Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ampullaadenoma.html. Accessed August 27th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Dysplastic, premalignant lesion of ampulla of Vater
Essential features
- Essentially the ampullary counterpart to colonic tubular / tubulovillous adenoma
- Often occurs in the setting of familial adenomatous polyposis
- Generally asymptomatic, with good prognosis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D37.6 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of ampulla of Vater
Epidemiology
- < 10% of periampullary neoplasms
- Age range: 32 - 86 years (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:506)
- Incidence 1:1,000 - 2,000 based on autopsy studies
- Generally occurs in older patients
- Increased incidence in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic but can cause gastric outlet obstruction or bleeding and rarely acute pancreatitis, biliary obstruction or intussusception
- Excellent prognosis if completely excised
- Often associated with concurrent pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (Mod Pathol 2001;14:139)
Diagnosis
- Endoscopic impression, confirmed on biopsy
- Interobserver variability for distinguishing low grade dysplasia / indefinite for dysplasia / reactive atypia is high on small biopsy samples (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1095)
Case reports
- 40 year old woman with jaundice (Surg Case Rep 2024;10:25)
- 49 year old woman with intussusception (Case Rep Gastroenterol 2016;10:545)
- 53 year old man with common bile duct stricture (Cytojournal 2017;14:19)
- 63 year old man who underwent robotic transduodenal ampullectomy (Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2021;25:150)
- 72 year old woman with giant ampullary adenoma (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2023;115:467)
Treatment
- Early or relatively confined lesions may be excised by endoscopic polypectomy or ampullectomy (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:506)
- Otherwise, requires pancreatoduodenectomy
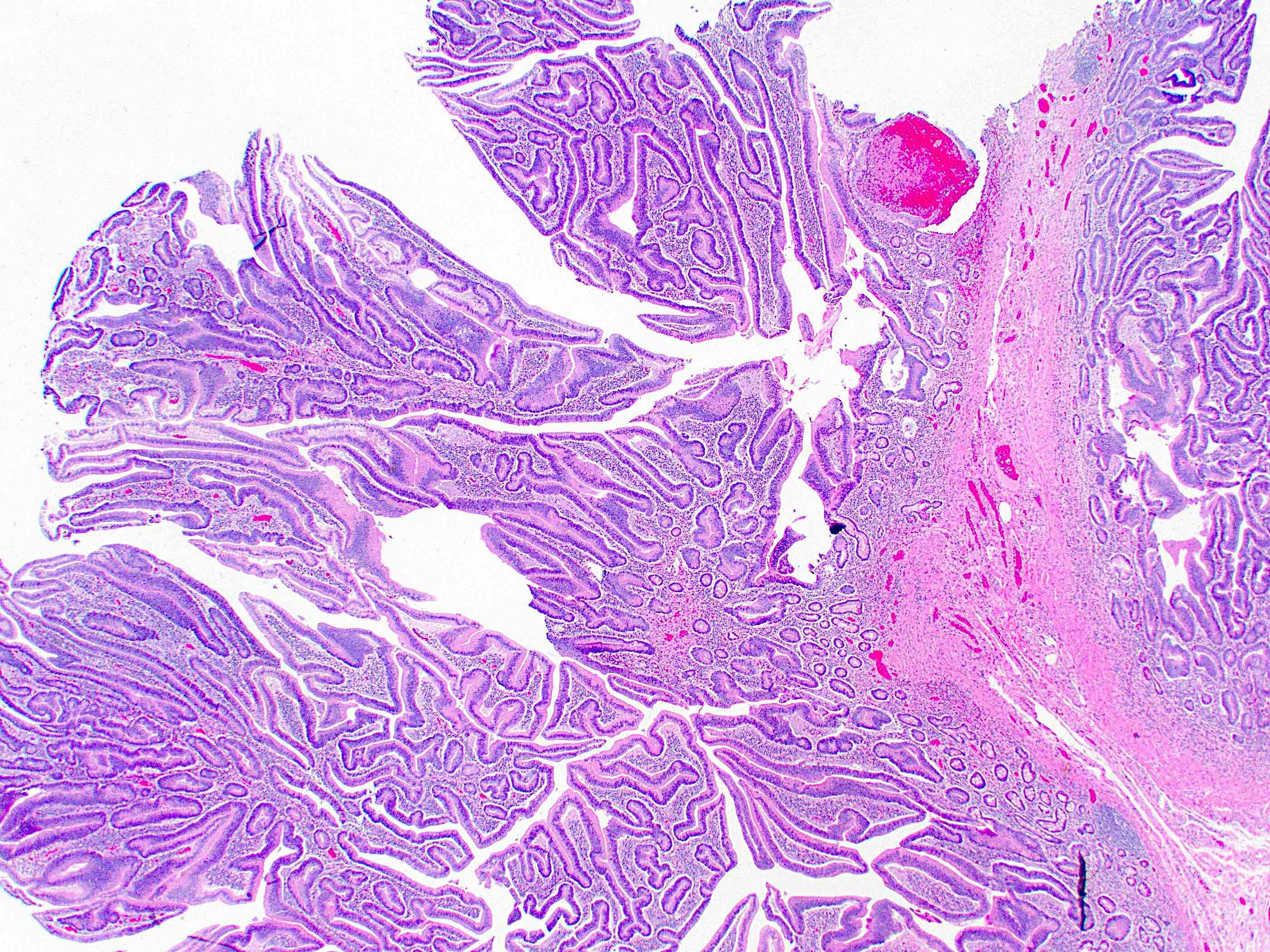
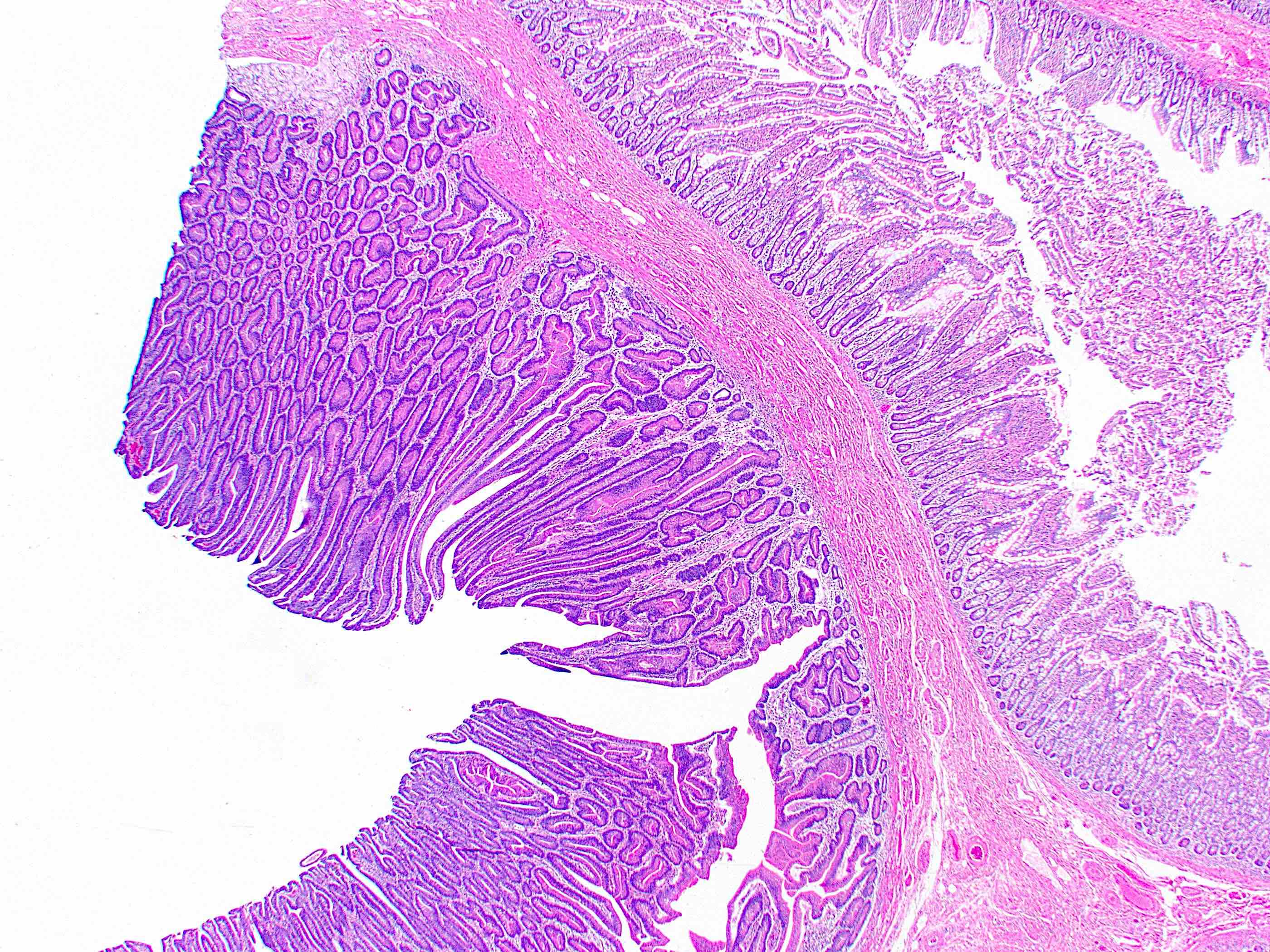
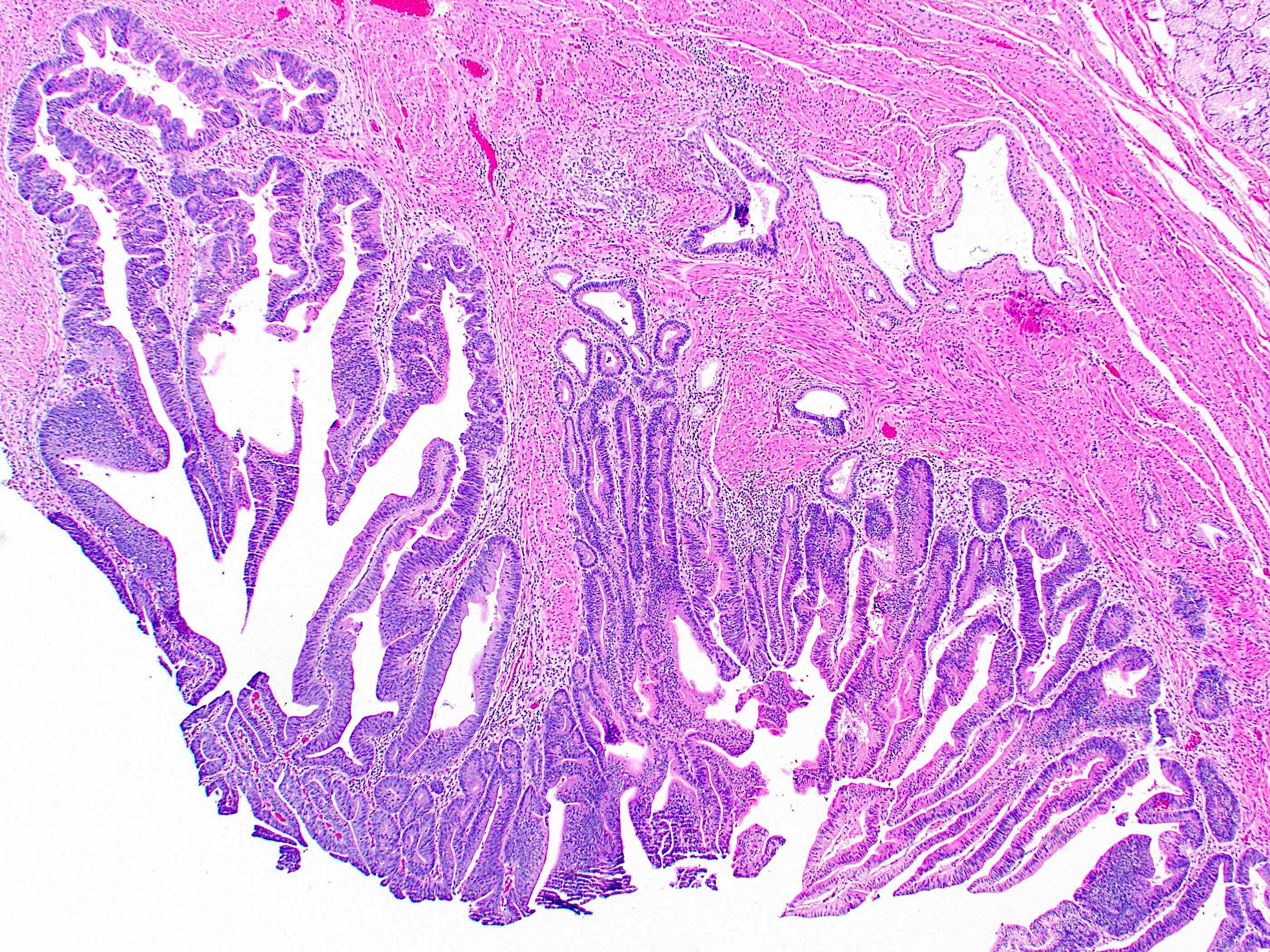
Gross description
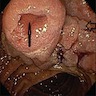
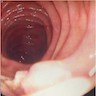
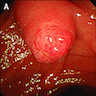
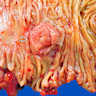
- Polypoid / exophytic mass
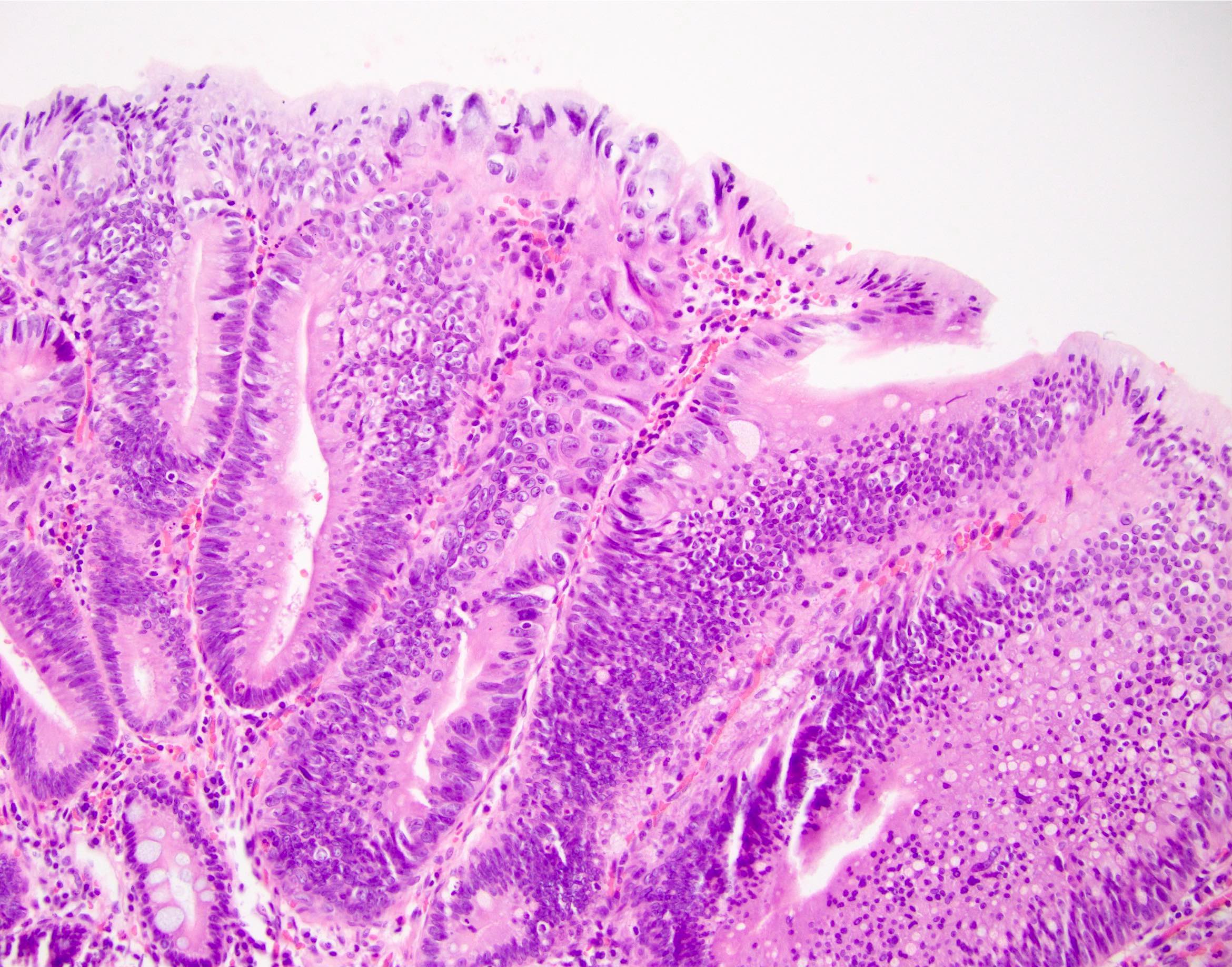
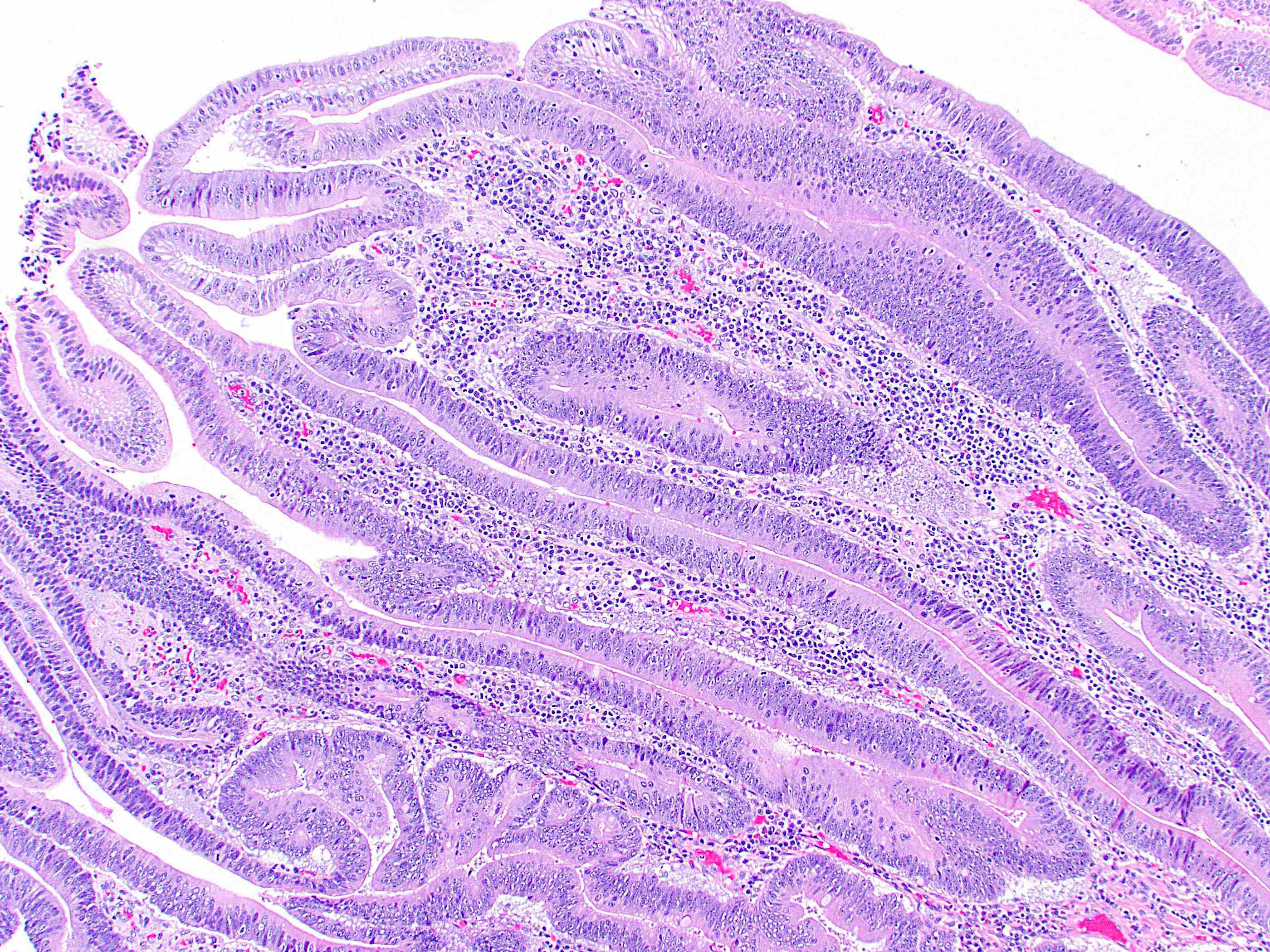
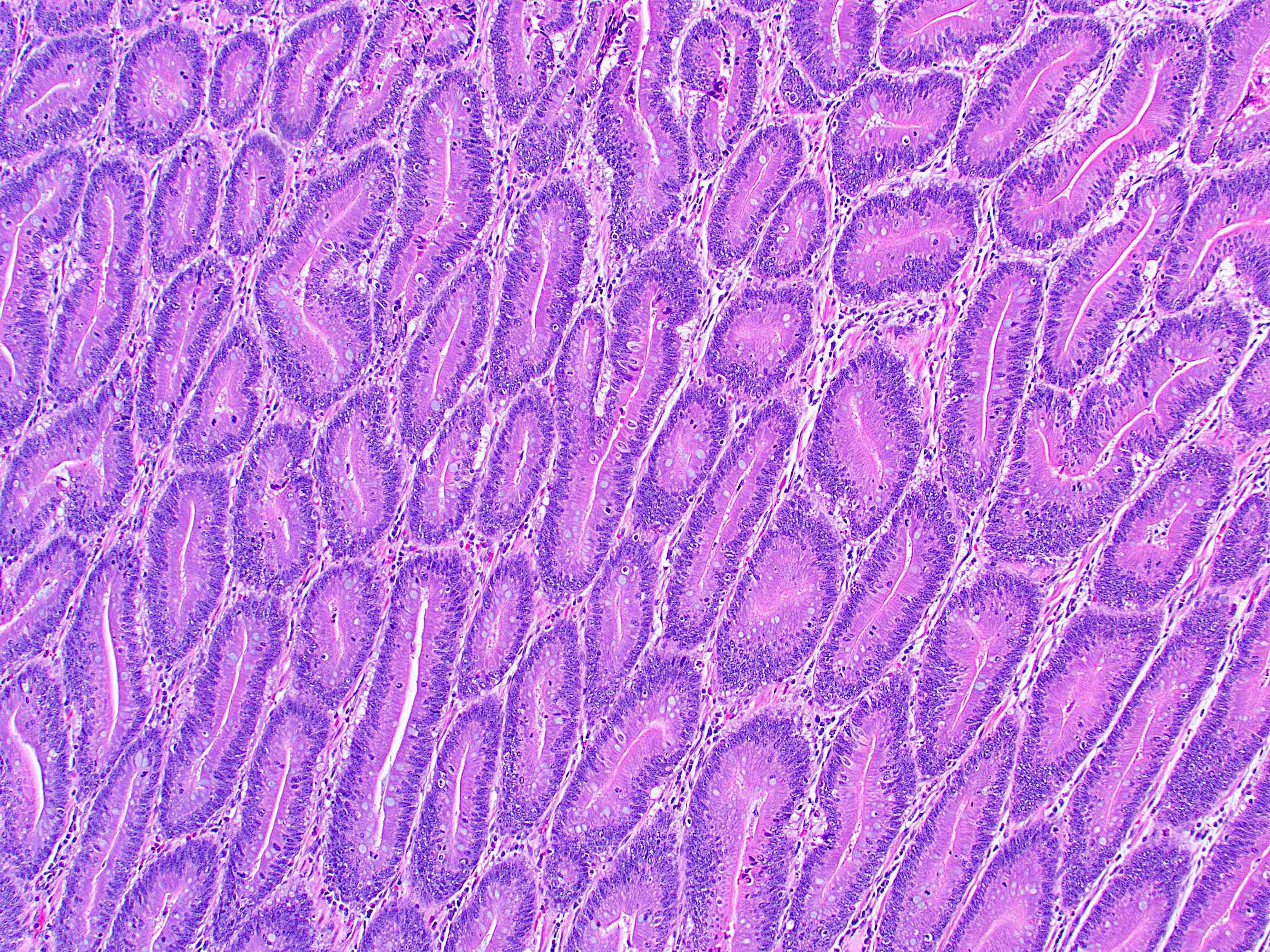
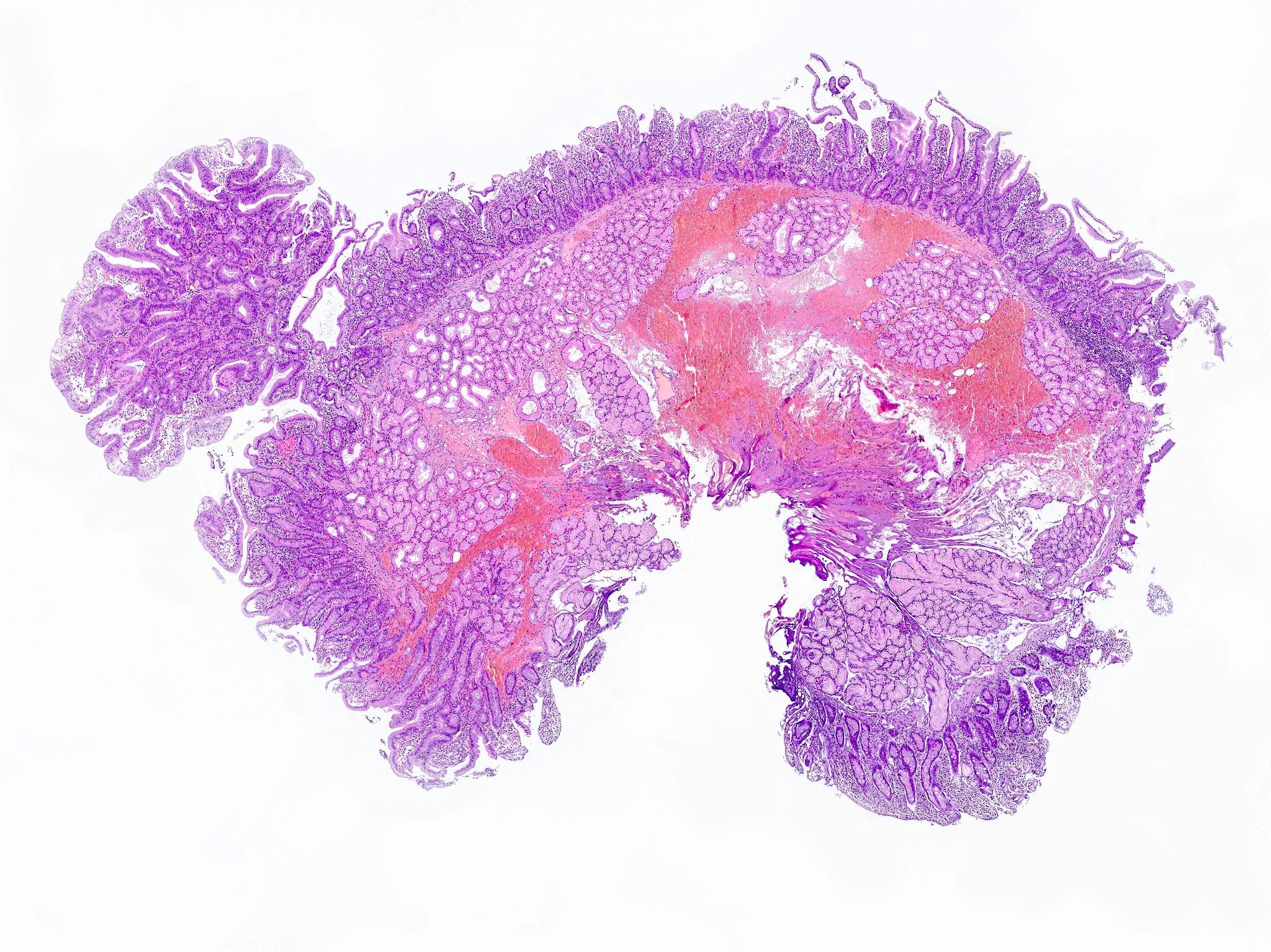
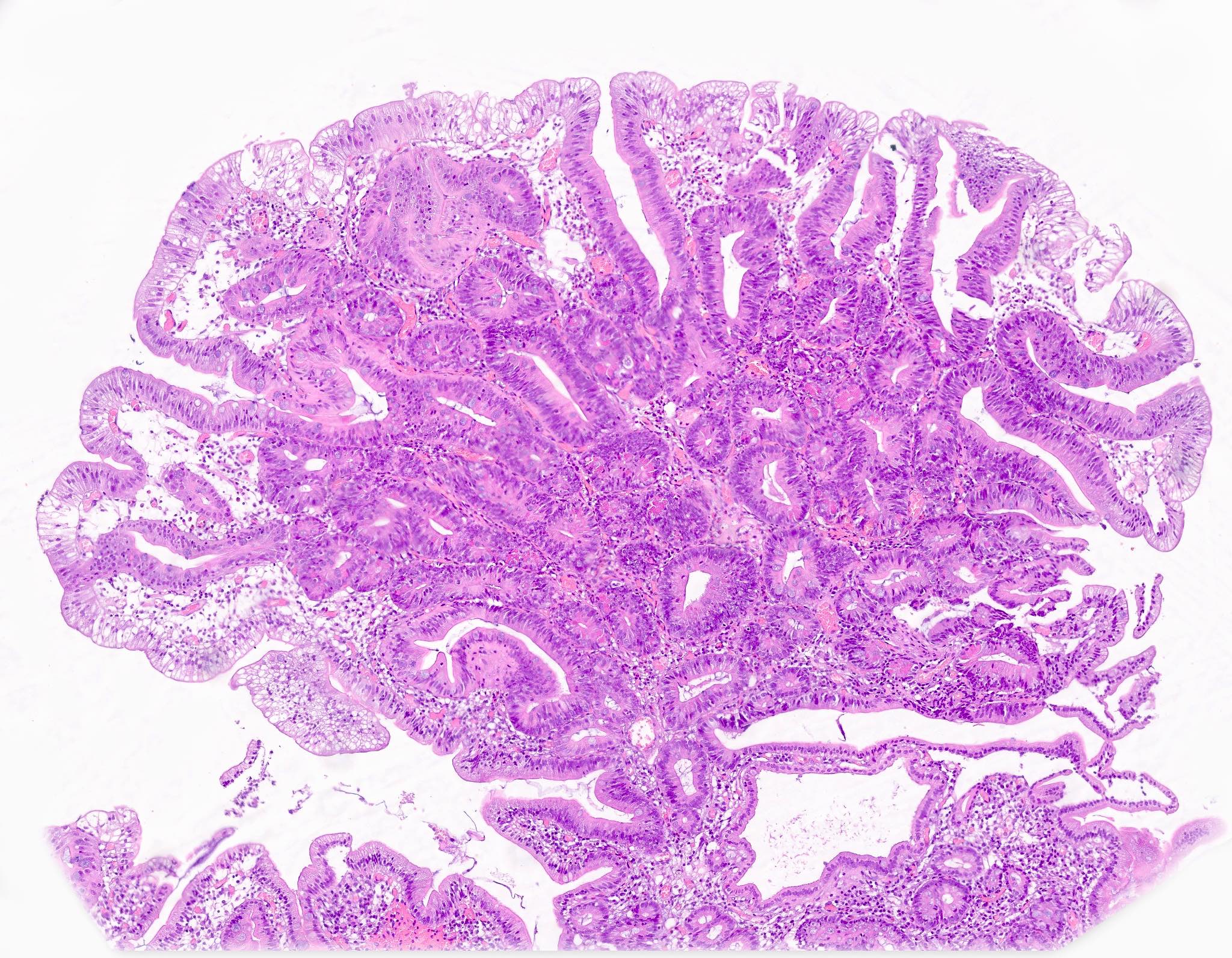
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Tubular, tubulovillous or villous, similar to adenomas in colon, with approximately half tubular and half villous (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:506)
- Low grade dysplasia demonstrates hyperchromatic, pencil shaped nuclei confined to the basal layer of cells, with limited architectural changes (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1291)
