Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Tjarks J. Angiosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticangiosarcoma.html. Accessed October 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Malignant neoplasm with vascular differentiation
Essential features
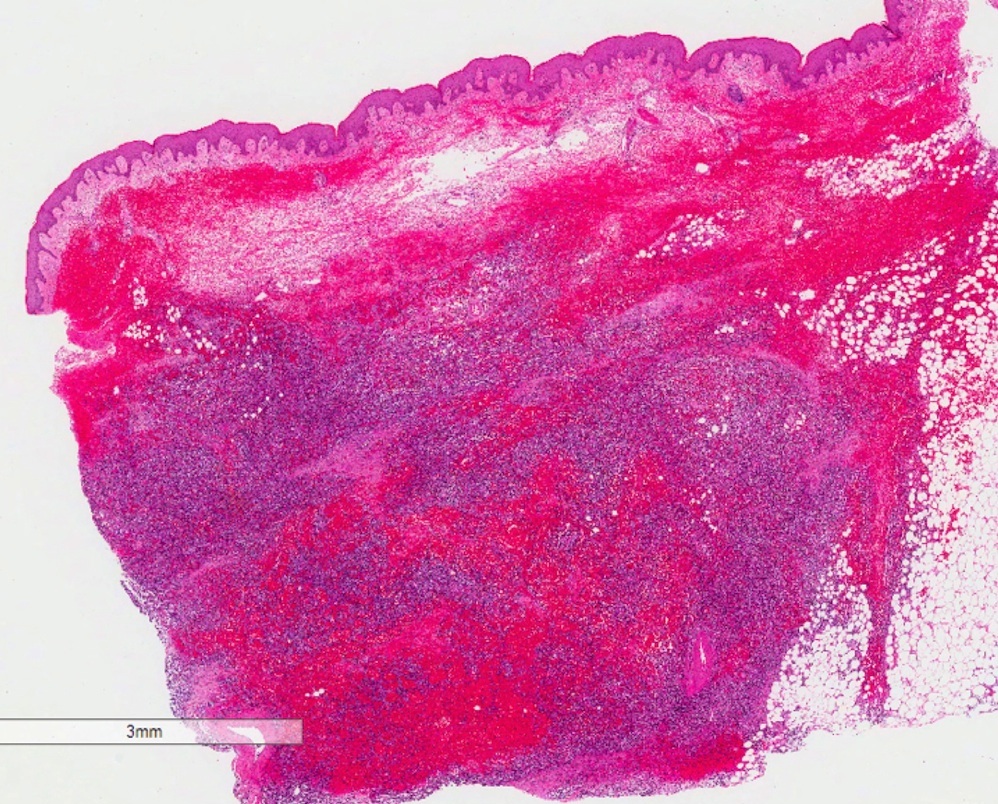
