Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Genco IS, Hajiyeva S. Collagenous spherulosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastcollageneousspherulosis.html. Accessed August 28th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nonneoplastic alteration characterized by spherules of basement membrane material surrounded by myoepithelial cells (Hoda: Rosen's Diagnosis of Breast Pathology by Needle Core Biopsy, 4th Edition, 2017)
- Almost always an incidental finding in association with proliferative lesions (papilloma, sclerosing adenosis and rarely carcinoma in situ) (Pathology 2017;49:181)
Essential features
- Benign proliferation with intraluminal pink basement membrane material (spherule) surrounded by myoepithelial cells
Terminology
- Collagenous spherulosis
- Simple spherulosis
- Mucinous spherulosis
- Adenoid cystic hyperplasia (not recommended due to confusion with adenoid cystic carcinoma)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Adult women
- Frequency < 1% of excision specimens (Hoda: Rosen's Diagnosis of Breast Pathology by Needle Core Biopsy, 4th Edition, 2017); likely underreported
Sites
- No specific site in the breast
Pathophysiology
- Unclear
- Accumulation of basement membrane material in spaces
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Usually incidental
- Very rarely presents as mass (Pathology 2017;49:181)
Diagnosis
- Based on histologic examination of removed tissue
Radiology description
- May present as radiologic or rarely as architectural distortion, density or mass (Pathology 2017;49:181)
Prognostic factors
- No evidence of association with precancerous state (Hoda: Rosen's Diagnosis of Breast Pathology by Needle Core Biopsy, 4th Edition, 2017)
- May be seen in association with neoplastic proliferations, particularly lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:20)
Case reports
