Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Andeen NK, Tretiakova M. Unclassified. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormalignantnos.html. Accessed April 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Not a distinct subtype of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) but a diagnostic category for tumors that do not readily fit into any of the RCC subtypes or have pure sarcomatoid / rhabdoid histology (IARC: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th Edition, 2016)
- Histologically heterogeneous, most commonly high grade
Essential features
- Heterogeneous group of RCC tumors that are not readily classifiable
- Immunohistochemistry, fluorescent in situ hybridization and other molecular techniques may aid in classification
- Important category enabling separation of unusual tumors from common subtypes and their further grouping / reclassification as distinct entities using advanced techniques
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C64.9 - malignant neoplasm of unspecified kidney, except renal pelvis
Epidemiology
- Age range 21 - 91 years, median ~60 (Histopathology 2018;72:305)
- Male predominance (Histopathology 2018;72:305)
- Comprise 0.7 - 7% of RCCs, 3 - 5% in specialized centers (J Urol 2002;168:950, BJU Int 2007;100:802, BJU Int 2012;110:786)
Sites
- Kidney
Clinical features
- Clinical presentation similar to other RCC subtypes (IARC: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th Edition, 2016)
- Most present at advanced stage and 60 - 80% are grade 3 - 4 (J Urol 2002;168:950, BJU Int 2007;100:802, BJU Int 2012;110:786, BJU Int 2007;100:802, Histopathology 2018;72:305)
- Compared to clear cell RCC, unclassified RCC present as larger tumors with frequent necrosis, higher incidence of nodal metastases and direct invasion into adjacent organs, higher risk of distant metastases and shorter median survival (J Urol 2002;168:950, BJU Int 2007;100:802, BJU Int 2012;110:786, Urology 2010;76:580)
Radiology description
- Radiographic features similar to other RCCs
Prognostic factors
- Outcome is often associated with grade, stage and clinicopathologic features known to be relevant in other forms of RCC (BJU Int 2012;110:786)
- The majority of studies show that unclassified RCC is more aggressive with 1.6 - 1.7X the mortality of clear cell RCC (J Urol 2002;168:950, BJU Int 2007;100:802, BJU Int 2012;110:786), however one study showed that overall cancer specific survival is similar in matched cohorts after adjusting for grade, stage and other parameters (Urology 2010;76:580)
- Despite that discrepancy, > 50% of high grade unclassified RCC are dead of disease within 2 years
- For low grade tumors there may be an indolent course
Case reports
- 32 year old man with prominent morphologic heterogeneity (J RPCA 2016;48:S127)
- 51 year old patient with grade 4 unclassified renal cell carcinoma (Cancer Biol Ther 2014;15:1439)
