Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Muller KE. Microcysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastcysts.html. Accessed September 12th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Round to ovoid fluid filled structures of variable size lined by bland epithelium, part of nonproliferative fibrocystic changes
Essential features
- Very common nonproliferative fibrocystic change
- Round to ovoid fluid filled cysts lined by flat, cuboidal or columnar cells that may be attenuated and denuded
- Cysts alone do not increase risk of breast cancer
Terminology
- Blue dome cysts: based on gross appearance
- Type 1 cysts:
- Na/K ratio of 3 or less: increased breast cancer risk; associated with higher levels of estrogen, melatonin, epidermal growth factor and DHEA-S and lower levels of TGF-B2 than type 2 cysts (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2007;103:331)
- Type 2 cysts:
- Na/K above 3: reduced breast cancer risk, although patients may have both types of cysts and type 2 cysts can be associated with cancer (Breast 2005;14:37)
- Microcysts: seen during imaging or microscopic exam; not palpable
- Macro or gross cysts: large enough to be palpated
Note:
- Type 1 and type 2 terminology is not commonly used
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Most common nonproliferative change in breast along with metaplastic changes
- Any age
- 20 - 25% of palpable breast abnormalities that underwent fine needle aspiration were simple cysts (Cancer 2001;93:263)
- Prevalence estimated between 50 - 90% (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006;97:115)
Sites
