Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Singh M, Dhankar N, Singh S, Khurana N. Hidrocystoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticapocrinecystadenoma.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign, cystic tumor of apocrine glands
- Affects middle aged adults with no gender predilection
Essential features
- Most commonly affects eyelids
- Usually solitary; multiple hidrocystomas have syndromic association
- Intradermal, dome shaped, translucent, bluish nodule up to 1 cm, lined by dual cuboidal or columnar layer histologically
Terminology
- Cystadenomas (more complex papillary projections), sudoriferous cysts, Moll gland cysts
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 70 years (MedGenMed 2006;8:57)
- No gender predilection
- Usually solitary, painless
- Solitary lesions are not familial but multiple hidrocystomas are associated with Goltz-Gorlin syndrome and Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome (a form of ectodermal dysplasia) (Acta Derm Venereol 2008;88:607, MedGenMed 2006;8:57)
Sites
- Predilection for head and neck region, most common site being the eyelids
- Despite its apocrine derivation, rare at sites rich in apocrine glands (groin, axilla, anogenital region, eyelids [Moll glands], ears [ceruminous glands])
Pathophysiology
- Exact pathogenesis is unknown
- Regarded as a proliferative tumor arising from the secretory part of the apocrine sweat glands, unlike earlier beliefs that it is a simple retention cyst
- References: Eplasty 2022;22:ic13, StatPearls: Apocrine Hidrocystoma [Accessed 4 April 2025]
Etiology
- Sun exposure may be considered a potential risk factor (StatPearls: Apocrine Hidrocystoma [Accessed 4 April 2025])
Clinical features
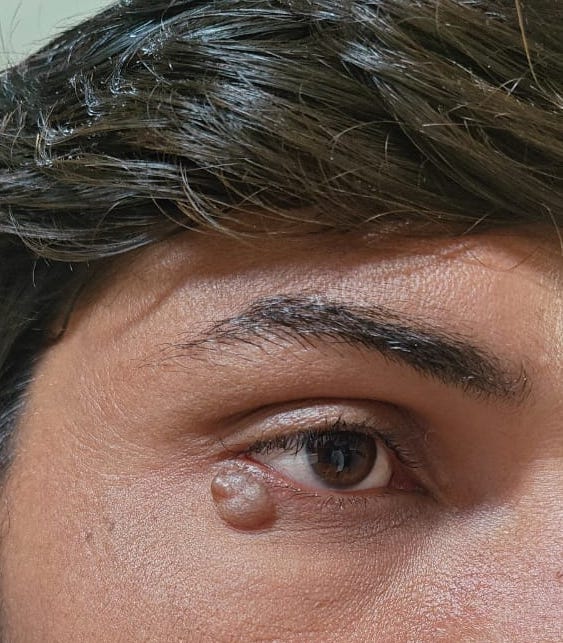
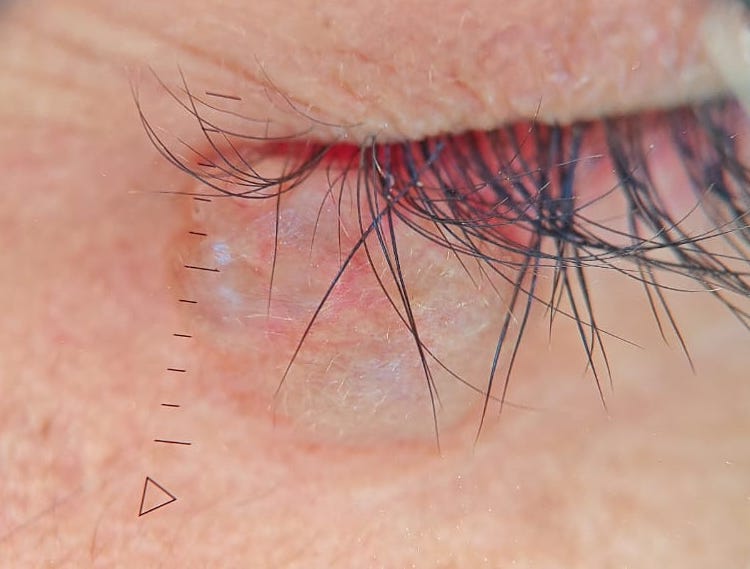
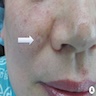
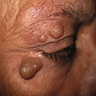
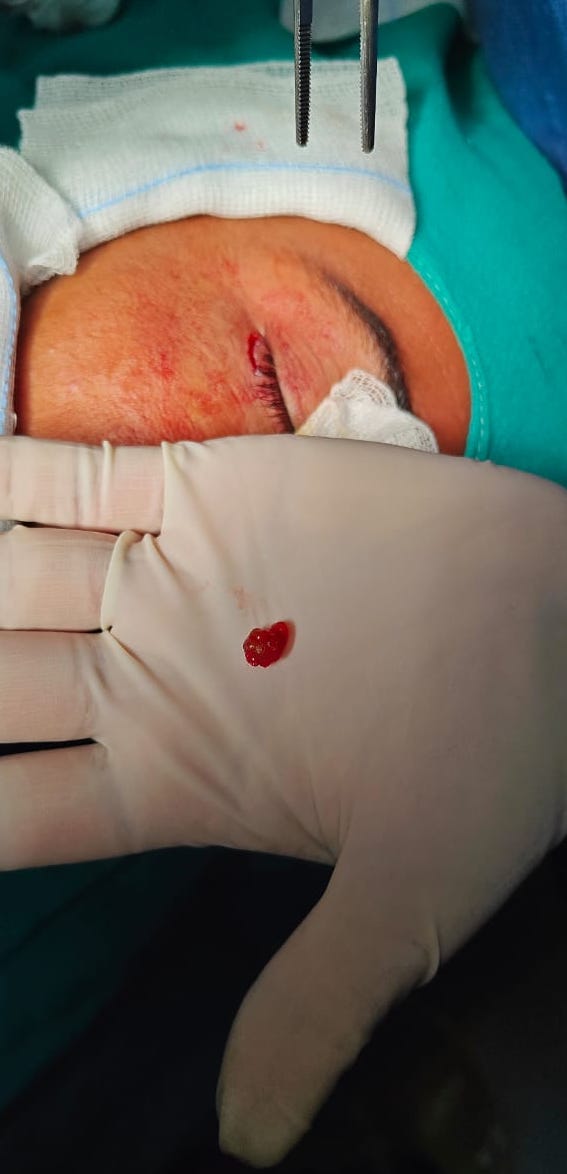
- Presents as an intradermal, moderately firm, dome shaped, translucent, bluish or purplish cystic nodule up to 1 cm (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:53)
- Cysts are gradually progressive until they reach a certain size (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:53)
- Multiple lesions on face, also called Robinson variant, usually in middle aged women (Clin Exp Dermatol 1995;20:323)