- 55 year old man with initial presentation of tongue metastasis (J Med Case Rep 2017;11:314)
- 56 year old man with response to PD-1 inhibitor (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2017;15:e517)
- 56 year old woman with spontaneous regression of pulmonary nodules after nephrectomy (Mol Clin Oncol 2016;5:49)
- 76 year old woman with unclassified mucinous renal cell carcinoma (Korean J Urol 2014;55:690)
Treatment
- No standardized treatment but whenever feasible immunotherapy with nephrectomy is warranted (J Urol 2002;168:950)
Gross description
- Median 5 cm with extensive involvement of kidney and frequent necrosis (Histopathology 2018;72:305)
Gross images
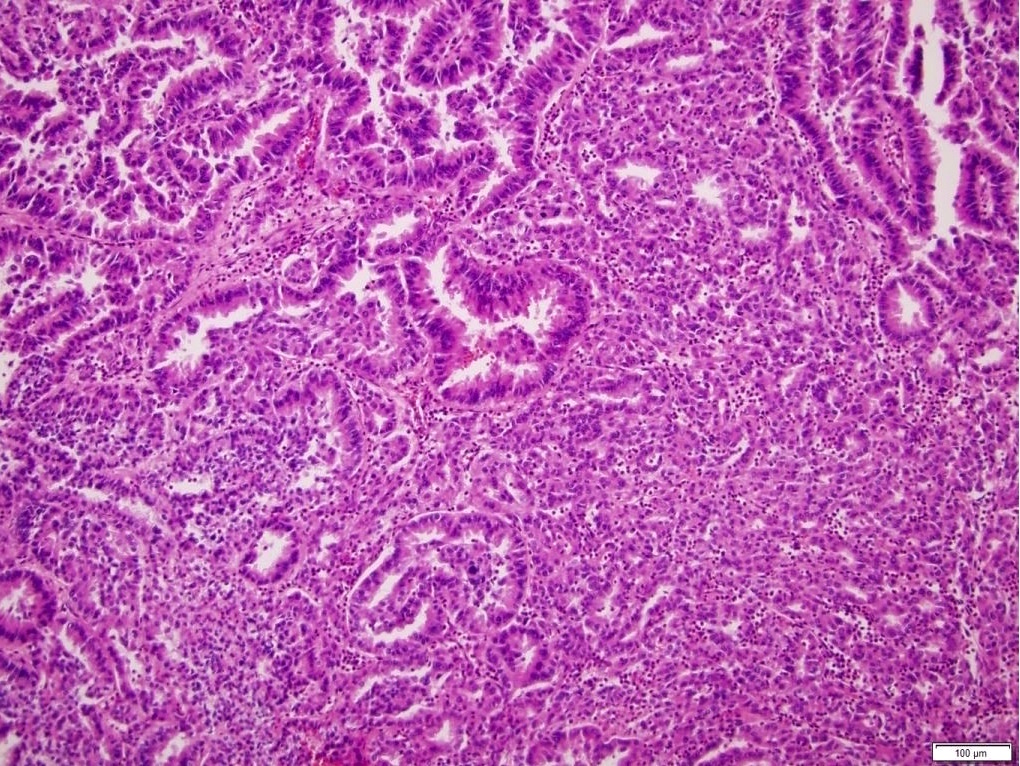
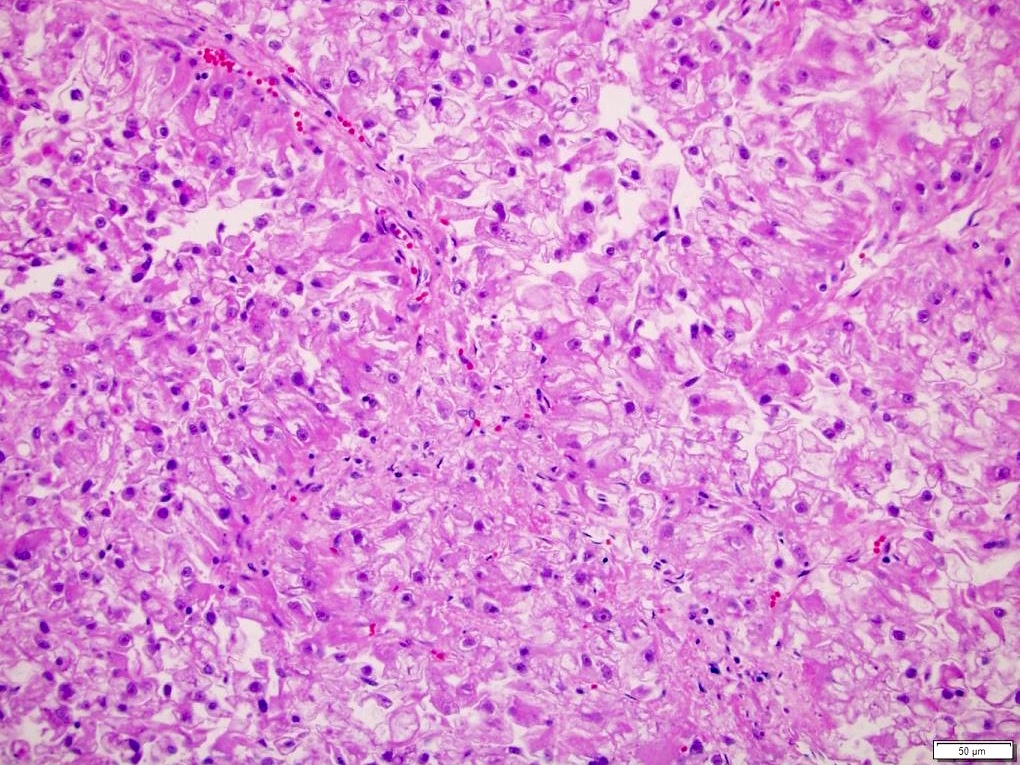
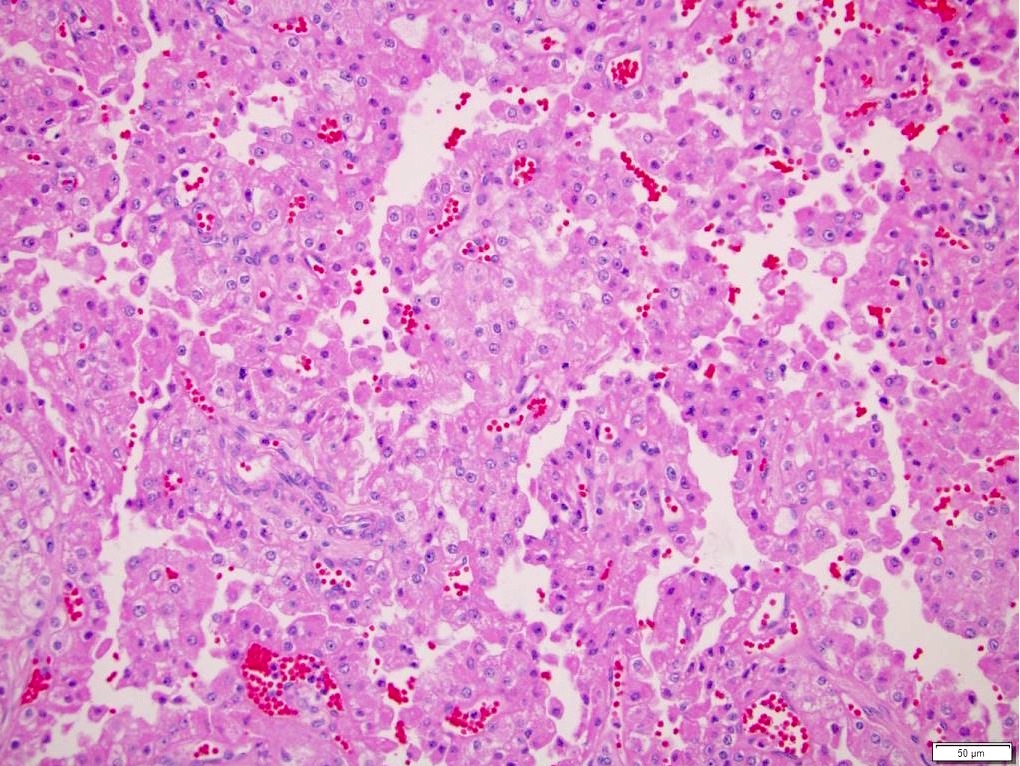
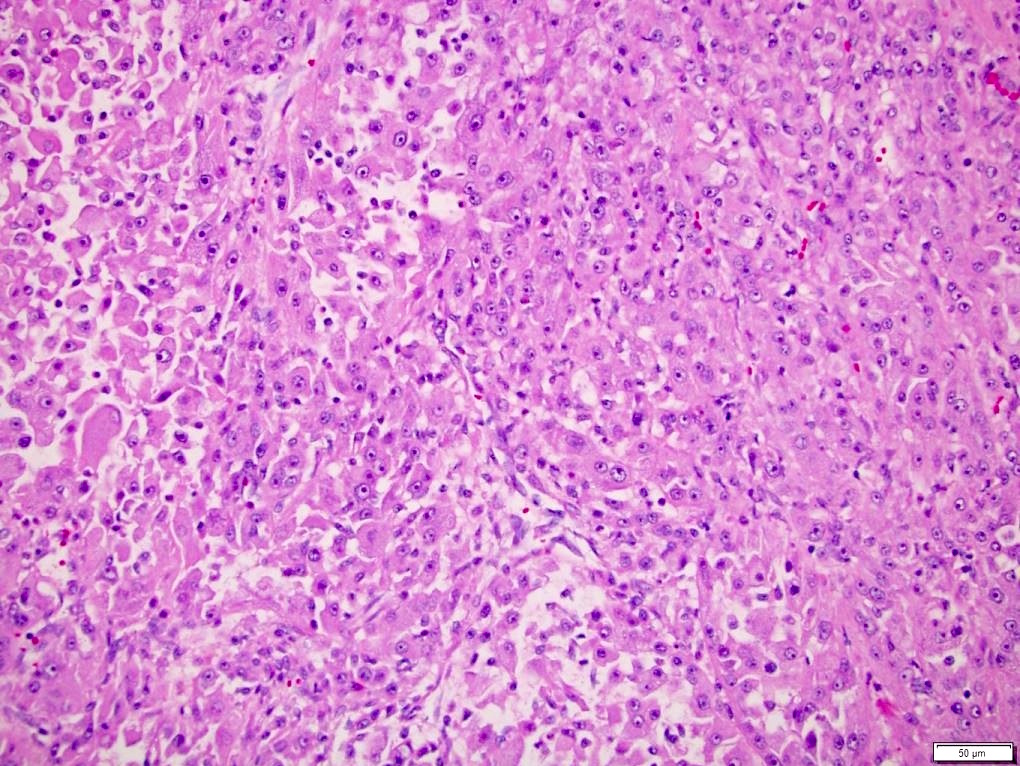
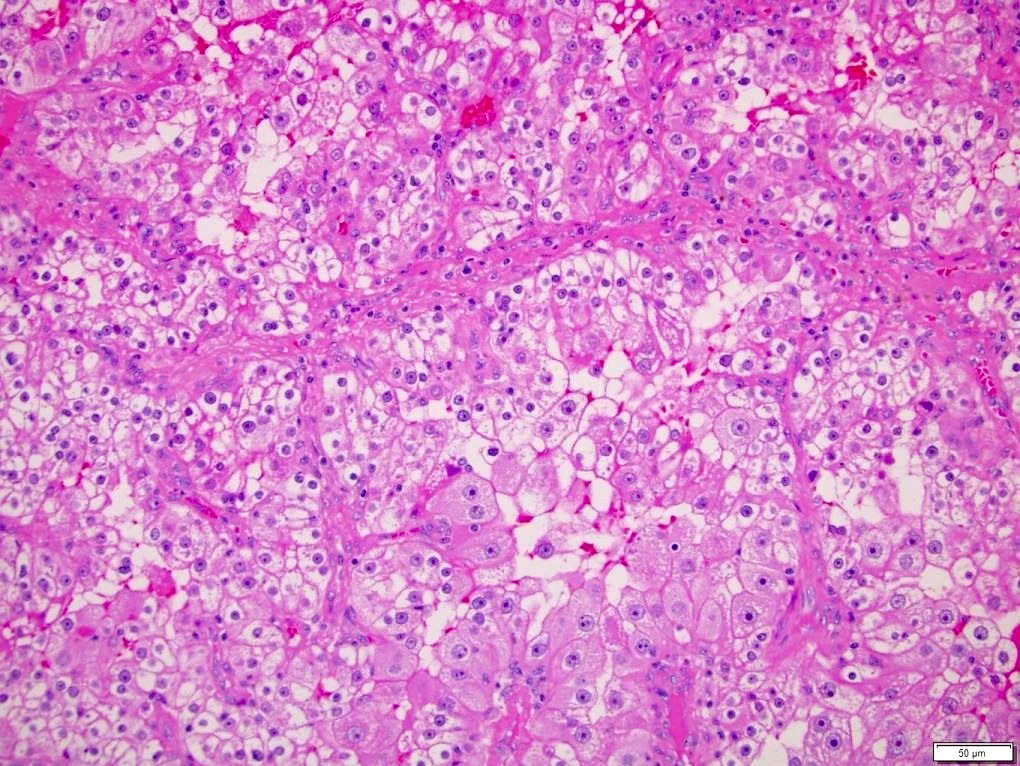
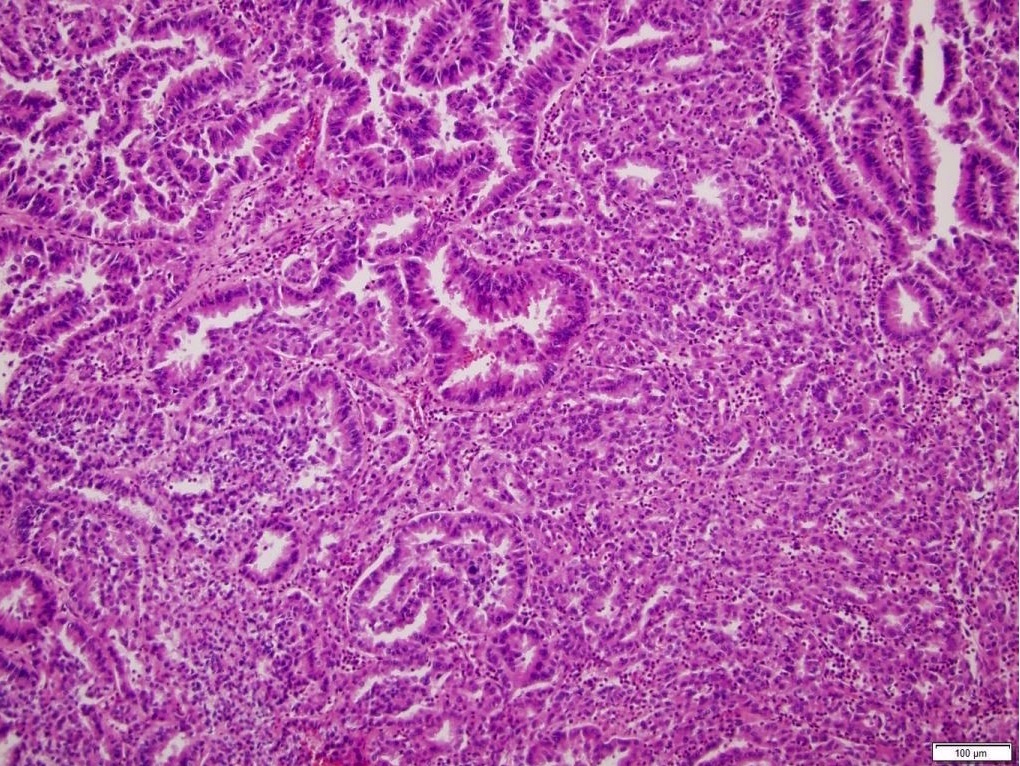
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Histologic features which do not resemble any classified subtype or have features of multiple subtypes, pure sarcomatoid or rhabdoid morphology
- High grade tumors often extremely heterogeneous with papillary, solid, sheet-like, nested, alveolar, tubular, glandular, rhabdoid or sarcomatoid architecture
- Cytoplasm often variable from eosinophilic to clear to amphophilic to spindled
- Majority are high nuclear grade, ISUP grade 3 or 4
- Necrosis, mitoses and vascular invasion are common
