Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Liao X. Pyloric gland adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderpyloricgland.html. Accessed September 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Grossly visible, noninvasive neoplasm of the gallbladder composed of uniform back to back mucinous glands arranged in a tubular configuration
- WHO classification
- Architecture is often complex
- Glands are bland looking pyloric type or Brunner gland-like
- There is minimal cytological atypia in most of the lesions
- By definition, the cytologic atypia is sufficient for low grade dysplasia
- Foci of high grade dysplasia can be seen in larger lesions
- If lesion is > 1 cm with dysplasia present, classification as intracholecystic papillary (tubular) neoplasm is recommended by some authors (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1279)
Essential features
- Grossly visible, complex, back to back, uniform mucinous glands of pyloric type or Brunner gland-like
- Usually > 0.5 cm and < 2 cm
- < 0.5 cm should be distinguished from nodular pyloric gland metaplasia, which by definition bears no cytologic atypia or dysplasia
- > 1 cm with dysplasia may be classified as intracholecystic papillary (tubular) neoplasm
Terminology
- Intracholecystic papillary tubular neoplasm, gastric pyloric, simple mucinous type
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Found in 0.1 - 10% of gallbladders removed for cholelithiasis or chronic cholecystitis (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:341, PLoS One 2020;15:e0237979, Adv Med 2018;2018:7539694)
- Accounts for ~82% of gallbladder adenomas (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1506)
- M = F (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1237)
- Mean age of 62.8 years (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1237)
Sites
- No specific site preference reported
- Can occur in the cystic duct with malignant transformation (BMC Cancer 2012;12:570)
