Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Hyde JT, Lee JB. Lobular capillary hemangioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticpyogenicgranuloma.html. Accessed August 25th, 2025.
Definition / general
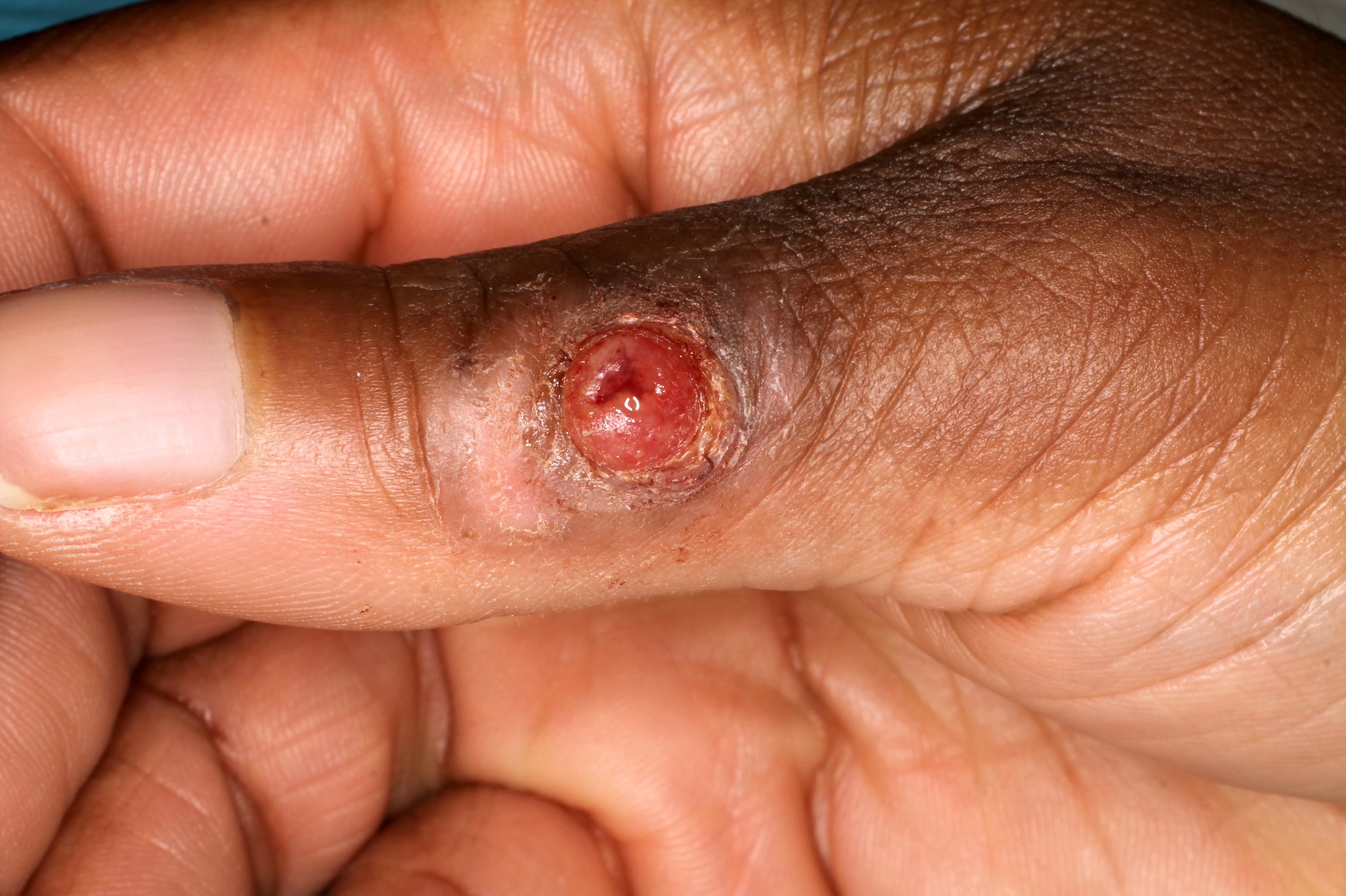
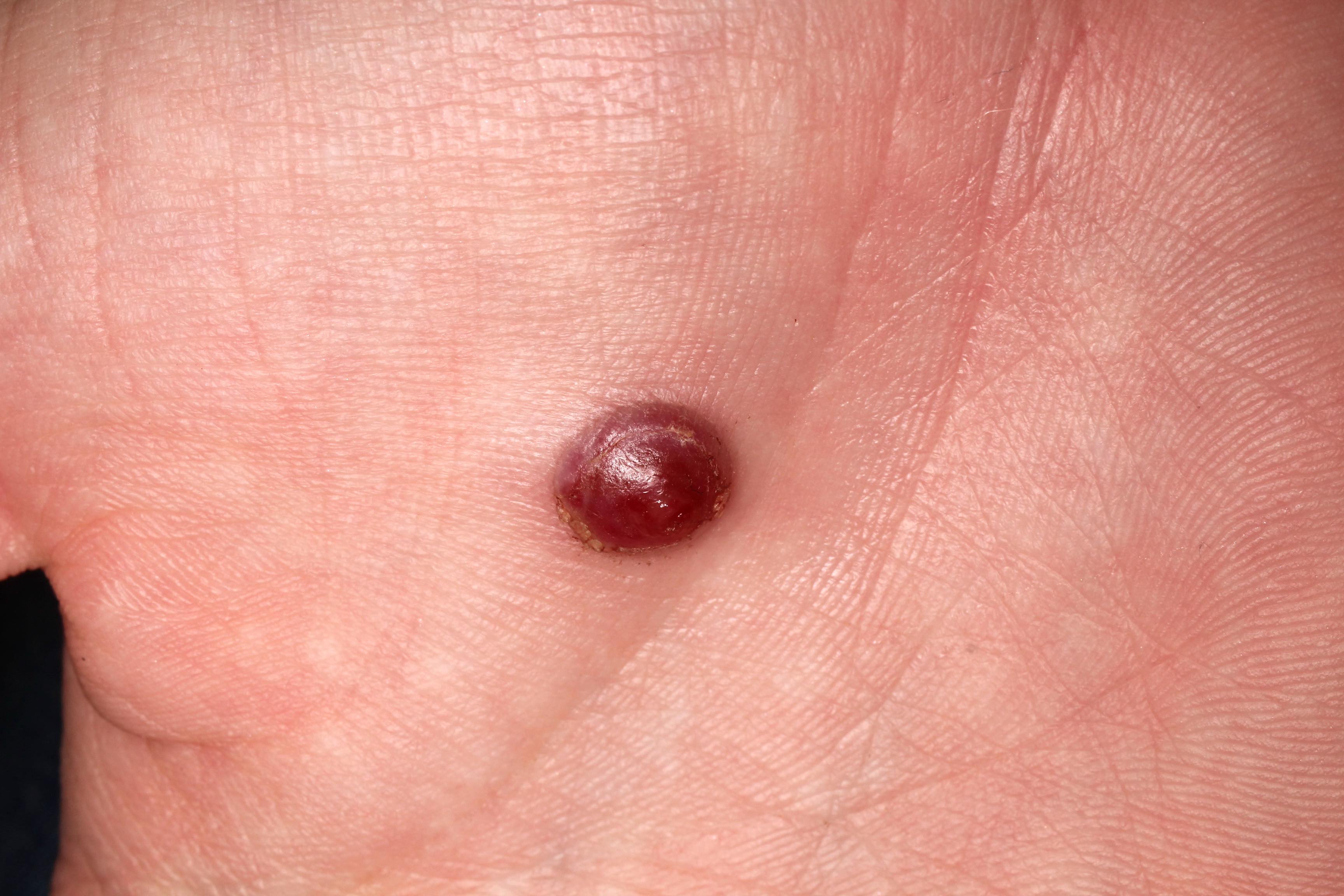
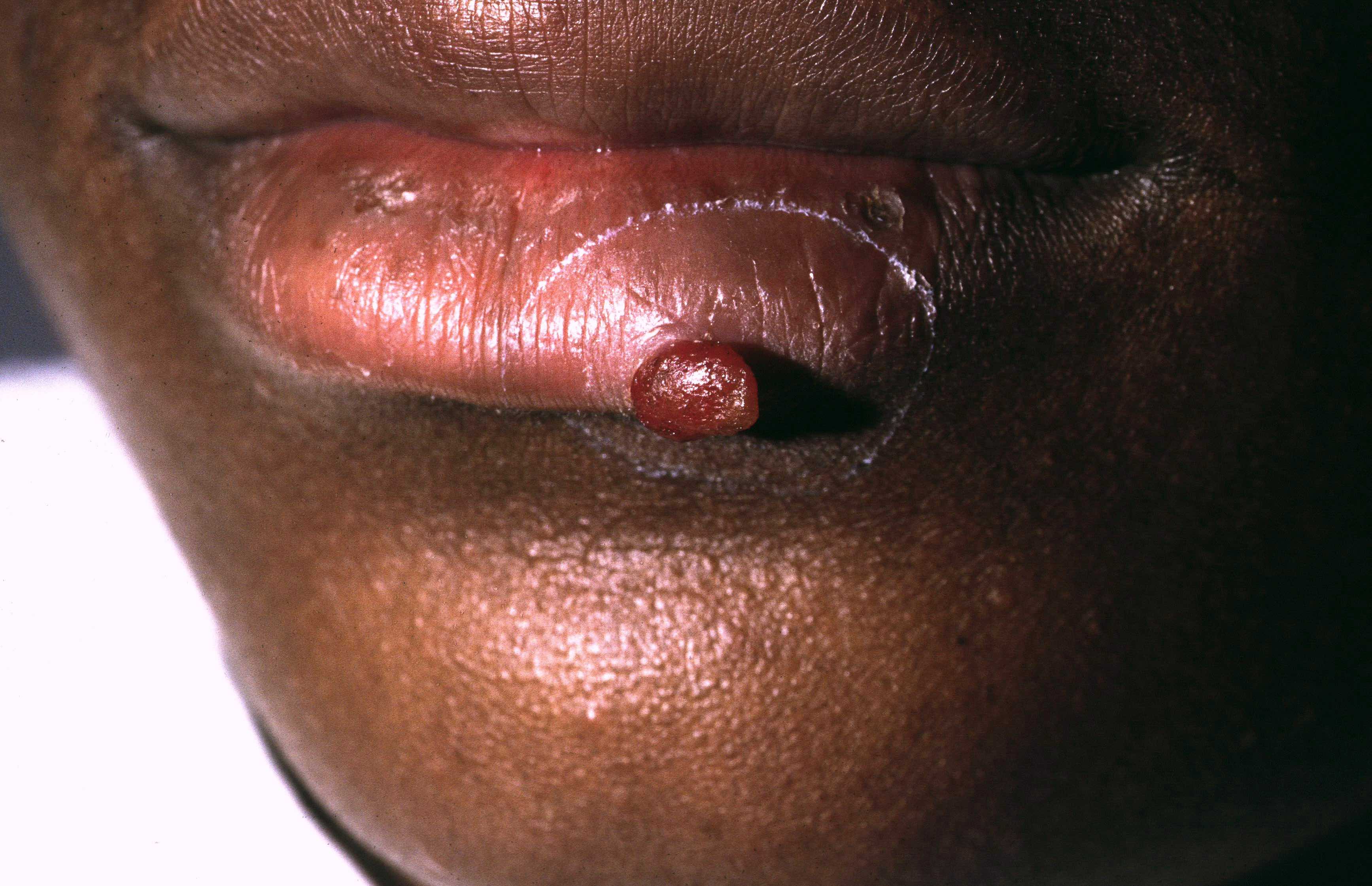
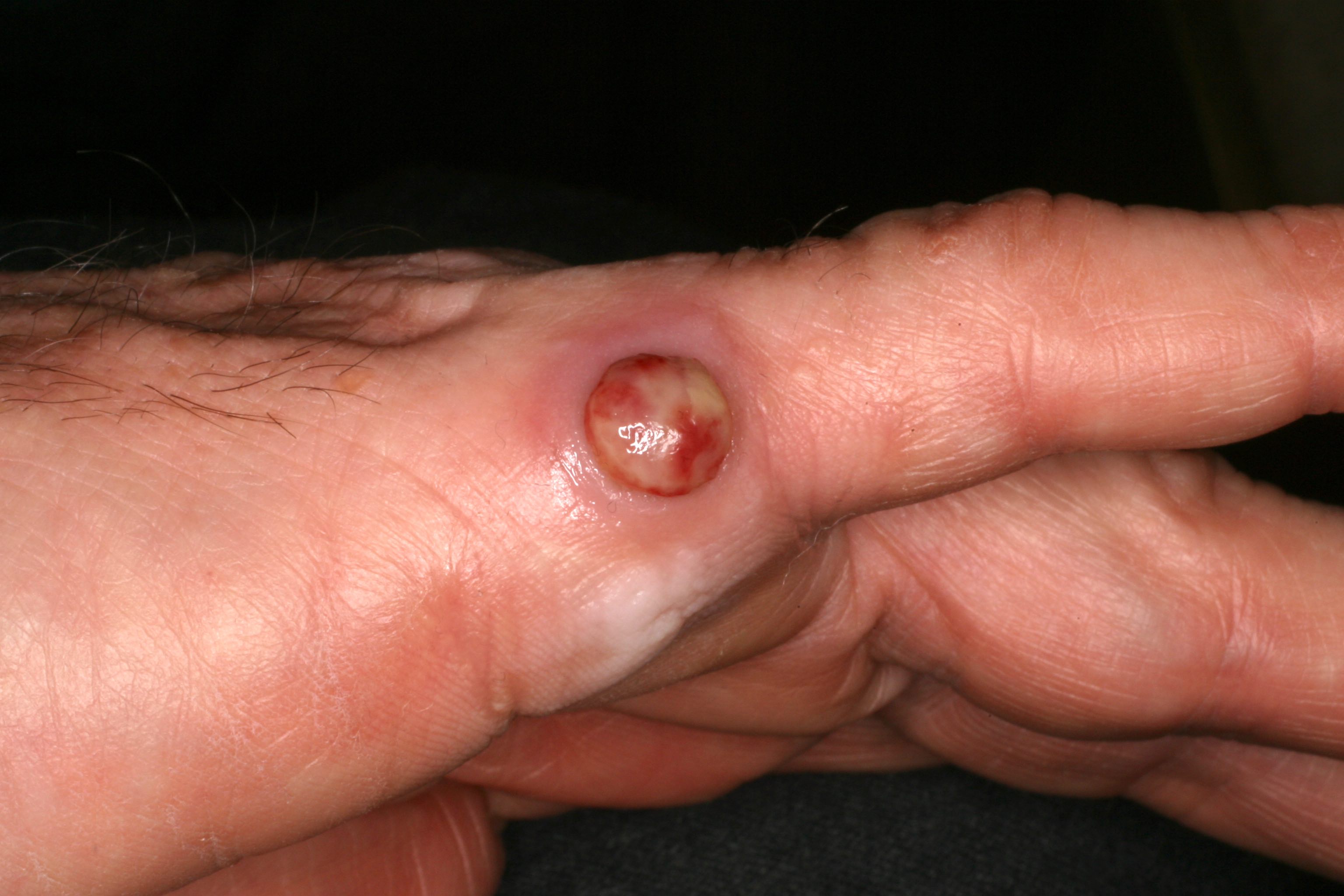
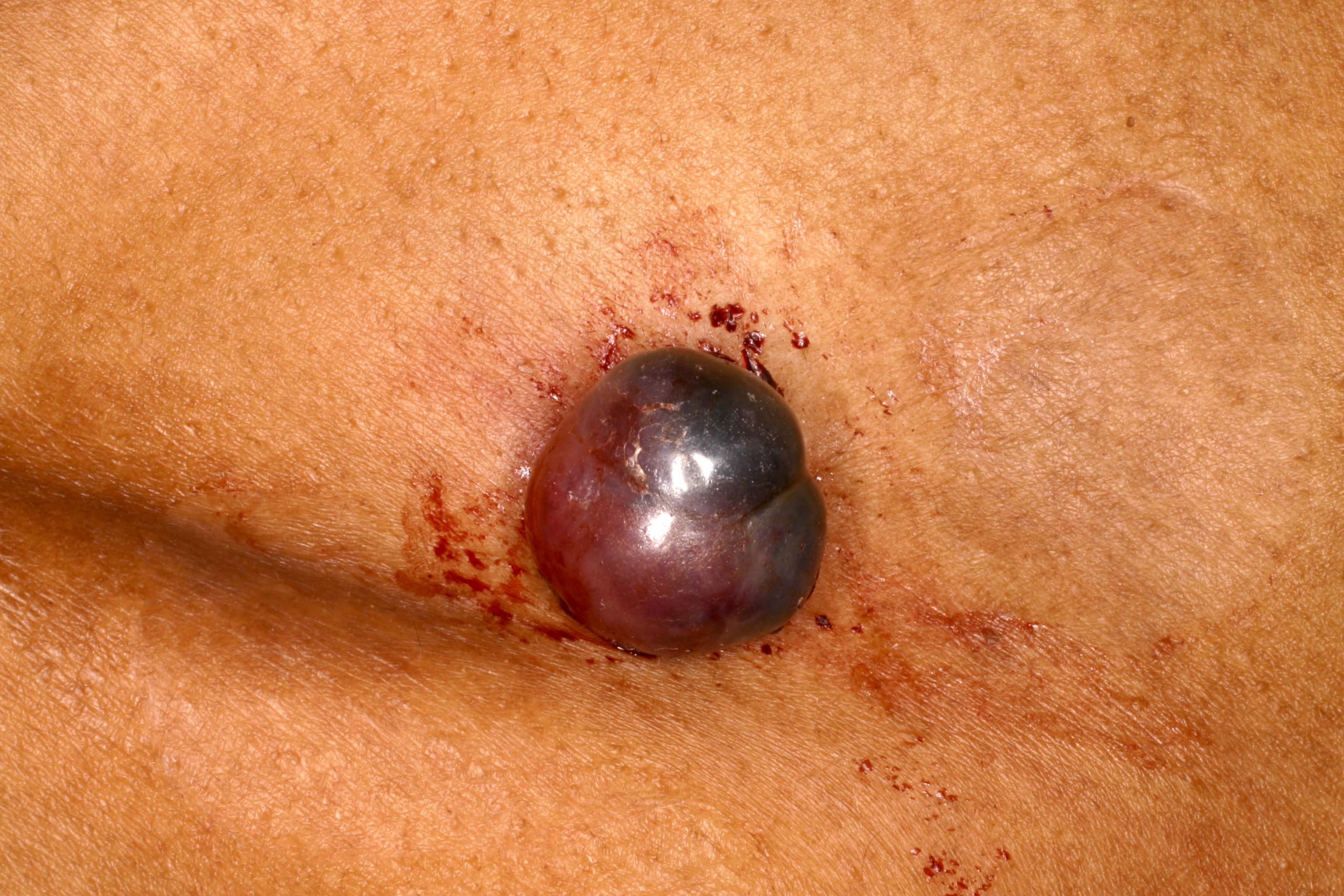
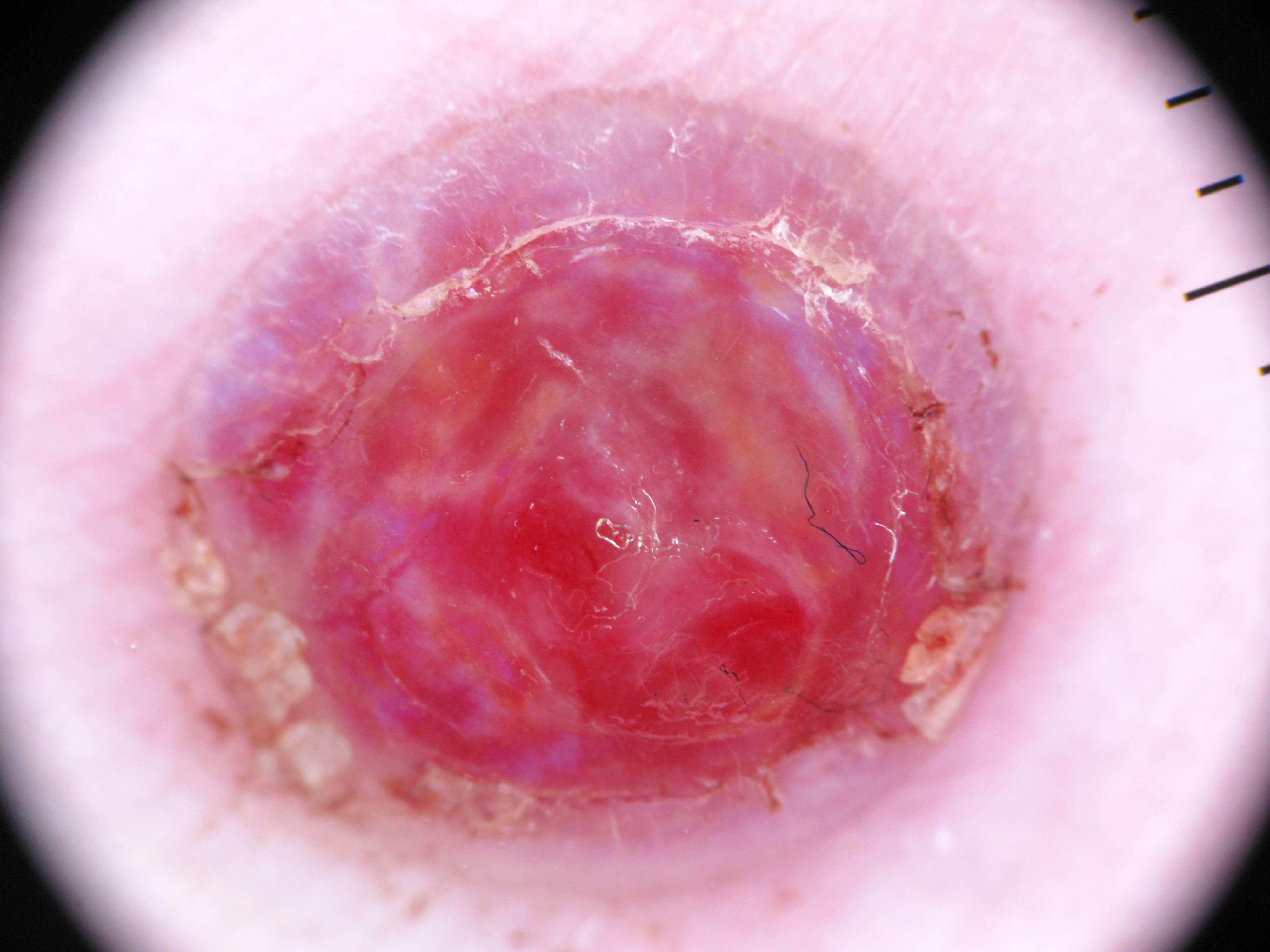
- Benign vascular lesion that is characterized by the proliferation of capillary sized blood vessels and typically presents as a solitary, rapidly growing, bright red papule that frequently bleeds following trauma
Essential features
- Rapidly growing, benign vascular lesion that frequently ulcerates and bleeds and is often located on sites of frequent trauma like the face, lips, mucosa and fingers
- Histopathologic features include lobules containing numerous capillary sized vessels in the dermis within an edematous stroma in early lesions or fibrotic stroma with fibrous septa in older lesions; secondary changes, such as a mixed cell inflammatory infiltrate, ulceration and granulation tissue formation, are common
- Treatment usually involves shave removal with electrodesiccation or surgical excision; may recur following treatment