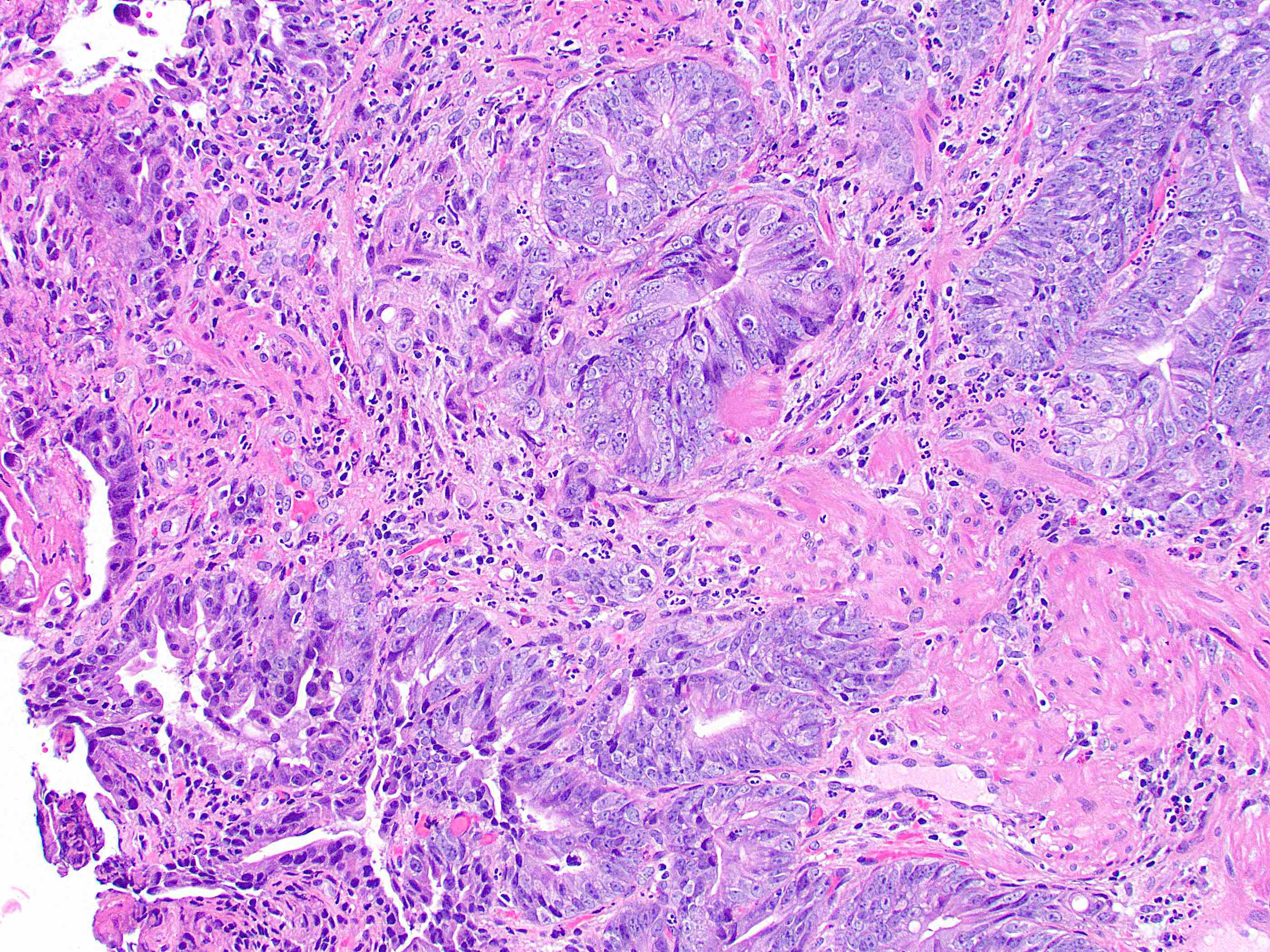
- High grade dysplasia demonstrates large, rounded nuclei with loss of polarity, along with architectural abnormalities such as cribriforming (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1291)
- Dysplastic epithelium may have only subtle changes of mild cellular stratification and fine chromatin pattern
- Often contain prominent Paneth cells (with coarse, large, red-pink, refractile granules in supranuclear cytoplasm), endocrine cells (dark, red-purple, fine, small granules in basal cytoplasm) and goblet cells
- May show high grade dysplasia or give rise to adenocarcinoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Endoscopic brush cytology is sensitive and specific for adenoma / carcinoma, although diagnosis of adenoma does not exclude coexisting carcinoma (Am J Clin Pathol 1998;109:540)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Sporadic and familial adenomatous polyposis related adenomas show similar molecular features to colorectal adenoma, with presence of APC and KRAS mutations
- BRAF mutations, TP53 alterations and DNA mismatch repair abnormalities are rare (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1388)
Sample pathology report
- Ampulla, polypectomy:
- Ampullary adenoma (low grade dysplasia)
- Negative for high grade dysplasia or malignancy
- Margins of resection negative for dysplasia
Differential diagnosis
- Duodenal (nonampullary) adenoma:
- Anatomic site is only distinction
- Intra-ampullary papillary tubular neoplasm (IAPN):
- Occurs deeper within the ampulla
- May have pancreatobiliary type or intestinal type epithelium (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1731)
- IAPNs are predominantly nonintestinal and very often harbor an infiltrating component (Am J Surg Pathol 2024;48:1093)
Practice question #1
Which of the following is true about adenomas of the ampulla of Vater?
- BRAF mutations are rarely seen
- Cases must be managed with pancreatoduodenectomy
- Patients with Lynch syndrome are at significantly increased risk
- Progression to adenocarcinoma is unusual
Practice answer #1
A. BRAF mutations are rarely seen. KRAS and APC mutations are more common, both in sporadic cases and in those from patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Answer B is incorrect because some cases can be managed endoscopically. Answer C is incorrect because patients with FAP, not Lynch syndrome, are at increased risk. Answer D is incorrect because progression to adenocarcinoma is an important risk.
Comment Here
Reference: Ampulla - Adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Ampulla - Adenoma
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
B. KRAS mutations are most commonly seen in ampullary adenomas, along with APC mutations. Answers A and C are incorrect because those genes are rarely mutated in such adenomas. Answer D is incorrect because STK11 mutations suggest a Peutz-Jeghers polyp.
Comment Here
Reference: Ampulla - Adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Ampulla - Adenoma