Etiology
- 50 - 65% associated with cholelithiasis (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1506)
- Commonly associated with pyloric gland metaplasia, which is possibly a precursor
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic and is an incidental finding
- When arising in the gallbladder neck, can lead to gallbladder distension and right upper quadrant pain
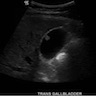
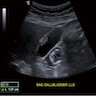
Radiology description
- Abdominal ultrasound is usually performed and shows polyps within the gallbladder (J Gastrointest Oncol 2016;7:S81)
Prognostic factors
- If invasive carcinoma is ruled out, pyloric gland adenoma is cured by cholecystectomy, even when high grade dysplasia is present
Case reports
- 37 year old woman with dyspeptic complaints found to have a 2 cm polypoid lesion (Turk J Gastroenterol 2014;25:234)
- 40 and 53 year old men each presented with a 1 cm polyp (J Gastrointest Oncol 2016;7:S81)
- 44 year old man with upper abdominal pain found to have a 2 cm polyp (Gastroenterology 2011;141:e3)
- 62 year old man with a 2 cm tumor with transition into well differentiated adenocarcinoma and high grade biliary intraepithelial neoplasia (BMC Cancer 2012;12:570)
Treatment
- Surgery (cholecystectomy) is indicated for any polypoid lesions ≥ 1 cm
Gross description
- < 2 cm, sessile or pedunculated
- Usually single but can be multiple
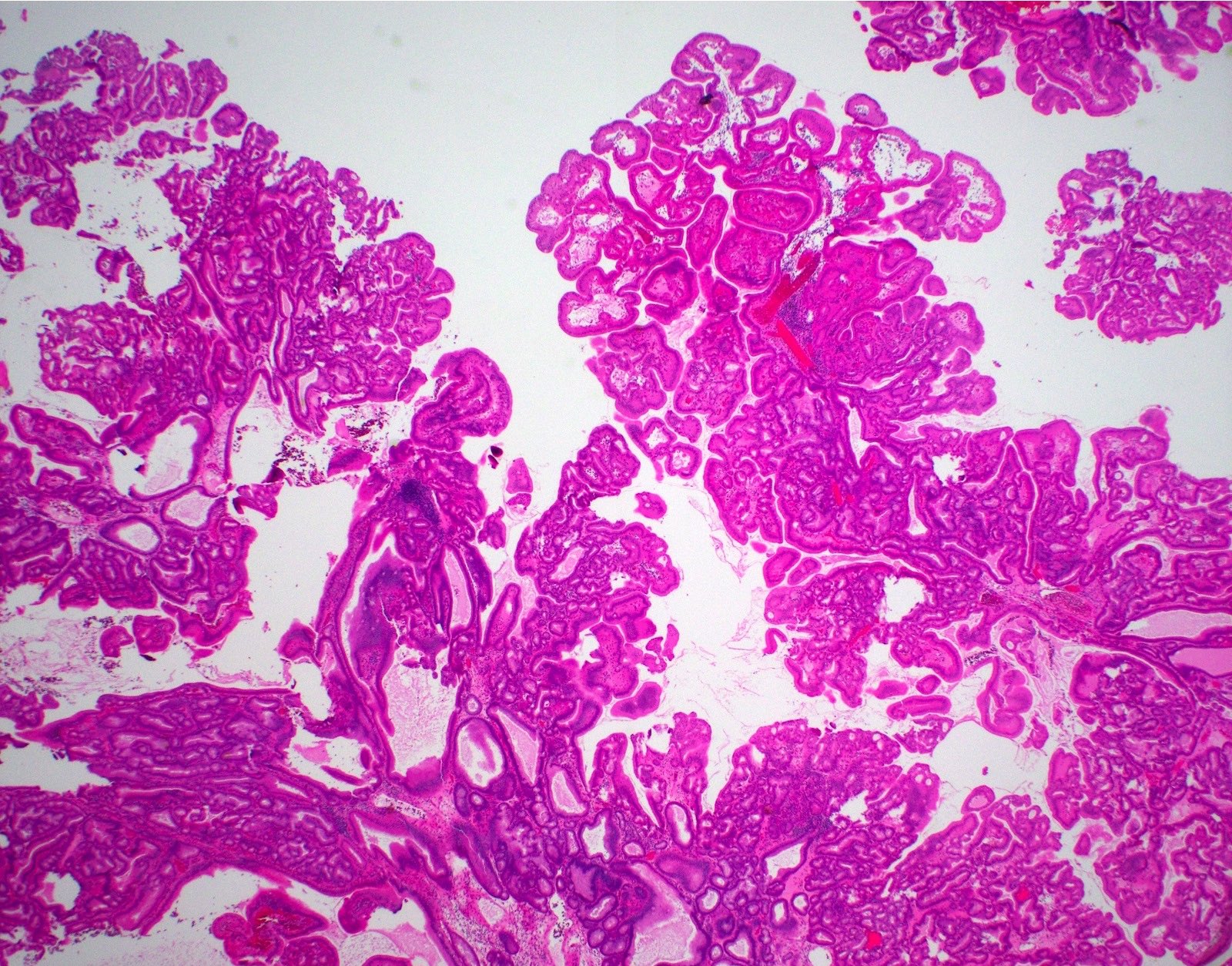
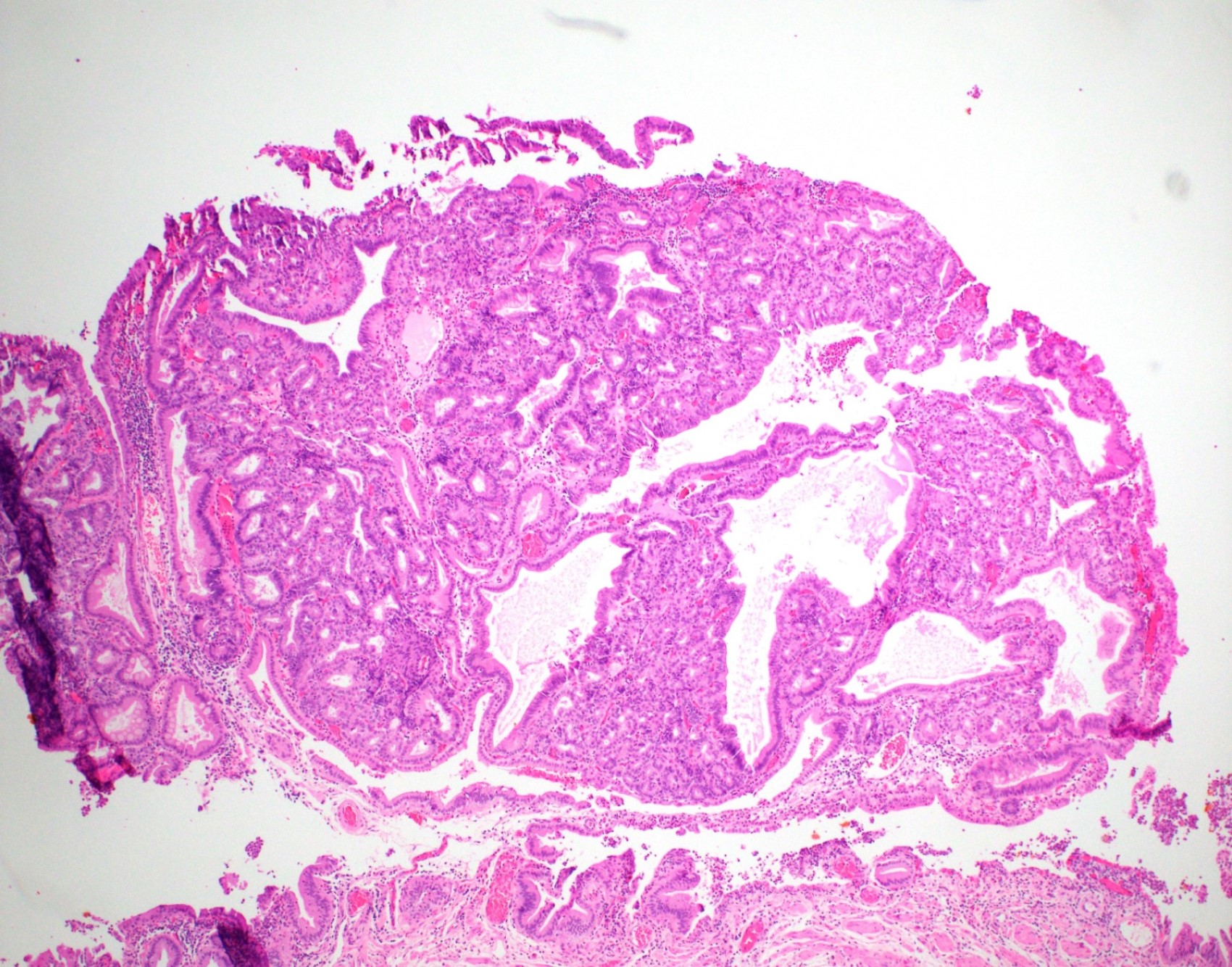
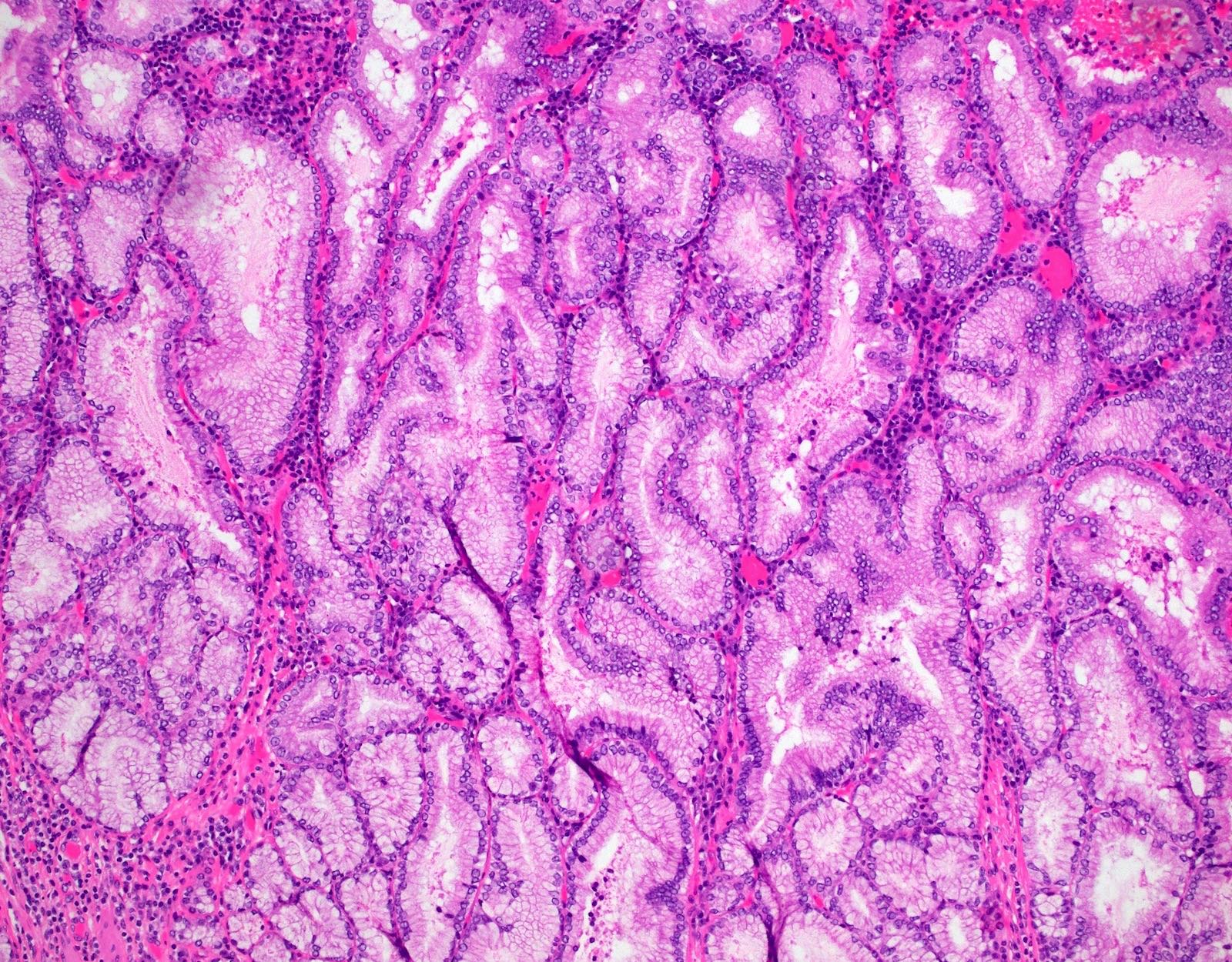
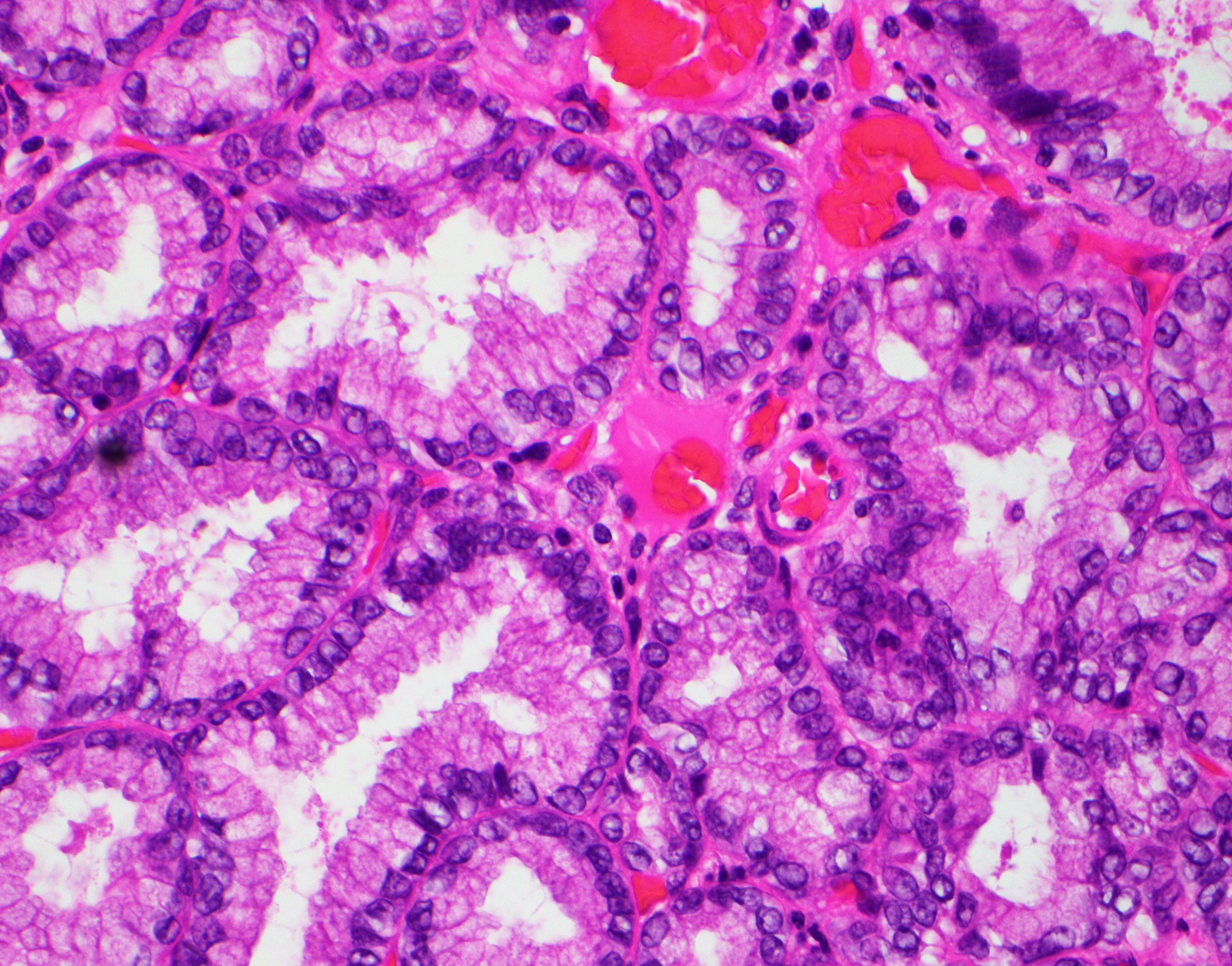
Microscopic (histologic) description
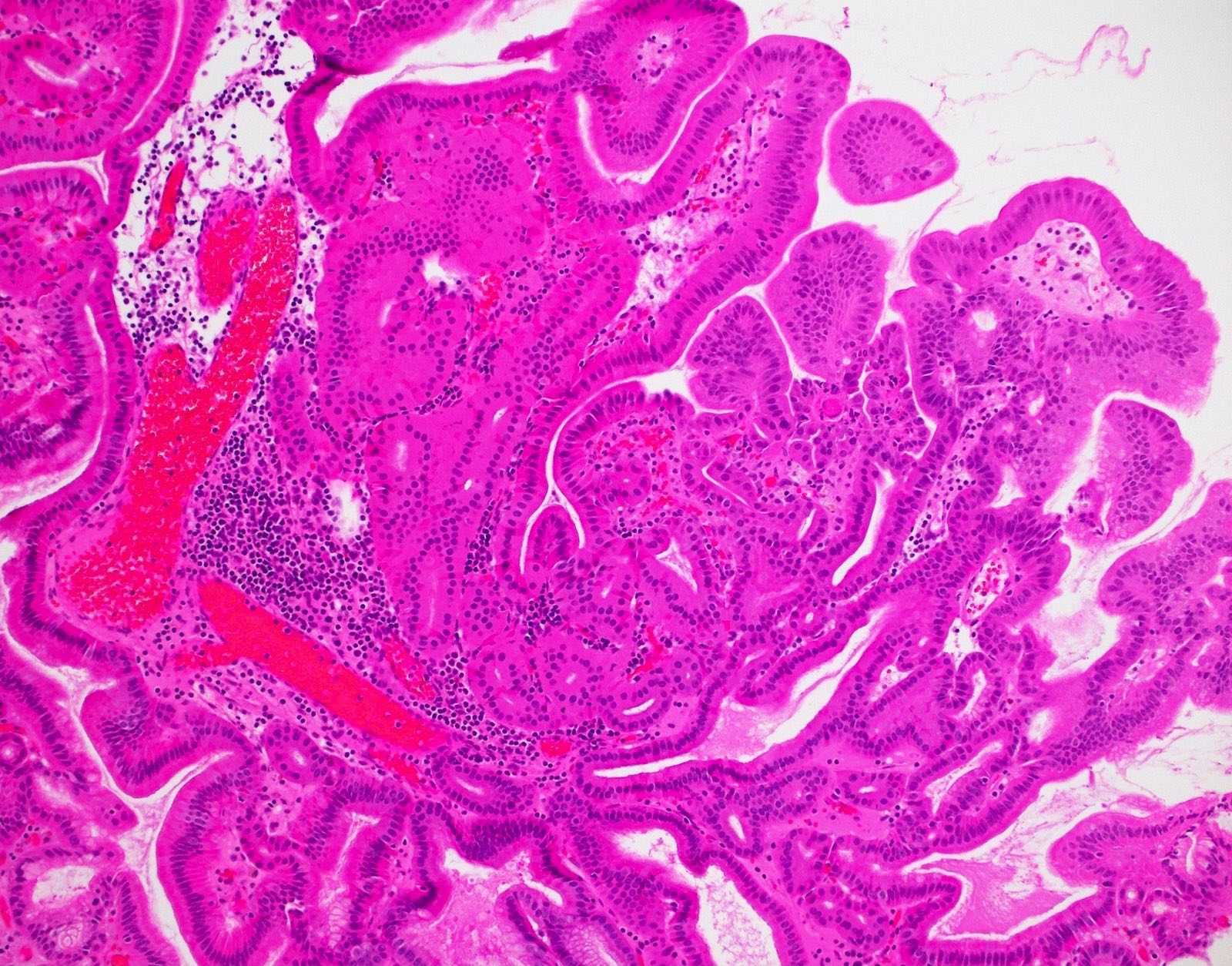
- Tightly packed, bland looking pyloric type or Brunner gland-like glands (Histopathology 2018;72:1007)
- Lined by cuboidal or columnar mucus secreting cells with apical mucinous cytoplasm
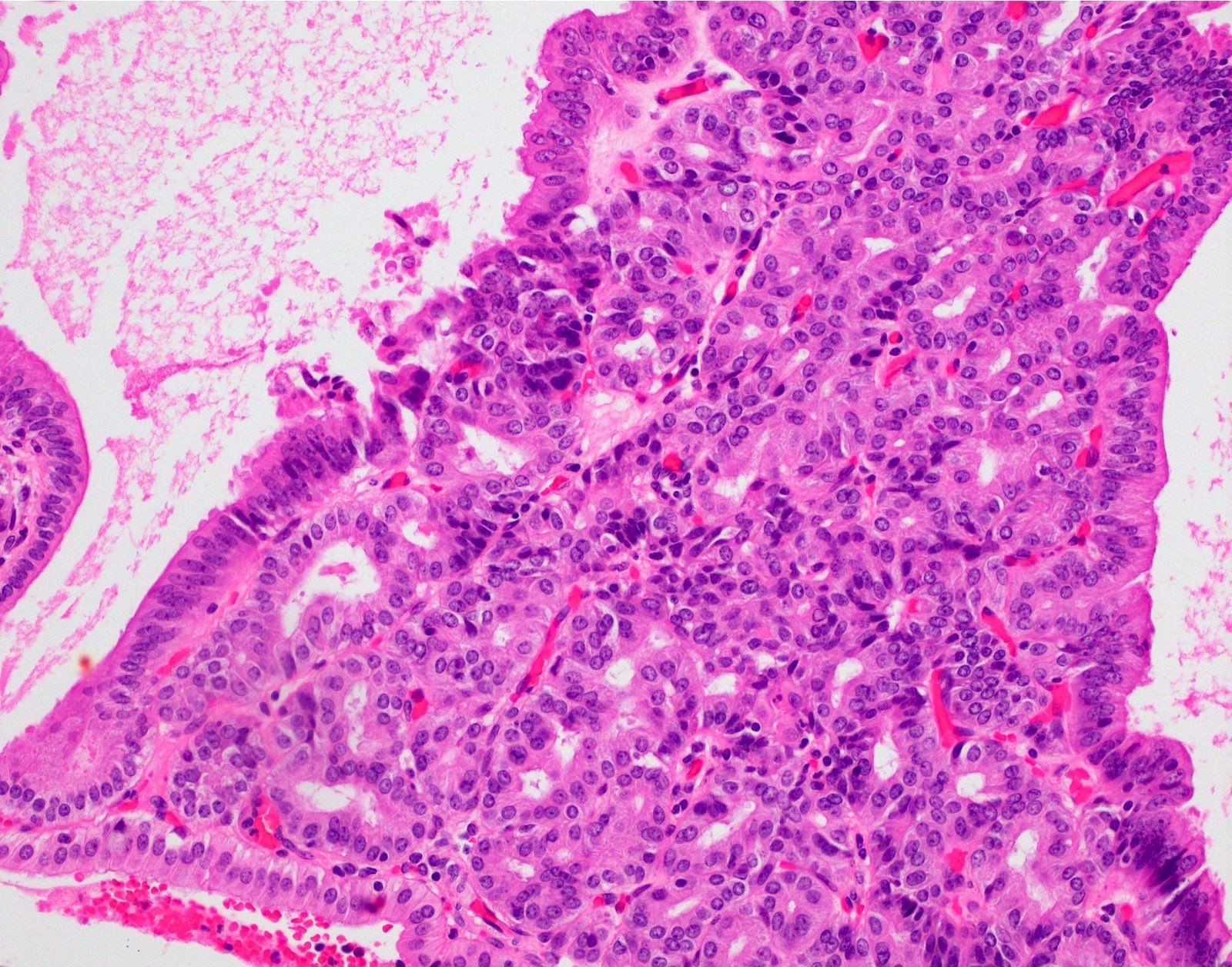
