Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2 | Practice question #3 | Practice answer #3Cite this page: McHugh KE, Plesec TP. Chronic cholecystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderchroniccholecystitis.html. Accessed September 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, typically secondary to gallstones
Essential features
- The most common disease of the gallbladder, typically secondary to cholelithiasis
- Variety of histologic findings, including variable amounts of mononuclear cell predominant inflammation, mucosal changes including metaplasia, muscular hypertrophy and transmural fibrosis
- Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses and ducts of Luschka should not be mistaken for invasive adenocarcinoma
Epidemiology
- Female predominance (StatPearls: Chronic Cholecystitis [Accessed 19 February 2020])
- Associated with cholelithiasis in > 90% of cases
Pathophysiology
- Can be a sequela of recurrent acute cholecystitis
- Typically related to cholelithiasis, either through direct mucosal irritation or via intermittent mechanical obstruction with associated alteration of bile chemistry
- Altered mechanics of gallbladder emptying plays crucial role
- Up to 33% of patients have bile cultures positive for bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, enterococci, Helicobacter pylori, etc.), the significance of which is uncertain (Br J Surg 2010;97:532, Scand J Gastroenterol 2005;40:96, Helicobacter 2018;23:e12457)
Etiology
- Cholelithiasis, though severity of disease poorly correlates with stone burden (In Vivo 2008;22:269)
- Risk factors correspond to those that increase risk of cholelithiasis: female sex, obesity, rapid weight loss, pregnancy, advanced age (Gastroenterol Nurs 2016;39:297)
Clinical features
- Does not always cause clinical symptoms
- Can present with dull right upper quadrant pain that radiates to mid back or right scapula (StatPearls: Chronic Cholecystitis [Accessed 19 February 2020])
- Murphy sign: right upper abdominal pain with deep palpation
- Abdominal discomfort often related to fatty food ingestion
- Nausea, vomiting, bloating, flatulence
Diagnosis
- Abdominal ultrasound (StatPearls: Chronic Cholecystitis [Accessed 19 February 2020])
- Abdominal CT with contrast
- HIDA (hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid) scan demonstrating a reduced ejection fraction (< 35%)
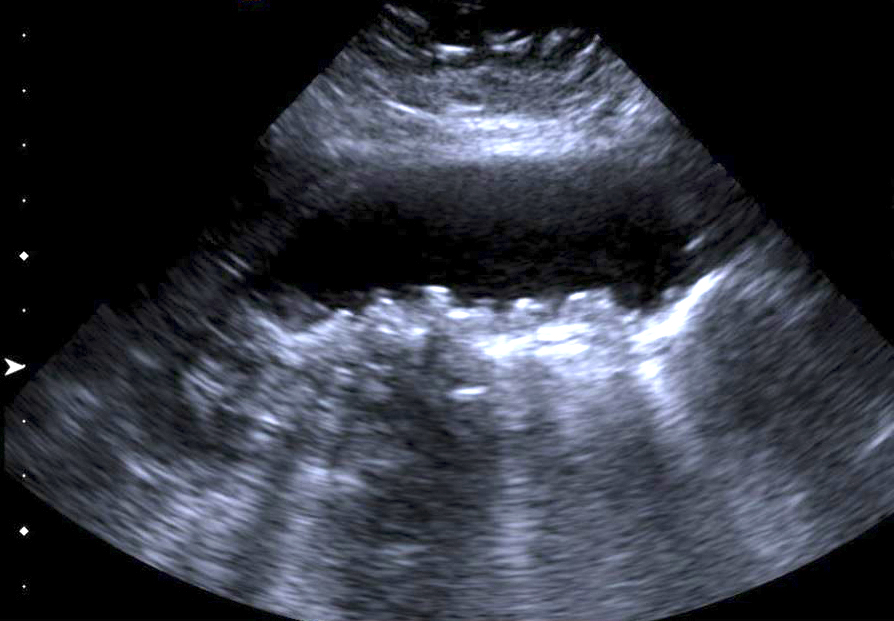
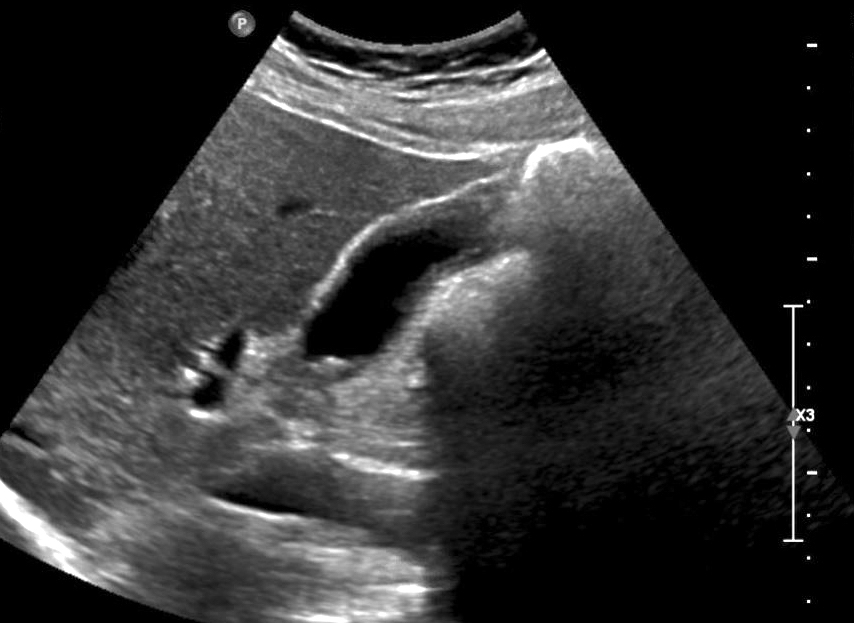
Radiology description
- Gallbladder wall thickening with associated cholelithiasis