- 48 year old woman with collagenous spherulosis in an adenomyoepithelioma (J Clin Pathol 2004;57:83)
- 50 year old woman with cystic mass with solid component (Breast J 2008;14:301)
- 51 year old woman with slow growing mass (Acta Cytol 2010;54:314)
- 47 year old and 51 year old women with cases of collagenous spherulosis associated with lobular carcinoma in situ (J Pathol Transl Med 2018;52:420)
- 53 year old woman with a 3.5 cm breast mass (Breast J 2000;6:199)
Treatment
- No treatment required
Gross description
- No specific gross features (usually not discernable from background breast tissue)
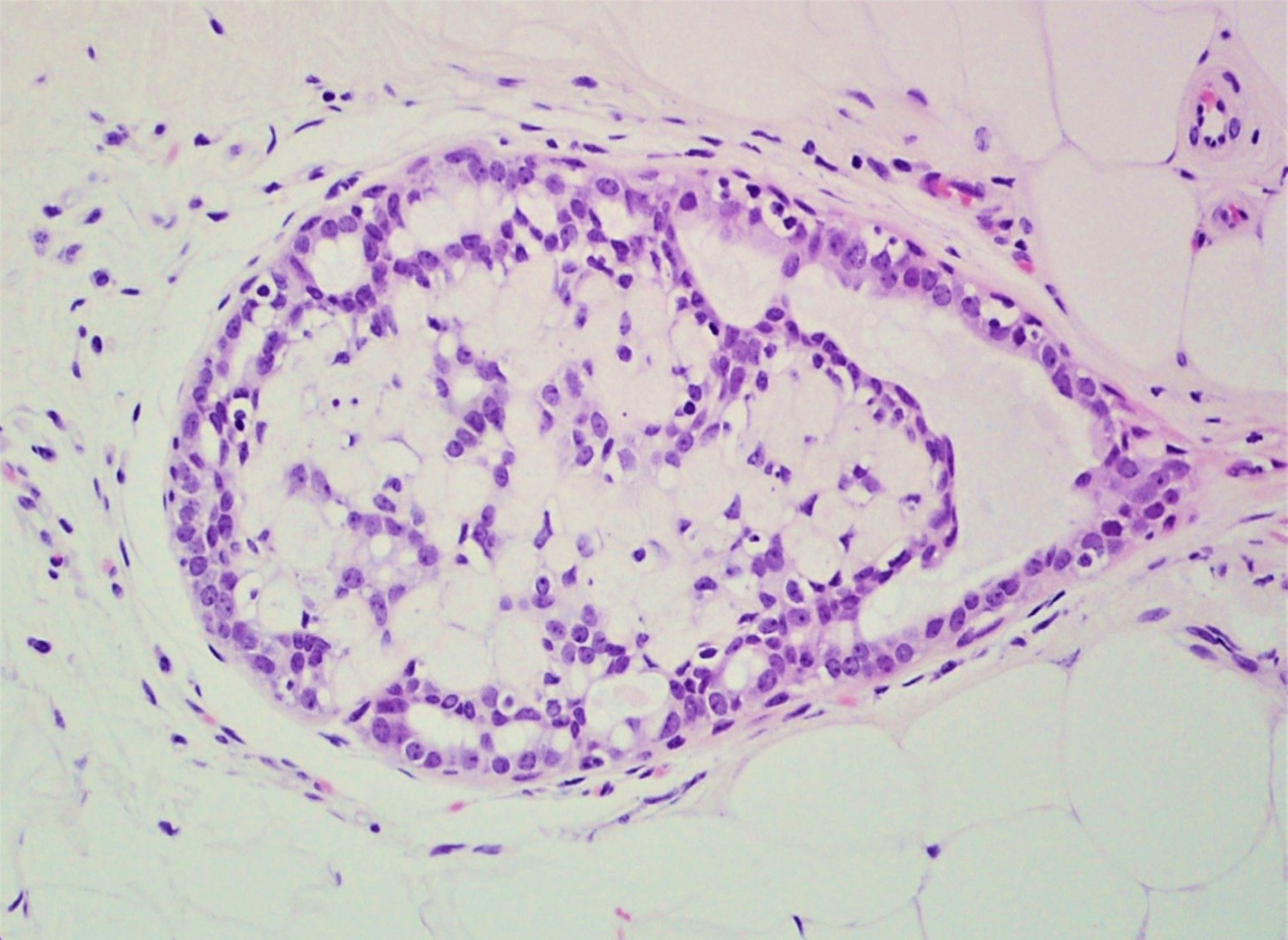
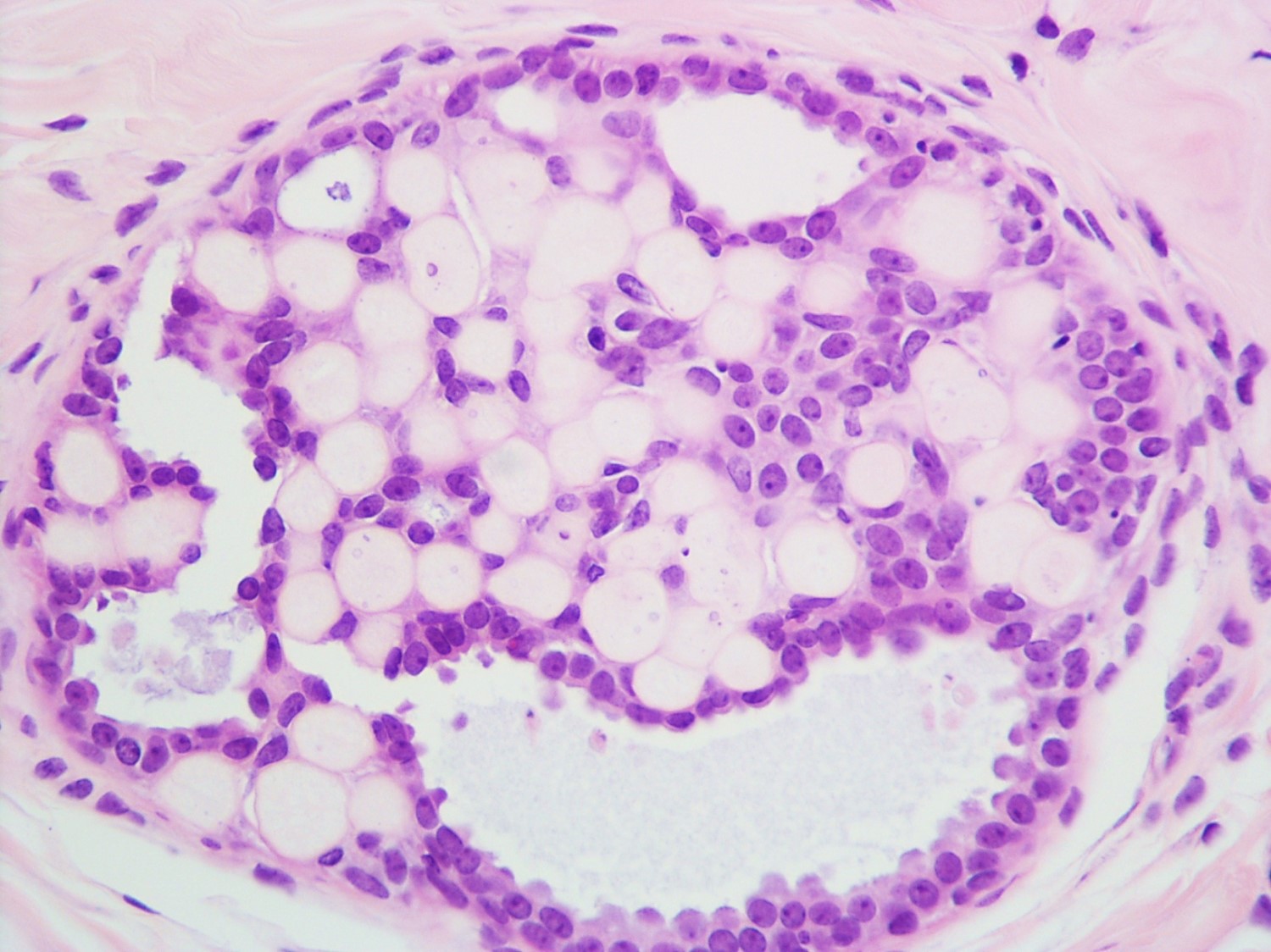
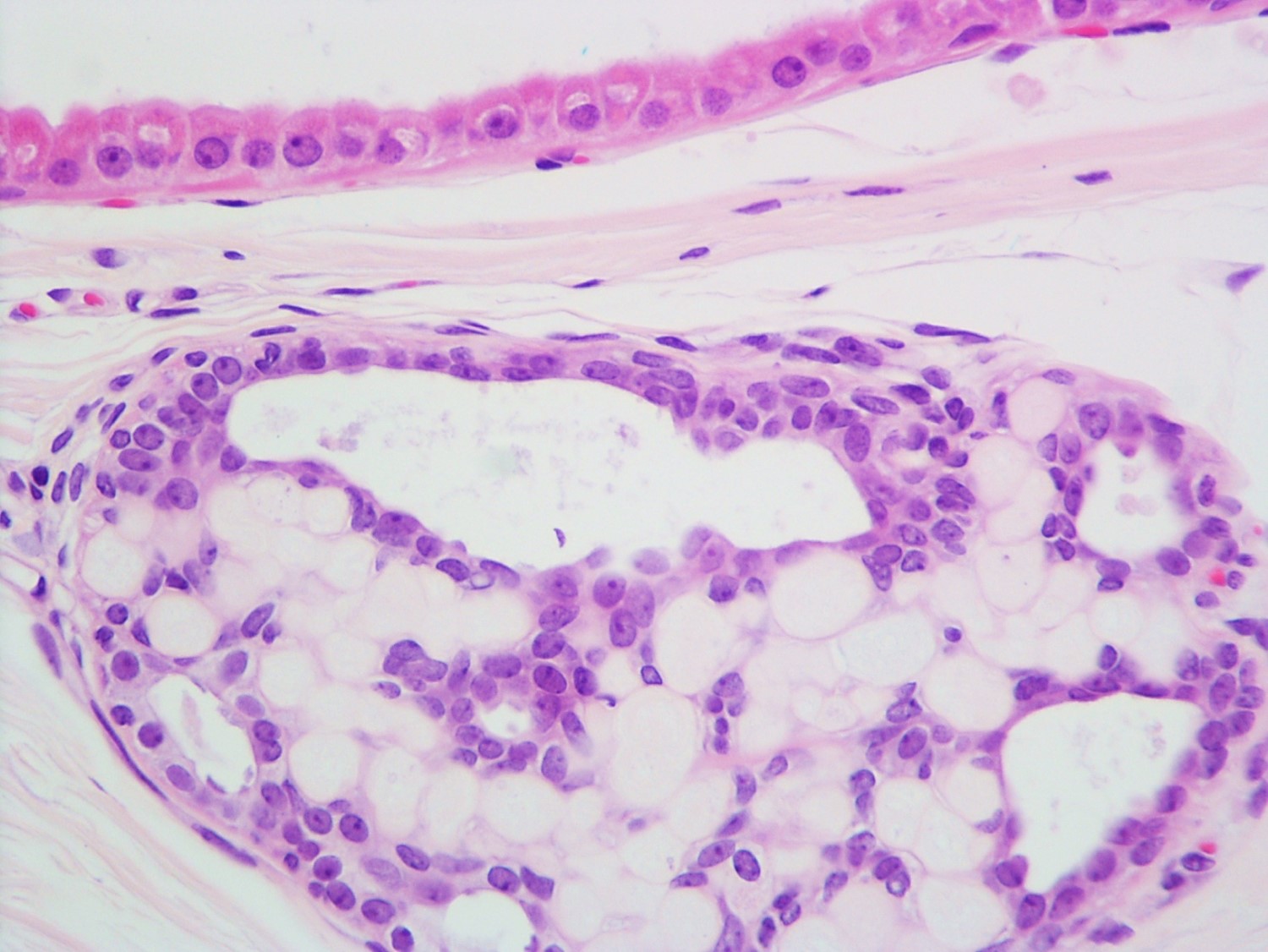
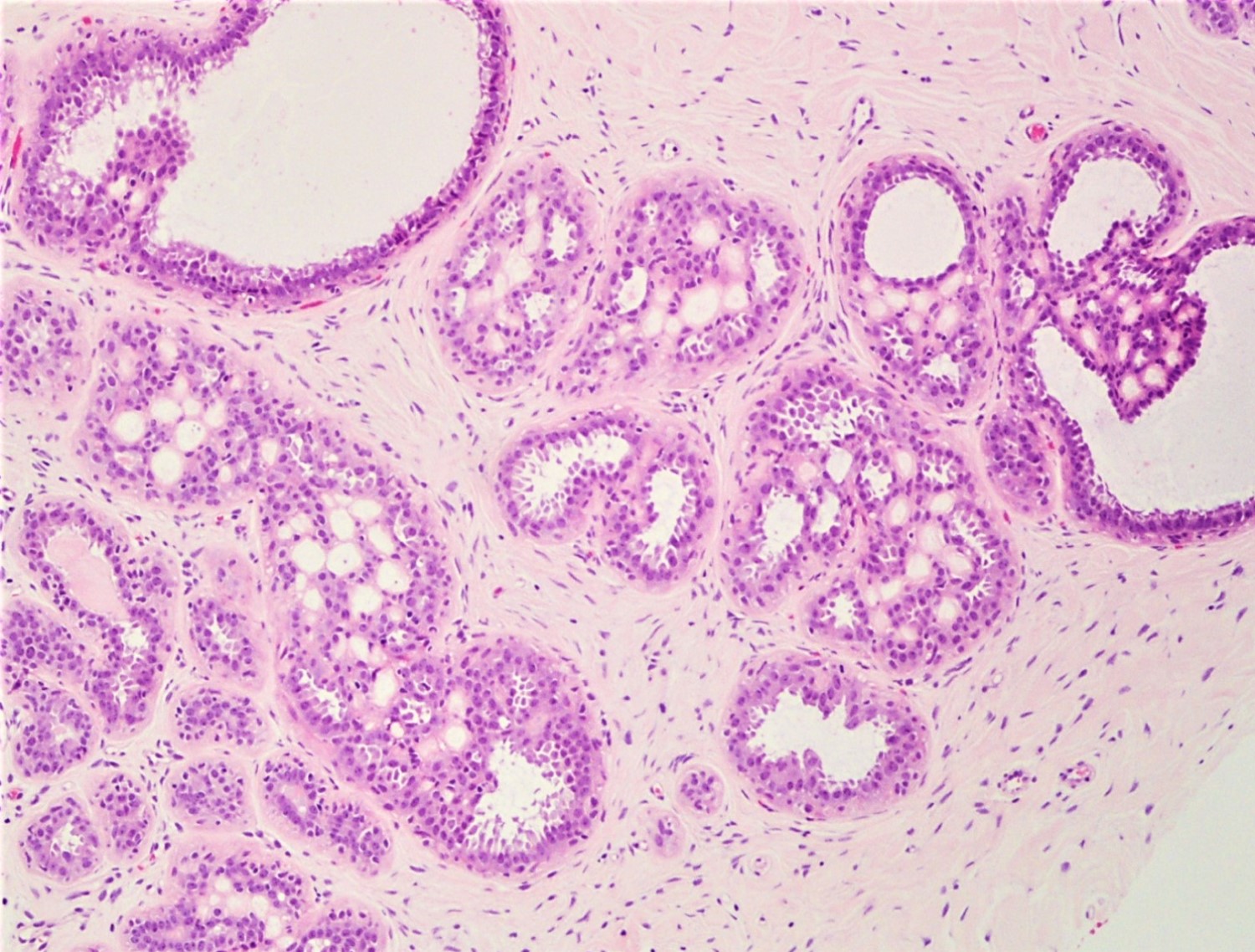
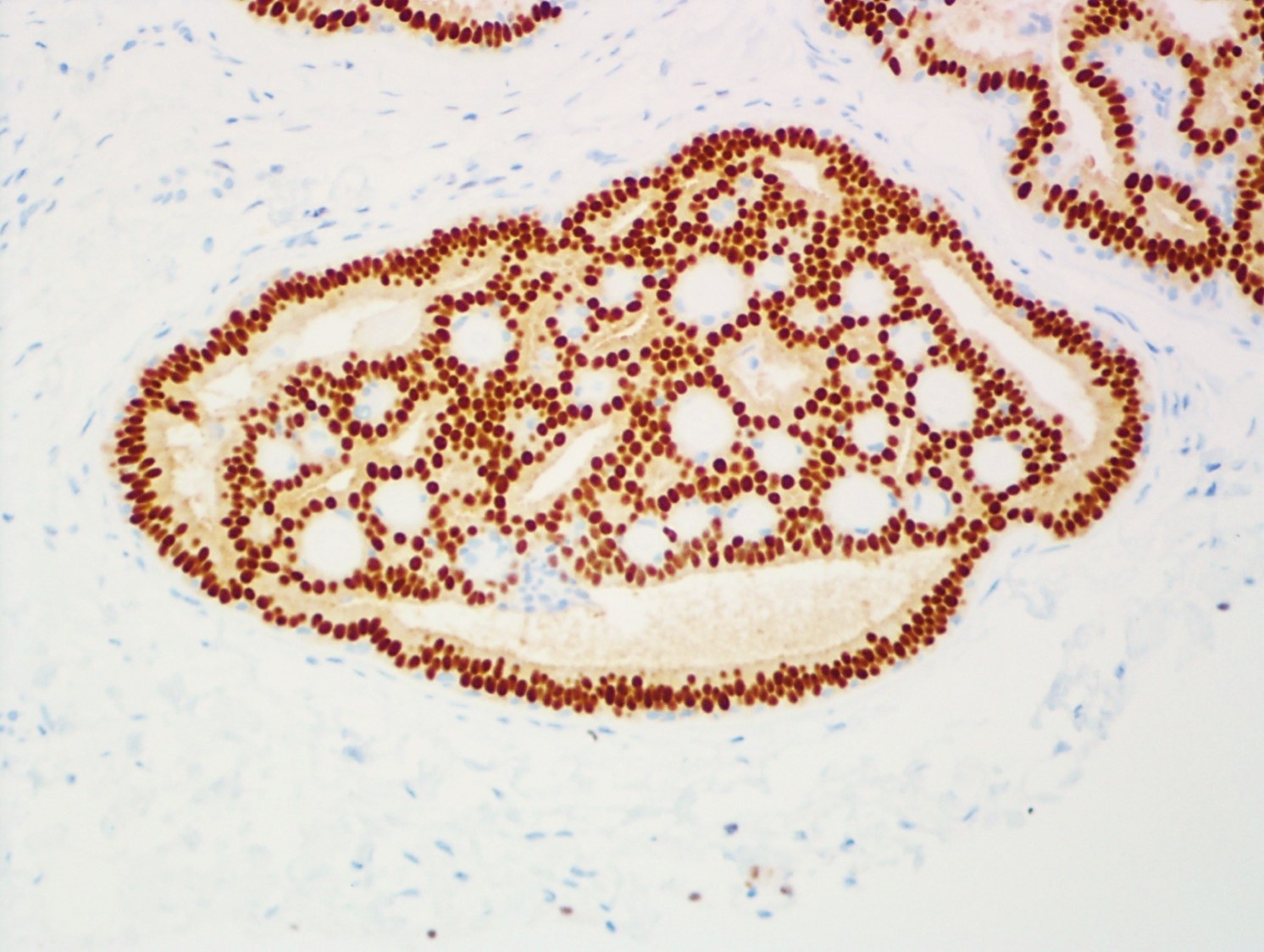
Microscopic (histologic) description
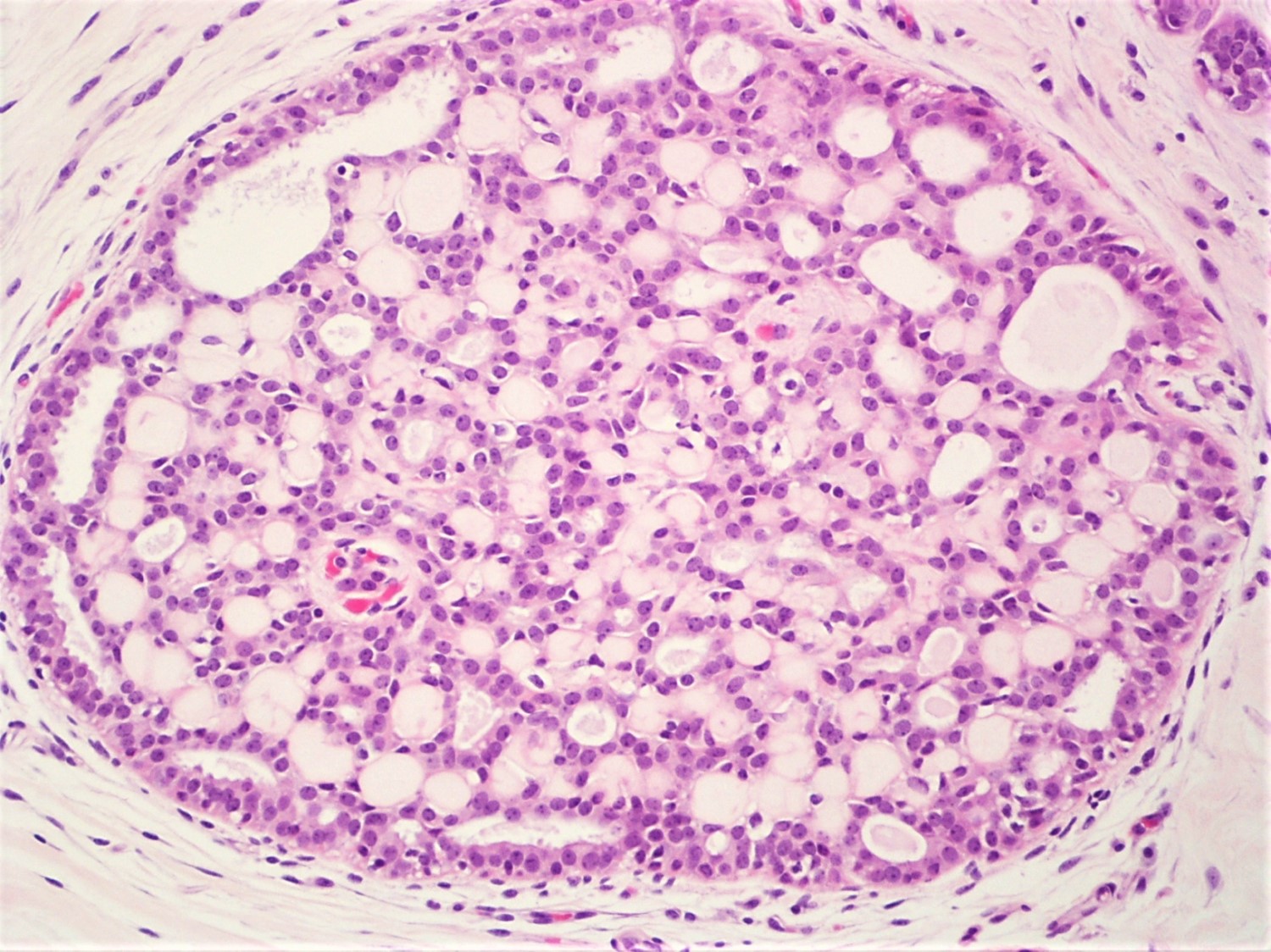
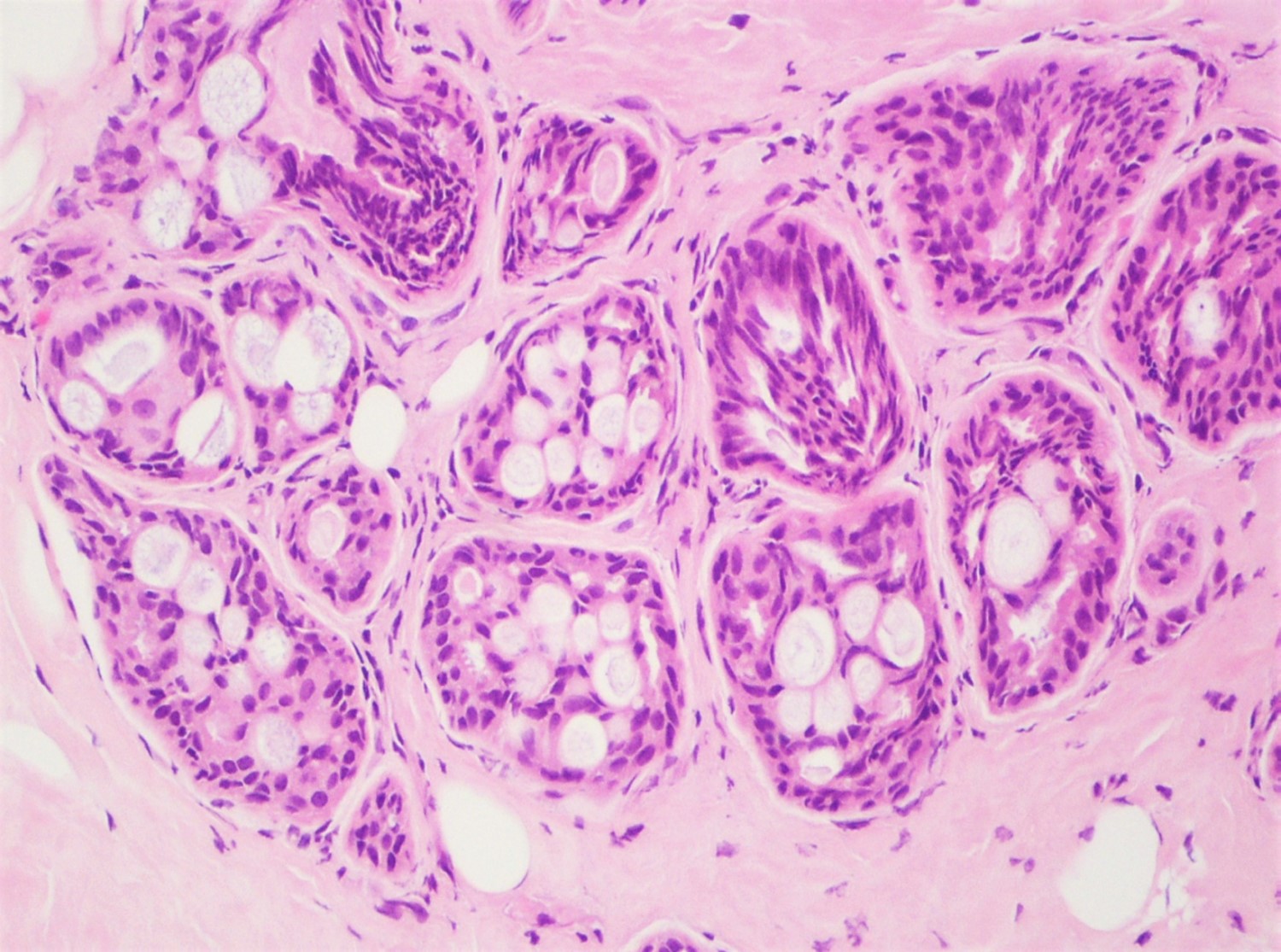