- Infiltrative vascular neoplasm with broad histologic profile ranging from a well differentiated neoplasm with frank vascular differentiation to a poorly differentiated tumor with epithelioid or spindled cells
- May mimic poorly differentiated carcinoma, inflammatory process, lymphoma or melanoma
Terminology
- Also known as hemangiosarcoma
Epidemiology
- Classically arises in one of three scenarios:
- Head and neck of the elderly
- Chronic lymphedema
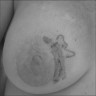
- Postradiation (usually in the setting of breast cancer)
Sites
- Sun exposed skin of the elderly (head and neck); breast with history of lymphedema or radiation therapy
Clinical features
- Wide age range (most common in adults)
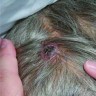
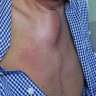
- Presents as purple nodules or plaques
- Highly aggressive
- Frequent recurrence and metastasis
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognosis - high mortality
- Epithelioid tumors are often more aggressive
Case reports
- 80 year old woman with secondary angiosarcoma postradiation and breast conserving therapy (J Clin Imaging Sci 2015;5:45)
Treatment
- Surgical resection with negative margins
- Chemotherapy is occasionally used
Gross description
- Violet elevated nodules with ill defined margins
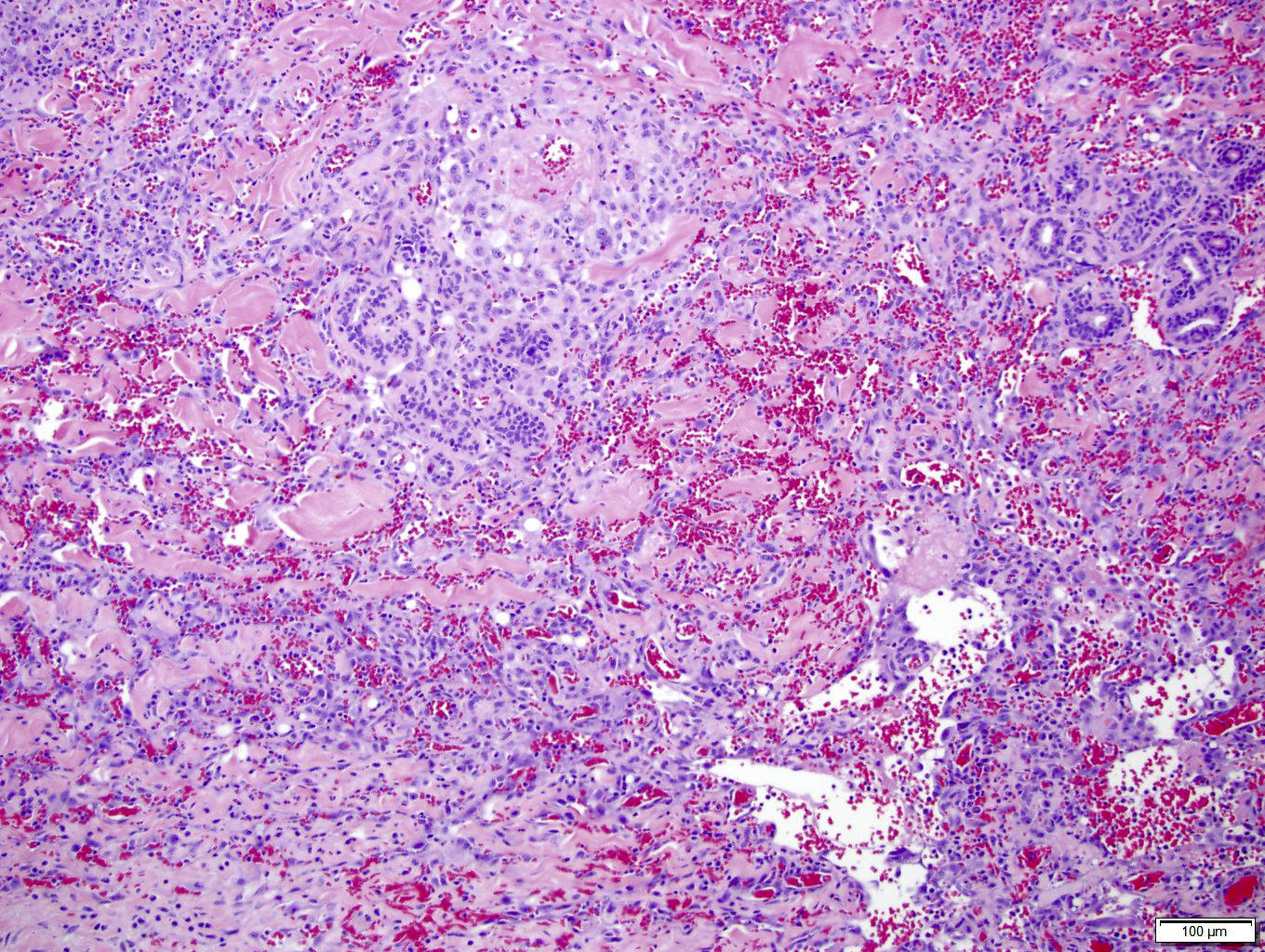
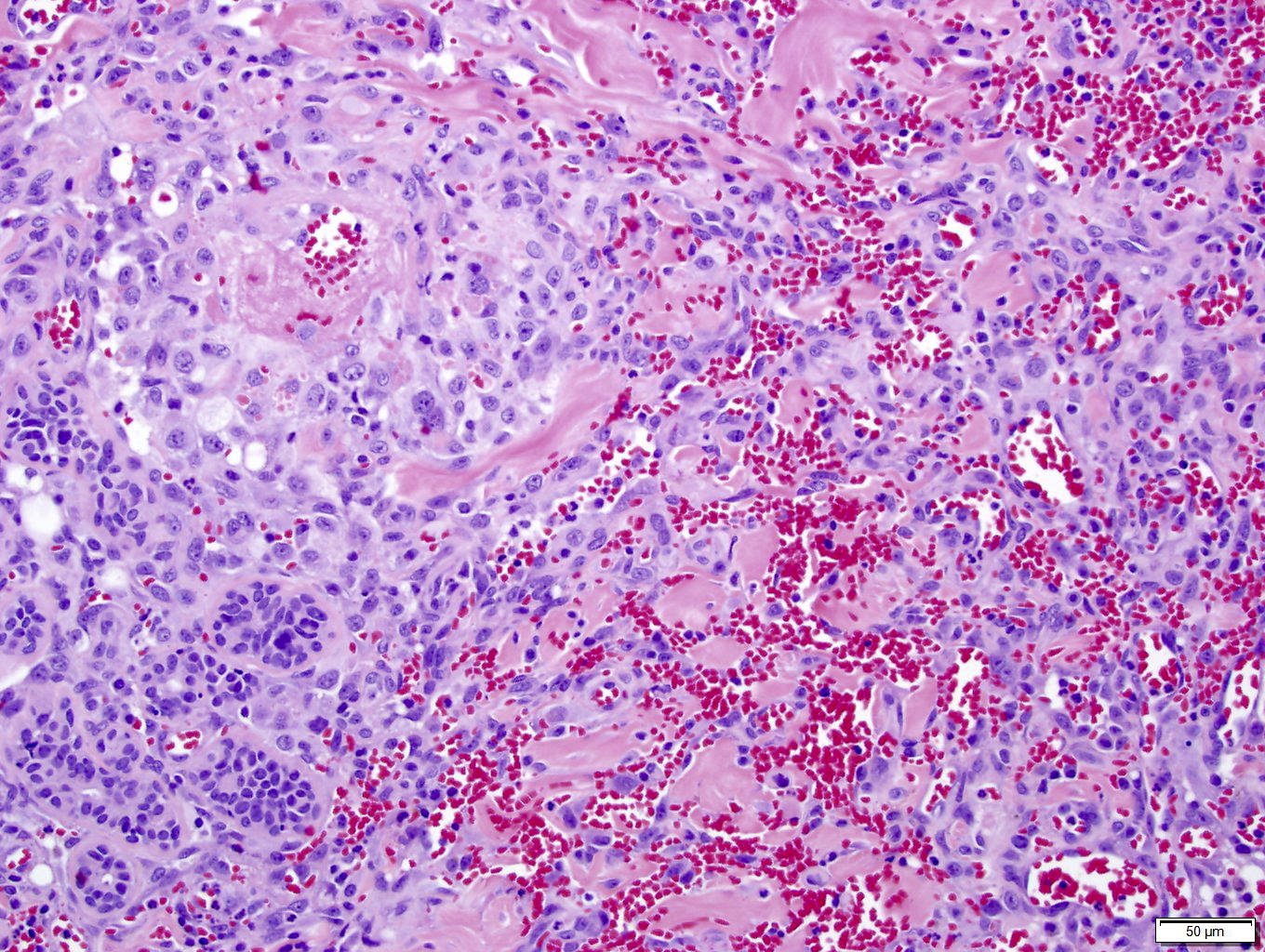
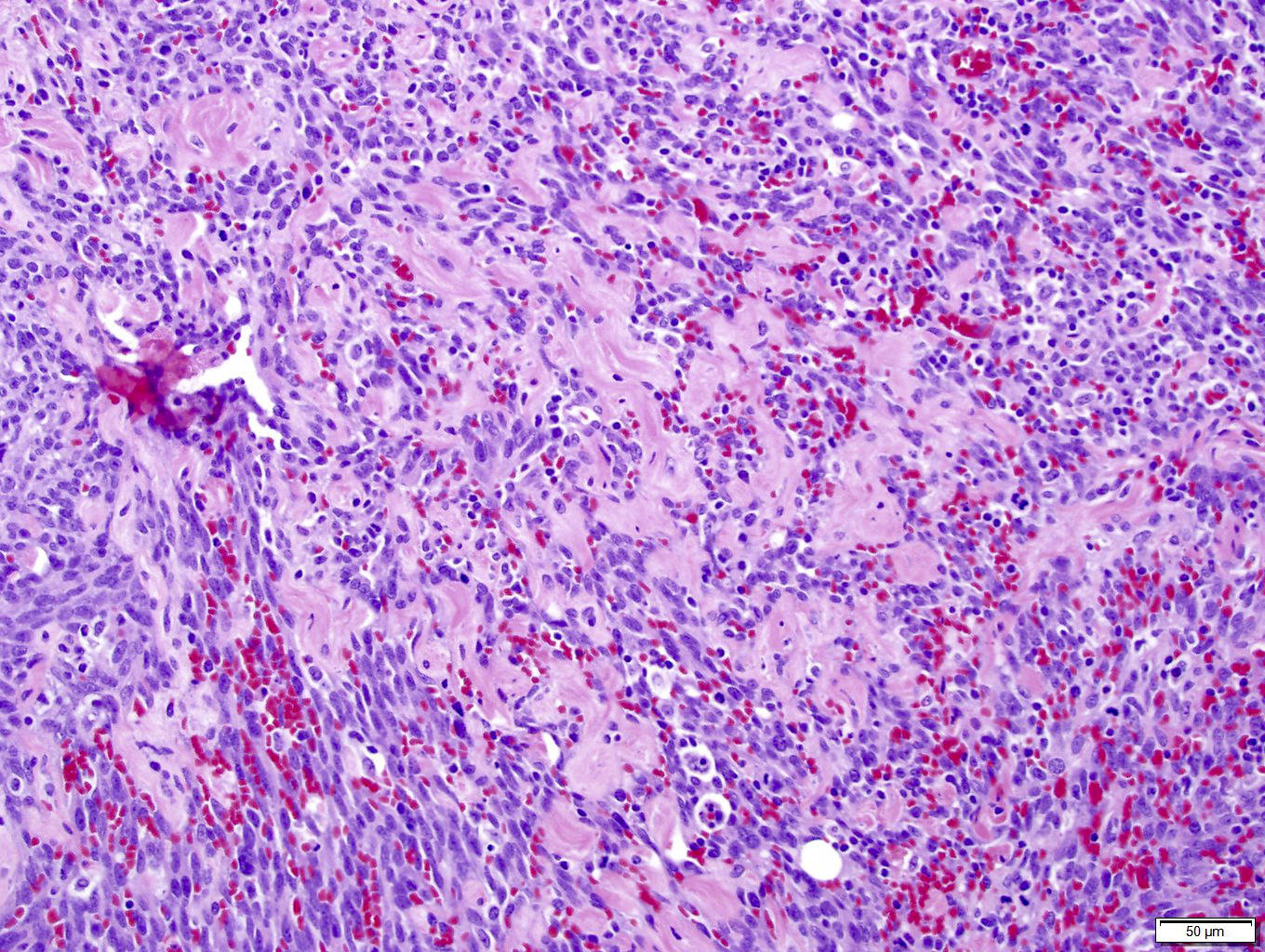
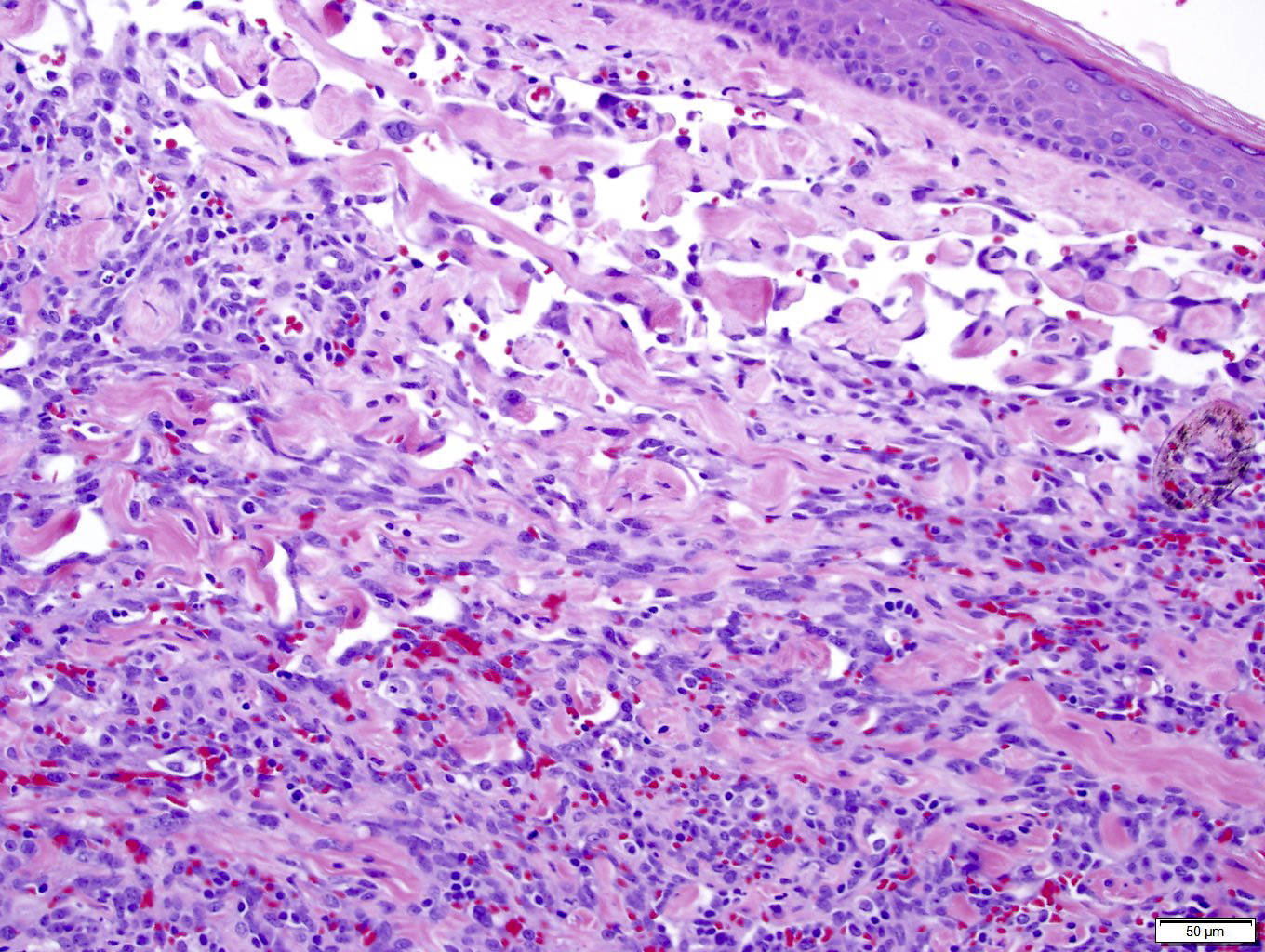
Microscopic (histologic) description
