Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Shankaralingappa S, Shankaralingappa A. Cribriform. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantcribriform.html. Accessed August 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Low grade invasive breast carcinoma microscopically characterized by a predominant cribriform pattern
- By WHO classification, a specific subtype of invasive breast carcinoma
- Variants:
- Pure: cribriform architecture is > 90% of the tumor
- Mixed: tumor composed of 10 - 90% of another morphological type (other than cribriform carcinoma)
Essential features
- Invasive breast carcinoma with > 90% of tumor composed of cribriform islands of malignant epithelial cells
- Low grade nuclei and sparse mitosis (grade 1)
- ER+ and HER2-
Terminology
- Invasive cribriform carcinoma (ICC)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8201/3 - cribriform carcinoma, NOS
- ICD-10: C50.9 - malignant neoplasm of breast of unspecified site
- ICD-11: 2C60 & XH1YZ3 - carcinoma of breast, specialized type & cribriform carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare (0.3 - 3.5% of breast carcinomas) (Ann Oncol 2009;20:1763)
- Mean age: 63 years, postmenopausal, rare in < 50 years
- Elderly males: 1.7% (BMC Cancer 2021;21:168)
Sites
- Breast
- Axilla - accessory breast tissue
Pathophysiology
- Luminal A molecular pathway / subtype of breast cancer (Cell Genom 2021:1;100067)
- Expresses hormone receptors and lacks HER2 overexpression
Etiology
- Unclear
Clinical features
- May present as a small lump / asymptomatic
- May be clinically occult
- Multifocal: 10 - 20% (Breast Care (Basel) 2013;8:149)
- Nodal metastases in 14% of pure ICC and 25% in mixed ICC (World J Surg Oncol 2012;10:251)
Diagnosis
- Breast imaging including mammogram and ultrasound of breast
- Cytologic or histologic examination of involved tissue
Radiology description
- Mammogram: density, asymmetry, spiculated mass, microcalcifications
- Ultrasound: mass