- Round or oval, relatively small, hyperchromatic, basally located nuclei with a small round conspicuous nucleolus
- Slight nuclear overlapping and increased N:C ratios when compared to background normal glands
- High grade dysplasia features more complex architecture, prominent nucleoli and loss of nuclear polarity
- Some glands may be cystically dilated
- There is minimal or no intervening stroma
- Paneth cells and neuroendocrine cells are often present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
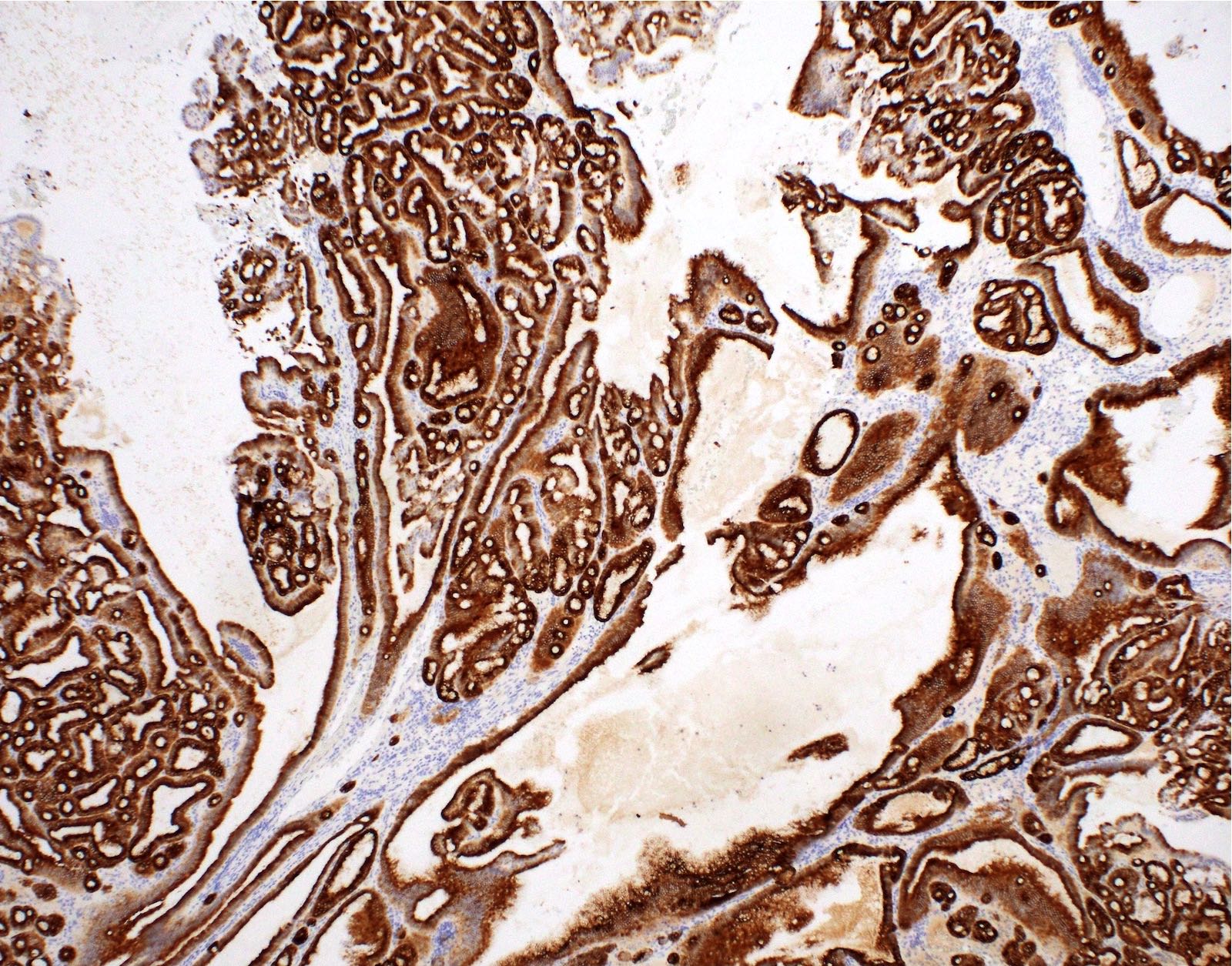
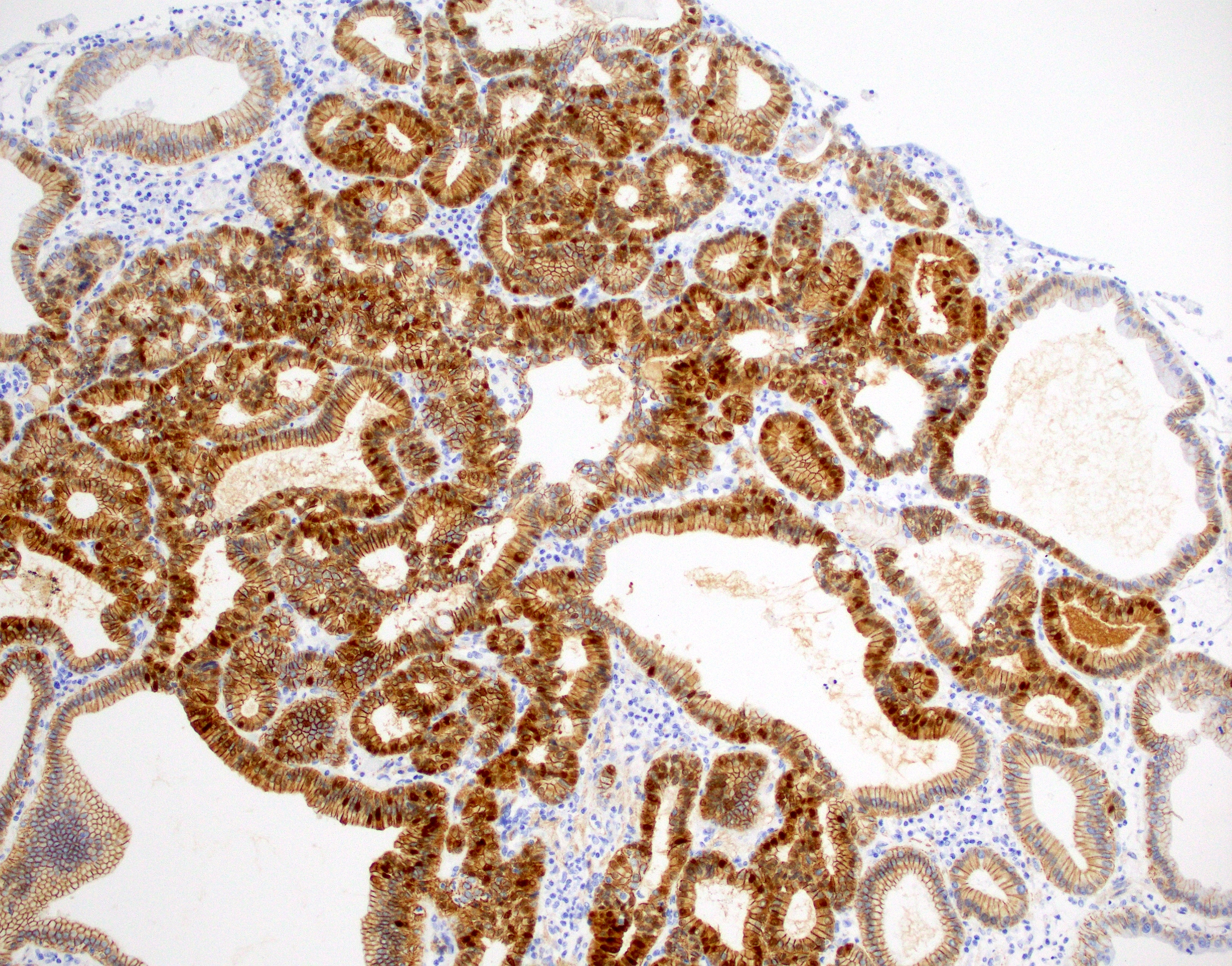
- CK7 and MUC6 (diffuse and strong)
- Nuclear beta catenin reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1237)
Negative stains
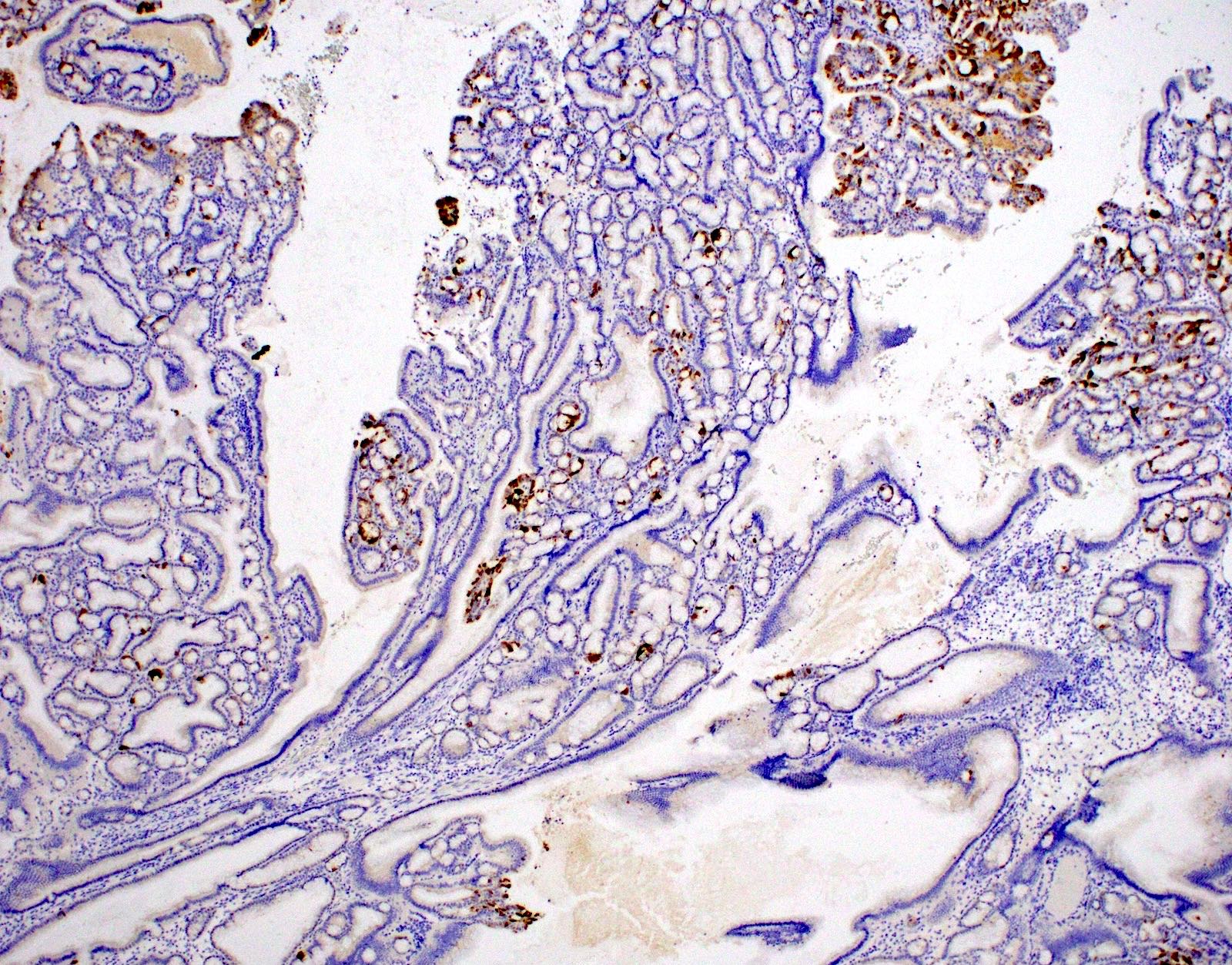
- MUC2, MUC5AC and CDX2 usually negative or only focally positive (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1237)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- CTNNB1 mutations detected in 60% and 100% in 2 separate studies (Hum Pathol 1999;30:21, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1237)