- Usually multifocal and bilateral
Pathophysiology
- Arises in the terminal ductal lobular unit (TDLU) → dilation and coalescence of lobular acini
- Gross cysts defined by Haagensen are palpable (Cancer 1989;63:2156)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Large cysts may present as a palpable mass
Diagnosis
- Fine needle aspiration:
- Mass disappears after aspiration and the fluid is nonbloody, yellow or green and serous, no further workup necessary (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:1240)
- Further workup starting with imaging required after aspiration if no fluid, bloody or tenacious fluid or mass persists (Am Fam Physician 2003;68:1983)
- Bloody or cloudy or turbid fluid should be sent for cytopathology review
Radiology description
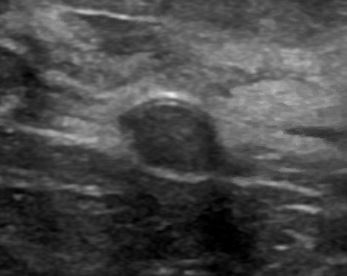
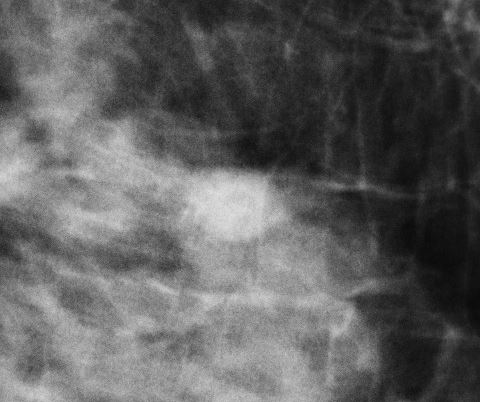
- Mammography: low density, circumscribed, round, oval or occasionally lobulated masses
- Amorphous, round microcalcifications may be present (Radiol Clin North Am 2010;48:931)
- Ultrasound: avascular, anechoic, oval or round mass with posterior enhancement, cyst flattens with compression, thin septations may be present (Radiol Clin North Am 2010;48:931)
- MRI: no contrast enhancement, hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2 (Radiol Clin North Am 2010;48:931)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Cysts alone: no increased risk of breast cancer (J Natl Cancer Inst 1978;61:1055, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1998;122:1053, N Engl J Med 1985;312:146)
- Cysts and family history of breast cancer, relative risk = 2.7 times higher (N Engl J Med 1985;312:146)
- Gross cysts: may be associated with slight (relative risk = 1.6) increased risk of breast cancer (N Engl J Med 1985;312:146, J Natl Cancer Inst 2004;96:616)
Case reports
- 37 year old man with breast cyst (Cureus 2019;11:e4814)
- 58 year old man with breast cyst (J Radiol Case Rep 2011;5:35)
- 3 family members with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and breast cysts (Iran J Kidney Dis 2009;3:246)
Treatment
- Aspiration / decompression if symptomatic or for diagnostic purposes (See Diagnosis section)
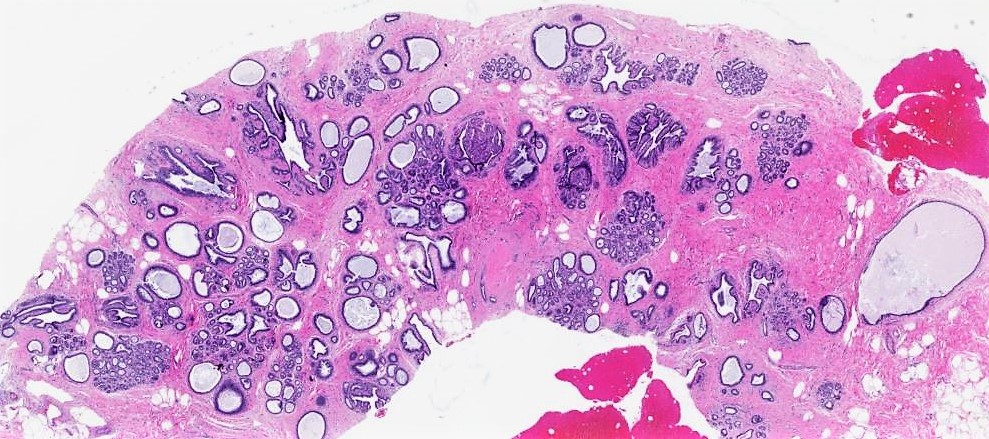
Gross description
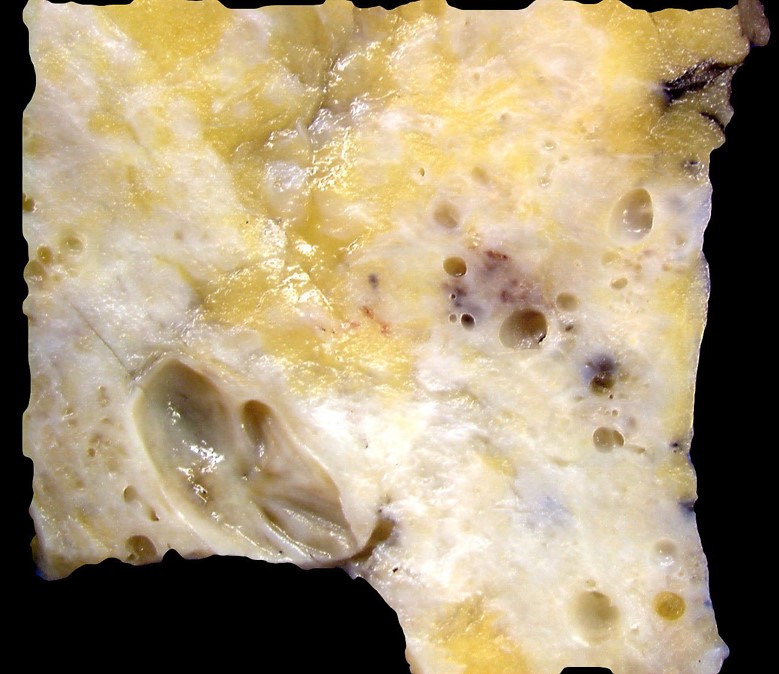
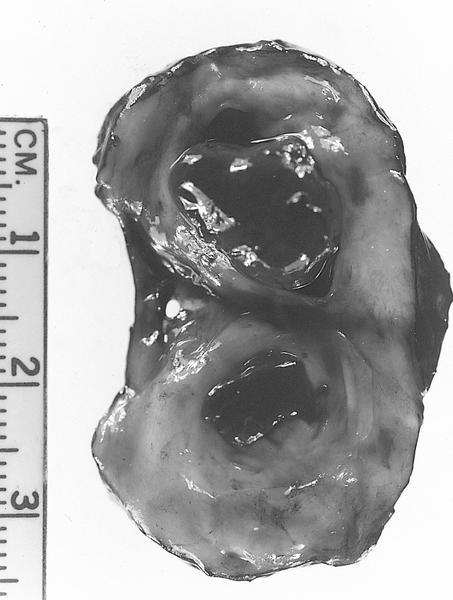
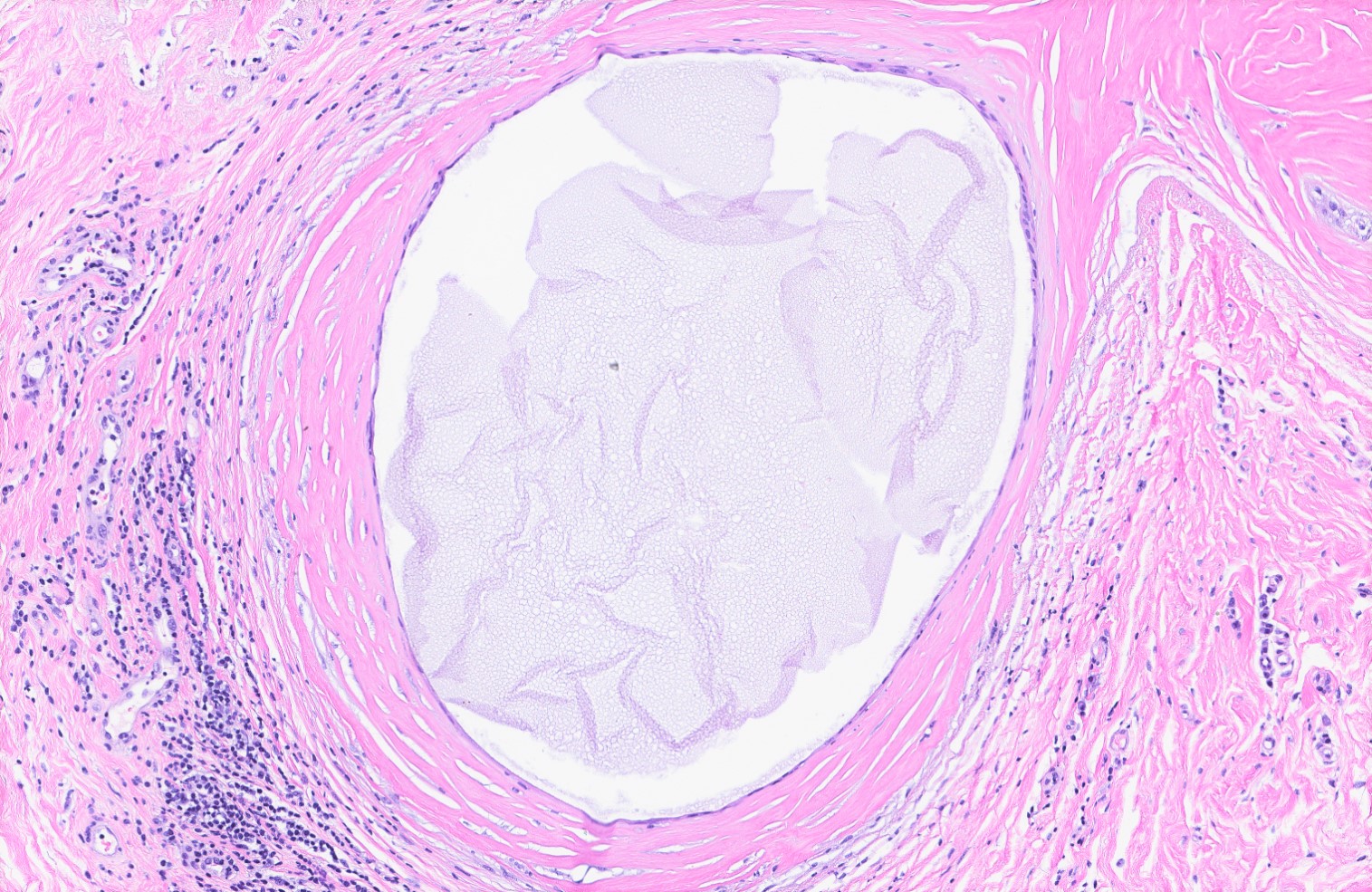
- Variable size, usually visible grossly, contains clear, straw colored or brown fluid
- Larger intact cysts may appear blue (blue domed cyst) (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006;97:115)
Gross images
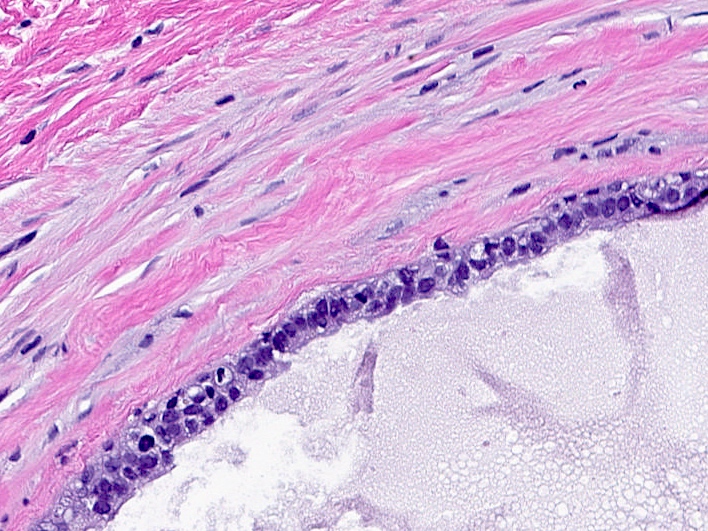
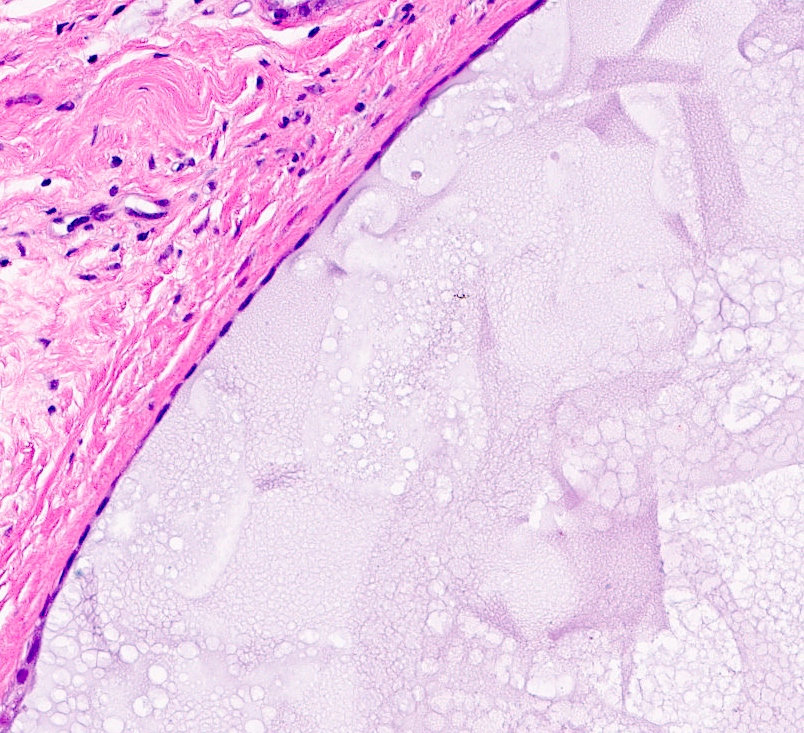
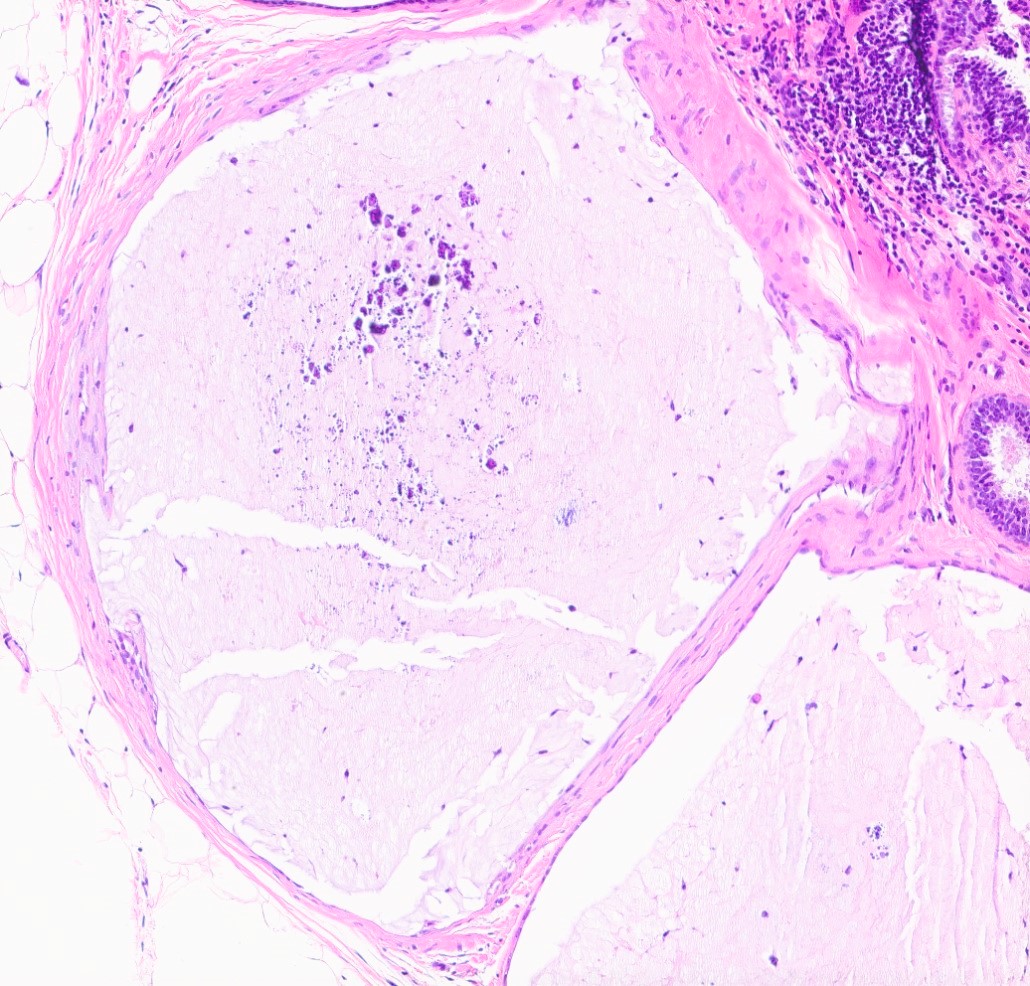
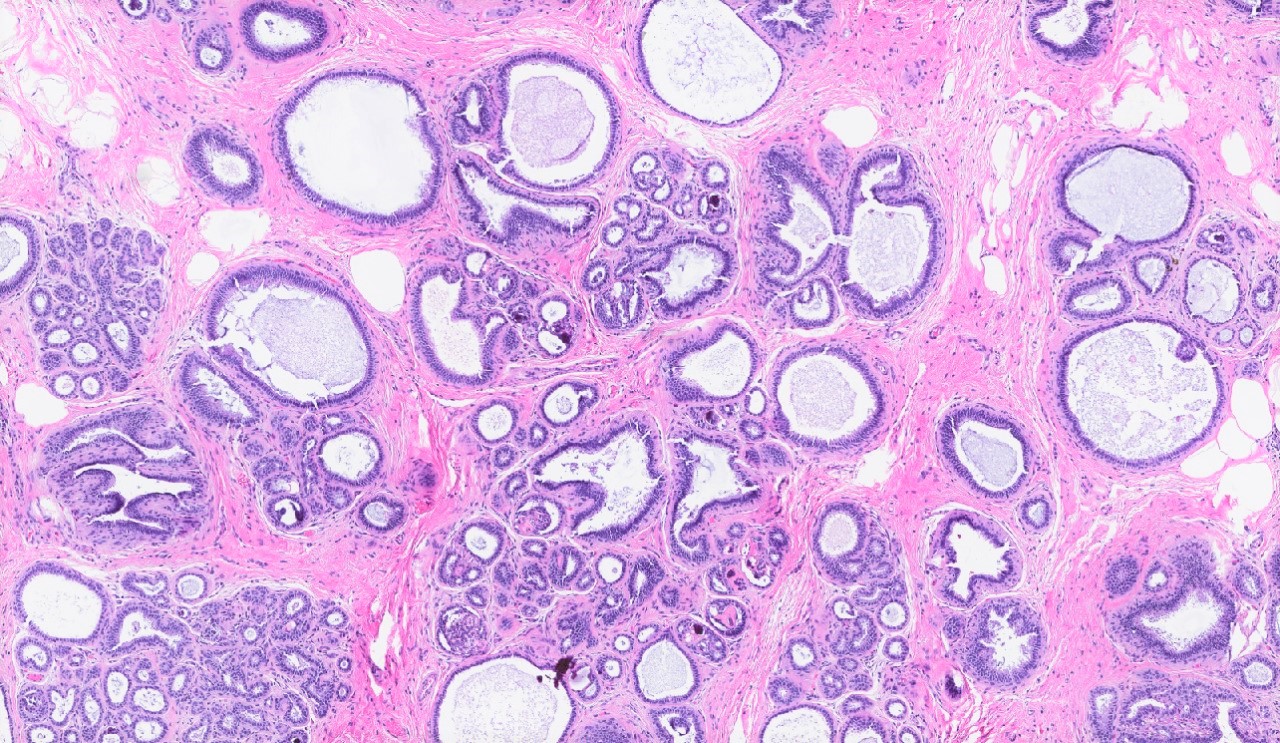
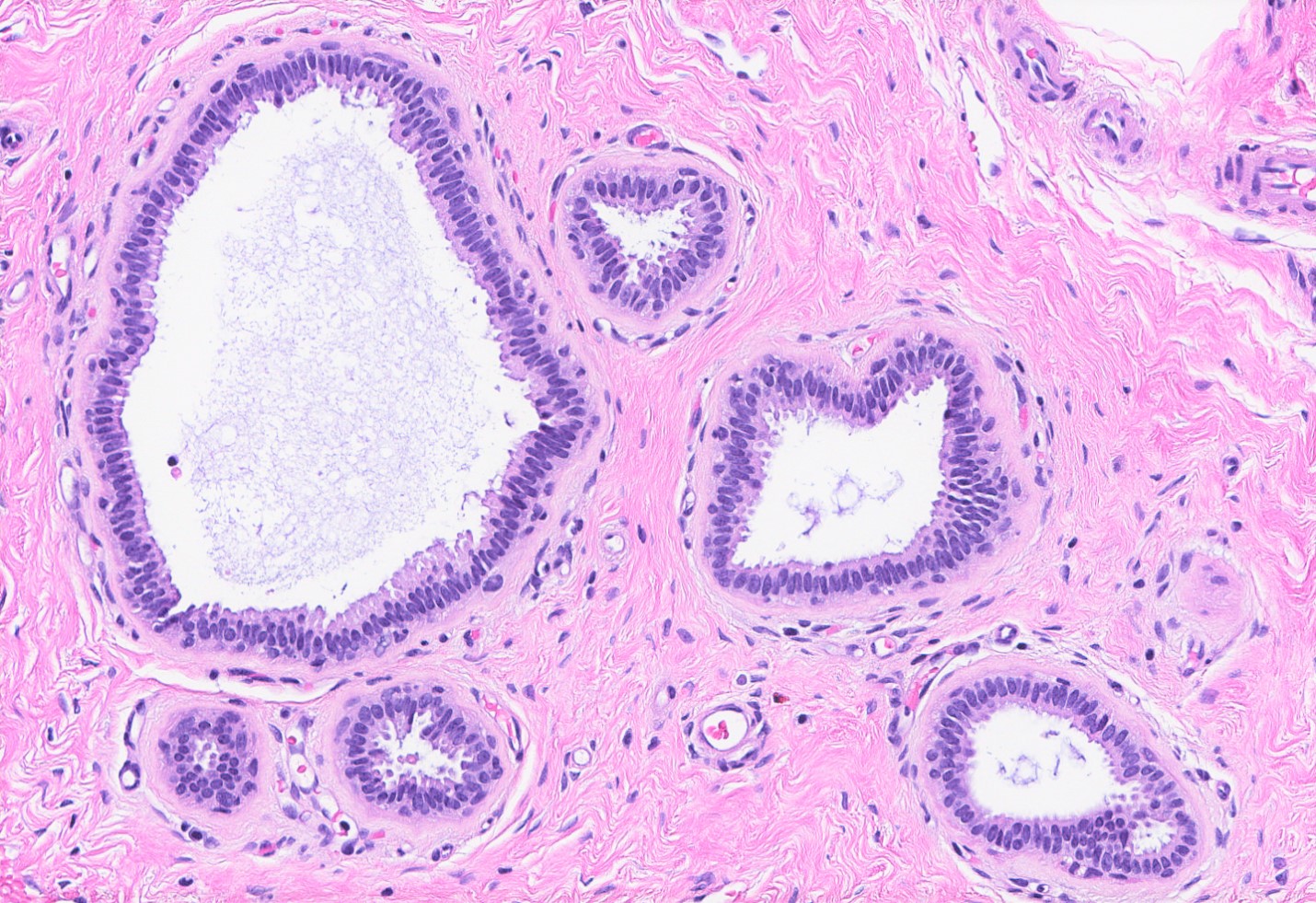
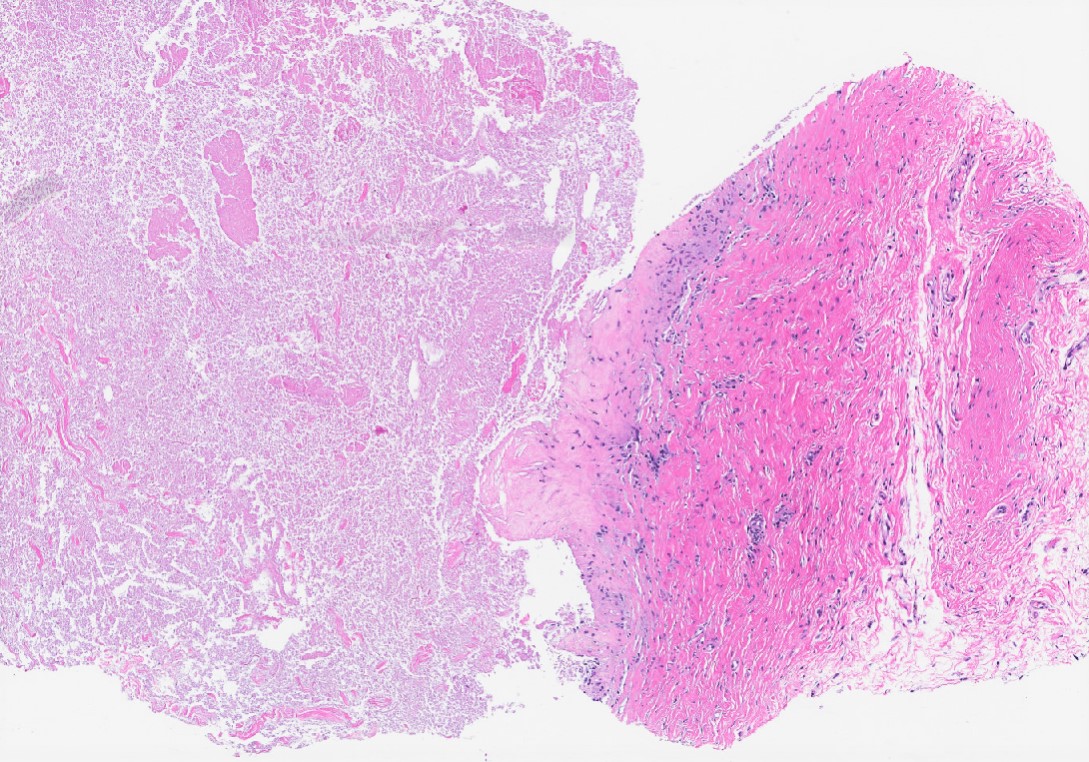
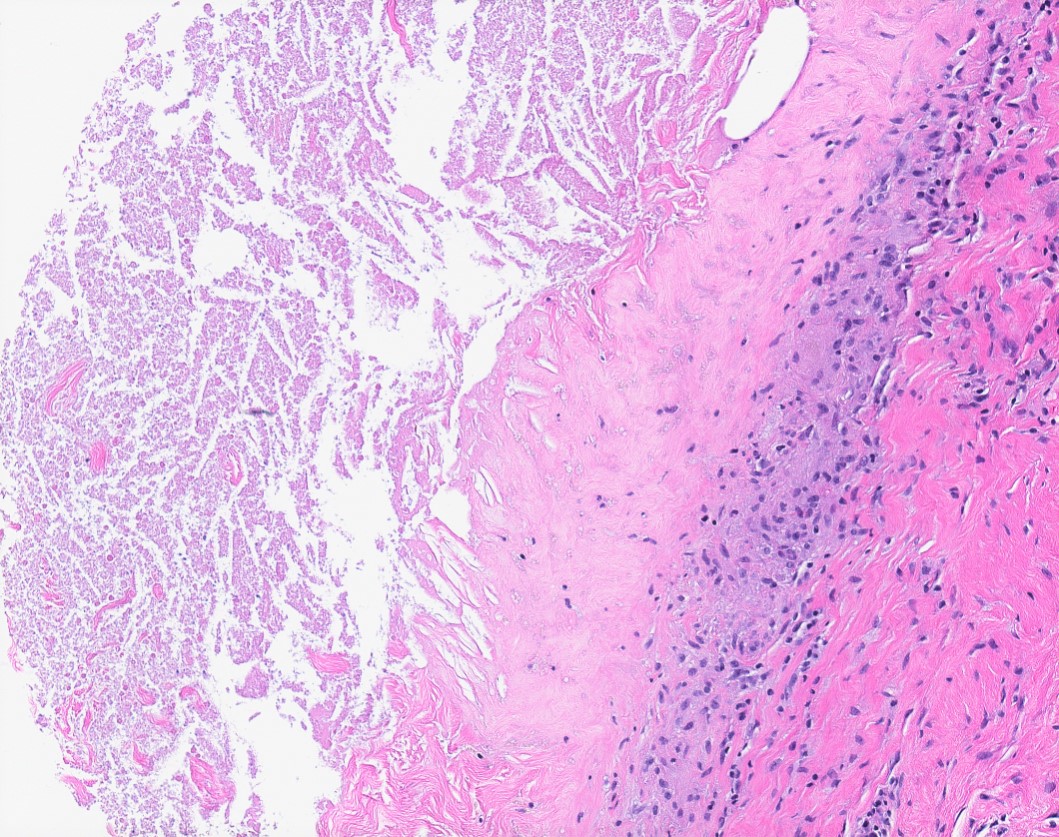
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Dilated glands lined by flat cuboidal or columnar cells
- Epithelium layer may be attenuated or absent
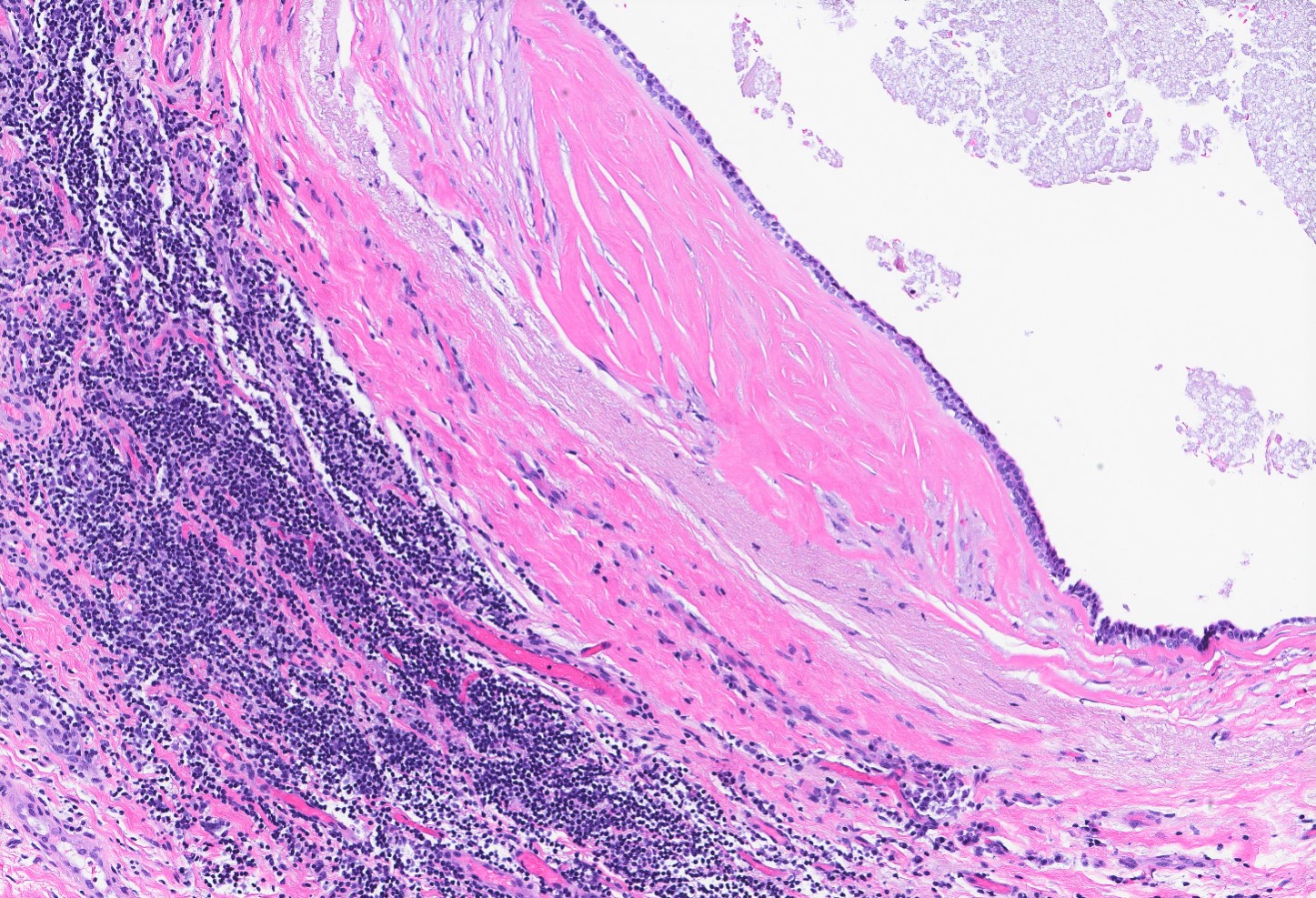
- Cyst wall may show dense fibrosis and scattered inflammatory cells
- May rupture and elicit inflammatory response with foamy macrophages, cholesterol clefts and fibrosis (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2002;75:213, Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006;97:115)
Microscopic (histologic) images
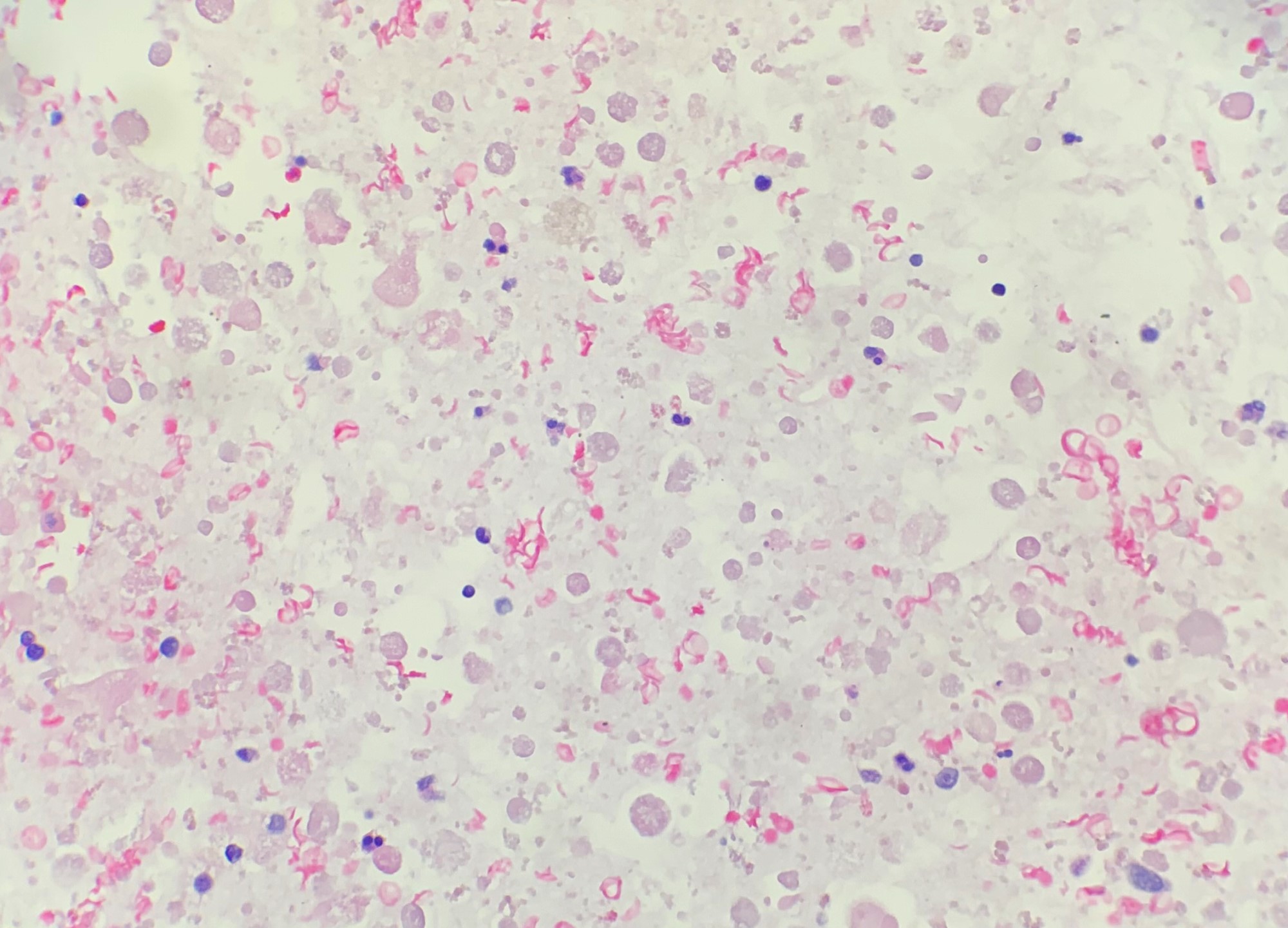
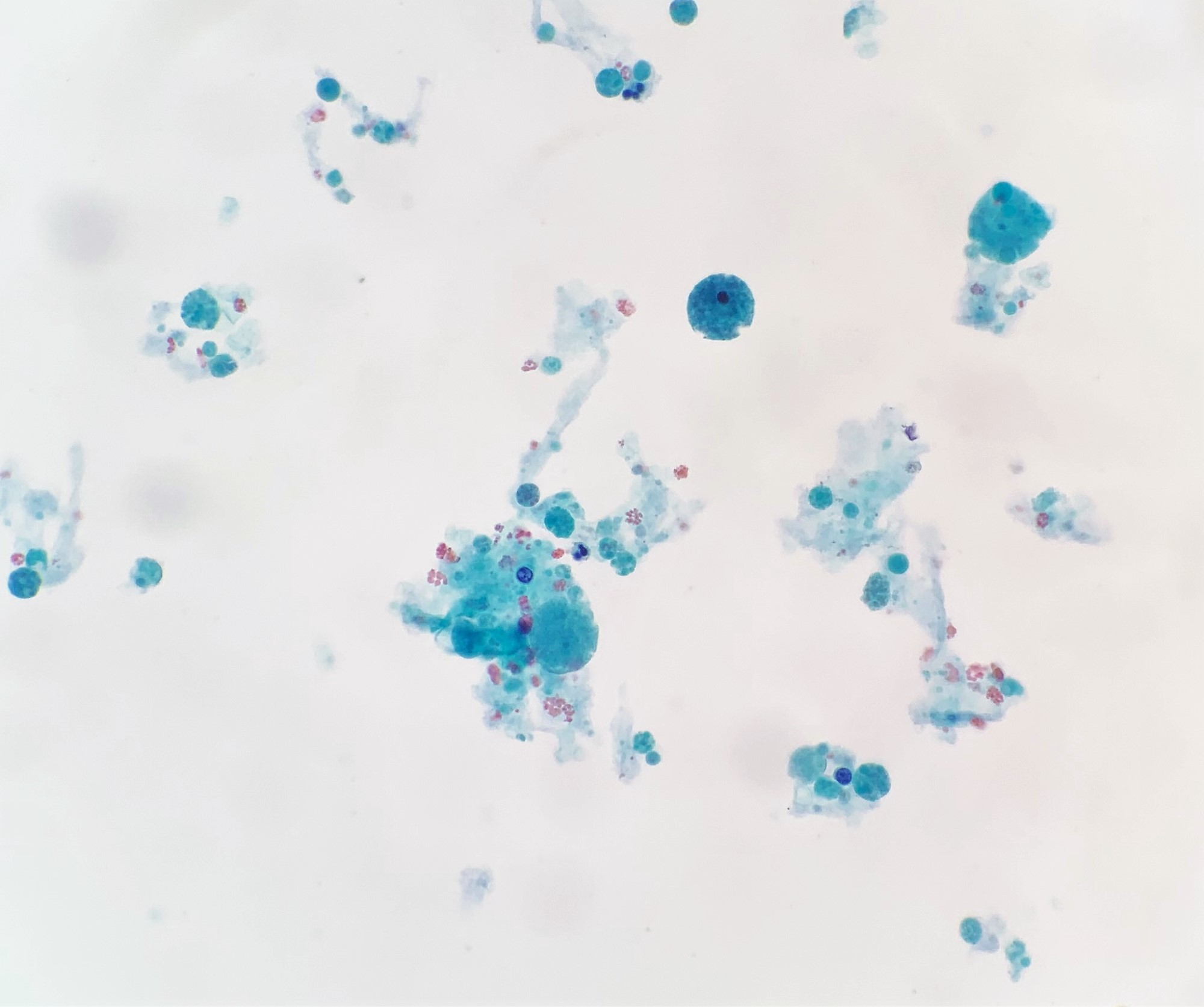
Cytology description
- Hypocellular aspirate, macrophages with other inflammatory cells, with or without few clusters of benign ductal epithelial and myoepithelial cells (Patholog Res Int 2011;2011:547580)
- Prior rupture of the cyst may result in turbid or milky fluid, degenerated cells and debris in an abundant background of inflammatory cells (Patholog Res Int 2011;2011:547580)
Cytology images
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, 2 o’clock, 1 cm from nipple, core needle biopsy:
- Benign breast tissue with fragments of cyst wall with surrounding fibrosis and chronic inflammation
Differential diagnosis
- Flat epithelial atypia:
- Low grade monomorphic cytologic atypia, cells lack polarity, apical tufting, increased N/C ratios, round nuclei with variably prominent nucleoli
- Cystic hypersecretory hyperplasia:
- Colloid-like secretions
- Duct ectasia:
- Elastic tissue in wall, macrophages in lumen and epithelium
- Ductal carcinoma in situ, clinging type:
- Typically high grade cytologic atypia, central necrosis
- Mucocele-like lesion:
- Cysts and dilated ducts are filled with mucin frequently with extravasated acellular mucin in periductal stroma
- May be associated with ADH
- Juvenile papillomatosis:
- Microcysts may be present, however, in addition, there is florid epithelial hyperplasia and papillomatosis
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2