Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Alexiev BA. Clear cell chondrosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/boneclearcellchondrosarcoma.html. Accessed May 14th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma is a low grade malignant cartilaginous epiphyseal neoplasm characterized by lobules of cells with abundant clear cytoplasm
Essential features
- Epiphyseal location
- Clear cells with abundant cytoplasm and centrally placed nucleus
- Presence of woven bone and osteoclast-like giant cells
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9242/3 - clear cell chondrosarcoma
- ICD-11: 2B50.Z & XH7XB9 - chondrosarcoma of bone and articular cartilage of unspecified sites & clear cell chondrosarcoma
Epidemiology
- Clear cell chondrosarcomas account for 2.7% of all chondrosarcomas (J Bone Oncol 2019;19:100267)
- Lesion most commonly occurs in adults, generally in the third or fourth decade (Pathologe 2000;21:449)
- Men are almost 3 times more likely to develop clear cell chondrosarcoma than women (Am J Surg Pathol 1984;8:223)
Sites
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma has a predilection for the epiphyses of long tubular bones (Pathologe 2000;21:449)
- Proximal femur is the most frequent site of involvement (68%), followed by the proximal humerus (23%) (Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:687)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Pain in the affected bone is the most common presenting symptom (Am J Surg Pathol 1984;8:223)
