Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Raza M, Qureshi MB, Ud Din N. Fibrous hamartoma of infancy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuefibroushamart.html. Accessed September 18th, 2025.
Definition / general
- A benign soft tissue neoplasm of infants and young children, showing organoid, triphasic morphology with bundles of bland fibroblastic / myofibroblastic cells, nodules of primitive, rounded or stellate cells with myxoid stroma and mature adipose tissue (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
Essential features
- Organoid, triphasic morphology, variable prominence of bundles of bland fibroblastic / myofibroblastic cells, nodules of primitive, rounded or stellate cells with myxoid stroma and mature adipose tissue (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
Terminology
- Subdermal fibrous tumor of infancy (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-11: LC2Y - other specified hamartomata derived from dermal connective tissue
Epidemiology
- Very rare; mean age at diagnosis: 15 months (range: birth to 14 years); 20% are congenital
- M:F = 2.7:1 (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
Sites
- Commonly involves the axilla, trunk, upper extremities and genital regions (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
Pathophysiology
- Generally considered to be hamartomatous; however, reports of sarcomatous transformation raise the possibility of neoplastic nature (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
- Recurrent EGFR exon 20 insertion / duplication mutations (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1713)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Solitary, painless and freely movable mass of subcutis or dermis
- Younger patients: rapidly growing, ill defined masses
- Older patients: growth slows and lesions show better demarcation
- Cutaneous changes as hyperhidrosis and hypertrichosis (Indian J Dermatol 2013;58:160)
