Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Frozen section description | Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Memon A, Ahmad Z, Minhas MK. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorpleomorphicxanthoastrocytoma.html. Accessed September 14th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a circumscribed astrocytic glioma with large multinucleated cells, spindle cells and xanthomatous cells with frequent eosinophilic granular bodies and rich reticulin network
- It is characterized by BRAF p.V600E mutation or other MAPK pathway gene alterations combined with homozygous CDKN2A / B deletion
- Can be graded CNS WHO grade 2 or 3
Essential features
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a circumscribed astrocytoma with superficial location often involving leptomeninges, most often located in temporal lobe
- Classic histology with pleomorphic, xanthomatous and multinucleated tumor cells, often with eosinophilic granular bodies and rich reticulin network
- It shows characteristic genetic alterations including BRAF p.V600E mutation and homozygous deletion of CDKN2A / B
- Assigned CNS WHO grade 2 and 3
Terminology
- Not recommended: pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features; anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma for CNS WHO grade 3
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9424/3 - pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- ICD-11: 2A00.0Y & XH99U2 - other specified gliomas of brain & pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Epidemiology
- PXA accounts for < 0.3% of primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors, with an annual incidence of < 0.7 cases per 100,000 population (Neuro Oncol 2019;21:v1)
- M = F; mean age at diagnosis is 26.3 years
- It typically develops in children and young adults; however, older patients may be affected (J Neurooncol 2012;110:99)
Sites
- Majority of tumors occur supratentorially, most commonly in temporal lobes
- Often superficially located with involvement of the overlying leptomeninges (Brain Pathol 2015;25:575)
- There are rare case reports of PXAs involving