- Pain history is of long duration, sometimes more than 5 years
- Sometimes, patients with a clear cell chondrosarcoma present with a pathological fracture (Case Rep Oncol Med 2021;2021:7205649)
Diagnosis
- Correlation of radiological and clinicopathological features is mandatory in the diagnosis of all bone tumors, including clear cell chondrosarcoma
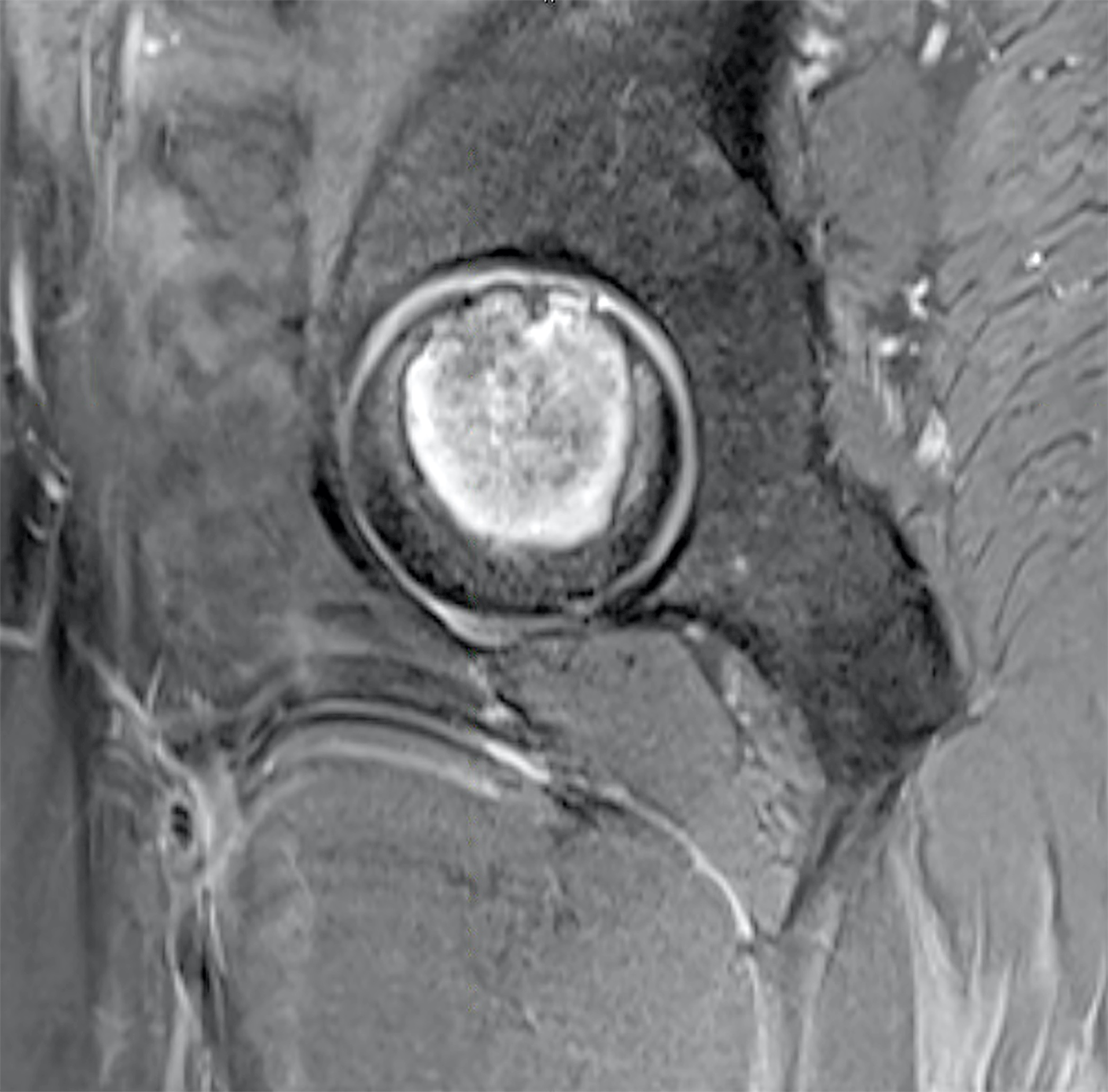
Radiology description
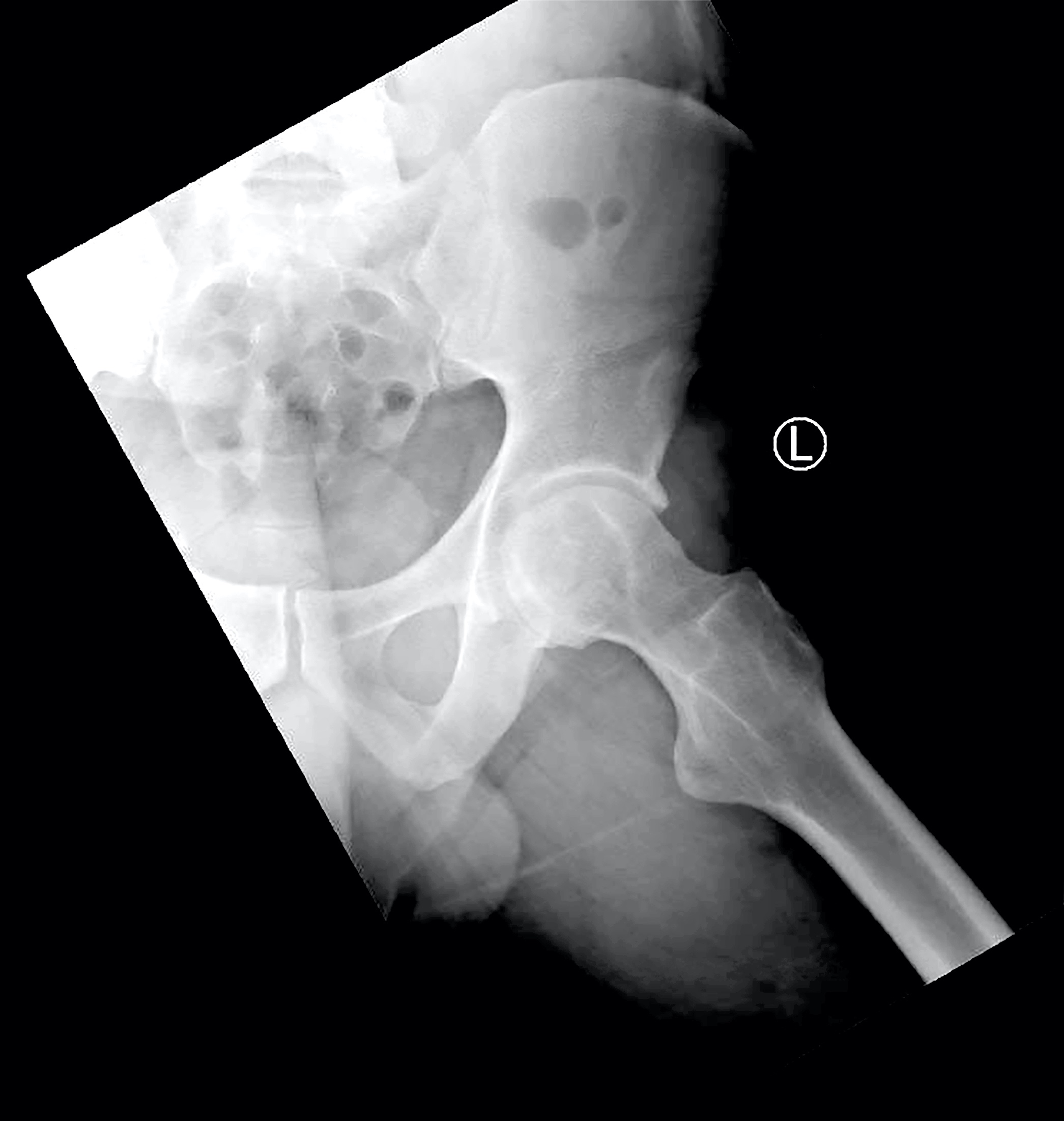
- Typical radiolographic manifestation of this tumor is a slow growing epiphyseal or epimetaphyseal osteolytic lesion with a sclerotic border (J Bone Oncol 2019;19:100267, Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:687)
- Subtle cartilaginous calcifications are seen in > 50% of cases and a periosteal reaction may also be present
- Lesions in the axial skeleton are typically expansile and destructive, often with soft tissue extension and a lack of mineralization (Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:687)
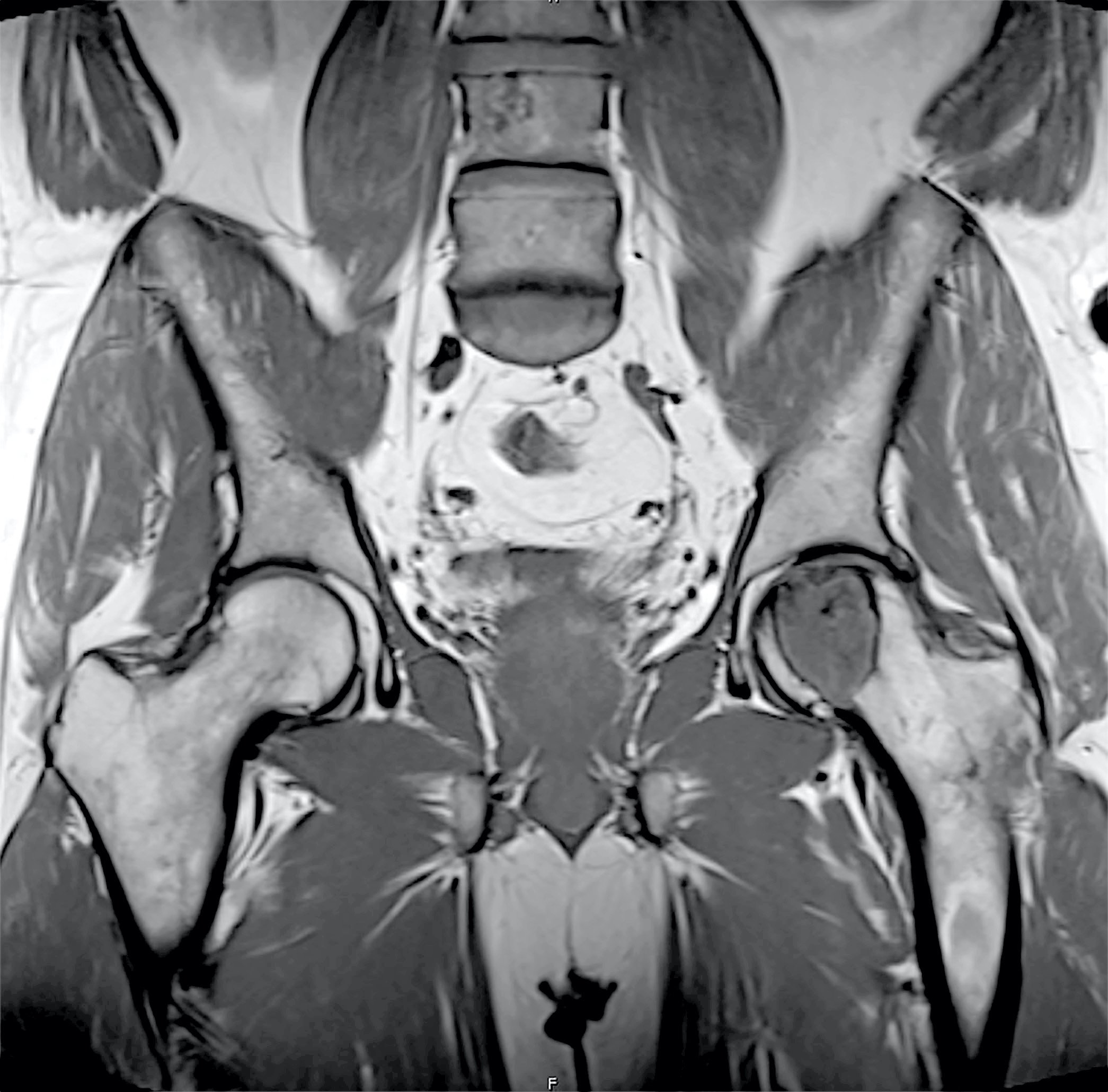
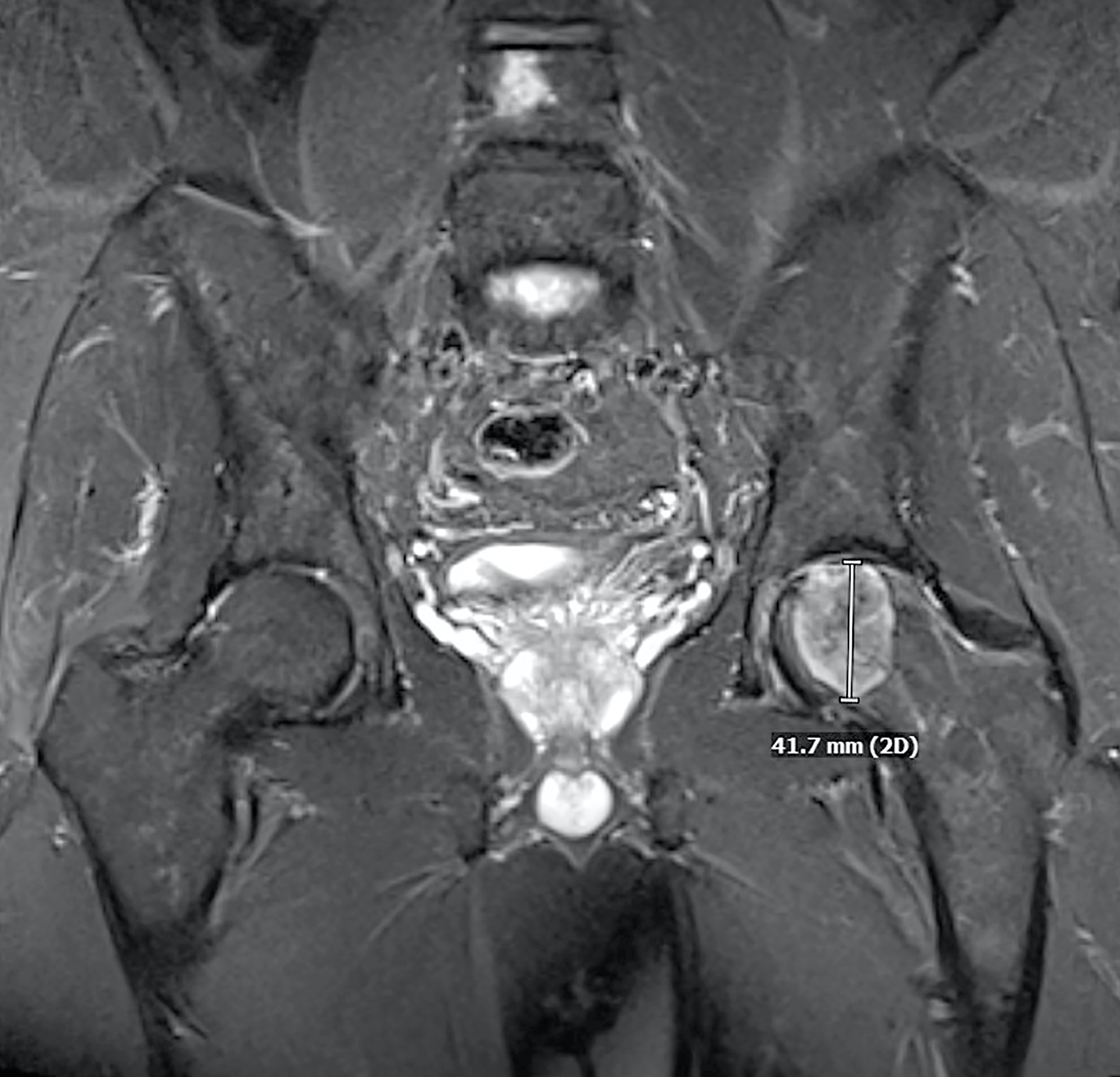
- MR imaging is superior to conventional radiographs for demonstrating the intramedullary extent of a lesion as well as soft tissue extension (Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:687)
- CT images better delineate the presence of cortical destruction and the character of matrix mineralization patterns (Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:687)