Terminology
- Pyogenic granuloma is the term most often used by clinicians; however, it is a misnomer as it is neither infectious nor granulomatous
- Tumor of pregnancy or granuloma gravidarum are names sometimes given when developed during pregnancy
ICD coding
- ICD-10: L98.0 - pyogenic granuloma
Epidemiology
- Demographics
- Affects individuals of all age groups, with the highest prevalence in young adults
- No gender predilection is observed
- Mucosal lesions may be more common in women (J Am Acad Dermatol 2000;42:1012)
- Risk factors
- Majority of cases with no apparent cause
- Recent history of trauma
- Pregnancy
- Oral contraceptives
- Systemic retinoids, BRAF inhibitors and EGFR inhibitors have been associated with lobular capillary hemangiomas, particularly in the periungual regions; however, some believe these lesions represent solely excessive granulation tissue (Open Access Maced J Med Sci 2017;5:423)
Sites
- Face, lips, gingiva, hands and fingers are the most common but may occur anywhere (Open Access Maced J Med Sci 2017;5:423)
Pathophysiology
- Unclear
- There is controversy about whether the proliferation of capillaries is a reactive or neoplastic process (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2024;12:e6160)
Etiology
- Most cases occur without an apparent cause
- Some cases are associated with recent trauma
- Higher incidence is noted during pregnancy and with the use of oral contraceptives, suggesting a possible hormonal influence
- Reference: Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2024;12:e6160
Clinical features
- Typically appears as a rapidly growing, bright red papule that is often pedunculated or polypoid on the skin or mucosa
- Lesion frequently ulcerates and bleeds
- Rare presentations include
- Multiple lesions with satellite formations
- May occur within a pre-existing capillary malformation, such as a port wine stain (Dermatol Reports 2021;13:9115)
- As a skin colored nodule if present in the deep dermis, subcutaneous tissue or intravascularly
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is usually made clinically but may be confirmed with a biopsy
Prognostic factors
- Benign but may recur after treatment
Case reports
- 15 year old boy with exophytic papule on the lower lip (Dent Traumatol 2020;36:446)
- 33 year old pregnant woman with bleeding intranasal lesion (Maedica (Bucur) 2024;19:160)
- 36 year old woman with bright red papule on the thumb (Dermatol Ther 2022;35:e15194)