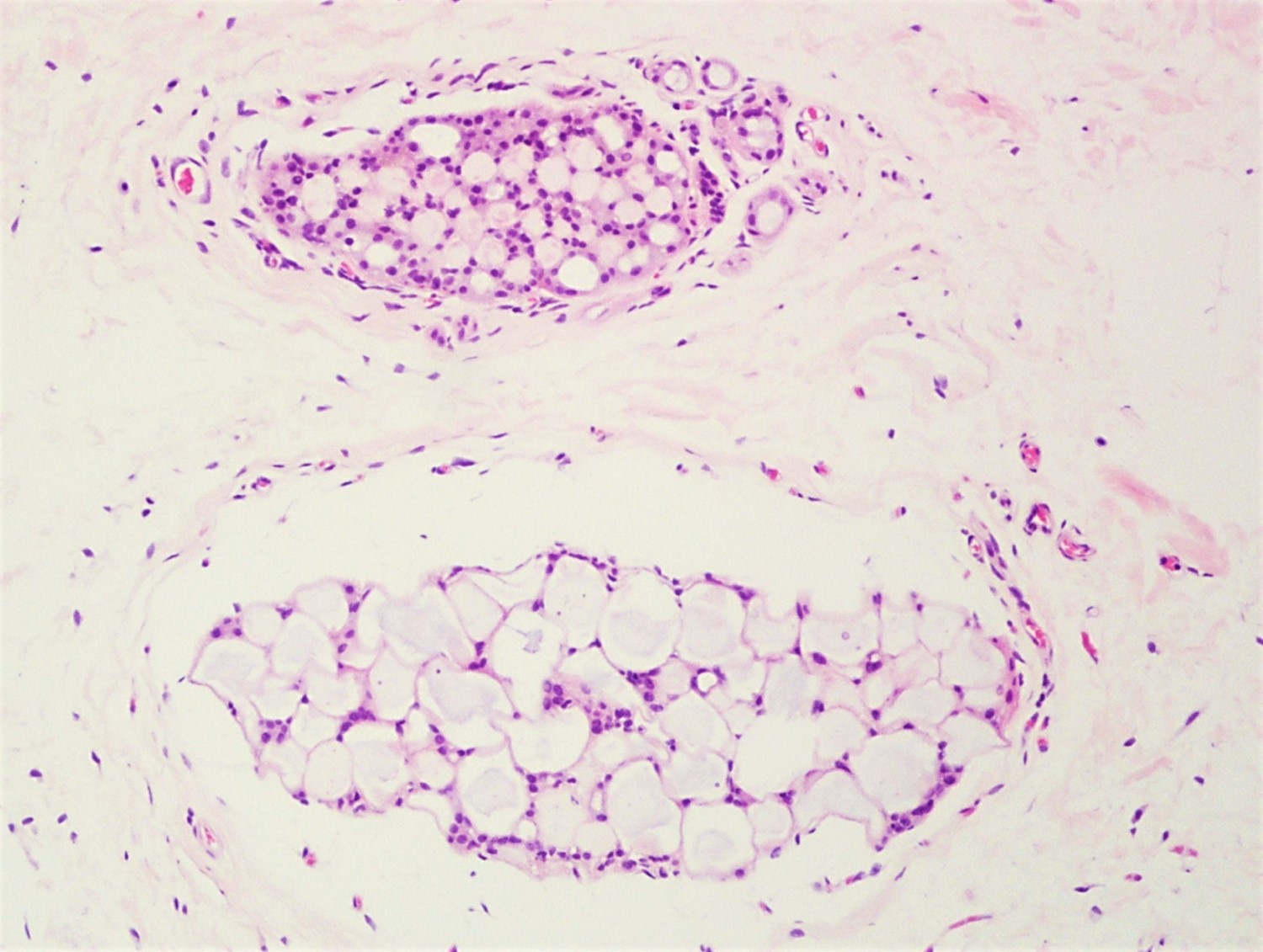
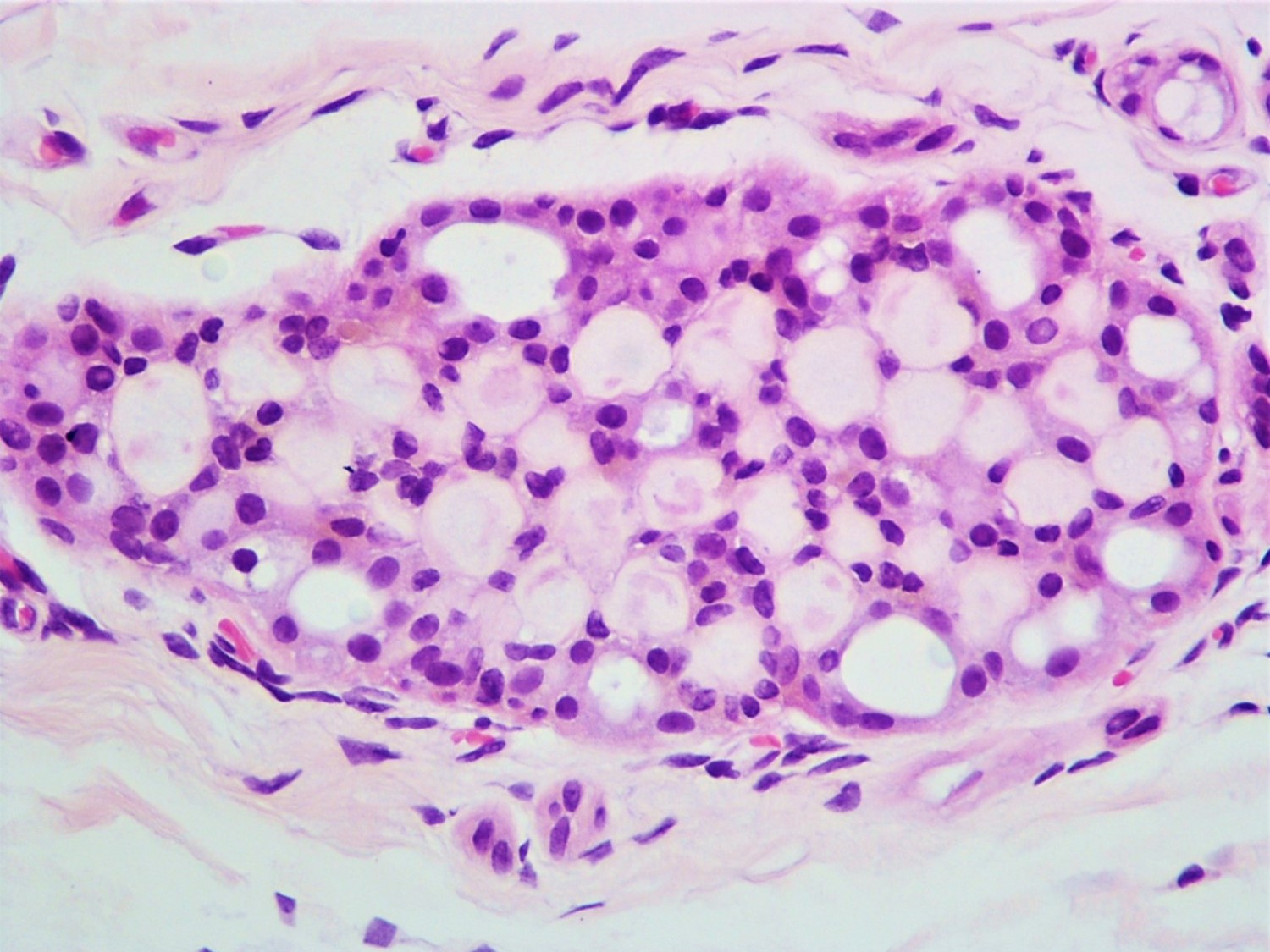
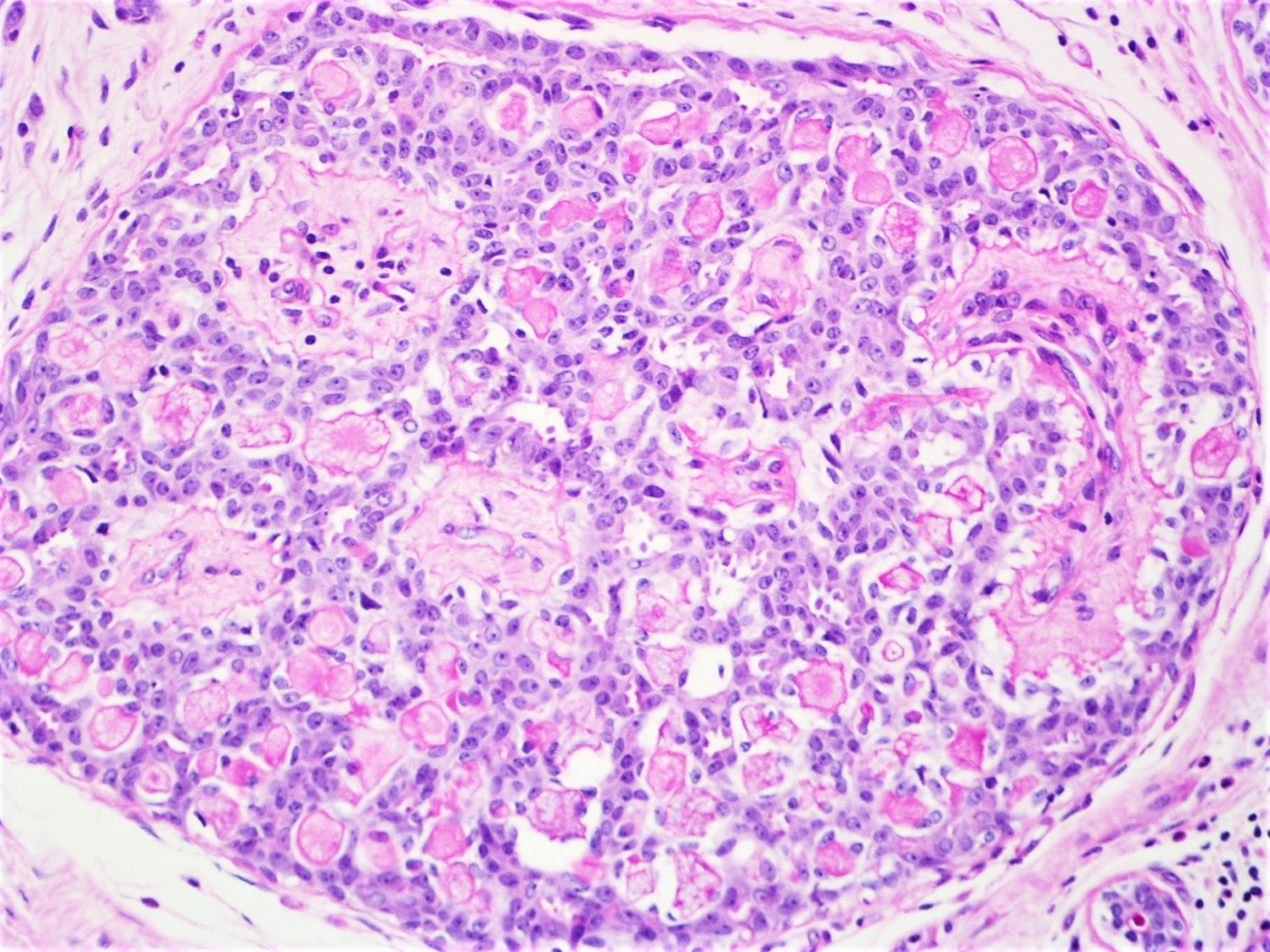
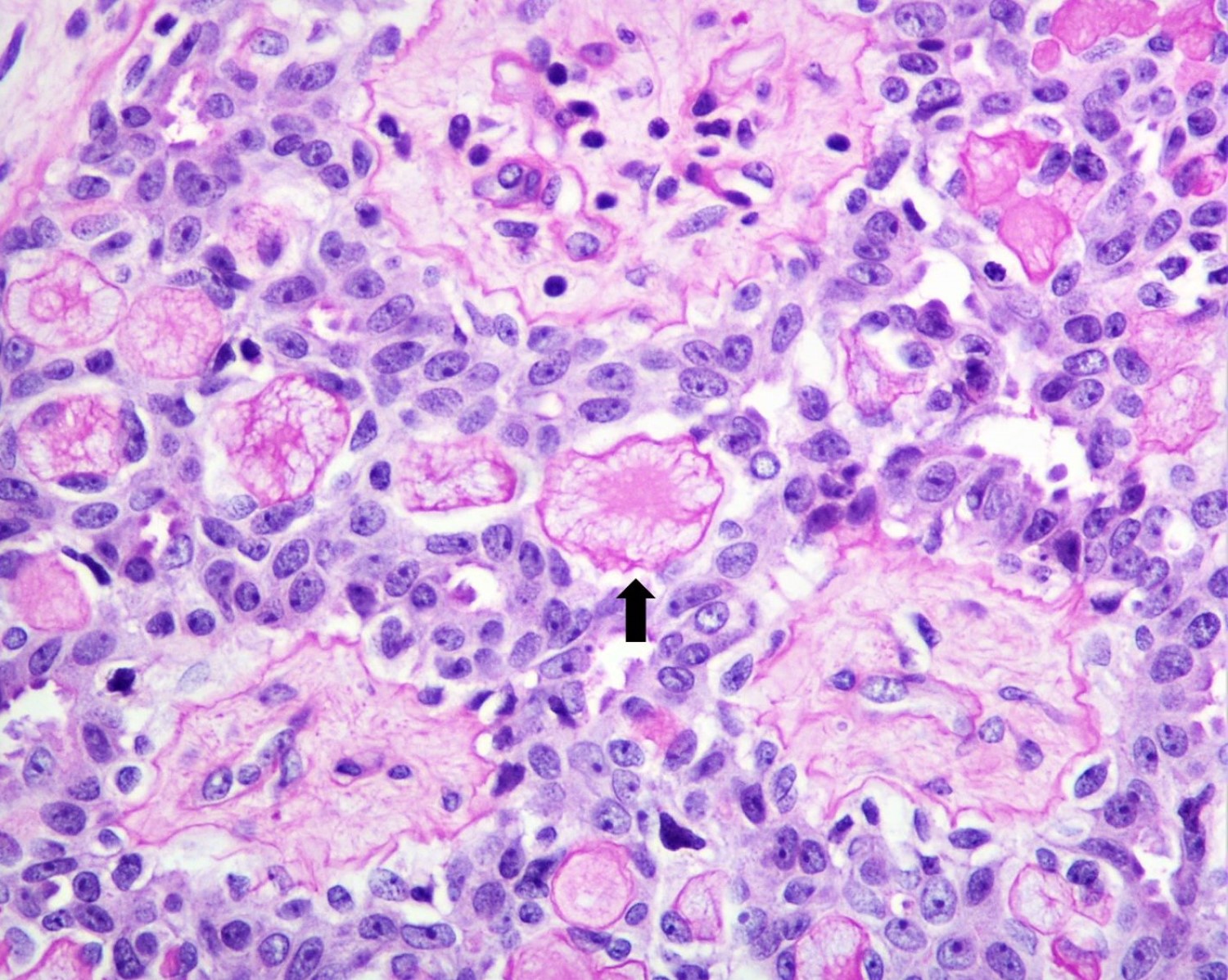
- Round spaces filled with acellular pink basement membrane material (spherules) (Pathology 2017;49:181)
- Spherules measure 20 - 100 μm in diameter (Hoda: Rosen's Diagnosis of Breast Pathology by Needle Core Biopsy, 4th Edition, 2017)
- Center of the spherules may be transparent but thin rim of basement membrane material always present
- Radiating stellate fibrils or microcalcifications may be seen in the spherules
- Spherules surrounded by small oval / spindle myoepithelial cells with interspersed cuboidal luminal cells
- Myoepithelial cells are uniformly present at the periphery of involved glands
- Majority associated with benign proliferative lesions, mostly intraductal papilloma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Iskender Sinan Genco, M.D. and Sabina Hajiyeva, M.D.
