Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Fels Elliott DR, Gill RM. HCC - undifferentiated variant. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorundifferentiatedhcc.html. Accessed August 8th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Primary liver tumor that can be diagnosed as carcinoma based on immunohistochemistry but cannot be further classified (Surg Pathol Clin 2013;6:367)
- May show molecular abnormalities supporting a diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
Essential features
- Primary liver tumor that can be diagnosed as carcinoma based on immunohistochemistry (e.g. cytokeratin+) but hepatocellular immunostains are negative (e.g. arginase1- and HepPar1-)
- Solid or trabecular growth pattern with high N/C ratios and nuclear pleomorphism
- May be albumin in situ hybridization (ISH)+
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C22.7 - Other specified carcinomas of liver
Epidemiology
- Rare, accounting for < 2% of all epithelial liver tumors (Torbenson: Tumors of the Liver, Series 4, 2018)
- Male preponderance
Clinical features
- May present with abdominal pain and fever (Intern Med 2011;50:519)
Prognostic factors
- May have worse prognosis in comparison to classic HCC (Torbenson: Tumors of the Liver, Series 4, 2018)
- Prognostic factors for HCC: stage (TNM), single lesion versus multifocal, size, vascular invasion, portal vein thrombosis, severity of underlying liver disease (Liver Int 2009;29:502, J Surg Oncol 2018;117:644)
Case reports
- 54 year old man with multiple liver tumors (Jpn J Clin Oncol 1998;28:401)
- 56 year old man with intraabdominal hemorrhage (Surg Case Rep 2017;3:12)
- 57 year old man with fever and right upper quadrant pain (Intern Med 2011;50:519)
Treatment
- Surgical resection
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)
- Transplantation (e.g. Milan criteria, modified by some institutions, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:203)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Solid or trabecular growth pattern
- High N/C ratio
- Pleomorphism
- No histologic features of classic HCC
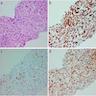
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Hepatocellular markers (arginase1, glypican 3, HepPar1)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- May be albumin ISH+
Sample pathology report
- Liver, mass, core biopsy:
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma; see comment
- Comment: This tumor shows a poorly differentiated carcinoma with tumor cells positive for pancytokeratin and negative for CK7, CK19, mucicarmine and hepatocellular markers (HepPar1, arginase1 and glypican 3). Albumin in situ hybridization is positive in tumor cells. We favor consideration as an undifferentiated hepatocellular carcinoma; correlation with molecular testing can be helpful (e.g. next generation sequencing cancer gene panel).
Differential diagnosis
- Poorly differentiated HCC: similar histologic appearance but positive for hepatocellular markers (HepPar1, arginase1 and glypican 3)
- Poorly differentiated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: similar histologic appearance but evidence of mucin production or molecular abnormalities characteristic of cholangiocarcinoma (e.g. IDH1 / 2 mutations)
- Metastatic undifferentiated carcinoma: similar histologic appearance, requires clinical / imaging correlation; albumin ISH-
Practice question #1
Which of the following features is true regarding the undifferentiated variant of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
- Albumin ISH is always negative
- Arginase1 is usually positive
- Cytokeratin is usually negative
- Has a better prognosis in comparison to classic HCC
- May show solid or trabecular growth pattern
Practice answer #1
E. May show solid or trabecular growth pattern
Comment Here
Reference: Undifferentiated hepatocellular carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Undifferentiated hepatocellular carcinoma
Practice question #2
Which variant of hepatocellular carcinoma is characterized by positive cytokeratin but albumin ISH and all hepatocellular markers are negative?
- Fibrolamellar
- Lymphoepithelioma-like
- Sarcomatoid
- Scirrhous
- Undifferentiated
Practice answer #2