Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Balgobind S, Gupta R. Warthin tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandswarthin.html. Accessed October 5th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign salivary gland tumor that is composed of oncocytic epithelial cells lining papillary and cystic structures in a lymphoid stroma
- Second most frequent benign tumor of the parotid gland (after pleomorphic adenoma) (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:412)
- Infarcted / metaplastic subtype may occur following FNA biopsy (Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 1989;14:205)
Essential features
- Benign salivary gland tumor
- Bilayered papillae and cysts lined by oncocytic cells and flattened basal cells
- Lymphoid stroma
Terminology
- Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, adenolymphoma, cystadenolymphoma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D11.9 - benign neoplasm of major salivary gland, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Accounts for 5 - 20% of all salivary tumors (J Clin Exp Dent 2013;5:e218)
- Mean age at diagnosis is 62 years (range: 12 - 92 years) (Laryngoscope 1983;93:695)
- M ≈ F
- Historically M > F (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1986;61:256)
- More common in smokers (Am J Epidemiol 1996;144:183)
Sites
- Almost exclusively involves the parotid gland, especially the inferior pole and periparotid lymph nodes (Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1998;36:52, Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993;31:43)
- Multifocality is detected in 12 - 20% of patients with bilaterality in 5 - 17% of patients (Oral Oncol 2002;38:35, Acta Otolaryngol 2006;126:1213)
Pathophysiology
- Probably arises from salivary ductal inclusions in parotid lymph nodes (Head Neck Pathol 2014;8:73, Head Neck Pathol 2021;15:438)
- Clonality studies have suggested a nonneoplastic nature (Hum Pathol 2000;31:1377, Mod Pathol 2005;18:964)
Etiology
- Strong link to cigarette smoking (especially when bilateral) (Am J Epidemiol 1996;144:183)