- MRI: enhancing focus or mass
Prognostic factors
- Pure ICC: excellent; usually less lymph node metastasis and lower stage
- Mixed ICC: prognosis poorer than pure but better than invasive ductal carcinoma of no special type (IDC, NST)
- Lymph node / distant metastasis is rare (BMC Cancer 2021;21:168)
- ICC: more favorable prognosis than invasive breast carcinoma with less cribriform pattern and low grade IDC (J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:445)
Case reports
- 59 year old woman, postmenopausal, presented with a large left breast mass of 13 years (World J Surg Oncol 2012;10:251)
- 64 year old man with tumor microcalcifications (Breast Cancer 2005;12:145)
- 68 year old woman with incidentally detected invasive cribriform carcinoma on CT (Clin Case Rep 2021;9:e05214)
- 12 cases of invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10:9917)
Treatment
- Primary surgical excision
- Postsurgical local radiation therapy (typically in the setting breast conserving therapy only for this special subtype of breast carcinoma)
- Endocrine therapy
Gross description
- Similar to IDC
- Usually small size, < 2 cm; some 2 - 5 cm; firm / hard spiculated mass, gritty if calcifications are present (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10:9917)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Irregular cribriform growth pattern > 90% of cells
- Nuclear grade I pure ICC: > 90% cribriform pattern
- Mixed: 10 - 90% other morphological type, other than cribriform carcinoma
- Low grade: Nottingham grade 1 tumors
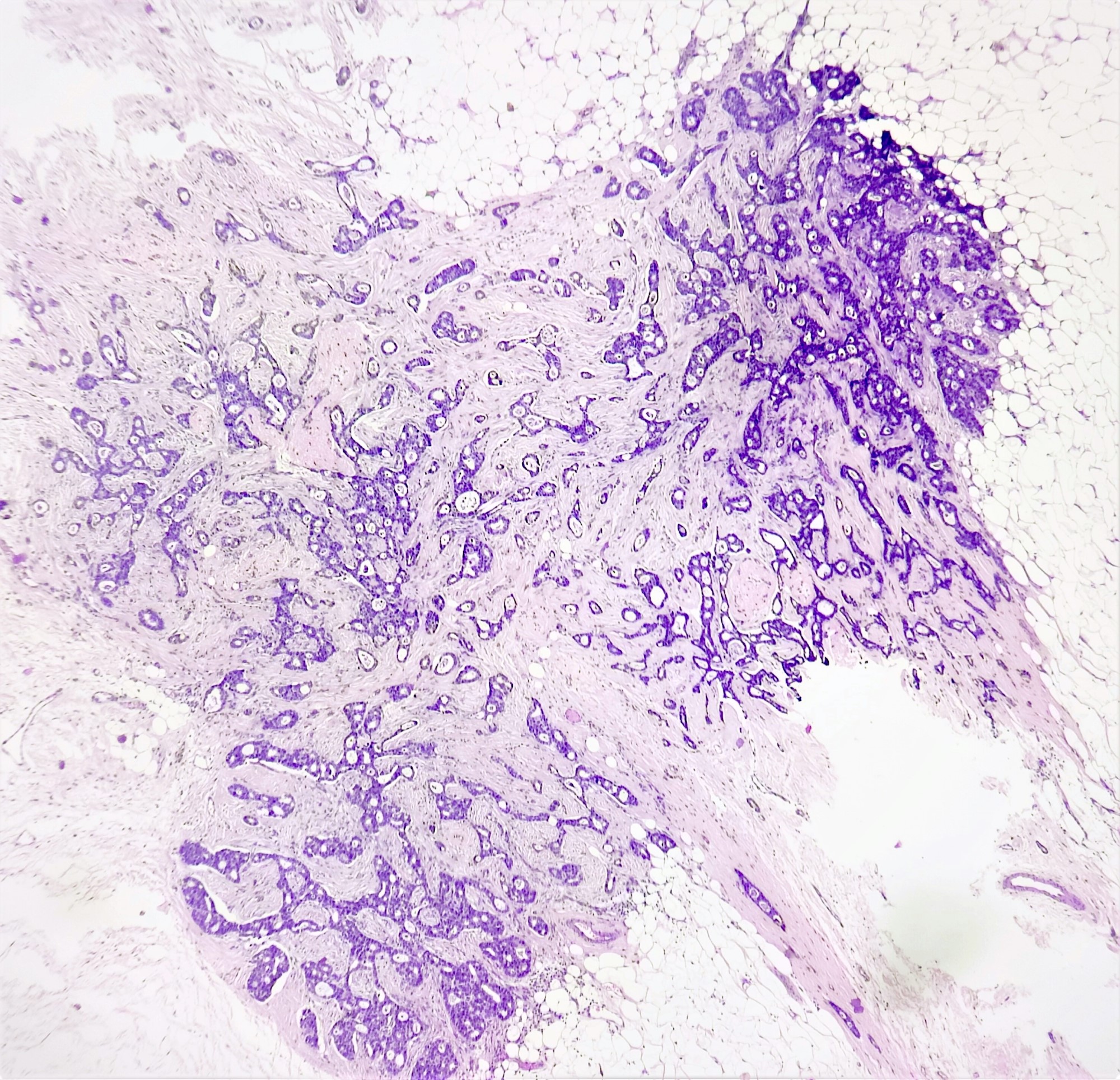
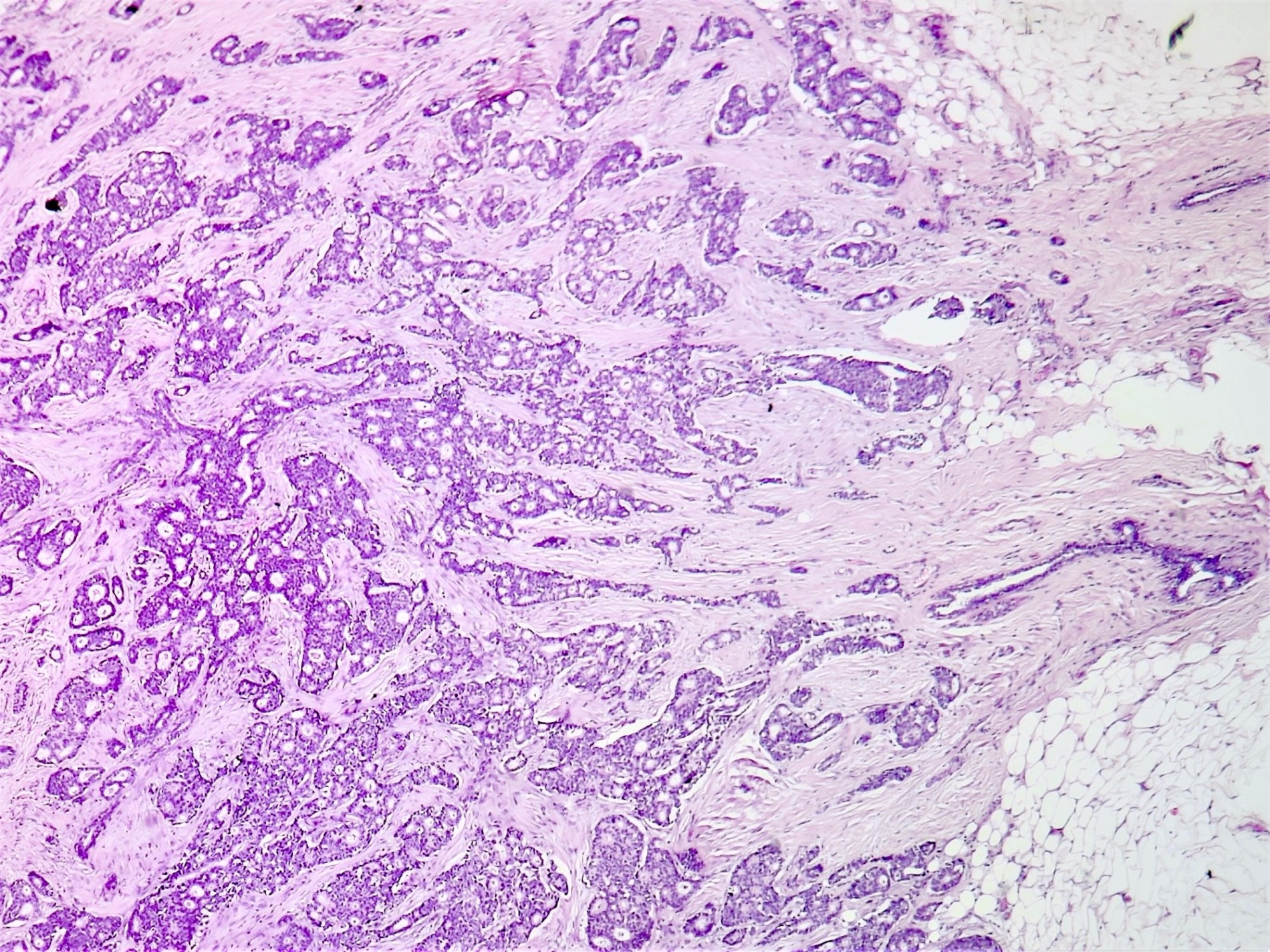
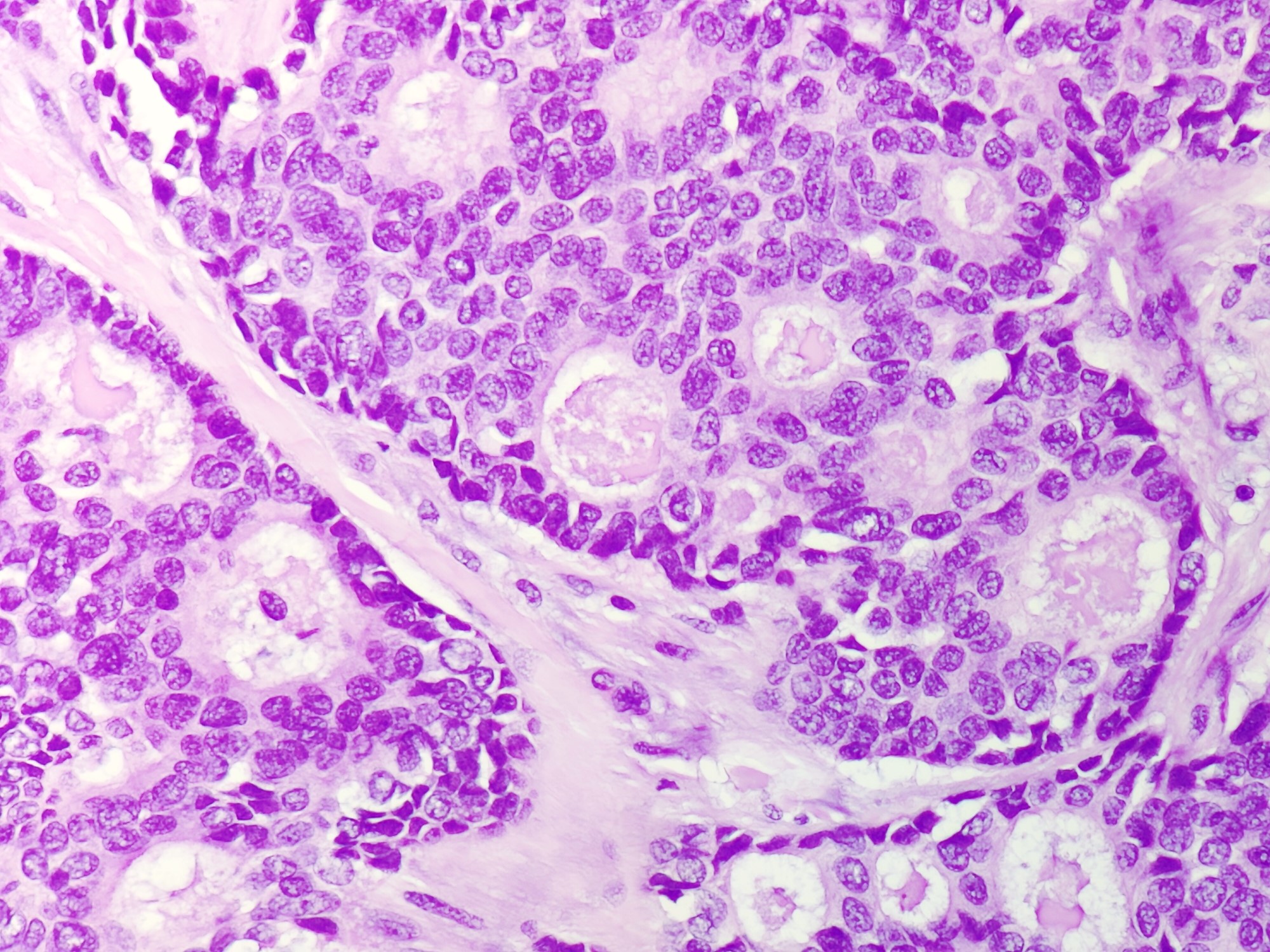
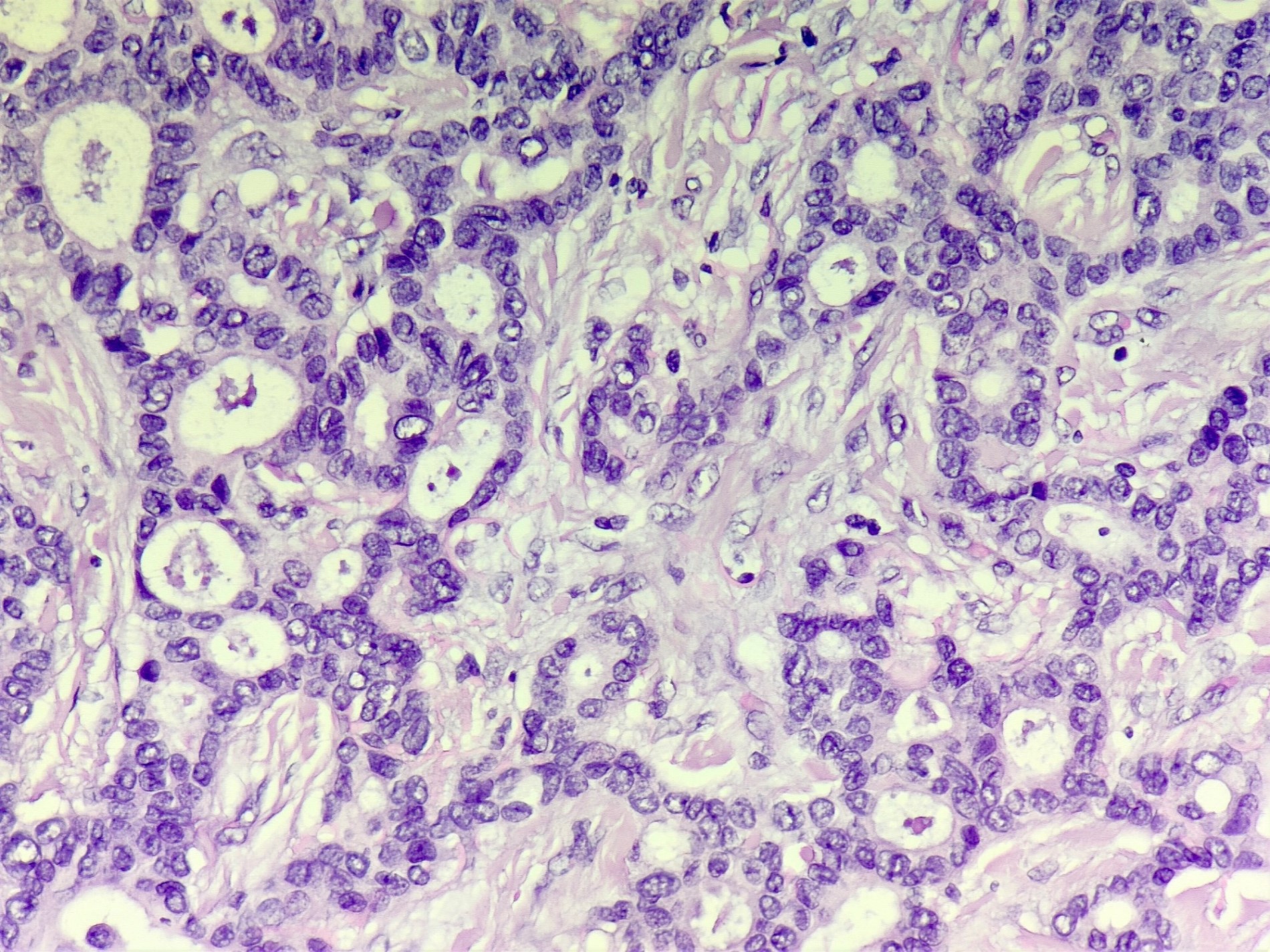
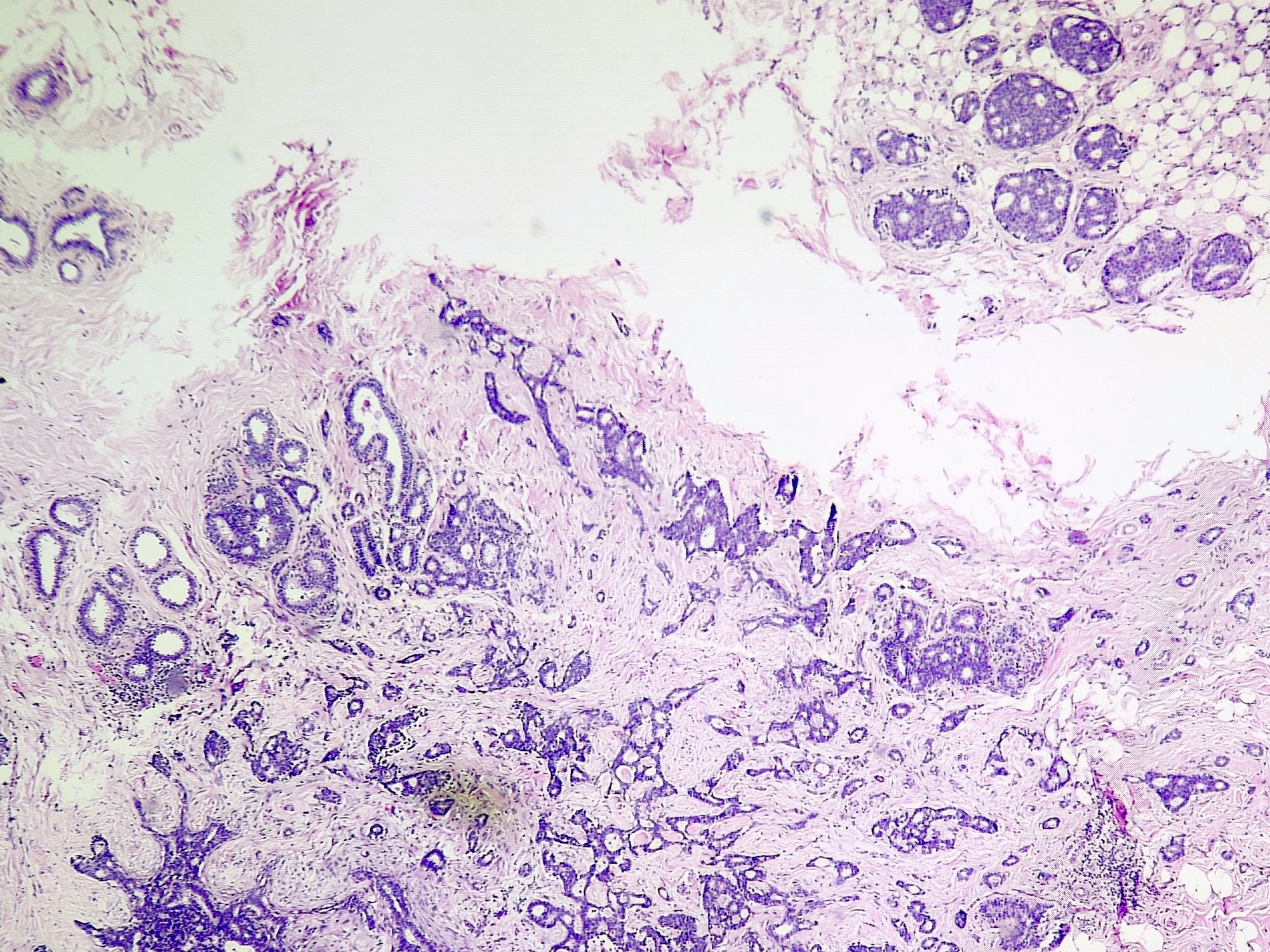
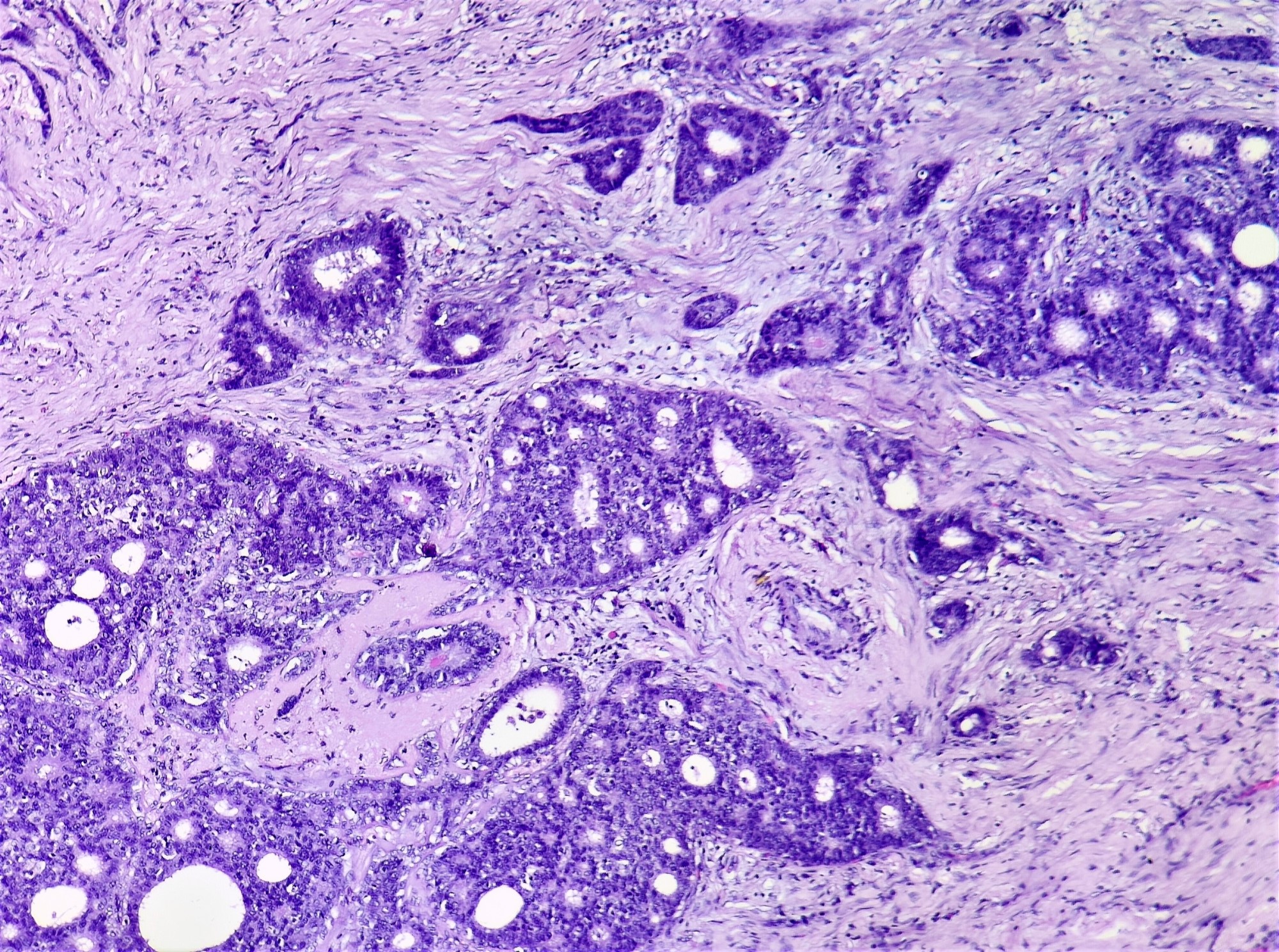
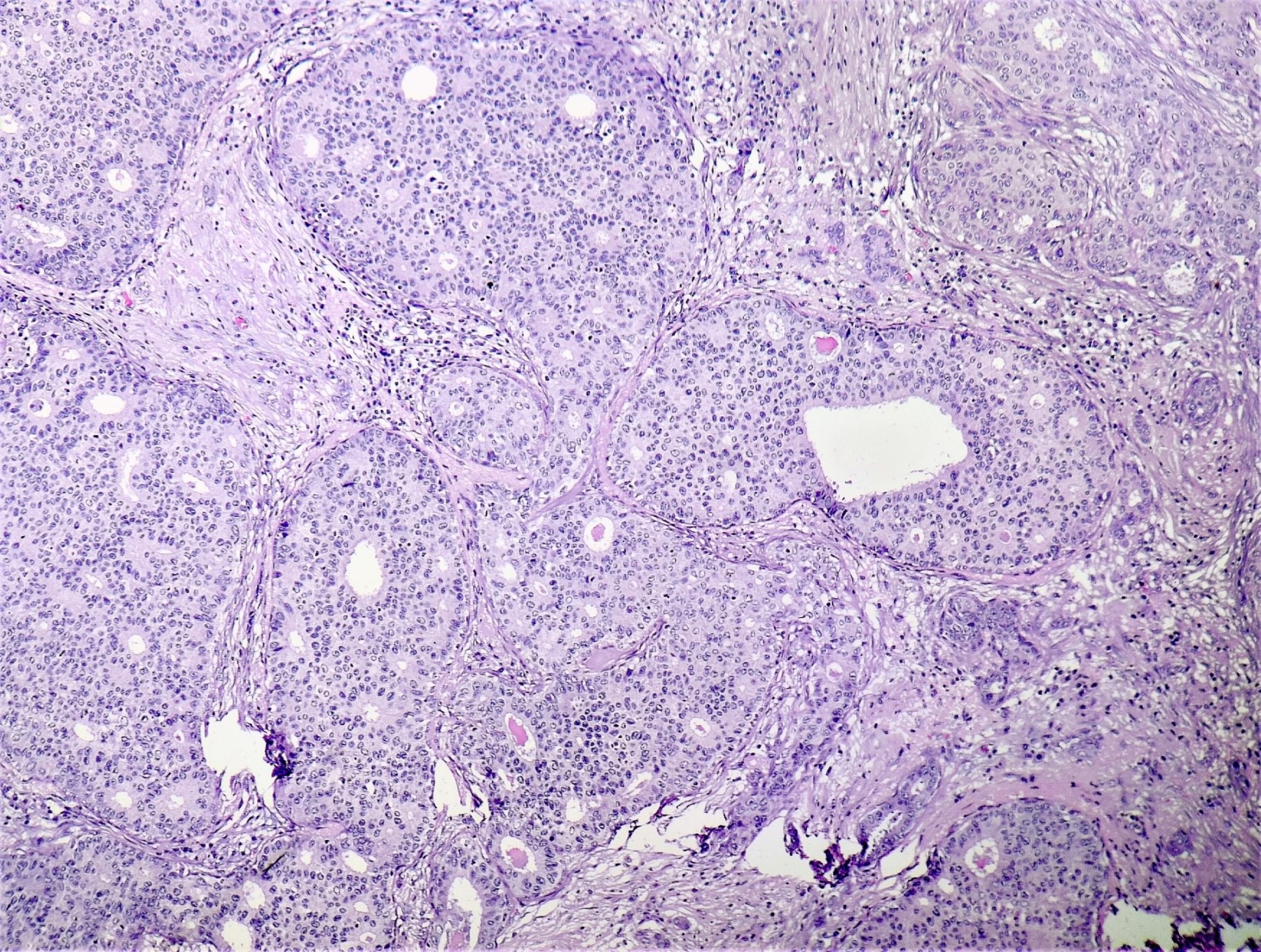
- Invasive islands or nests of malignant cells with round or angulated contours and well defined cribriform spaces formed by arches of epithelial cells; this gives a sieve-like appearance