- Rarely associated with tuberous sclerosis and William syndrome (Pediatr Radiol 2009;39:743, Br J Dermatol 2007;156:1052)
Diagnosis
- Primarily based on histological findings of characteristic triphasic morphology with bland fibroblastic / myofibroblastic cell bundles, primitive mesenchyme nodules and mature adipose tissue
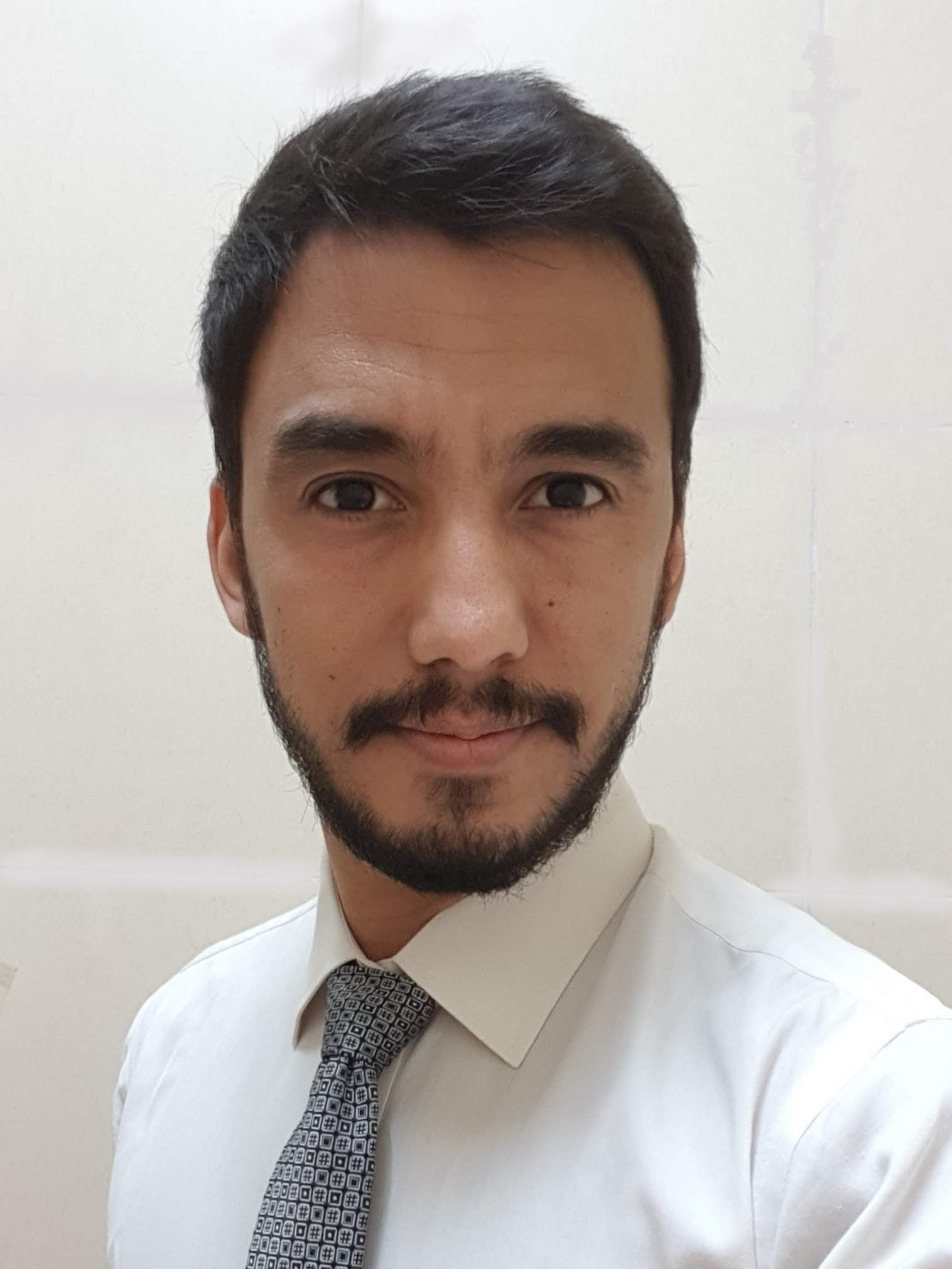
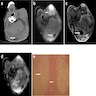
Radiology description
- CT / MRI shows traversing strands of adipose / fibrous intensities with parallel or whirling appearance, in most cases (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2019;20:356)
Prognostic factors
- Cured with local excision (J Am Acad Dermatol 2006;54:800)
- Recurrence rate is very low
- 2 cases with sarcomatous areas resembling undifferentiated sarcoma have been reported (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
Case reports
- 8 month old boy with fibrous hamartoma of infancy in the scrotum (European J Pediatr Surg Rep 2019;7:e100)