- Other suggested risk factors include radiation exposure in atomic bomb survivors and autoimmune diseases (especially thyroiditis) (Cancer 1997;79:1465, Acta Otolaryngol 1997;117:623, J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2015;43:427)
Clinical features
- Presents with a painless, slow growing and fluctuant mass in the lower pole of the parotid gland (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1986;61:256)
- Glucose avid on PET and often incidentally detected during PET work up (Am J Otolaryngol 2015;36:259)
Radiology description
- Parotid tail location
- Cystic change, multifocality
- Avidity on PET CT (Am J Otolaryngol 2015;36:259)
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognosis (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:37)
- Recurrence is usually due to inadequate excision (Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2008;37:831)
- Malignant transformation has rarely been reported but is increasingly thought to represent Warthin-like carcinomas rather than true Warthin tumors (J Oral Pathol Med 1994;23:330, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1479)
Case reports
- 50 year old man presented with painless swelling over the right lower side of the face (J Clin Diagn Res 2014;8:ZD37)
- 69 year old man presented with right parotid tumor of 1 year duration (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:12)
- 71 year old man with left parotid mass, slowly growing over a period of 12 years (Surgeries 2020;1:46)
Treatment
- Surgical excision with adequate margins is usually curative (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:37)
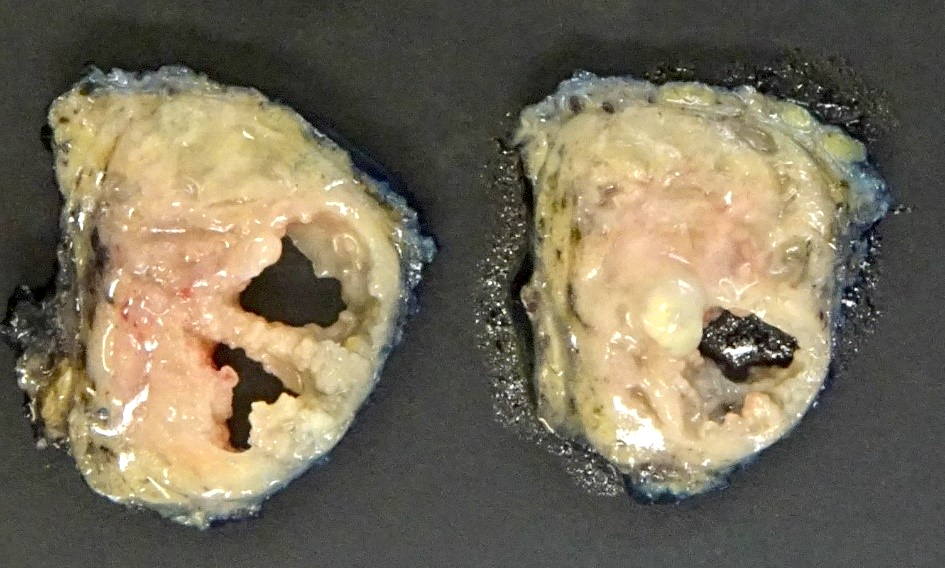
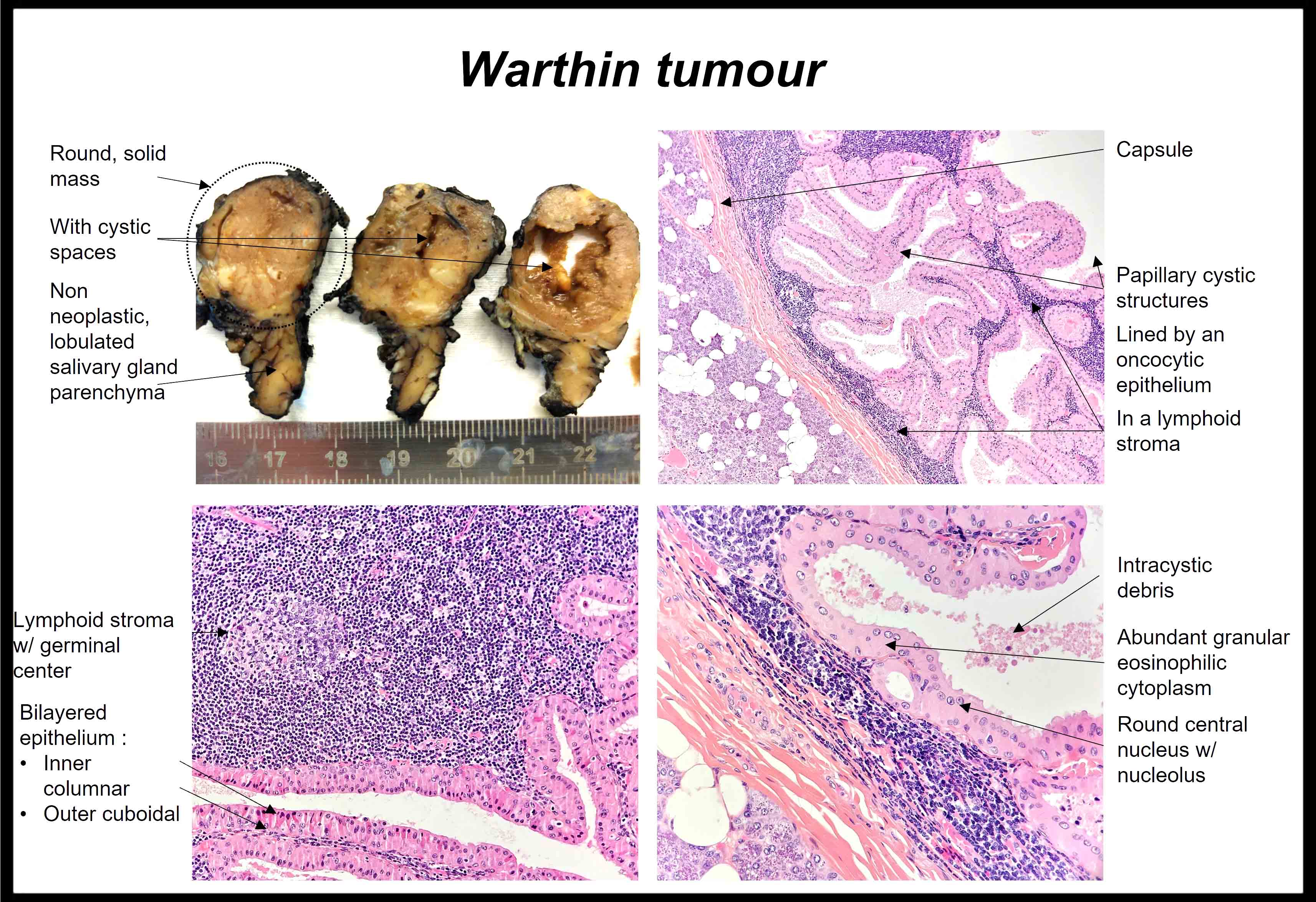
Gross description
- Most are well circumscribed oval masses, 20 - 50 mm in diameter (Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;71:839)
- Solid areas and multiple cysts with papillary projections are apparent on the cut surface
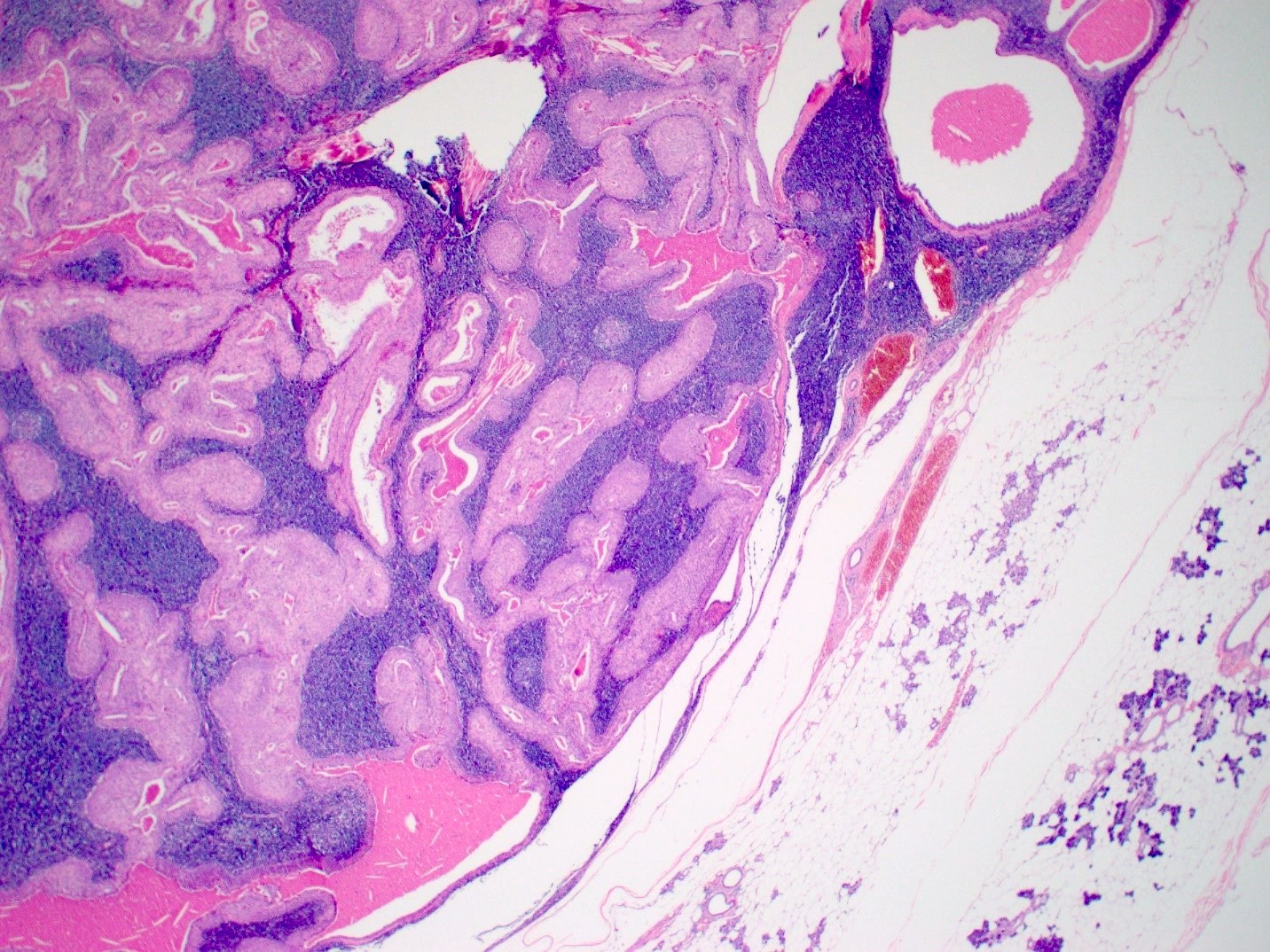
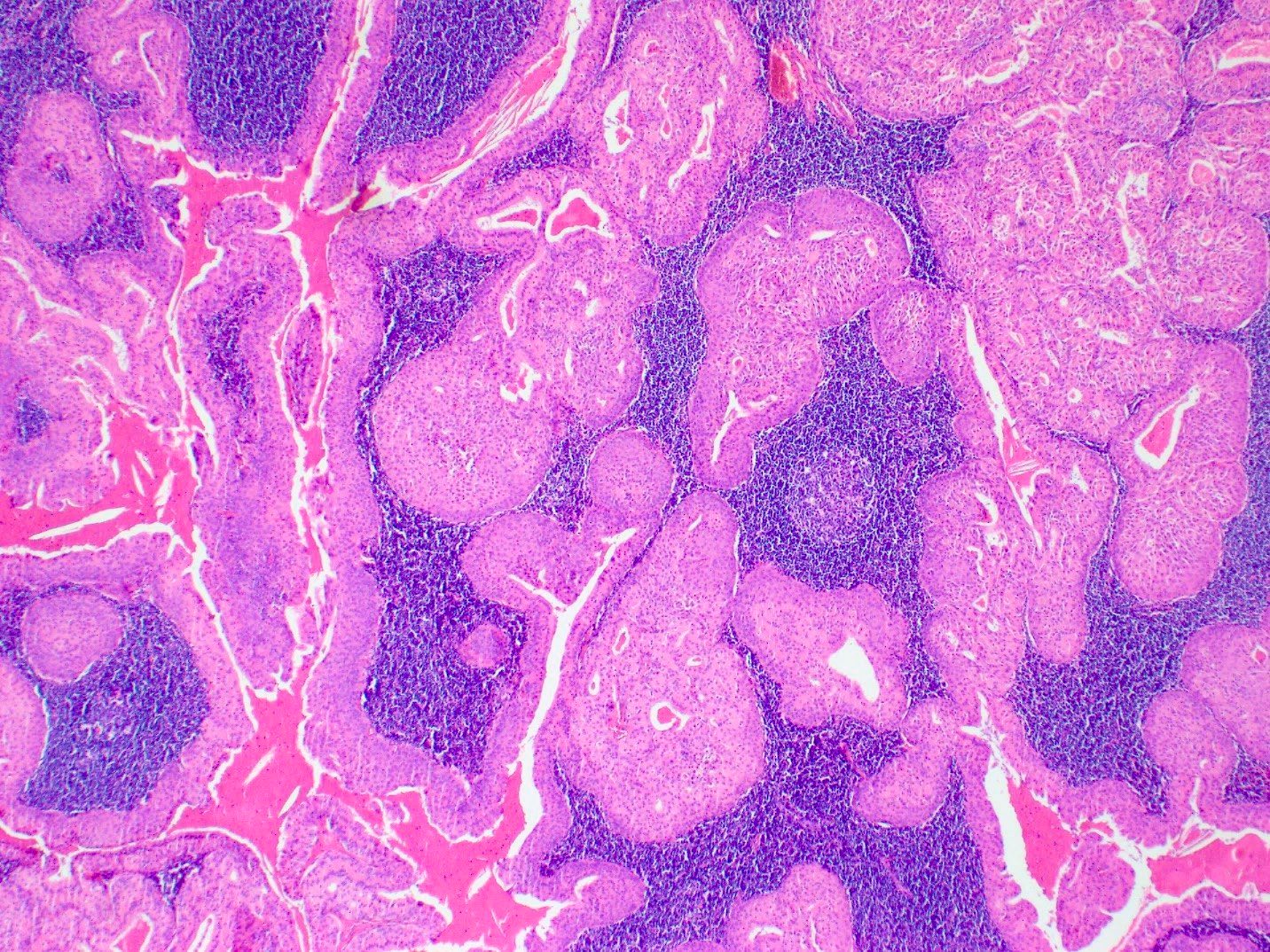
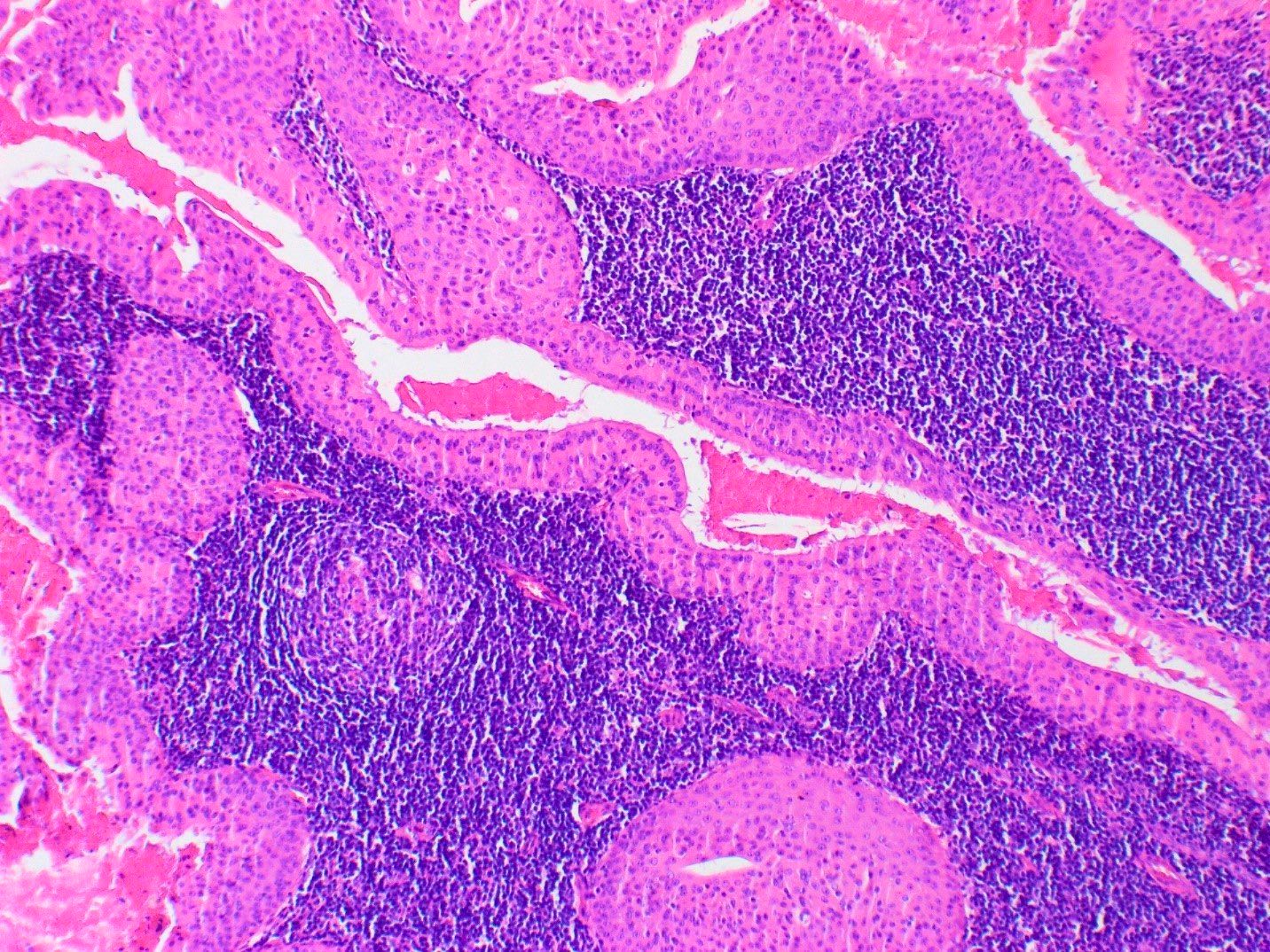
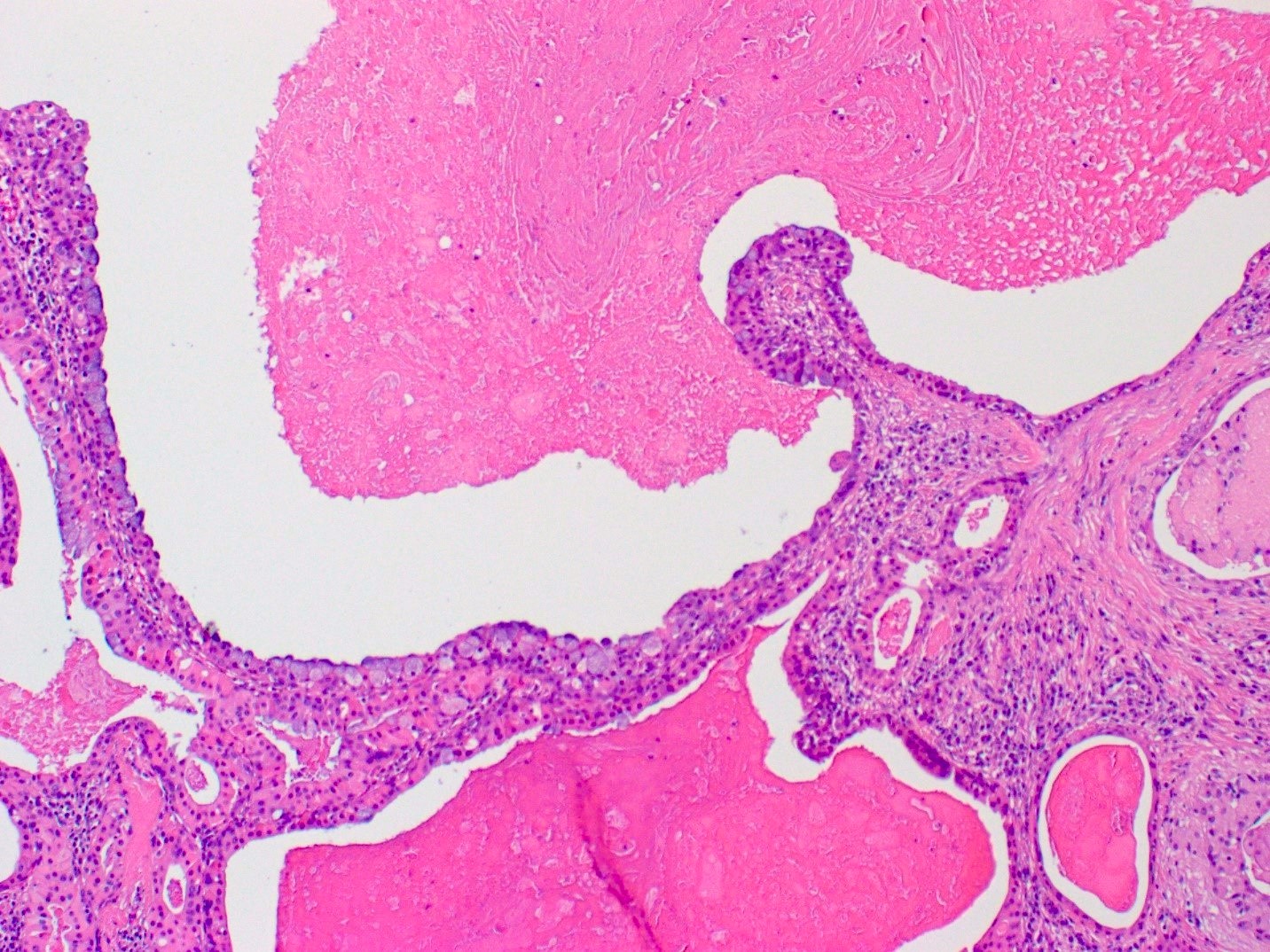
