Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Martinez Ciarpaglini C. Tubulovillous / villous adenoma . PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumortvadenoma.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Advanced precursor lesion of colorectal cancer (Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015;1:15065)
- Tubulovillous adenoma: 20 - 80% villosity
- Villous adenoma: > 80% villosity (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:212)
Essential features
- Recognized as the precursor lesion of chromosomal unstable colorectal cancer (Pathologica 2021;113:218)
- Low grade dysplasia is an intrinsic feature
- Associated with oncogene KRAS mutation in 50% of cases
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D12.6 - benign neoplasm of colon, unspecified
Sites
- More frequent in distal colorectum than in proximal colon (68.4% versus 31.6%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:212)
Pathophysiology
- Conventional adenoma carcinoma sequence with oncogene (KRAS) activation and tumor suppressor (APC, SMAD4 and TP53) inactivation
- Associated with chromosomal unstable colorectal cancer (Cancer Biol Med 2016;13:120)
Clinical features
- Mean age of 62 years (Eur J Cancer 2005;41:416)
- M:F = 1.6:1
- Though most cases are asymptomatic, some present with a history of rectal bleeding (StatPearls: Villous Adenoma [Accessed 31 May 2022])
Diagnosis
- Screening or surveillance colonoscopy identifies and removes lesion, followed by tissue diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- Villous or tubulovillous histology is associated with increased risk of colorectal neoplasia: 16.8% versus 9.7% compared with tubular adenomas
- Increased risk of malignant transformation in cases with high grade dysplasia (↑ 1.77x) (Gastroenterology 2012;143:844)
- Risk of recurrence with malignancy after excision is associated with piecemeal endoscopic resection (Surg Endosc 2021;35:2500)
Case reports
- 62 year old woman presented with rectal bleeding and fleshy mass protruding from the anal canal (World J Surg Oncol 2019;17:109)
- 69 year old man with acute appendicitis (Int J Surg Case Rep 2019;61:60)
- 78 year old woman with tubulovillous adenoma of the cecum with squamous metaplasia (Int J Surg Pathol 2009;17:340)
Treatment
- Endoscopic resection
- When possible, en bloc resection should be the goal for the management (Surg Endosc 2021;35:2500)
