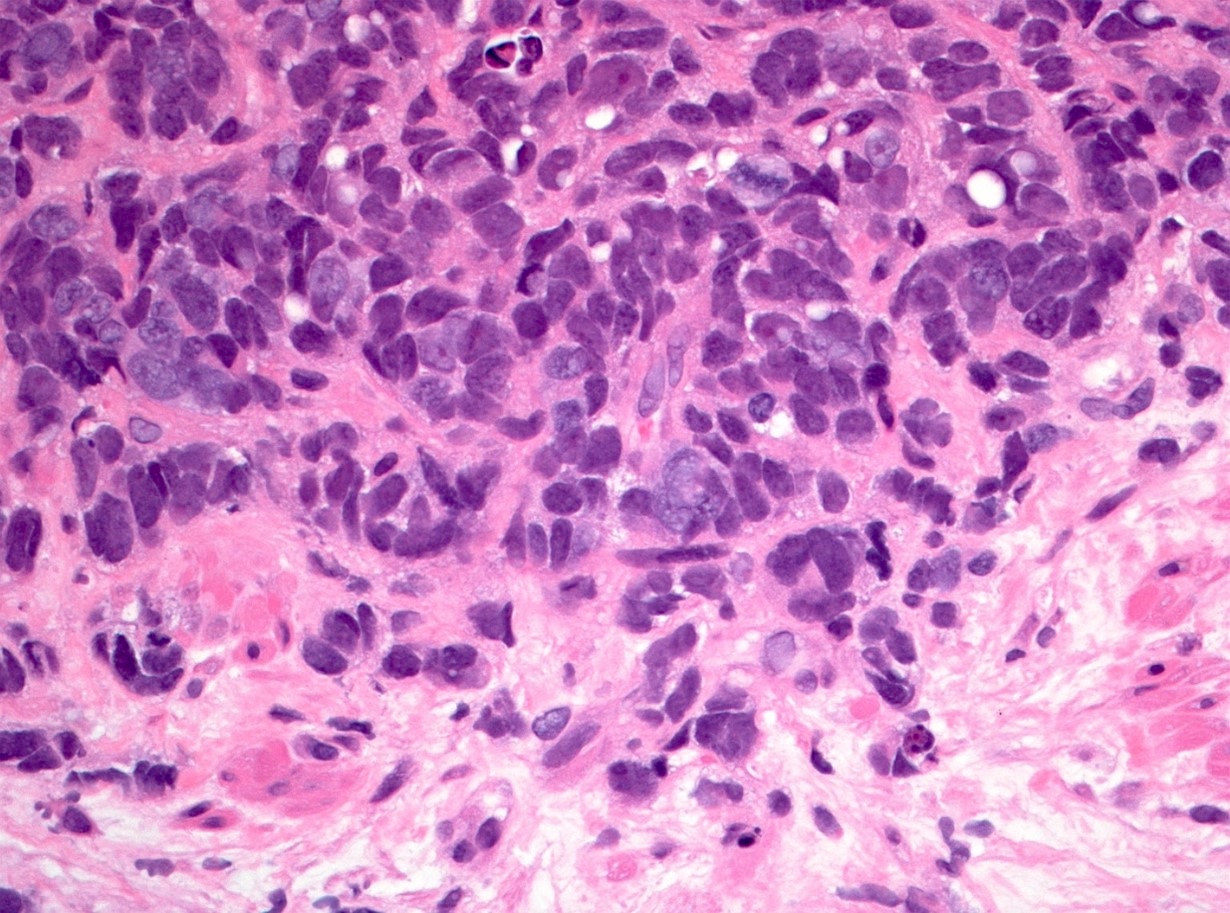
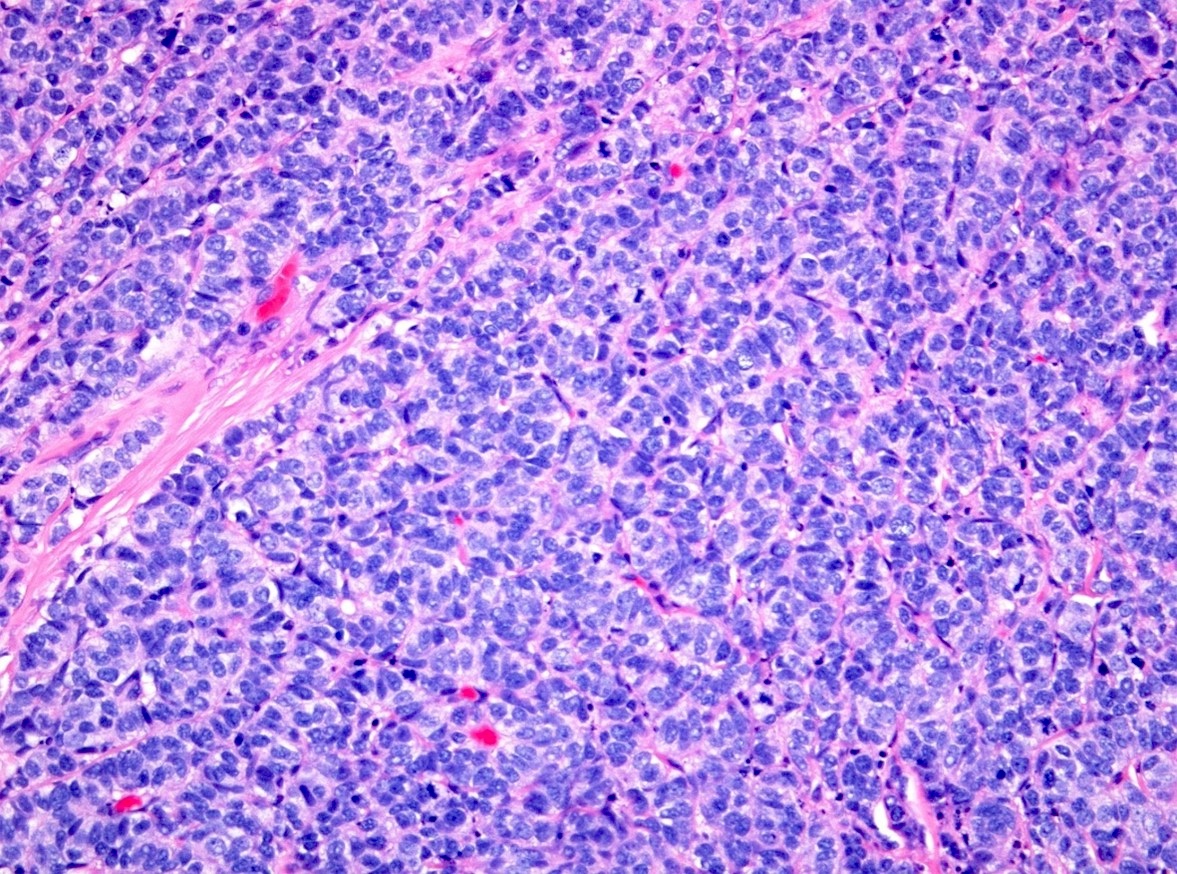
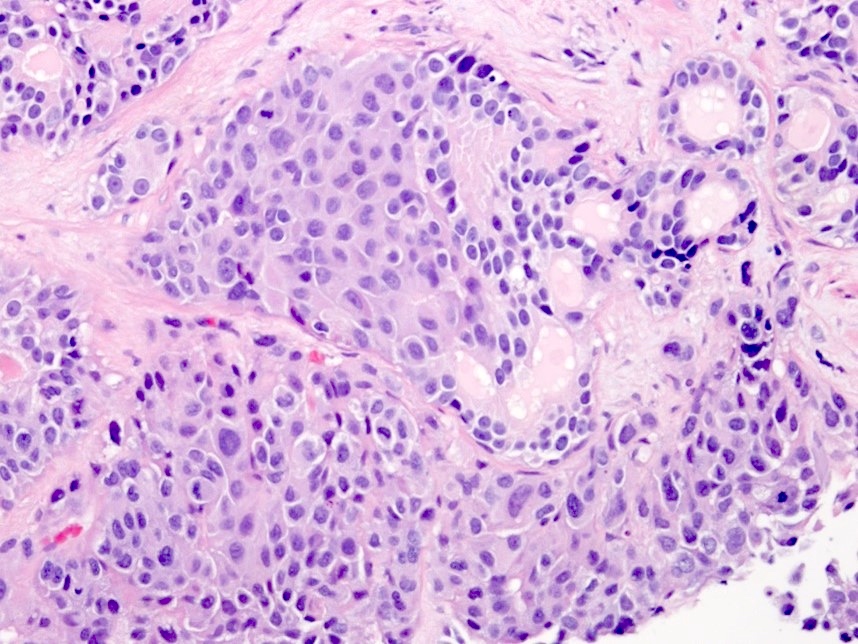
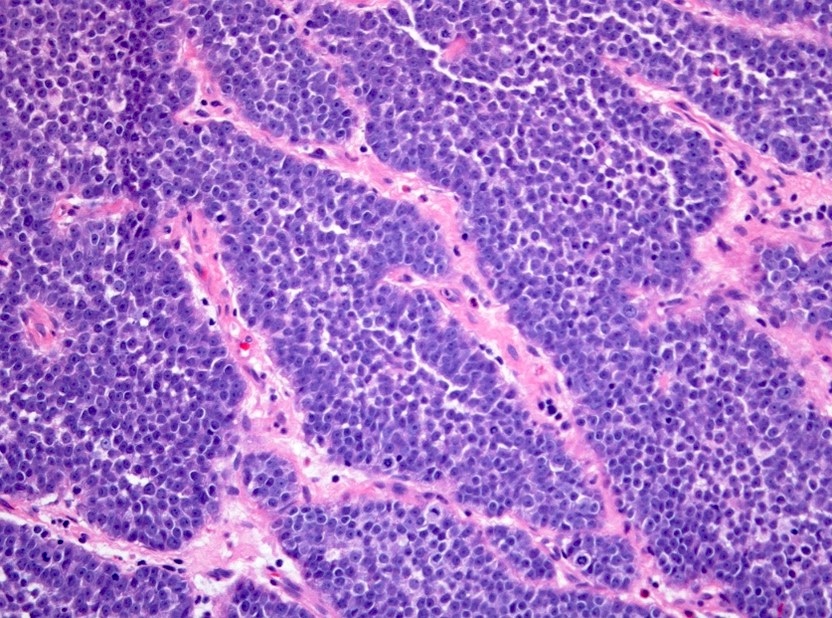
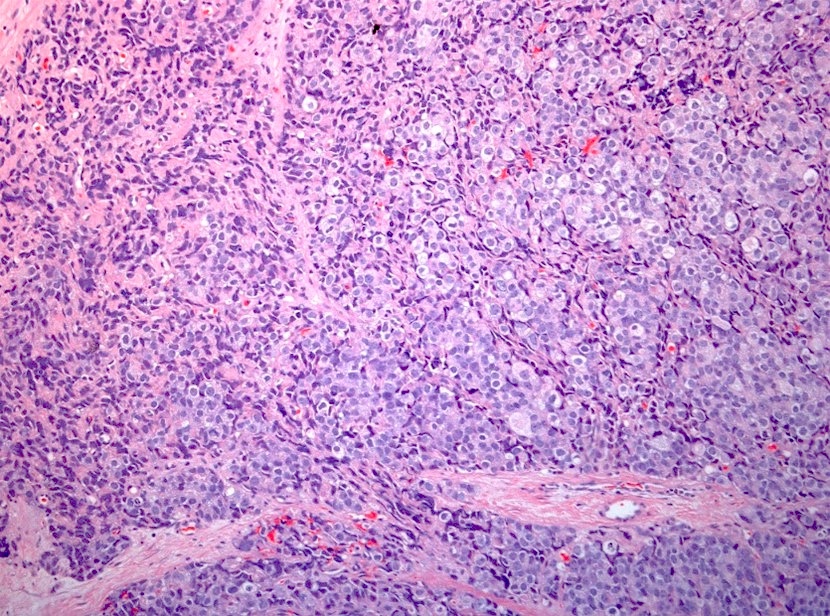
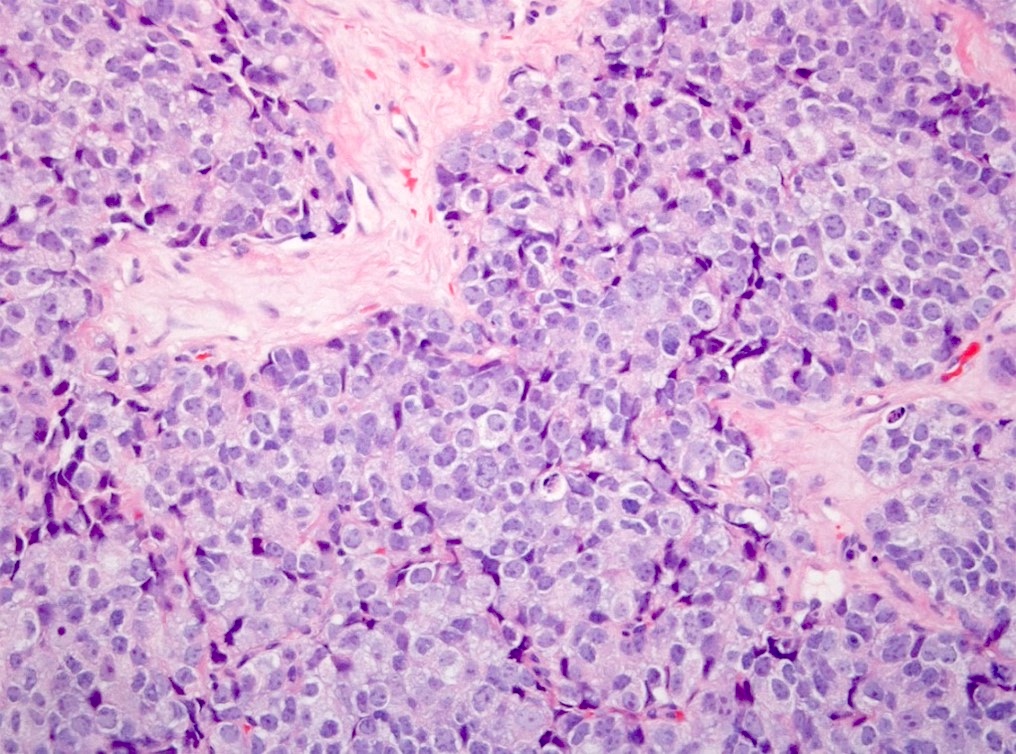
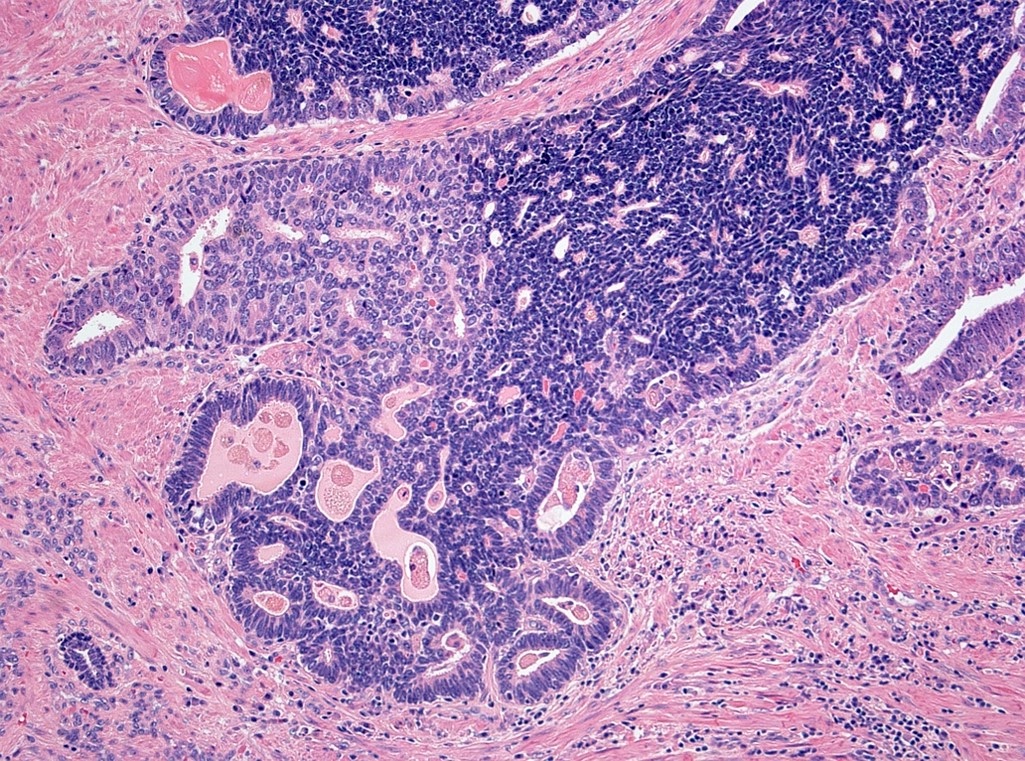
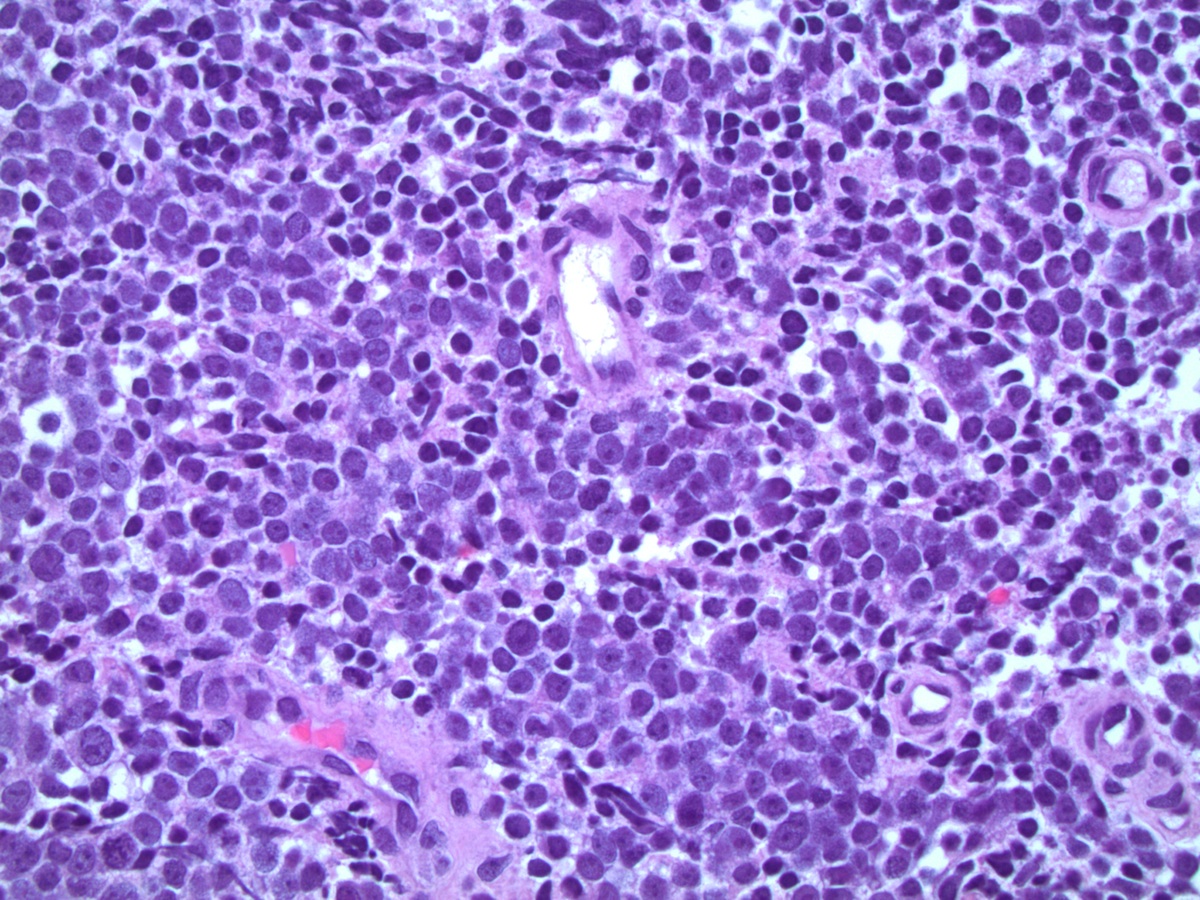
Microscopic (histologic) description
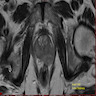
- Small sized tumor cells (diameter of ~3 lymphocytes) with hyperchromatic nuclei, inconspicuous nucleoli and scarce cytoplasm, showing nuclear molding and crush artefact (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:756)
- Presence of pleomorphic giant cells in a minority of cases
- Tumor cells with more open chromatin and visible (not prominent) nucleoli in ~33% of cases