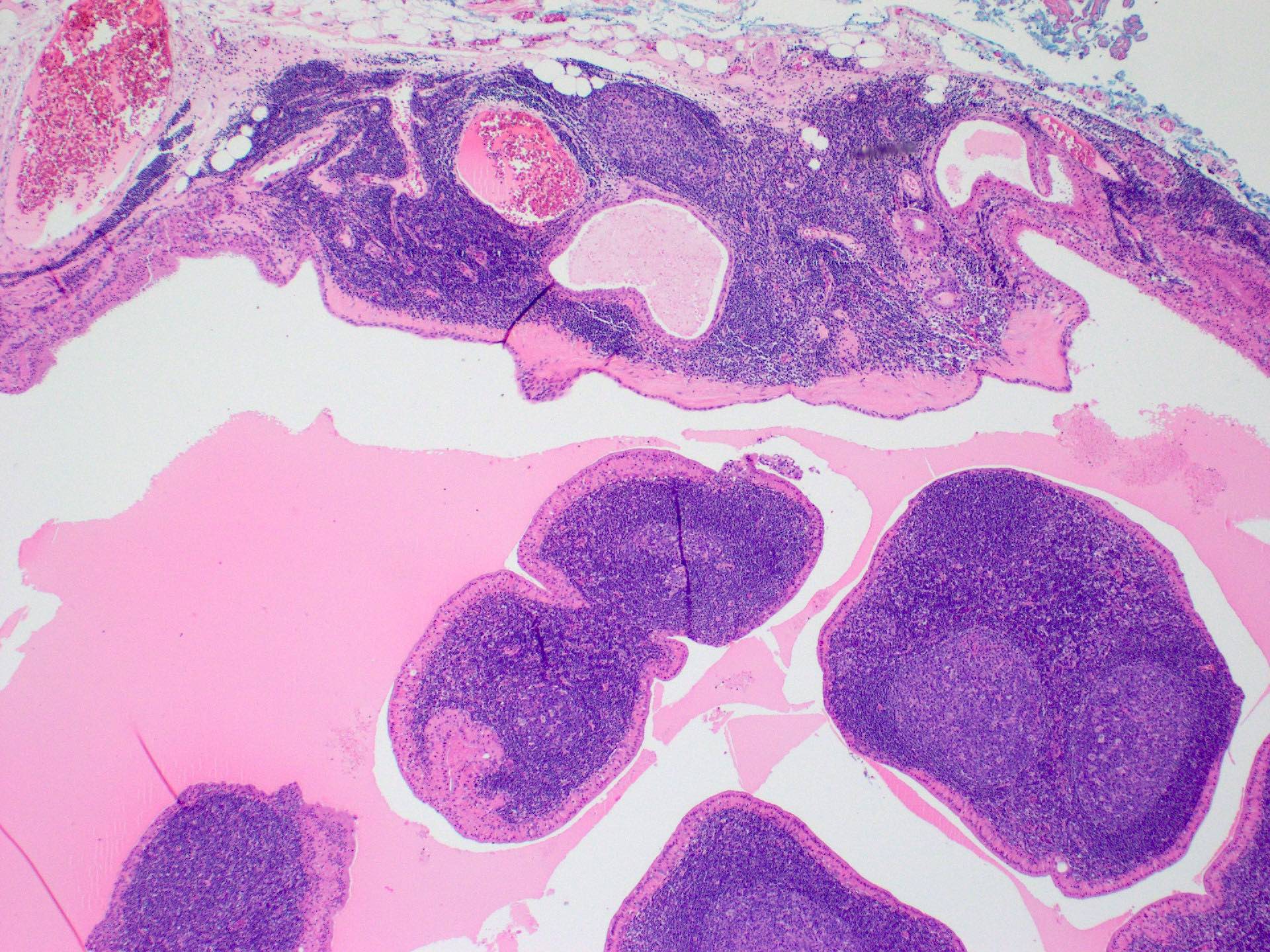
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Varying proportions of papillary cystic structures lined by bilayered oncocytic epithelial cells and surrounded by a lymphoid stroma including germinal centers
- Epithelial component is comprised of inner columnar and outer cuboidal cells
- Limited foci of squamous, mucous, ciliated and sebaceous cells can be present
- Infarcted / metaplastic subtype (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1743, Histopathology 1999;35:432):
- Bilayered epithelium is replaced by squamous metaplastic epithelium with no atypia
- Mucinous metaplasia may also be present
- Biopsy site reaction may be present with necrosis, squamous metaplasia and a stromal reaction (including granuloma formation)
- Stroma poor tumors have bilayered oncocytic lining but minimal lymphoid stroma (Oral Oncol 2002;38:163)
Microscopic (histologic) images
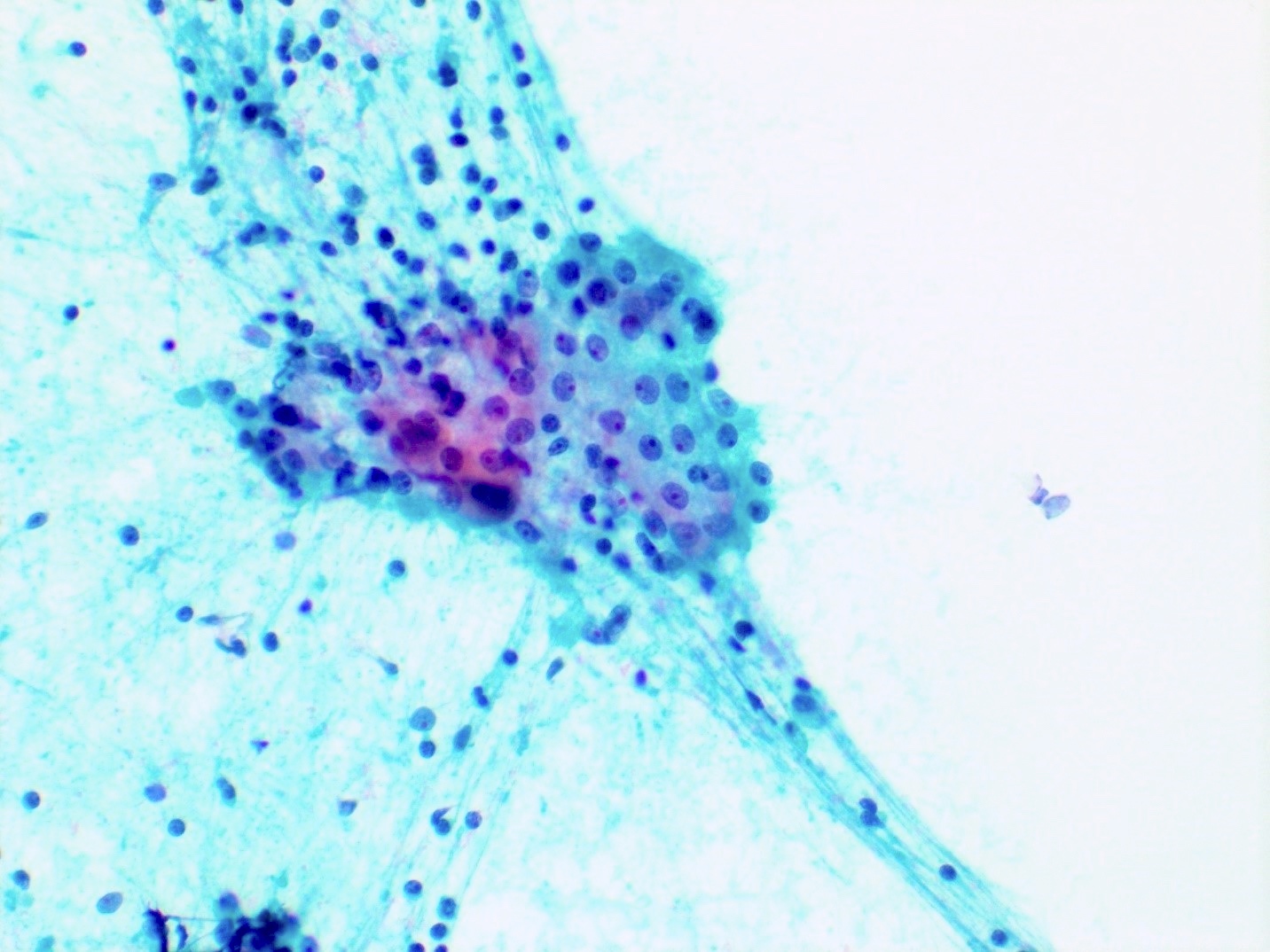
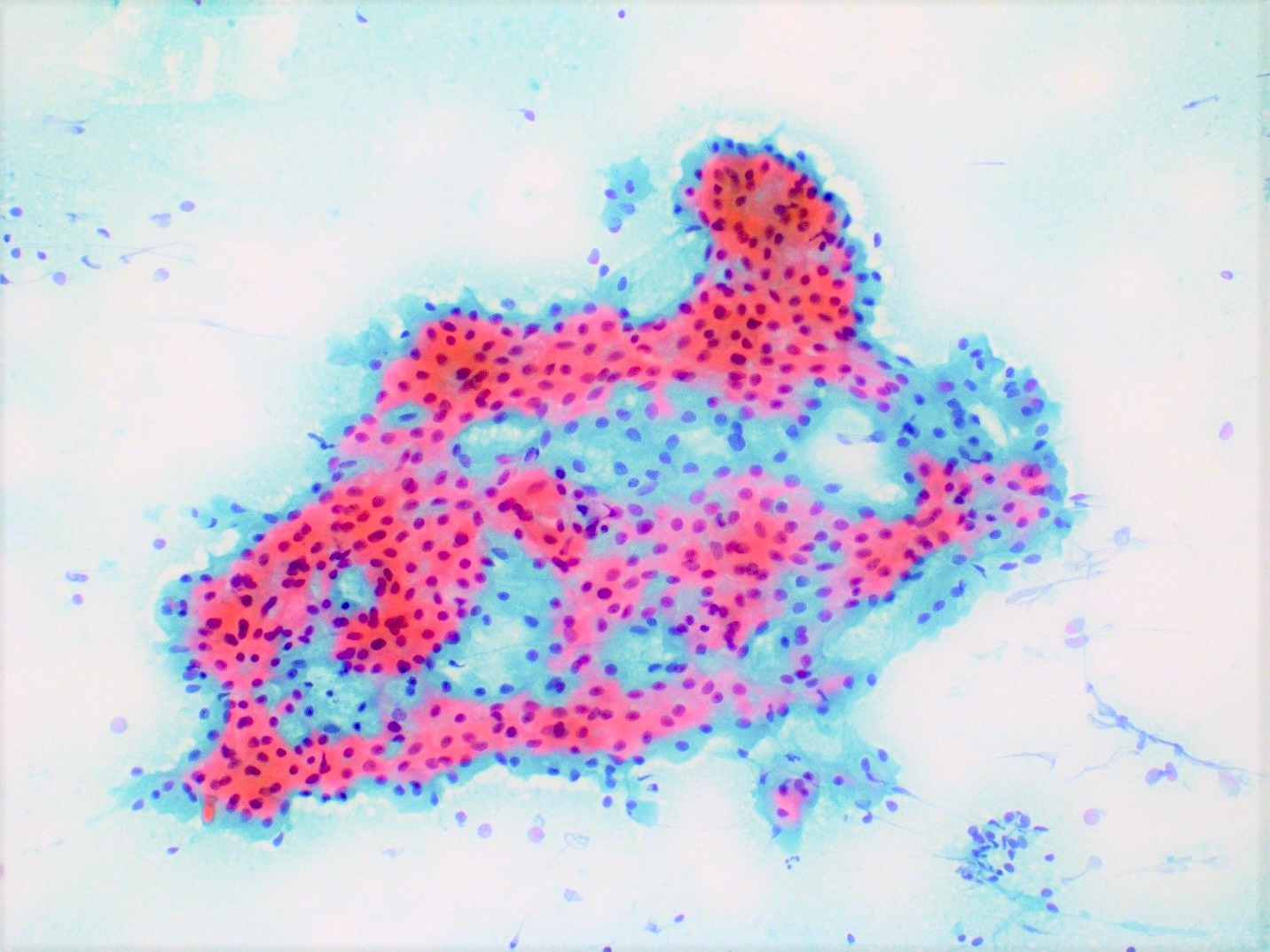
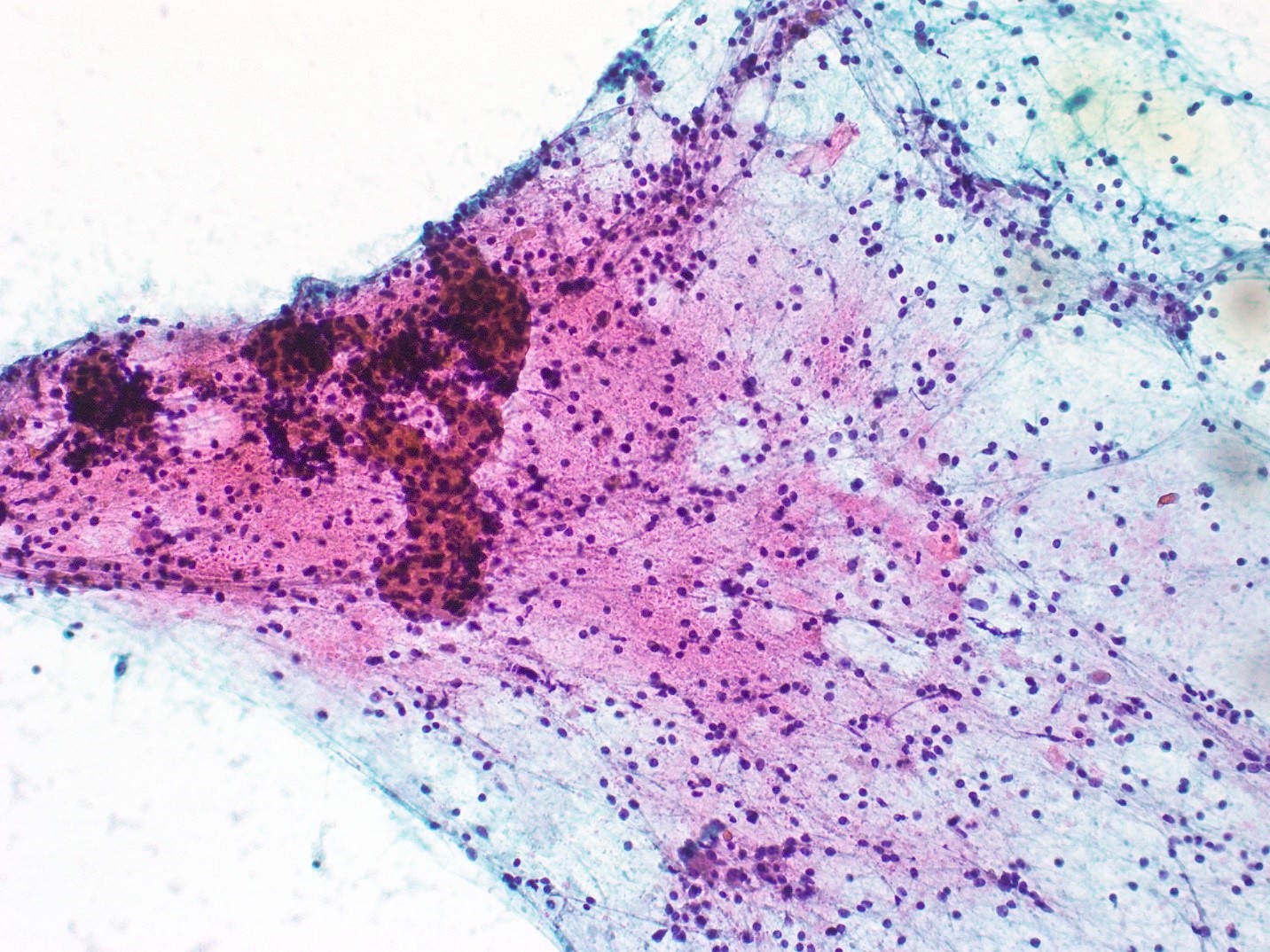