- May be purely sarcomatoid or rhabdoid, must exclude possibility of a distinct subtype RCC
- Low grade tumors often resemble oncocytoma but with more solid architecture, increased pleomorphism, more than occasional mitoses and focal necrosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- A study of 62 high grade unclassified RCCs revealed mutations in NF2 (18%), SETD2 (18%), BAP1 (13%), KMT2C (10%) and MTOR (8%) (Nat Commun 2016;7:13131)
- Chromosome genomic array testing (array CGH) and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays are both useful tools in resolving 80 - 94% of unclassified RCCs with ~50% cases reclassified as clear cell RCC
- Reclassified tumors show characteristic cytogenetic changes of certain subtype plus numerous additional copy number aberrations (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1276)
Differential diagnosis
- Diagnosis of exclusion requiring extensive work up
- Additional sampling of tumor: identify areas with classic morphologic and immunophenotypic features (often clear cell RCC) (AJSP Rvw and Rep 2017;22:301)
- IHC: PAX8, PAX2, CAIX, CD10, CK7, CK20, AMACR, CD117, HMB45, MelanA, CathepsinK, EMA, 34βE12, GATA3, p63, vimentin, TFE3, 2SC, SDHB, INI1 (AJSP Rvw and Rep 2017;22:301)
- FISH: TFE3, TFEB, 3p
- Evidence of genetic conditions: oncocytic neoplasms associated with tuberous sclerosis or Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1457, Histol Histopathol 2013;28:1257)