- Cerebellum (Surg Neurol 2007;68:89, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2004;146:1241)
- Spinal cord (J Neurosurg Spine 2006;5:72)
- Pituitary stalk (Neurol India 2018;66:1193)
- Pineal gland (Brain Tumor Pathol 2013;30:242)
- Retina (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:79)
- Intraventricular location (Cureus 2023;15:e35975, Cureus 2018;10:e2665)
Pathophysiology
- It is thought to originate from subpial astrocytes, supported by its frequent superficial location in the cerebral hemispheres and by the fact that both share similar ultrastructural features (Radiol Med 2022;127:1134)
- BRAF mutation or other MAPK pathway alterations combined with homozygous deletion of CDKN2A / B (Brain Pathol 2019;29:85, Brain Pathol 2021;31:20)
- PXAs with TERT promoter mutations are associated with shorter overall survival (Acta Neuropathol 2013;126:907, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:5)
- PXAs rarely harbor TP53 mutations (Neurogenetics 2001;3:159)
- Alterations in other genes (including SMARCB1, BCOR, BCORL1, ARID1A, ATRX, PTEN, FANCA, FANCD2, FANCI, FANCM, PRKDC, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, NOTCH4 and BCL6) have been described with unclear pathogenetic significance in PXAs (Brain Pathol 2019;29:85)
Etiology
- No known specific etiology
- Rare cases have been reported in patients with
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (Clin Neuropathol 2012;31:152, Clin Neuropathol 2012;31:54)
- DiGeorge syndrome (J Neurooncol 2011;102:509)
- Familial melanoma astrocytoma syndrome (Clin Neuropathol 2017;36:213)
- Down syndrome (Front Oncol 2019;9:277)
- Sturge-Weber syndrome (Pediatr Radiol 2005;35:910)
Clinical features
- Many patients present with long history of epileptic seizures
- Other symptoms that are related to raised intracranial pressure include headaches, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, diplopia and somnolence (CNS Oncol 2019;8:CNS39, Cureus 2023;15:e35975)
Diagnosis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most effective imaging method
- Diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy or surgical excision; gross total resection may not be achieved in deeply situated or widely infiltrative tumors