- Tumor cell arrangement in sheets with irregular outlines with occasional rosette forming
- Apoptosis and (geographic) necrosis frequently present
- In the majority of mixed cases, there is a gradual morphological translation between the adenocarcinoma and small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma component (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:65)
- Grading is not applicable for small cell neuroendocrine prostate carcinoma
- In mixed carcinomas, the grade group of the acinar adenocarcinoma component should be reported
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Theodorus van der Kwast, M.D., Ph.D. and Debra Zynger, M.D.
Positive stains
- MIB1 (> 80%)
- Neuroendocrine markers (at least 1 marker positive in 80% of cases)
- p53 expression (50 - 60%)
- References: Hum Pathol 2018;79:151, Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:890
Negative stains
- Prostate markers (positive in 10 - 20% of cases)
- Loss of expression
- References: Hum Pathol 2018;79:151, Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:890
Electron microscopy description
- Presence of neurosecretory granules
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- TMPRSS2::ERG fusion in 50% of cases detectable by FISH (Hum Pathol 2013;44:2227)
- Presence of TMPRSS2::ERG fusion is evidence of prostate origin of the small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma since those of other sites (lung, bladder) do not have this specific gene fusion
Sample pathology report
- Prostate, radical prostatectomy:
- Mixed small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (70%) and adenocarcinoma, grade group 3 (30%) (see synoptic report)