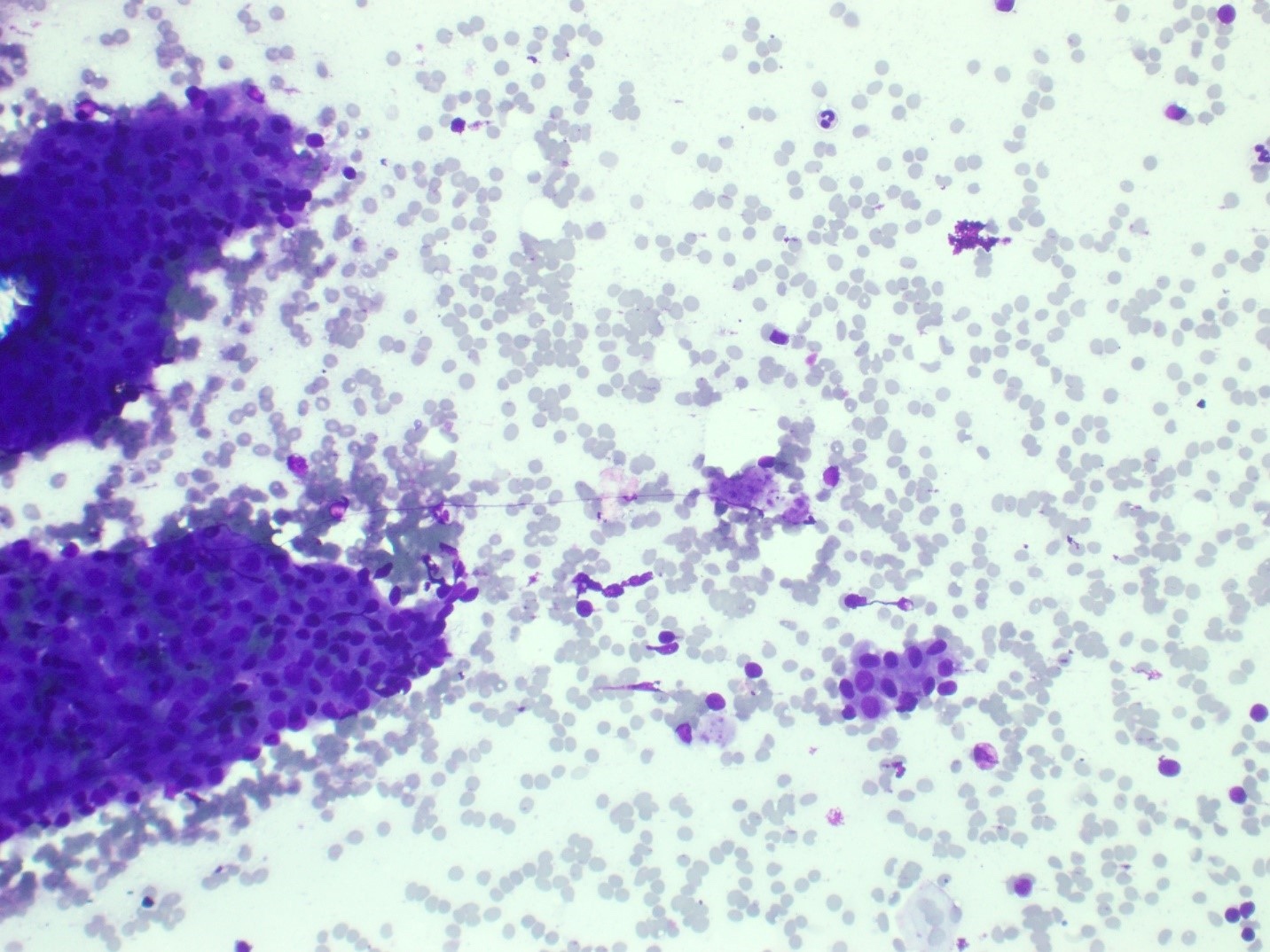
Cytology description
- Small cohesive sheets of oncocytes with abundant granular cytoplasm
- Central round nucleus with prominent nucleolus
- Numerous lymphocytes with granular debris in the background
- Reference: Cibas: Cytology - Diagnostic Principles and Clinical Correlates, 5th Edition, 2020
Cytology images
Positive stains
- All epithelial cells are positive for pancytokeratin
- CK7, CK8 / CK18 and EMA are positive in luminal (or inner) epithelial cells
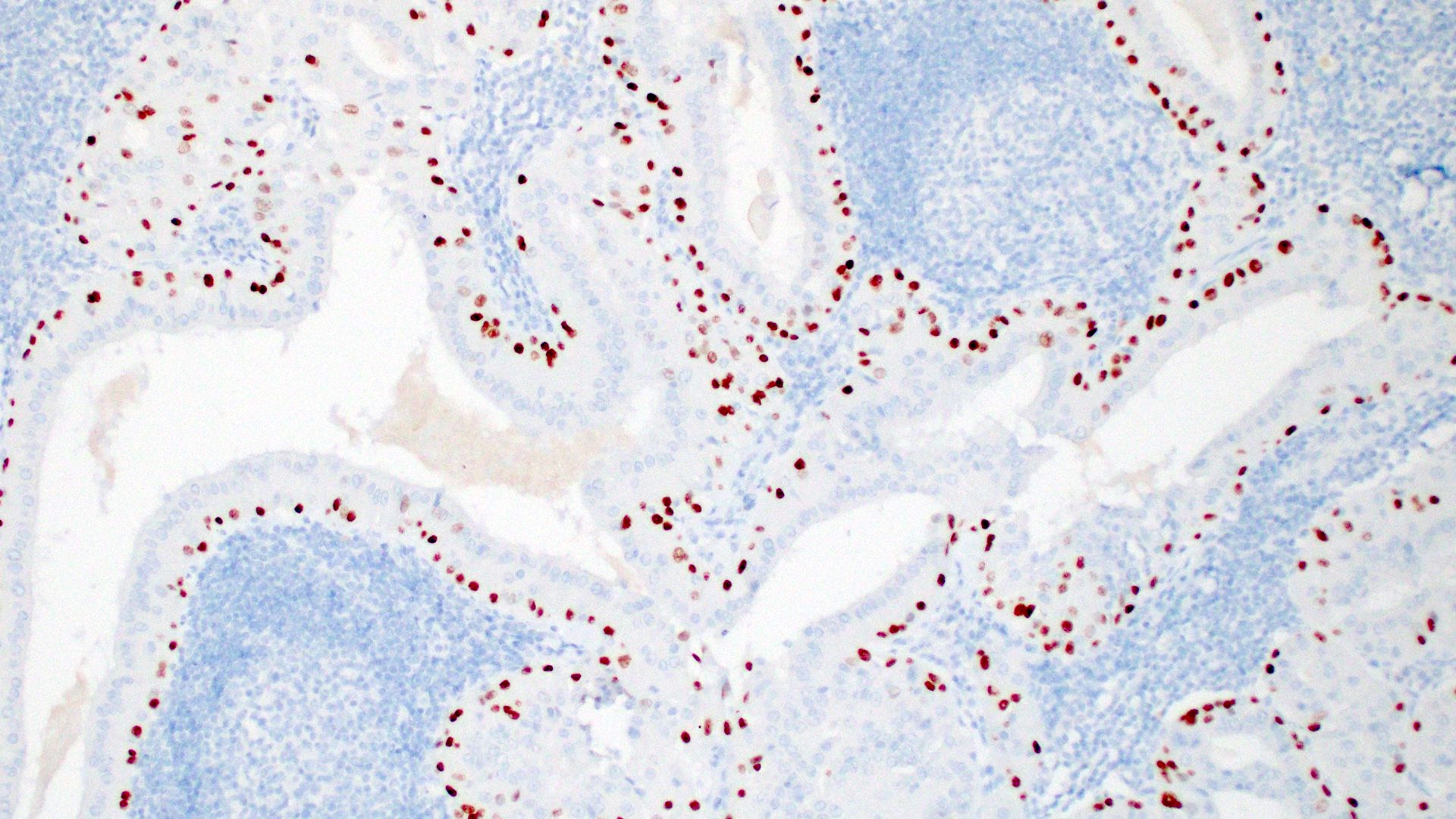
- p63 and p40 show heterogenous nuclear staining of the basal cells (see Microscopic (histologic) images) (Interv Med Appl Sci 2016;8:41)
- Lymphoid cells are positive for: B cell markers (CD20) and T cell markers (CD3, CD4, CD8)
Electron microscopy description
- Oncocytic epithelial cells show cytoplasm filled with mitochondria on electron microscopy (Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2005;25:150)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Absent MAML2 fusion (positive in mucoepidermoid carcinoma)