- 40 year old man with exophytic mass on the thumb (J Surg Case Rep 2023;2023:rjad157)
- 45 year old woman with friable pedunculated papule on the upper lip (N Engl J Med 2022;387:1979)
Treatment
- Shave removal followed by electrodesiccation or electrocautery is often sufficient, especially for smaller lesions
- Complete excision
- Other less common treatments include silver nitrate and laser therapy
- Reference: Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2024;12:e6160
Clinical images
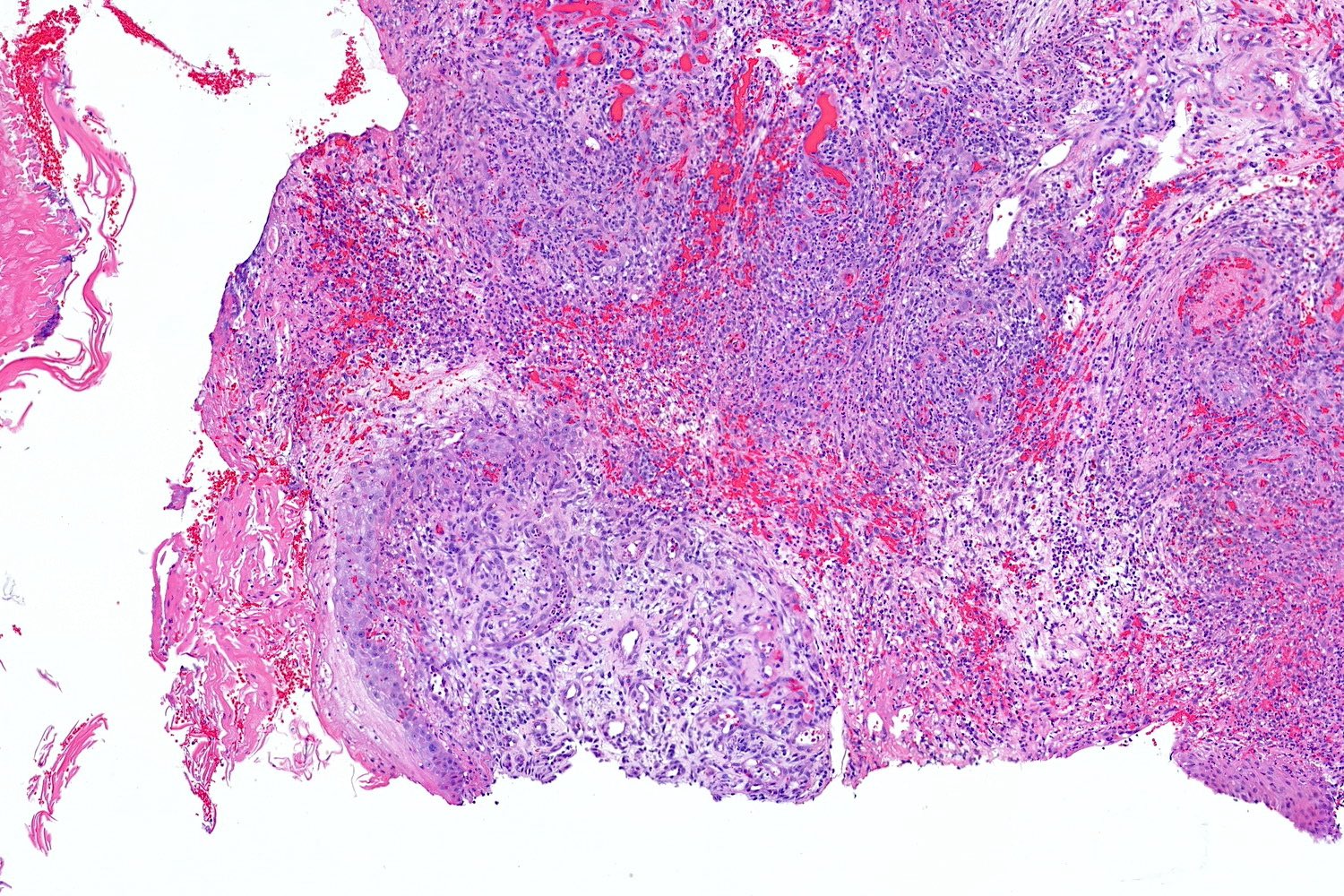
Microscopic (histologic) description
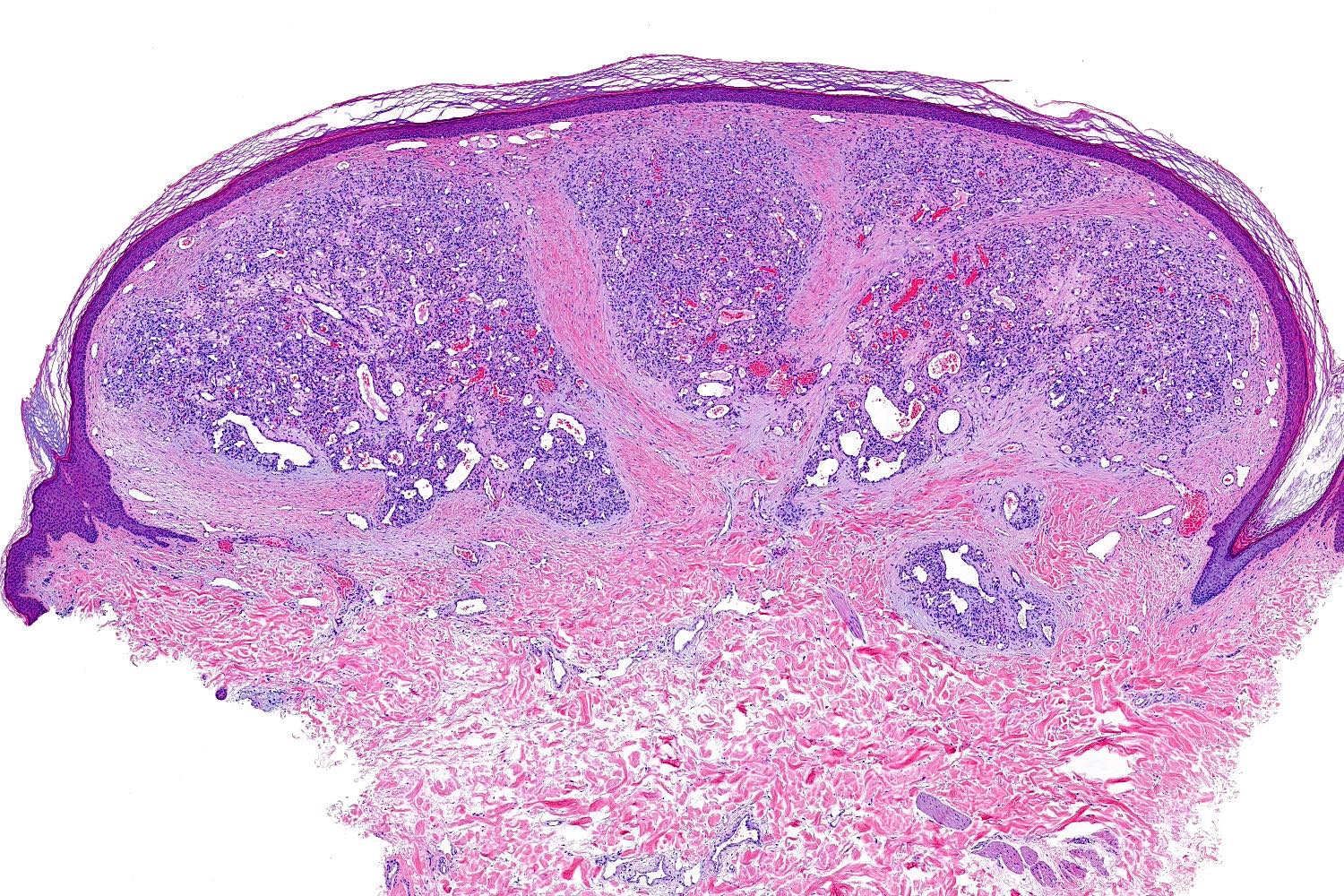
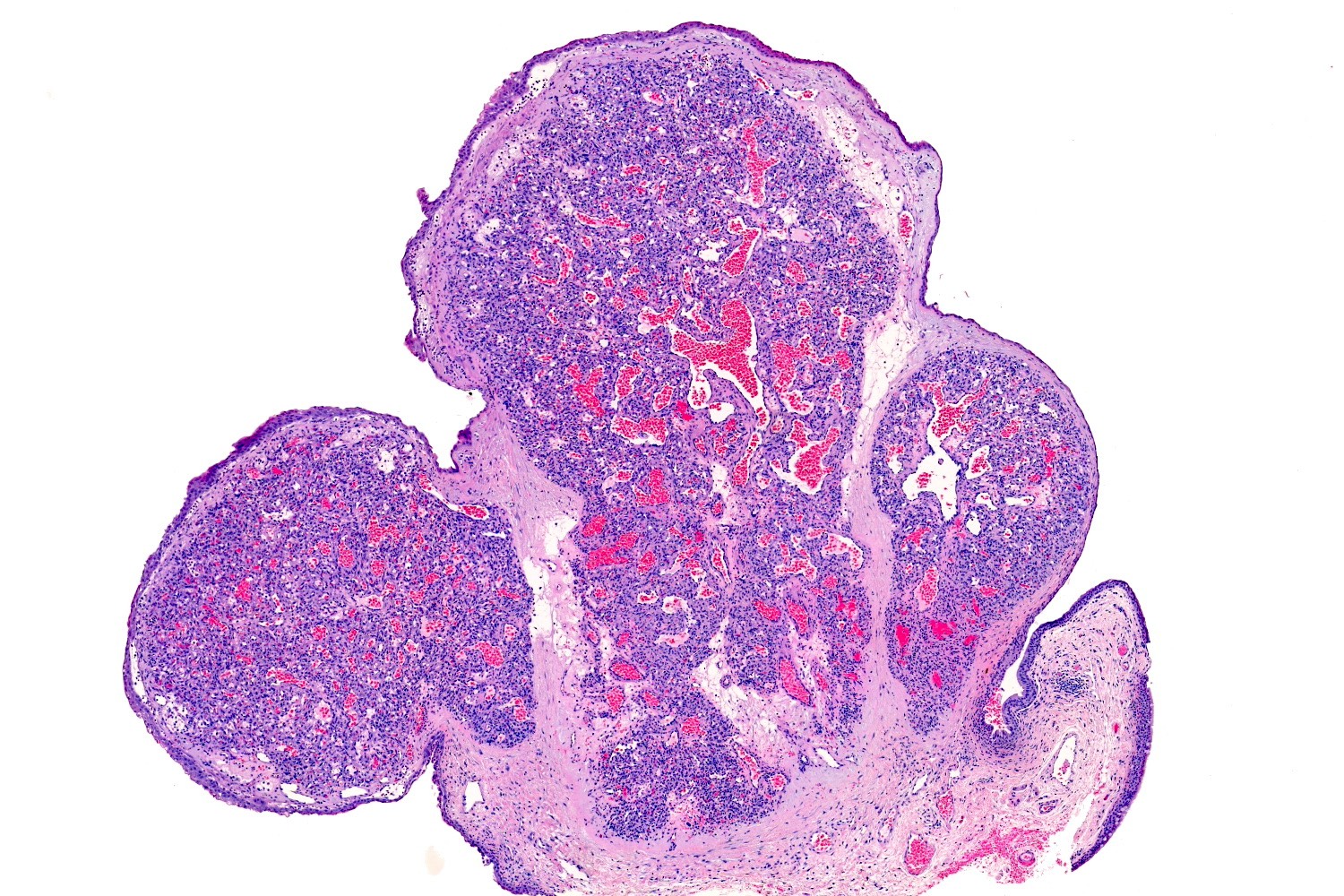
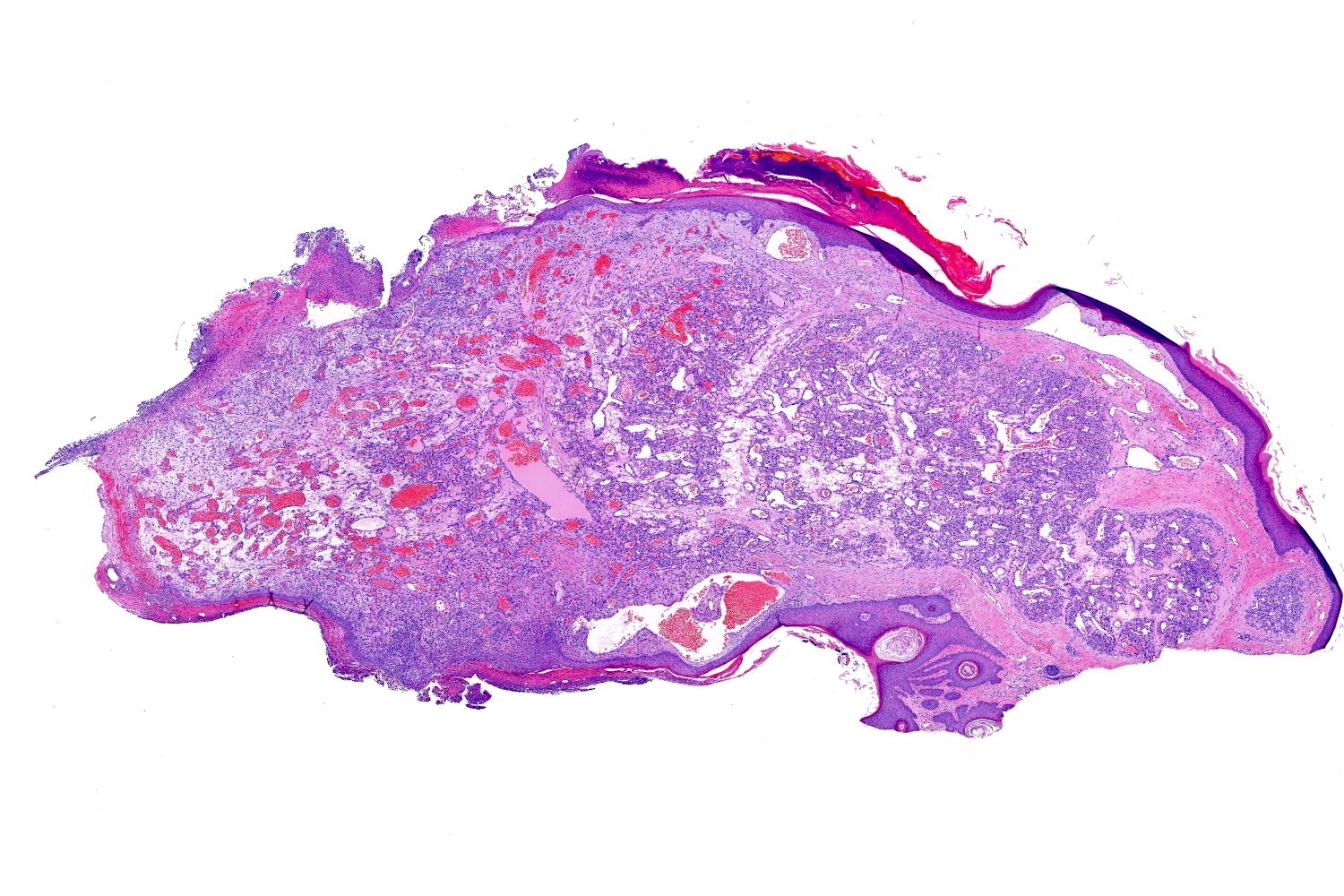
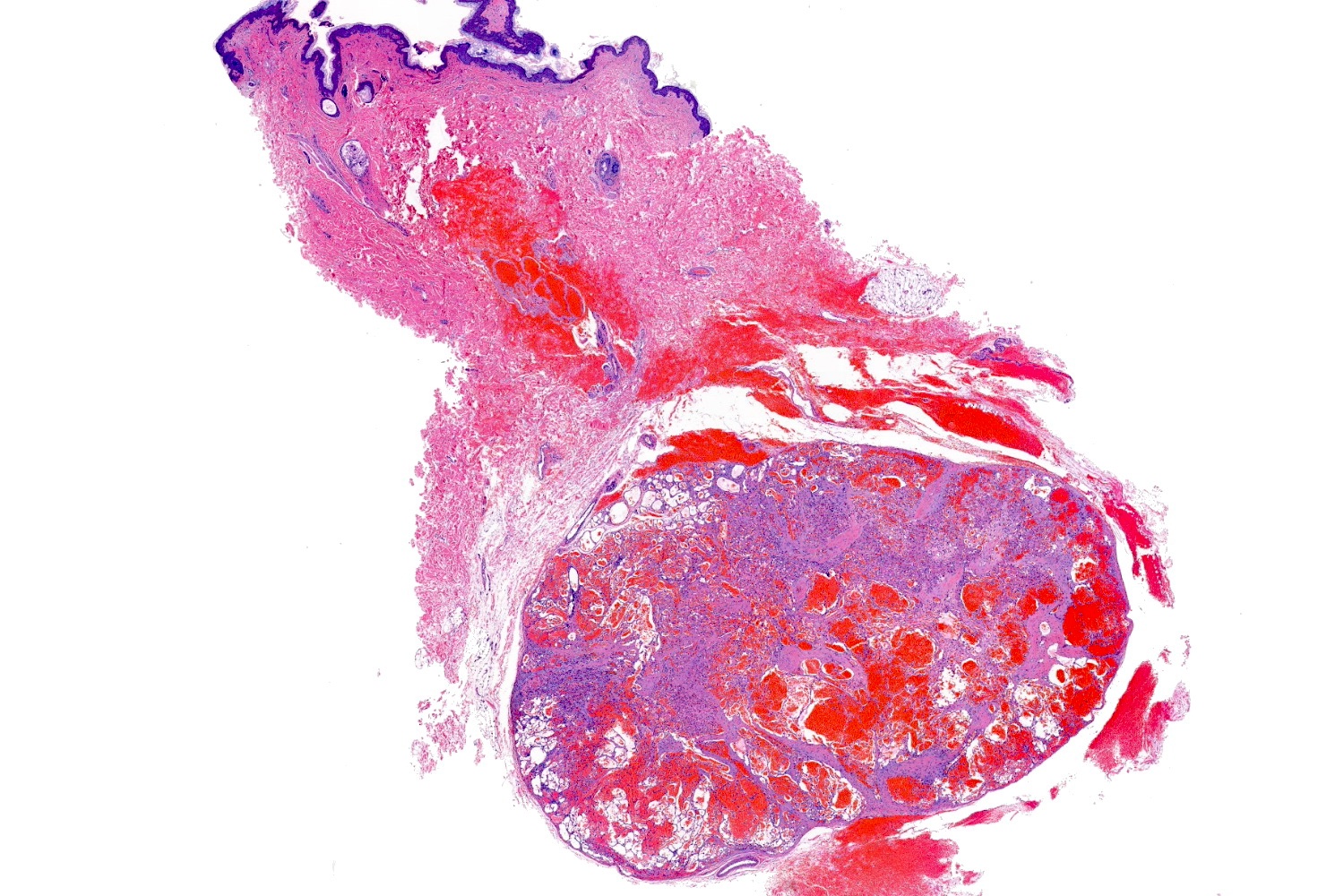
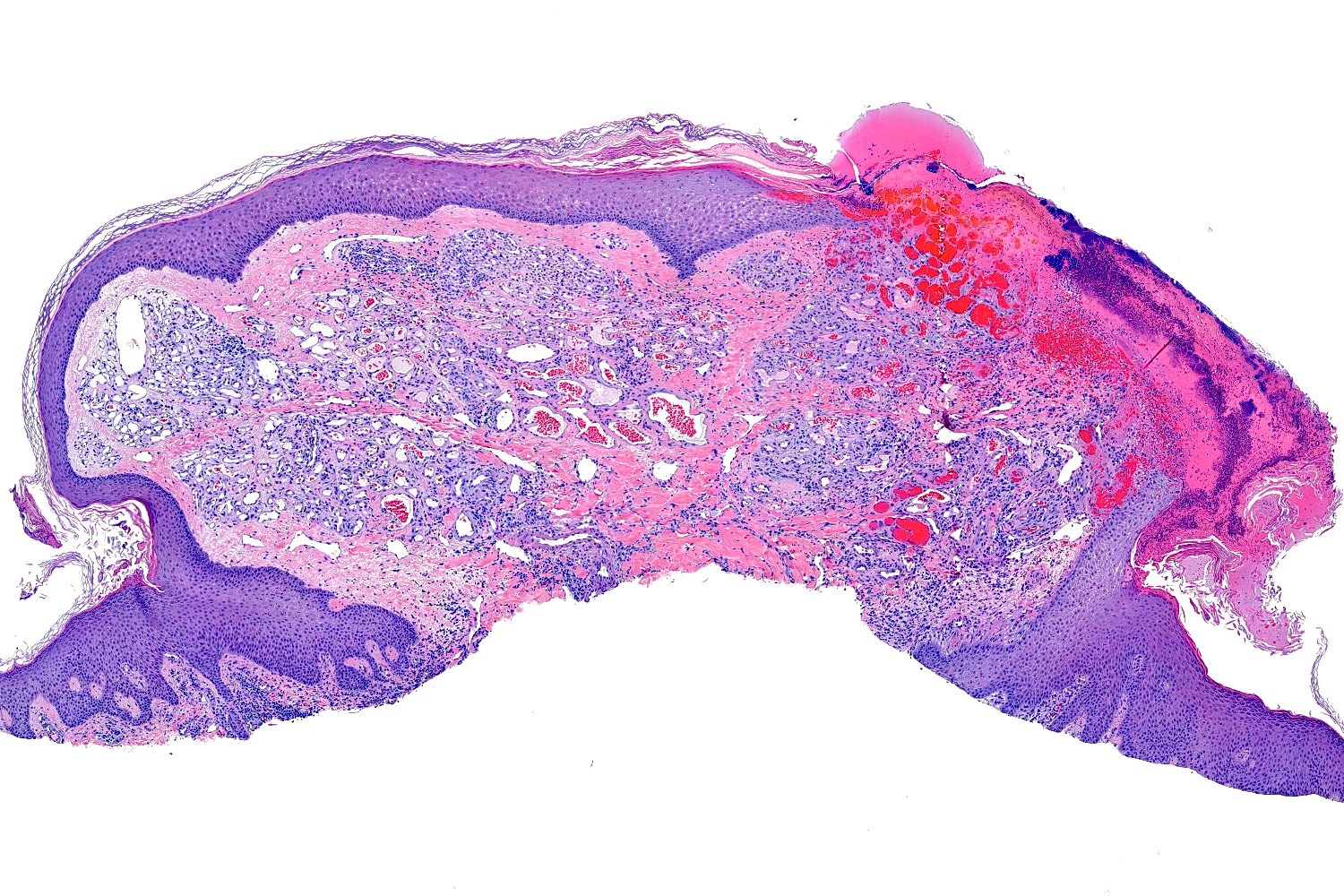
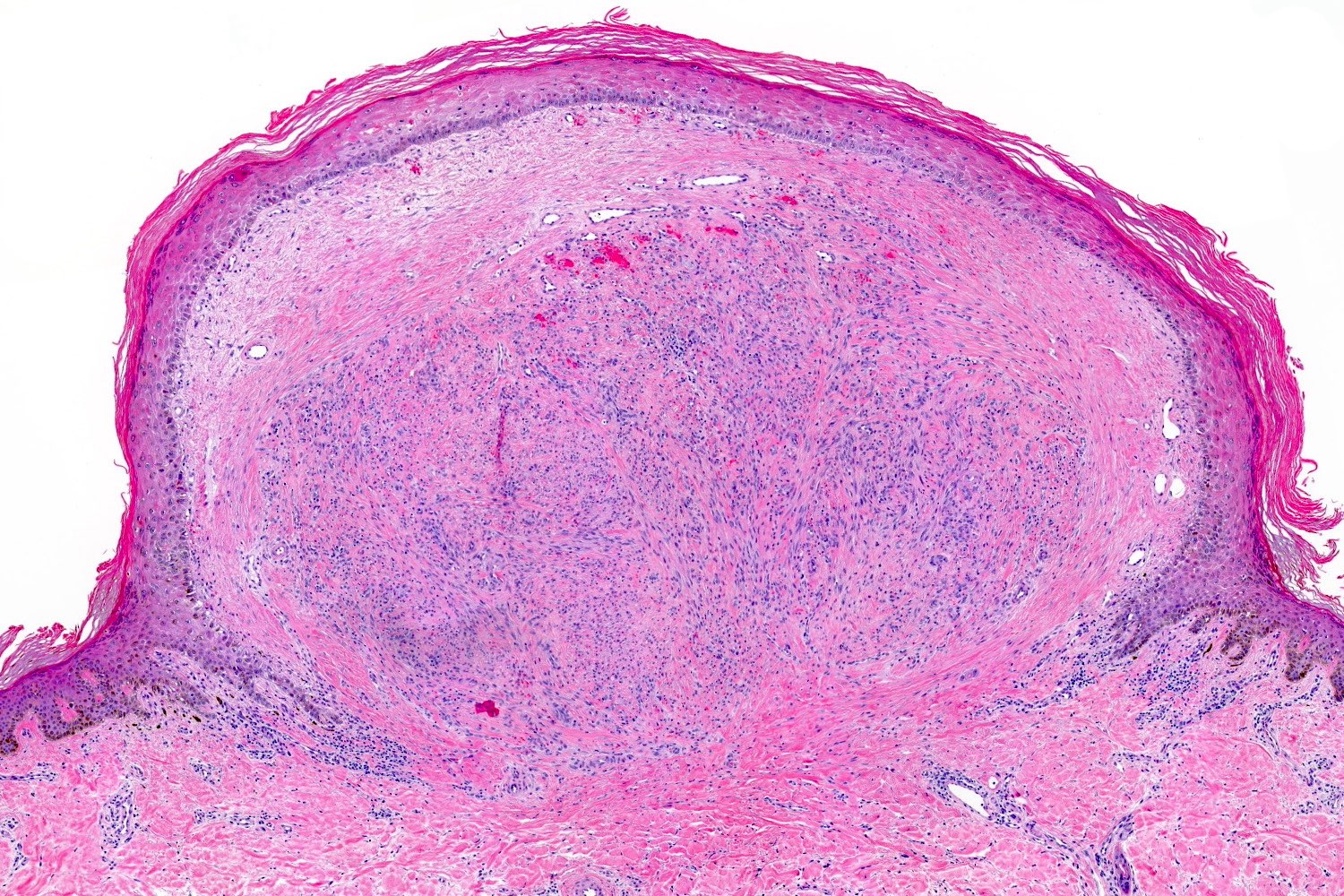
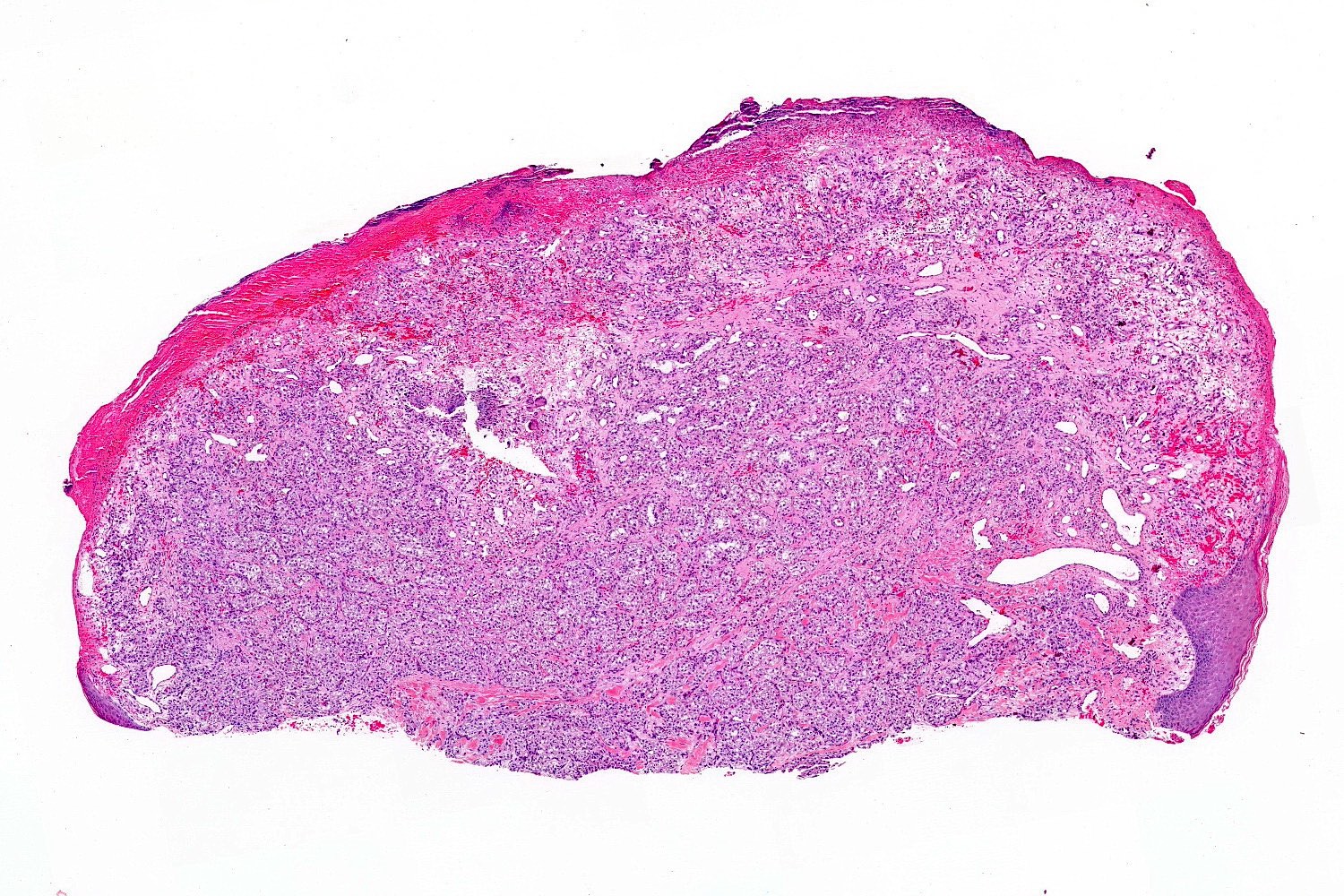
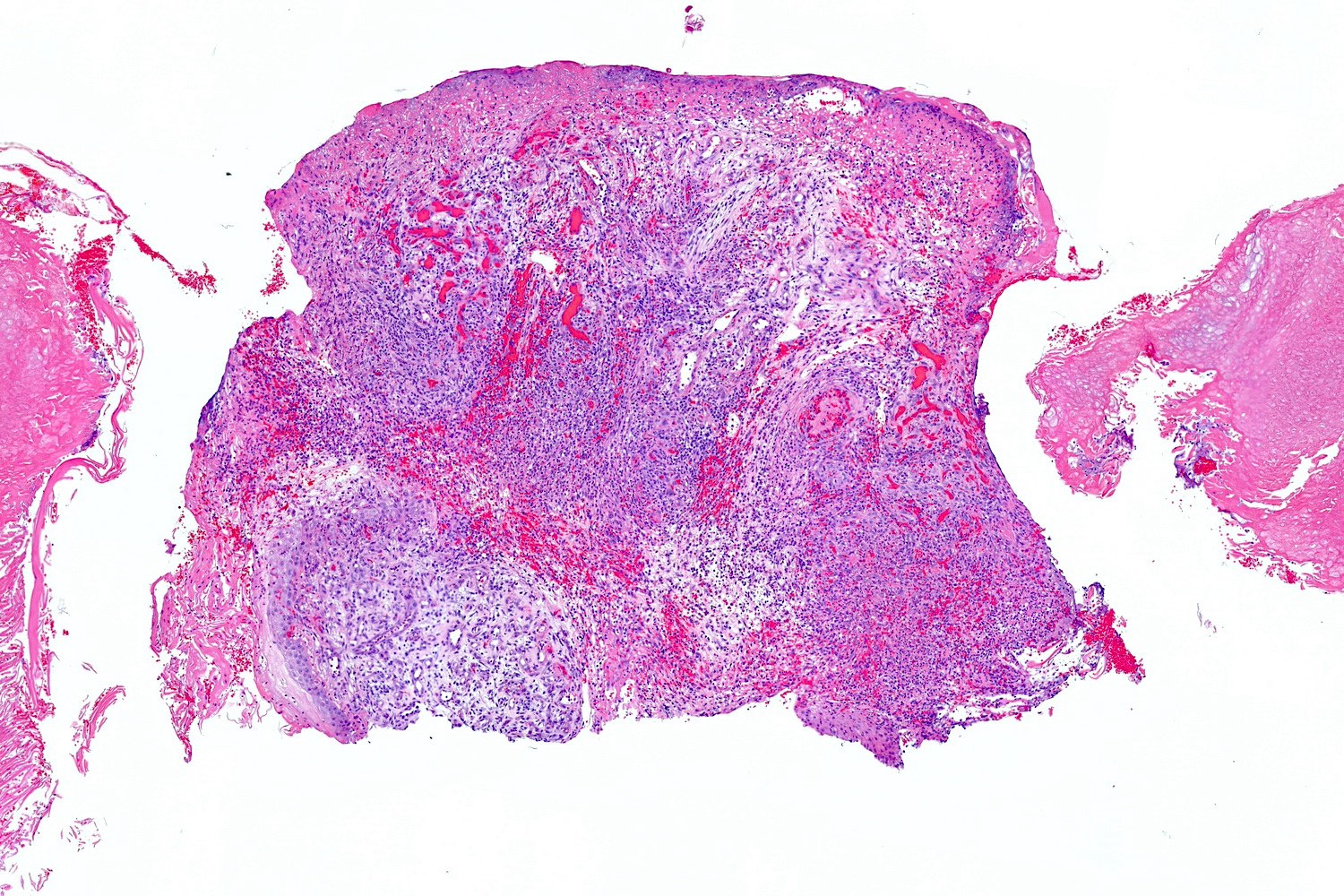
- Frequently exophytic or polypoid, though may also be sessile
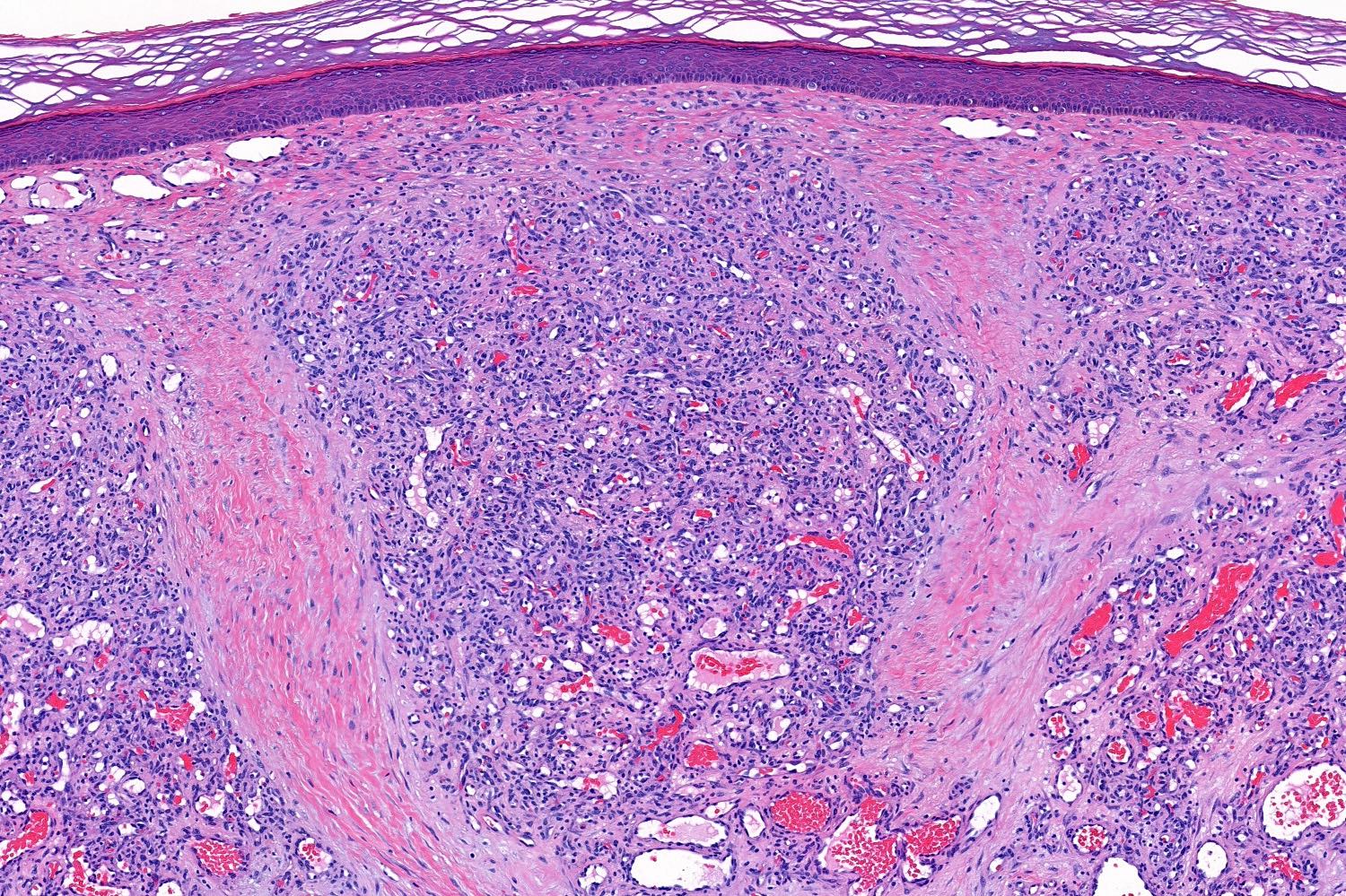
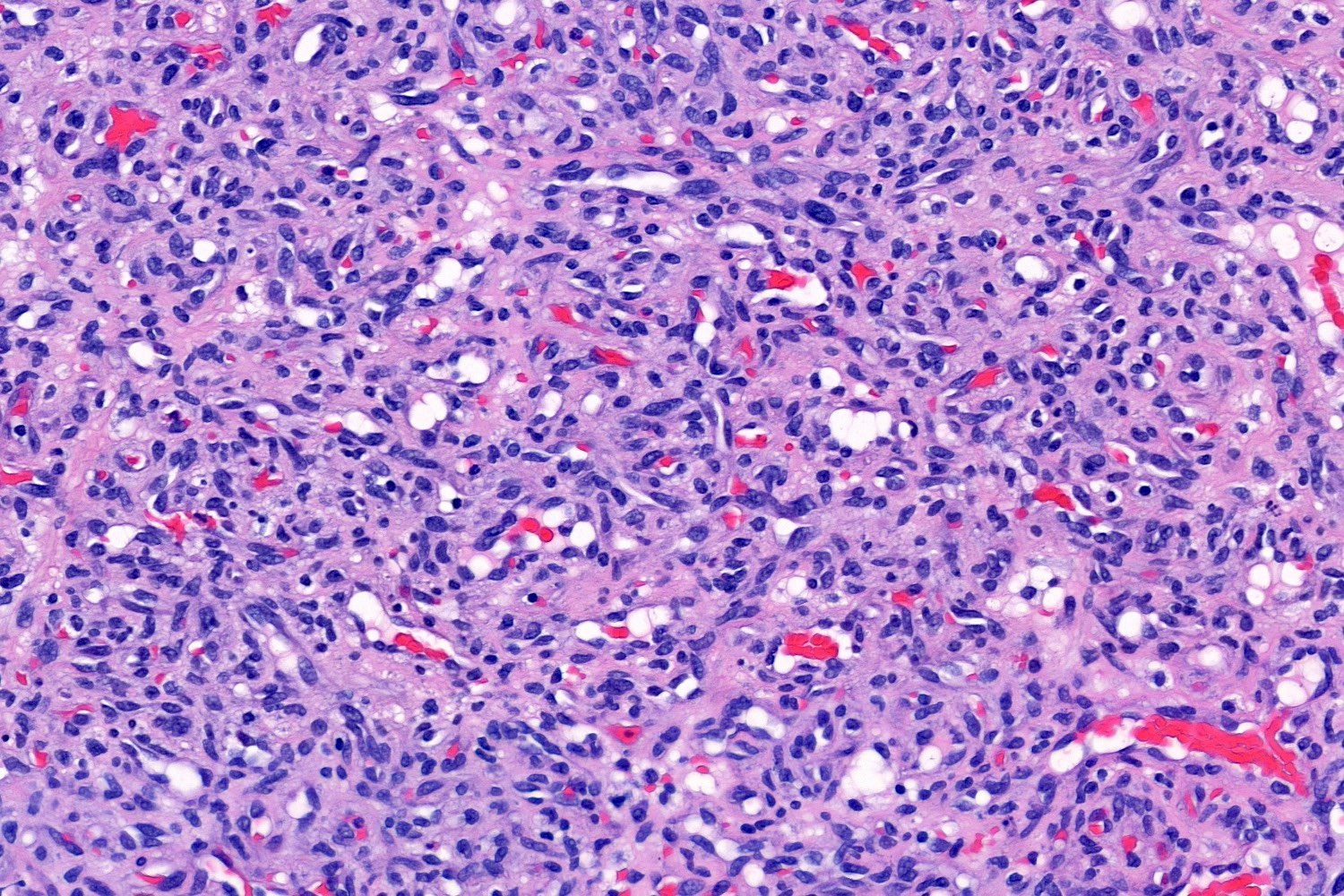
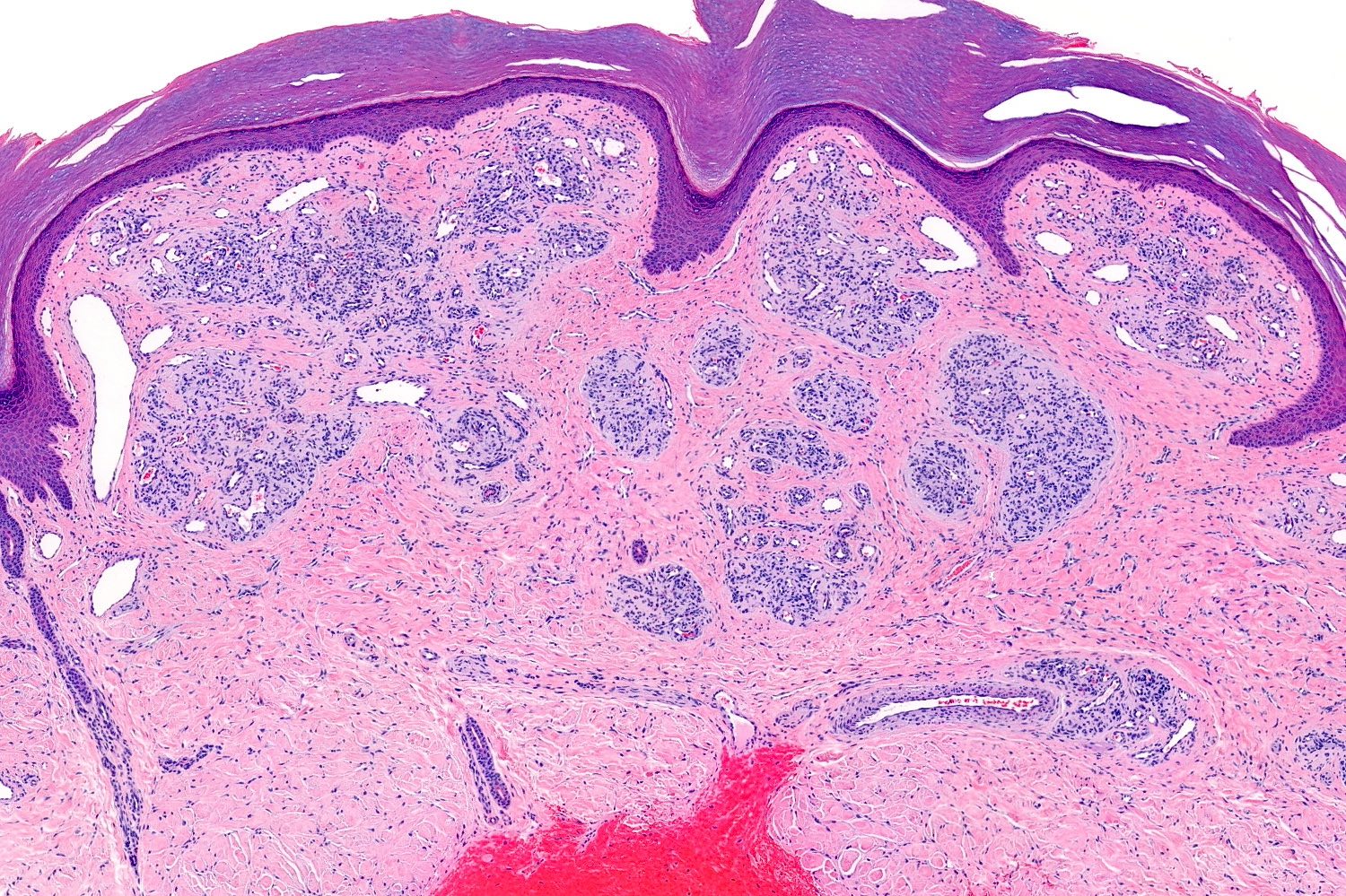
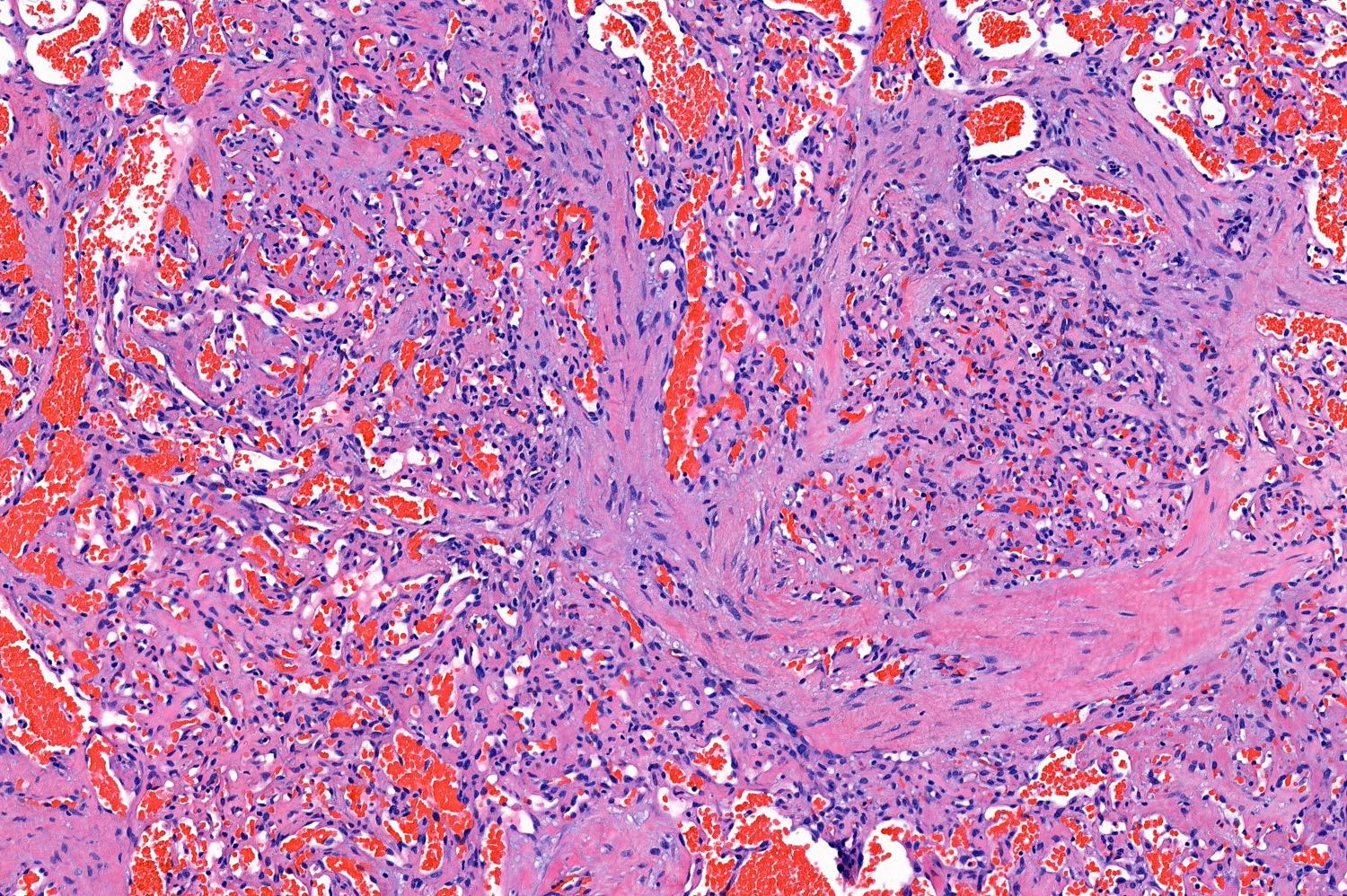
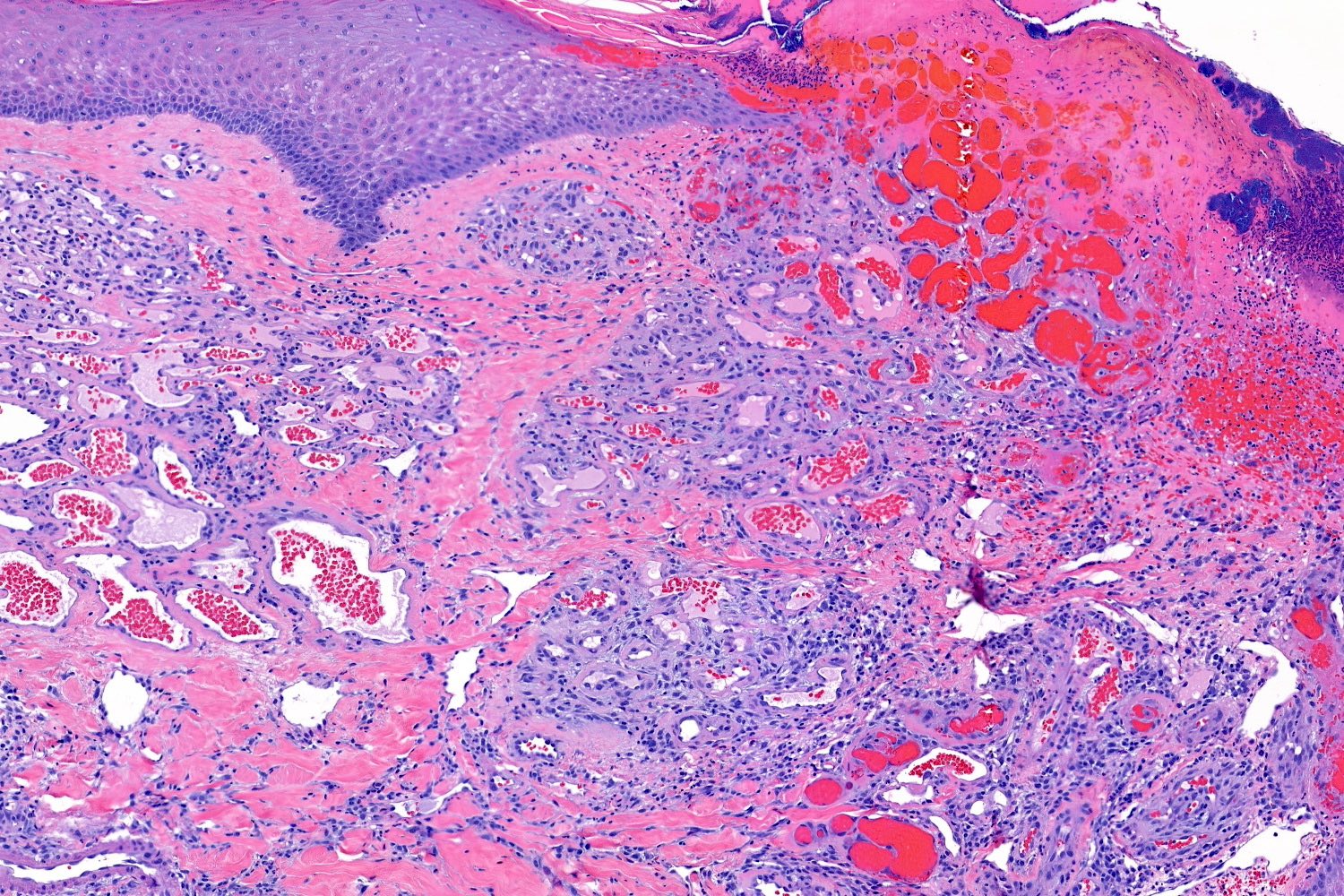
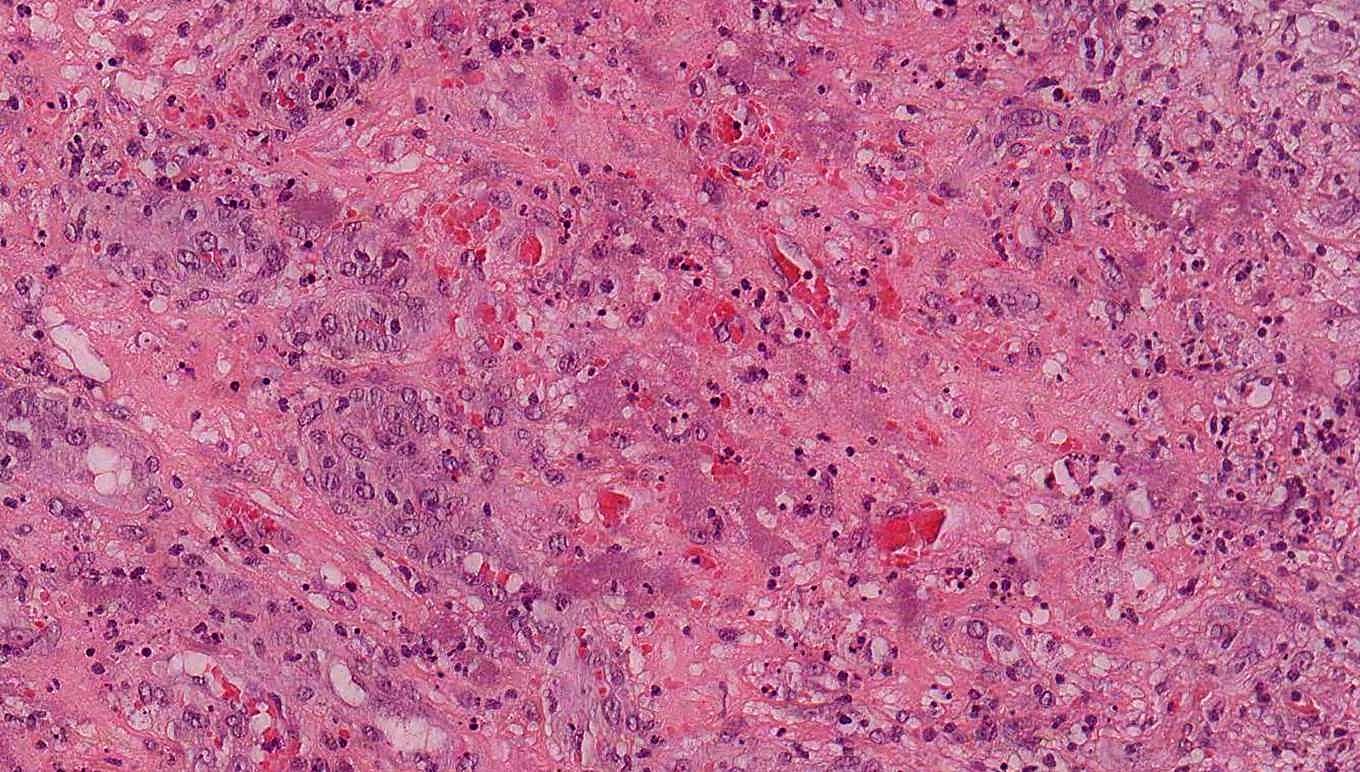
