Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Jorns JM. Flat epithelial atypia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastflatepithelialatypia.html. Accessed October 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Introduced by World Health Organization (WHO) Working Group on Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Breast to encompass columnar cell lesions with low grade / monomorphic cytologic atypia that lack architectural features of atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) or low grade ductal carcinoma in situ (LG DCIS)
Essential features
- Atypical epithelial proliferation with one to several layers of disorganized, monotonous, low columnar to cuboidal cells without architectural atypia
Terminology
- WHO acceptable:
- Flat epithelial atypia
- Also columnar alteration with atypia (columnar cell change with atypia or columnar cell hyperplasia with atypia)
- Not recommended by WHO:
- Low grade clinging carcinoma (monomorphous type)
- Atypical cystic lobules
- Atypical lobules type A
- Other (historical):
- Flat ductal intraepithelial neoplasia grade 1A (DIN1A)
- Atypical columnar alternation with prominent apical spouts and secretions
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Seen in 3.8 - 10% of core needle biopsy samples (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:802)
- Radiologically classified as B3 - uncertain malignant potential (Hum Pathol 2010;41:522)
Sites
- Breast terminal duct lobular units (TDLUs)
Etiology
- Biology still being investigated - may be an early neoplastic breast lesion (Semin Diagn Pathol 2010;27:37)
- Mitochondrial DNA sequencing and phylogenetic tree clustering revealed direct transitions between flat epithelial atypia and low grade ductal carcinoma in situ in 10 of 10 cases, supporting the interpretation of flat epithelial atypia as part of the low grade pathway in the development of breast cancer (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1247)
- Shares features with other nonobligate precursor lesions (atypical ductal hyperplasia, atypical lobular hyperplasia, classic lobular carcinoma in situ and low grade ductal carcinoma in situ), supporting the low grade breast neoplasia pathway (Surg Pathol Clin 2018;11:177)
Clinical features
- Diagnosis is reproducible with available histologic diagnostic criteria (Mod Pathol 2006;19:172)
- Underdiagnosed; often coexists with lobular neoplasia (Histopathology 2007;50:859)
- Associated with tubular carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:417)
Diagnosis
- Imaging guided (frequently stereotactic due to mammographically detected calcifications) needle core or surgical excisional biopsy with tissue histologic examination
Radiology description
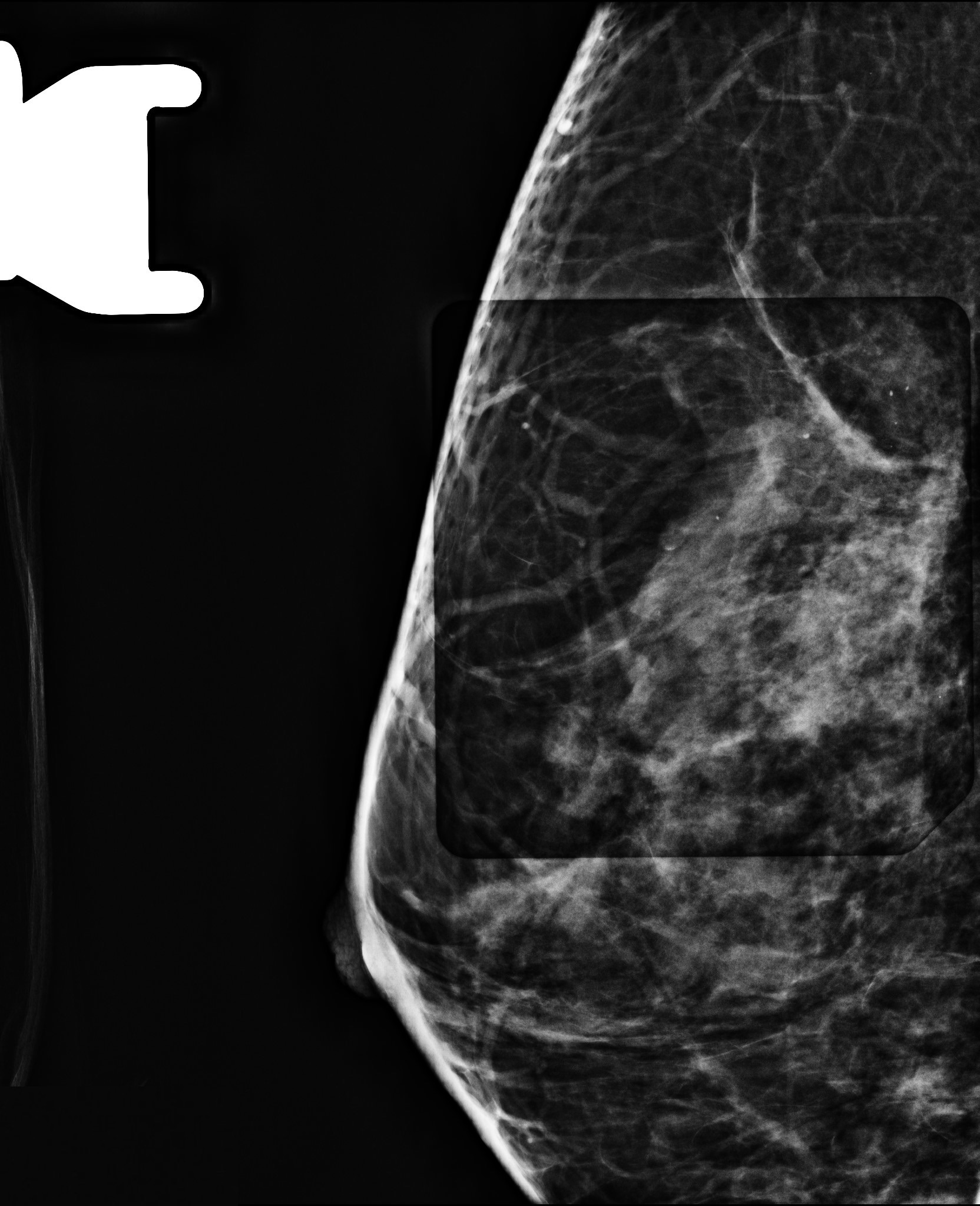
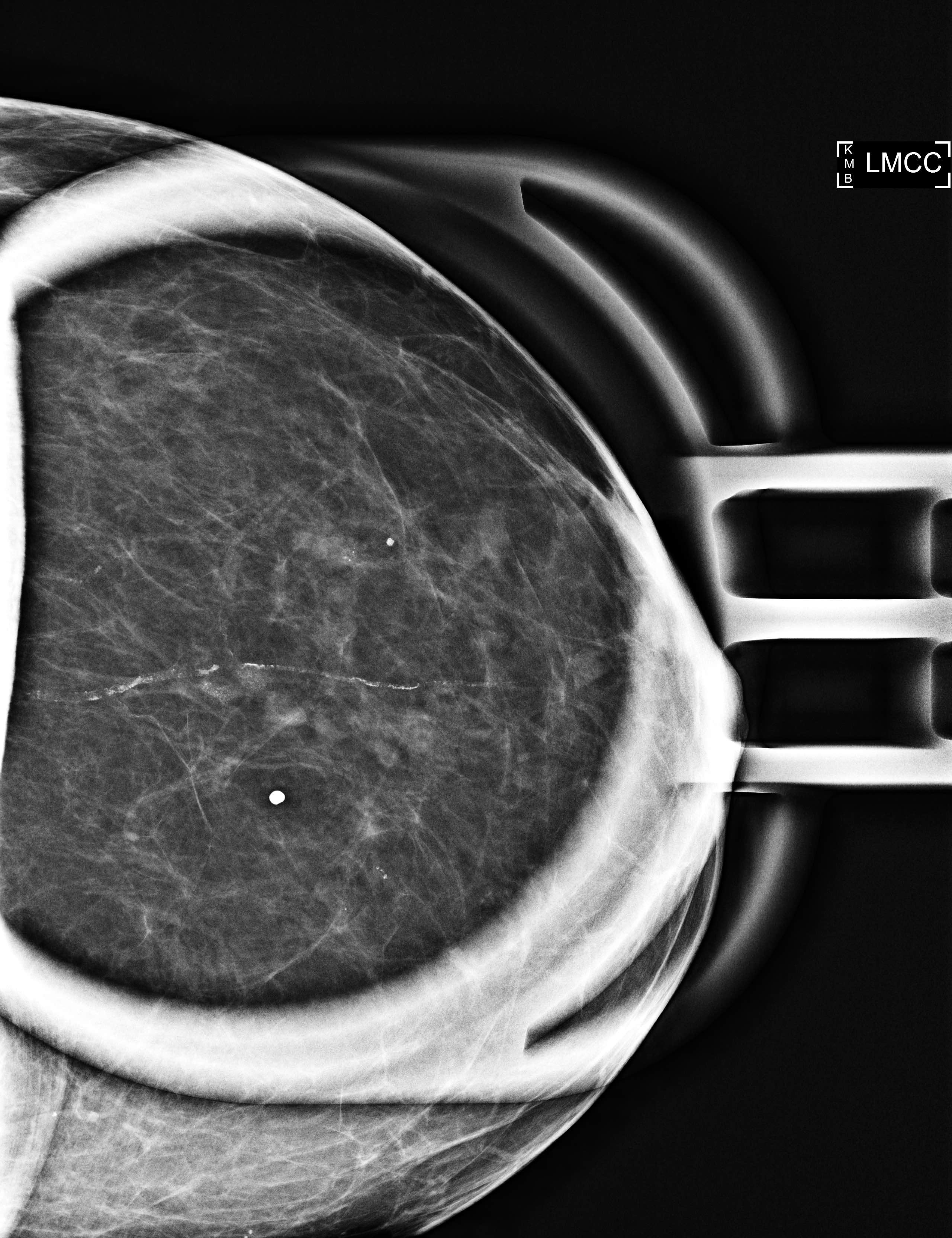
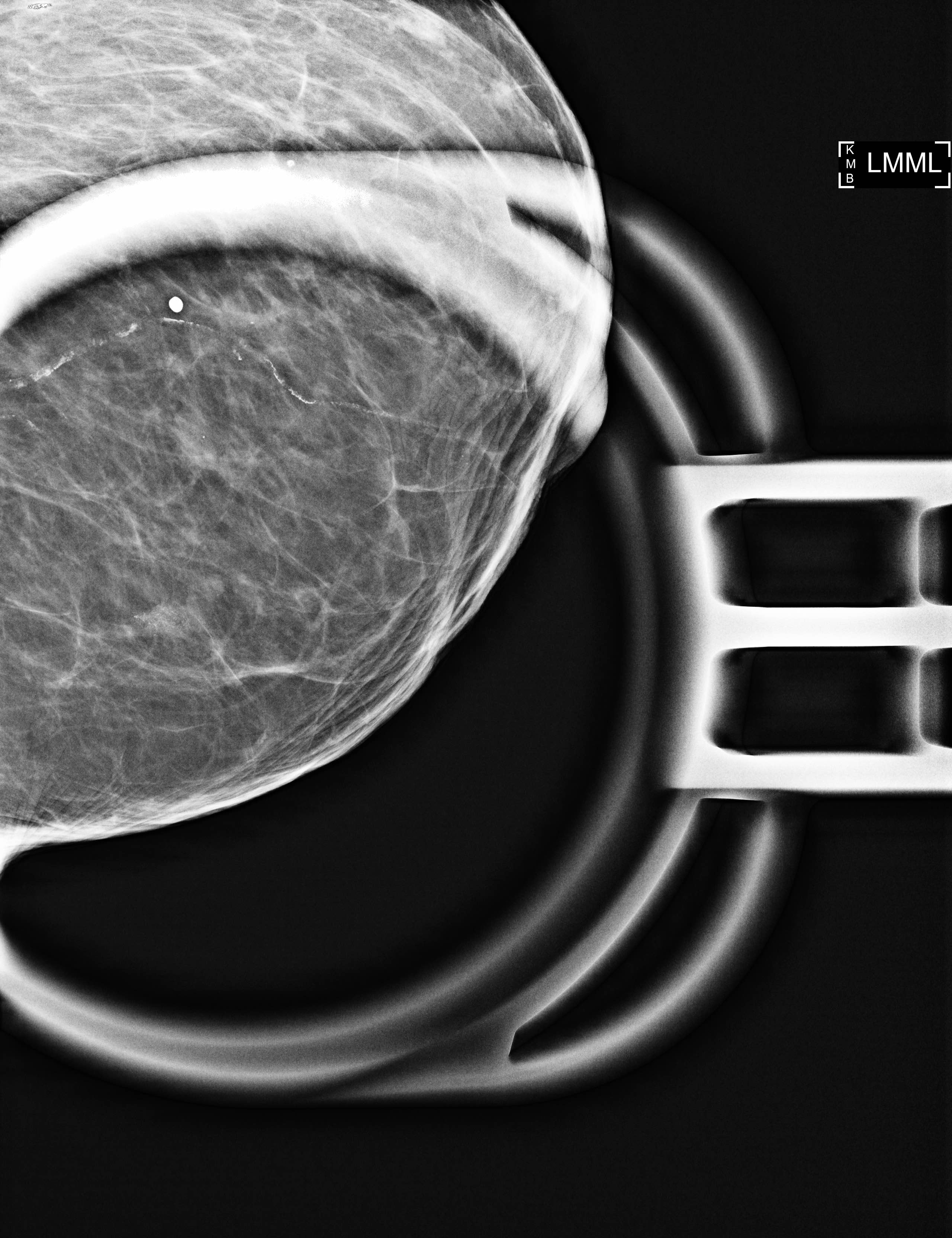
- Grouped amorphous calcifications on mammography (frequent) (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;197:740)
- No radiologic correlate / incidental (occasional)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Subsequent excision after core biopsy shows atypical ductal hyperplasia, atypical lobular hyperplasia, ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive carcinoma in 5 - 15%
- Risk for ductal carcinoma in situ / invasive carcinoma after core biopsy varies:
- Slightly increased warranting follow up (Virchows Arch 2007;451:883, Breast 2014;23:352)
- Similar to traditional atypical ductal hyperplasia warranting excision (Hum Pathol 2007;38:35, J Clin Pathol 2011;64:1001, Virchows Arch 2012;461:419)
- Warranting excision if > 1 cm (J Radiol 2006;87:1671)
- Clonally related to invasive tubular carcinoma and thought to be a nonobligate precursor (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1646)
Case reports
- 47 year old woman with sonographic features of flat epithelial atypia manifesting as a nonmass-like lesion (Am J Case Rep 2019;20:340)
Treatment
- No consensus on whether to excise after biopsy diagnosis of pure flat epithelial atypia
- Recommended:
- See Breast J 2010;16:55, Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:802, Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;125:121, Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:133
- Or consider since upgrade risk is not negligible (Ann Clin Lab Sci 2009;39:270)
- If residual microcalcification / lesion present due to possibility of atypical ductal hyperplasia / atypical lobular hyperplasia (17.2%) or ductal carcinoma in situ (5.4%) or if size > 1 cm (Breast J 2014;20:606, Breast Cancer 2015;22:634, J Radiol 2006;87:1671)
- See Breast J 2010;16:55, Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:802, Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;125:121, Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:133
- Not recommended:
- If pure flat epithelial atypia and 9 or 11 gauge biopsy has removed most of small radiologic target (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1078, Clin Breast Cancer 2013;13:450)
- If only low radiologic risk calcifications are present (Mod Pathol 2009;22:762)
- If concordant pathology and imaging results and patient has serial breast imaging and no prior / concurrent carcinoma (Mayo Clin Proc 2014;89:536, Eur J Surg Oncol 2020;46:235, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:182)
- In general, according to some authors, due to insufficient data for evidence based guidelines (Cancer 2015;121:1548)
- Recommended:
Gross description
- No discernible lesion (typically a microscopic finding only)
Microscopic (histologic) description
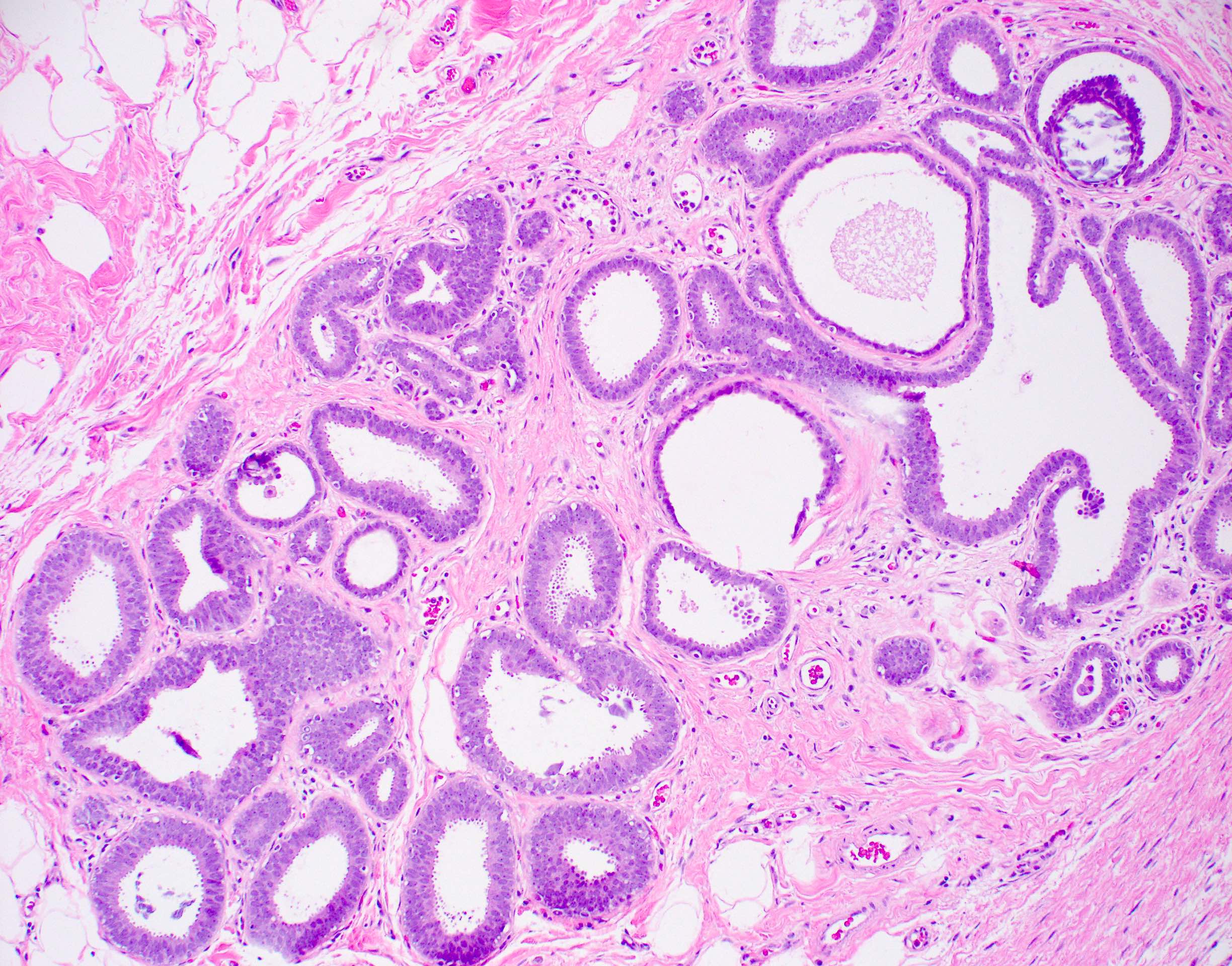
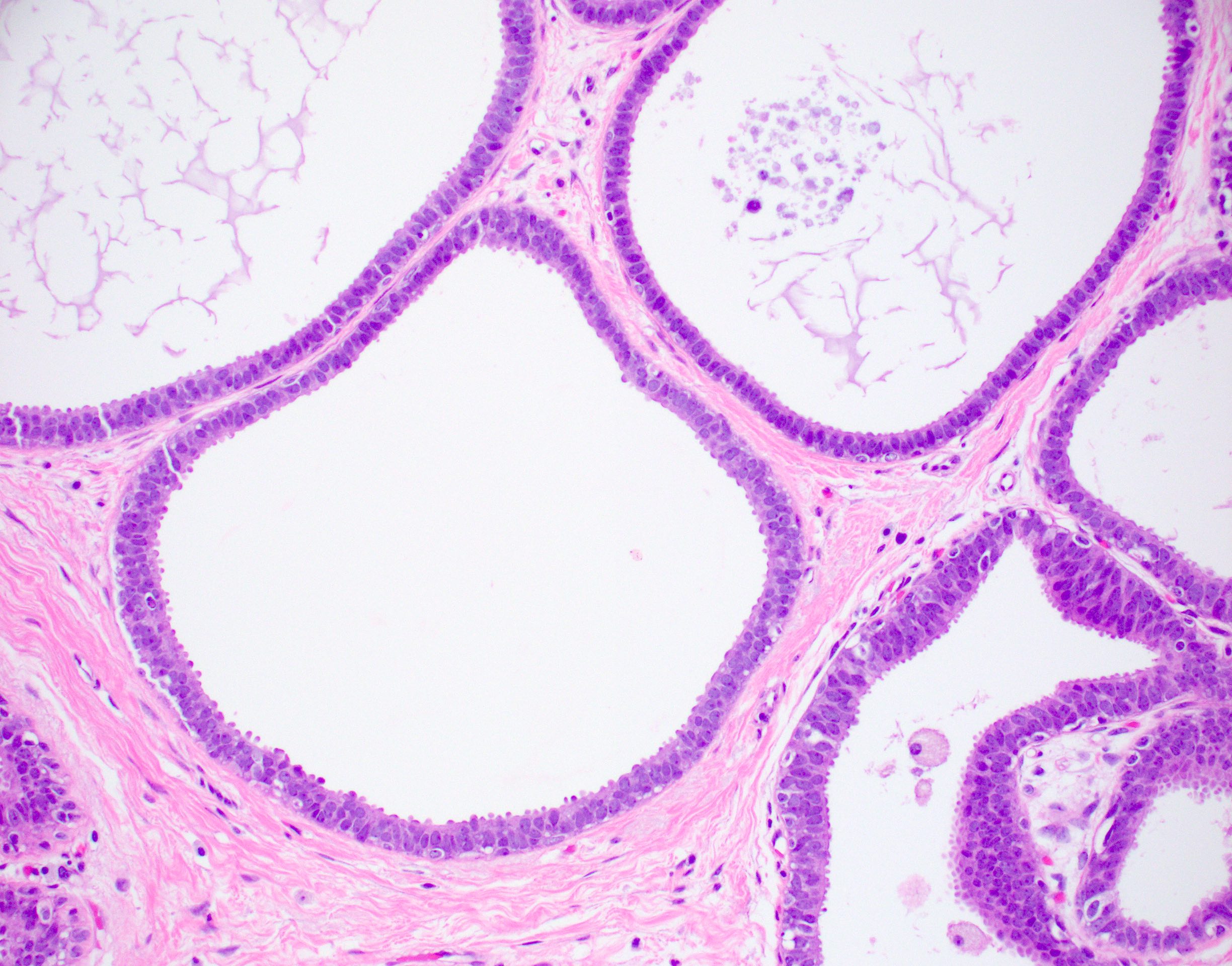
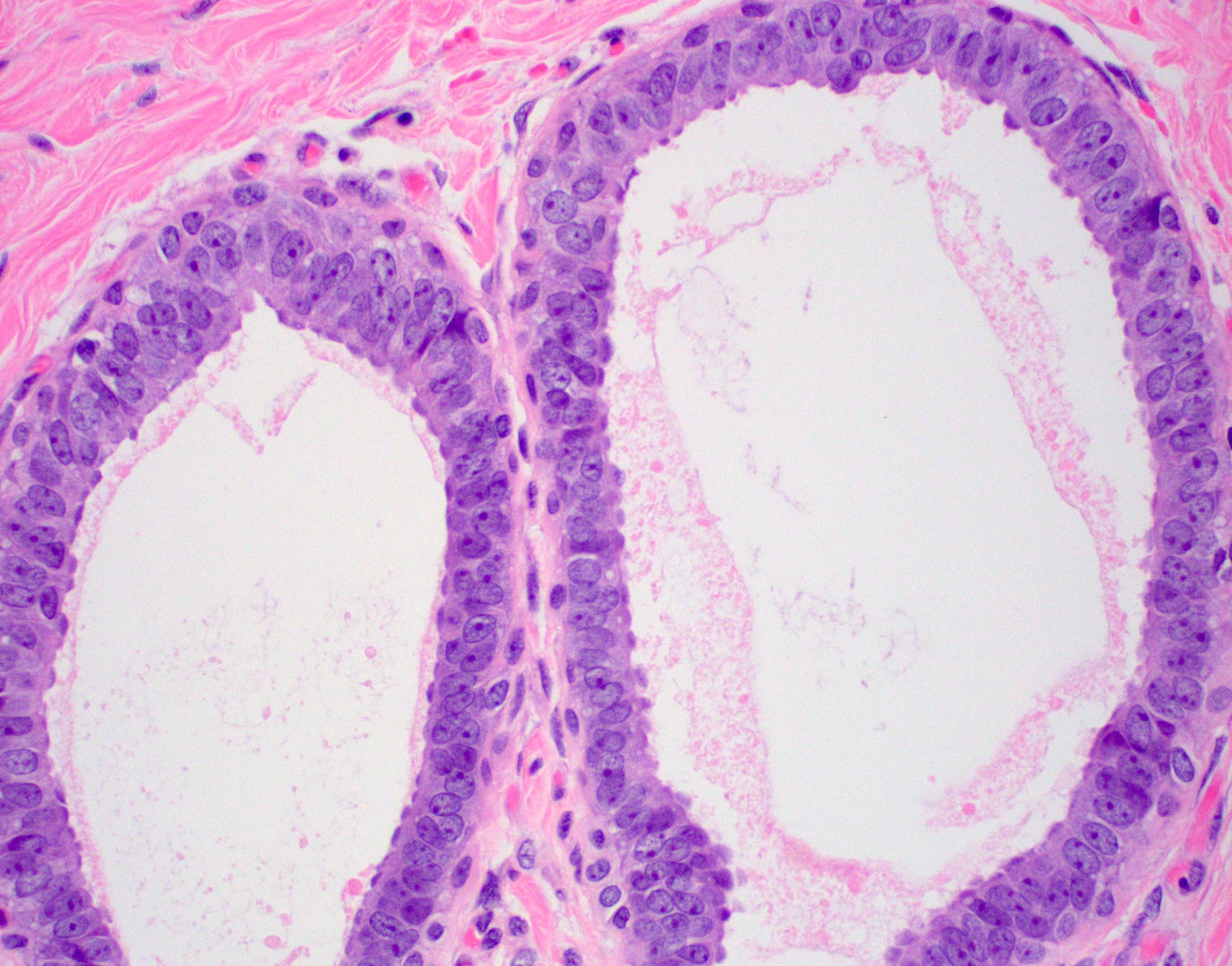
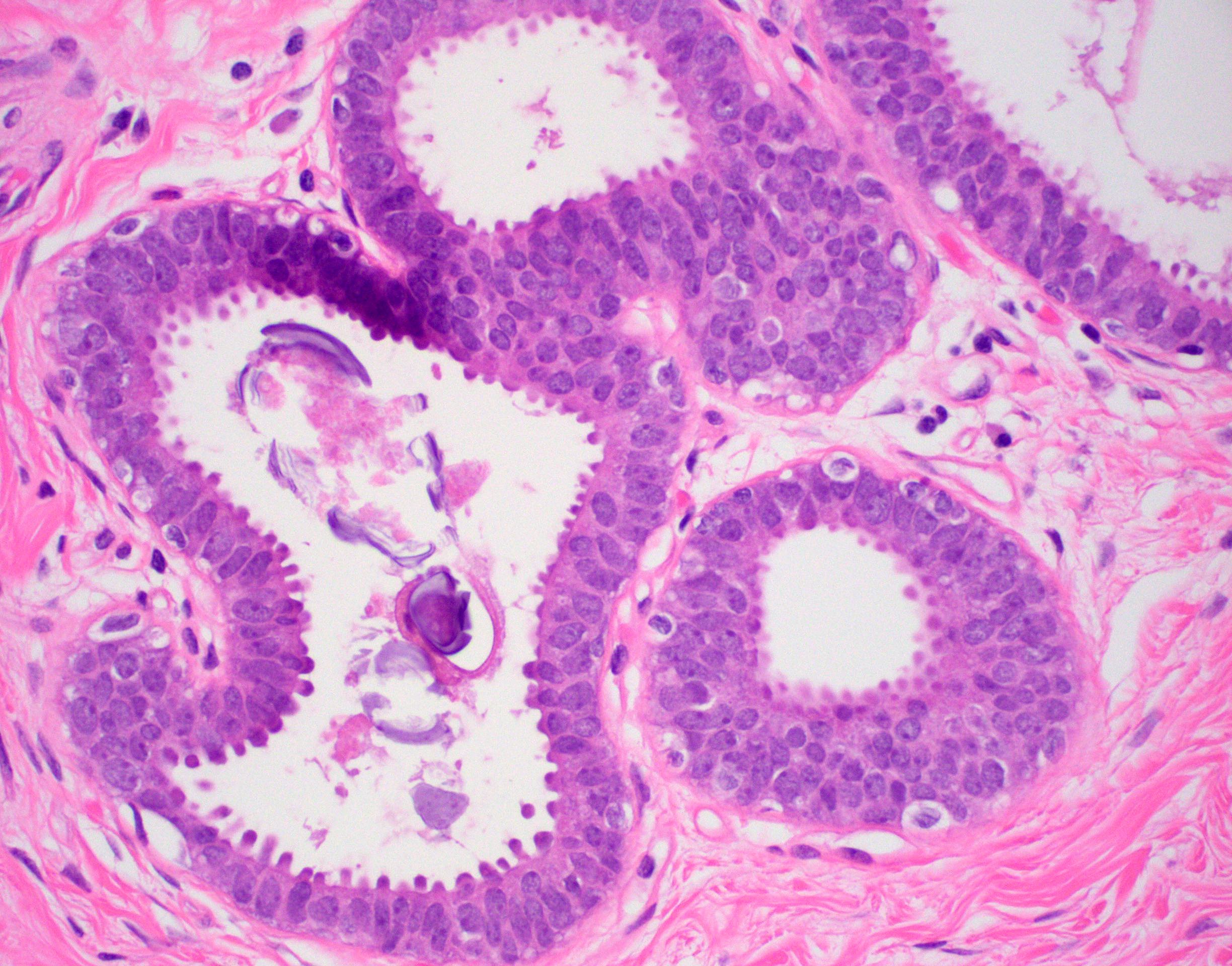
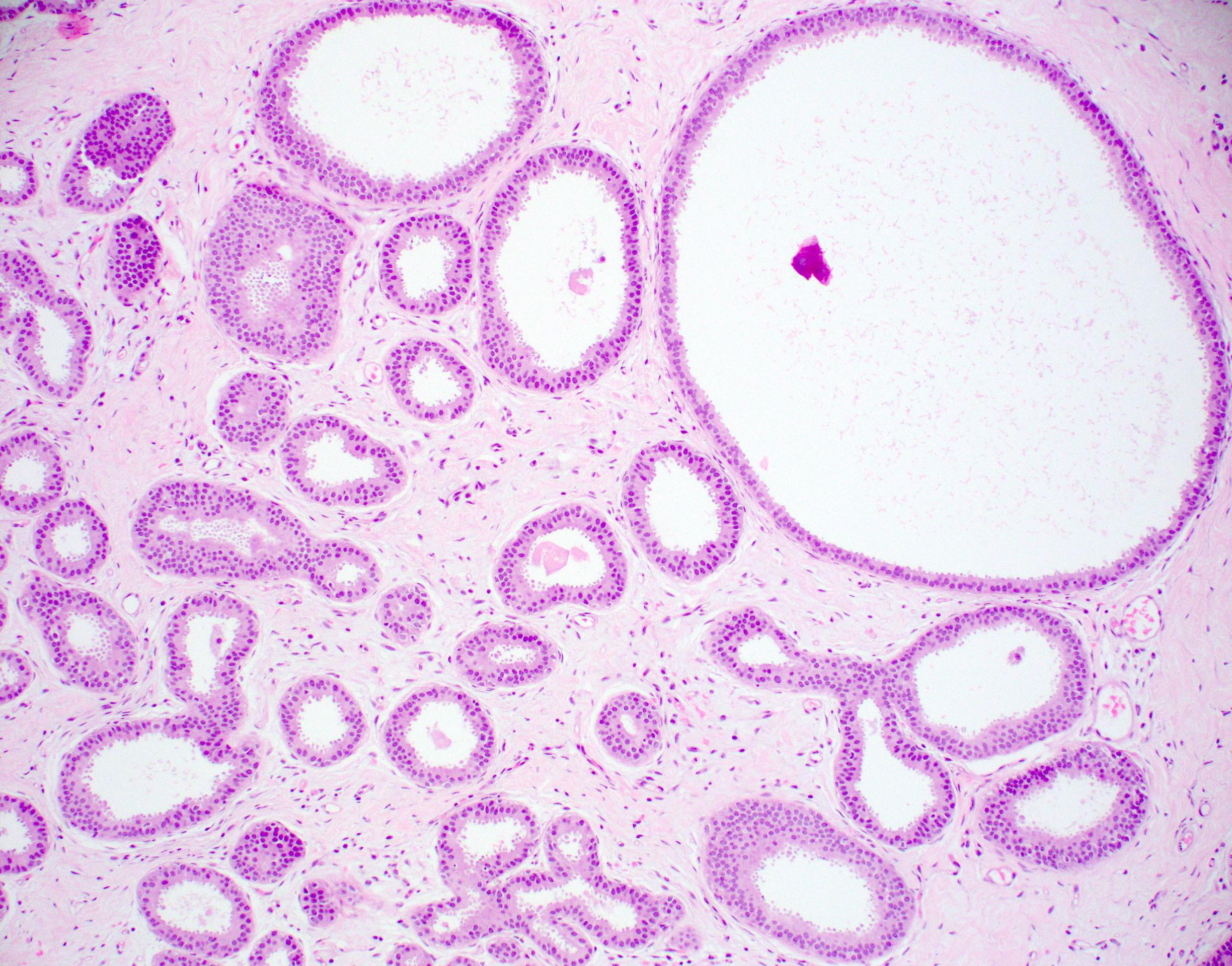
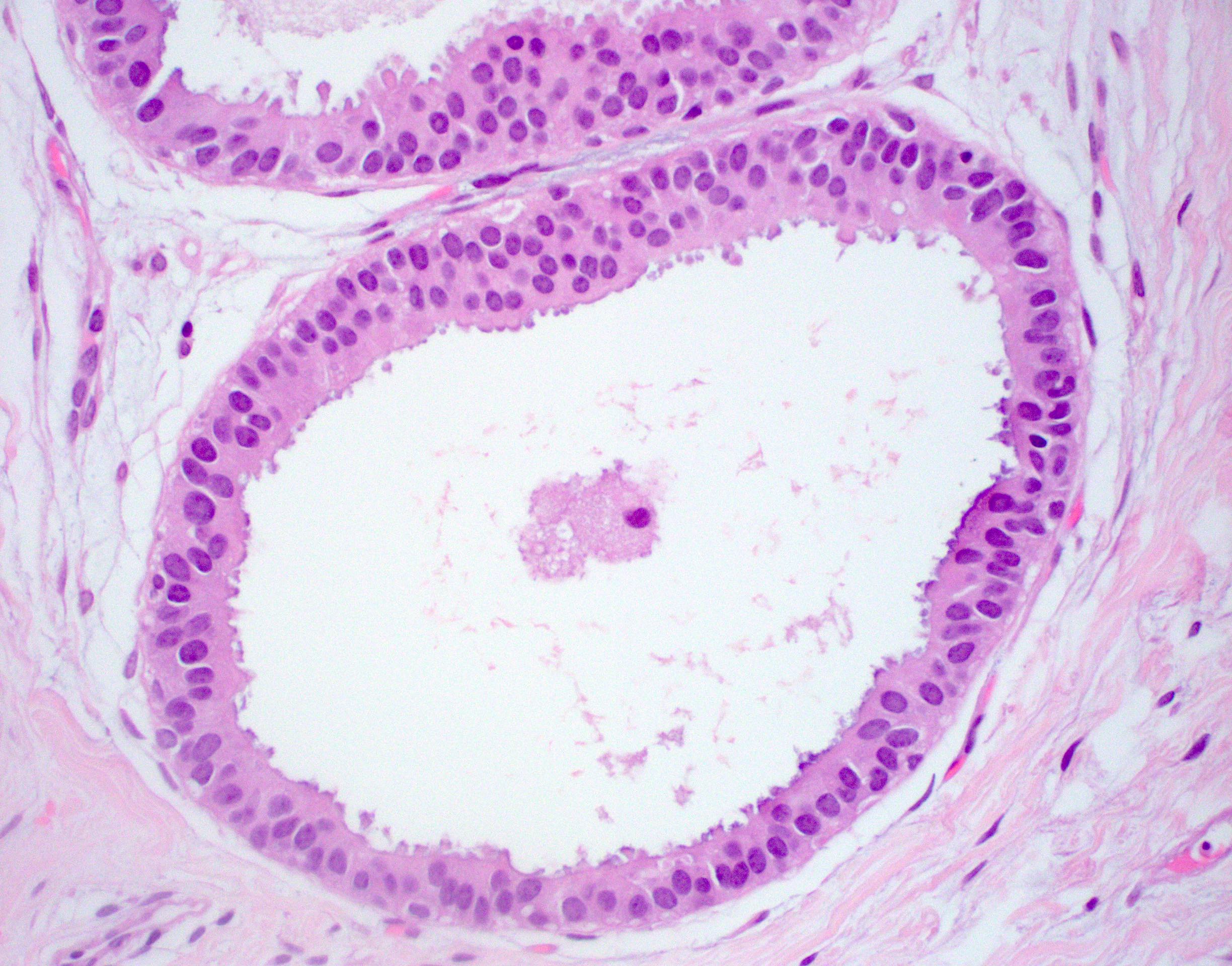
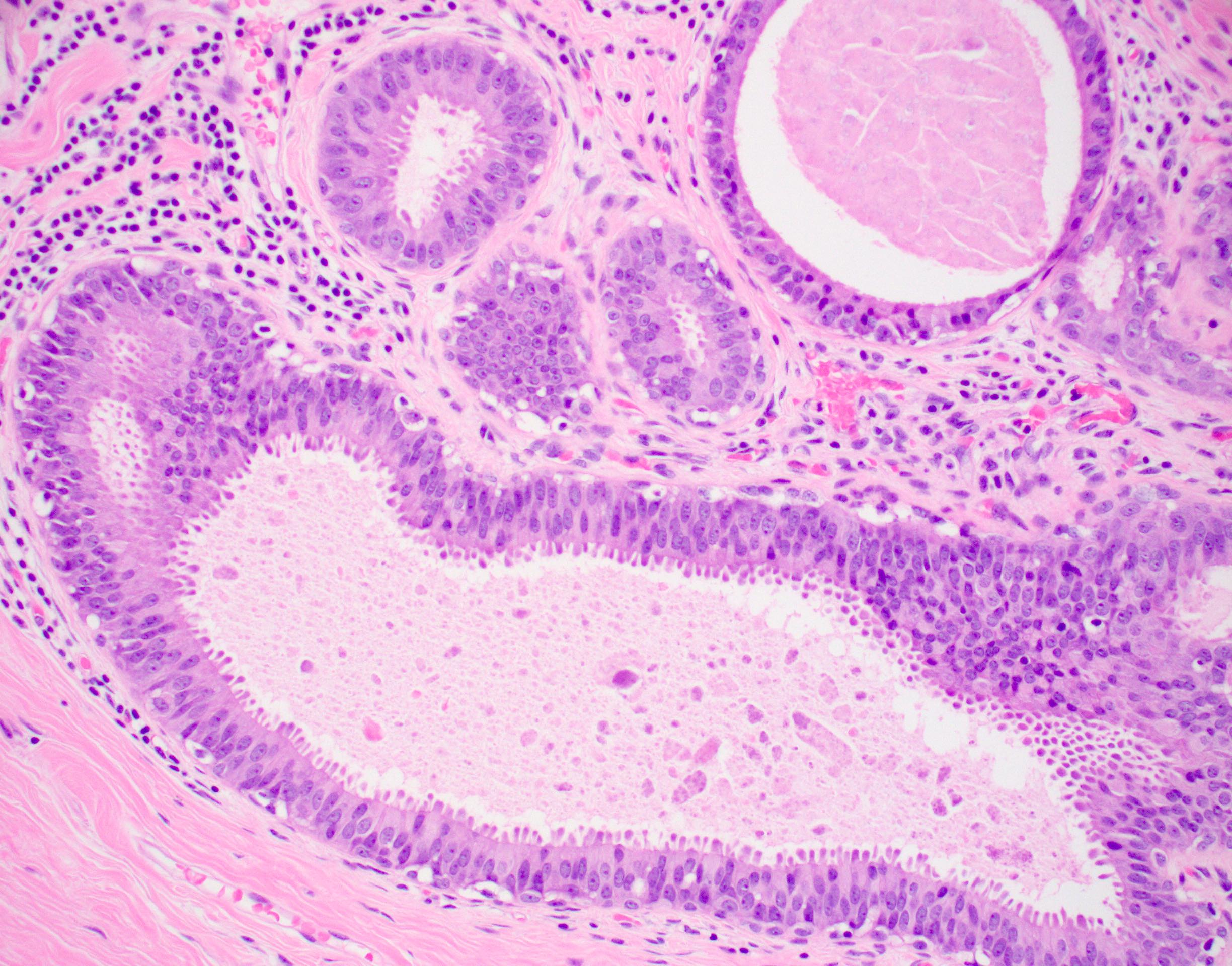
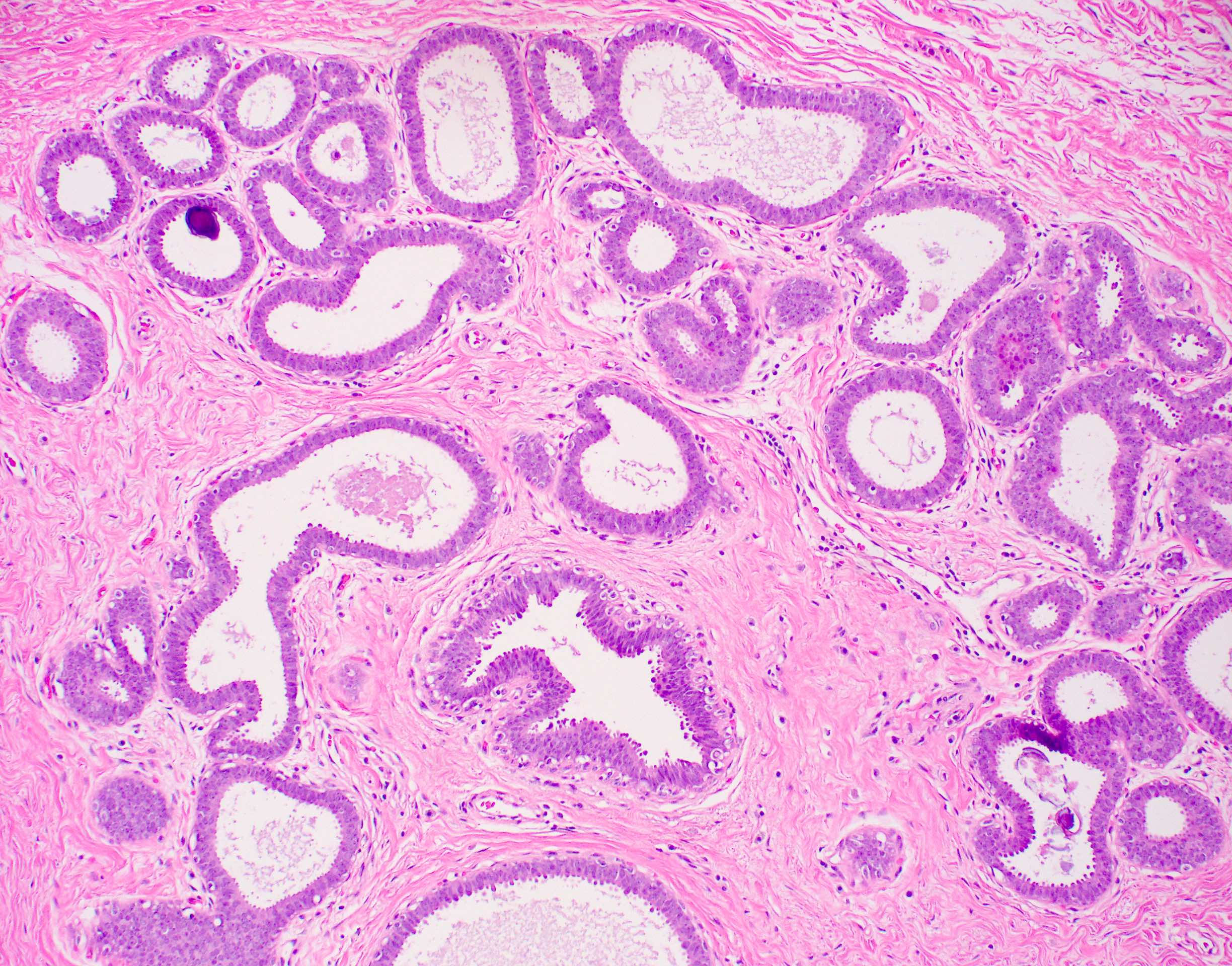
- Atypia that does not fulfill criteria of atypical ductal hyperplasia or low grade ductal carcinoma in situ due to flat growth pattern (i.e. cytologic atypia and lack of architectural atypia)
- Distention of terminal duct lobular unit with dilated glands
- Glands usually more blue than normal terminal duct lobular units at low power
- Frequent secretions and calcifications within cystically dilated glands
- Atypical epithelial proliferation with lack of regular orientation perpendicular to basement membrane
- One to several layers of low columnar or cuboidal cells with low grade cytologic atypia resembling low grade ductal carcinoma in situ
- Increased nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio (imparts blue low power appearance)
- Prominent apical tufting (snouts)
- Nuclei are usually round with variably prominent nucleoli
- Apocrine features such as eosinophilic cytoplasm may be present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Flat sheets of atypical cells with enlarged nuclei, distinct cell borders; indistinguishable from well differentiated in situ and invasive carcinoma (Diagn Cytopathol 2007;35:73)
Positive stains
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase catalytic subunit (P13KCA) mutations frequently observed similar to other breast epithelial proliferations (Mod Pathol 2014;27:740)
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, core biopsy:
- Flat epithelial atypia (FEA) with microcalcifications
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia:
- Architectural features of atypical ductal hyperplasia (arcades / bridges / papillations / fenestrations) are present
- Lacks prominent apical snouts
- Columnar cell change:
- Lacks atypia (no prominent nucleoli, less basophilic)
- Ovoid nuclei perpendicular to basement membrane (no loss of polarity)
- Lacks prominent apical snouts
- Ductal carcinoma in situ, clinging type:
- Increased cytologic atypia
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
C. Flat epithelial atypia
The pictured lesion has classic features of flat epithelial atypia (FEA), at low power showing a terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) with dilated, blue glands owing to increased nuclear:cytoplasmic ratios, which at high power show loss of orientation toward lumina and prominent apical tufting or snouts. Other current WHO accepted names include columnar cell alteration (change / hyperplasia) with atypia. Atypical cystic lobules, atypical lobules type A and low grade clinging carcinoma (monomorphous type) are terms that are not recommended for use by the WHO.
Comment Here
Reference: Flat epithelial atypia of breast
The pictured lesion has classic features of flat epithelial atypia (FEA), at low power showing a terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) with dilated, blue glands owing to increased nuclear:cytoplasmic ratios, which at high power show loss of orientation toward lumina and prominent apical tufting or snouts. Other current WHO accepted names include columnar cell alteration (change / hyperplasia) with atypia. Atypical cystic lobules, atypical lobules type A and low grade clinging carcinoma (monomorphous type) are terms that are not recommended for use by the WHO.
Comment Here
Reference: Flat epithelial atypia of breast
Practice question #2
Flat epithelial atypia most commonly has the corresponding imaging feature of
- Calcifications on mammography
- Enhancing mass on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Filling defect on ductogram (galactogram)
- Mass on ultrasound
Practice answer #2
A. Calcifications on mammography
Flat epithelial atypia (FEA) is typically diagnosed by stereotactic biopsy of mammographically detected intraluminal calcifications. Less frequently, it constitutes an incidental finding on biopsy or excision. It does not typically present as mass on imaging nor a filling defect on ductogram or galactogram.
Comment Here
Reference: Flat epithelial atypia of breast
Flat epithelial atypia (FEA) is typically diagnosed by stereotactic biopsy of mammographically detected intraluminal calcifications. Less frequently, it constitutes an incidental finding on biopsy or excision. It does not typically present as mass on imaging nor a filling defect on ductogram or galactogram.
Comment Here
Reference: Flat epithelial atypia of breast