- May be precursor to apocrine carcinoma (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:53)
- Do not exhibit seasonal variations in size or number (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:53)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis by examination of a translucent cystic lesion with a bluish hue on an eyelid (MedGenMed 2006;8:57)
- Dermoscopy findings: smooth surface with a translucent appearance (Dermatol Pract Concept 2022;12:e2022090)
- Color may vary depending on the cyst contents and surrounding tissue; vascular structures may be visible, especially in cases of inflammation or irritation
- Biopsy is confirmatory
Case reports
- 16 year old boy with nipple apocrine hidrocystoma (Asian J Surg 2023;46:5872)
- 19 year old man with apocrine hidrocystoma of the parotid gland (Ear Nose Throat J 2023;102:NP549)
- 41 year old man with giant multicystic cystadenoma of Cowper gland (Int Braz J Urol 2013;39:741)
- 42 year old woman with multiple apocrine hidrocystomas of bilateral axillae with inflammation (Ann Dermatol 2024;36:62)
- 48 year old man with apocrine adenocarcinoma in the setting of apocrine hidrocystoma of the leg (Dermatol Online J 2019;25:13030)
- 55 year old woman with apocrine hidrocystoma of the nail bed (Am J Dermatopathol 2024;46:433)
- 69 year old man with apocrine hidrocystoma affecting the oral mucosa (Case Rep Dent 2017;2017:9382812)
- 75 year old man with multiple apocrine hidrocystomas (J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:171)
Treatment
- No treatment required
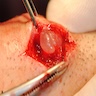
- Surgical excision with narrow margins (Dermatol Surg 2001;27:382)
- Prognosis following excision is excellent due to the benign nature
- Needle puncture: less effective, with higher recurrence rates (Dermatol Surg 2016;42:134, Eplasty 2022;22:ic13)
- Sclerotherapy: cyst puncture followed by injection of hypertonic glucose or trichloroacetic acid
- Botulinum toxin A: emerging as a potential option for multiple lesions (Br J Dermatol 2017;176:488)
- Laser treatments: carbon dioxide laser vaporization (J Dermatolog Treat 2001;12:97)
Clinical images
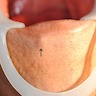
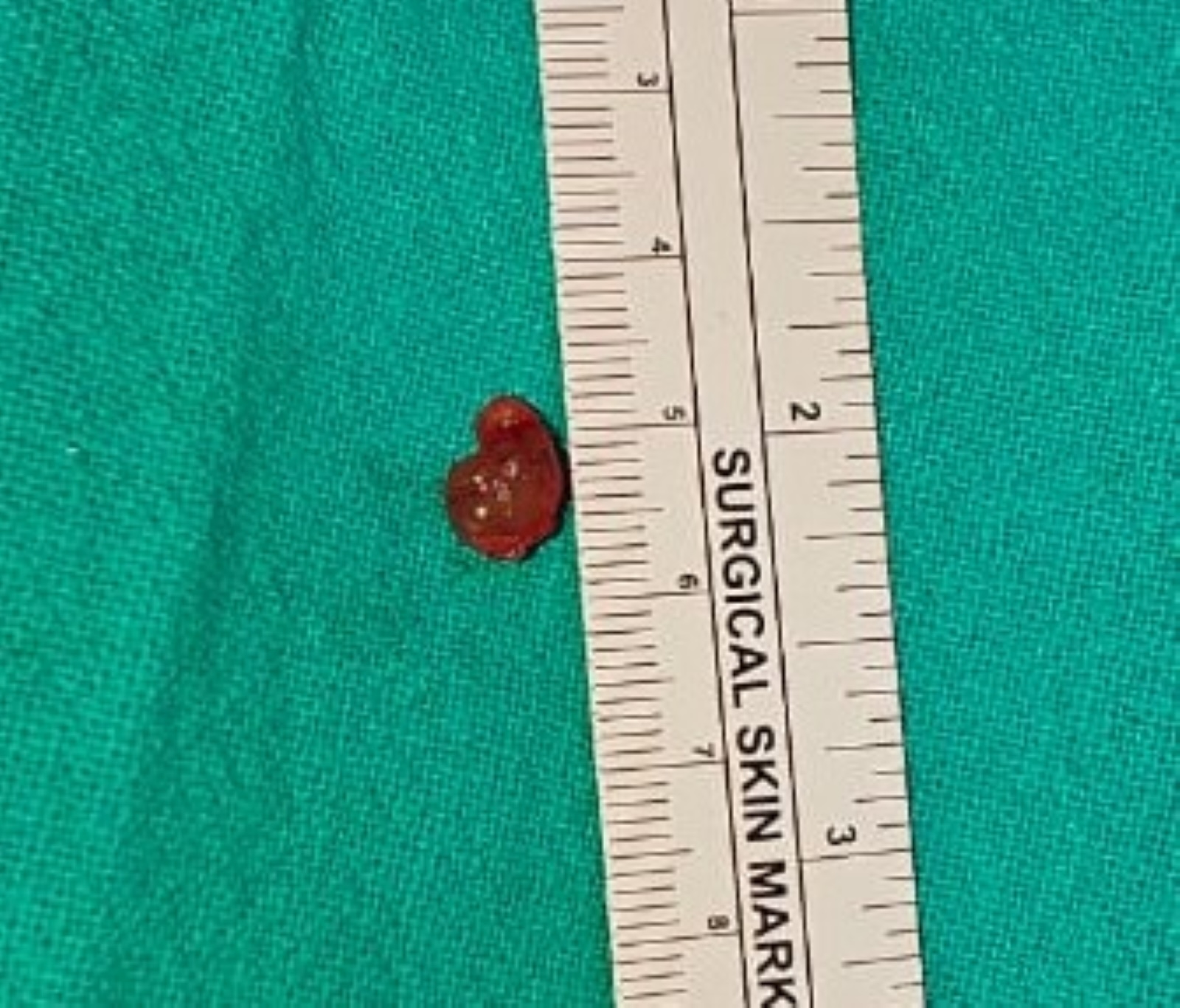
Gross description
- Unilocular cystic lesion with clear to brown fluid
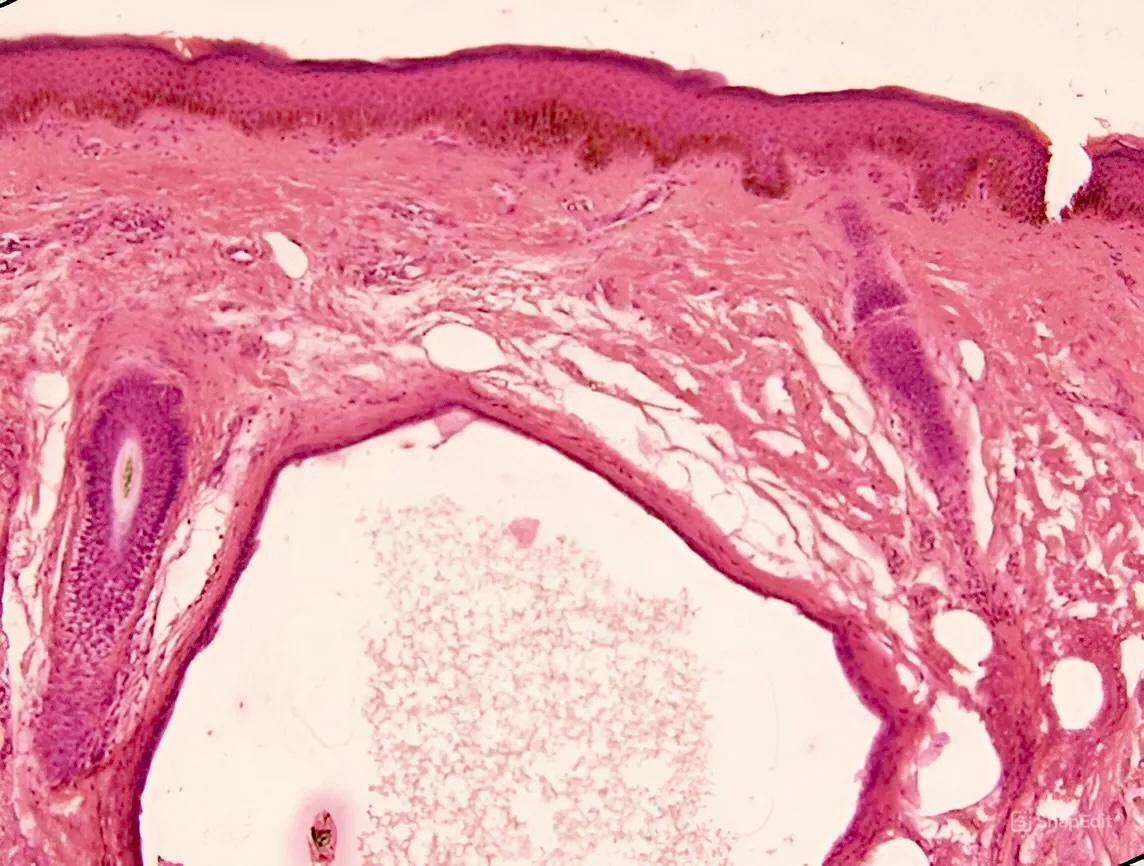
Microscopic (histologic) description