- Characterized by lobules in the dermis that contain numerous capillary sized vessels
- Lobules are separated by fibrous septa or trabeculae, especially in older lesions
- Stroma is often edematous and more mucinous in early lesions, becoming more fibrotic with time
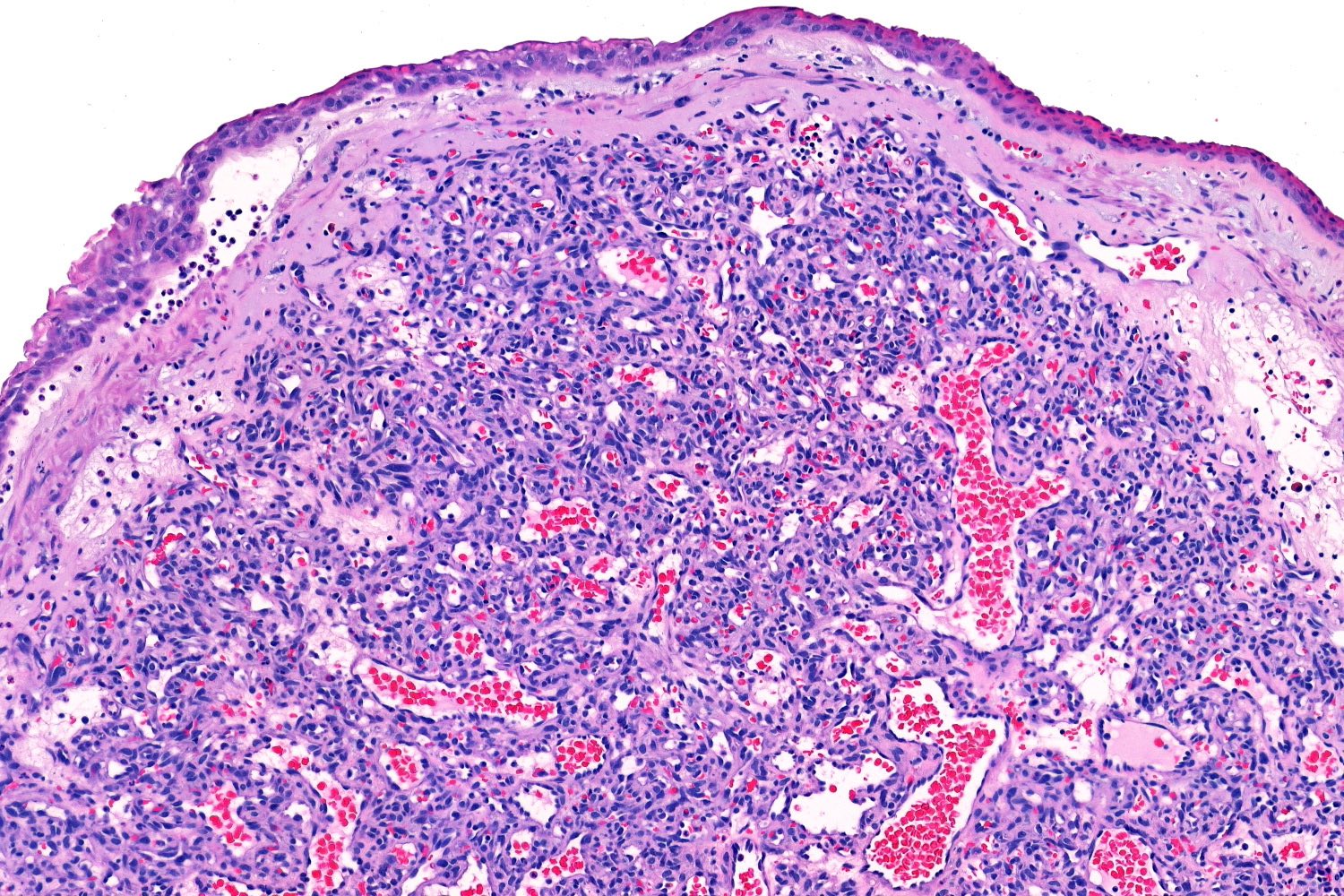
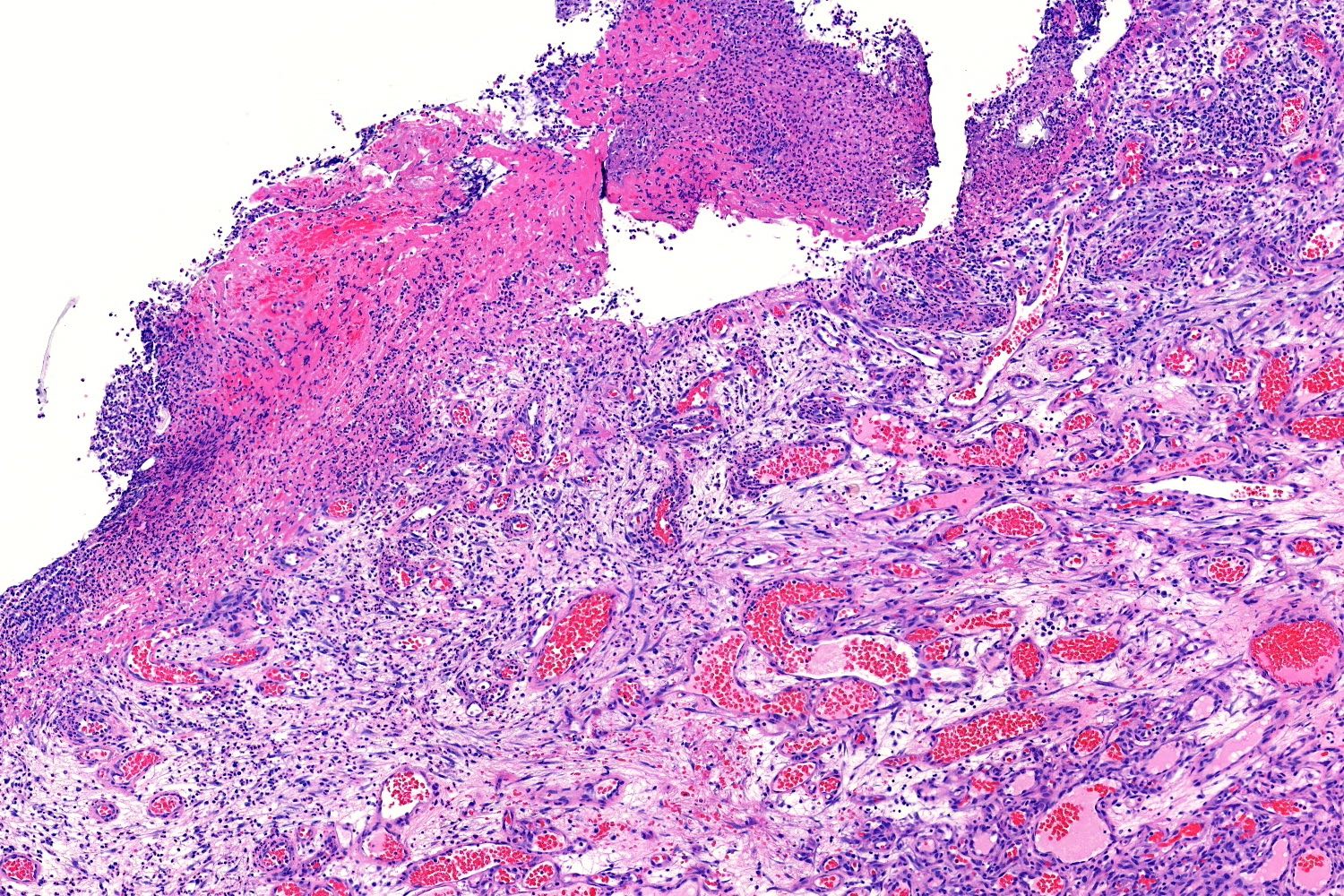
- Epidermal collarette is commonly observed
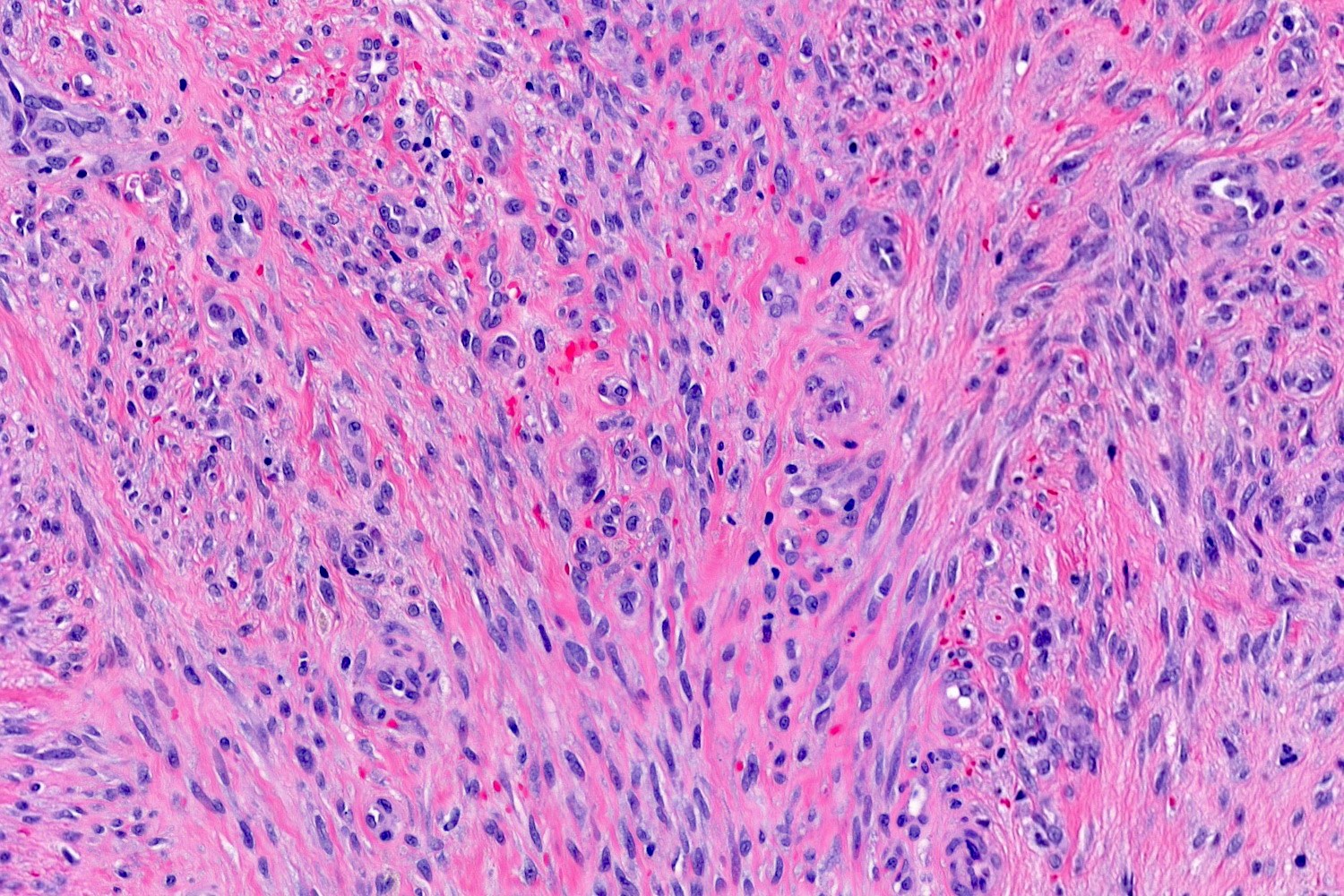
- Cytologic features include bland endothelial cells that may be plump; mitotic figures may be frequent
- Fibroblasts and pericytes are also present
- Secondary changes may obscure the underlying architecture and morphology, which may only be present at the base of the lesion
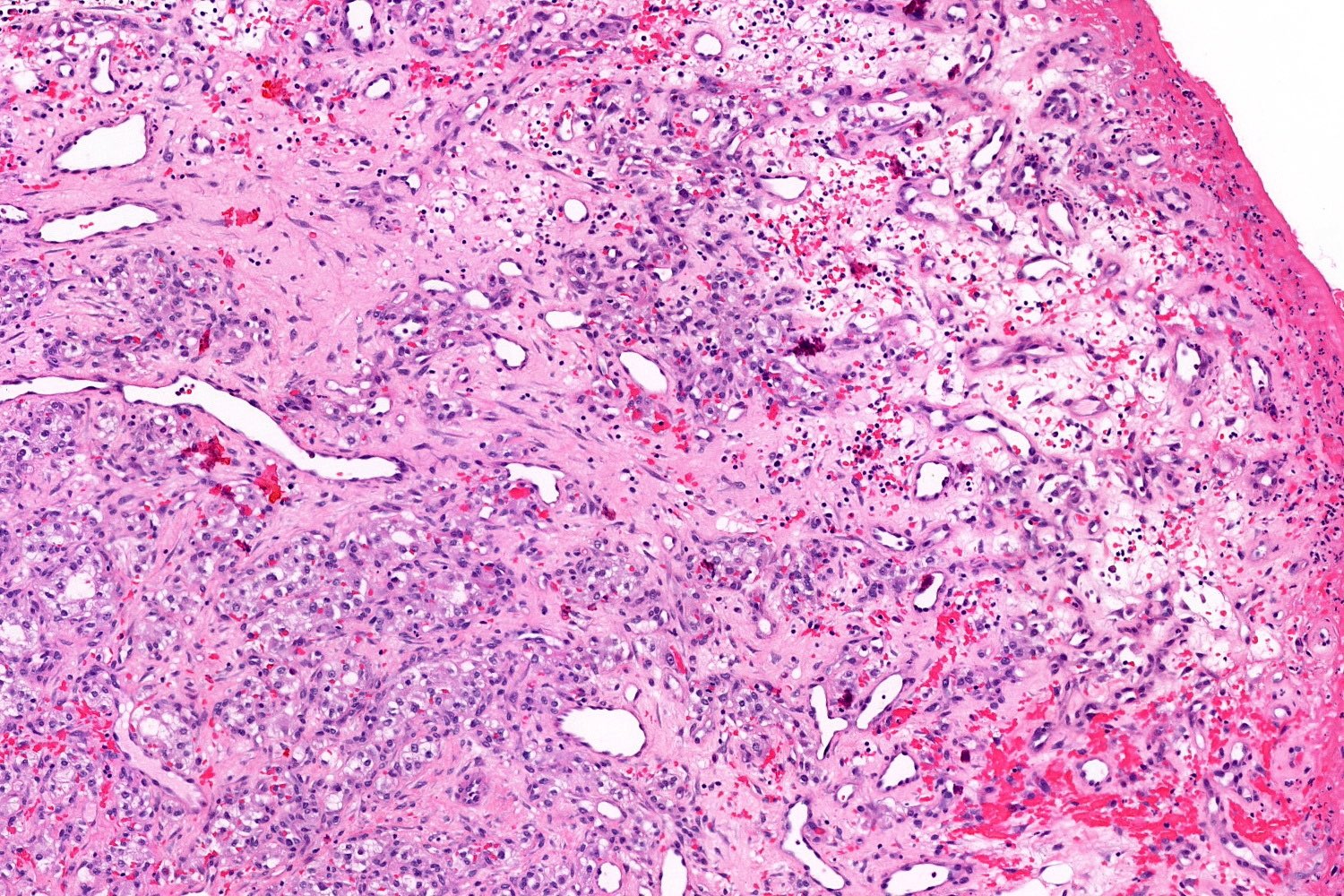
- Ulceration at the surface of the lesion is common
- Granulation tissue may be present at the surface of ulcerated lesions
- Secondary mixed cell infiltrate with lymphocytes and neutrophils is common (Am J Surg Pathol 1980;4:470)
- May rarely be present intravascularly, affect the deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue or internal organs (Cureus 2023;15:e45142, Am J Dermatopathol 2007;29:408, Case Rep Pathol 2022;2022:5641608)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- ERG
- CD31
- CD34
- FLI1
- Factor VIII