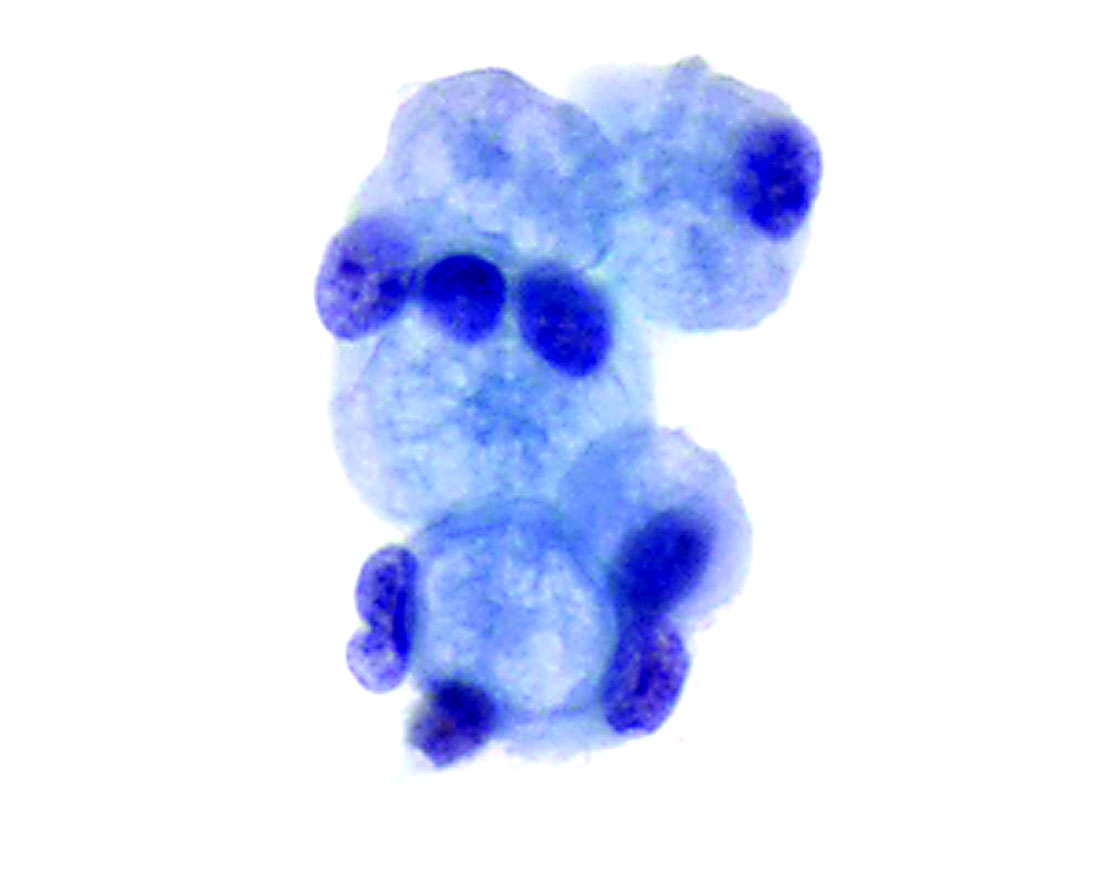
Cytology description
- Hyalinized green (Papanicolaou stain) or dark purple (Giemsa stain) spherules (Cytopathology 2010;21:157)
- 20 - 60 μm in diameter
- Present in the center of epithelial clusters (Cytopathology 2002;13:116)
- Surrounded by 1 - 2 layers of small uniform oval / spindle cells (Cytopathology 2002;13:116, Acta Cytol 2010;54:314)
Positive stains
- Myoepithelial cells:
- Cytoplasmic: alpha smooth muscle actin, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, calponin, CK5/6 (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1351)
- Membranous: CD10 (Pathol Res Pract 2012;208:405)
- Nuclear: p63, S100 (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1351)
- Basement membrane material:
- PAS, mucicarmine, type IV collagen, laminin (Pathology 2017;49:181)
Negative stains
- Myoepithelial cells: KIT / CD117, ER and CK7 (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1351)
Electron microscopy description
- Myoepithelial cells with intracytoplasmic myofilaments (Breast J 2000;6:199)
- Spherules composed of collagen fibers and external laminar material (Ultrastruct Pathol 1998;22:239)
Videos
Breast calcifications
Sample pathology report
- Breast, left, 3 o'clock, stereotactic core biopsy:
- Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) involving collagenous spherulosis, with microcalcifications (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemical stain for E-cadherin is negative in LCIS, supporting the diagnosis. Controls are appropriate.
Differential diagnosis
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Invasive pattern
- Intraluminal material is denser
- Myoepithelial cells are negative for CD10
- Luminal cells are positive for KIT / CD117, negative for ER and PR
- Ductal carcinoma in situ, cribriform type:
- Cribriform spaces are rounder and more regular (cookie cutter appearance)
- No pink material present in cribriform spaces
- Cribriform spaces surrounded by luminal cells, not myoepithelial cells
- Negative for CK5/6
- Lobular carcinoma in situ, signet ring cell type:
- Intracytoplasmic vacuoles
- Negative for E-cadherin
- Some, but not all, features of low grade ductal carcinoma in situ (see above)
- Negative for CK5/6
Additional references
Practice question #1
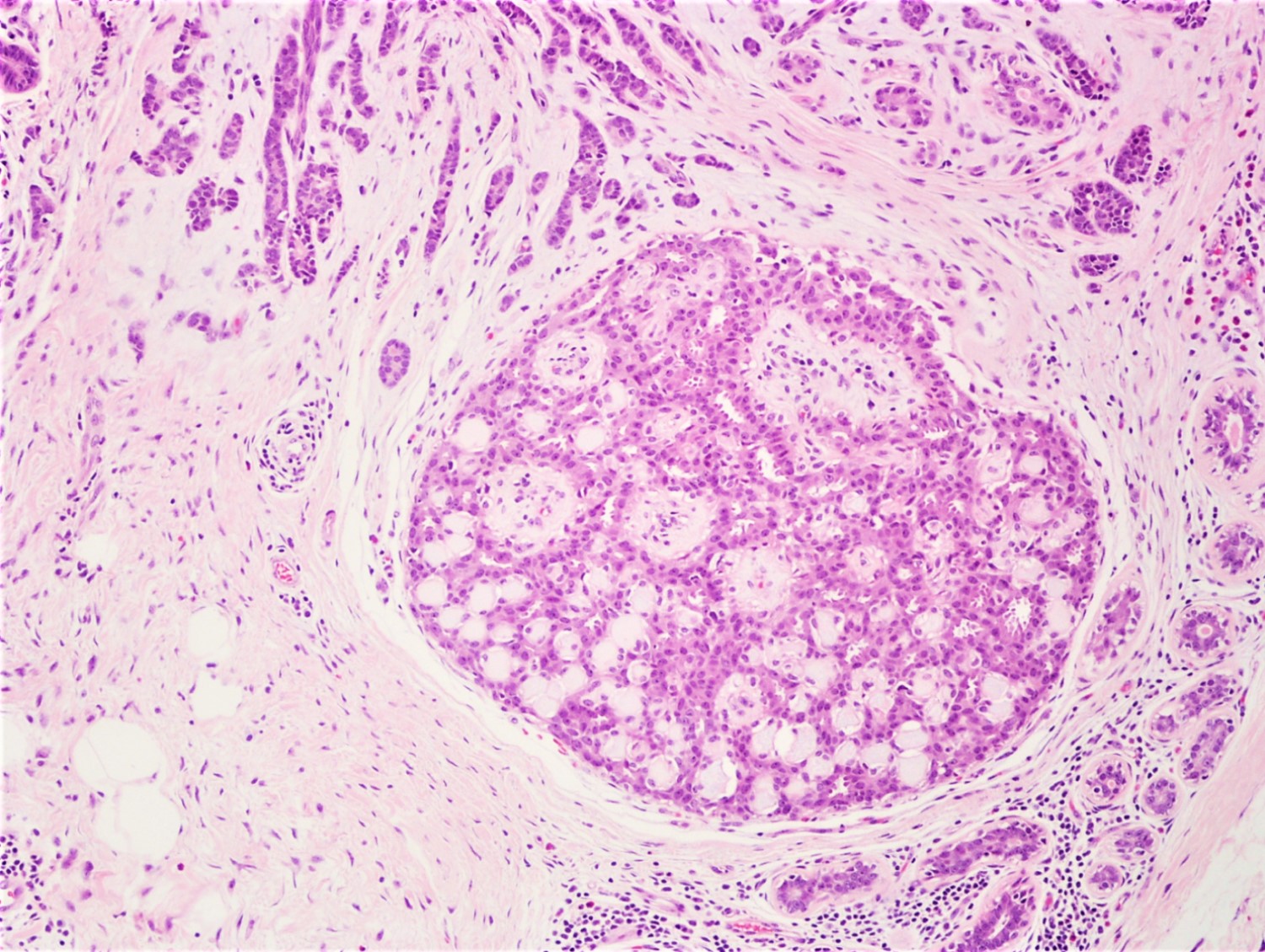
A premenopausal woman had a stereotactic breast core biopsy for calcifications. Microscopic examination revealed fibrocystic changes with microcalcifications as well as the microscopic finding shown above (H&E). Regarding this entity, which of the following statements is true?