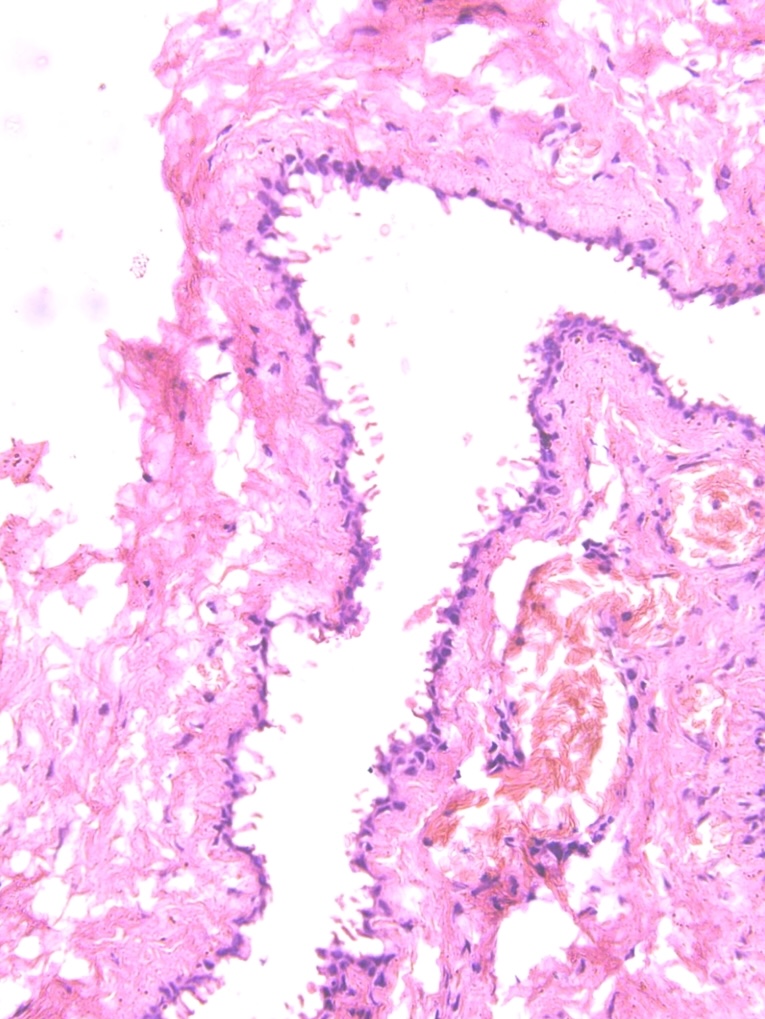
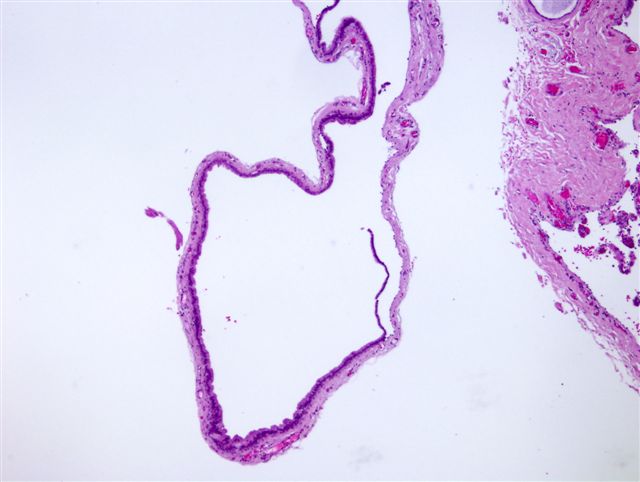
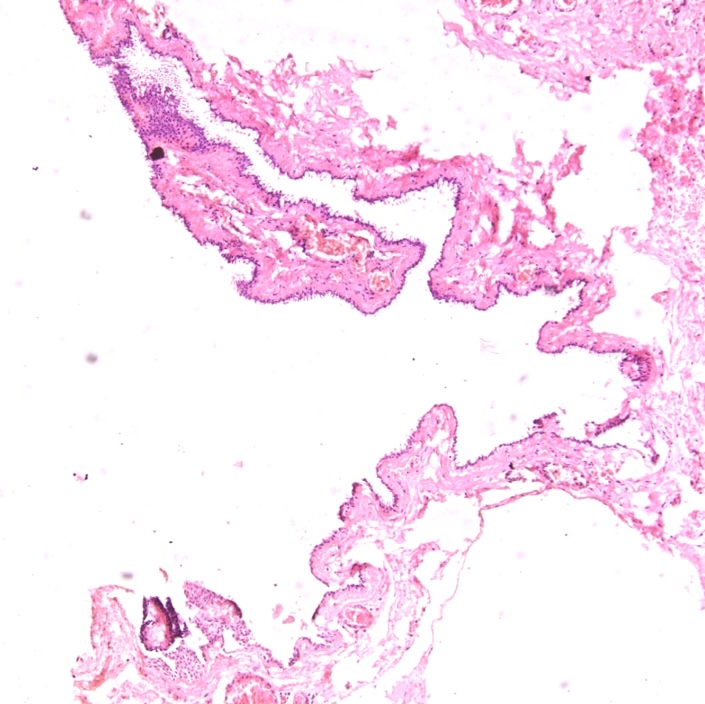
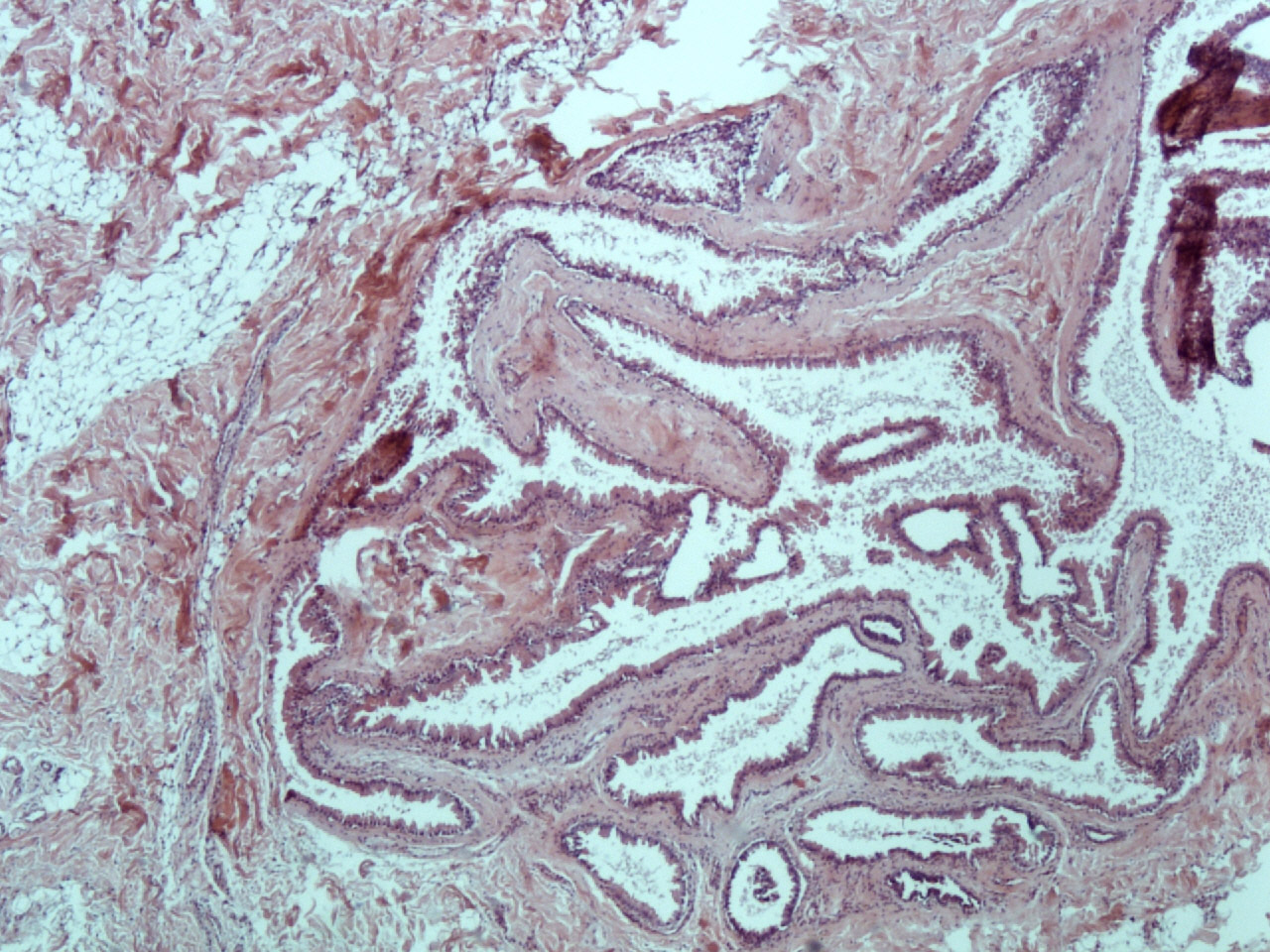
- Large unilocular or multilocular cystic space within dermis
- Fibrous pseudocapsule is often present
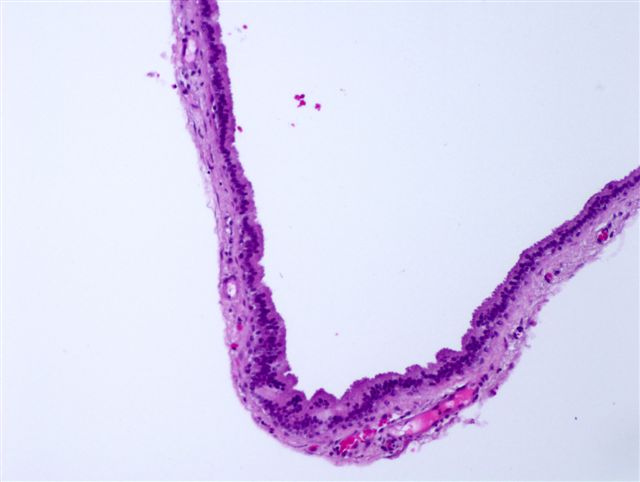
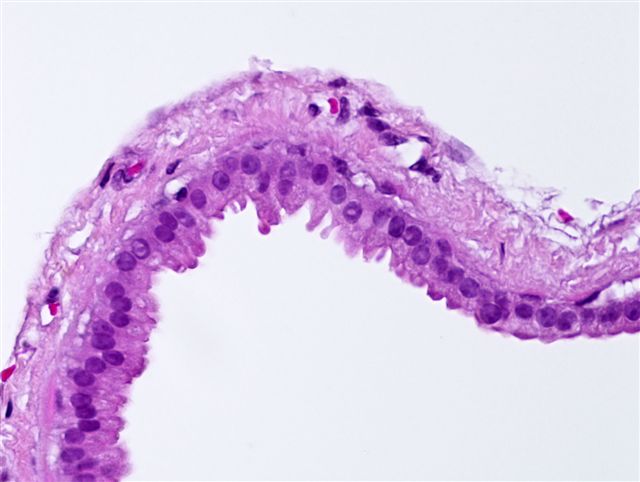
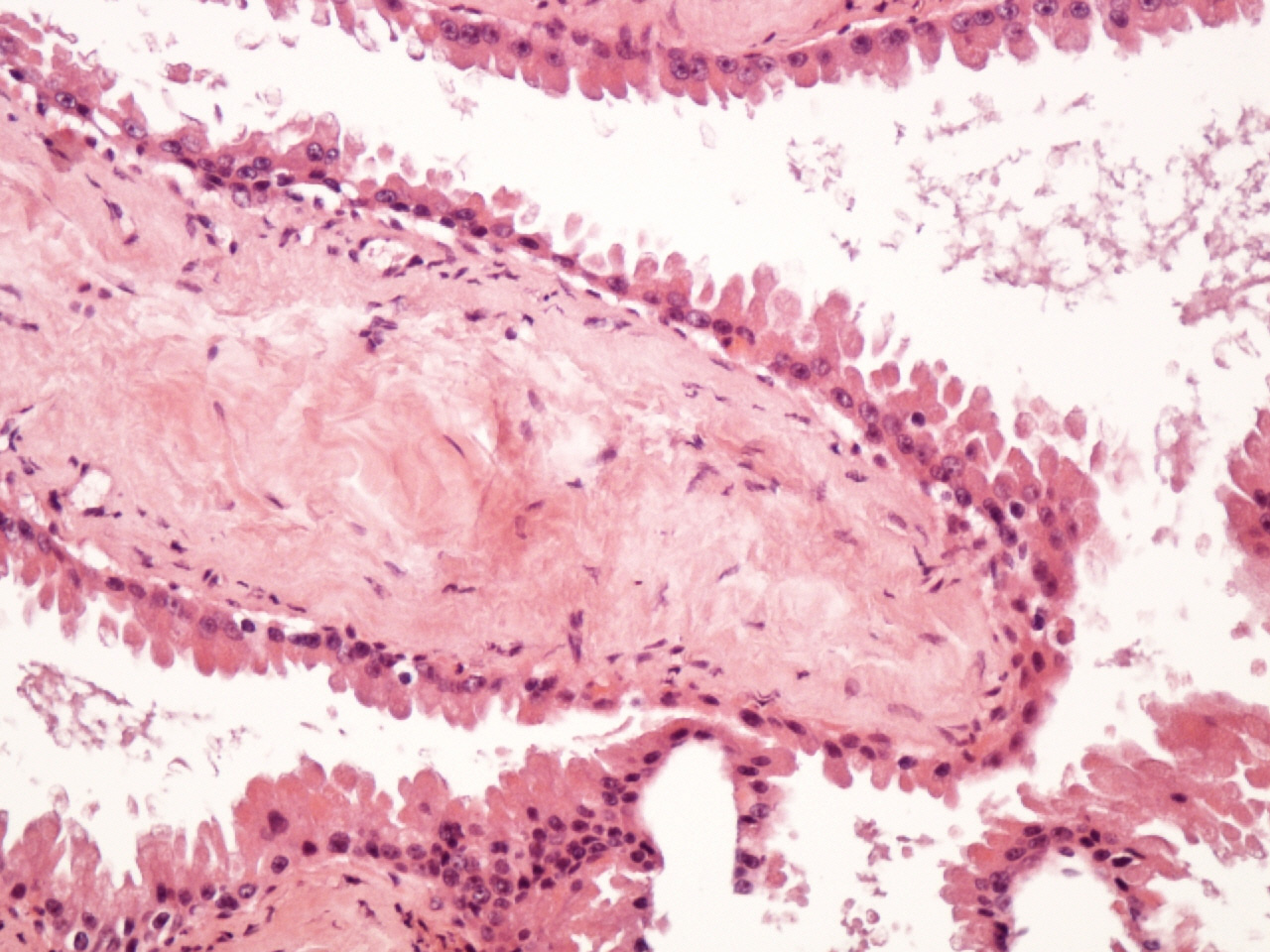
- Typically, cystic spaces are lined by a double layer of epithelial cells: an outer layer of flattened vacuolated myoepithelial cells and an inner layer of cuboidal or columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and basally located, round or oval vesicular nuclei (secretory cells)
- Decapitation secretions and apical snouts are usually present
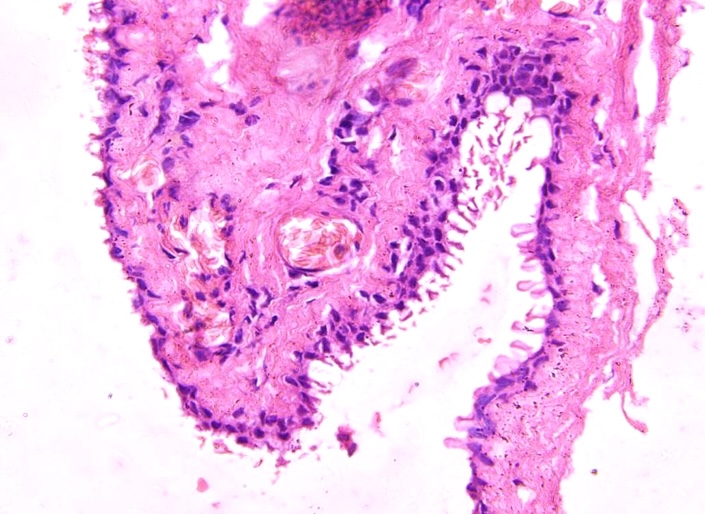
- Small papillary projections into the lumen can be occasionally seen: lesion described as cystadenoma (Int J Surg Case Rep 2024;114:109085)
- WHO states that the terms hidrocystoma and cutaneous cystadenoma may be used interchangeably; while hidrocystoma denotes a simpler cyst, cystadenoma refers to relatively complex lesions
- Often adjacent to hyperplastic apocrine glands
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Not required for routine diagnosis
- AE1 / AE3, CK7, CK18, EMA and CEA: luminal cells
- Smooth muscle actin (SMA), p63: myoepithelial cells
- HER2 (Mod Pathol 2004;17:28)
- GCDFP-15 in luminal cells (Head Neck Pathol 2014;8:117)
- Human milk fat globulin 1 (HMFG1) (J Cutan Pathol 2023;50:536)
- PAS positive, diastase resistant granules may be evident in the cytoplasm of the inner lining cells and occasionally iron or melanin is also demonstrable
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- 2 types of cells: secretory cells with granules resembling lipid droplets and basal (myoepithelial) cells
- Lumen filled with cytoplasmic fragments detached from apical portions of secretory cells (SAGE Open Med Case Rep 2022;10:2050313X221097770)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, eyelid, excision:
- Hidrocystoma (see comment)
- Comment: Histologic sections examined show skin with unremarkable epidermis. Dermis shows a cyst lined by dual layer composed of outer myoepithelial cells and inner columnar cells with decapitation secretions and apical snouting. Intraluminal homogenous, eosinophilic secretions are also seen.
Differential diagnosis
- Eccrine hidrocystoma (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:53):
- Considered to be a retention cyst of eccrine duct rather than a proliferative lesion
- Common site is head and neck region, more commonly eyelids and periorbital area
- Clinically, translucent bluish papules, rarely > 5 mm in size
- Eccrine hidrocystomas are known to increase in size during summers or after heat exposure and decrease during winters
- Cyst is lined by bland bilayer
- Inner lining with basally located round nuclei and moderate pale cytoplasm; no decapitation secretions or snouts
- Outer layer is composed of myoepithelial layer
- Negative for CK7, CK18, GCDFP-15, S100 and PAS (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2021;30:53)
- Lacrimal gland cyst (Am J Ophthalmol 2013;155:380):
- Clinically characterized by rubbery, mobile nodule on the eyelid; may have a bluish hue
- Histologically, fluid filled cyst in association with normal lacrimal tissue
- Cyst lined by single or double layer of epithelium; may be cuboidal or stratified squamous epithelium
- Present in proximity to normal lacrimal gland structure with surrounding chronic inflammatory infiltrate
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
A. Associated with Goltz-Gorlin syndrome. Despite its apocrine derivation, hidrocystomas are rare at sites rich in apocrine glands. Answer B is incorrect because it has predilection for head and neck region, the most common site being the eyelids. Answer C is incorrect because luminal cells are positive for GCDFP-15. Answer D is incorrect because malignant transformation is extremely rare.
Comment Here
Reference: Hidrocystoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hidrocystoma
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
B. Hidrocystoma most commonly presents as a bluish, painless nodule on an eyelid. The microscopy image shows a cystic space lined by double layer of epithelial cells. Answer A is incorrect because an epidermal inclusion cyst is lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Answer C is incorrect because a milium cyst is lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Answer D is incorrect because steatocystoma is lined by squamous epithelium with sebaceous glands in the cyst wall.
Comment Here
Reference: Hidrocystoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hidrocystoma