- 13 month old boy with giant fibrous hamartoma of infancy in left lower extremity (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19489)
- 15 month old girl with a firm plaque presenting with hypertrichosis and hyperhidrosis on her lower back (Pediatr Dermatol 2015;32:533)
- 5 year old boy with fibrous hamartoma of infancy on the back with William syndrome (Br J Dermatol 2007;156:1052)
Treatment
- Complete local excision
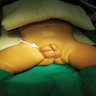
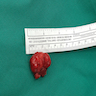
Clinical images
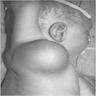
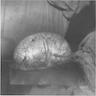
Gross description
- Usually small (mean size: 3 cm); giant lesions are rarely reported (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
- Ill defined with fleshy to yellow cut surface and soft consistency (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:394)
Frozen section description
- Fibrous tissue with bland spindle cells (Ocul Oncol Pathol 2017;3:8)
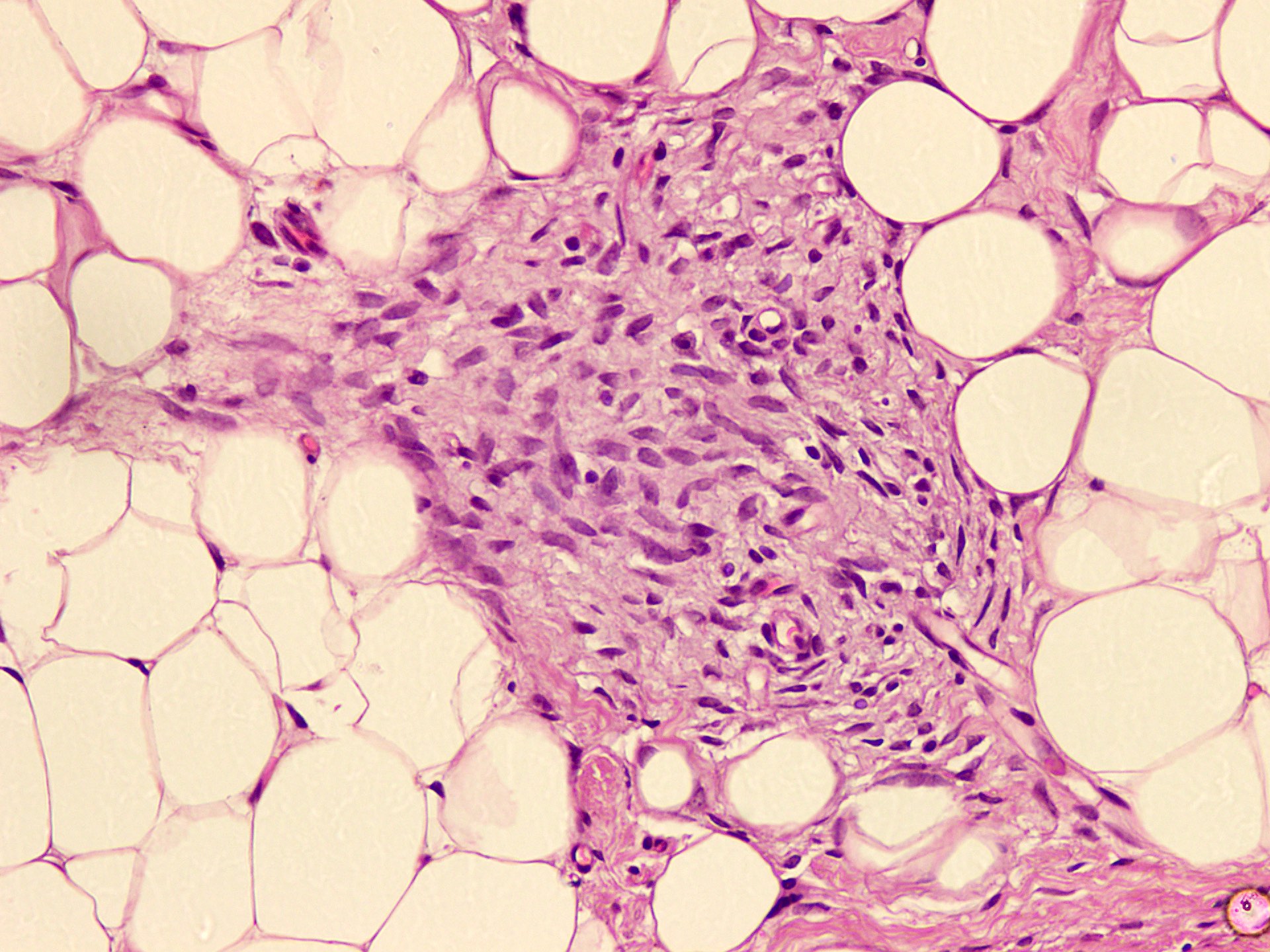
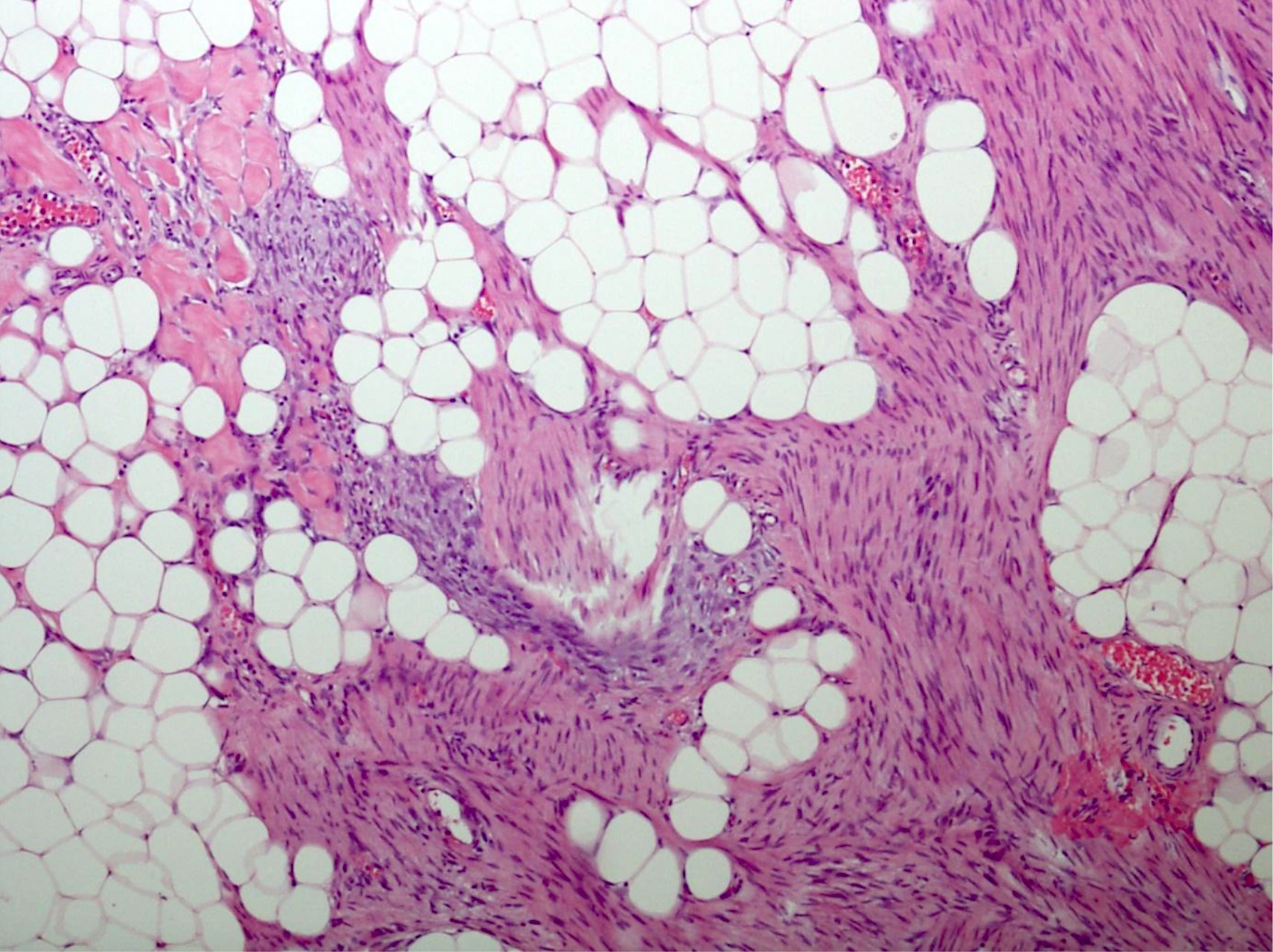