- SMA (stains pericytes) (Pathol Int 2003;53:1)
Negative stains
Videos
Pyogenic granuloma under the microscope
(lobular capillary hemangioma)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, shave biopsy:
- Lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma) (see comment)
- Comment: Microscopic examination reveals an exophytic lesion composed of lobules of numerous capillary sized blood vessels separated by fibrous septa consistent with a lobular capillary hemangioma.
Differential diagnosis
- Hemangioma (cherry angioma):
- Traumatized or ulcerated hemangiomas may resemble lobular capillary hemangioma
- Vessels are fewer in number and larger in caliber
- Granulation tissue:
- Irregularly distributed, larger dilated vessels within a loose, edematous stroma
- Secondary granulation may be observed superficially overlying a lobular capillary hemangioma
- Kaposi sarcoma (nodular stage):
- Pyogenic granuloma-like Kaposi sarcoma has been described (Dermatol Online J 2012;18:4)
- Displays areas with erythrocytes and hyaline globules between spindle cells
- Positive for D2-40 (podoplanin) and HHV8 (LNA)
- Bacillary angiomatosis:
- Characterized by basophilic granular aggregations representing the bacteria
- Presence of scattered neutrophils
- Endothelial cells appear more pale pink in color
- Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (cutaneous):
- Commonly located on the scalp
- Demonstrates clear cell differentiation
- Shows marked cytologic atypia
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 30 year old woman presents with a bleeding papule on the right hand for 2 weeks duration. A shave biopsy of the lesion is performed. Based on the histopathologic images above, what is the diagnosis?
- Bacillary angiomatosis
- Granulation tissue
- Lobular capillary hemangioma
- Pyogenic granuloma-like Kaposi sarcoma
- Ulcerated cherry angioma
Practice answer #1
C. Lobular capillary hemangioma. The base of the lesion shows lobules of capillary sized vessels of a lobular capillary hemangioma. Answer B is incorrect because the surface of the lobular capillary hemangioma is ulcerated and granulation tissue is present below the ulcer; however, toward the base of the specimen are capillary sized vessels of a lobular capillary hemangioma. Answer A is incorrect because basophilic aggregates of bacteria are not present. Answer E is incorrect because the capillary sized caliber vessels toward the base of the lesion are too small for a cherry hemangioma. Answer D is incorrect because spindled endothelial cells with intervening erythrocytes are not present.
Comment Here
Reference: Lobular capillary hemangioma
Comment Here
Reference: Lobular capillary hemangioma
Practice question #2
Which of the following is an important distinguishing feature of a lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma)?
- Capillary sized vessels
- Extravasated erythrocytes
- Hyaline globules
- Large caliber vessels
- Presence of basophilic granular material
Practice answer #2
A. Capillary sized vessels. The vessels of a lobular capillary hemangioma are small, numerous and typically in multiple lobules. Answer B is incorrect because many vascular proliferations have extravasated erythrocytes and therefore this is not a feature used to distinguish between various vascular entities. Answer C is incorrect because hyaline globules may be seen in other vascular lesions (such as Kaposi sarcoma) but are not characteristic of lobular capillary hemangiomas. Answer E is incorrect because basophilic granular material is seen in bacillary angiomatosis, which can mimic lobular capillary hemangioma both clinically and histopathologically. .
Comment Here
Reference: Lobular capillary hemangioma
Comment Here
Reference: Lobular capillary hemangioma