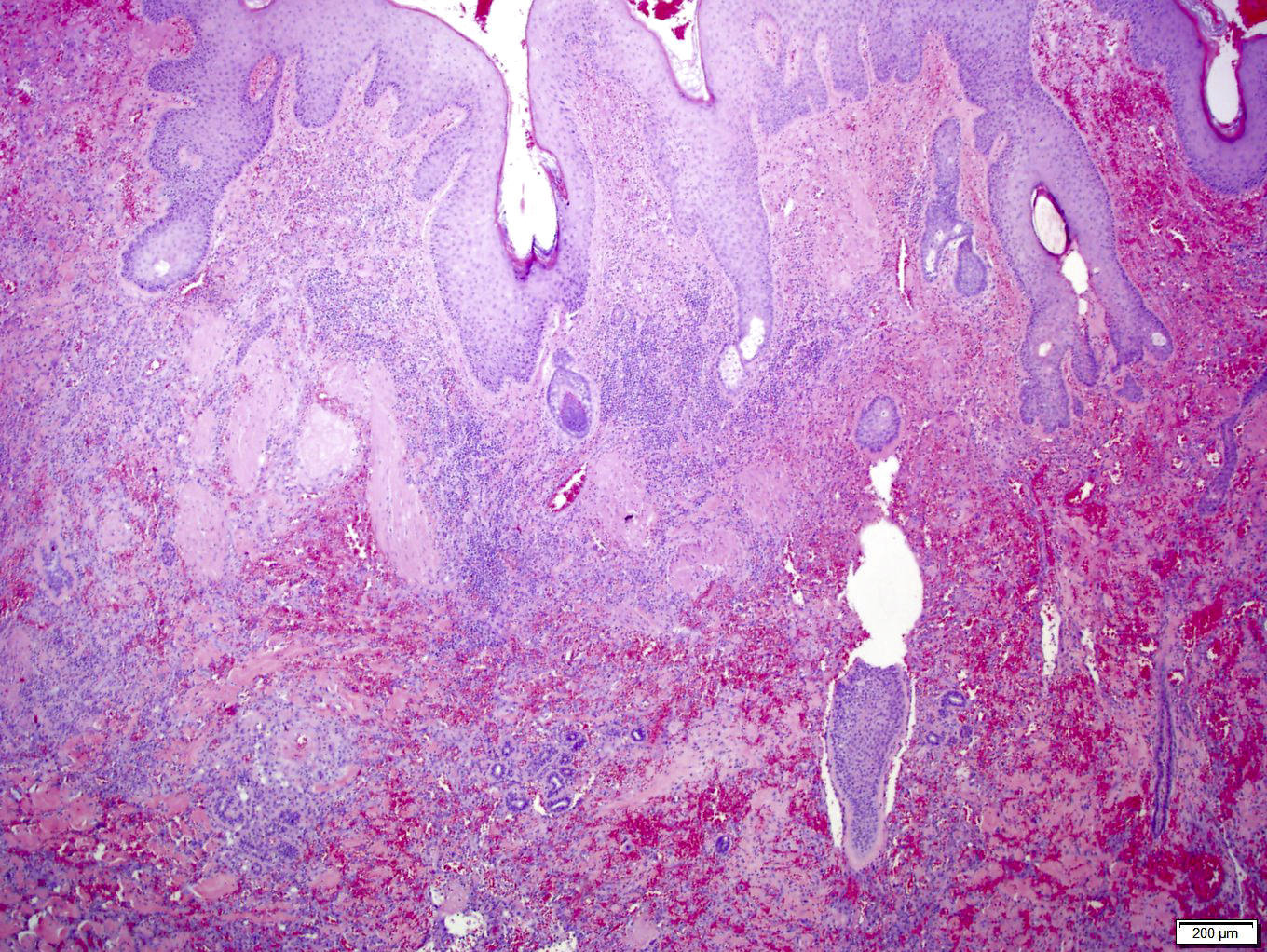
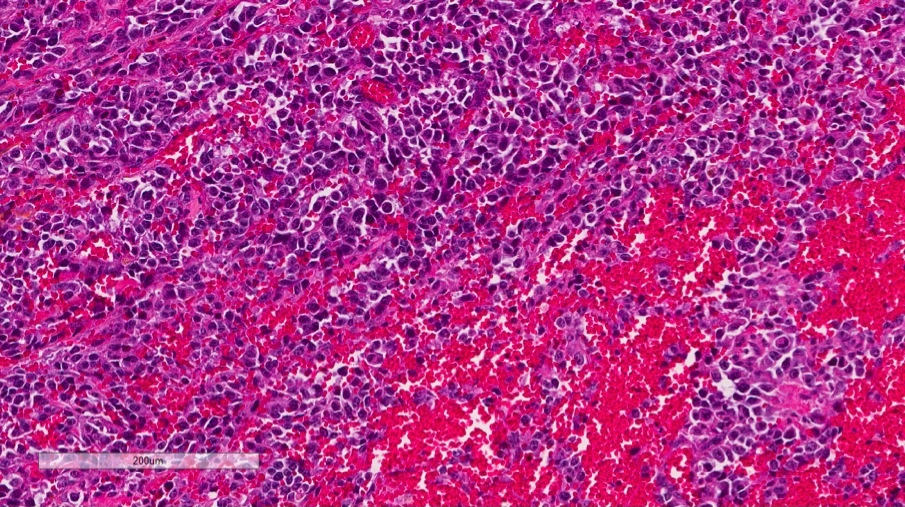
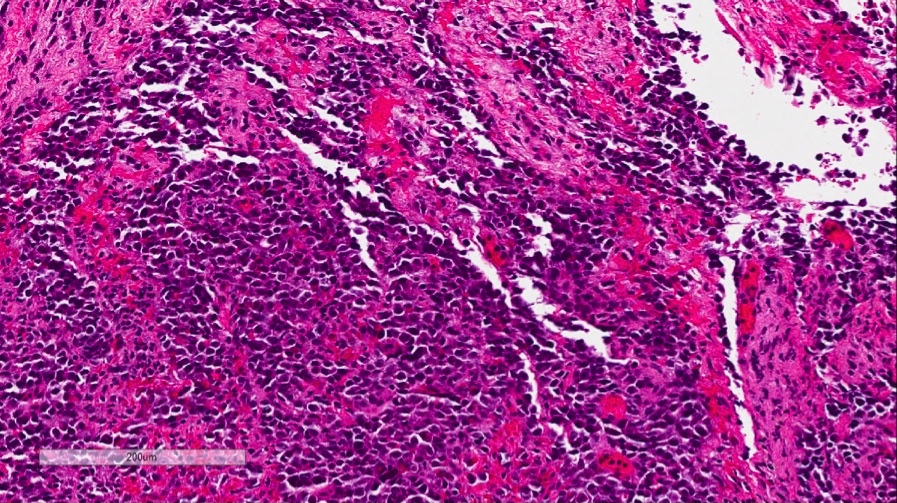
- Infiltrating, freely anastomosing channels lined by spindled to epithelioid endothelial cells with variable atypia, surrounding adnexae and dissecting dermal collagen
- Endothelial cells may have multilayered appearance
- May have free floating intraluminal endothelial cells (“fish in the creek”)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- MYC (8q24) amplification seen in great majority radiation / lymphedema associated tumors
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical fibroxanthoma
- Atypical vascular lesion
- Hemangioma
- Kaposi sarcoma
Additional references