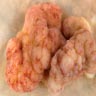
Gross description
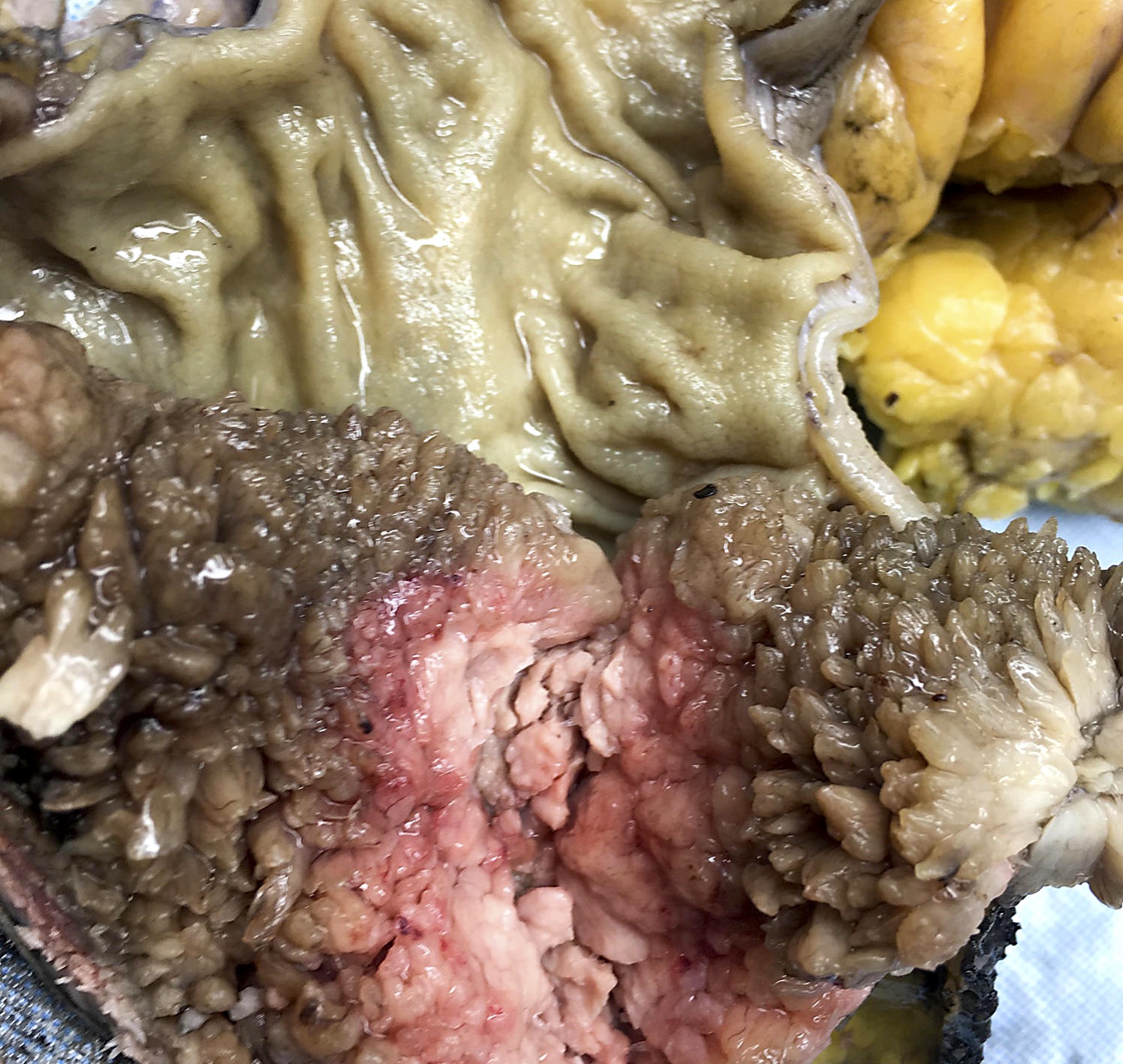
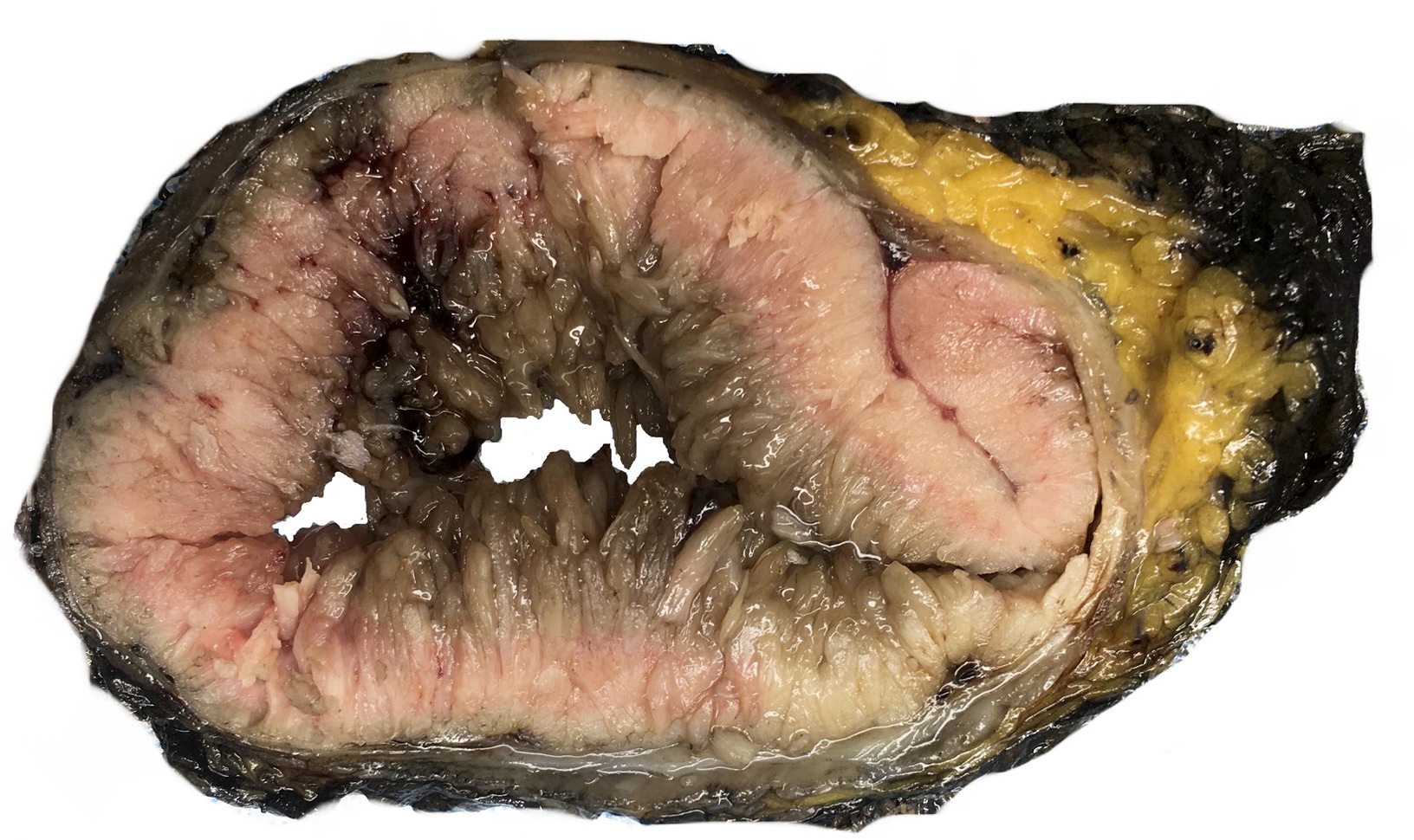
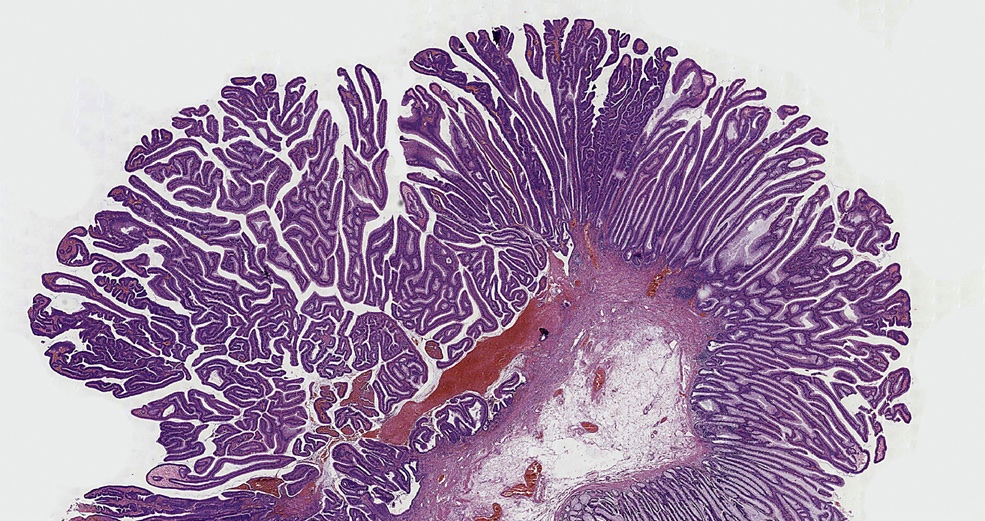
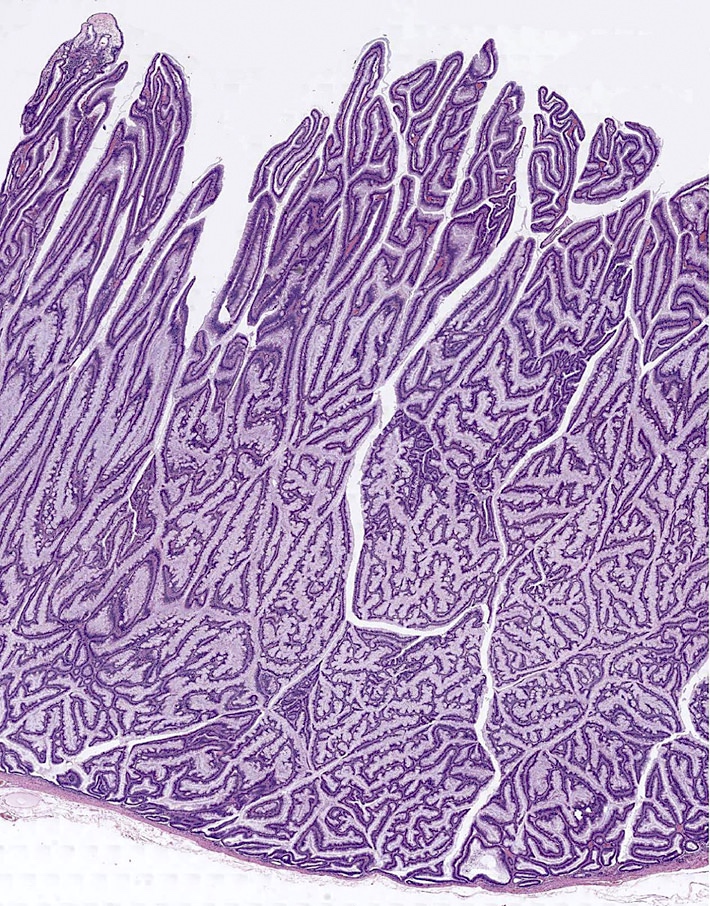
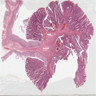
- Pedunculated or sessile polypoid lesions with macroscopic finger-like projections
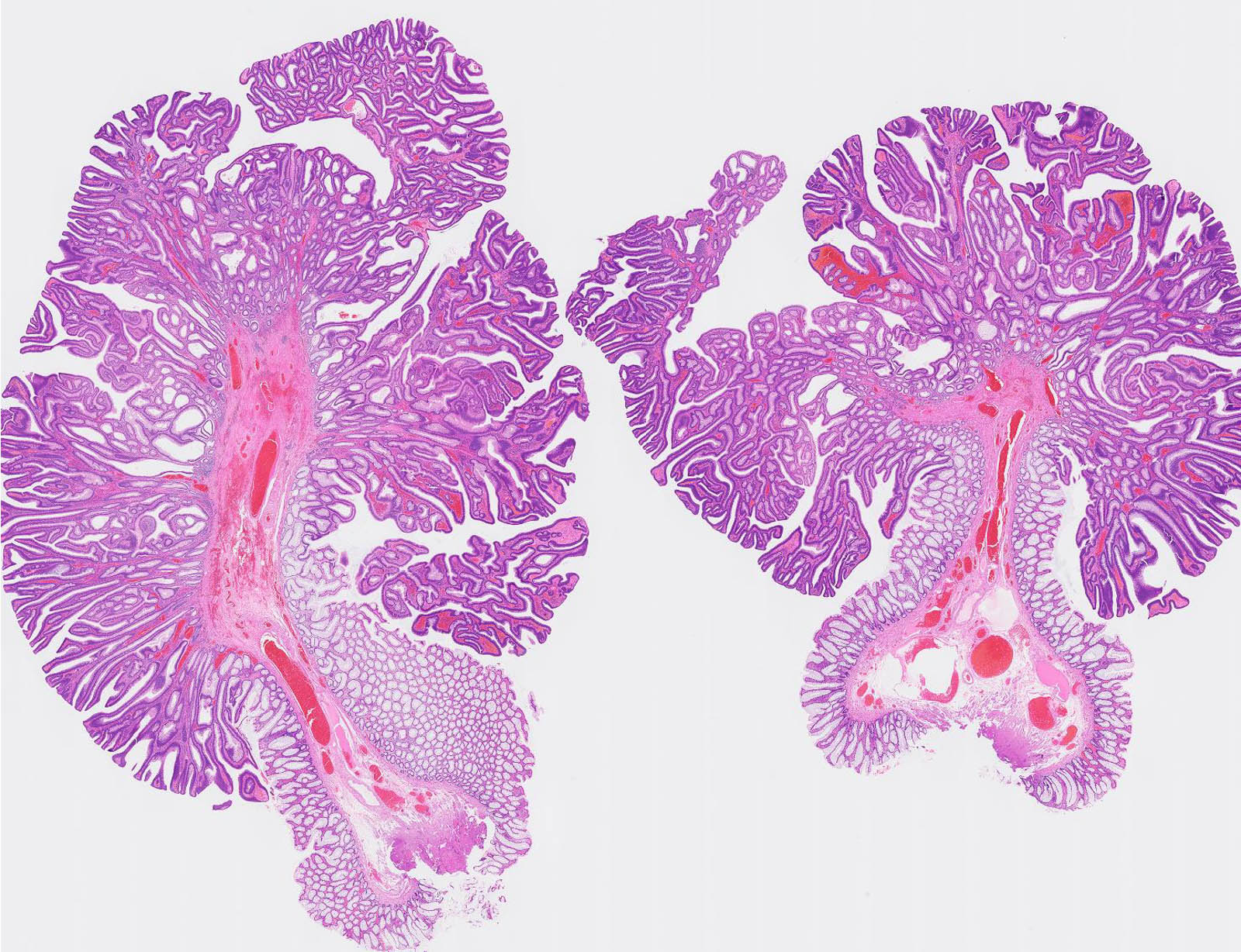
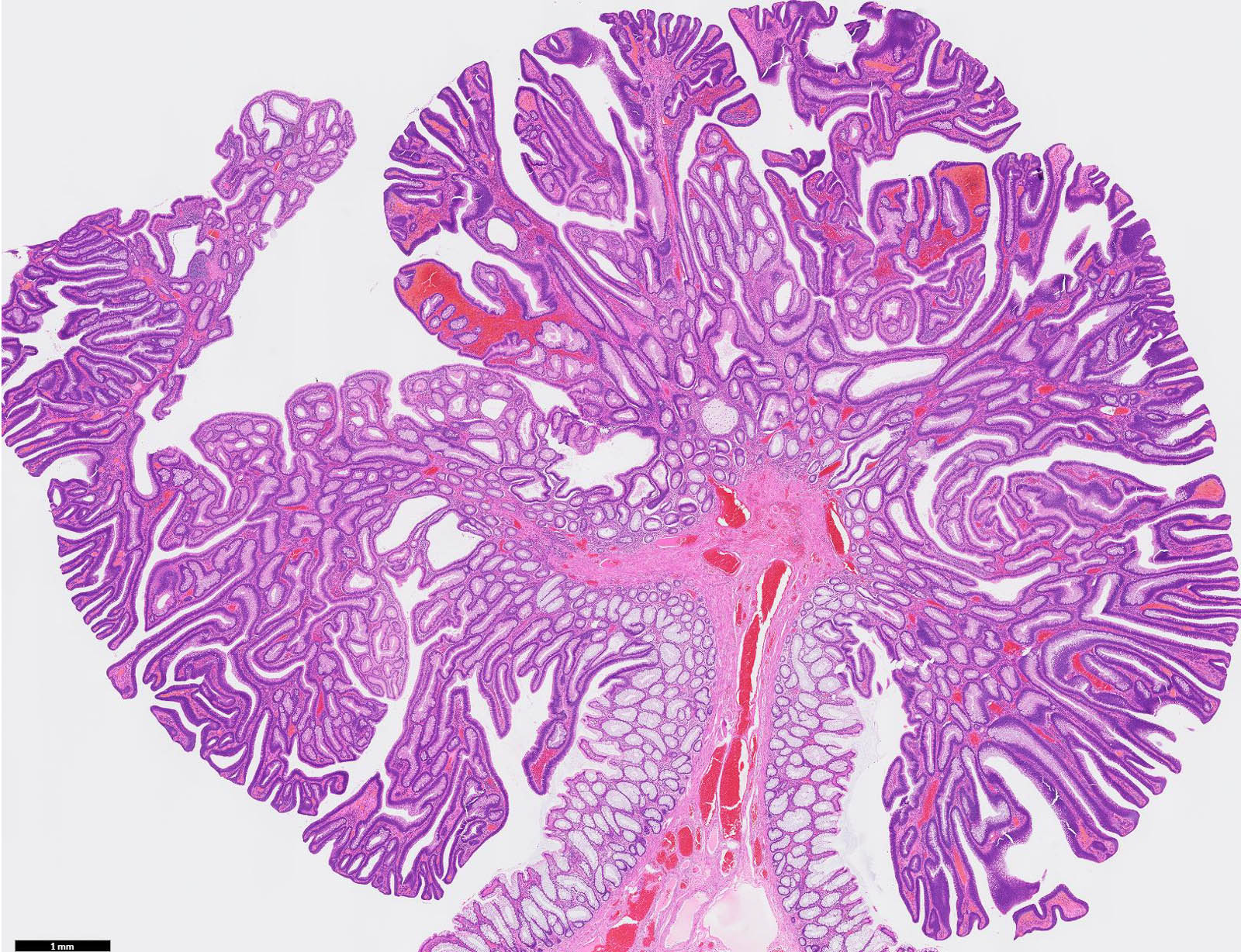
Gross images
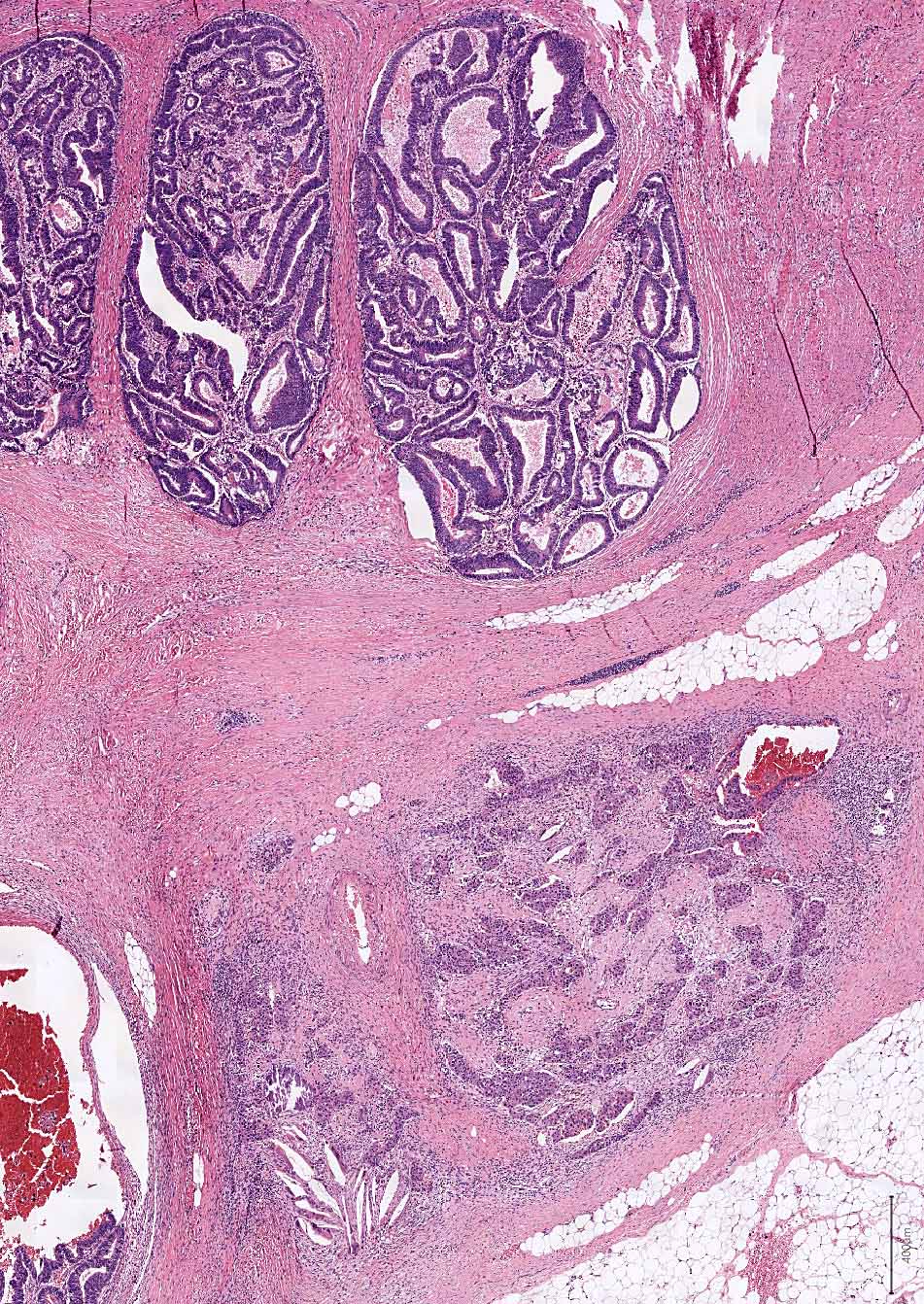
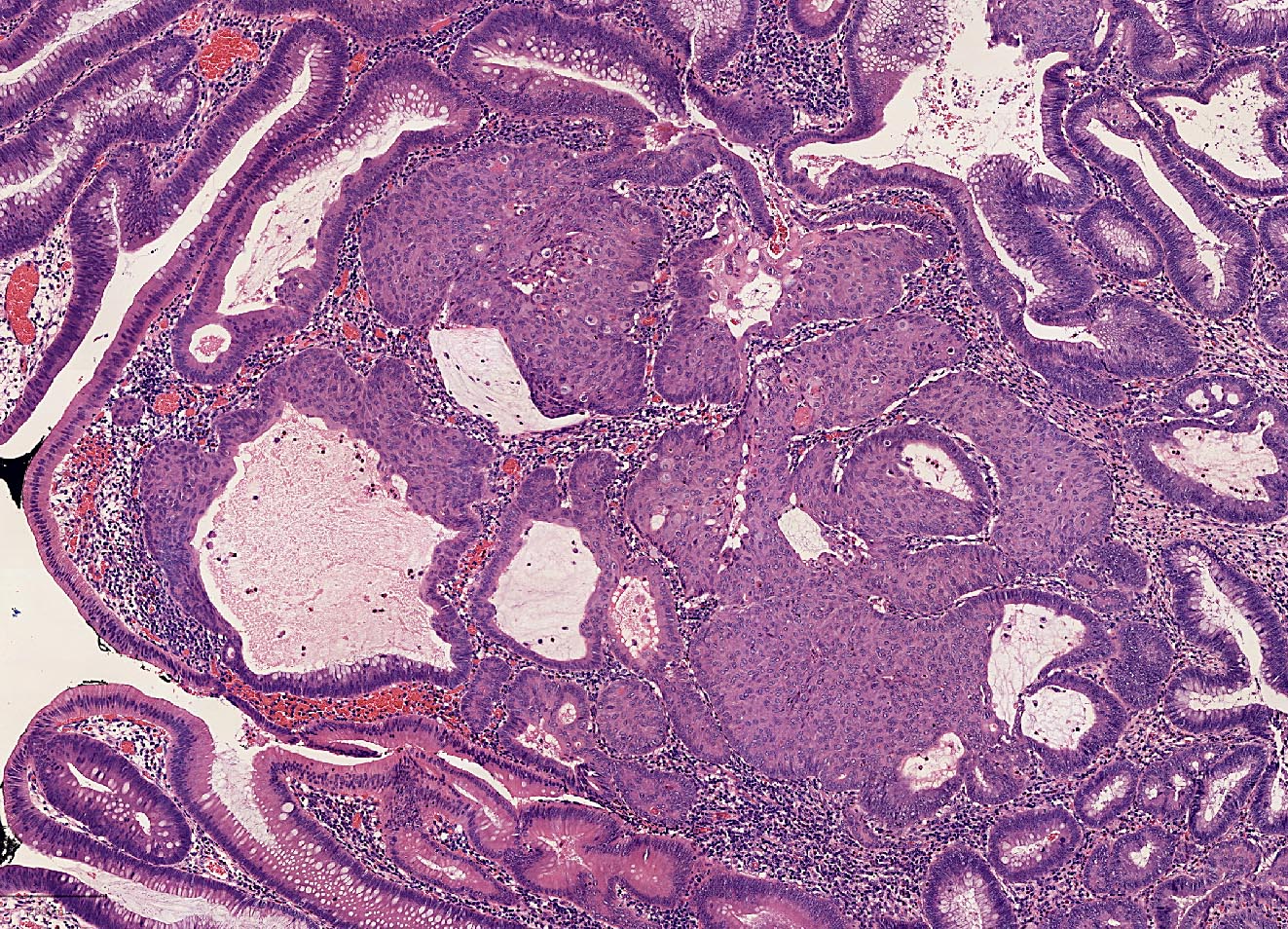
Microscopic (histologic) description
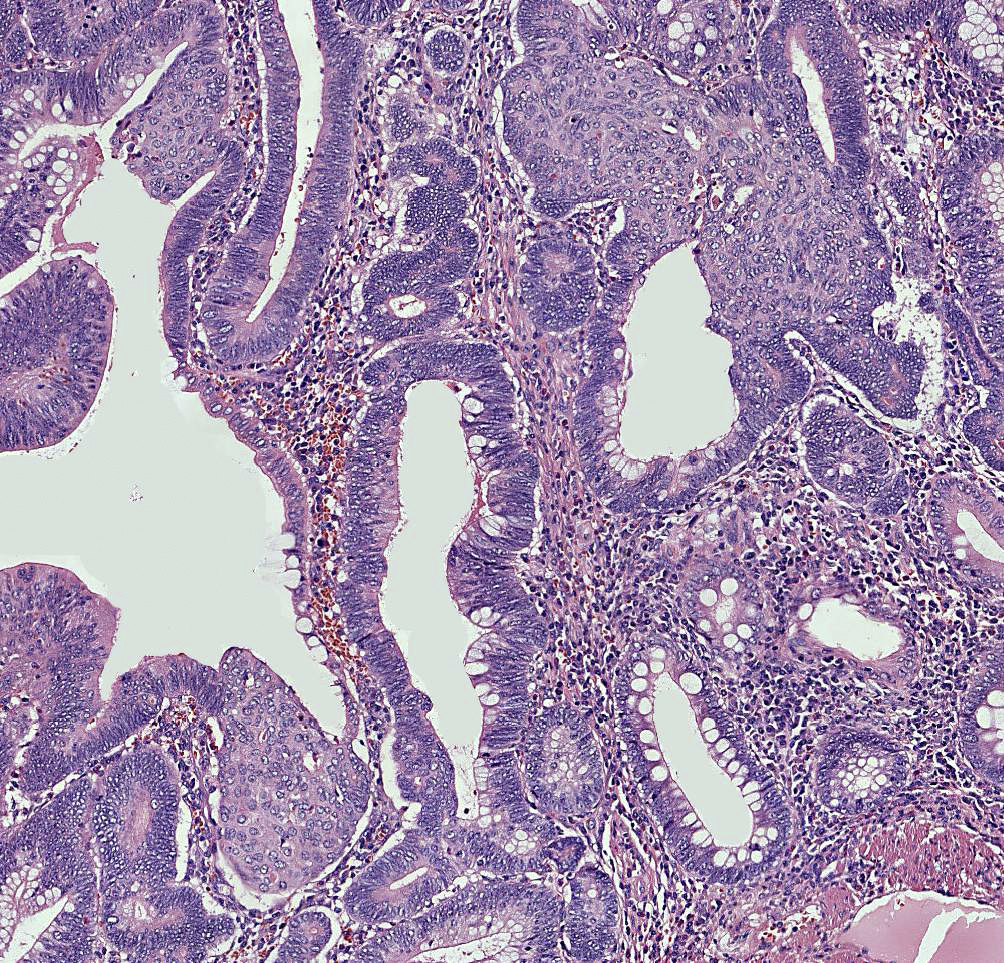
- Low grade dysplasia is a constituent feature
- Epithelial, finger-like projections, away from the muscularis mucosae, formed by fibrovascular cores lined by dysplastic epithelium (villous architecture)
- Percentage of villosity defines diagnostic terminology
- 20 - 80% = tubulovillous adenoma
- > 80% = villous adenoma
- Crowded pseudostratification of cells with elongated nuclei occupying the basal half of the cytoplasm
- Pleomorphism and atypical mitoses should be absent or minimally present
- Mitotic activity and minimal loss of cell polarity are allowed
- Architecturally, the crypts should maintain a resemblance to normal colon, without significant crowding, cribriform or complex forms
- Squamous metaplasia as solid nests of squamous cells in direct continuity with adenomatous glands may be seen in about 0.4% of colorectal adenomas (Histopathology 2021;78:348)
- Paneth cell metaplasia is a frequent finding (17 - 23%), especially in proximal locations; osseous metaplasia has been reported (Histopathology 2021;78:348)
- Neuroendocrine metaplasia refers to the presence of scattered foci of neuroendocrine cells that lack significant nuclear atypia, mitotic activity or necrosis; these cells comprise < 30% of the lesion (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;42:69)
- Clusters of neuroendocrine metaplasia are usually < 2 mm and limited to the lamina propria without disturbing the overall architecture (Histopathology 2021;78:348)
- Ectopic crypt foci are a frequent finding (J Clin Pathol 2016;69:1063)
- High grade dysplasia can be seen (carcinoma in situ or intraepithelial / intramucosal carcinoma are not recommended terms)
- Increased nucleus to cytoplasm ratio
- Significant loss of cell polarity: nuclear stratification through the entire thickness of the epithelium
- Round nuclei with open appearing chromatin and increasingly prominent nucleoli
- Significant pleomorphism and atypical mitoses
- Abnormal architecture includes cribriform structures with back to back glands, prominent glandular budding and intraluminal papillary tufting (StatPearls: Villous Adenoma [Accessed 31 May 2022])
- Poor interobserver agreement for assessment of the villous component and high grade dysplasia have been demonstrated (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:427)
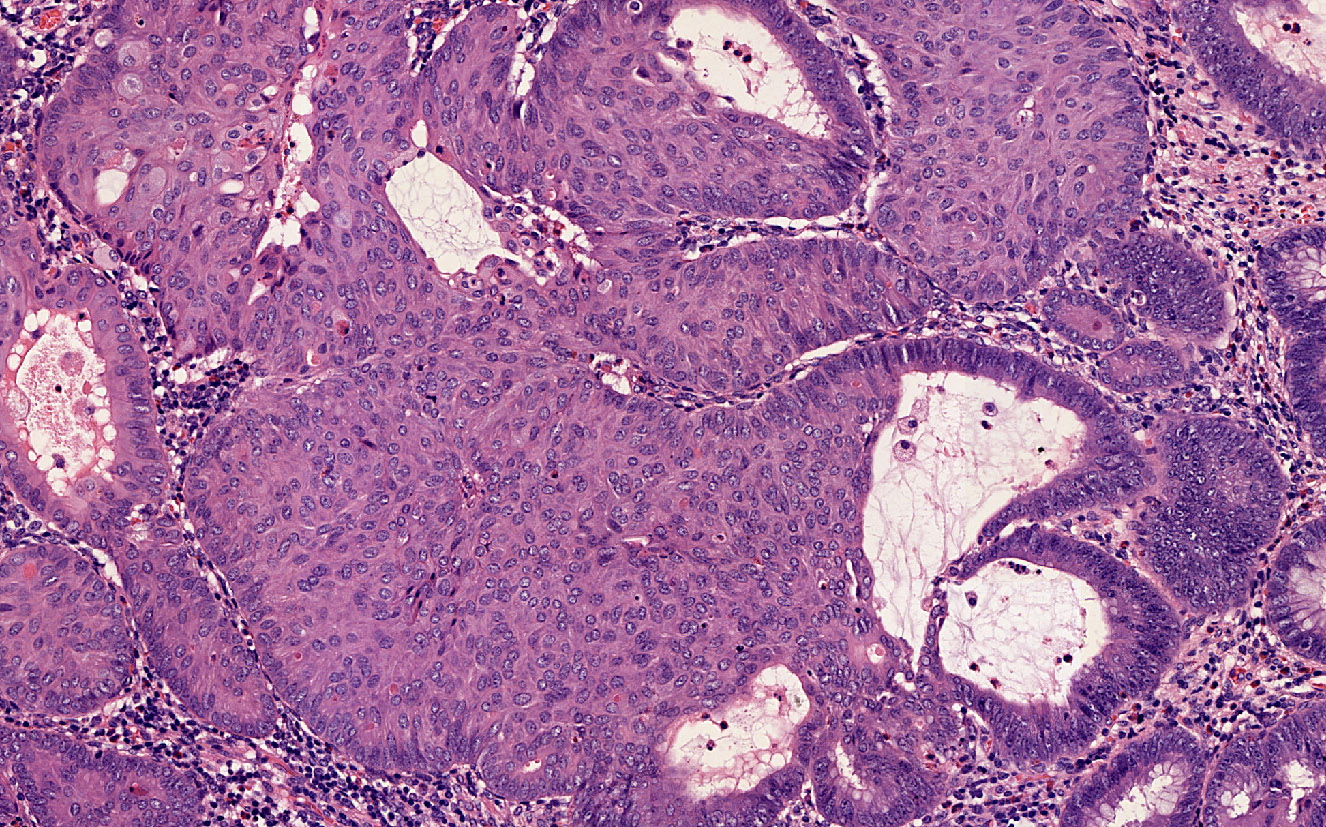
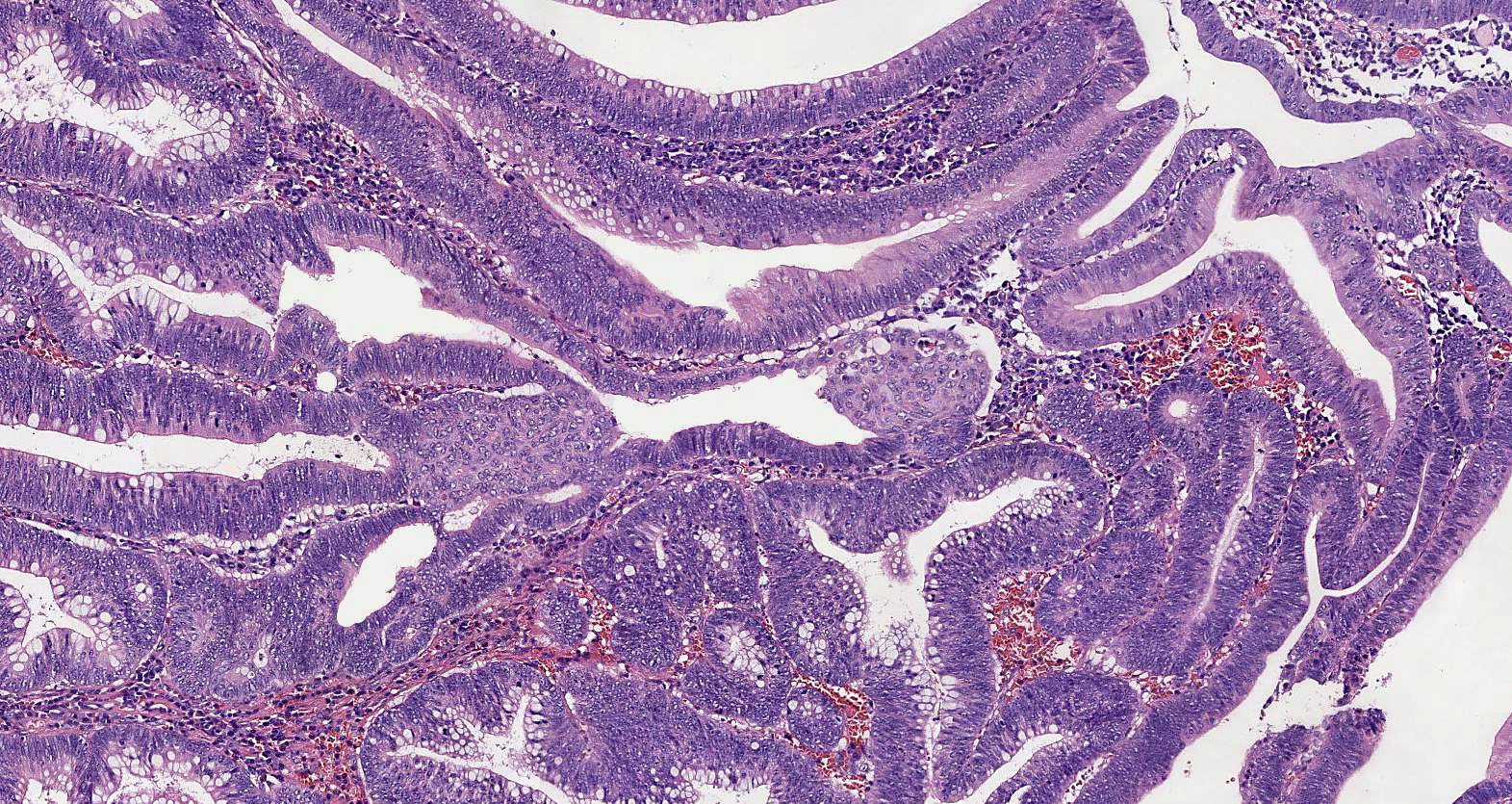
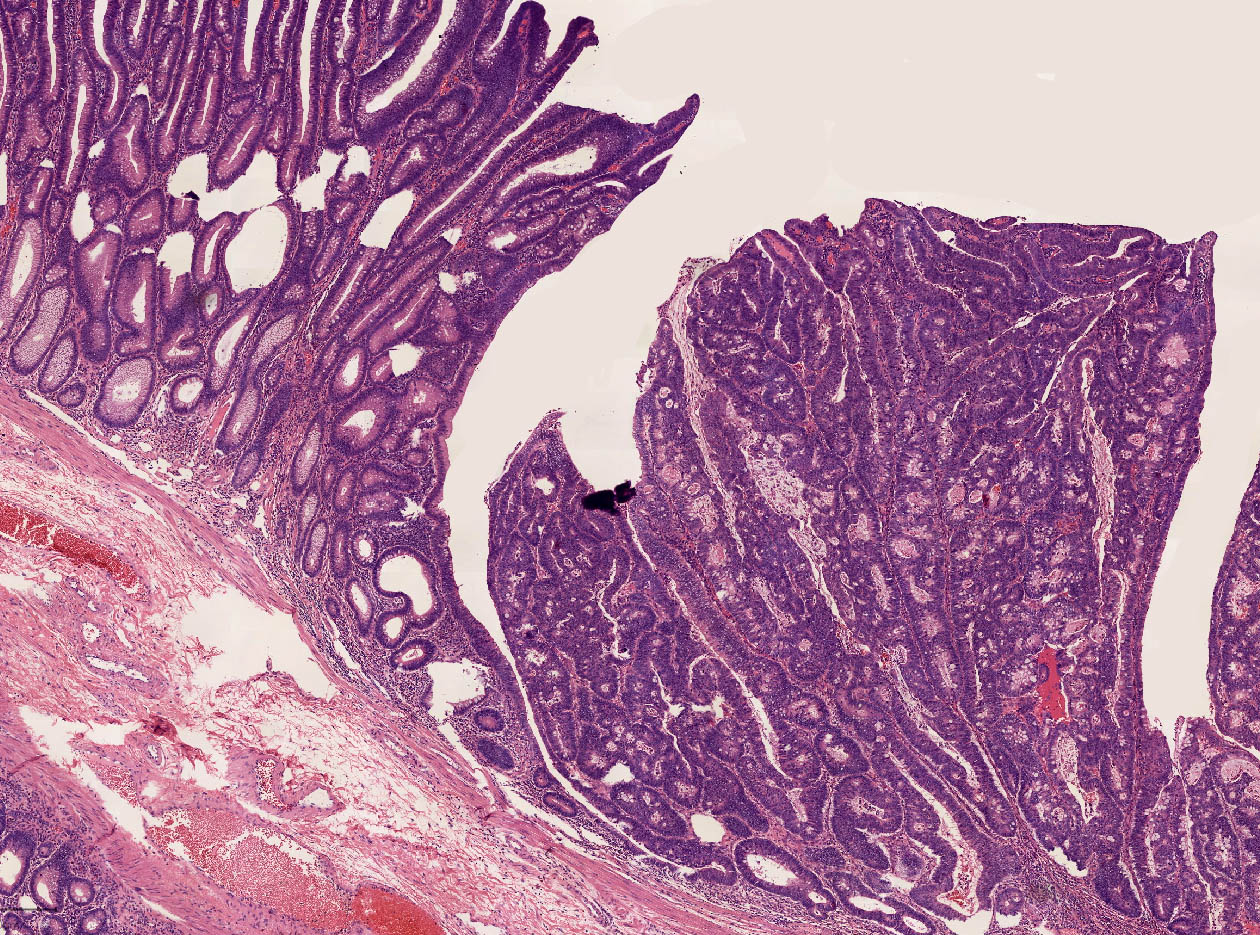
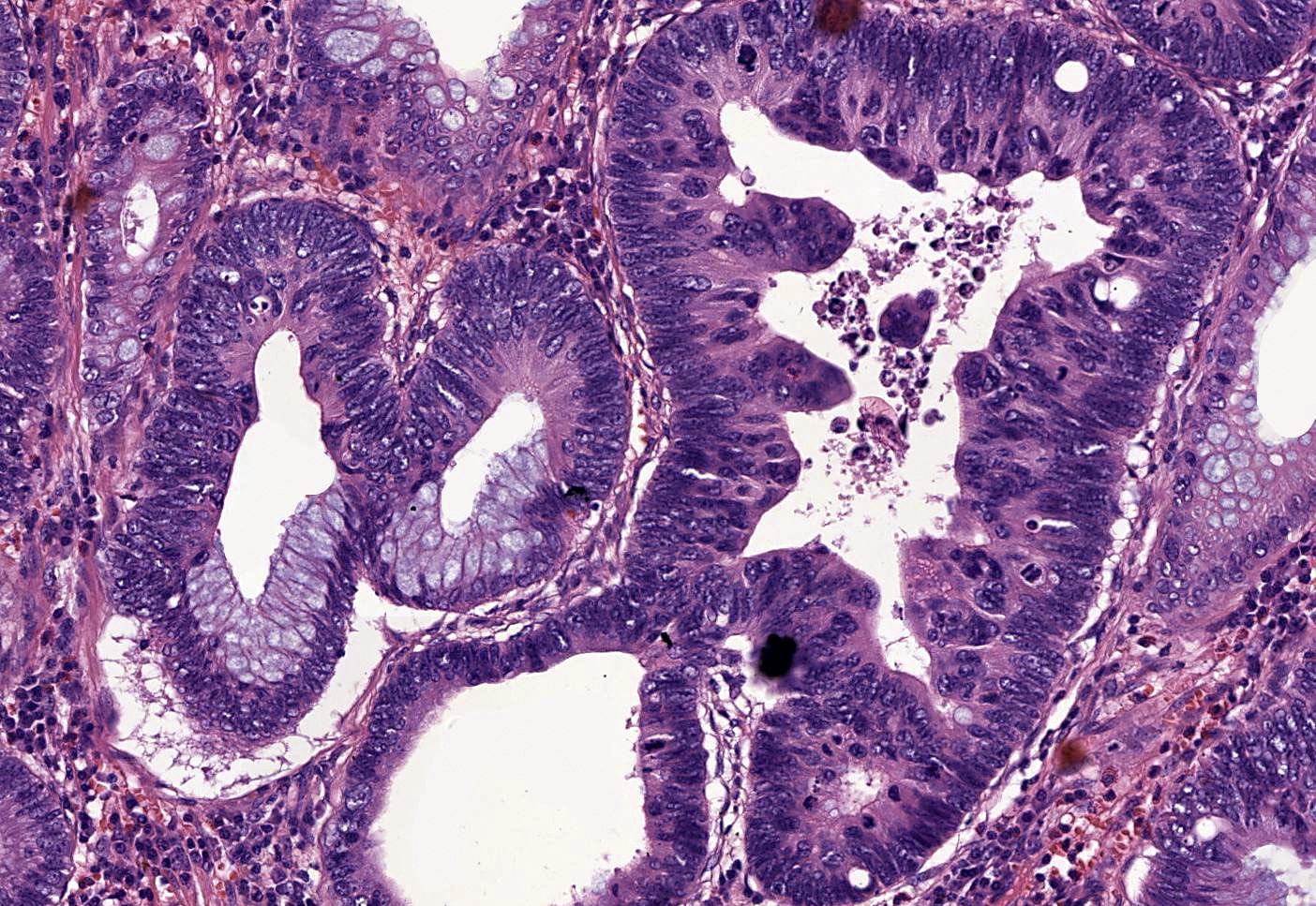
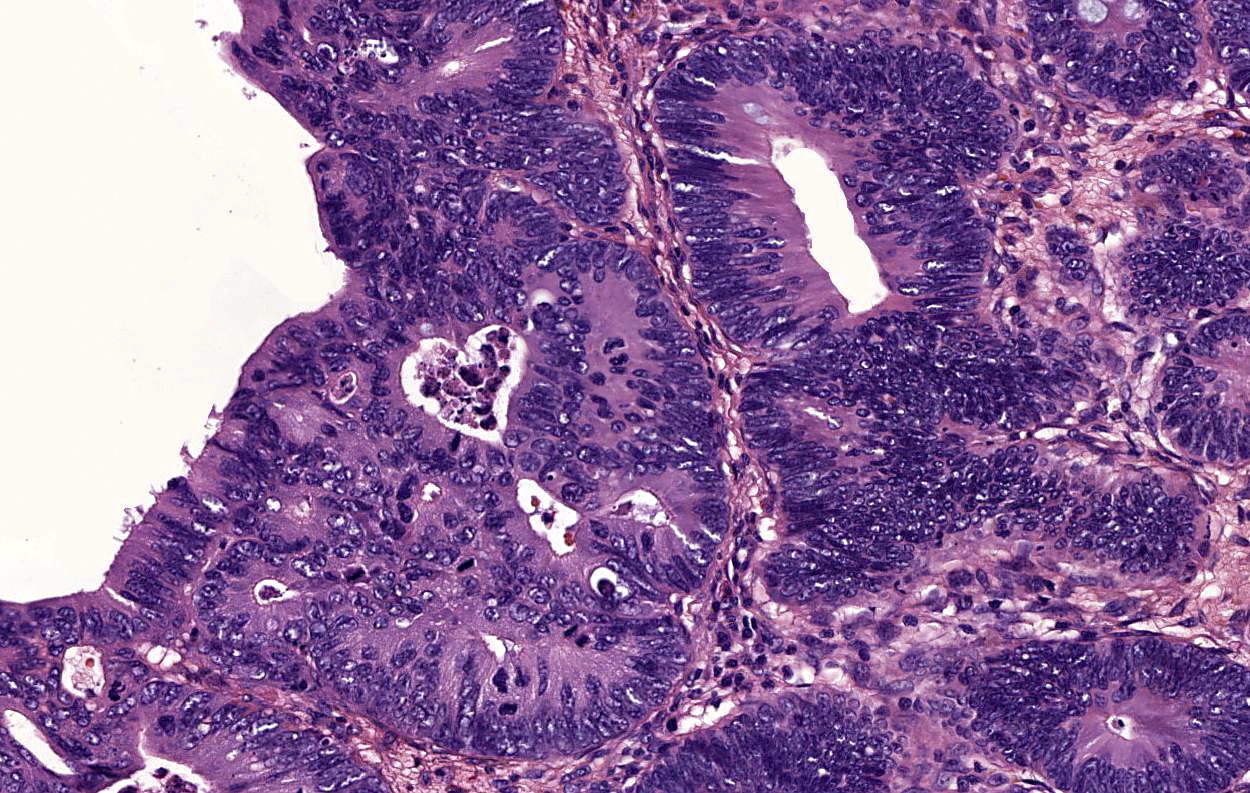
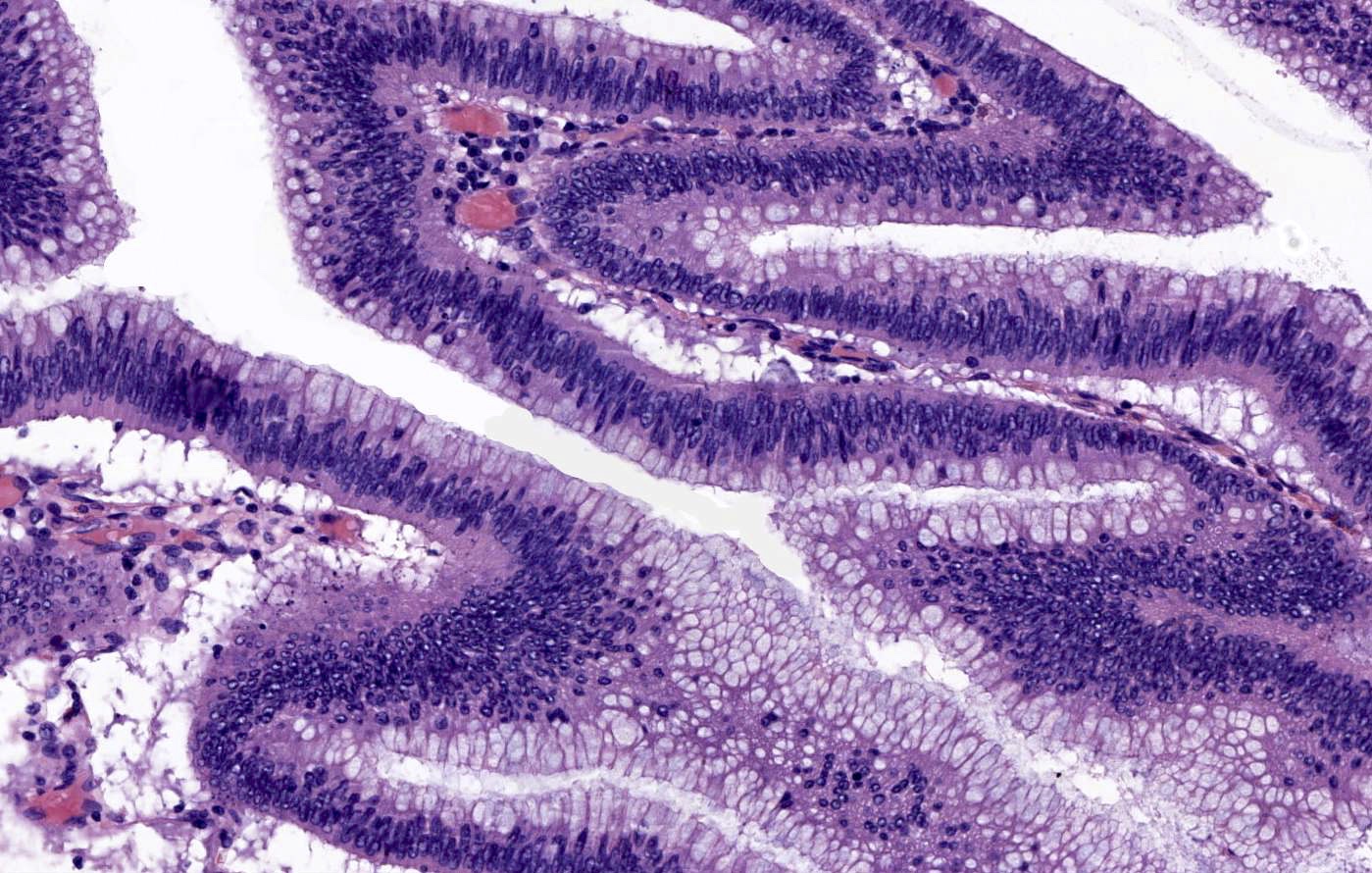
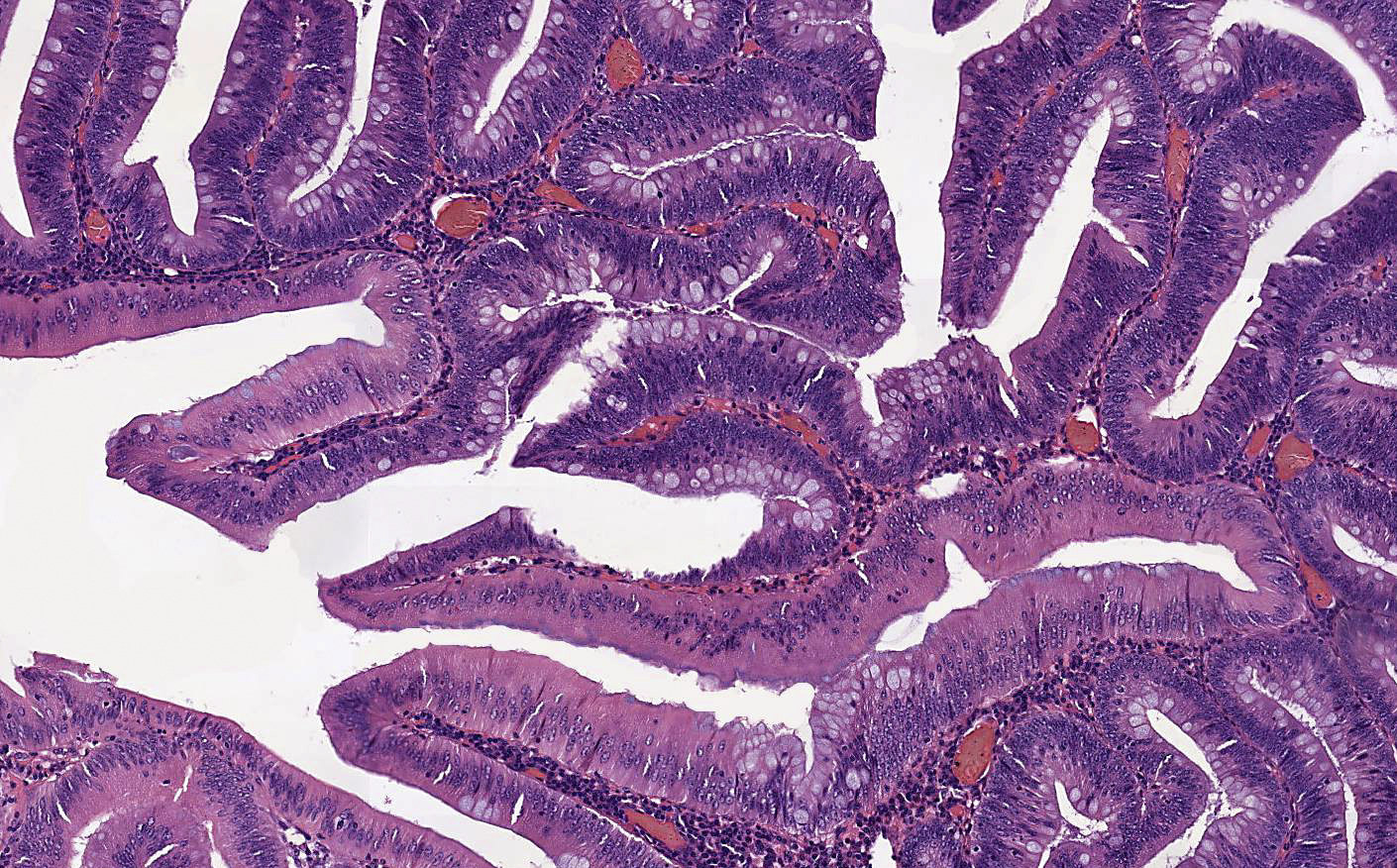
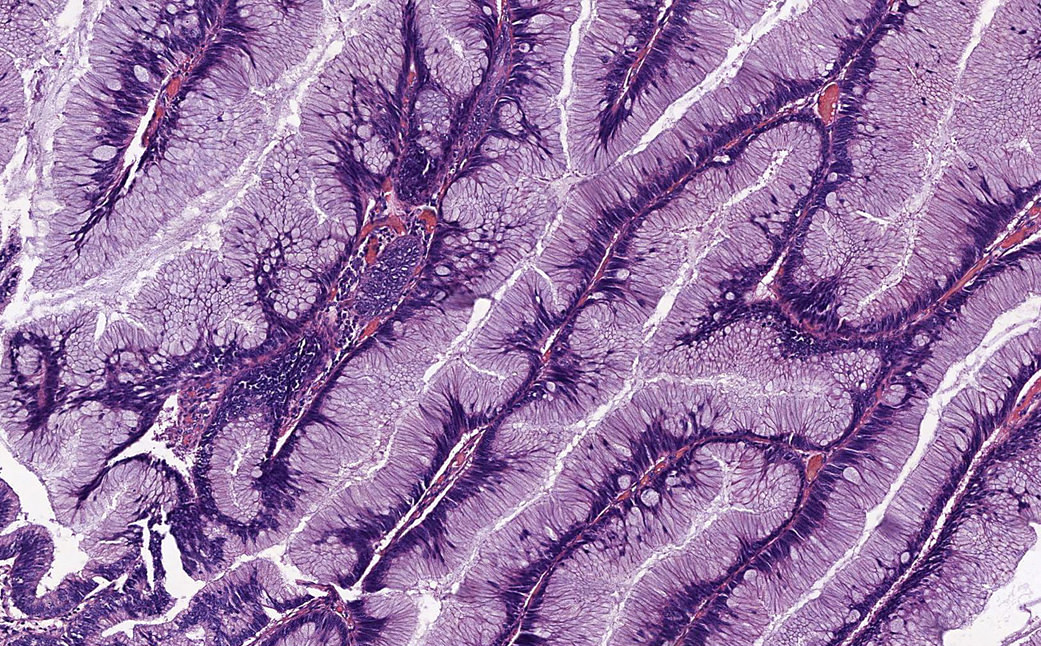
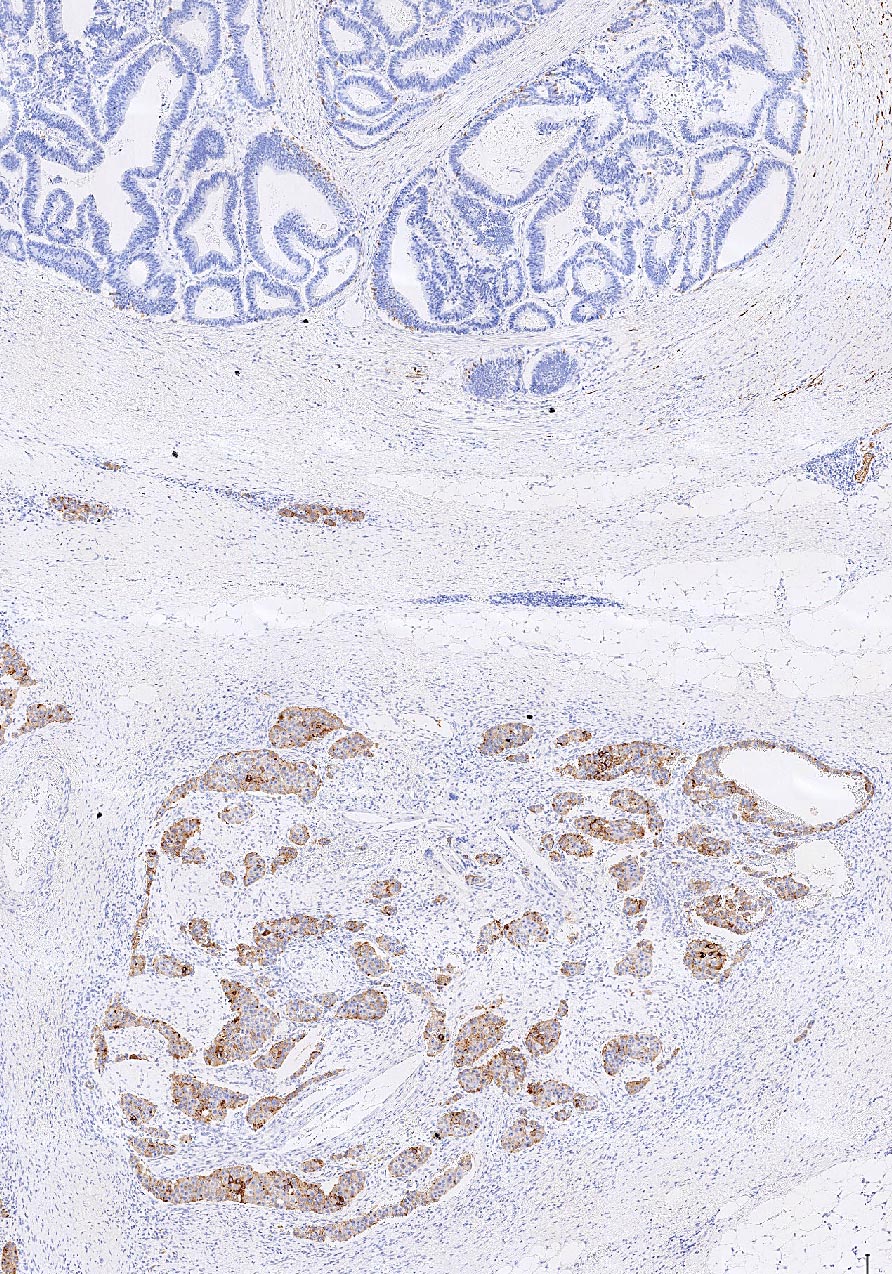
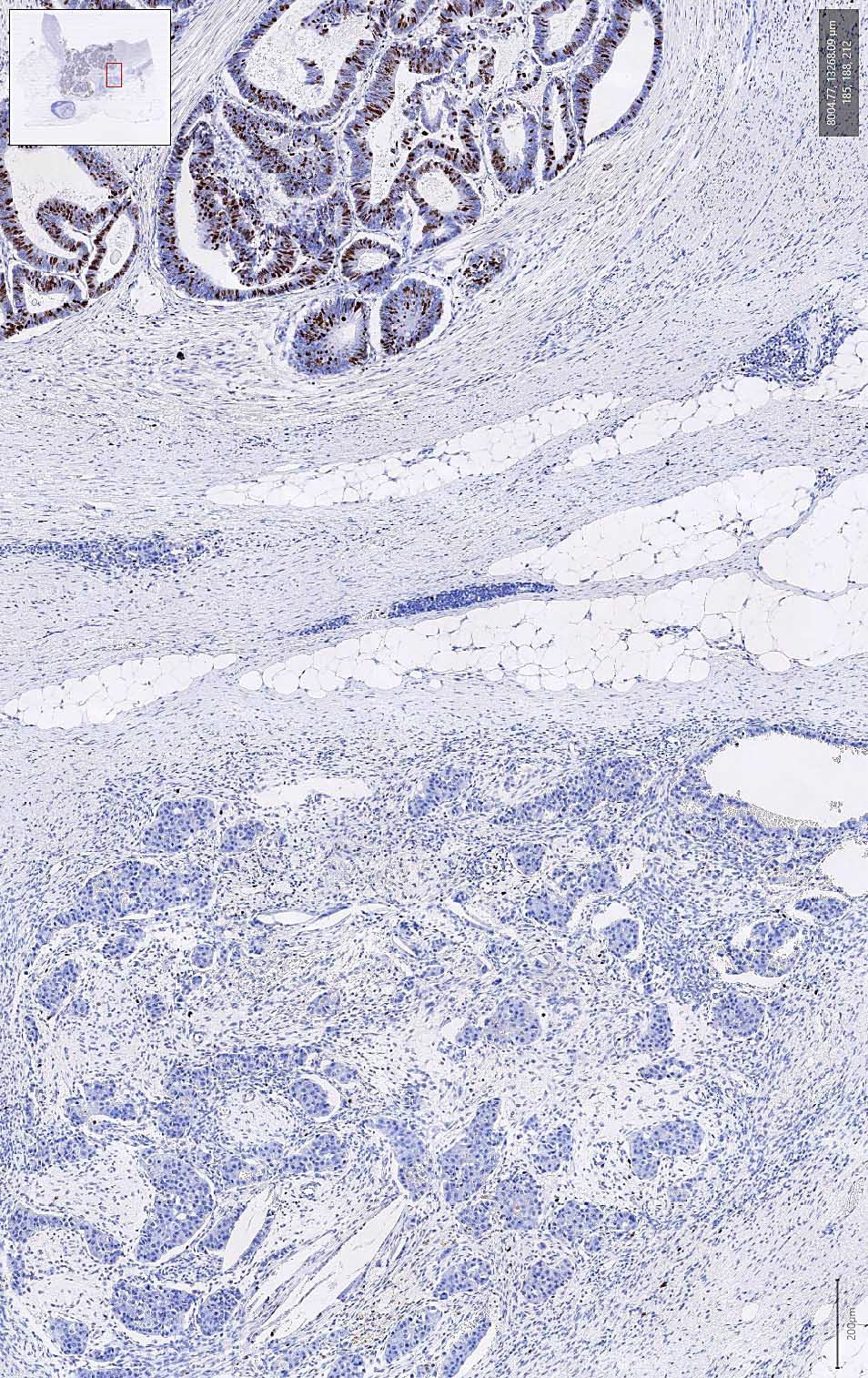
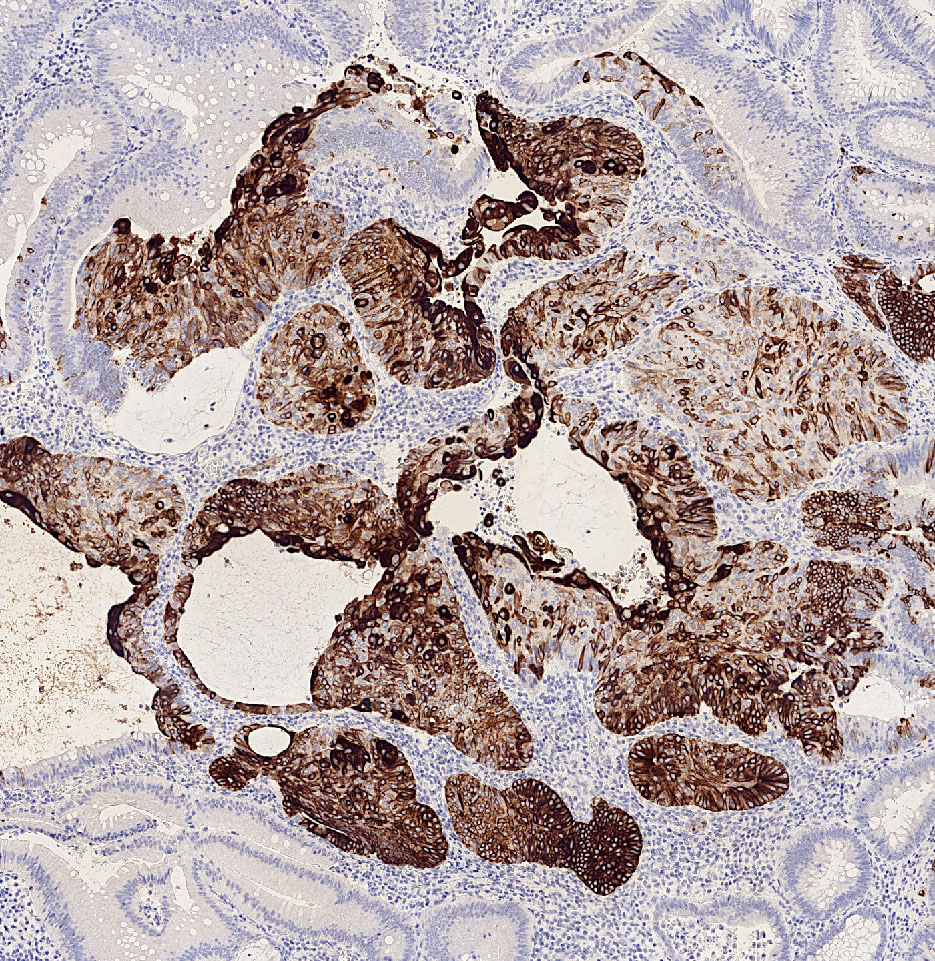
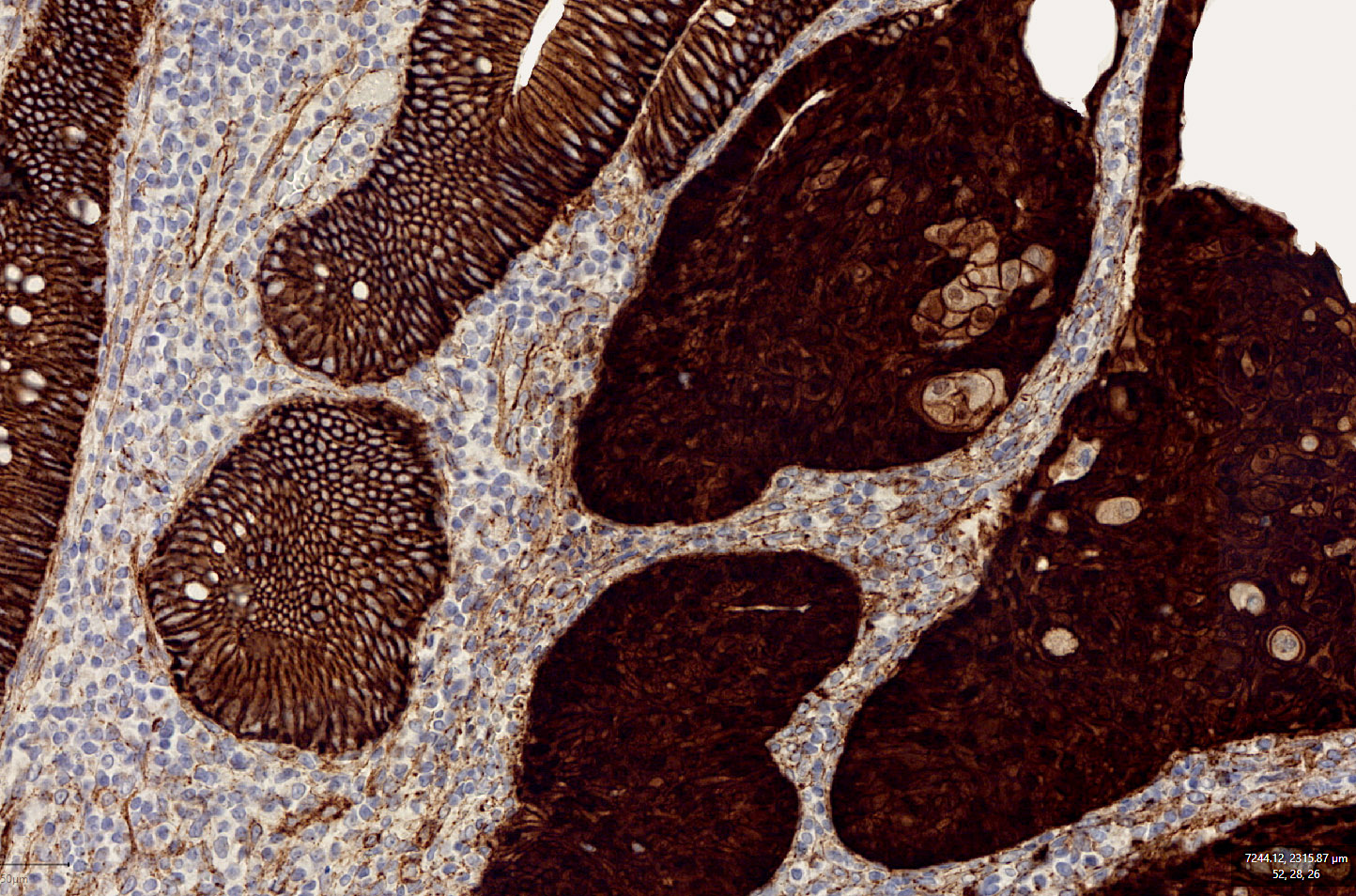
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Carolina Martinez Ciarpaglini, M.D., Ph.D., Jijgee Munkhdelger, M.D., Ph.D. and Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D.
Positive stains
- CK20: positive in 95% of cases (Dig Dis Sci 2005;50:1741)
- CDX2 (Gut 2002;51:184)
- p53: more frequent and intense in adenomas with high grade dysplasia (50%) than in those with low grade dysplasia (28%) (Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:980)
- Beta catenin: cytoplasmic and nuclear immunoreactivity in areas of intestinal metaplasia (Histopathology 2021;78:348)
- CK5/6 and cyclin D1 overexpression in areas of squamous metaplasia (Histopathology 2021;78:348)
Negative stains
- CK7: usually negative but may be positive in approximately 5% of cases (Dig Dis Sci 2005;50:1741)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- KRAS mutations in 52% (Pathol Oncol Res 2012;18:1077)
- Even subtle villous change in tubular adenoma is associated with more frequent KRAS and P53 mutations (Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015;1:15065)
- Routine screening of mismatch repair proteins (MMR) in polyps is not effective in identifying Lynch syndrome carriers (Clin Colorectal Cancer 2017;16:173)
- Most cases associated with Lynch syndrome show loss of MMR protein expression, especially when high grade dysplasia in present (Mod Pathol 2012;25:722)
Sample pathology report
- Colon, polyp at 12 cm, endoscopic polypectomy:
- Tubulovillous adenoma with high grade dysplasia
- Colon, polyp at 14 cm, endoscopic polypectomy:
- Villous adenoma
Differential diagnosis
- Traditional serrated adenoma:
- Exophytic tubulovillous or villous polypoid architecture with at least 2 of 3 constituent features (J Clin Pathol 2016;69:6, BMJ Open Gastroenterol 2019;6:e000317):
- Striking granular eosinophilic cytoplasm; prominent cytoplasmic eosinophilia that occupies > 50% of tubulovillous / villous adenoma is uncommon (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:212)
- Presence of ectopic crypt foci: more extensive small and short crypts with no relation to the underlying muscularis mucosae (Histopathology 2015;66:308)
- Luminal serration is defined as deep clefts and slit-like spaces that lead to broad luminal fronds imparting a mushroom-like appearance (not present in tubulovillous and villous adenoma) (Histopathology 2015;66:308)
- Exophytic tubulovillous or villous polypoid architecture with at least 2 of 3 constituent features (J Clin Pathol 2016;69:6, BMJ Open Gastroenterol 2019;6:e000317):
- Tubular adenoma:
- Adenomatous polyp with disorganized glands (tubular appearance) and flat surface
- May show some villous component, representing < 20% of the lesion (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:212)
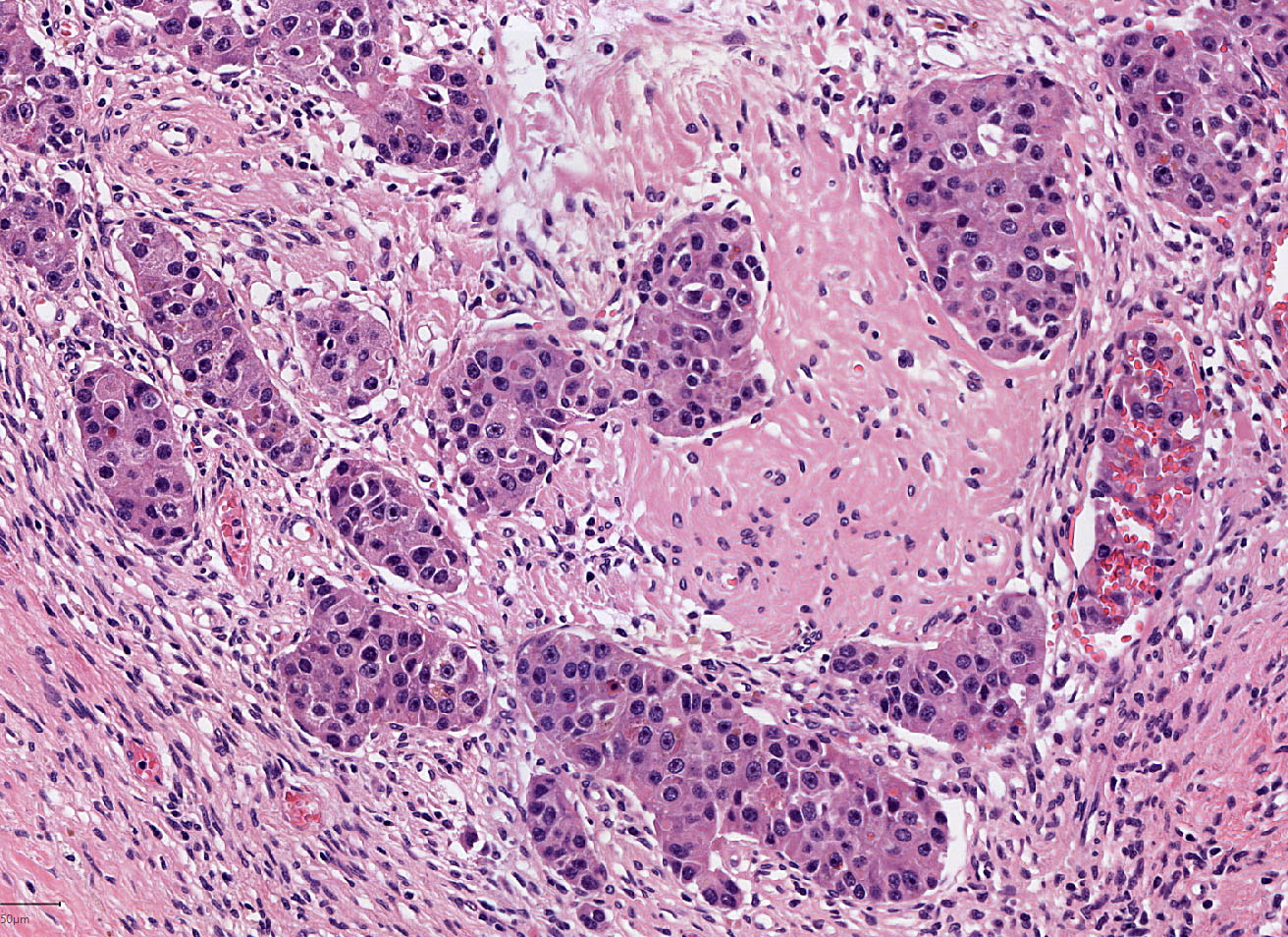
- Adenoma-like adenocarcinoma:
- Invasive carcinoma with architectural and cytologic features resembling villous adenoma; differential diagnosis with villous adenoma may be a challenge
- Finding of epithelial islands surrounded by desmoplastic stroma favors this diagnosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1460)
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. Tubulovillous adenoma with squamous metaplasia
Comment here
Reference: Tubulovillous / villous adenoma
Comment here
Reference: Tubulovillous / villous adenoma
Practice question #2
Which of the following is true about villous adenoma?
- Frequently associated with KRAS mutations
- Precursor lesion in the serrated pathway of colorectal development
- Presents the same risk of malignant transformation as tubular adenoma
- Routine screening of MMR proteins for Lynch syndrome in this lesion is useful
Practice answer #2
A. Frequently associated with KRAS mutations
Comment here
Reference: Tubulovillous / villous adenoma
Comment here
Reference: Tubulovillous / villous adenoma