- On T1 weighted sequences, the tumor is typically of low signal intensity (Skeletal Radiol 2002;31:88, Skeletal Radiol 2003;32:687)
- On T2 weighted sequences, there is a heterogeneous pattern with overall low to intermediate signal intensity (Skeletal Radiol 2002;31:88)
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma and chondroblastoma may have a very similar radiographic appearance, which prevents a reliable differentiation of the 2 tumors (Skeletal Radiol 2002;31:88)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis of clear cell chondrosarcoma is excellent when treated adequately with wide surgical resection, with 10 year disease survival approaching 90% (Radiol Case Rep 2015;8:848)
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma has a tendency for very late recurrence and metastasis 20 years after initial diagnosis
- Metastases in lungs and other skeletal sites develop in 15 - 20% of cases
- Bone metastases are as common as pulmonary metastases (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2020;478:2537)
- Dedifferentiation to high grade sarcoma has been reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1079)
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with a mass in the thoracolumbar region (Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2021;72:103154)
- 50 year old woman with proximal left femur mass (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:766)
- 55 year old woman with lytic lesion in right femoral head (J Clin Orthop Trauma 2017;8:93)
- 67 year old man with right humeral head mass (Radiol Case Rep 2015;8:848)
- 70 year old man with T7-8 thoracic spine mass (Int J Surg Pathol 2017;25:181)
Treatment
- Wide en bloc resection with clear margins is usually curative (Am J Surg Pathol 1984;8:223, Clin Orthop Relat Res 2020;478:2537)
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma can recur locally or distantly in the bones and lungs in the long term; therefore, patients should be informed of the risk of very late recurrence and the necessity for decades of surveillance to detect any local recurrence or lung and bone metastases (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2020;478:2537)
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma is not sensitive to radiation or chemotherapy (Radiol Case Rep 2015;8:848)
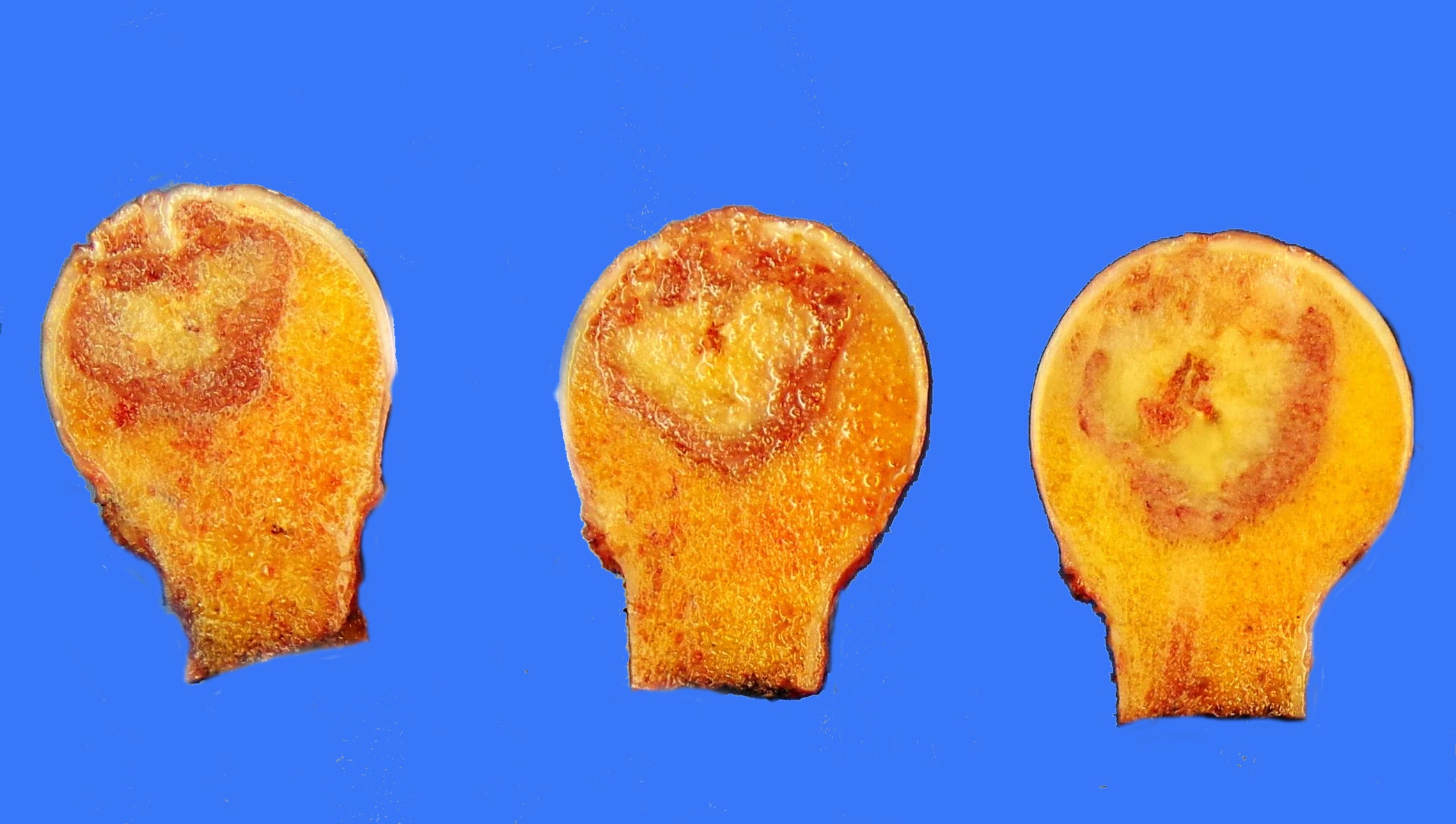
Gross description
- Firm lobular pattern of growth (Head Neck Oncol 2012;4:13)
- Yellow-white, well defined, sometimes with cystic areas (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:766)
- Lesions contain soft but gritty material
- Features of hyaline cartilage can be focal or absent
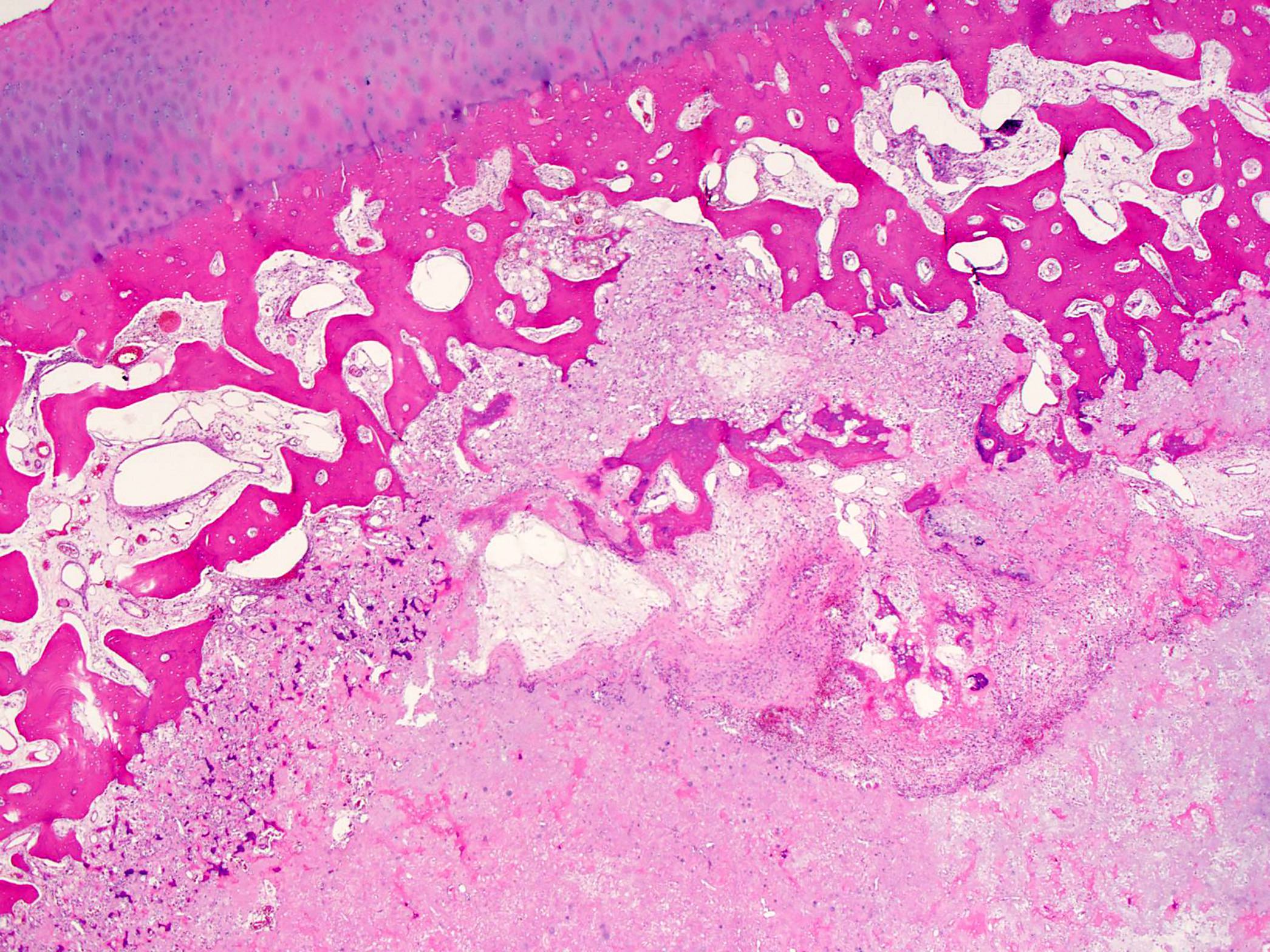
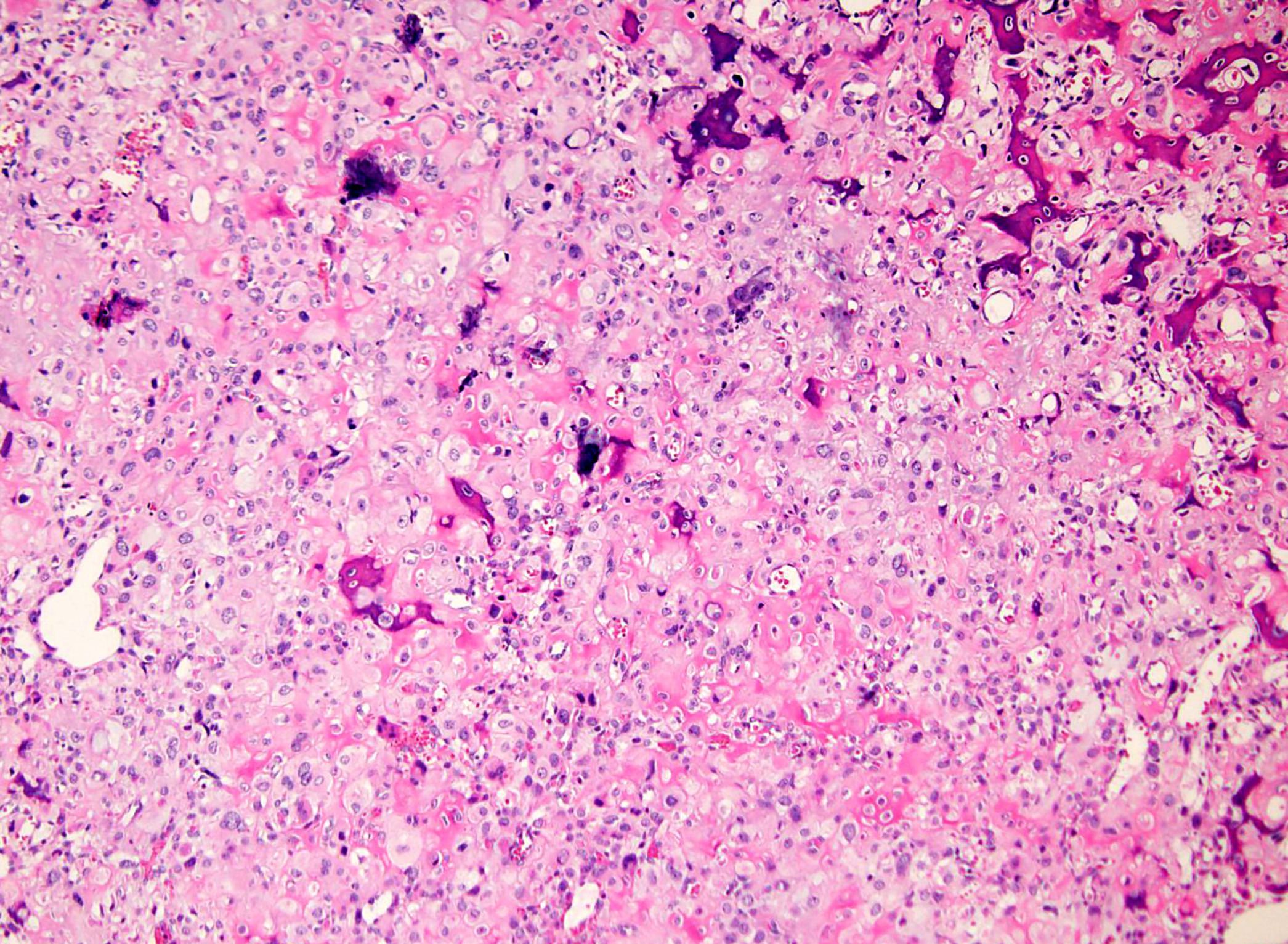
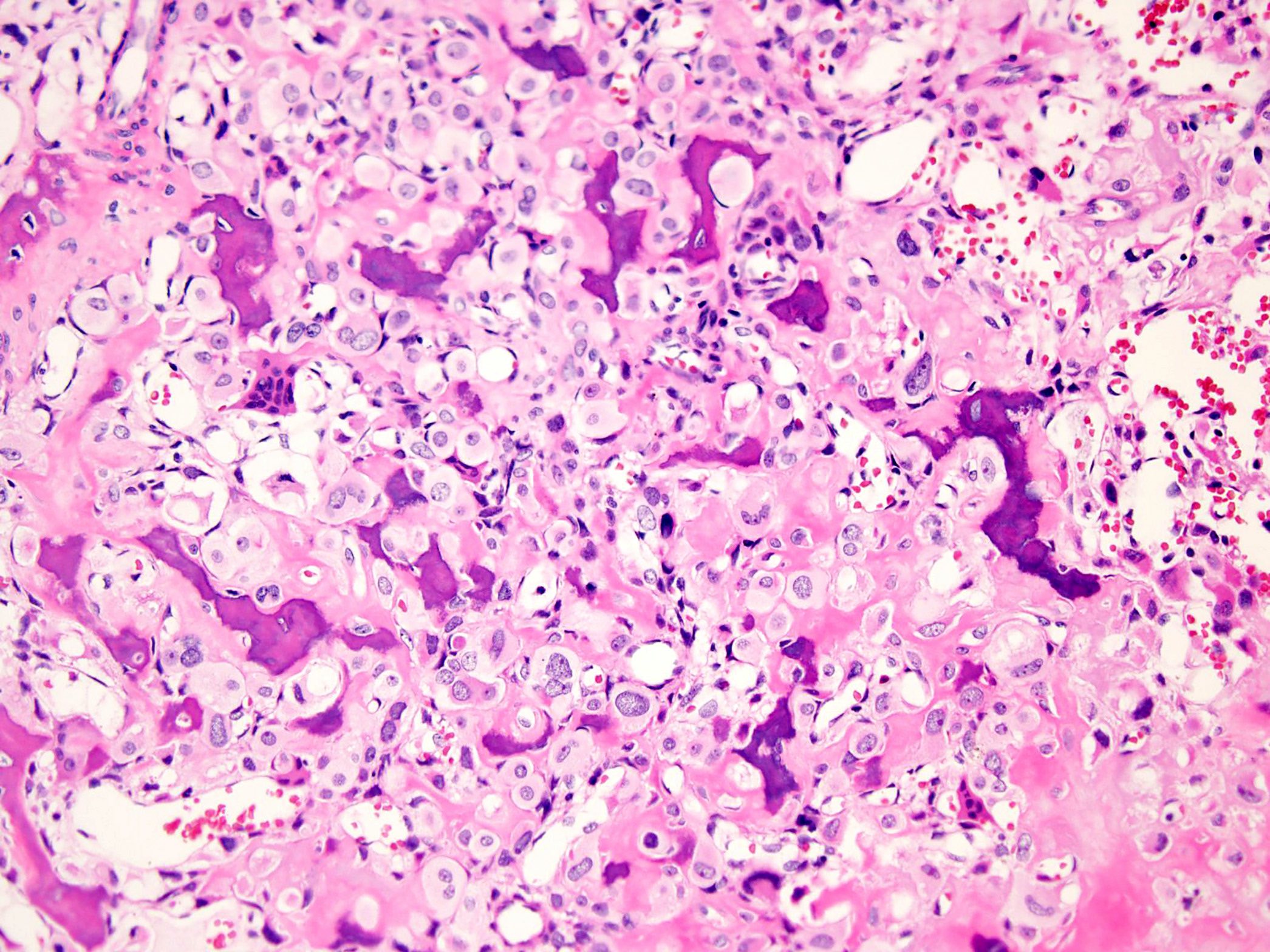
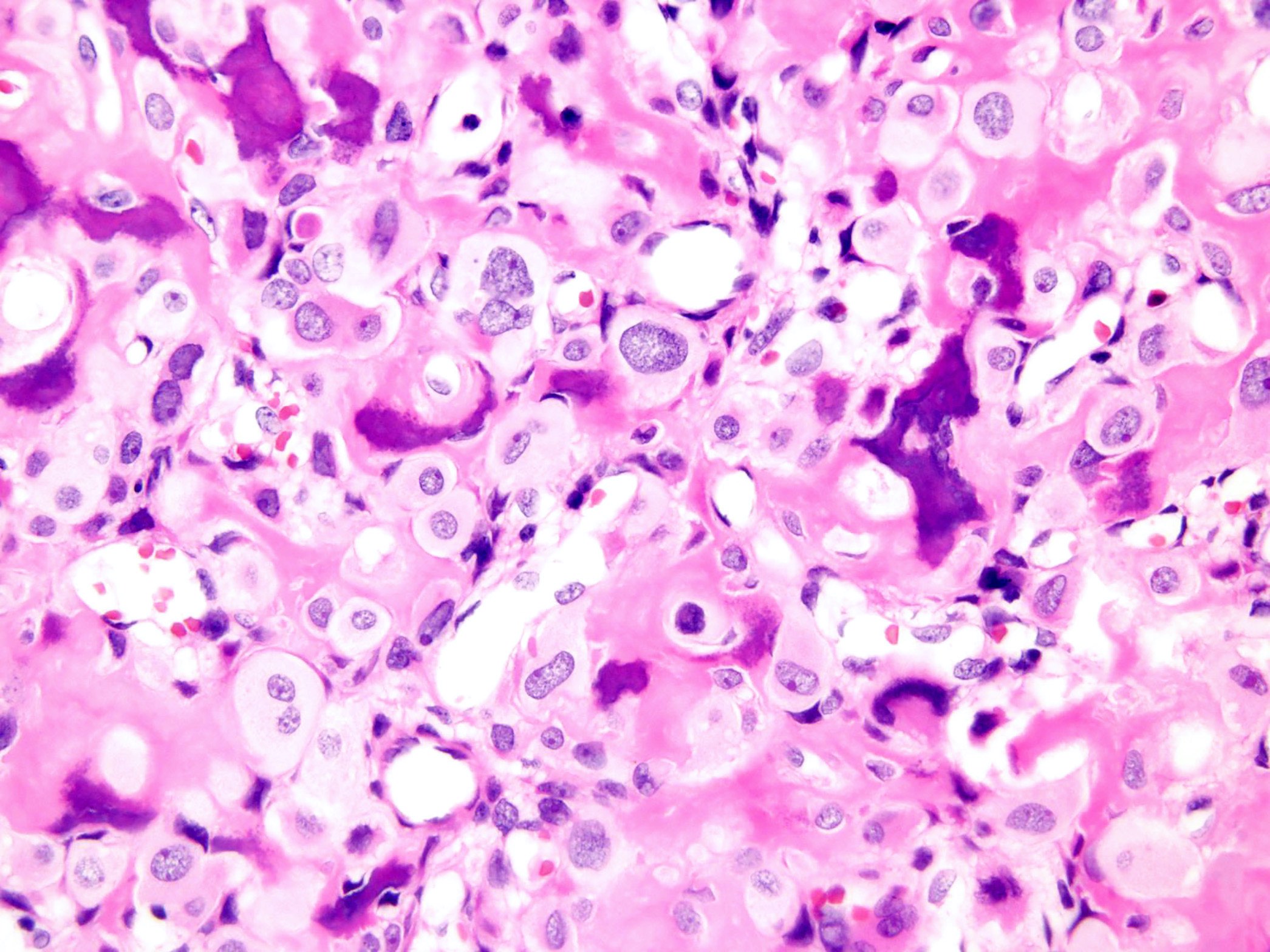