- Comprised of a clonal (neoplastic) proliferation
- Epithelial cells interspersed between spaces are negative for ER
- Flattened (myoepithelial) cells around spaces are positive for CD10
- Luminal epithelial cells are positive for KIT / CD117
- Surgical excision should be performed
Practice answer #1
C. The flattened (myoepithelial) cells around spaces are positive for CD10. The picture shows slightly expanded ducts with spaces filled with eosinophilic material. The spaces are surrounded by small oval / spindle myoepithelial cells with interspersed cuboidal luminal cells, features consistent with collagenous spherulosis. Collagenous spherulosis is a benign finding and does not require treatment. Adenoid cystic carcinoma is the main differential diagnosis which shows MYB-NFIB fusion gene, is negative for ER and PR, positive for KIT / CD117 and should be surgically excised.
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous spherulosis
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous spherulosis
Practice question #2
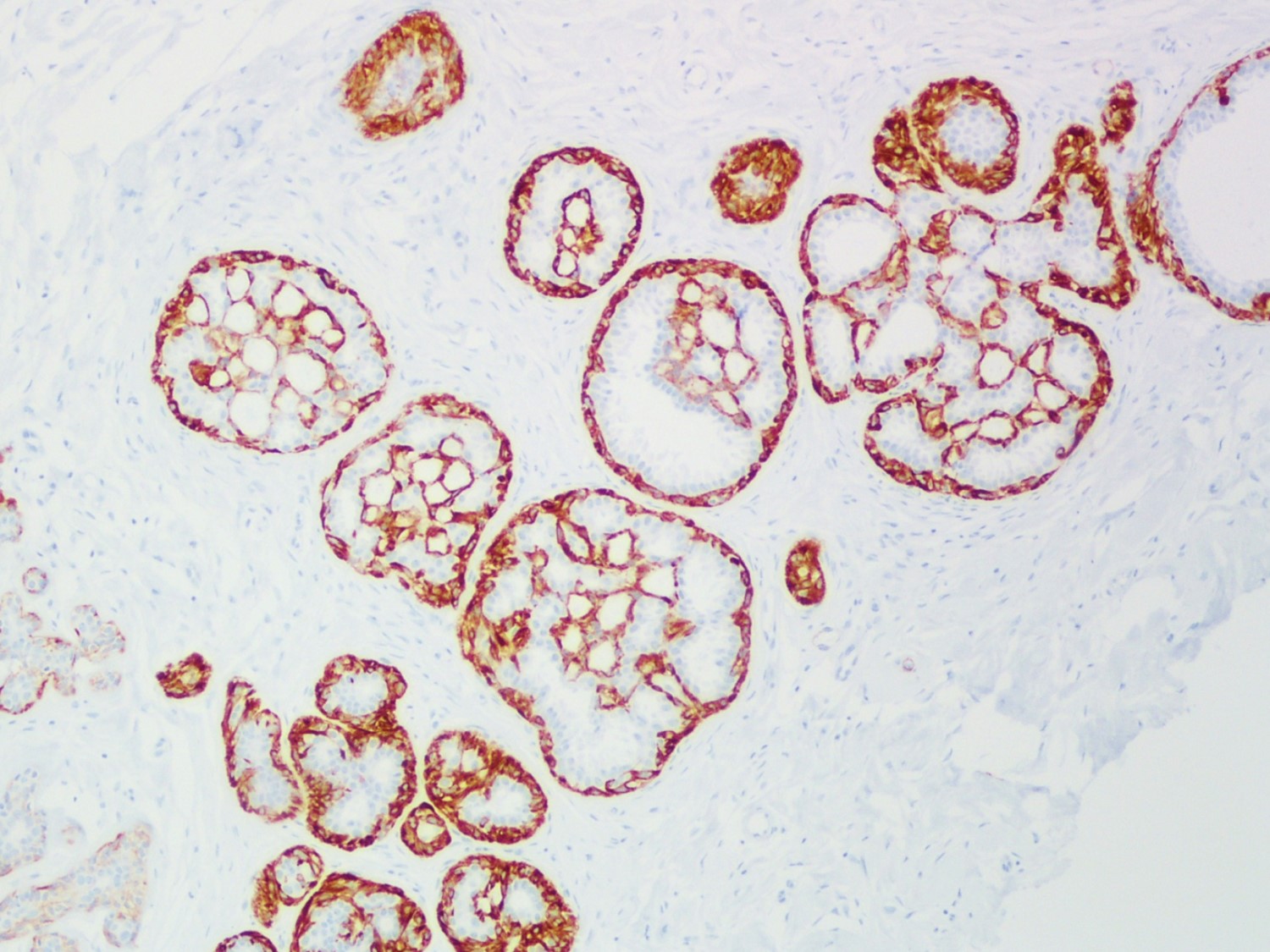
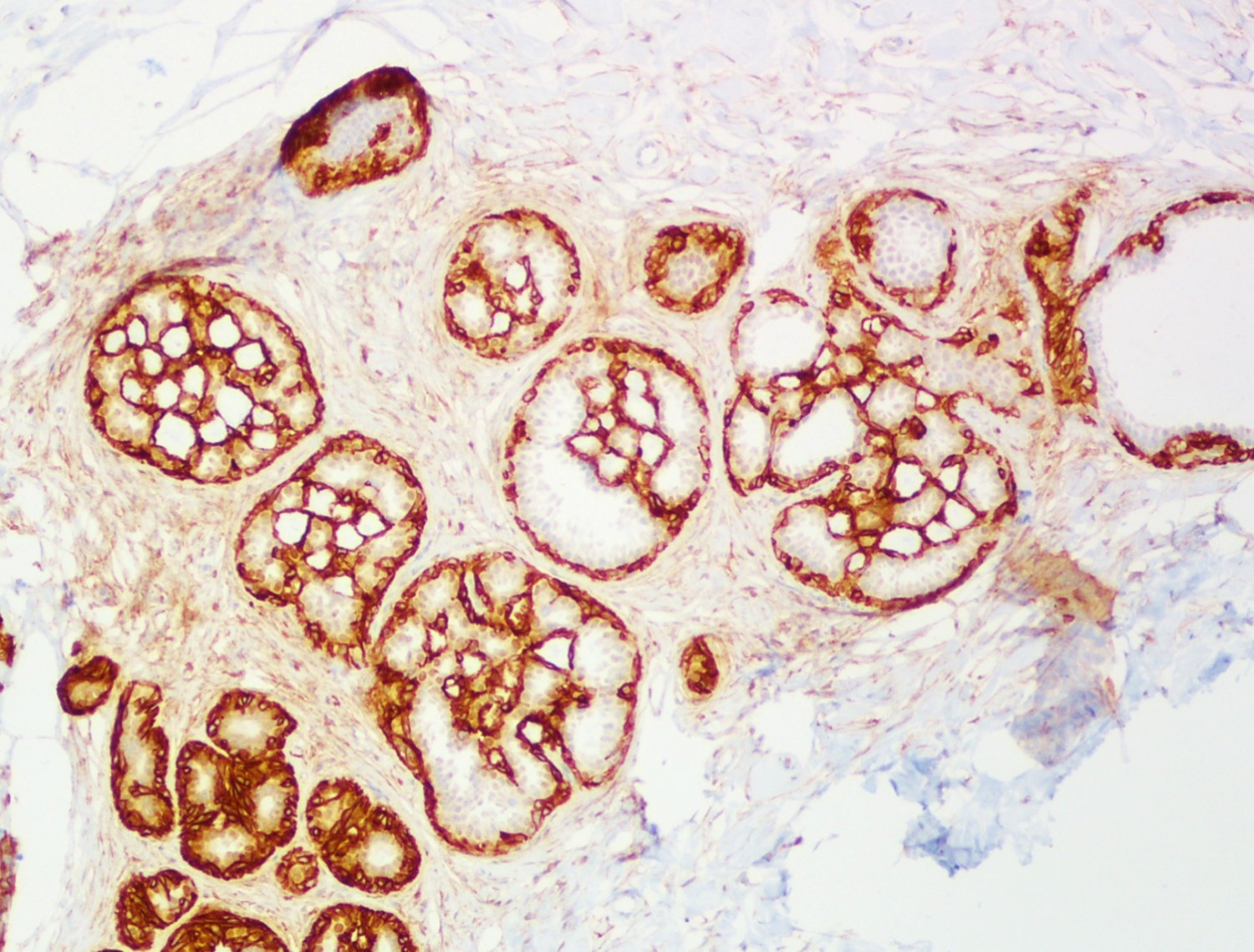
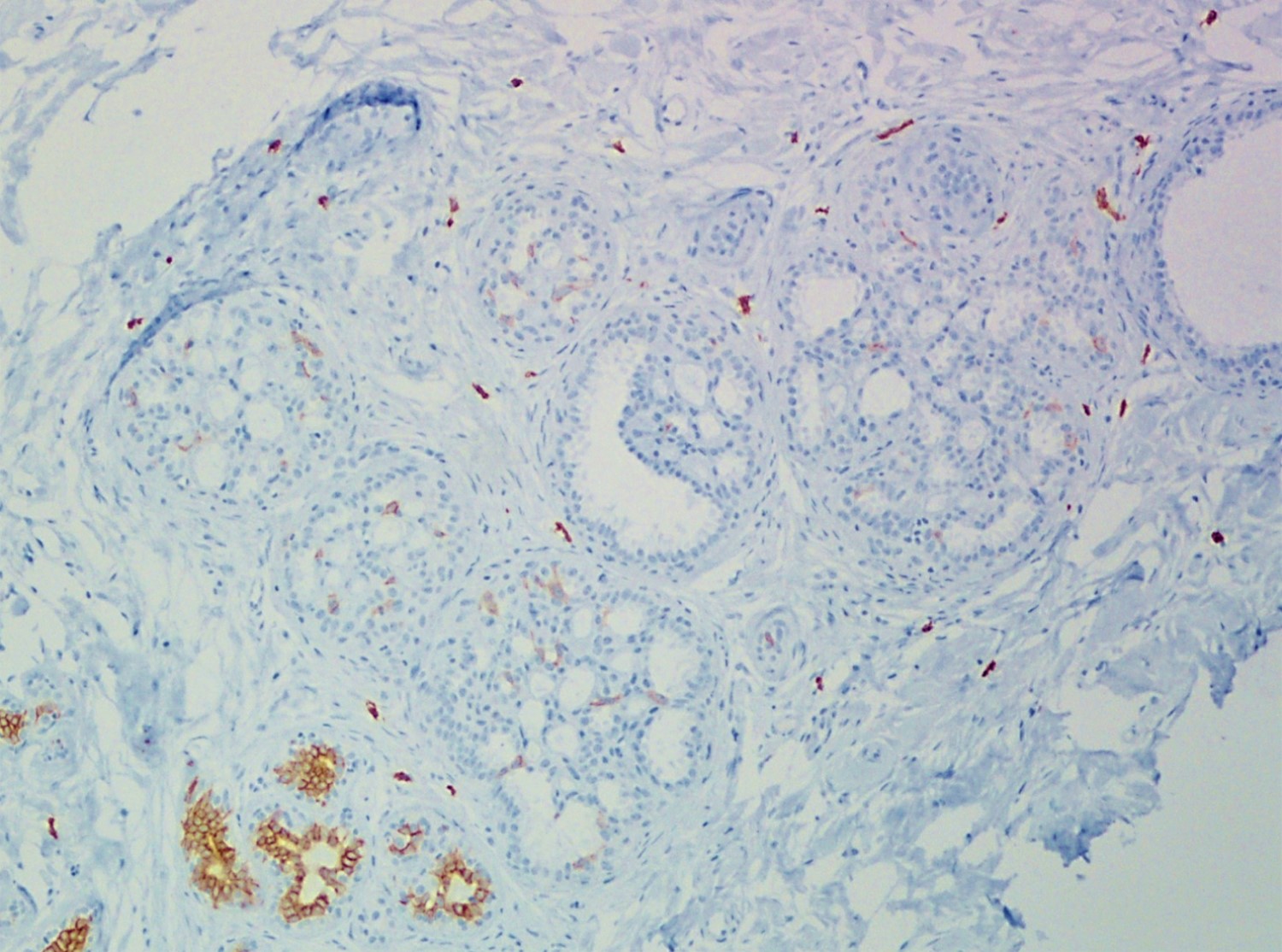
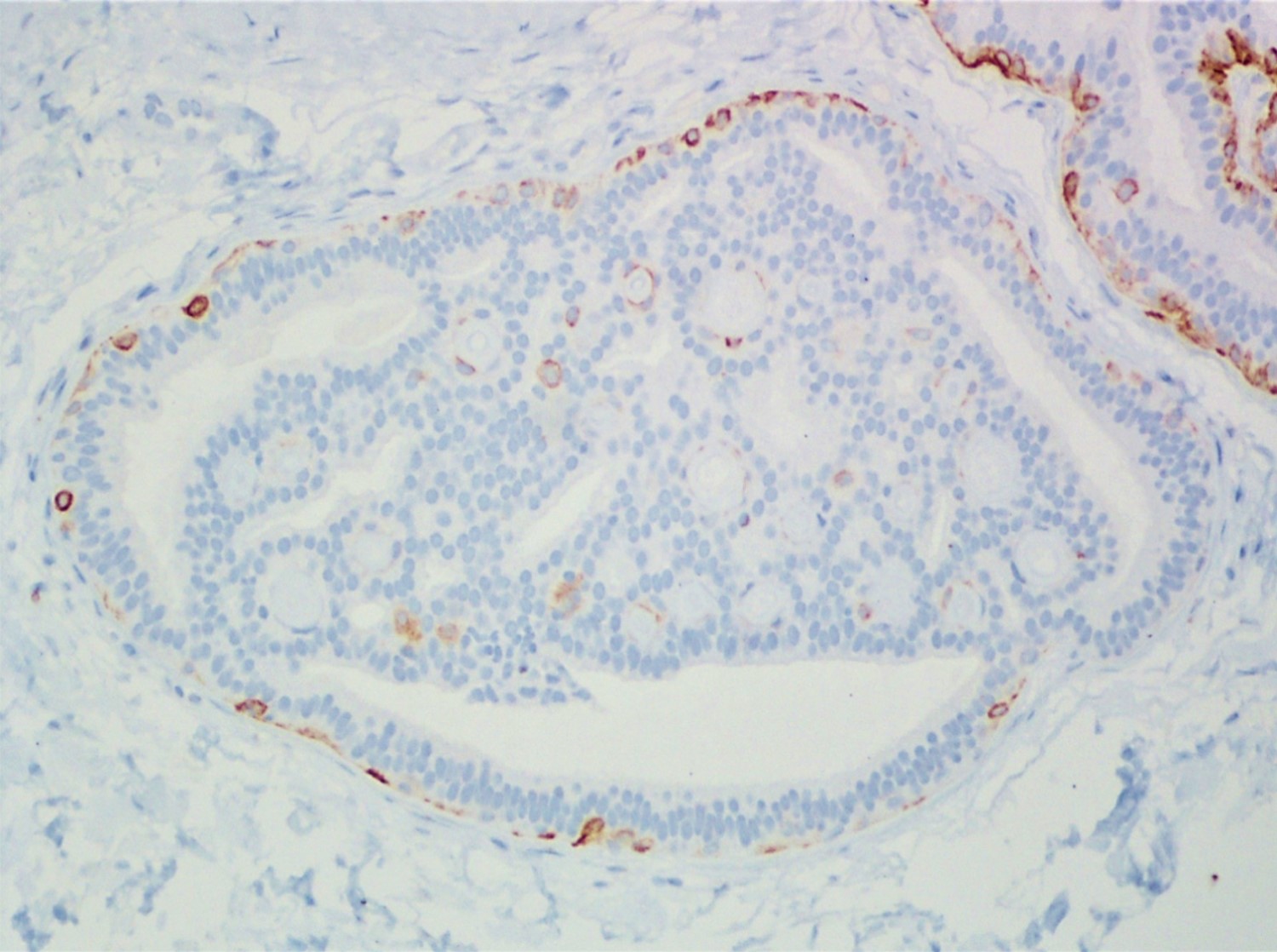
