Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Tranesh G. Vellus hair cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticvelloushaircyst.html. Accessed September 7th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Originally reported in children and young adults
- No gender or racial predilection
Epidemiology
- Occasionally associated with renal failure or various genodermatoses, including pachyonychia congenita, anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
- Rarely associated with Lowe syndrome, an oculocerebrorenal syndrome characterized by Fanconi-type renal failure, intellectual disabilities, ocular abnormalities
- Cases may be inherited (autosomal dominant), which may be manifest at birth, and is more likely to show cysts on extensor aspects of limbs
Sites
- Small, multiple cysts over chest wall and extremities
Pathophysiology
- Eruptive vellus hair cysts probably develop due to occlusion of the infundibulum of vellus hairs with resultant cystic dilatation and retention of keratinous debris and vellus hairs
- The primary cause of the obstruction is unknown
- They may also represent follicular hamartomas
Clinical features
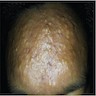
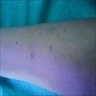
- Patients present with numerous asymptomatic, discrete, soft, flesh-colored or reddish-brown papules, 1 - 5 mm across, particularly over the parasternal area, although the distribution may be quite widespread
Case reports
- 12 year old girl with eruptive vellus hair cyst presenting as asymptomatic follicular papules (Indian Dermatol Online J 2013;4:213)
- 15 year old boy with eruptive vellus hair cysts (Dermatology 2012;224:15)
- 18 year old man with facial variant of eruptive vellus hair cyst (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2014;80:96)
Treatment
- Local surgery
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
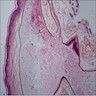
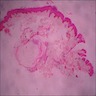
- Mid-dermal cyst containing laminated keratin and many vellus hairs
- Epithelial lining consists of several layers of squamous epithelium, often with a granular cell layer
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Pigmented follicular cyst
- Steatocystoma multiplex
Additional references