- Organoid triphasic appearance with fat, fibrocollagenous tissue and immature, myxoid to basophilic, mesenchymal components; mitoses and calcification are rare; necrosis is absent
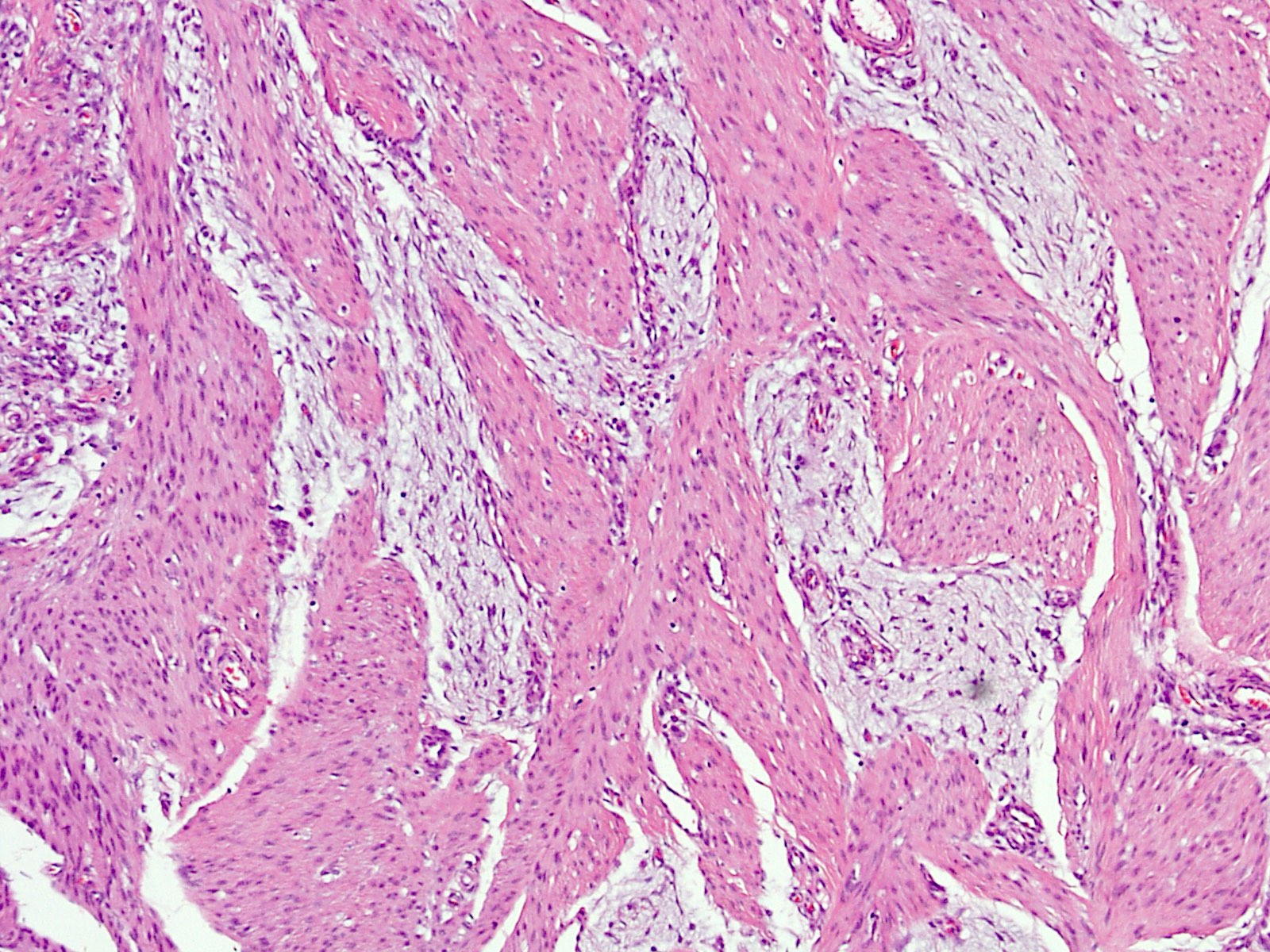
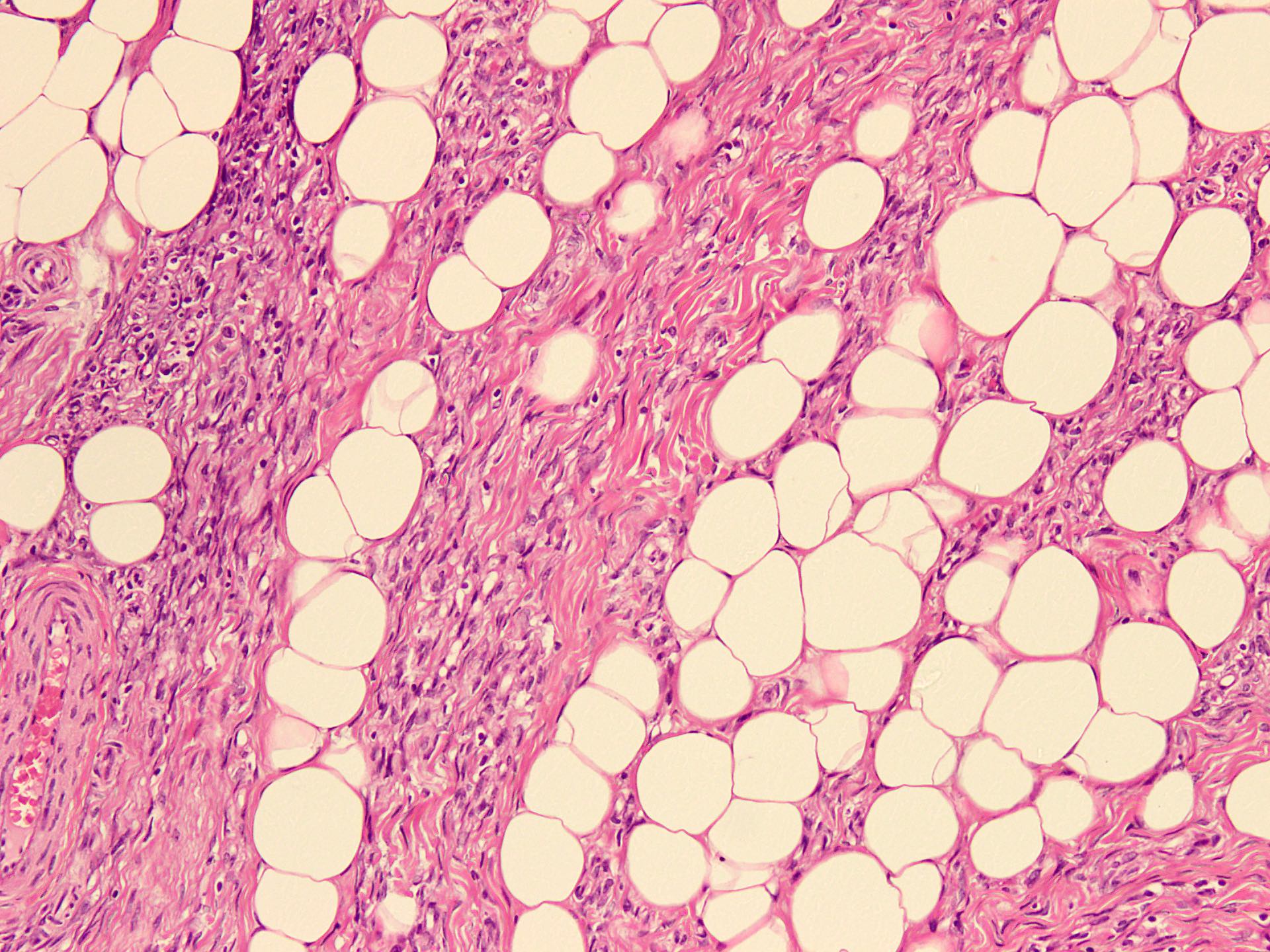
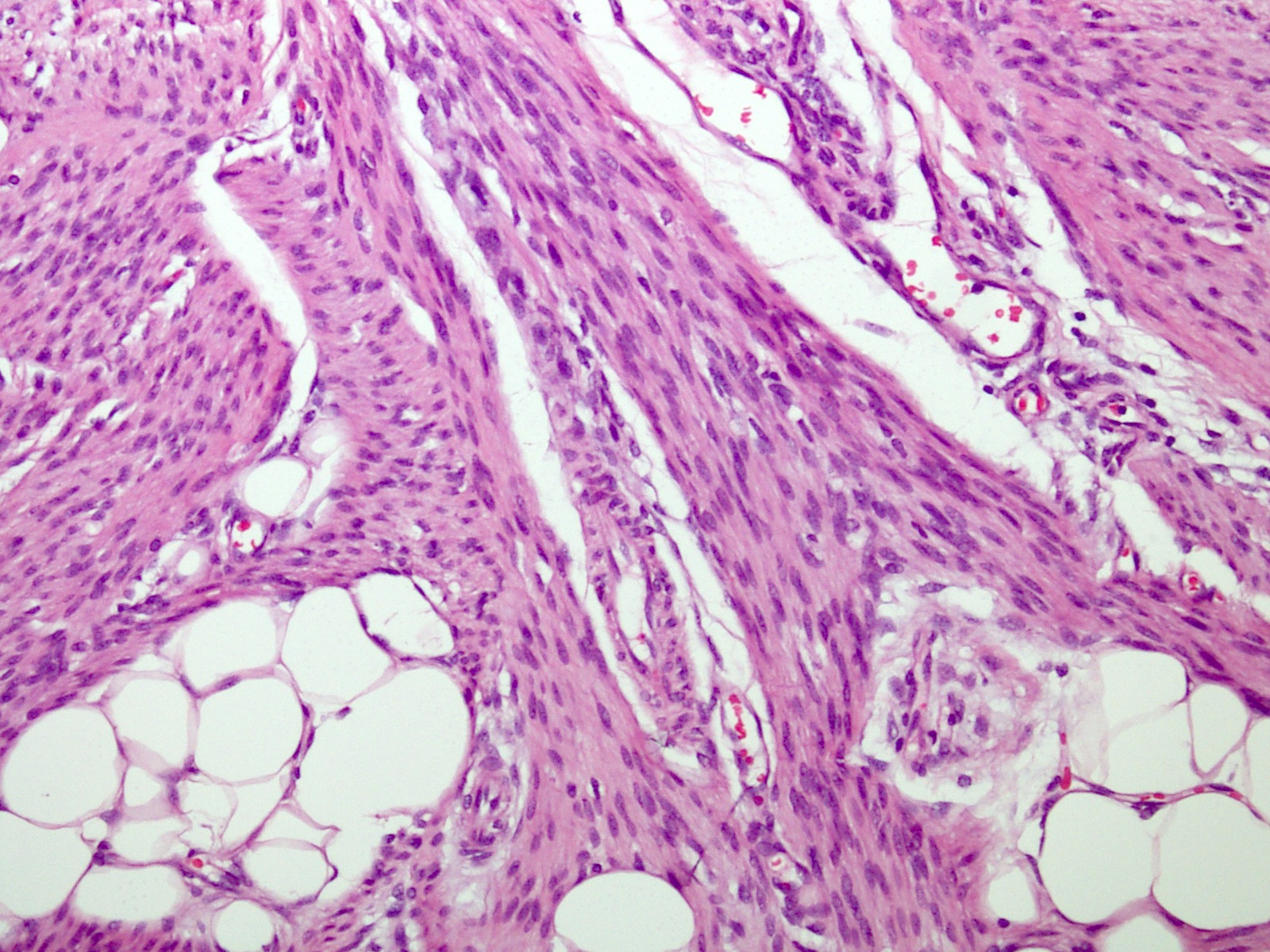
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Variable amounts of 3 components arranged in an organoid pattern
- Mature adipose tissue
- Intersection fascicles of fibrous tissue with prominent collagen deposition; fibroblastic cells show dark wavy nuclei and scant cytoplasm
- Myxoid to basophilic areas with haphazardly arranged bland looking primitive spindle to stellate cells
- Angiectoid areas in 33 - 50% of cases; these areas show densely sclerotic pseudoangiomatous foci with slit-like spaces lined by plump tumor cells, resembling giant cell fibroblastoma (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
- Mitoses are rare, necrosis is absent