- Diagnostic molecular DNA methylome profile
- Next generation sequencing (NGS)
- Chromosome microarray
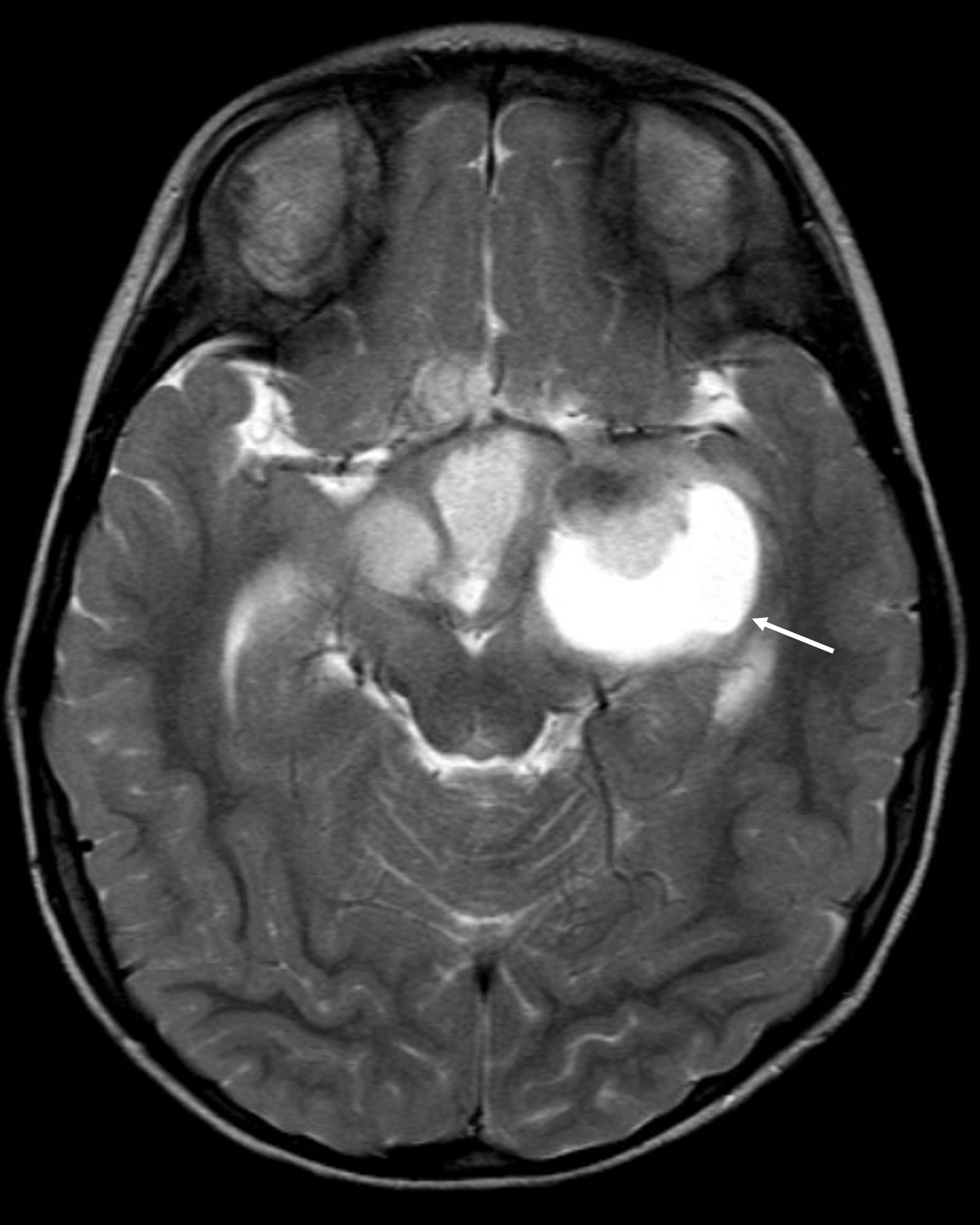
Radiology description
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Variable appearance (hypodense, hyperdense or mixed)
- May be well or poorly demarcated
- With strong and sometimes heterogenous contrast enhancement
- Tumor cysts are usually hypodense
- Calcification is rare
- Due to superficial location, it may cause scalloping of overlying bone
- MRI scan
- Variable / heterogeneous appearance, often with cystic component
- Solid component is either hypointense or isointense to gray matter on T1 weighted images
- Hyperintense or mixed signal on T2 weighted and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images
- Cystic component is isointense to cerebrospinal fluid
- Postcontrast enhancement is moderate to strong
- Adjacent edema is not pronounced (Sci Rep 2018;8:14275)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- PXA frequently recurs and is associated with decreased survival compared to other circumscribed low grade gliomas in children and young adults
- Malignant progression is more common in PXA than in other RAS / MAPK driven circumscribed low grade gliomas (Brain Pathol 2015;25:575)
- Extent of surgical excision is the most significant prognostic factor associated with recurrence (Cancer 1999;85:2033)
- Prognostic significance of CNS WHO grading in PXA has been confirmed by 2 large independent studies (Neuro Oncol 2020;22:1474, Brain Pathol 2021;31:20)
- MAPK pathway gene alterations, particularly BRAF p.V600E as well as homozygous deletion of CDKN2A or CDKN2B, are not associated with tumor grade or prognosis (Brain Pathol 2018;28:172, Acta Neuropathol 2011;121:397)
- TERT promoter alteration is associated with more aggressive phenotype and a marker of anaplastic transformation (World Neurosurg 2019;126:624, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:5)
Case reports
- 18 year old woman with a pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma in the left cerebellum (World Neurosurg 2020;139:577)