Sample pathology report
- Salivary gland, parotidectomy:
- Warthin tumor (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a well circumscribed tumor with a papillary architecture. The papillae are lined by bilayered oncocytic epithelial cells with a surrounding lymphoid stroma, containing germinal centers.
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphoepithelial cyst:
- Dilated cystic structure lined by squamous / columnar epithelium with lymphoid follicles in the cyst wall
- Lacks papillary architecture
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Critical consideration in Warthin tumors with metaplastic squamous or mucinous cells
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma can show Warthin-like variant (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1479)
- p63 and CK5/6 are diffusely positive in mucoepidermoid carcinoma (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:64)
- S100 is negative in mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- MAML2 fusions are present in mucoepidermoid carcinoma, absent in Warthin tumor
- Warthin-like mucoepidermoid carcinoma lacks the classic oncocytic bilayer of Warthin tumor and tends to show more complex epithelial organization (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1479, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:130)
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
A. Classic Warthin tumor. The photograph shows features of a classic Warthin tumor with papillary structures lined by bilayered oncocytic epithelium. The other entities on the list do not match the entity shown on the H&E photograph provided.
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin tumor
Practice question #2
Which of the following is a risk factor for developing a Warthin tumor?
- Alcohol abuse
- Cigarette smoking
- Intravenous drug use
- MAML2 translocation
Practice answer #2
B. Cigarette smoking. The other risk factors listed have not been proven to be associated with Warthin tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin tumor