- Inflammatory cell infiltrate with aggregate formation may occupy most of the lesion
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Moderately cellular smears with mature adipose tissue admixed with short spindle to plump cells and numerous naked nuclei (Diagn Cytopathol 2003;28:272)
- Myxoid to collagenized background
- No cytological atypia or mitosis
Positive stains
- SMA in fibroblastic areas (55%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:394)
- CD34 in primitive mesenchymal cells and angiectoid areas (Mod Pathol 2017;30:474)
- BCL2 in primitive mesenchymal cells (100%), variable in fibroblastic / myofibroblastic areas (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:394)
- S100 in adipocytic areas only (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:394)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Cells with features of both fibroblasts (and possibly myofibroblasts) and occasional fusiform banded fibers (Luse bodies) (Hum Pathol 1982;13:586)
- Cellular myxoid areas showed prominent vasoformative proliferation (Hum Pathol 1984;15:717)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- EGFR exon 20 insertion / duplication mutations (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1713)
Videos
Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
Sample pathology report
- Axilla, excisional biopsy:
- Fibrous hamartoma of infancy, 3.5 cm (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show an ill defined, vaguely organoid lesion in the subcutaneous tissue. It is composed of abundant mature adipose tissue, fibrous tissue and myxoid spindle cells nodules. Fibrous areas show dense hyalinization with slit-like spaces, lined by bland spindle cells. Myxoid nodules show haphazardly arranged primitive spindle cells. No hyperchromatic, multinucleated, floret-like giant cells are noted. There is no significant mitotic activity. Necrosis and calcification are also absent. CD34 is positive in fibrous areas and myxoid nodules. The lesion appears to be completely excised.