- Subtypes of RCC
- Clear cell: + CAIX, CD10, vimentin; loss of 3p by FISH
- Papillary: + AMACR, CD10 (apical); +/- CK7
- Chromophobe: + CK7
- MiTF family translocation associated: + TFE3 or TFEB; translocation of TFE3 or TFEB by FISH
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (fumarate hydratase deficient): +2SC; - FH
- SDH deficient: - SDHB
- Non-RCC:
- Angiomyolipoma, including epithelioid type: + HMB45, MelanA; - AE1 / AE3, PAX8
- Urothelial carcinoma of renal pelvis: based in renal pelvis; often + CK7, CK20, p63; - PAX8
- Metastasis
- Nonepithelial neoplasms infrequently seen in kidney (sarcoma, lymphoma)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following is true about unclassified RCC?
- Any degree of staining for an immunohistochemical marker of interest (including TFE3, 2SC, CAIX) can establish the underlying diagnosis
- Areas with classic morphologic and immunophenotypic features of clear cell RCC or chromophobe RCC indicate the likely underlying etiology
- Unclassified RCC is a specific morphologic diagnosis
- Unclassified RCC is always high grade
Board review style answer #1
B. Areas with classic morphologic and immunophenotypic features of clear cell RCC or chromophobe RCC indicate the likely underlying etiology
Comment Here
Reference: Unclassified renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Unclassified renal cell carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2