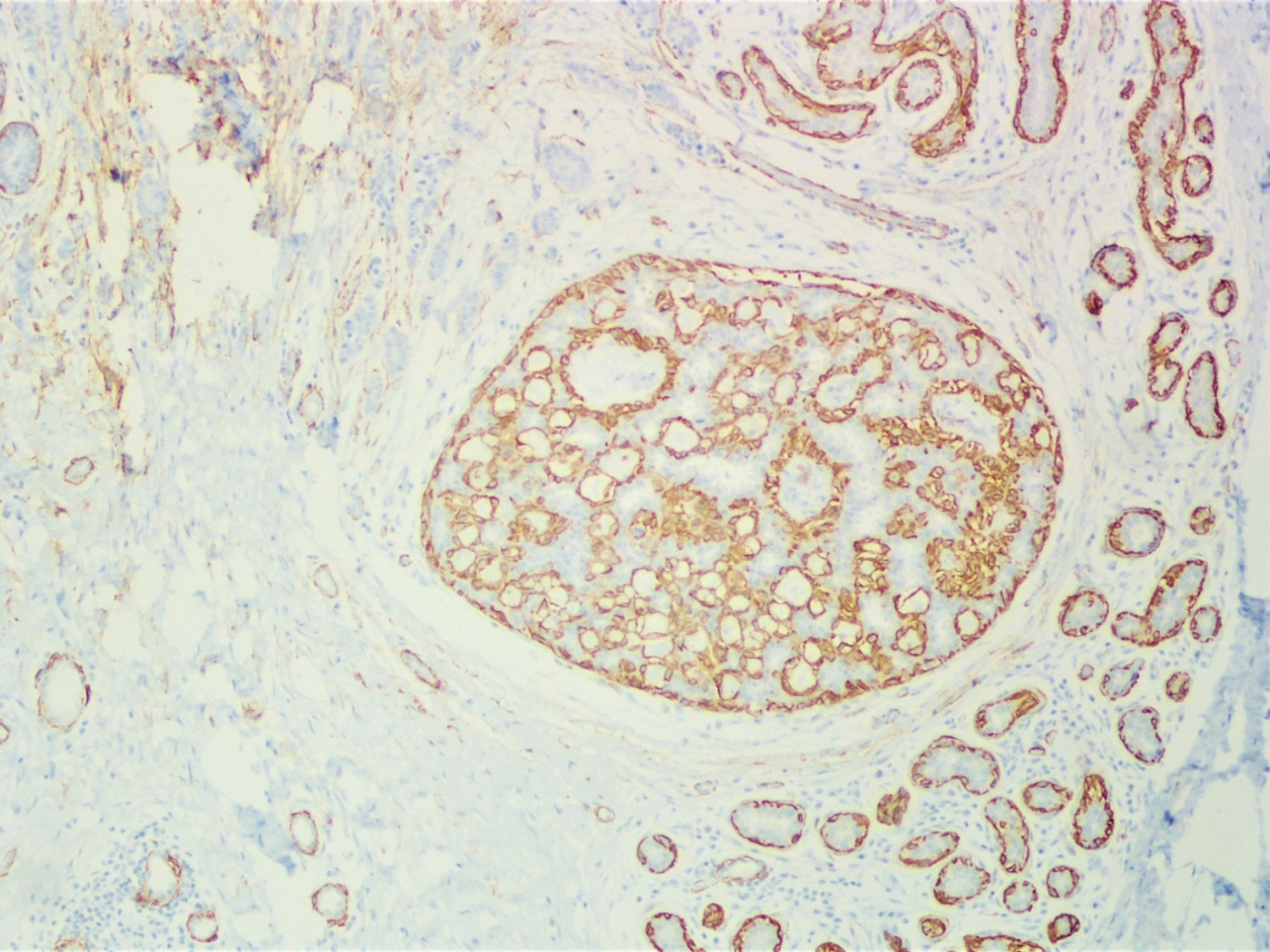
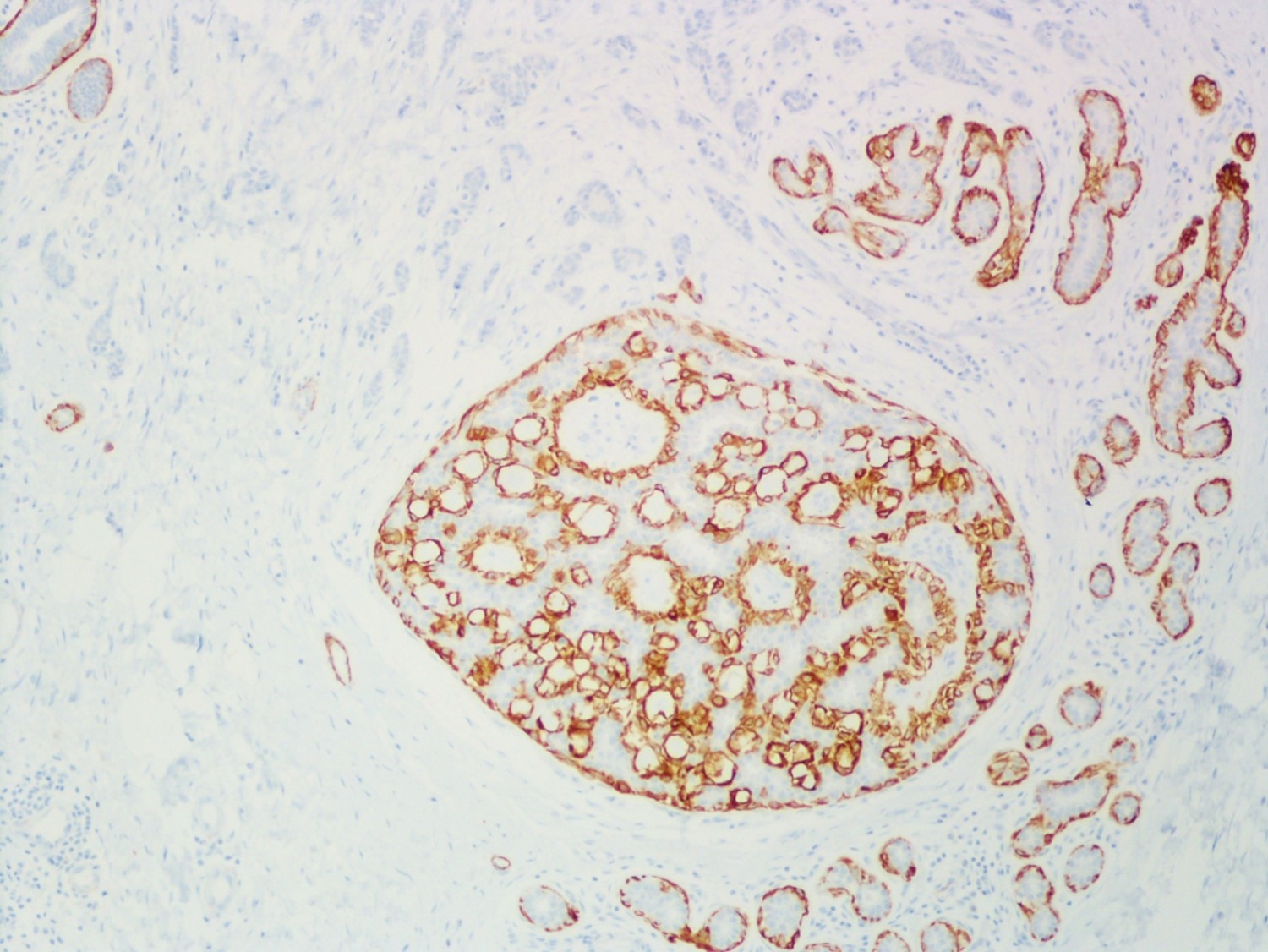
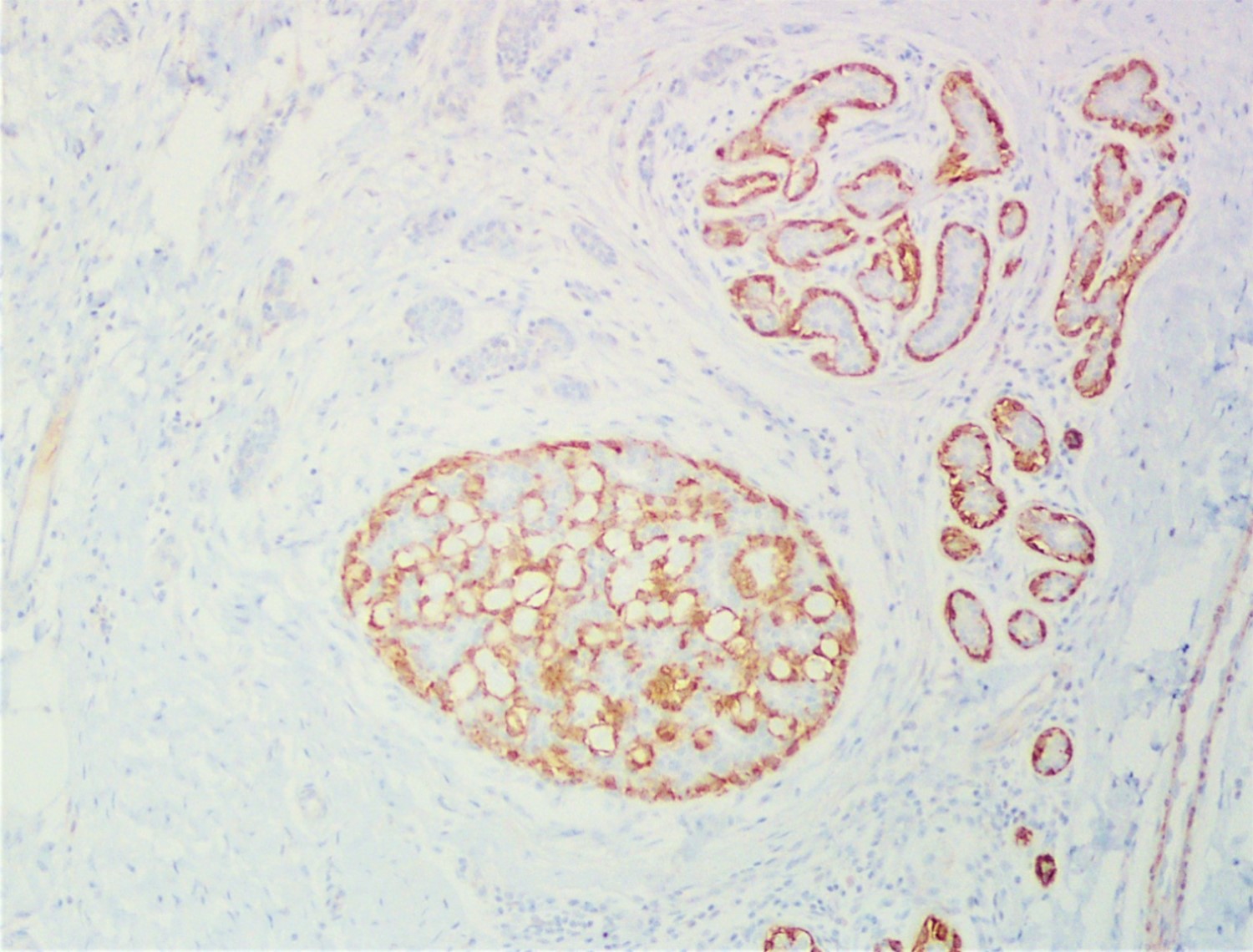
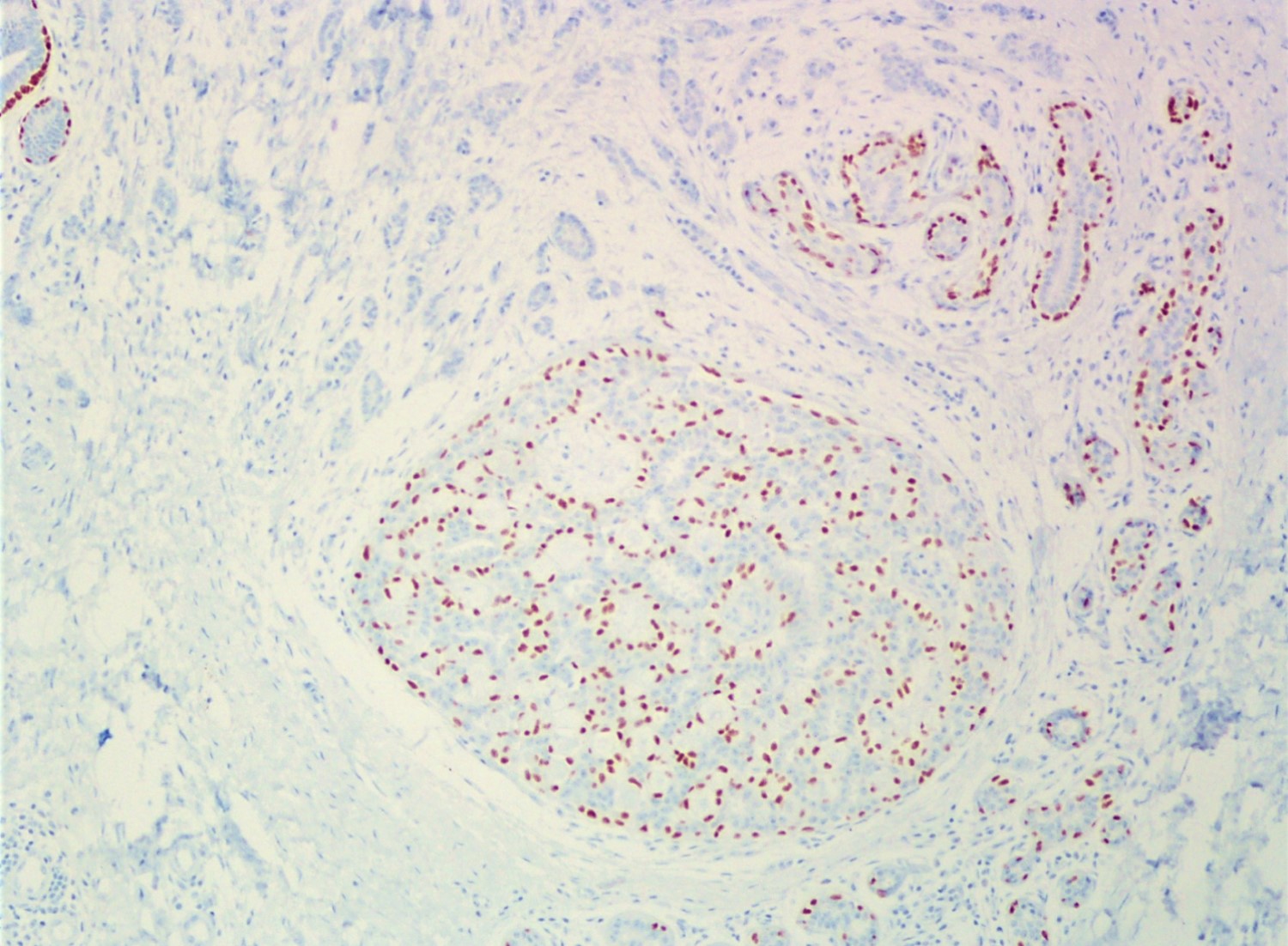
A 34 year old woman was diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma on core biopsy and subsequently underwent surgical excision. One of the surgical specimen sections showed the microscopic lesion with cribriform architecture (middle) adjacent to invasive carcinoma. Based on the provided H&E, SMMH, and PAS stains, what is the correct diagnosis?
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia
- Collagenous spherulosis
- Ductal carcinoma in situ
- Lobular carcinoma in situ involving ductal carcinoma in situ
- Usual ductal hyperplasia
Practice answer #2
B. Collagenous spherulosis
The H&E slide shows invasive carcinoma (upper), benign breast tissue (right lower), and a duct with cribriform architecture (middle). SMMH highlights the myoepithelial cells around the cribriform spaces and the periphery of the involved duct, whereas invasive carcinoma is negative for SMMH. This lesion with cribriform architecture represents collagenous spherulosis. PAS stain highlights the basement membrane material within the cribriform spaces produced by the surrounding myoepithelial cells. The other options may also show cribriform architecture but do not have myoepithelial cells surrounding the cribriform spaces. PAS stain helps confirm the diagnosis of collagenous spherulosis, but does not entirely rule out the other options.
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous spherulosis
The H&E slide shows invasive carcinoma (upper), benign breast tissue (right lower), and a duct with cribriform architecture (middle). SMMH highlights the myoepithelial cells around the cribriform spaces and the periphery of the involved duct, whereas invasive carcinoma is negative for SMMH. This lesion with cribriform architecture represents collagenous spherulosis. PAS stain highlights the basement membrane material within the cribriform spaces produced by the surrounding myoepithelial cells. The other options may also show cribriform architecture but do not have myoepithelial cells surrounding the cribriform spaces. PAS stain helps confirm the diagnosis of collagenous spherulosis, but does not entirely rule out the other options.
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous spherulosis