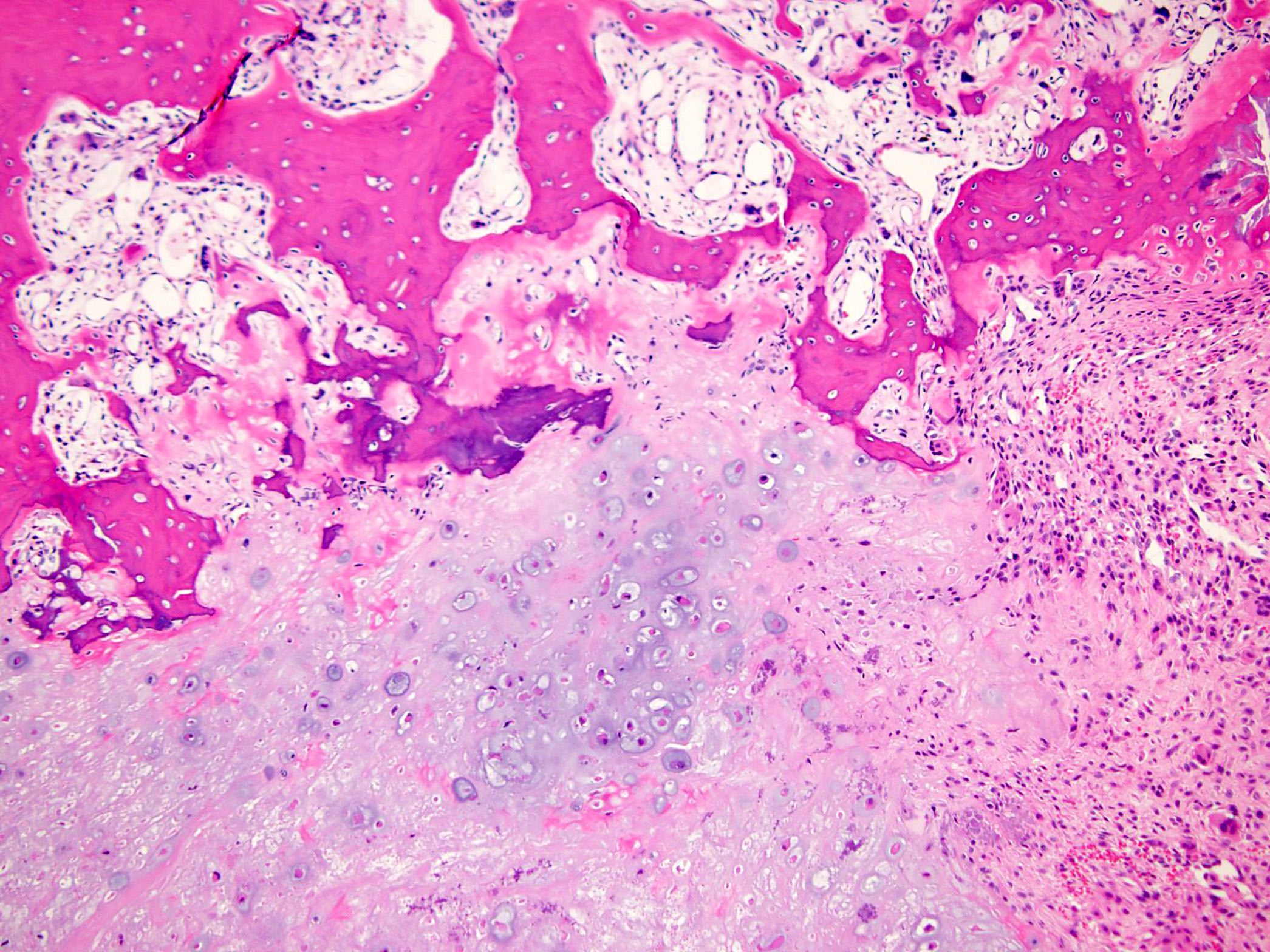
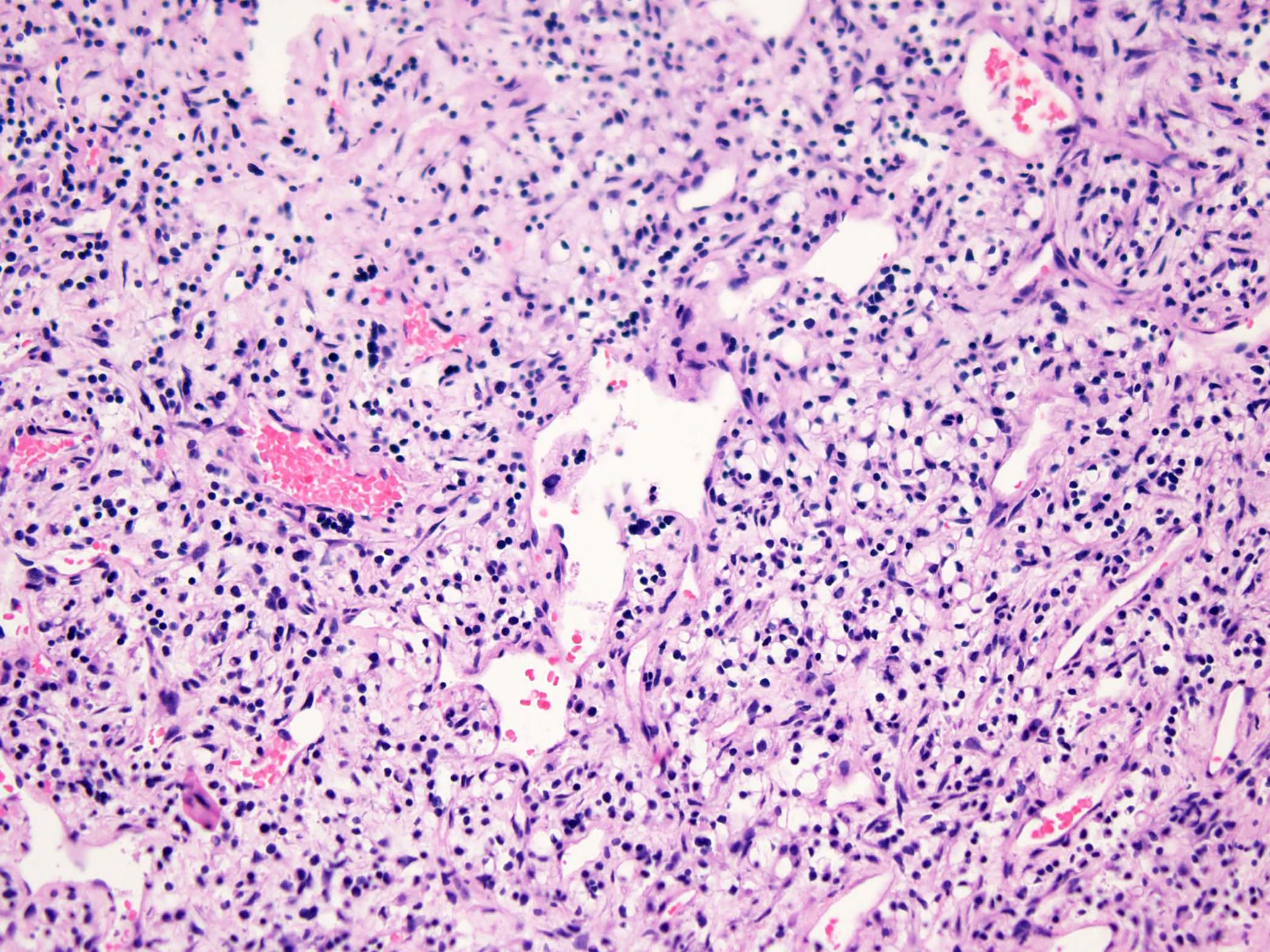
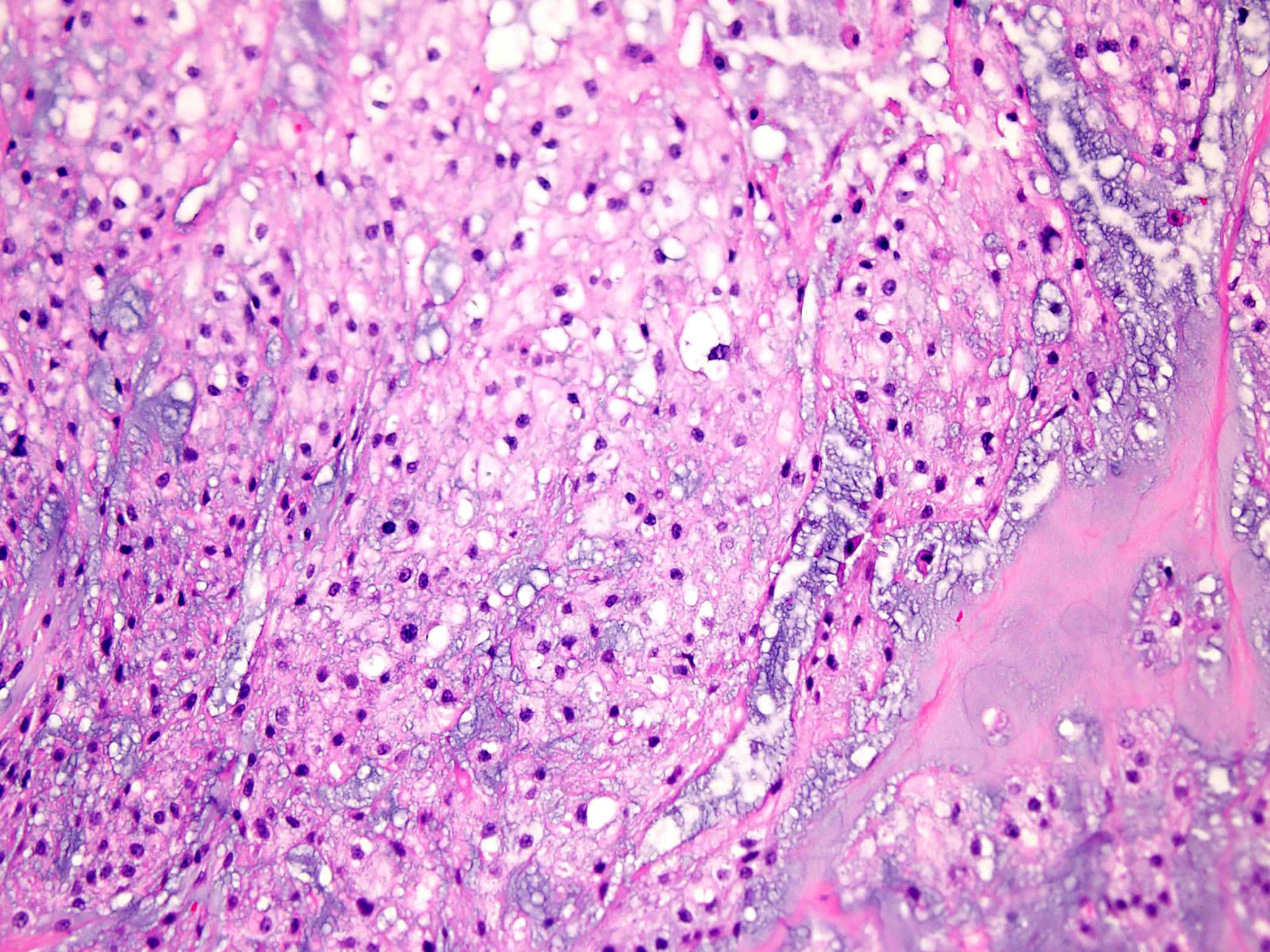
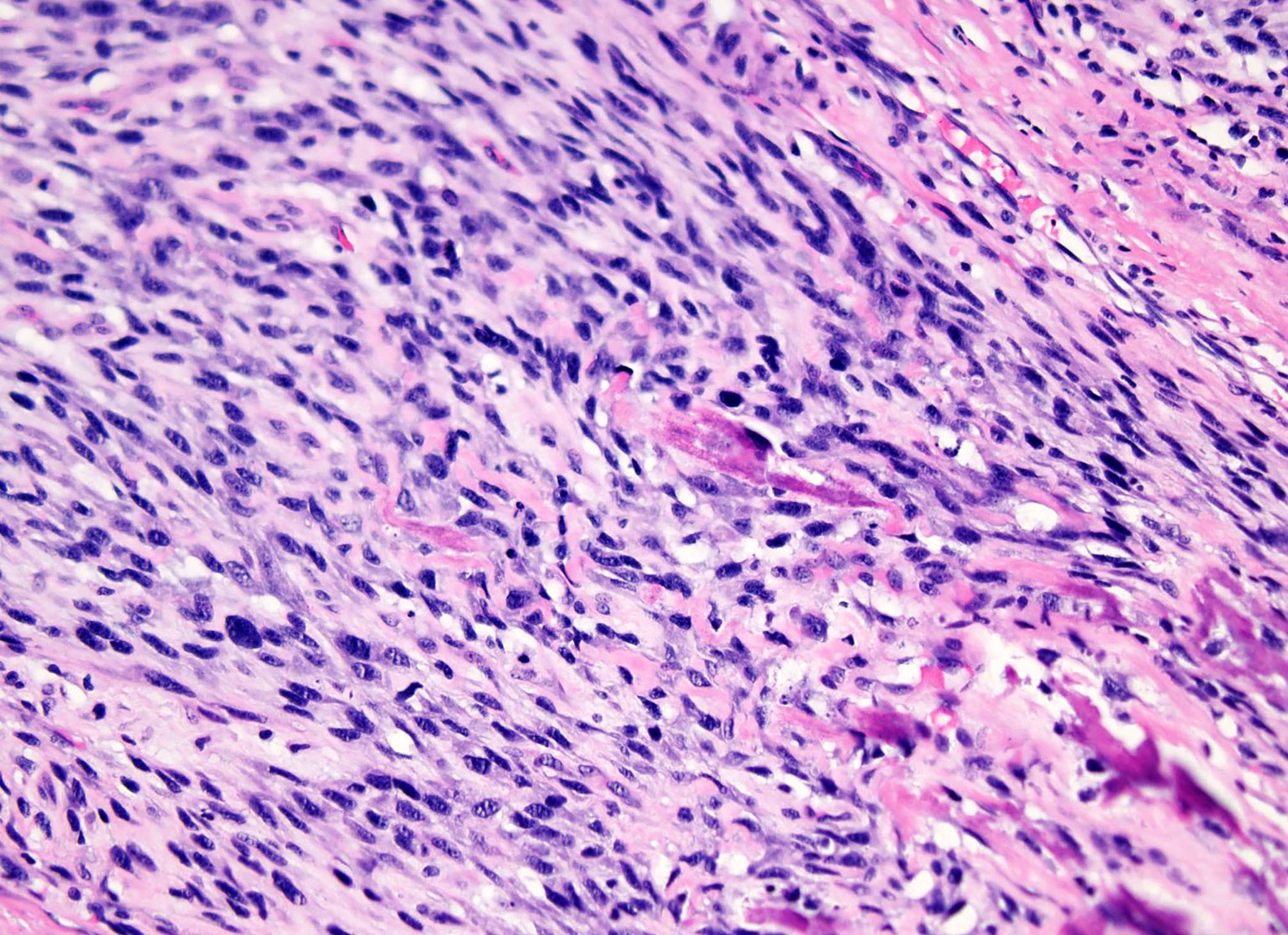
Microscopic (histologic) description
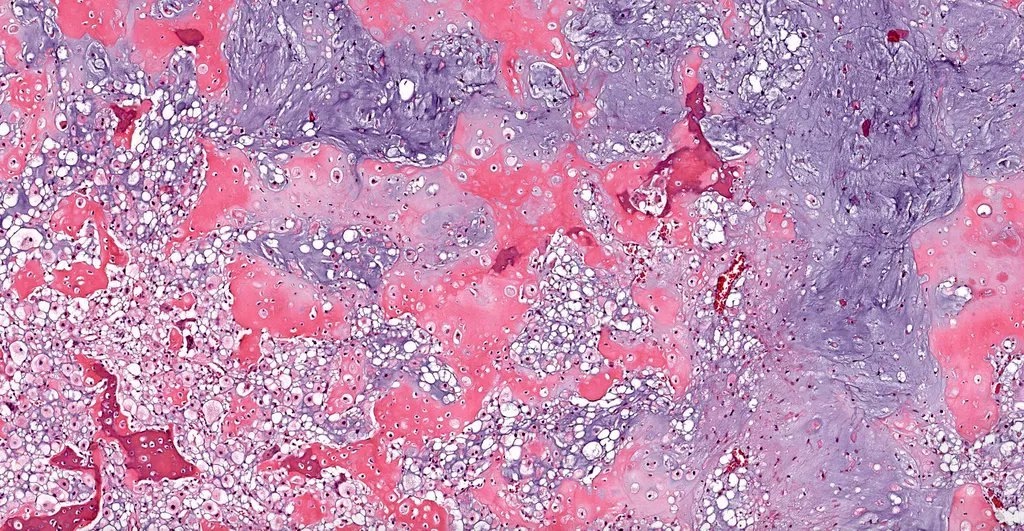
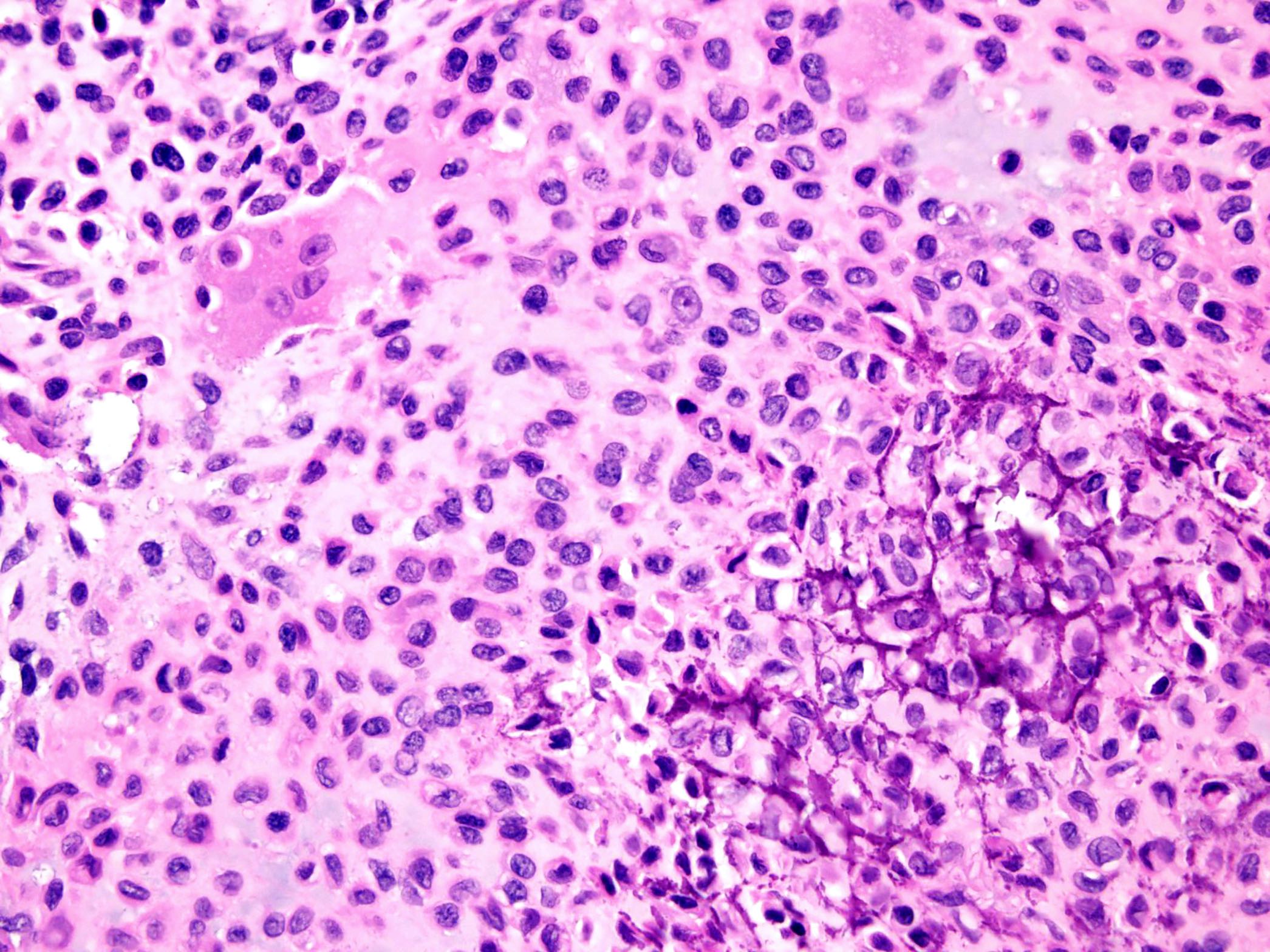
- Round or polygonal cells with abundant clear or slightly eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in lobules or sheets (Hum Pathol 1996;27:1301)
- Large round nuclei with minor atypia and central nucleoli
- Woven bone formation and osteoclast-like giant cells (Histopathology 1999;34:447)
- Rare mitotic figures
- Areas of conventional low grade chondrosarcoma can be observed in approximately half of cases (J Bone Joint Surg Am 1976;58:676)
- Dedifferentiation may occur (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1079)
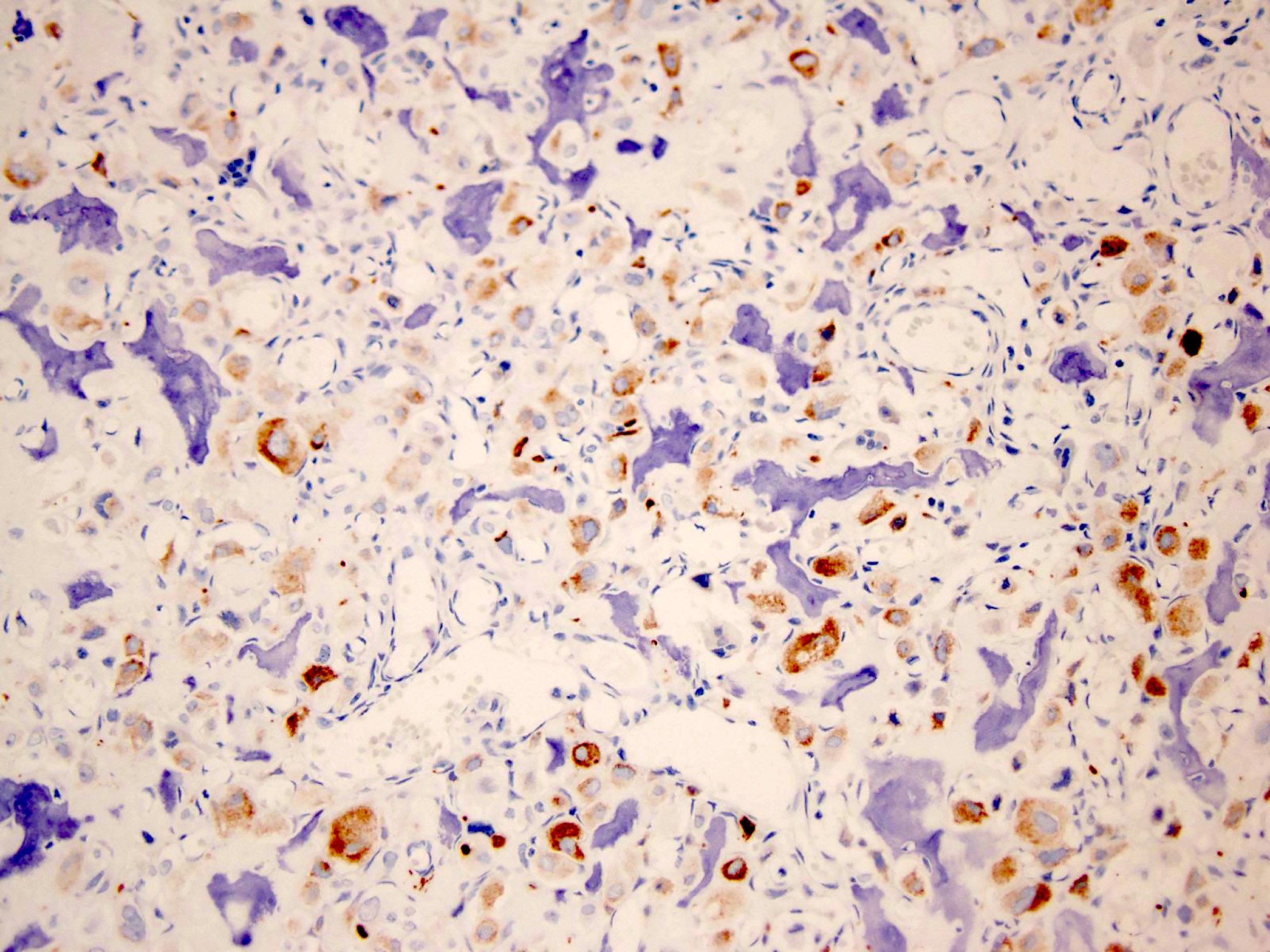
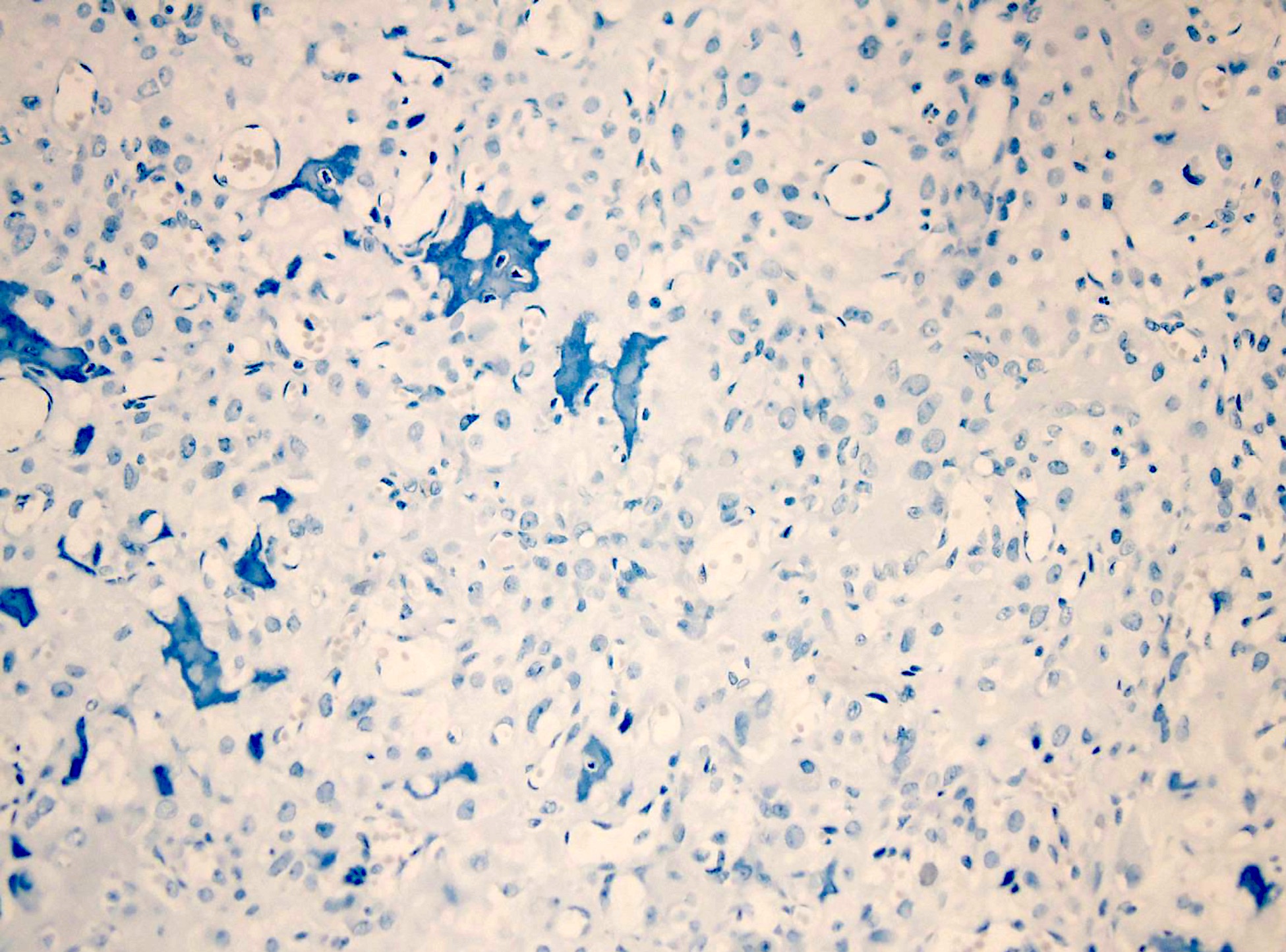
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Low to intermediate cellular smears of clusters and single round or oval tumor cells (Diagn Cytopathol 2021;49:46)
- Tumor cells with rounded nuclei (sometimes binucleated) and rich vacuolated cytoplasm
- Low grade cellular atypia
- Chondroid background matrix
- Occasional osteoclast-like giant cells in background
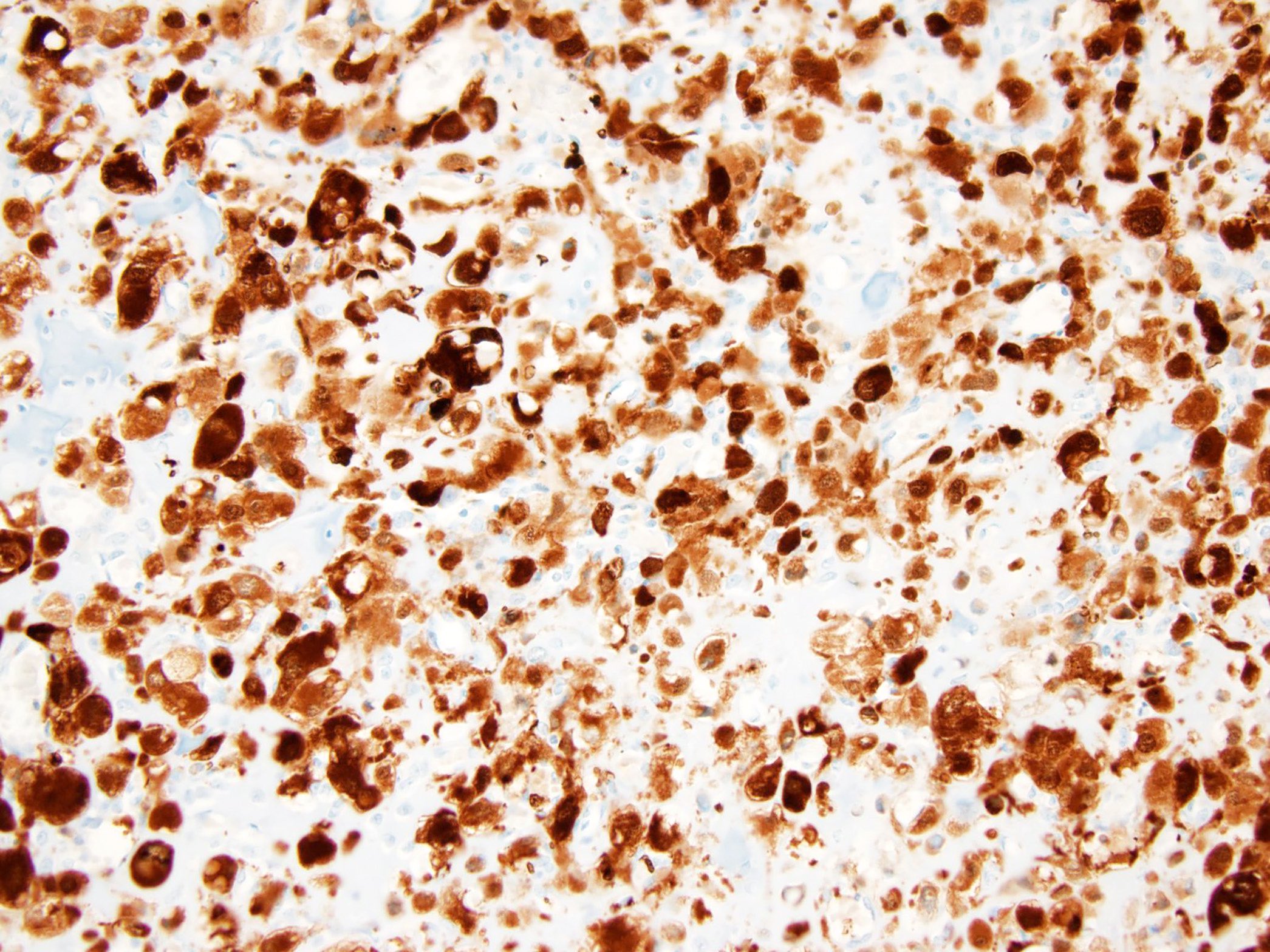
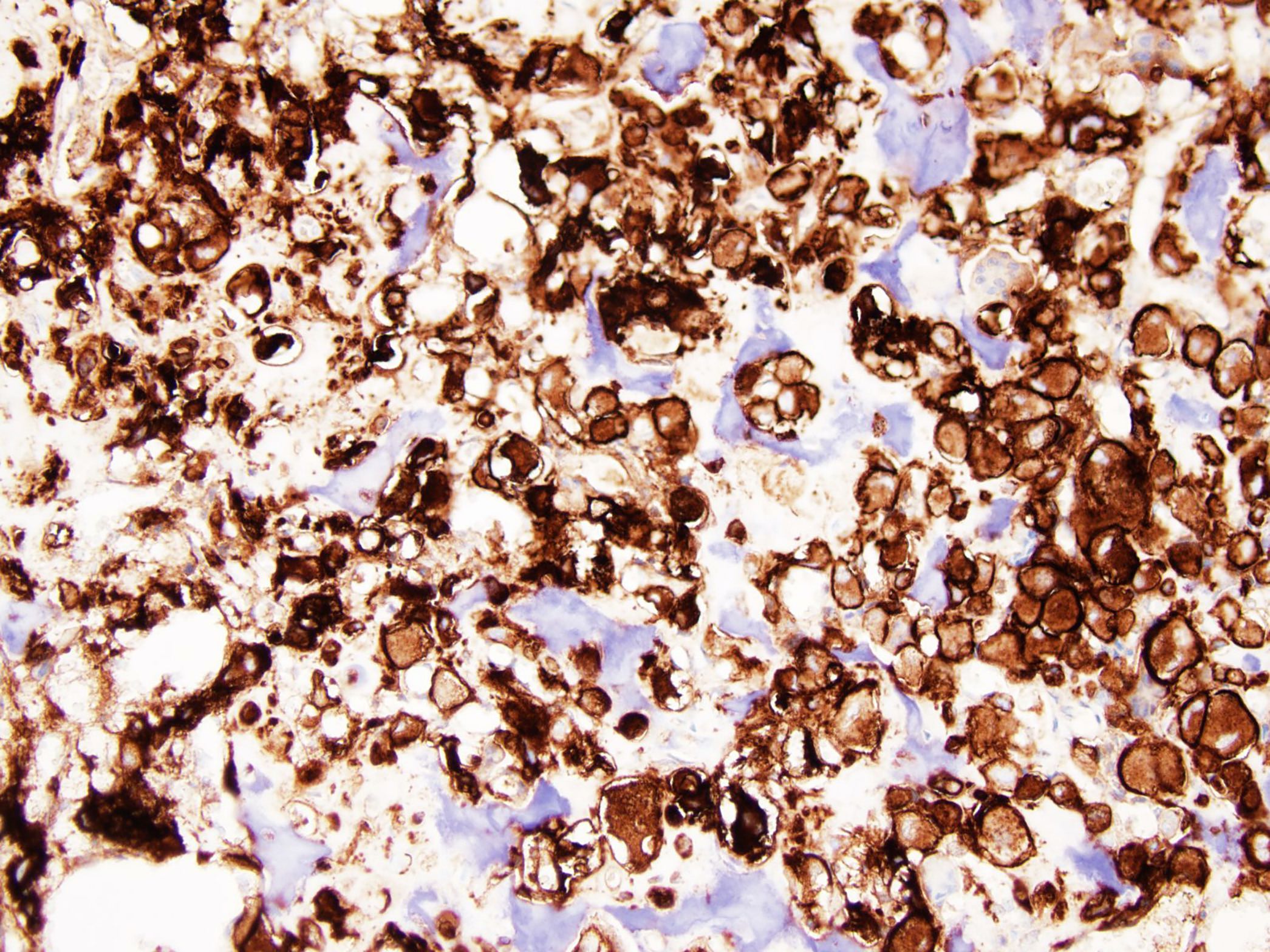
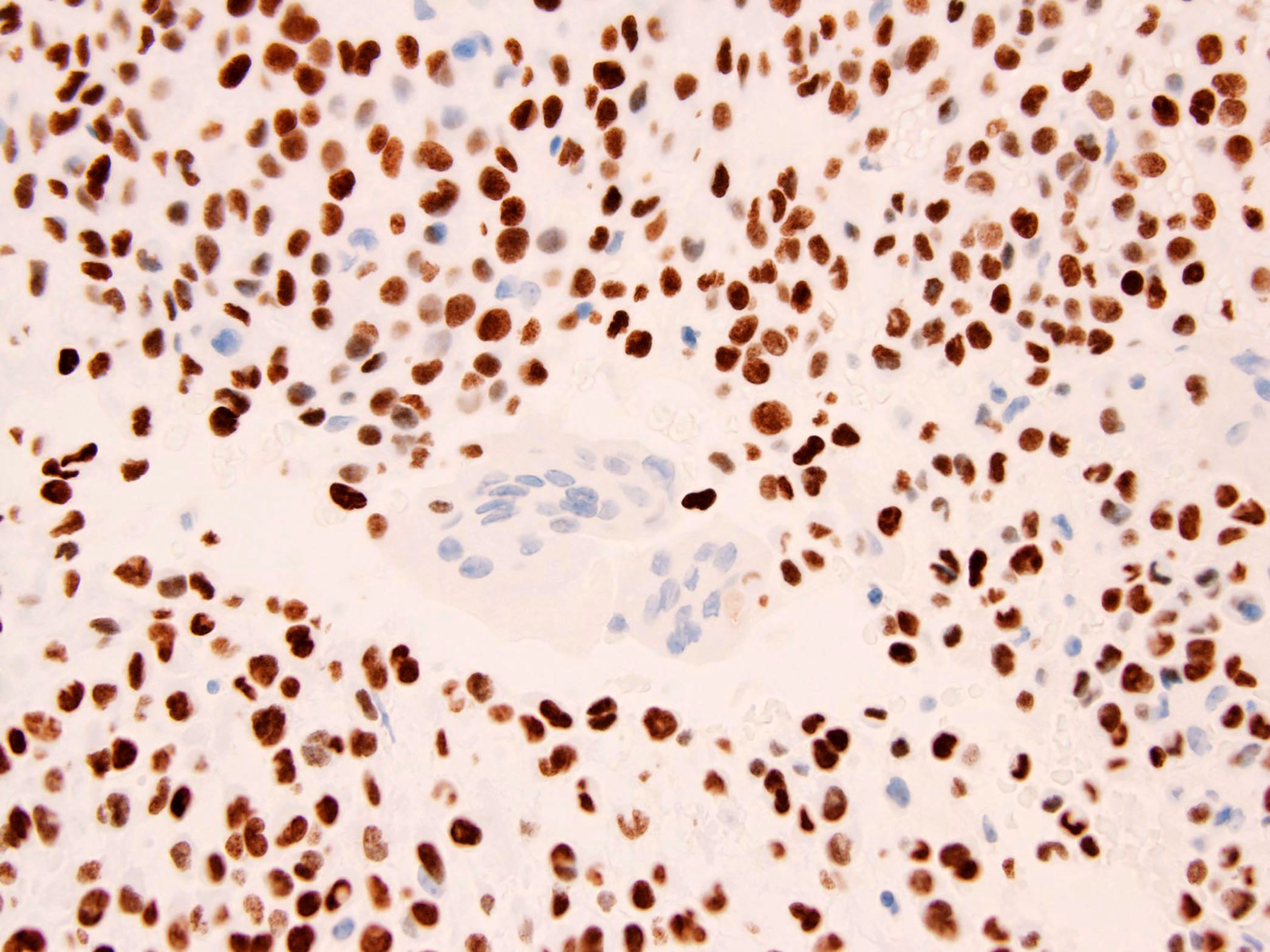
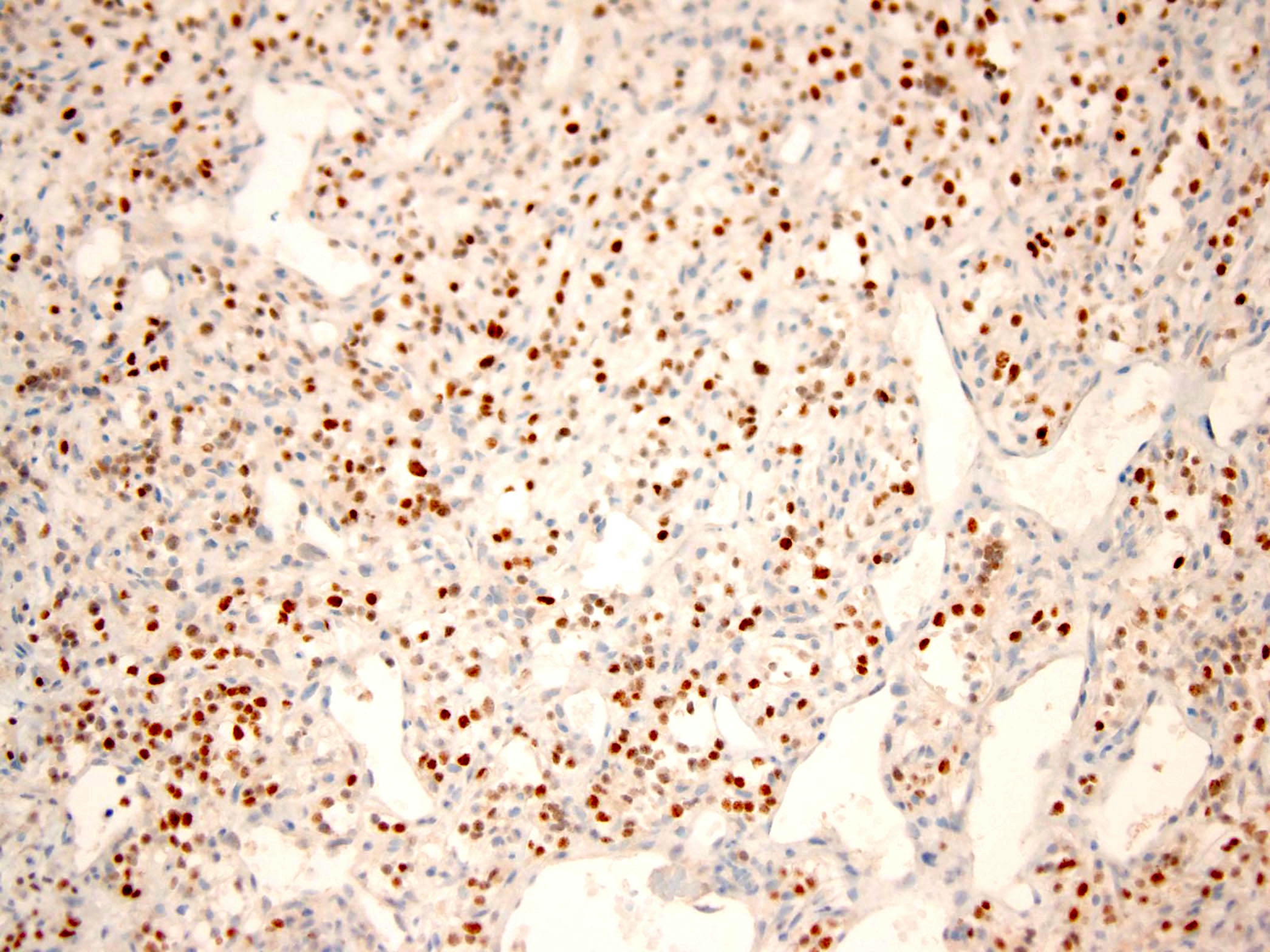
Positive stains