- Positive for established extraprostatic extension (right posterior), bladder neck invasion (right) and bilateral seminal vesicle invasion (pT3b)
- Positive for intraductal carcinoma
- Positive for lymphovascular space invasion
- Surgical margin positive for small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma component (right posterior)
- ~40% of the prostate volume involved by carcinoma
Differential diagnosis
- Adenocarcinoma, grade group 5:
- Prominent nucleoli
- Ample cytoplasm
- Low proliferative activity
- Small cell-like change in intraductal carcinoma:
- Largely within prostatic ducts; may expand in invasive carcinoma
- No / scarce proliferation
- Scattered neuroendocrine cells (immunohistochemistry)
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of prostate:
- Ample pale to amphophilic cytoplasm
- Large nuclei with coarse chromatin and conspicuous nucleoli
Practice question #1
Which of the following is true about de novo small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate?
- Can be diagnosed by morphological features alone even in the complete absence of neuroendocrine marker expression
- Has the same metastatic site distribution as grade group 5 prostate adenocarcinoma
- Is more common than treatment related small cell carcinoma
- Occurs more often in a pure form as compared to mixed small cell / conventional adenocarcinoma
Practice answer #1
A. Can be diagnosed by morphological features alone even in the complete absence of neuroendocrine marker expression. Morphological features are sufficient to make a diagnosis of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate. Although most would express at least 1 neuroendocrine marker, some are entirely negative for all tested neuroendocrine markers. Answer D is incorrect because small cell neuroendocrine is more commonly seen in association with conventional adenocarcinoma. Answer C is incorrect because androgen receptor axis targeted therapy may induce small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (transdifferentiation) and this process is more common with current intensive therapies of metastatic hormone therapy resistant prostate cancer. Answer B is incorrect because small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate metastases have a predilection for visceral sites (e.g., liver, brain) as compared to conventional acinar adenocarcinoma metastases.
Comment Here
Reference: Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma