Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Xu B. Inflammatory sinonasal polyp, including antrochoanal polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/nasalpolypinflammatory.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, nonneoplastic inflammatory outgrowth of sinonasal mucosa
- Most common type of sinonasal polyp
- Most common space occupying lesion of the sinonasal tract (J Clin Diagn Res 2014;8:FC04)
- Antrochoanal polyp is an inflammatory sinonasal polyp that extends from the maxillary sinus through the ostium into the nasal cavity / nasopharynx
Essential features
- Benign, nonneoplastic polyp characterized by edematous stroma infiltrated by mixed inflammatory cells
Terminology
- Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
- Nasal polyps
ICD coding
- ICD-10: J33.9 - nasal polyp, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Occurs in 2 - 10% of population (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021;9:4117, StatPearls: Nasal Polyps [Accessed 12 January 2022])
Sites
- Commonly bilateral and multifocal (Pak J Med Sci 2020;36:146)
- Most frequently involves nasal cavity and ethmoid sinus (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2016;4:565)
Pathophysiology
- Defected epithelial cell barrier, increased exposure to bacteria and dysfunctioning host immune system may play a role in the pathogenesis (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2016;4:565)
Etiology
- Most frequently occurs in the setting of chronic rhinosinusitis
- Other risk factors include allergy, systemic vasculitis, cystic fibrosis, sensitivity to aspirin and nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs (StatPearls: Nasal Polyps [Accessed 12 January 2022])
Clinical features
- Most common symptoms: obstruction, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, facial pressure and pain (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2016;4:565)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis can be rendered based on the typical endoscopic or histologic findings
Radiology description
- Smooth soft tissue masses commonly originate in the ethmoid sinuses and protrude into the nasal cavity (Eur Radiol 2006;16:872)
- Hypodense but may be hyperdense due to concurrent fungal infection or increased protein content
- May demonstrate adjacent bony remodeling or erosion
Prognostic factors
- Recurrence rate is approximately 60% in patients followed for at least 10 years
- Presence of asthma is associated with increased risk of recurrence
- Reference: Am J Rhinol Allergy 2021;35:449
Case reports
- 21 and 32 year old men with infarcted angiomatous nasal polyps (Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2005;262:225)
- 4 cases of angiomatous nasal polyps (Cureus 2020;12:e7642)
Treatment
- Medical treatments include nasal corticosteroid and high volume saline irrigation (JAMA 2015;314:926)
- Sinus surgery for patients failed medical management (J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2016;4:565)
Gross description
- Usually multiple and bilateral and involve nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
- Have translucent, moist or edematous cut surface
- Broad base of attachment is present
- Usually not destructive
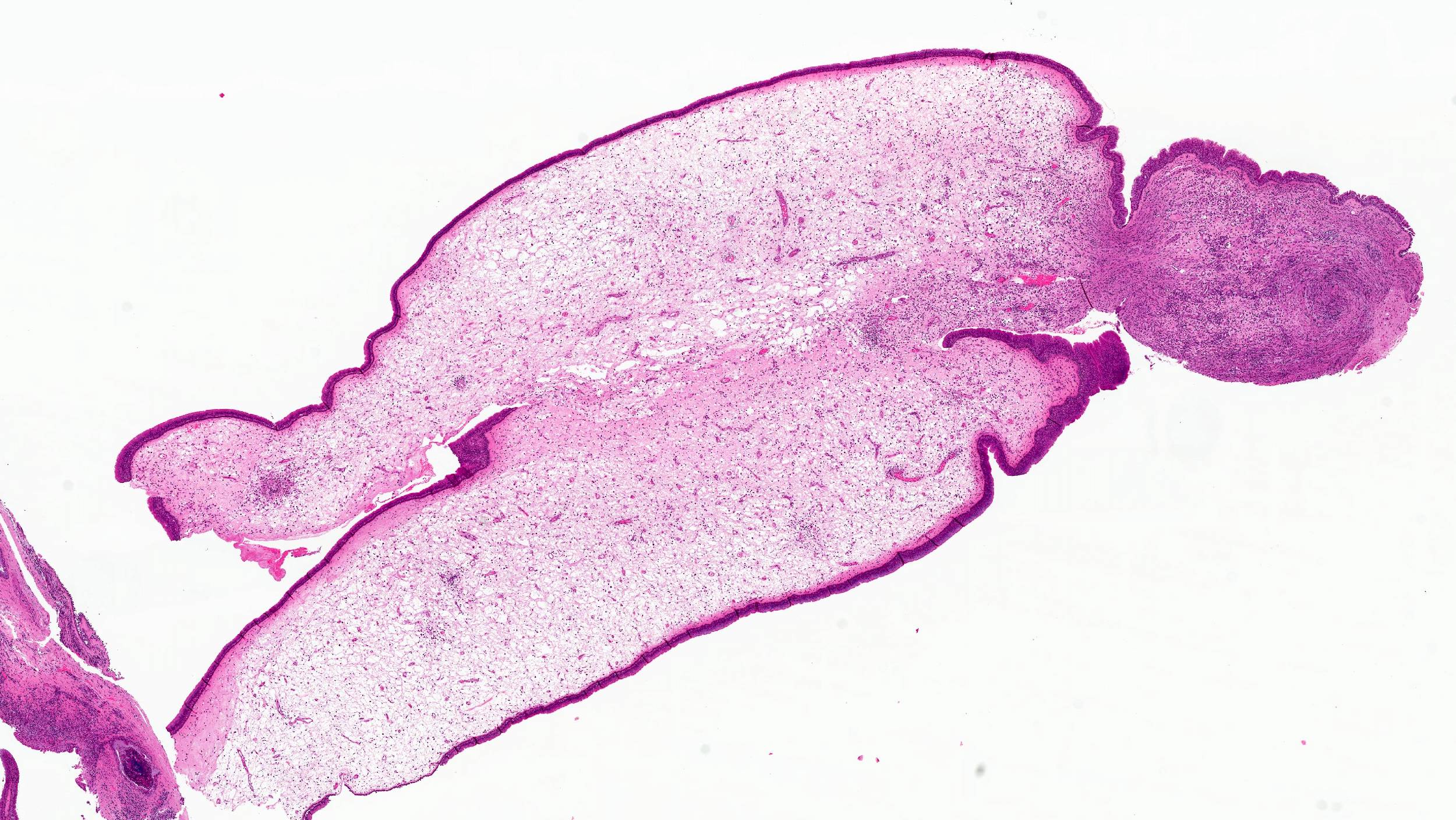
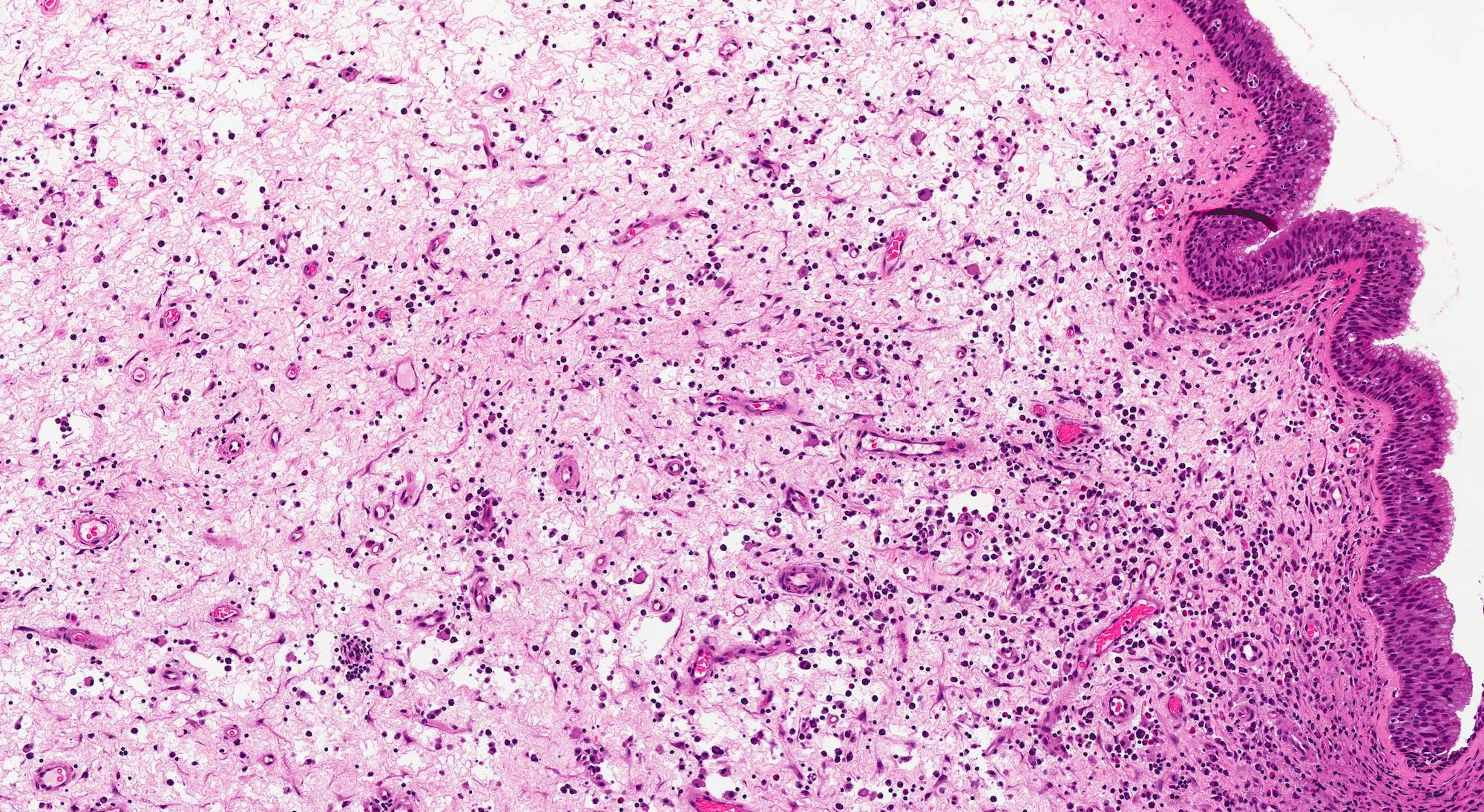
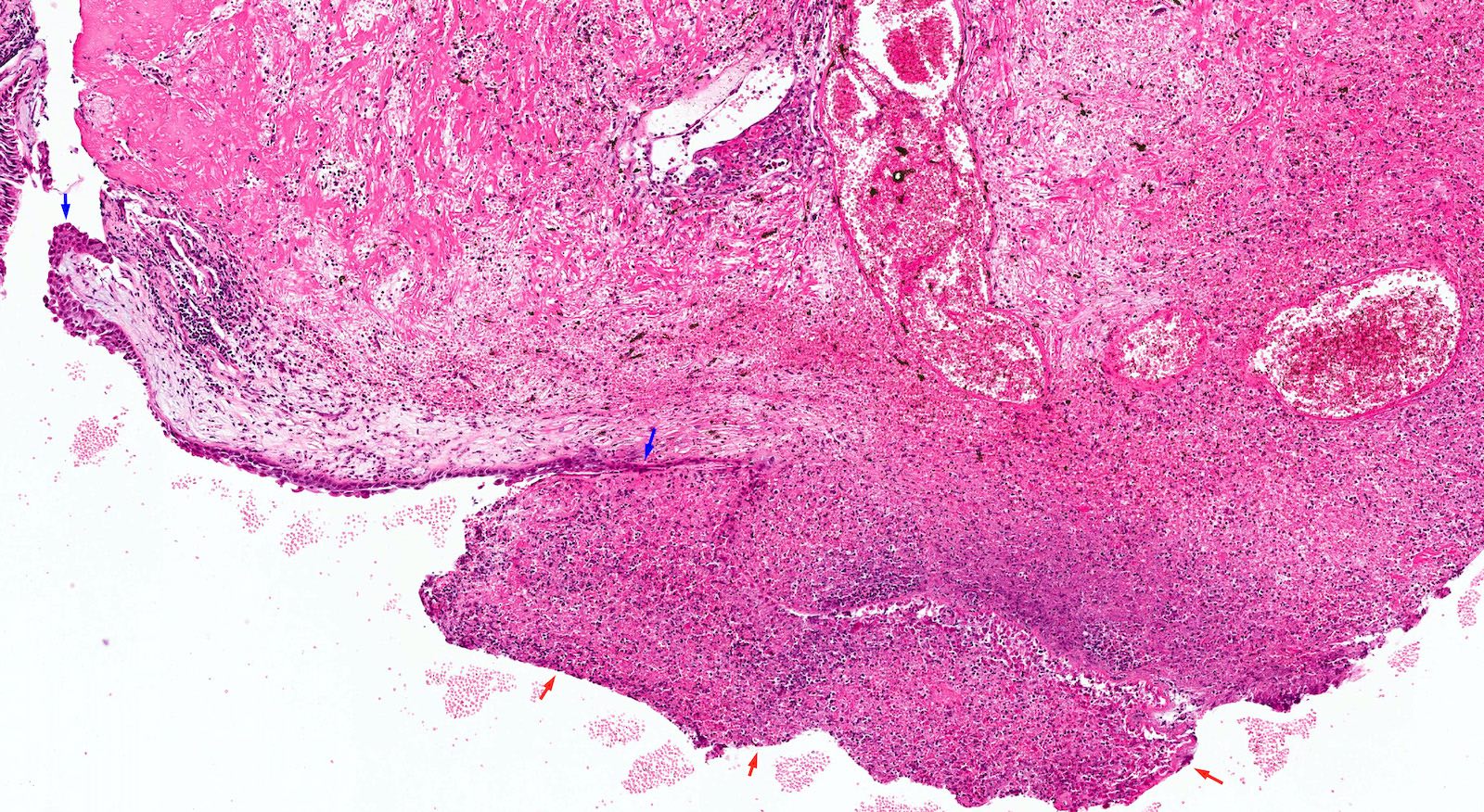
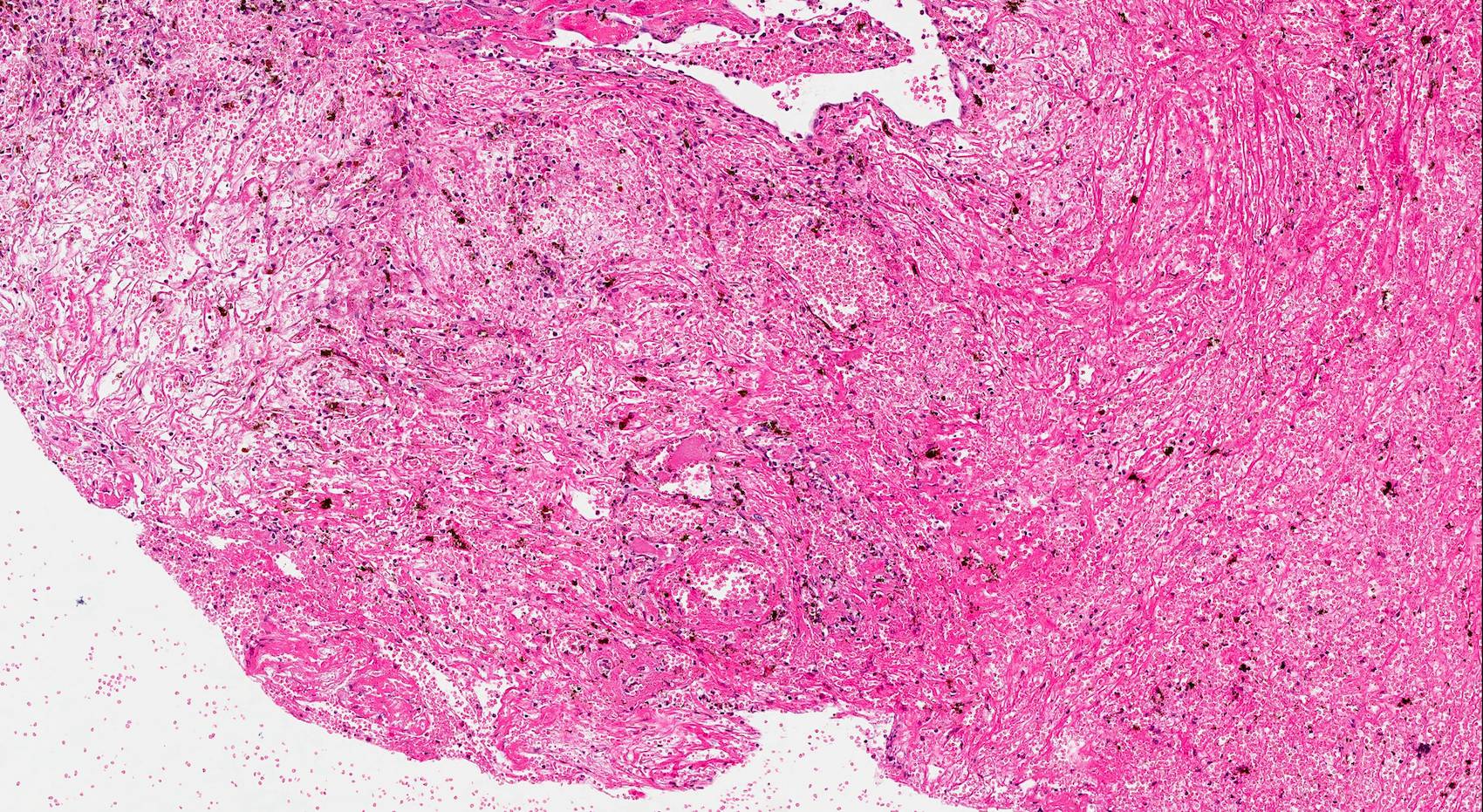
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Edematous, fibrotic or loosely myxoid stroma covered by respiratory epithelium
- Infiltrated by mixed inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils, neutrophils and mast cells
- Surface epithelium can show ulceration or squamous metaplasia
- May have bizarre stromal cells (large and pleomorphic)
- Submucosal glands are decreased or absent
- Concurrent fungal infection may be seen
- Rarely, osseous metaplasia may be present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Nasal cavity, left, excision:
- Inflammatory sinonasal polyp
Differential diagnosis
- Sinonasal papilloma:
- Inflammatory polyp lacks the epithelial proliferation, the thickened epithelial lining or the inverted growth pattern seen in sinonasal papilloma
- Respiratory epithelial adenomatoid hamartoma:
- Inflammatory polyp lacks the proliferation of respiratory epithelium and thickened basement membrane typical of respiratory epithelial adenomatoid hamartoma
- Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma:
- Can be polypoid but characterized by cellular spindle cells in the stroma showing biphenotypic neural and myoid differentiation
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, embryonal (botryoid) type:
Practice question #1
What is the most common polypoid lesion in the sinonasal cavity?
- Angiofibroma
- Inflammatory sinonasal polyp
- Respiratory epithelial adenomatoid hamartoma
- Sinonasal papilloma
Practice answer #1
B. Inflammatory sinonasal polyp is the most common polypoid lesion and space occupying lesion in the sinonasal tract.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory sinonasal polyp, including antrochoanal polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory sinonasal polyp, including antrochoanal polyp
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
B. This is an inflammatory sinonasal polyp, a nonneoplastic benign lesion characterized by edematous stroma and inflammatory infiltrates.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory sinonasal polyp, including antrochoanal polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory sinonasal polyp, including antrochoanal polyp