Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Postoperative spindle cell nodule. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderpostopspindle.html. Accessed April 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Reactive lesion that occurs weeks to months after transurethral resection of prostate (in men) or bladder lesions in area of surgery
- Similar features as inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor but with a history of surgery
- First described in 1990 (Urology 1990;35:342, J Urol 1990;143:824)
Terminology
- Also called pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferation (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:787)
Epidemiology
- Usually women
Clinical features
- Sometimes incidental
- May present with hematuria or obstructive voiding symptoms
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis
Treatment
- Transurethral resection; no recurrences or metastases (Hum Pathol 2007;38:753)
Gross description
- Friable nodule, mean size 1 cm
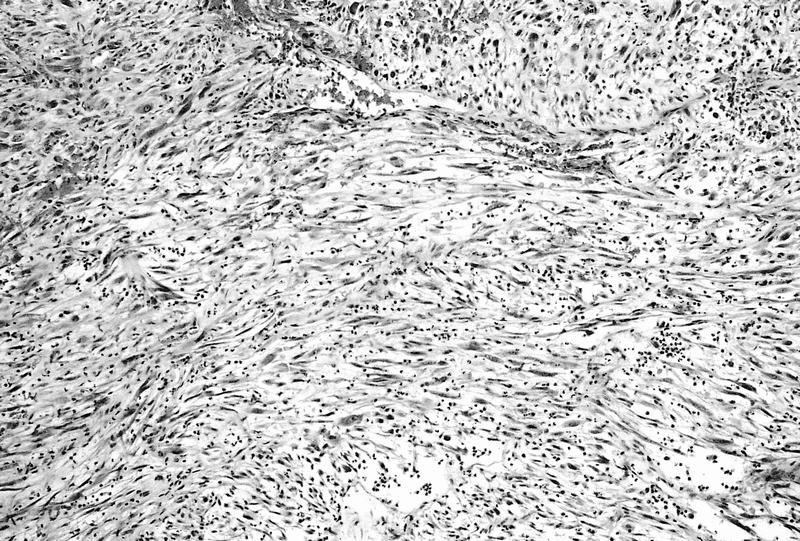
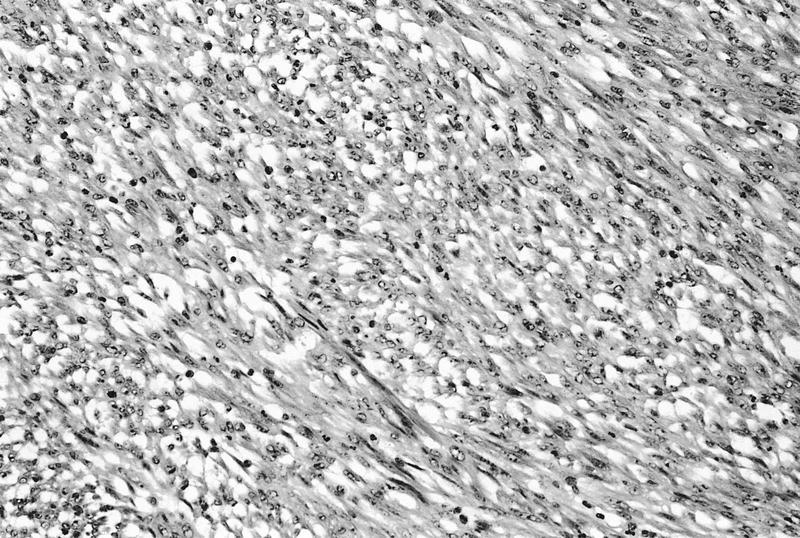
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cellular, fascicular growth pattern of plump or elongated spindle cells which infiltrate the bladder wall and may focally destroy muscle
- Delicate network of small blood vessels in edematous or myxoid stroma with red blood cell extravasation
- Ulcerated surface with acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrate
- May show low to high mitotic activity but no atypical mitotic figures, resembles sarcoma but no atypia
- No necrosis, no significant pleomorphism
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- May have intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (Diagn Cytopathol 1992;8:171)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- May have trisomy 7 (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2007;174:147)
Differential diagnosis
- Kaposi sarcoma:
- No history of recent procedure, primarily a vascular tumor
- Myxoid leiomyosarcoma:
- No history of recent procedure; has smooth muscle morphology, pleomorphism, atypical mitotic figures, necrosis
Additional references