Differential diagnosis
- Lipofibromatosis:
- Peak incidence in first decade
- Common in hand and extremities
- Long fascicles of uniform bland spindle cells in a collagenized stroma
- Lacks the immature mesenchymal component
- Giant cell fibroblastoma:
- Mean age at diagnosis is 6 years
- Most cases occur in trunk, groin and axilla
- Can mimic, with cases showing prominent angeictoid areas
- Scattered hyperchromatic, multinucleated, floret-like giant cells are discriminatory
- Positive for t(17;22), which results in COL1A1::PDGFB fusion
- Calcifying aponeurotic fibromas:
- Occurs in the first or second decade of life
- Commonly involves hand, wrist and foot
- Infiltrative fascicles of fibroblastic cells
- Calcified, vaguely chondroid looking nodules surrounded by epithelioid cells
- Osteoclast-like giant cells adjacent to chondroid nodules
- FN1::EGF fusion gene has been recently documented
- Lipoblastoma:
- Most cases occur during first 3 years of life
- Commonly involves lower and upper extremities
- May pose a challenge in cases with prominent nodular myxoid zones of immature mesenchymal tissue
- Has a more distinctive lobular architecture
- Nuclear staining for PLAG1
- Infantile myofibroma:
- Congenital in 67% of cases
- 3 subtypes: solitary, multiple and generalized
- Fascicles of bland spindle cells infiltrating adipose tissue
- Hemangiopericytoma-like vessels surrounded by primitive round or polygonal cells
- Lacks abundant fat and often shows a distinctive perivascular growth pattern at the periphery
- Sometimes shows necrosis or calcification in the center
- Fibromatosis:
- Usually deep seated
- Lacks primitive mesenchymal component
- Beta catenin positive
- Cellular schwannoma:
- Can mimic cases with predominance of immature mesenchymal nodules
- S100 positive in spindle cells
- Infantile fibrosarcoma:
- Can mimic cases with predominance of immature mesenchymal nodules
- Unusually large, hypercellular and frequent mitoses
- ETV6::NTRK3 gene fusion
Additional references
Practice question #1
An 11 month old boy was incidentally found to have a soft lump in the axilla. An excisional biopsy was performed and a representative section is shown in the image above. CD34 positivity was seen in fibrous and myxoid areas. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnosis?
- Fibromatosis
- Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
- Giant cell fibroblastoma
- Spindle cell hemangioma
- Spindle cell lipoma
Practice answer #1
B. Fibrous hamartoma of infancy. 3 essential elements of fibrous hamartoma of infancy are visible. Presence of immature myxoid spindle cell aggregates is unique to this entity and is not seen in fibromatosis, giant cell fibroblastoma or spindle cell hemangioma. CD34 positive angiectoid areas are not seen in spindle cell lipoma, which otherwise may closely resemble fibrous hamartoma of infancy.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
Practice question #2
Which of the following genetic alterations has been recently associated with fibrous hamartoma of infancy?
- COL1A1::PDGFB gene fusion
- CTNNB1 gene mutation
- EGFR gene mutation
- ETV6::NTRK3 gene fusion
- PDGFRB gene mutation
Practice answer #2
C. EGFR gene mutation. COL1A1::PDGFB gene fusion is associated with giant cell fibroblastoma, while CTNNB1 gene mutation is present in fibromatosis. EGFR gene mutation (EGFR exon 20 insertion / duplication) has been recently described in fibrous hamartoma of infancy. ETV6::NTRK3 gene fusion is seen in infantile fibrosarcoma and PDGFRB gene mutation is associated with myofibroma.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous hamartoma of infancy