- S100 (Histopathology 1999;34:447)
- D2-40 (APMIS 2009;117:518)
- Keratin AE1 / AE3 (Hum Pathol 2013;44:237)
- Type II collagen (Pathology 2006;38:35)
- Vimentin
Negative stains
- Osteocalcin (Hum Pathol 2013;44:237)
- CD117 (APMIS 2009;117:518)
- Actin
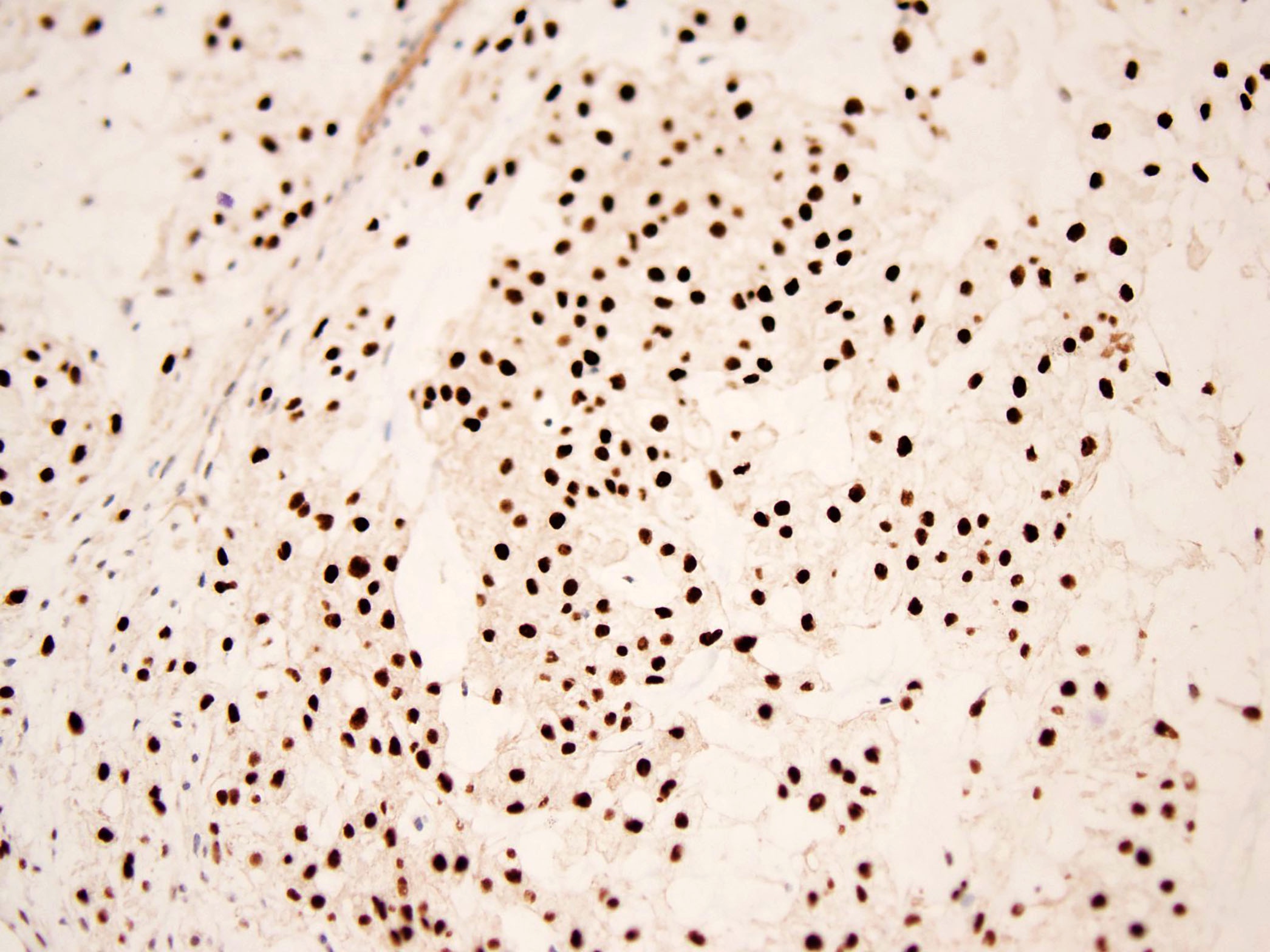
- H3K36M*
- *In a recent study, 1 of 10 clear cell chondrosarcomas showed expression of H3K36M (Histopathology 2016;69:121)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Rb pathway is affected in 95% of clear cell chondrosarcomas (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012;51:899)
- 1 of 15 clear cell chondrosarcomas investigated for histone 3.3 mutations (to date) has shown K36M mutations in H3F3B, a highly specific driver mutation for chondroblastoma, suggesting a pathogenetic relation in at least a small subset of tumors (Nat Genet 2013;45:1479)
- Neither IDH1 nor IDH2 mutations are detected
Sample pathology report
- Right femoral head, resection:
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma, low grade (see comment)
- Margins of resection are negative, with sarcoma closest at 2 cm from the lateral soft tissue margin
- Comment: The tumor is composed of cells with abundant clear or slightly eosinophilic cytoplasm and large round nuclei with mild pleomorphism and small nucleoli. The cells are arranged in sheets and lobules, admixed with trabeculae of woven bone and scattered osteoclast-like giant cells. Mitotic figures are rare (1/10 