- KRAS mutation reported in a subset (Hum Pathol 1999;30:21, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1237)
- TP53 and GNAS mutations usually not identified
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Pyloric gland adenoma
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Pyloric gland adenoma with focal high grade dysplasia
Differential diagnosis
- Pyloric gland metaplasia:
- Size is the most important criteria; metaplasia is usually < 0.5 cm and does not form a discrete mass
- Intracholecystic papillary (tubular) neoplasm:
- Considered an umbrella term for any neoplastic polyps, adenomas and papillary neoplasms that are ≥ 1 cm
- Can be further divided into several categories by morphology
- Biliary, gastric, intestinal and oncocytic
- Pyloric gland adenoma is currently not included under this umbrella
- However, terms may be interchangeable between intracholecystic papillary (tubular) neoplasm and pyloric gland adenomas that are ≥ 1 cm with invasive carcinoma
Additional references
Practice question #1
A polypoid lesion of the gallbladder is identified by ultrasound and is resected. Based on the photomicrograph above, which of the following statements is true?
- Aberrant expression of CDX2 is a frequent feature
- Frequently shows MUC5AC positivity
- It is a precursor lesion for most of the gallbladder adenocarcinomas
- Occurs predominantly in males
- Usually CK7 positive
Practice answer #1
E. Usually CK7 positive, as this is a pyloric gland adenoma. Answer A is incorrect because they do not often express CDX2. Answer B is incorrect because they frequently show MUC6 positivity. Answer C is incorrect because it is a precursor lesion to some but not most of the gallbladder adenocarcinomas. Answer D is incorrect because they occur predominantly in female patients.
Comment Here
Reference: Pyloric gland adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pyloric gland adenoma
Practice question #2
Regarding pyloric gland adenoma of the gallbladder, which of the following is correct?
- Frequently shows p53 aberrant expression
- Lesions > 1 cm can be reclassified as intracholecystic papillary neoplasm
- They are not associated with chronic cholecystitis
- Those are benign lesions and never progress to cancer
Practice answer #2
B. Lesions > 1 cm can be reclassified as intracholecystic papillary neoplasm. If the lesion is > 1 cm with dysplasia present, classification as intracholecystic papillary (tubular) neoplasm is recommended by some authors. Answer C is incorrect because pyloric gland adenoma is often associated with background chronic cholecystitis. Answer A is incorrect because p53 usually shows normal wild type expression in those lesions. Answer D is incorrect because they can progress to cancer.
Comment Here
Reference: Pyloric gland adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pyloric gland adenoma