- Tumor cells: small, mild / moderate pleomorphism, no nuclear atypia
- No / sparse mitotic activity
- Desmoplastic stroma
- Mucin positive secretion, microcalcifications in lumen
- Osteoclastic giant cells may be seen
- Myoepithelial cells absent
- Associated with cribriform ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
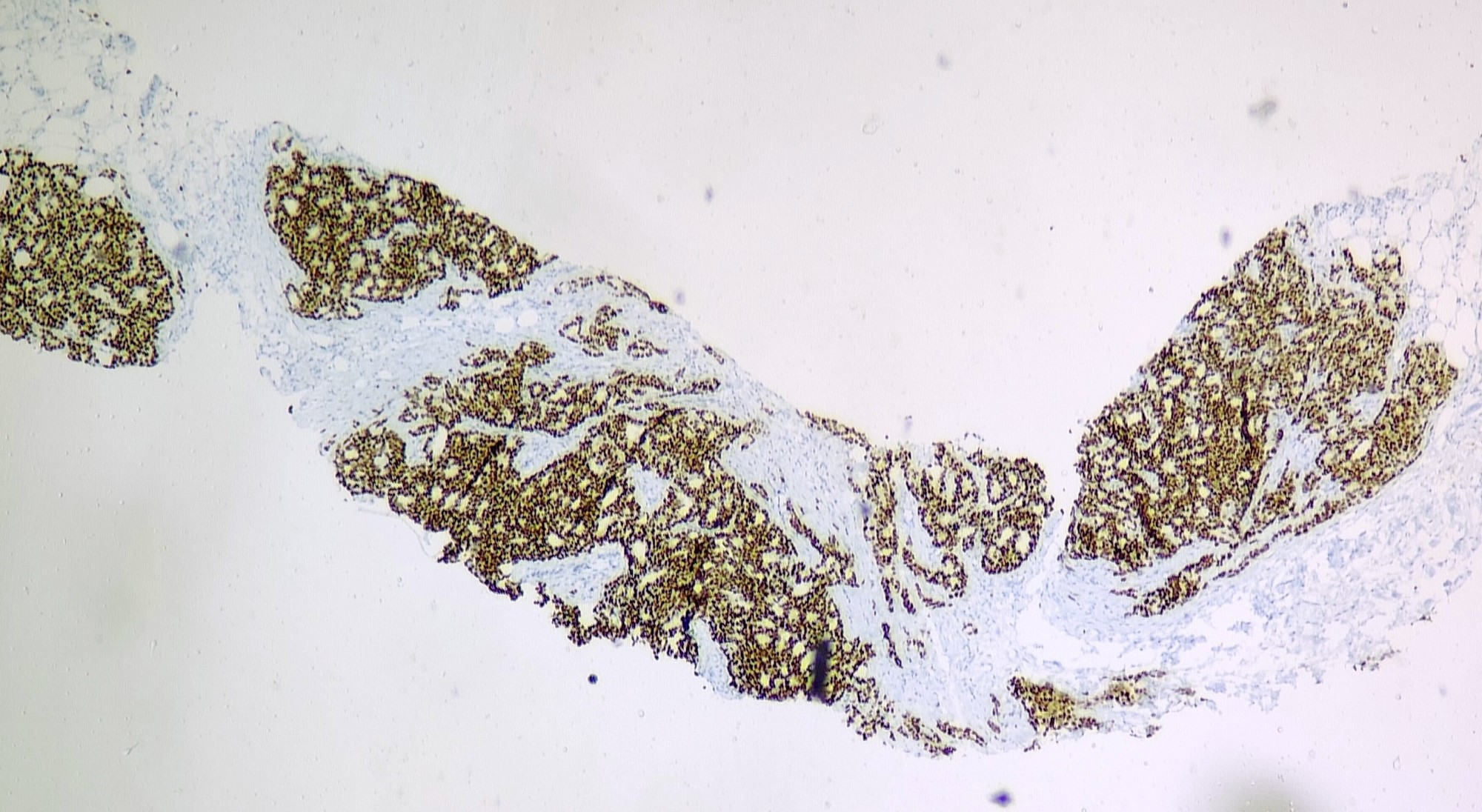
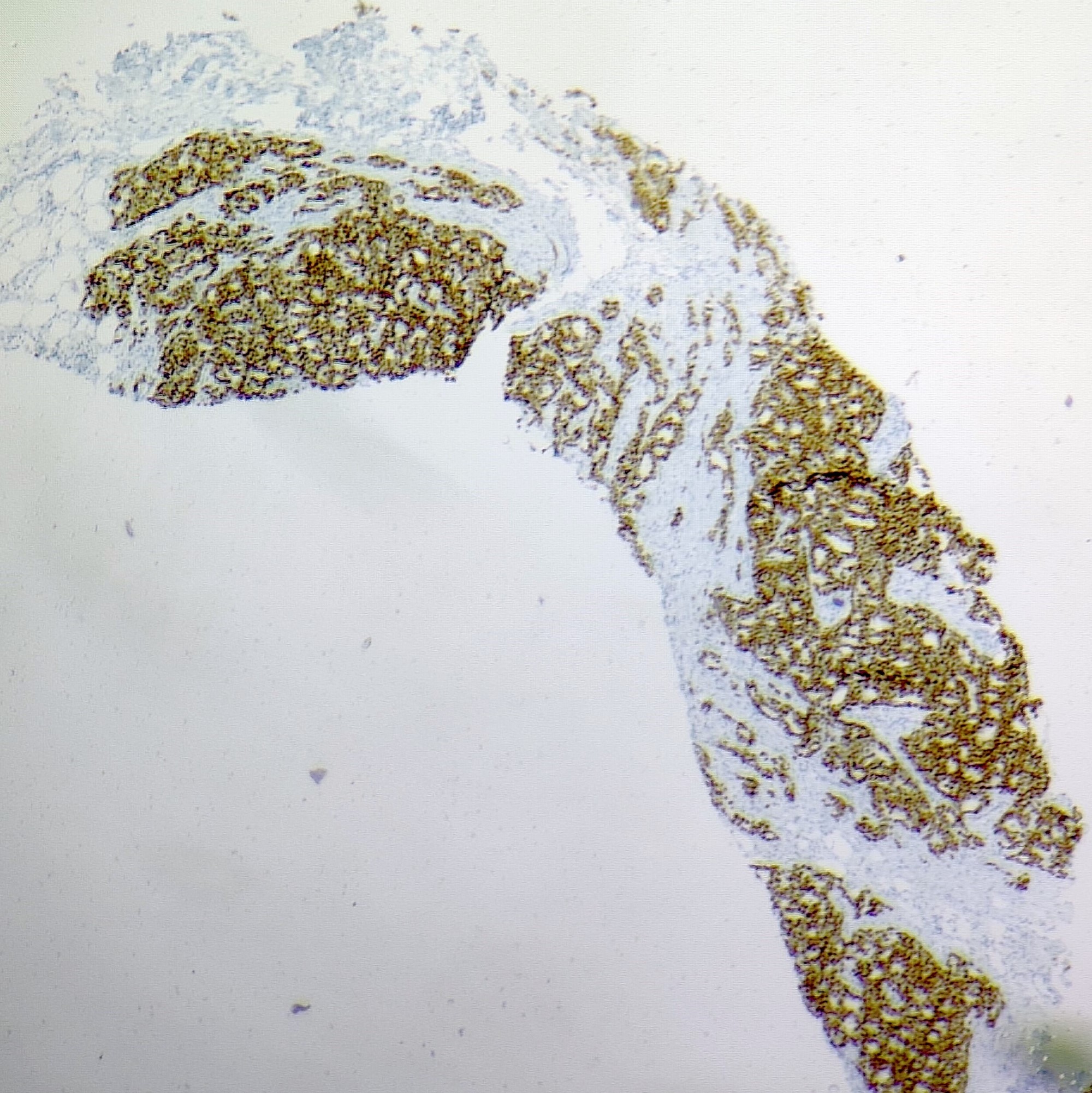
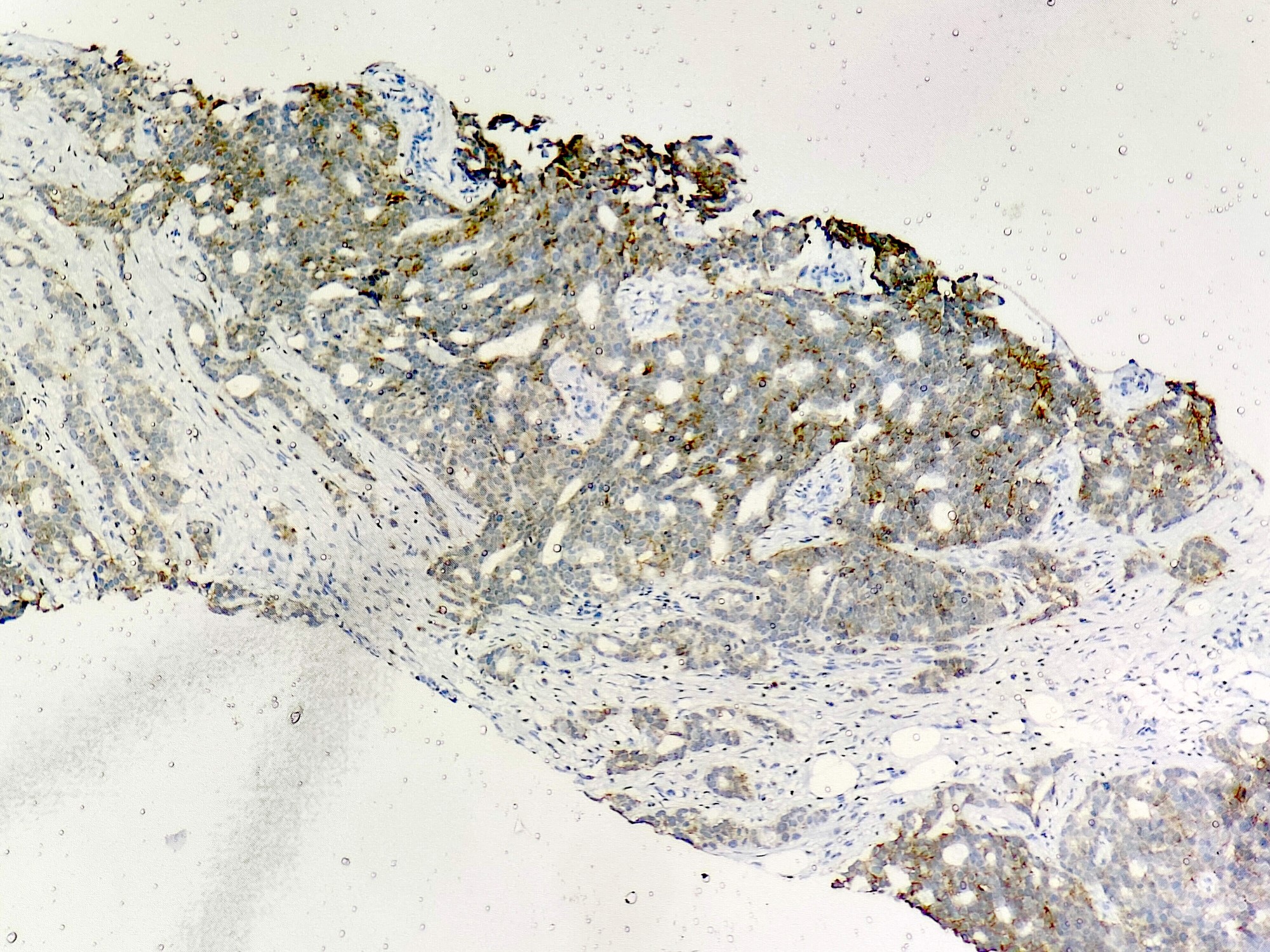
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Sunitha Shankaralingappa, M.B.B.S, M.D., D.M.
Cytology description
- Cytologic features and limitations
- 3D clusters and cohesive sheets of bland ductal cells, cribriform pattern (Acta Cytol 2001;45:593)
- Naked bipolar nuclei and myoepithelial cells are absent
- Definitive diagnosis on cytology is rare; core needle biopsy is preferred
Negative stains
- HER2
- Myoepithelial markers: distinguish ICC from cribriform DCIS
Electron microscopy description
- Numerous mitochondria
- Luminal surfaces have abundant microvilli (Ultrastruct Pathol 1994;18:519)
Sample pathology report
- Breast, right, modified radical mastectomy
- Invasive cribriform carcinoma, grade 1, measuring 1.5 cm
- Immunohistochemical biomarker results: estrogen receptor positive (90%, strong intensity), progesterone receptor positive (50%, moderate intensity), HER2 negative (score 0).
Differential diagnosis
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Cribriform DCIS:
- Noninfiltrating
- Regularly distributed clusters
- Myoepithelial cells are present
- Collagenous spherulosis:
- Circumscribed, intraductal or intralobular proliferation
- Fibrillar / laminated spherules
- Myoepithelial cells are present
- Lacks cytologic atypia
- Well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor:
- Intracytoplasmic argyrophilic granules
- Salt and pepper chromatin
- Neuroendocrine markers are positive
- Well differentiated invasive breast cancer of no special type (NST):
- May share similar nuclear features but lacks prominent cribriform architecture
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 62 year old woman underwent a core needle biopsy for a lump, 1.2 cm in diameter, detected on mammogram. The histopathology pattern is shown above. Which statement is true regarding this tumor?
- Has an increased chance of distant metastasis
- Lesion is high grade
- Strong and diffuse positivity for ER
- Strongly positive (3+) for HER2 by IHC
Practice answer #1
C. Strong and diffuse positivity for ER. This biopsy shows cribriform carcinoma. This type of breast carcinoma is seen in elderly, postmenopausal women and is most often detected on mammogram. It is strongly positive for ER, usually positive for PR and negative for HER2. It is a low grade tumor (Nottingham grade I) with a good prognosis and lower frequency of lymph node and distant metastasis.
Comment Here
Reference: Cribriform carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cribriform carcinoma
Practice question #2
Which of the following is one of the diagnostic criteria for invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast?
- < 50% component of tubular carcinoma
- ER, PR, HER2 negative
- At least 90% of tumor composed of cribriform islands with low grade nuclei
- Presence of myoepithelial cells on IHC
Practice answer #2
C. Nuclear grade I in at least 90% of cells. Invasive cribriform carcinoma (ICC) is an infiltrating breast carcinoma with predominantly cribriform pattern. It is pure when > 90% of tumor is of cribriform pattern. It is termed mixed ICC when the other invasive component constitutes 10 - 90%. It is a low grade tumor with grade I nuclei and sparse mitotic activity. It is differentiated from cribriform DCIS by absence of myoepithelium. ICC is a luminal A molecular subtype of breast carcinoma and expresses hormone receptors and lacks HER2 overexpression.
Comment Here
Reference: Cribriform carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cribriform carcinoma