high power fields). Areas with hyaline cartilaginous matrix with moderate cellularity and mild nuclear atypia are also present. There is entrapment of pre-existing lamellar bone and invasion of the subchondral bone plate. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells are strongly positive for S100 and D2-40 and show focal immunoreactivity for keratin AE1 / AE3. Stains for H3K36M and PAX8 are negative.
- This constellation of morphological and immunohistochemical features strongly supports the diagnosis of clear cell chondrosarcoma. The prognosis of clear cell chondrosarcoma is excellent when treated adequately with wide surgical resection. However, clear cell chondrosarcoma has a tendency for very late recurrence and metastasis 20 years after initial diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Chondroblastoma:
- Chondroblastoma most commonly occurs in the first and second decades
- Sheets of chondroblastic cells with small grooved nuclei (Pathol Res Pract 2022;231:153777)
- Islands of eosinophilic chondroid matrix
- Pericellular lace-like or chicken wire calcifications
- Positive for H3K36M (Cancer Cytopathol 2018;126:552)
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
- Typically, compact nests and sheets of cells with clear cytoplasm
- Rich capillary network which consists of delicate, thin walled, chicken wire vessels (Virchows Arch 2021;479:1187)
- No woven bone formation
- Positive for PAX8 (Semin Diagn Pathol 2022;39:1)
- Negative for S100 and D2-40
- Chordoma:
- Usually arises in bones of the axial skeleton
- Large epithelioid cells with bubbly cytoplasm (physaliphorous cells) embedded within an abundant extracellular myxoid matrix (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:386)
- Positive for brachyury
- Conventional osteosarcoma:
- Conventional osteosarcoma commonly contains variable amounts of neoplastic cartilage
- Tumor usually develops in the metaphysis of long bones
- Essential for the diagnosis is the identification of neoplastic bone formation (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:555)
- Neoplastic cells typically demonstrate severe anaplasia and pleomorphism
- Mitotic activity is usually brisk and atypical mitotic figures are often present
- Negative for S100 and D2-40
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about clear cell chondrosarcoma?
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma has poor prognosis
- Clear cell chondrosarcoma is sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy
- Late recurrences and even distant metastases may occur
- Most clear cell chondrosarcomas have IDH1 or IDH2 mutations
- Most often affects the metaphysis of long bones
Board review style answer #2
C. Late recurrences and even distant metastases may occur
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell chondrosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell chondrosarcoma