- Gallbladder may appear contracted or distended (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e11851)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Majority of uncomplicated cases have an excellent outcome (Am J Surg 2003;185:91)
- With elective cholecystectomy, bile duct injuries do occur with regular frequency (Endoscopy 2018;50:577)
- Biliary leakage reported in up to 3% of cases (Visc Med 2017;33:184)
- Generally, a very low risk (< 0.5%) of associated incidental carcinoma (Rev Col Bras Cir 2020;46:e20192279, Surgery 2001;129:699)
Case reports
- 44 year old man with gallstones and chronic cholecystitis revealing metachronous gallbladder metastasis from renal clear cell carcinoma (ANZ J Surg 2020;90:E87)
- 45 year old woman with porcelain gallbladder secondary to chronic cholecystitis, without adenocarcinoma (Mymensingh Med J 2019;28:694)
- 53 year old man with history of colorectal adenocarcinoma with progressively elevating CEA secondary to chronic cholecystitis (J Surg Case Rep 2019;2019:rjz138)
- 70 year old man with chronic cholecystitis secondary to biliary taeniasis (Am J Trop Med Hyg 2019;100:135)
Treatment
- Elective cholecystectomy (Am J Surg 2003;185:91)
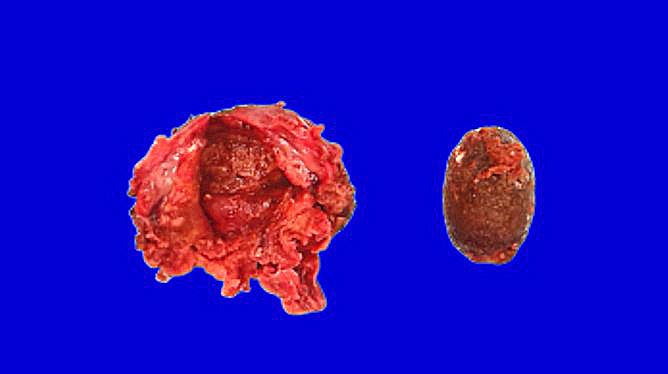
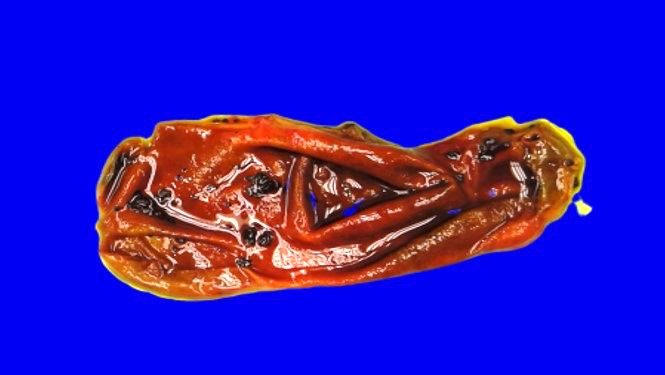
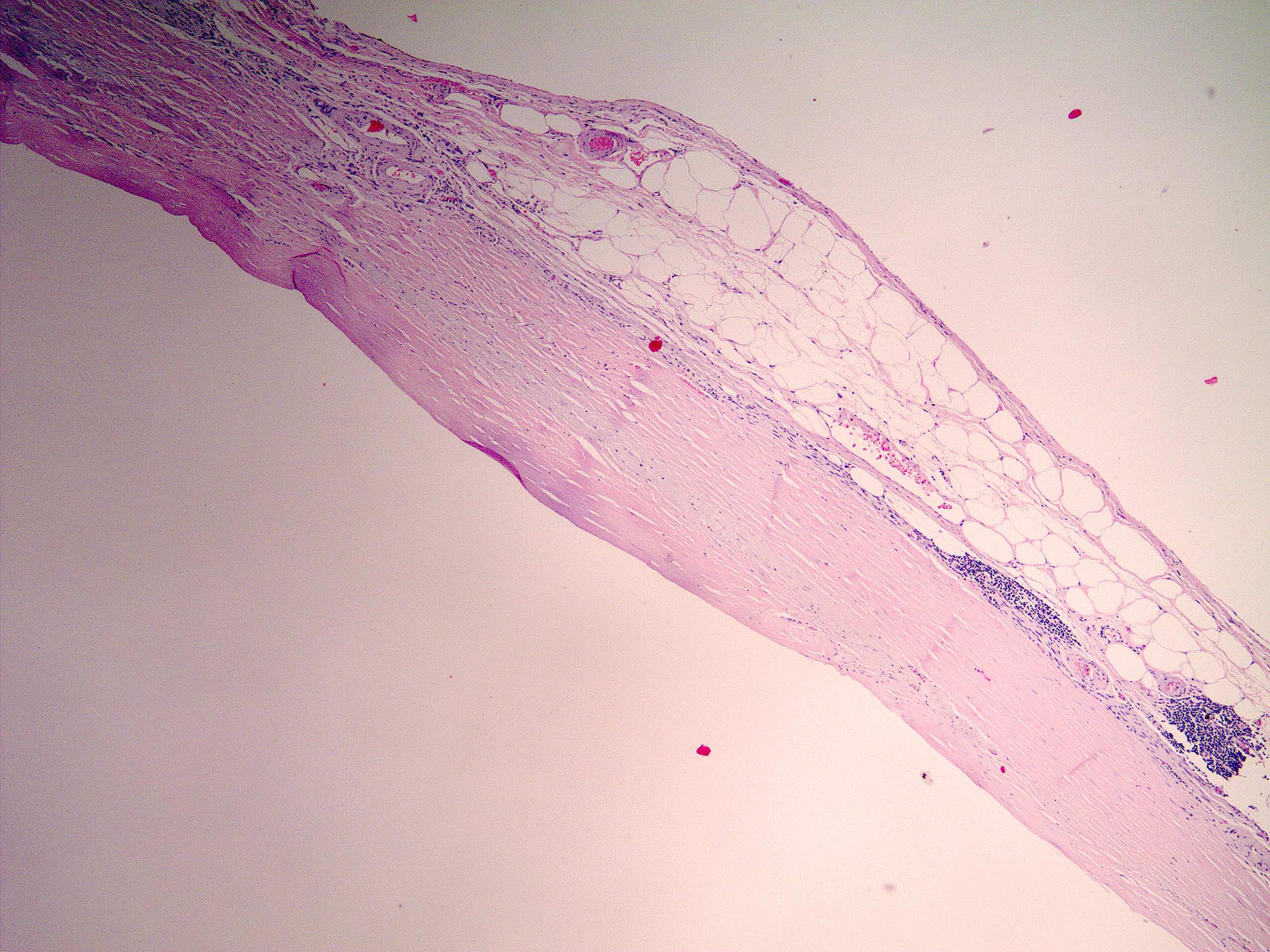
Gross description
- Nearly normal to thickened gallbladder wall (StatPearls: Chronic Cholecystitis [Accessed 19 February 2020])
- Gallbladder may appear shrunken due to marked fibrosis
- Severe cases show adhesions to adjacent organs
- Variable mucosal appearance: can be granular, ulcerated, polypoid
Gross images
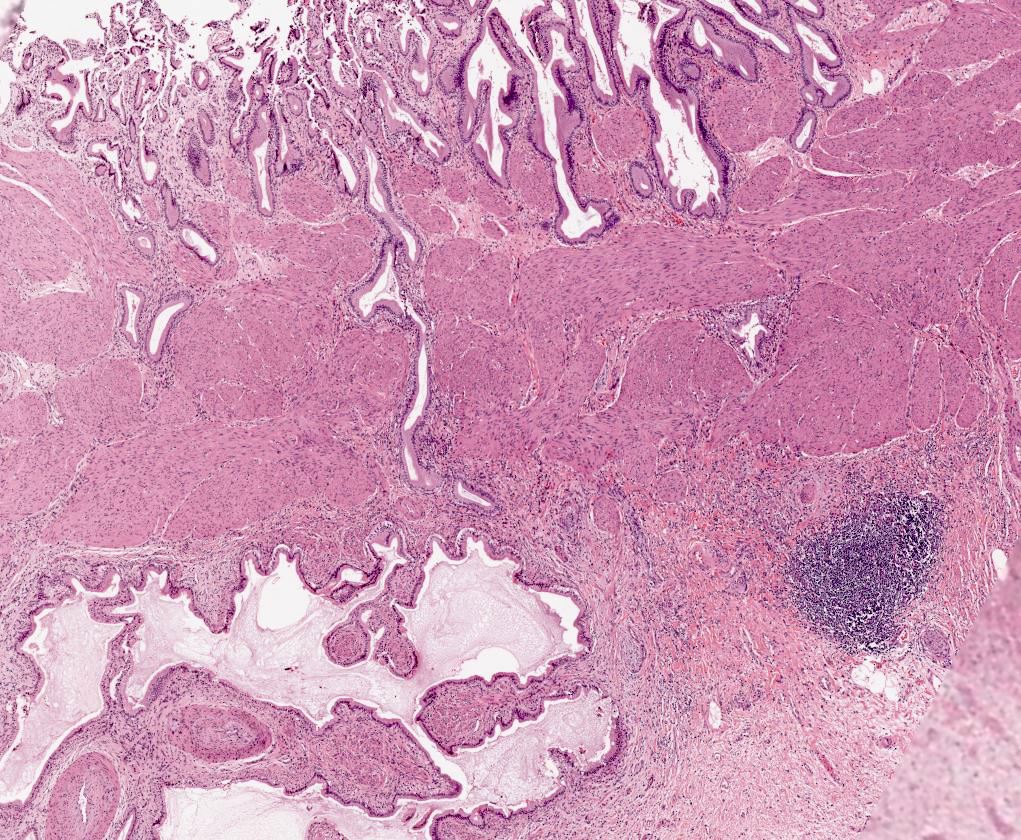
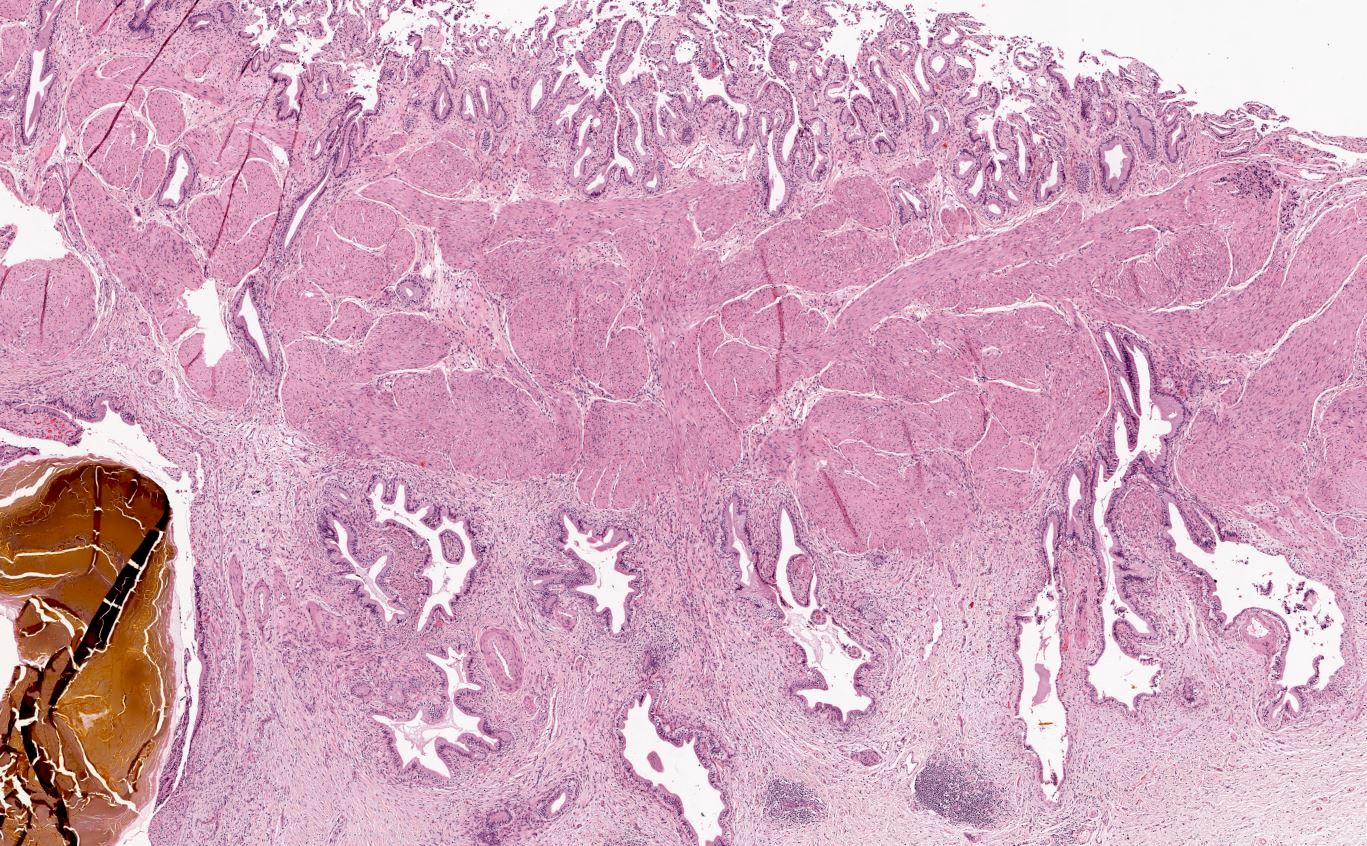
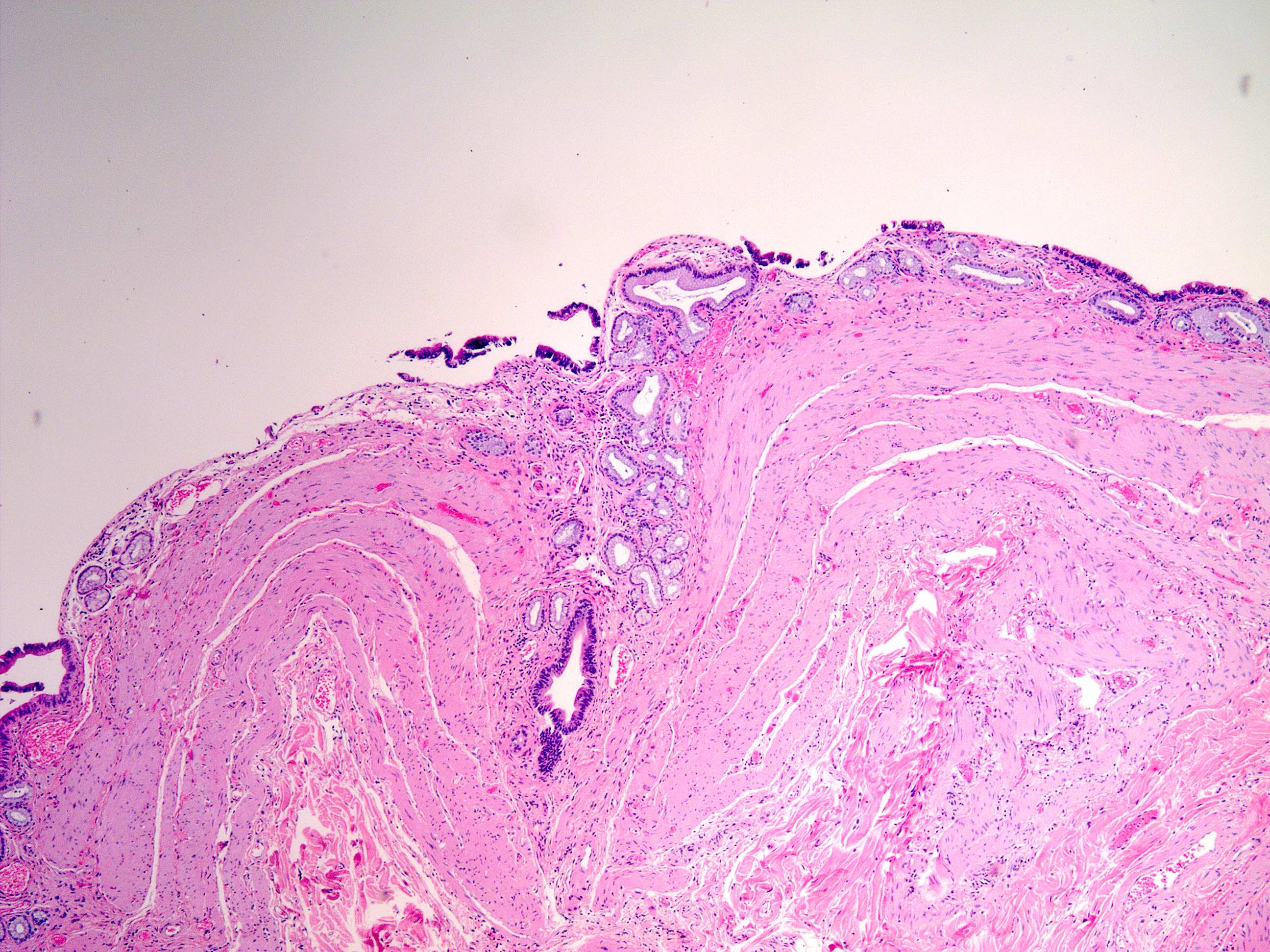
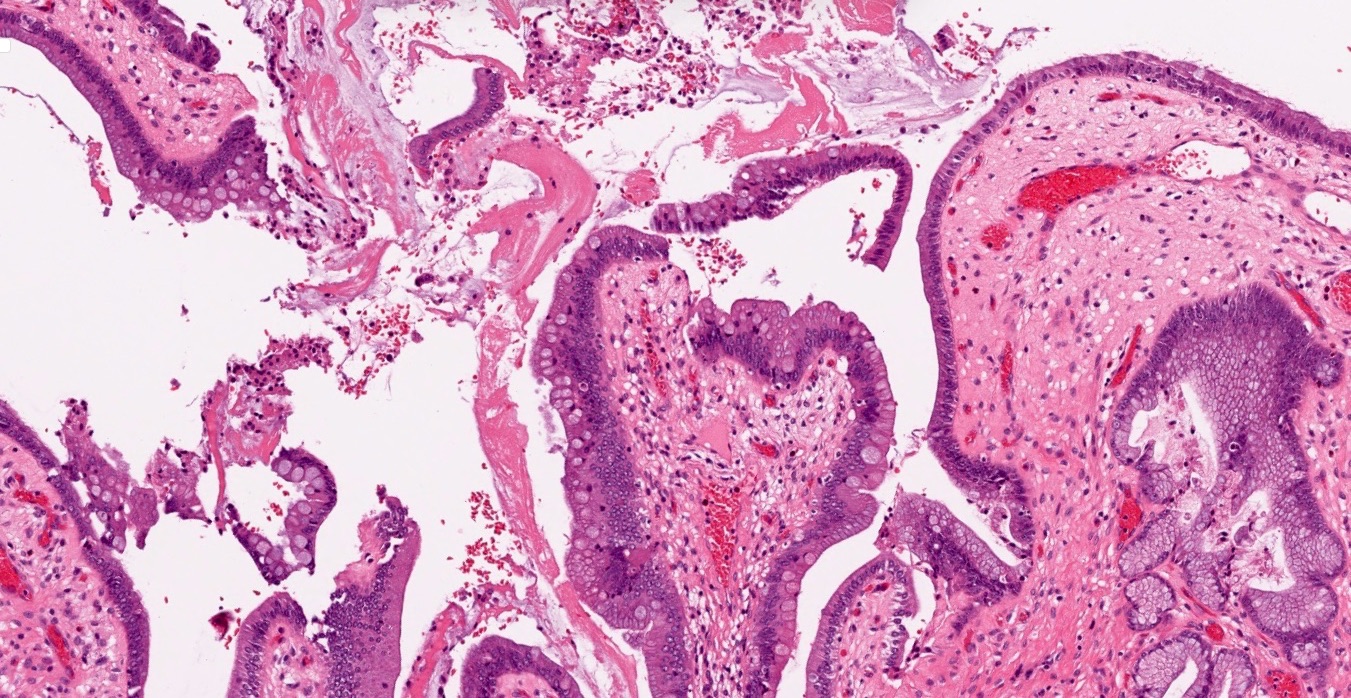
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Variable amounts of predominantly mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate in lamina propria, which may extend into the muscularis and pericholecystic tissues
- Inflammatory infiltrate predominantly consists of T lymphocytes, with some plasma cells, histiocytes and occasional eosinophils (Ann Diagn Pathol 2003;7:147)
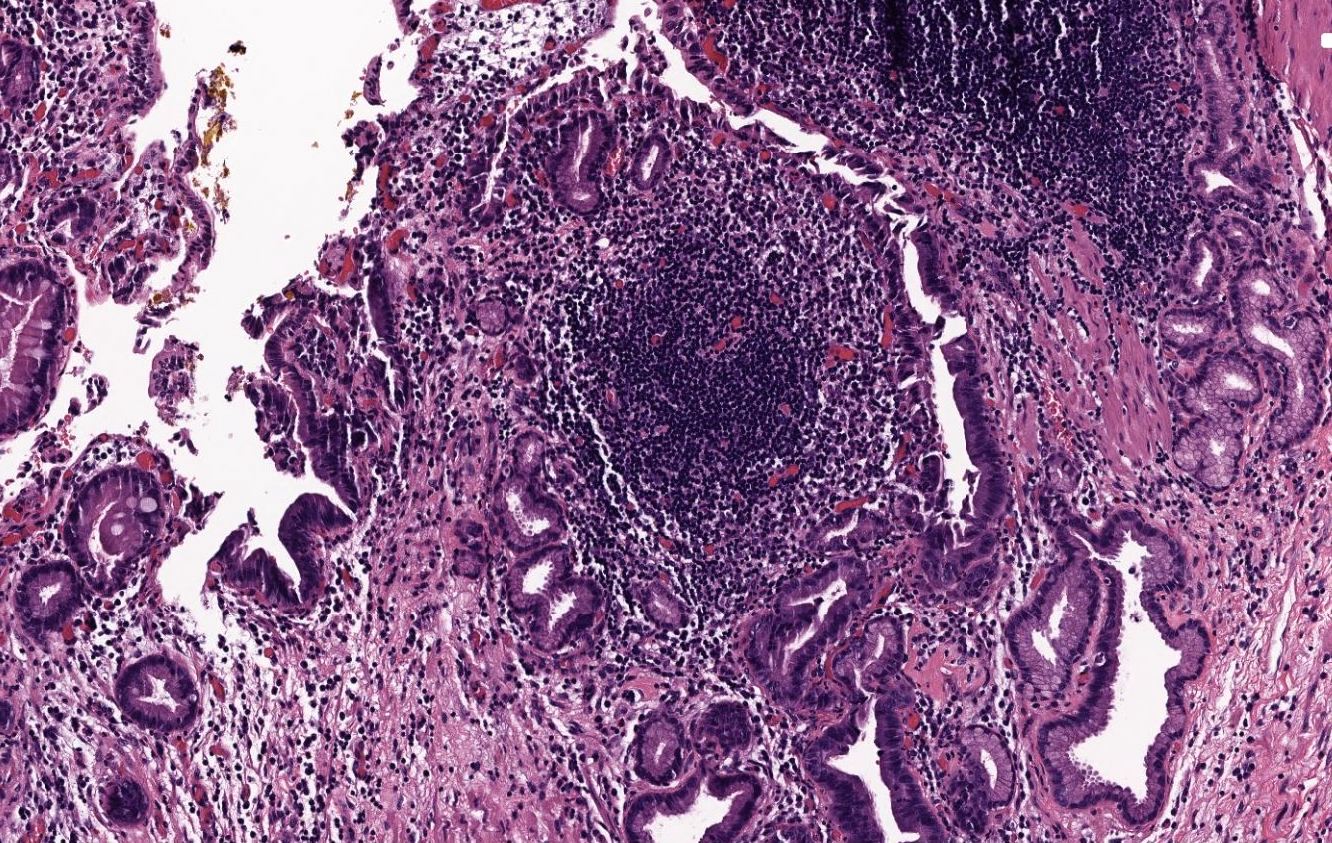
- Inflammation typically rather minimal; occasional lymphoid follicles may be seen in lamina propria
- Hypertrophy of muscularis and variable degrees of mural fibrosis, elastosis, neural hyperplasia
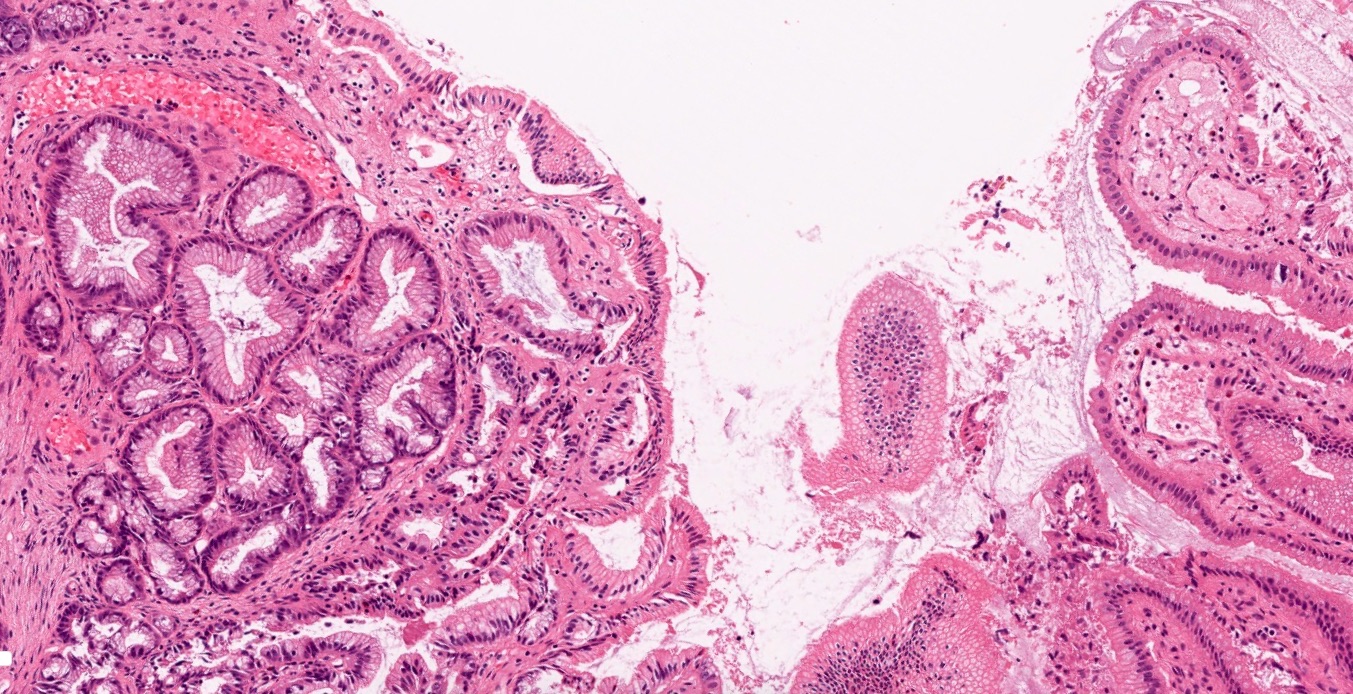
- Accentuation of Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses (pseudodiverticula)
- Adenomyomatous hyperplasia may occur
- Variable mucosal changes: normal, atrophic, ulcerated, hyperplastic
- Metaplastic changes common: foveolar metaplasia, pyloric gland metaplasia, intestinal metaplasia
- Hyalinizing variant: dense paucicellular hyalinizing fibrosis effacing ≥ 80% of normal histologic structures, resulting in a thinned gallbladder wall with (porcelain gallbladder) or without dystrophic calcification
- Increased frequency of associated carcinoma (Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 2016;16:e416, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1104)
- IgG4 associated variant: increased frequency of transmural lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrates, extramural inflammatory nodules, increased eosinophils, phlebitis and increased IgG4 plasma cells by immunostain
- Associated with autoimmune pancreatitis (Dig Dis Sci 2011;56:1290)
- 2 patterns of inflammation associated with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease: marked chronic cholecystitis (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease) and nodular lymphoid aggregates (Crohn's disease > ulcerative colitis) (J Crohns Colitis 2012;6:895)
- Beware of invasive adenocarcinoma mimics: adenomyoma, Luschka ducts
- In rare instances, reactive / hyperplastic ducts of Luschka can be seen isolated to the gallbladder adventitia (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:883)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis
Differential diagnosis
- Normal gallbladder:
- Lacks significant expansion of the lamina propria by an inflammatory infiltrate, thickened muscularis or mural fibrosis
- Lymphoma:
- Lymphoma of the gallbladder is exceedingly rare (0.1 - 0.2% of cholecystectomies) and is generally identified as part of a systemic disease
- The most common primary lymphoma of the gallbladder is MALT lymphoma (BMJ Case Rep 2017;2017:bcr2017220161)
- Primary MALT lymphoma of gallbladder is typically identified on presurgical imaging as gallbladder wall thickening or a polypoid lesion
- Lymphoplasmacytic cholecystitis:
- Plasma cell rich inflammatory infiltrate that diffusely involves the mucosa and is primarily confined to the lamina propria (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1313)
- Typically but not always associated with autoimmune disorders (e.g. ulcerative colitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, autoimmune pancreatitis) (Am J Clin Pathol 2014;142:209)
- Also termed sclerosing cholangitis, as it is believed to fall within the spectrum of IgG4 related autoimmune disorders
- AIDS related cholecystitis:
- Typically presents as acalculous cholecystitis; > 50% of cases are idiopathic (Clin Infect Dis 1995;21:852)
- Can be related to infectious agents, particularly cytomegalovirus and cryptosporidia
- In cryptosporidia related cases, associated inflammation may be minimal
- Follicular cholecystitis:
- Numerous prominent lymphoid follicles in lamina propria throughout gallbladder
- Rare and accounts for < 0.1% of cholecystectomies (Hum Pathol 2019;88:1)
- Up to 5% of otherwise ordinary chronic cholecystitis may show scattered, occasional follicle formation
- Eosinophilic cholecystitis:
- Massive infiltration of the gallbladder by sheets of eosinophils with few, if any, other intervening inflammatory cells (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:215)
- Common to see eosinophils as part of the mixed inflammatory milieu of chronic (and acute) cholecystitis
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis:
- Prominent proliferation of foamy macrophages, in addition to admixed lymphocytes, plasma cells and foreign body type giant cells
- Thought to be secondary to mucosal ulceration or rupture of Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses with bile extravasation
- Grossly, may display diffuse plaque-like thickening of gallbladder wall or a discrete mass lesion (pseudotumor)
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 40 year old woman with a BMI of 36 undergoes cholecystectomy for intermittent, dull right upper quadrant abdominal pain, reproducible on physical examination with deep palpation. Sections of gallbladder wall show the following
What is the best interpretation of these findings?
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Cystadenocarcinoma
- Dilated ducts of Luschka
- Intracholecystic papillary tubular neoplasm (ICPN)
- Invasive adenocarcinoma
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
What is the most common cause of elective cholecystectomy in the United States?
- Acute cholecystitis
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Eosinophilic cholecystitis
- Follicular cholecystitis
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
Practice answer #2
Practice question #3
Which of the following variants of chronic cholecystitis has an established increased risk of associated adenocarcinoma?
- Adenomyomatous chronic cholecystitis
- Diffuse lymphoplasmacytic cholecystitis
- Follicular cholecystitis
- Hyalinizing cholecystitis
- IgG4 associated cholecystitis
Practice answer #3