- 22 and 43 year old men presented with repeated generalized seizures (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22478)
- 28 year old man had a sudden limb twitch and visited a local hospital (Int J Gen Med 2020;13:1581)
- 32 year old woman with a mass in her medial right temporal lobe (Diagn Cytopathol 2022;50:E240)
- 33 year old man with an intraventricular anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (Cureus 2023;15:e35975)
- 48 year old healthy man presented with progressive right upper limb weakness (Cureus 2022;14:e23060)
Treatment
- For CNS WHO grade 2 PXAs, early intervention with complete surgical excision is treatment of choice and can be followed by wait and watch strategy (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:e315)
- For CNS WHO grade 3 PXAs, postoperative radiotherapy may be offered in adults (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:e315)
- Radiotherapy may play a role for residual or recurrent disease
- Traditional systemic therapies have shown limited benefit in treating PXA
- Targeted BRAF inhibition, alone or in combination with other treatments including MEK inhibition, has been associated with marked radiographic responses in BRAF mutated PXA (CNS Oncol 2019;8:CNS39)
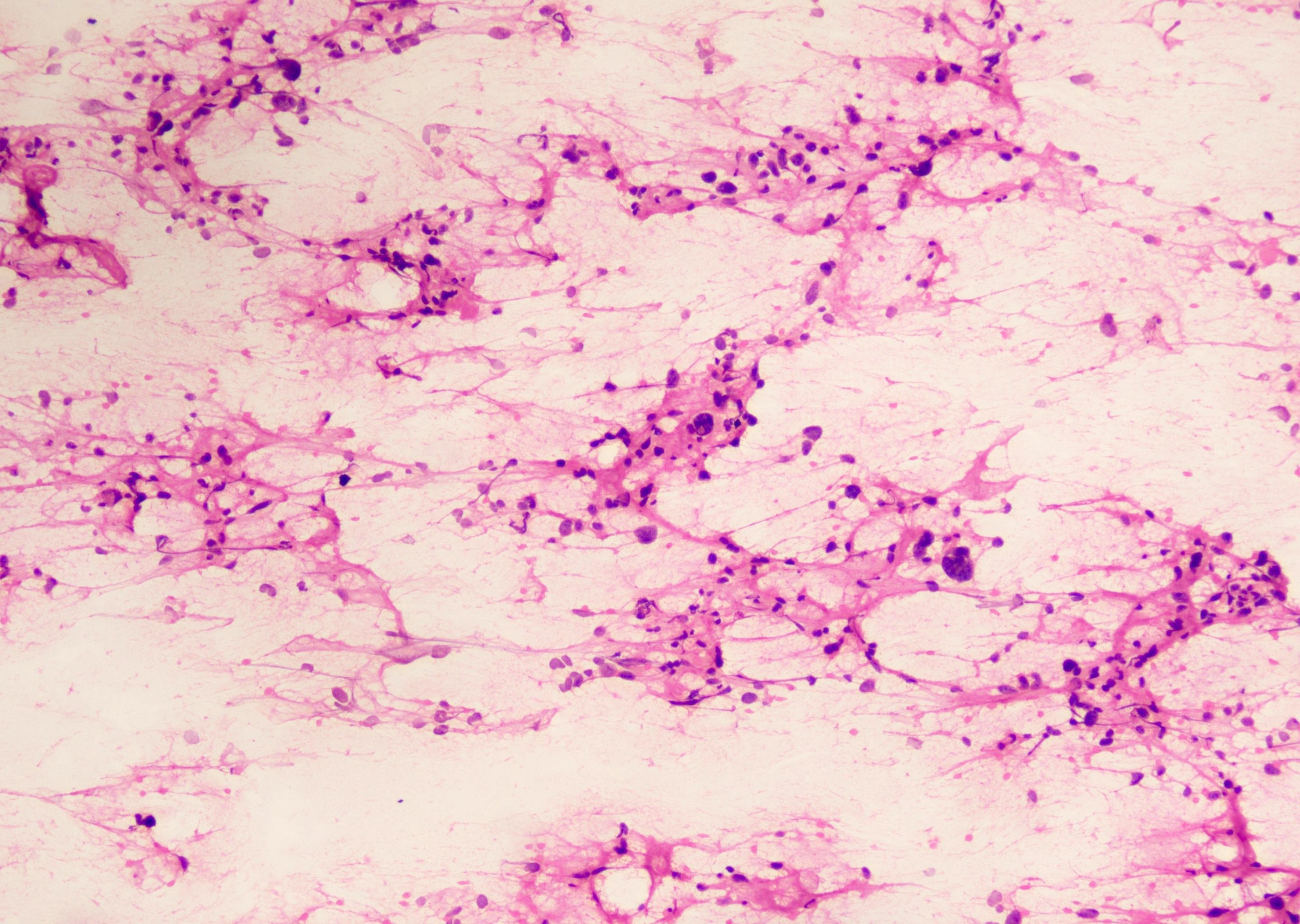
Frozen section description
- Variable population of spindled to pleomorphic tumor cells with long and coarse cytoplasmic processes and fibrillary fragments with vessels
- Multinucleated giant cells and tumor cells with microvacuolization resembling xanthomatous cells can be seen (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:339)
- Sometimes eosinophilic granular bodies are observed
Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images
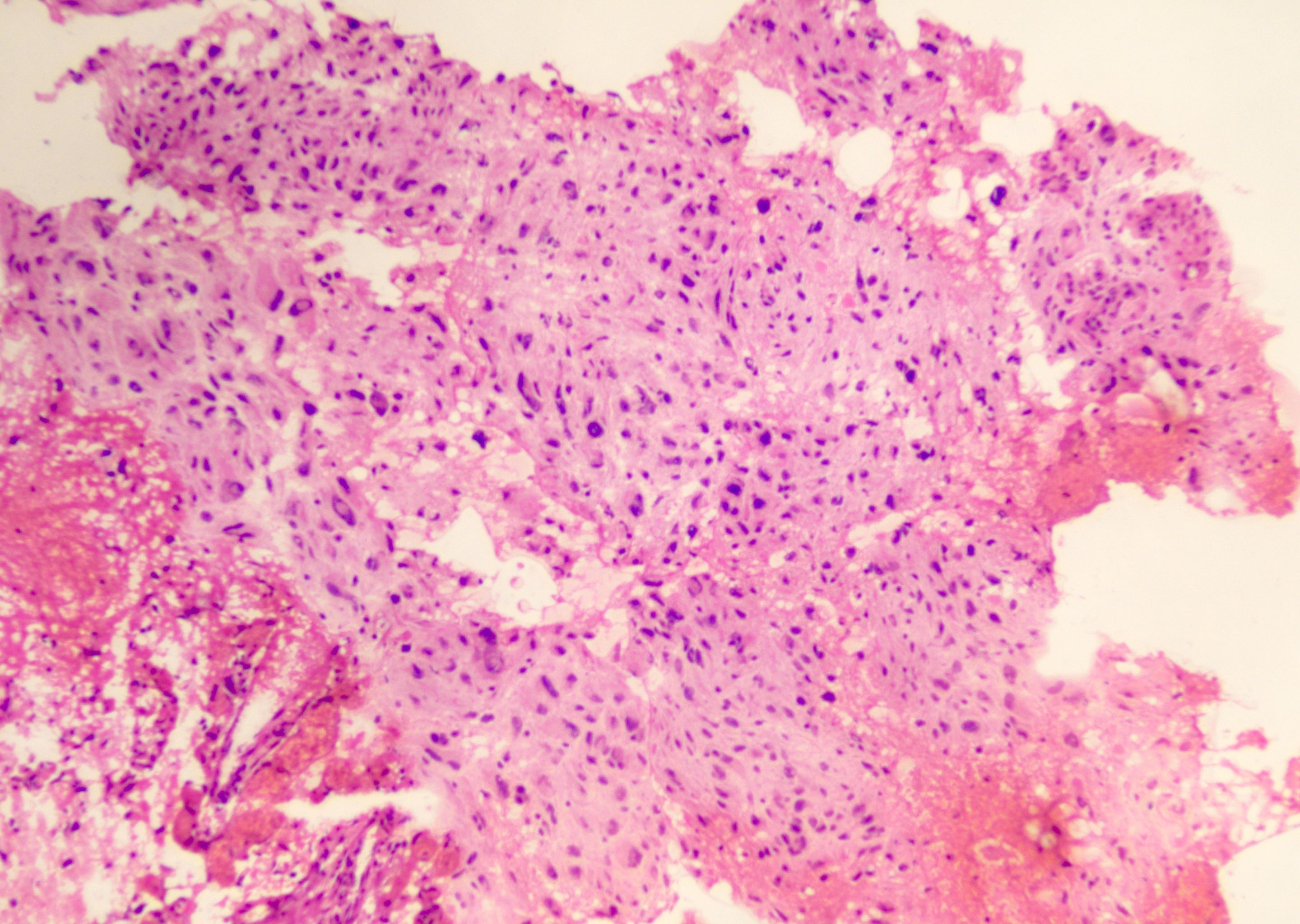
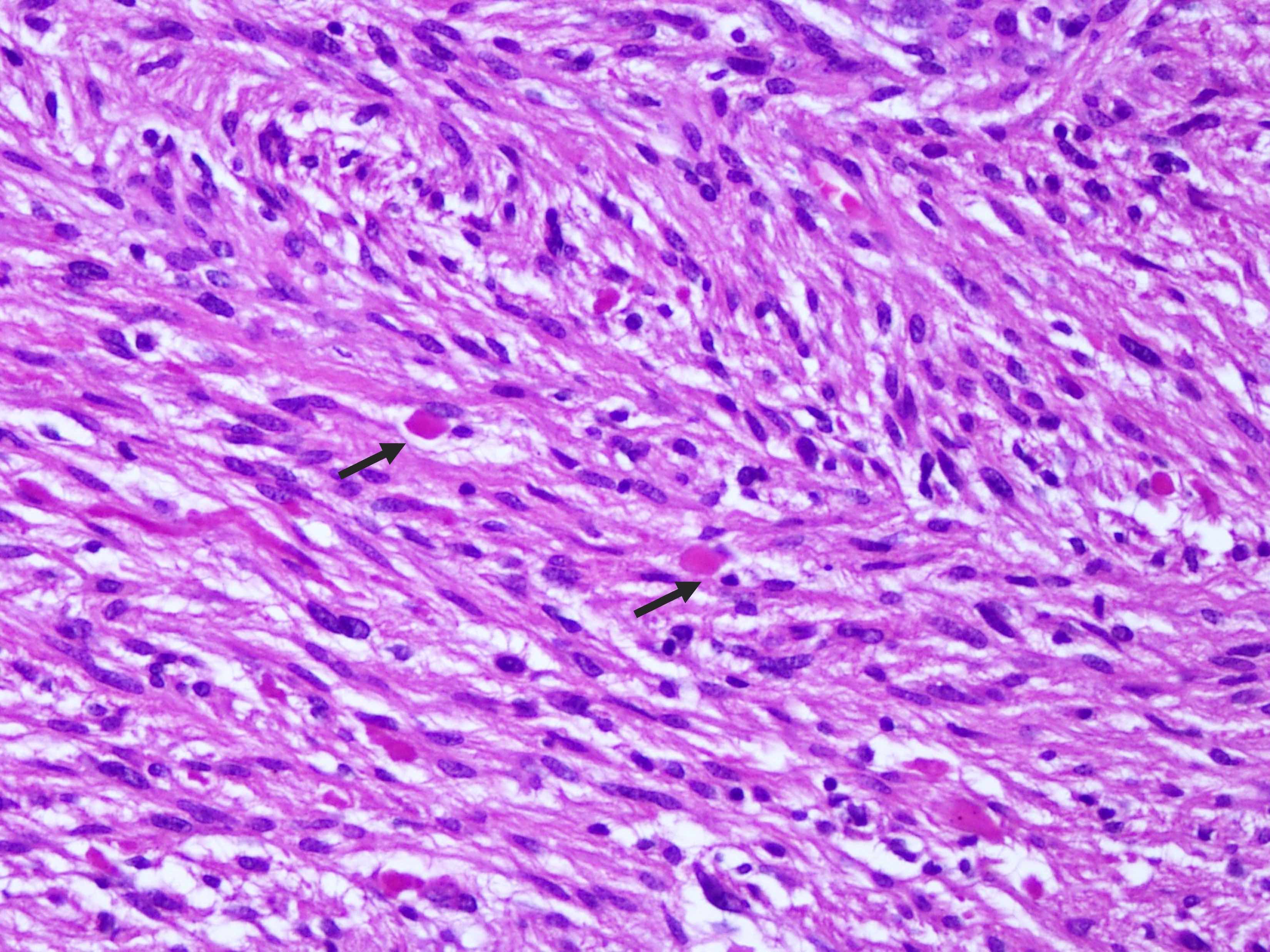
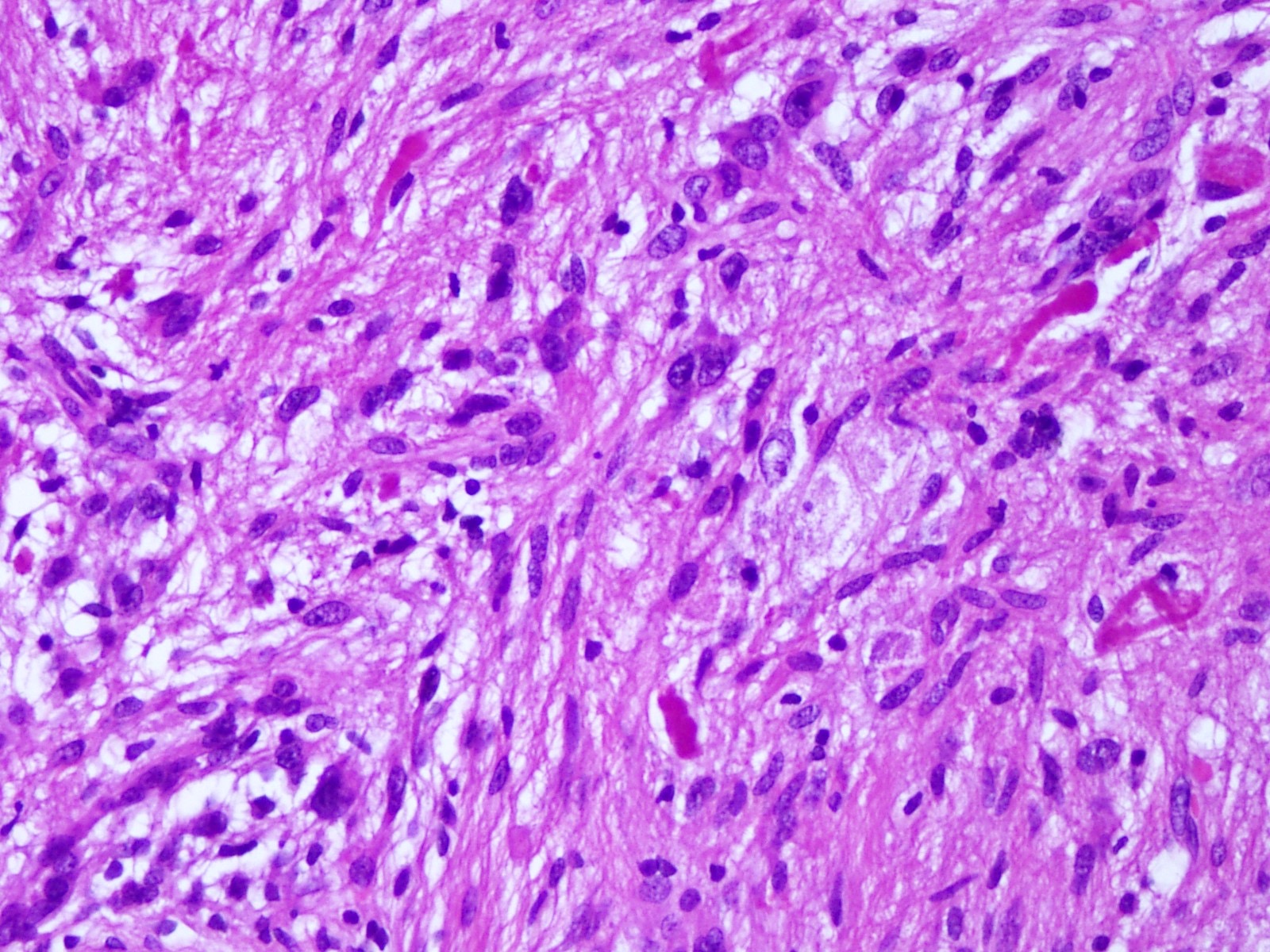
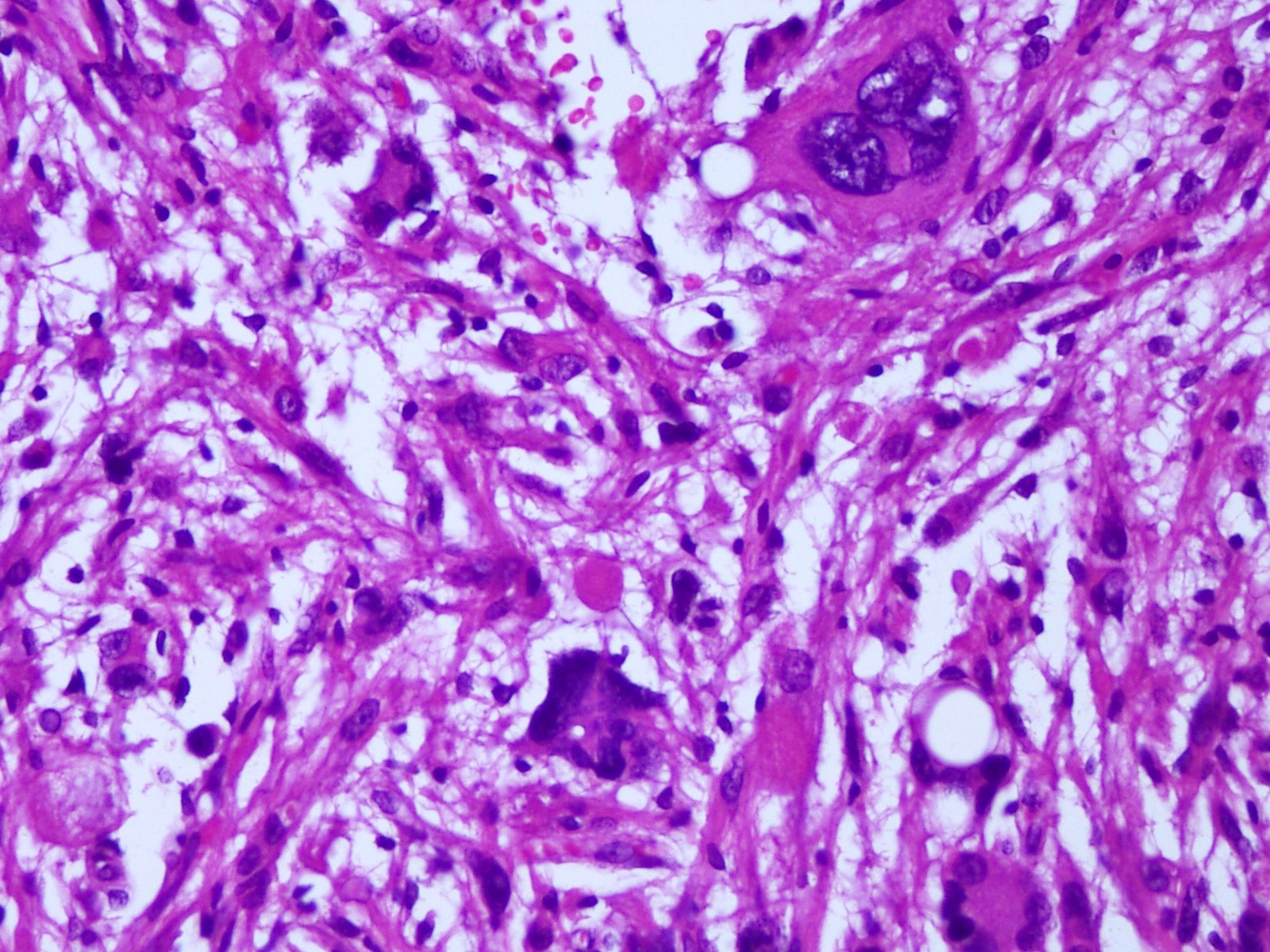
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mostly solid, noninfiltrative growth pattern; however, microscopic infiltration can be seen at the periphery
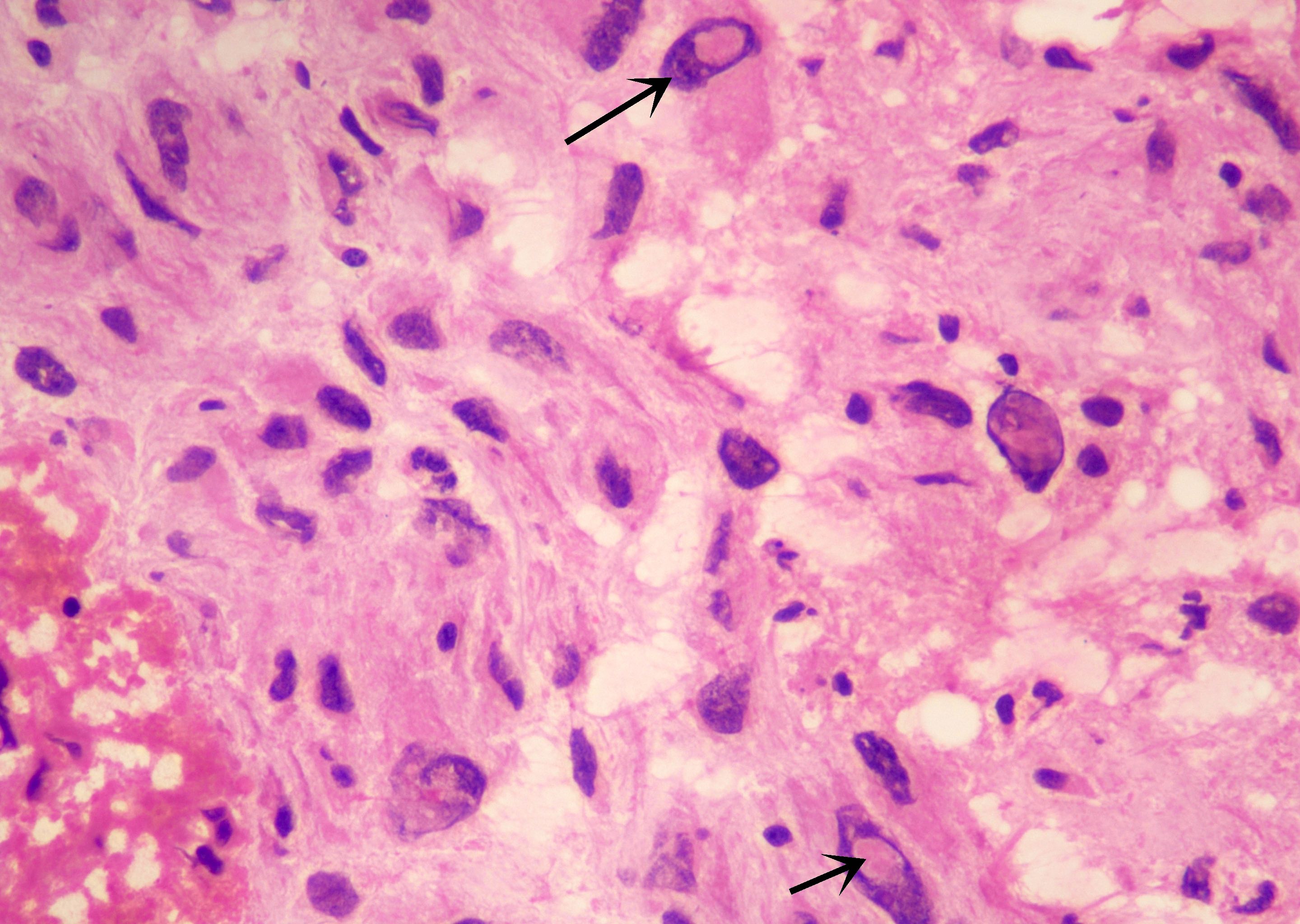
- Mixture of spindled, epithelioid, pleomorphic and multinucleated tumor cells, with some showing vacuolated cytoplasm (xanthomatous cells)
- Intranuclear inclusions, prominent nucleoli and perivascular lymphocytic infiltration are common (Cancer 1999;85:2033)
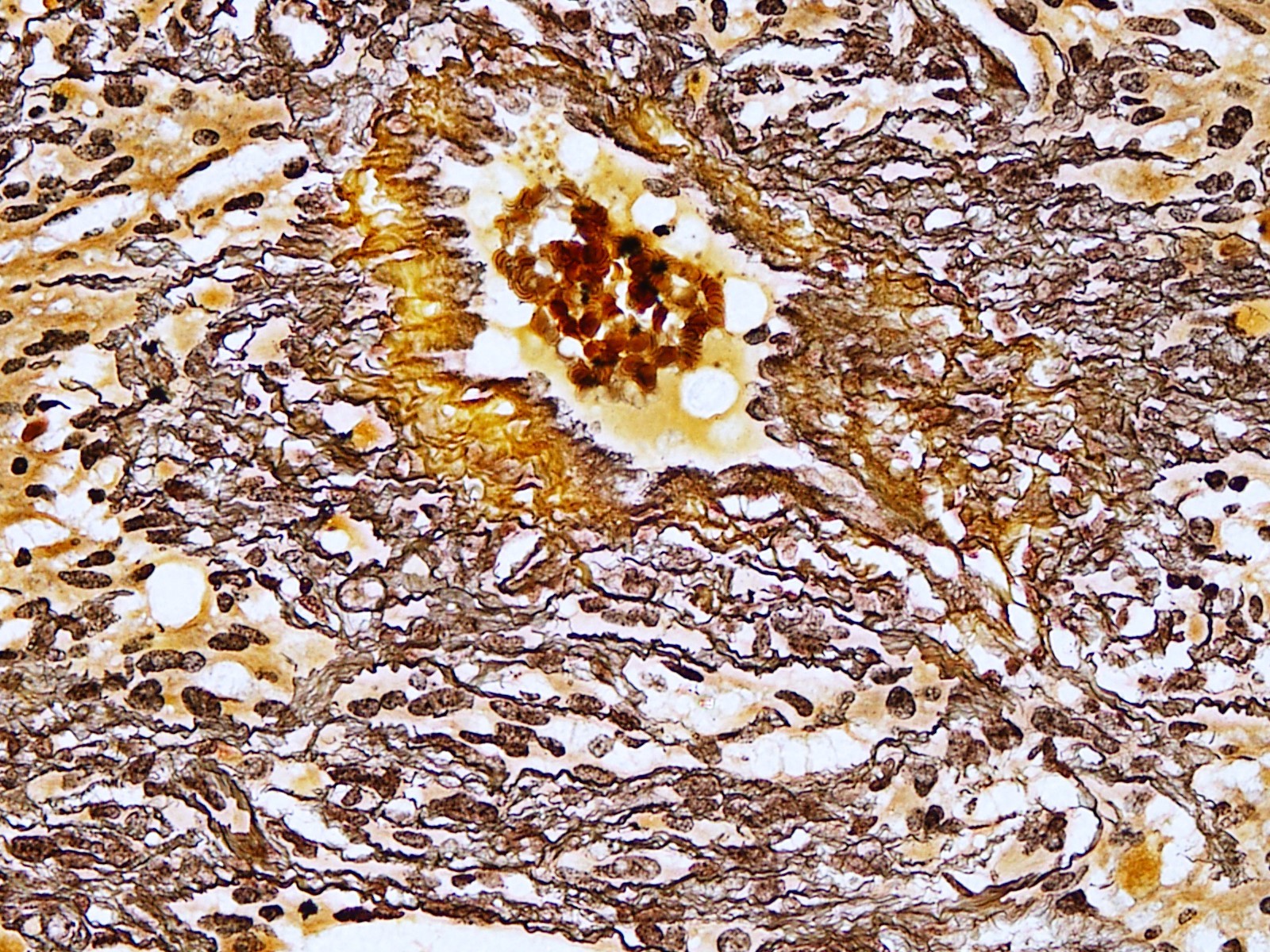
- Frequent eosinophilic granular bodies and dense reticulin deposition
- CNS WHO grading
- CNS WHO grade 2 is assigned to tumors with < 5 mitoses/10 high power fields (HPF)
- Necrosis is commonly seen in tumors with high mitotic activity; however, its significance in isolation is unclear
- Microvascular proliferation is uncommon (Cancer 1999;85:2033)
- CNS WHO grade 3 PXAs may demonstrate less pleomorphism and more diffusely infiltrative pattern
- In CNS WHO grade 3 tumors, a mean Ki67 labeling index of 15% has been reported, whereas it is generally < 1% in CNS WHO grade 2 tumors
- Common cytological patterns of anaplasia include monomorphic small cells, fibrillary morphology, epithelioid and rhabdoid morphology (Brain Pathol 2018;28:172)
Microscopic (histologic) images
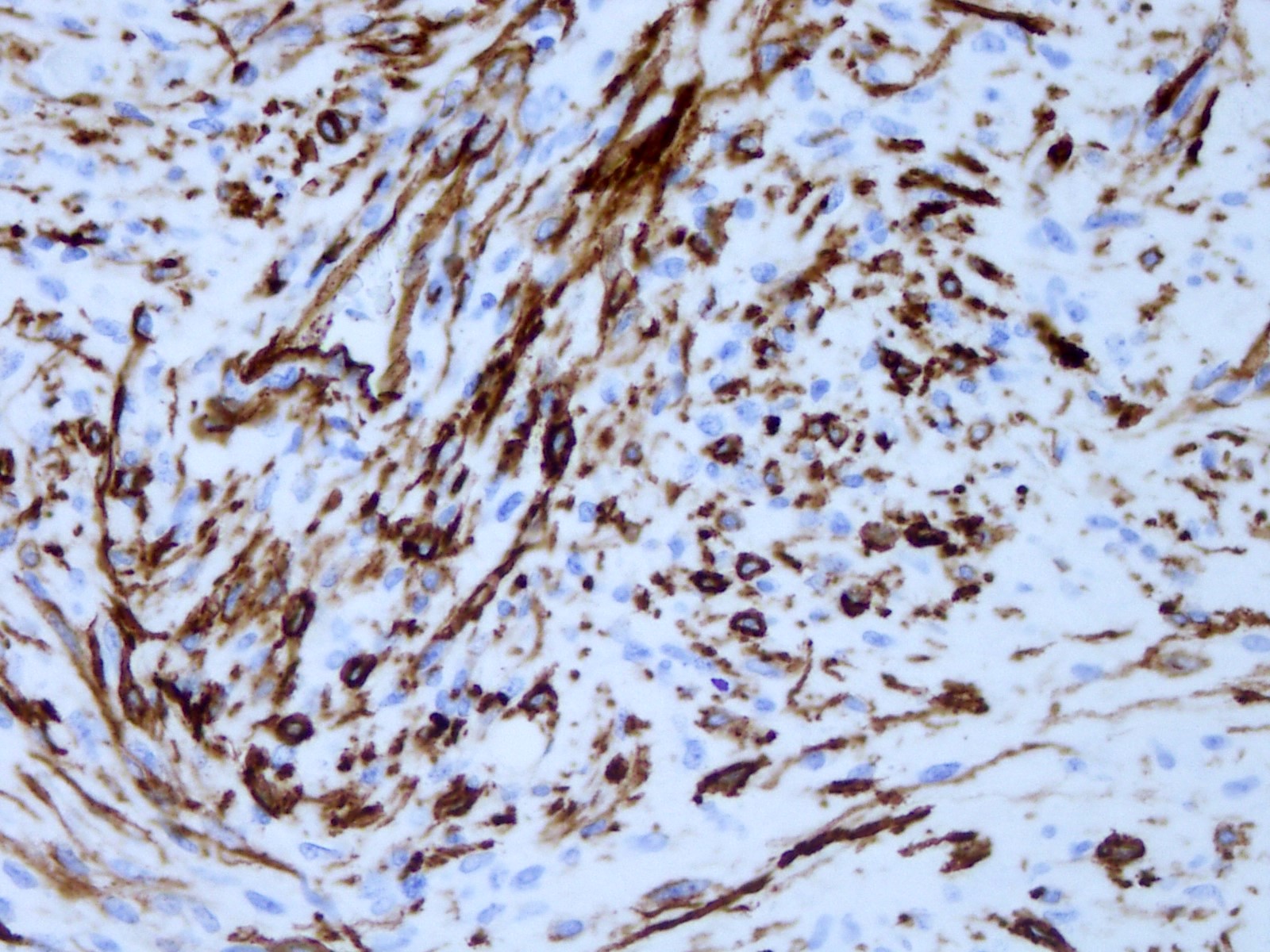
Positive stains
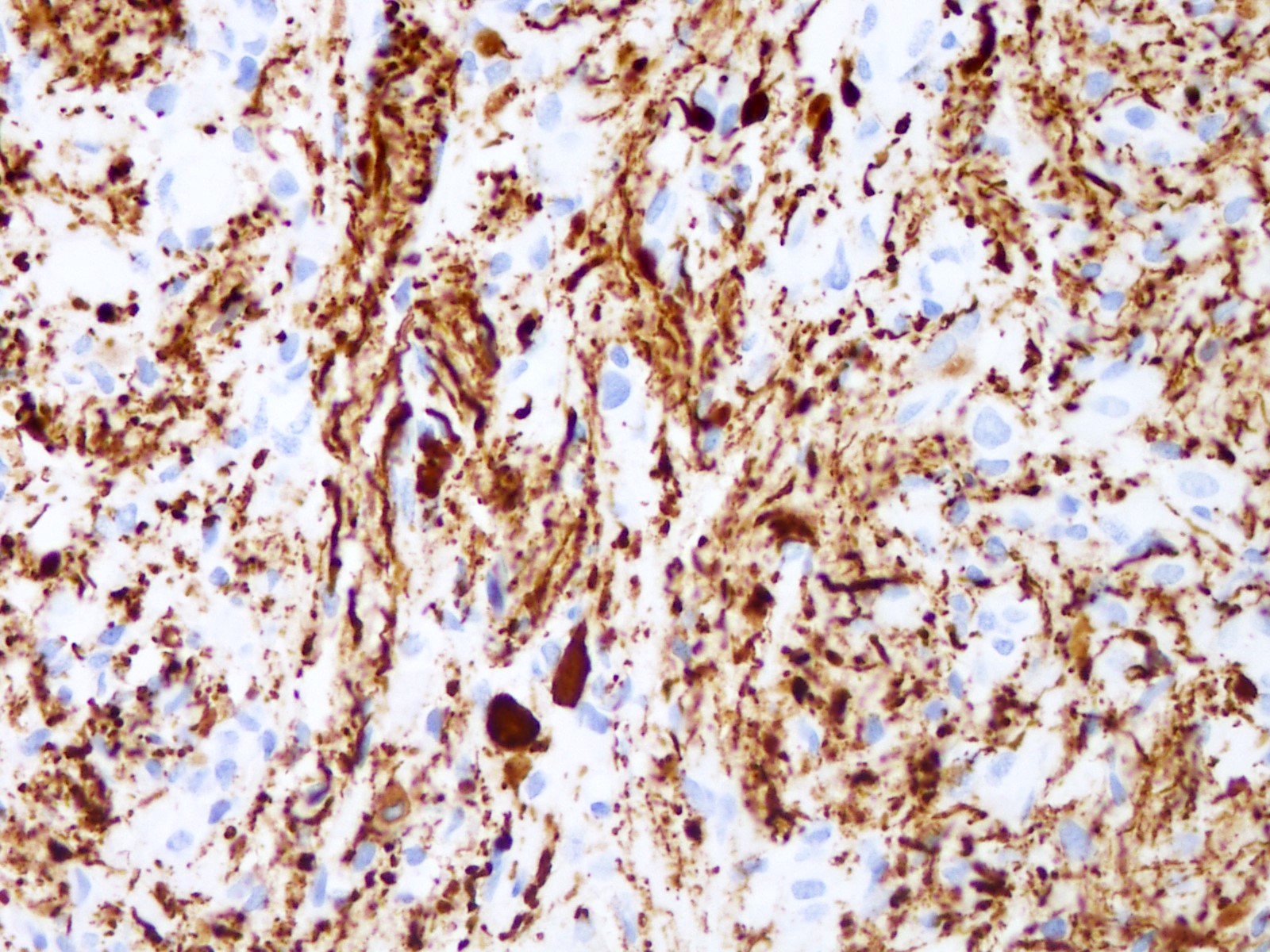
- GFAP, Olig2 and S100 are usually diffusely positive (Cancer 1999;85:2033)
- Most tumors express CD34 (Acta Neuropathol 2003;105:358)
- Reticulin stain demonstrates rich reticulin network around individual tumor cells
- PAS stain is helpful for identifying eosinophilic granular bodies
- Focal expression of neuronal markers (synaptophysin, neurofilament, class III β tubulin and MAP2) is seen in some PXAs (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:479)
- BRAF p.V600E (VE1 antibody) expression is seen in 60 - 80% of cases (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2013;1:20)
- Focal SMARCB1 (INI1) loss has been reported in rare cases that underwent malignant transformation to tumors resembling atypical teratoid / rhabdoid tumors (Brain Pathol 2018;28:172)
Negative stains
- Negative for IDH1 R132H staining
- TP53 usually demonstrates wild type staining pattern (weak expression in rare tumor cells) (Neurogenetics 2001;3:159)
Electron microscopy description
- Presence of relatively few organelles, abundant filaments and microtubules, are characteristic of astrocytes
- Existence of basal laminas in the extracellular space surrounding the surface of the tumor cells and the presence of localized cytoplasmic densities associated with the plasma membrane adjacent to the basal lamina resembling hemidesmosomes (Cancer 1983;52:2055)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- MAPK pathway gene alterations
- Virtually all PXAs harbor alterations in a gene of the MAPK pathway, causing aberrant activation of this pathway
- The most frequent is the missense mutation of BRAF p.V600E occurring in 60 - 80% of PXAs (Acta Neuropathol 2011;121:397, PLoS One 2011;6:e17948, Brain Pathol 2019;29:85, Brain Pathol 2021;31:20)
- In BRAF p.V600E negative tumors, other MAPK pathway gene alterations are found, mostly involving other BRAF alterations (non-p.V600e mutations, non-KIAA1549::BRAF fusions), NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, RAF1 or NF1 (Brain Pathol 2018;28:172)
- CDKN2A or CDKN2B homozygous deletion
- ~94% of PXAs harbor homozygous deletions of CDKN2A / B (Brain Pathol 2019;29:85, Brain Pathol 2021;31:20)
- Combination of BRAF p.V600E mutation and CDKN2A or CDKN2B homozygous deletion is highly suggestive of PXA, although rare cases of ganglioglioma, epithelioid glioblastoma and high grade astrocytoma with piloid features may also have this molecular profile (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2018;6:47, Brain Pathol 2018;28:656, Brain Pathol 2018;28:663, Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:273)
- TERT alterations
- TERT promoter mutations and less commonly, TERT amplification have been found in PXA, more commonly in anaplastic tumors (Acta Neuropathol 2013;126:907)
- Presence of canonical pTERT mutation has been shown to be a robust indicator for poor prognosis in methylation class PXA (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:5)
- Some PXAs can also harbor gain of chromosome 7 and loss of chromosome 10 (+7 / -10), similar to glioblastomas; however, unlike glioblastomas, PXAs virtually never demonstrate tyrosine kinase receptor gene amplifications (such as EGFR amplification) (Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:793)
Videos
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma:
a brief review
Sample pathology report
- Temporal lobe lesion, gross total resection:
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, BRAF V600E mutant, CNS WHO grade 2
- Histological classification: pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- CNS WHO grade: 2
- Molecular information: BRAF V600E mutation, combined with homozygous deletion of CDKN2A / B
Differential diagnosis
- Ganglioglioma:
- Both show presence of eosinophilic granular bodies, lymphocytic infiltration, CD34 expression and BRAF p.V600E mutation
- Presence of true ganglion cells in gangliogliomas and absence of xanthomatous cells
- Absence of reticulin rich network surrounding individual tumor cells in gangliogliomas
- Absence of homozygous deletion of CDKN2A / B in gangliogliomas
- Giant cell glioblastoma:
- Both show gross circumscription, reticulin deposition, marked pleomorphism, multinucleated giant cells and lymphocytic infiltration
- Presence of neuronal antigens in PXAs, which are usually absent in giant cell glioblastoma
- TP53 is mutated in most giant cell glioblastomas (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:1187)
- Epithelioid glioblastoma:
- Both can show presence of epithelioid cells, frank anaplasia and BRAF p.V600E mutation
- Prior history of a CNS WHO grade 2 PXA can be helpful
- There is a PXA-like epithelioid glioblastoma subset, which clusters by methylation profiling with canonical PXAs with BRAF p.V600E mutation (79%), CDKN2A homozygous deletion (61%) and TERT promoter mutations (30%) (Brain Pathol 2018;28:656)
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 25 year old man presented with history of recurrent headaches and seizures. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed a solid circumscribed lesion in the temporal cortex with abnormal intensity. Biopsy revealed pleomorphic tumor cells with admixed xanthomatous cells and multinucleated giant cells. Eosinophilic granular bodies were noted along with reticulin rich network. There was no visible mitosis, microvascular proliferation or necrosis. On molecular testing, there was a BRAF p.V600E mutation. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Epithelioid glioblastoma
- Ganglioglioma
- Giant cell glioblastoma
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
Practice answer #1
D. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. The clinical scenario describes characteristic radiological, histological and genetic profile of pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Answers A and C are incorrect because BRAF p.V600E mutation is reported in as many as 50% of glioblastoma with epithelioid morphology and rarely in giant cell glioblastoma; however, these show mitoses (including atypical mitoses) or microvascular proliferation and necrosis on histology. Answer B is incorrect because ganglioglioma also harbors BRAF p.V600E mutation but has distinctive morphology. Answer E is incorrect because subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) may rarely show BRAF p.V600E mutation but has characteristic radiological and morphological features.
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Practice question #2
A 20 year old woman presented with history of epileptic seizures. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed a solid circumscribed lesion in the temporal cortex with abnormal intensity. Biopsy revealed characteristic histological features of pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma including pleomorphic tumor cells with admixed xanthomatous cells, multinucleated giant cells and eosinophilic granular bodies. What is the most frequently mutated gene?
- BRAF V600E
- EGFR
- Histone H3
- IDH1
- TERT promoter
Practice answer #2
A. BRAF V600E. The most frequently found mutated gene in PXAs is BRAF, which encodes an intracellular component of the MAPK pathway. Answers B and E are incorrect because EGFR and TERT promoter mutations are rare in low grade gliomas. These are characteristically seen in high grade astrocytomas. Answer D is incorrect because IDH1 is characteristically mutated in adult type diffuse gliomas. Answer C is incorrect because H3 K27M is altered in diffuse midline gliomas.
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma