Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Pokharel A, Wang GY. Desmoplastic fibroblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticcollagenousfibroma.html. Accessed September 16th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Also called desmoplastic fibroblastoma
- Rare paucicellular tumor consisting of dense collagen fibers with scattered stellate and spindled fibroblasts involving the subcutis or skeletal muscles
- Benign clinical behavior with no reported tumor recurrence
Essential features
- Most frequently found in the subcutis, with up to 25% found in the skeletal muscles (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676)
- Essential to distinguish from other more aggressive fibroblastic and myofibroblastic neoplasms
- Treatment is simple excision
Terminology
- Desmoplastic fibroblastoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8810/0 - desmoplastic fibroblastoma
- ICD-11: EE6Y & XH2ZF3 - other specified fibromatous disorders of skin and soft tissue & desmoplastic fibroblastoma
Epidemiology
- Rare (largest series is 63 cases) (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676)
- M:F = 4:1
- Median age of 50 - 60 years
Sites
- Most common in upper extremities (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1077)
- Followed by lower extremities (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676)
- Rarely head and neck (Clin Case Rep 2022;10:e6029)
Pathophysiology
- Translocation involving the long arm of chromosome 11, particularly 11q12
- Reported translocations include t(2;11)(q31;q12) and t(11;17)(q12;p11.2) (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2004;149:161, Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2009;192:73, Cancer Genet 2011;204:569)
- 11q12 rearrangement results in the overexpression of FOSL1 (Histopathology 2016;69:1012, Lab Invest 2012;92:735, J Pathol 2023;259:119)
Etiology
- Unknown at this time
Clinical features
- Solitary, painless, slow growing nodule (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676, In Vivo 2021;35:69)
- Size ranges from 1 to 20 cm (median size: 3 cm) (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676, In Vivo 2021;35:69)
Diagnosis
- Histopathology is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis
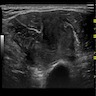
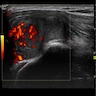
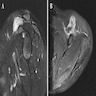
Radiology description
- Relatively well defined, lobulated, increased soft tissue density (Skeletal Radiol 2019;48:637)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Simple excision is curative
- No recurrence or metastasis reported (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1077, Hum Pathol 1998;29:676)
Case reports
- 45 year old man with mass in supraclavicular region (Ear Nose Throat J 2022 Aug 27 [Epub ahead of print])
- 56 year old woman with mass in the pleural cavity (Thorac Cancer 2021;12:2961)
- 61 year old man with painless mass on the left ring finger (Case Rep Oncol 2023;16:478)
- 66 year old woman with axillary mass (Case Rep Orthop 2020;2020:9780263)
- 79 year old man with chest wall mass (Surg Case Rep 2021;7:86)
Treatment
- Surgical excision
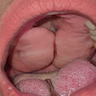
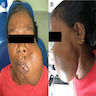
Clinical images
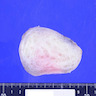
Gross description
- Firm, well circumscribed, lobulated mass (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676)
- Uniform white-gray cut surface
- No necrosis or hemorrhage
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Intraoperative frozen section analysis is usually not performed
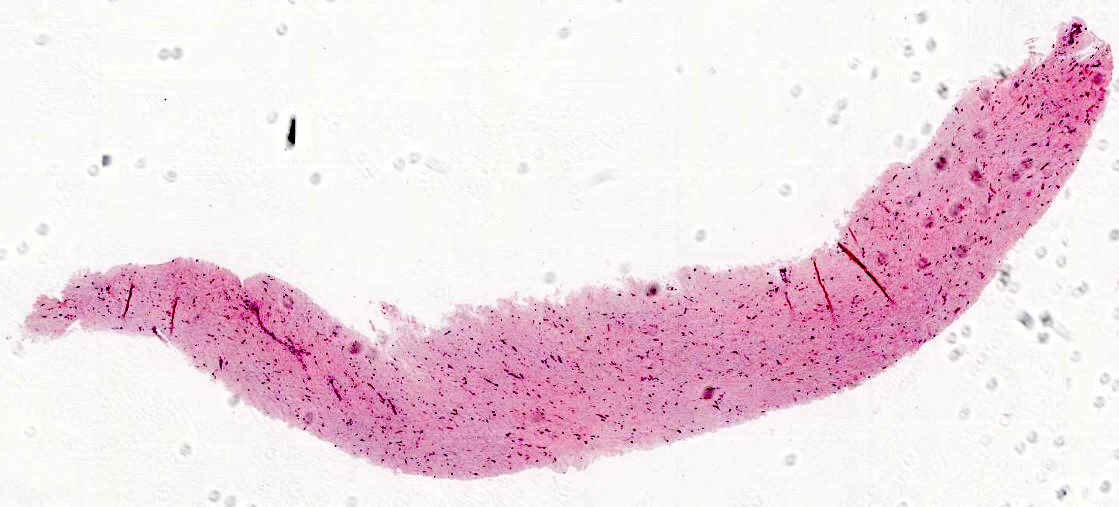
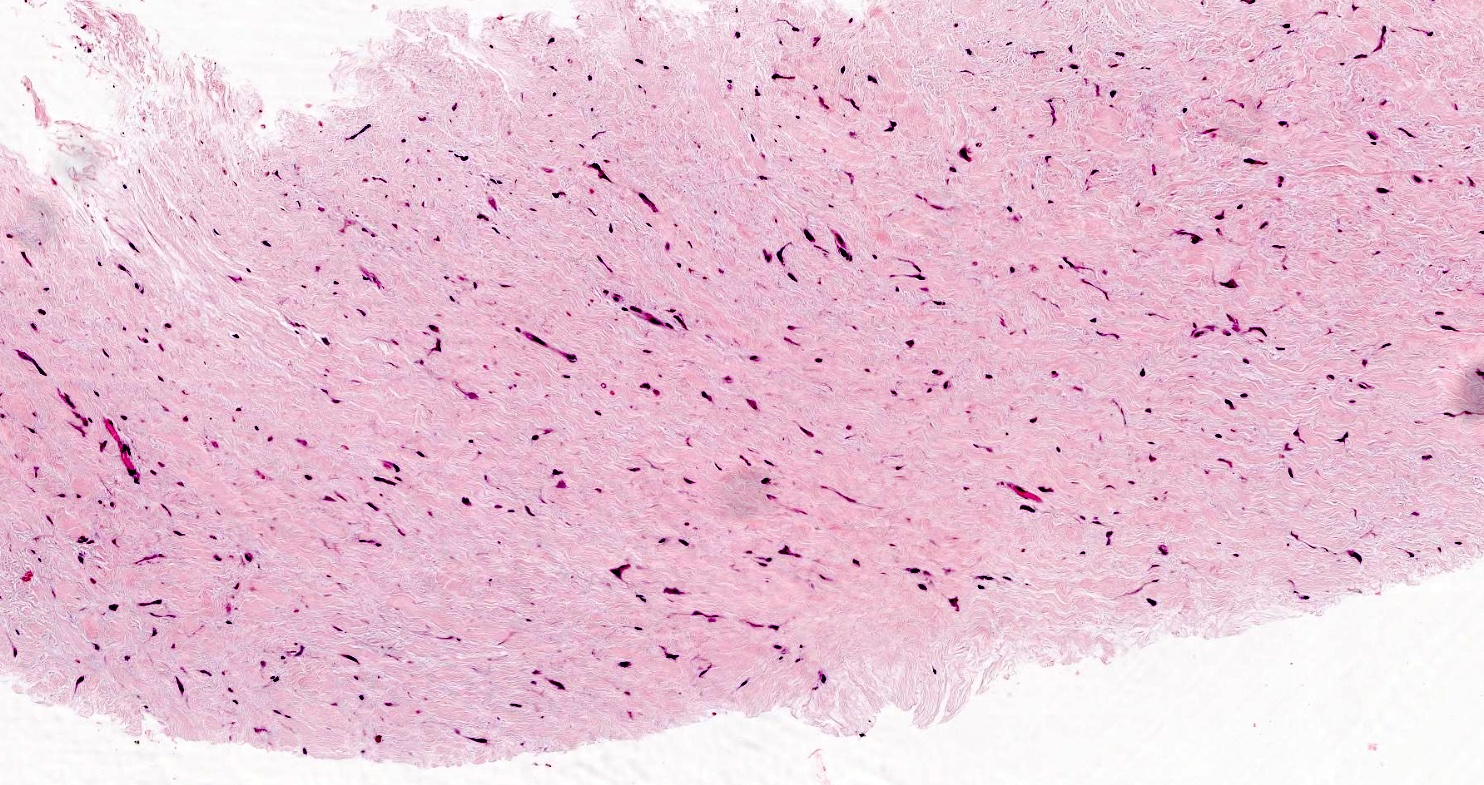
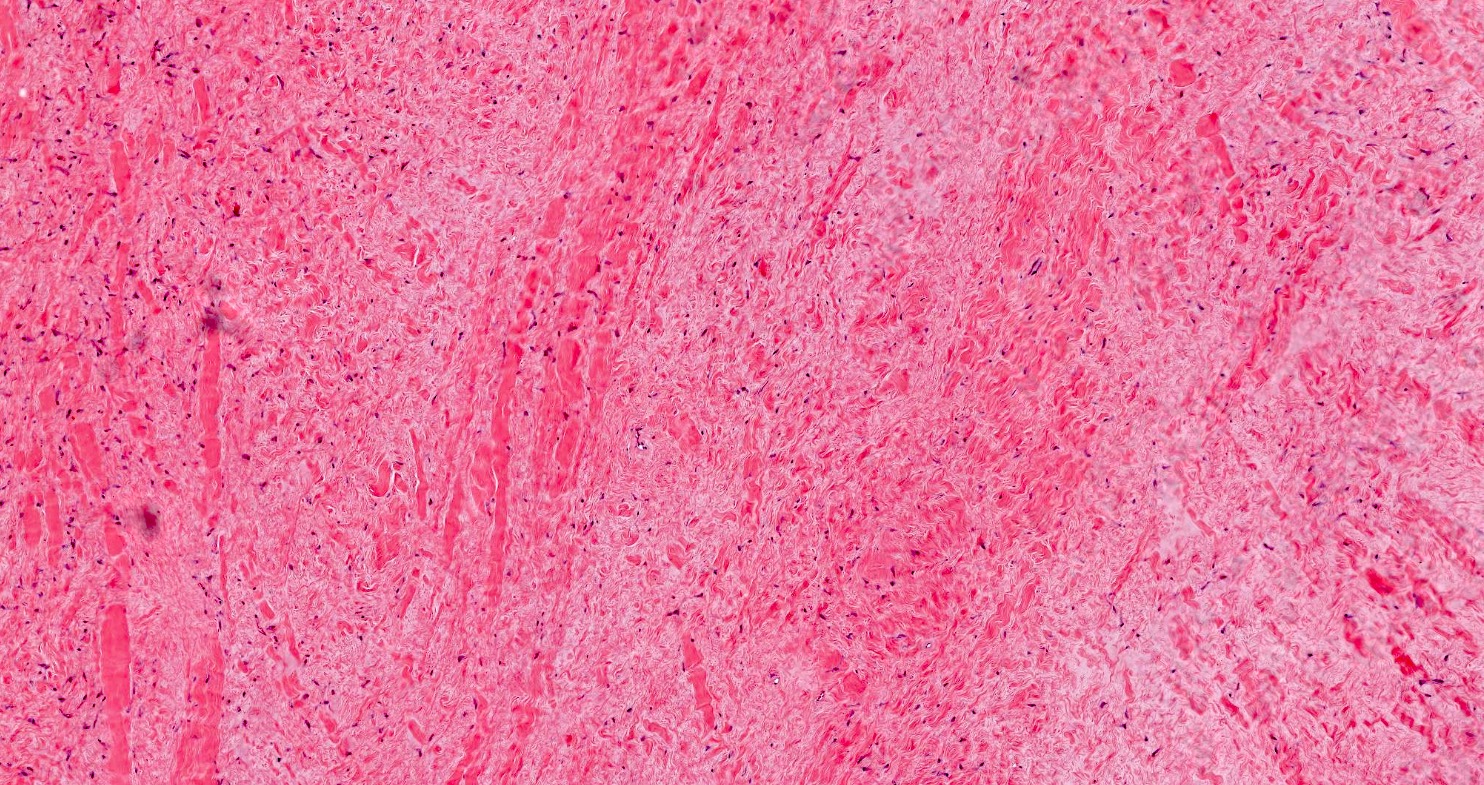
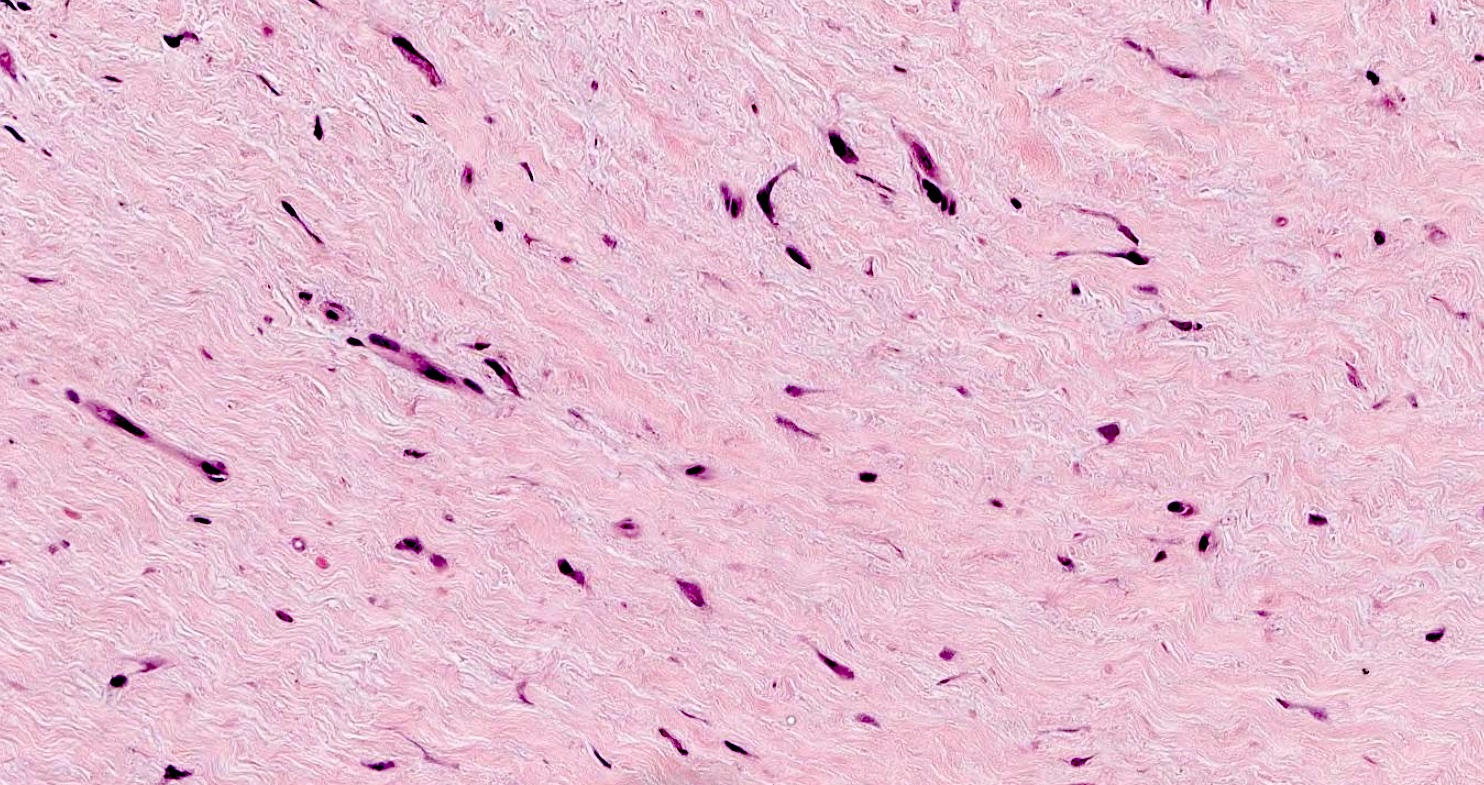
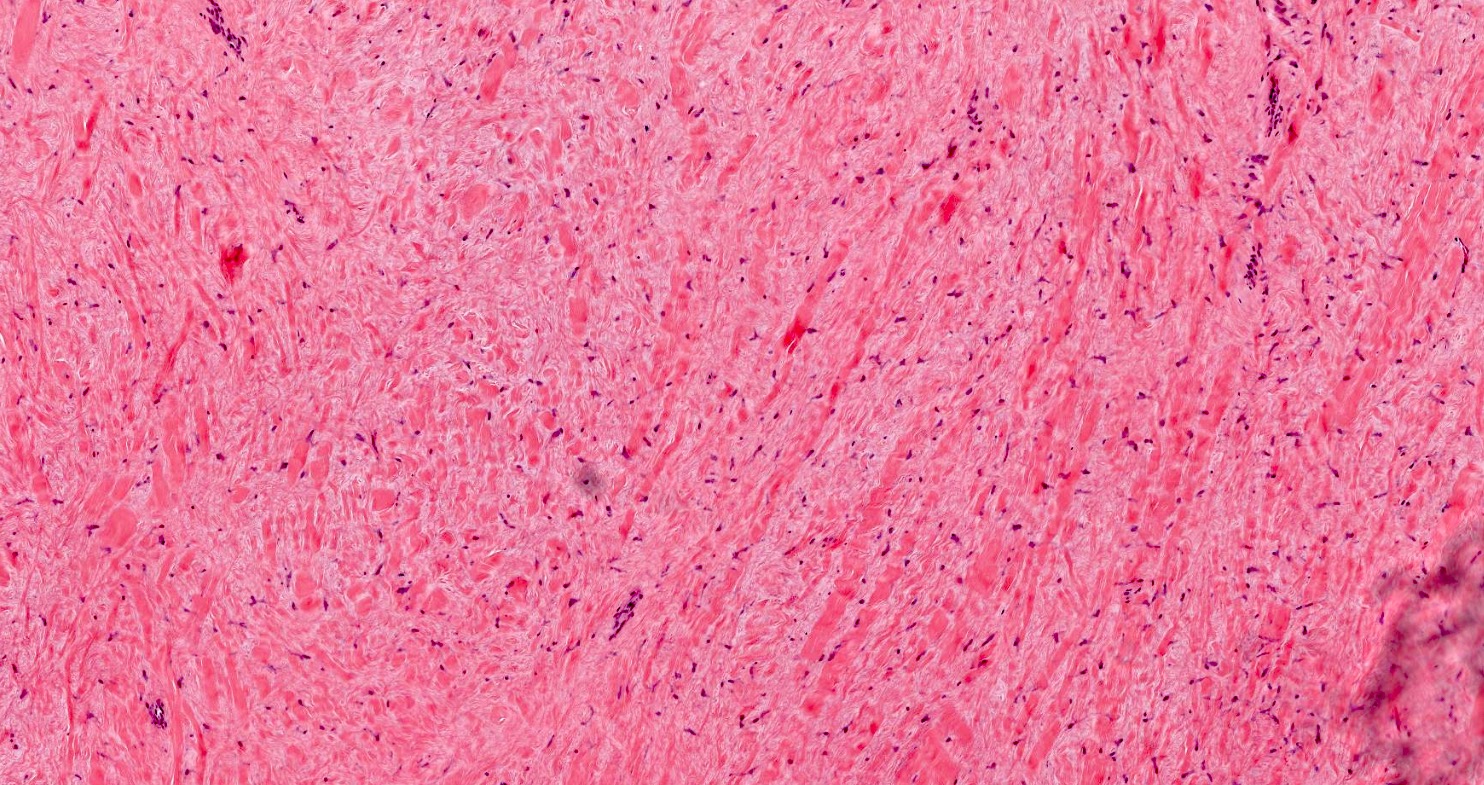
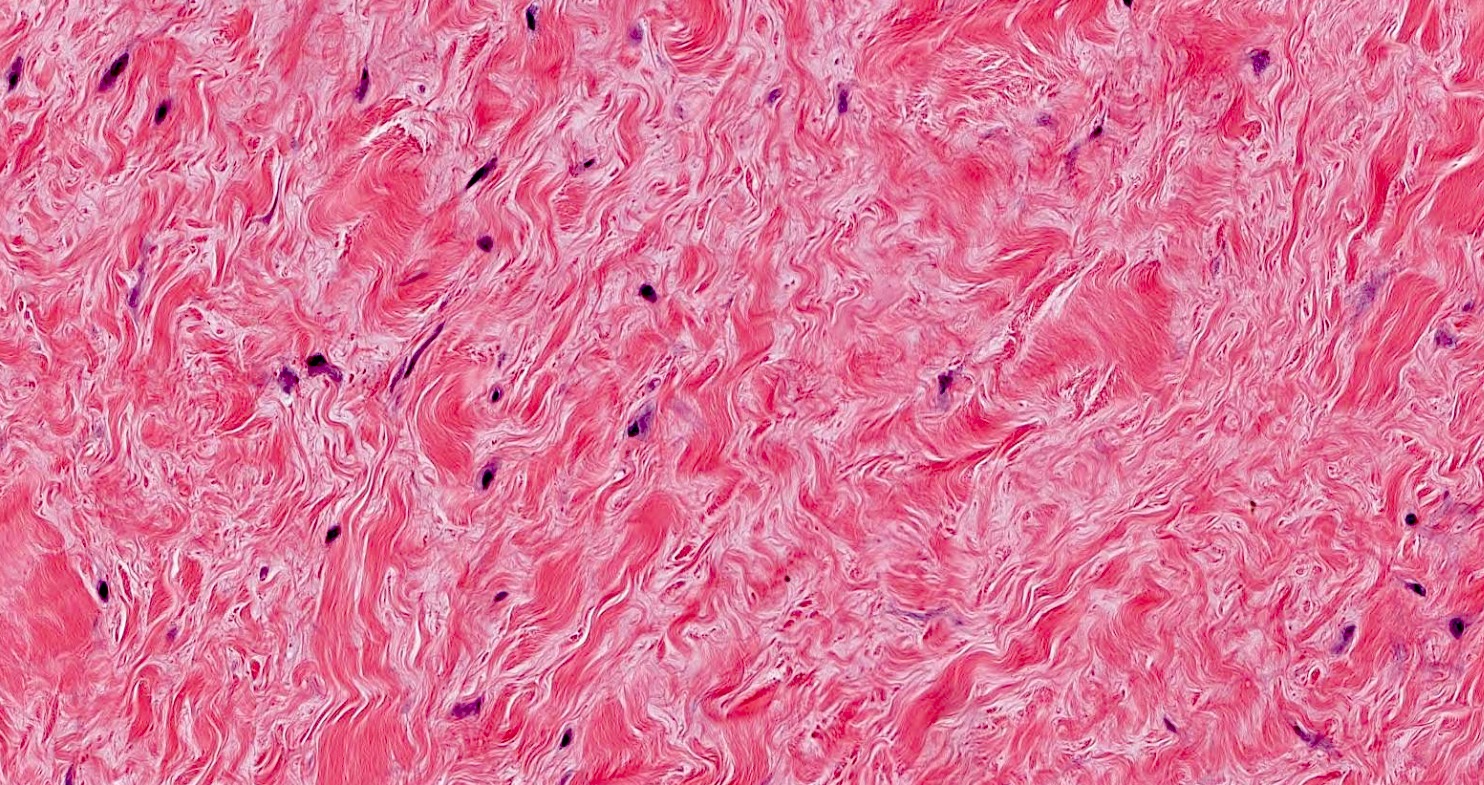
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed but may infiltrate fat or less commonly skeletal muscles (Hum Pathol 1998;29:676)
- Hypocellular with fibromyxoid or collagenous stroma
- Bland spindled to stellate shaped fibroblasts
- Minimal vasculature
- Minimal to absent mitotic activity
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Cytology is usually not performed
Positive stains
- Immunohistochemical (IHC) stains are usually not needed for diagnosis
- Most IHC stains are nonspecific
- Diffuse and strong nuclear reactivity with FOSL1 (In Vivo 2021;35:69)
- Variable SMA positive
- Rare focal keratin expression
Negative stains
- CD34
- Desmin
- S100
- EMA
- Beta catenin
- MUC4
- References: In Vivo 2021;35:69, J Cutan Pathol 2024;51:70
Electron microscopy description
- Electron microscopy is not usually performed
- Tumor cells show features of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Translocations involving 11q12, including t(2;11)(q31;q12) and t(11;17)(q12;p11.2) (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2004;149:161, Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2009;192:73, Cancer Genet 2011;204:569)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Desmoplastic fibroblastoma (collagenous fibroma) versus sclerotic / plywood fibroma
Desmoplastic fibroblastoma (collagenous fibroma)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, chest, biopsy:
- Collagenous fibroma (desmoplastic fibroblastoma) (see comment)
- Comment: Sections demonstrate a well circumscribed hypocellular proliferation of stellate fibroblasts in a collagenous stroma, consistent with a collagenous fibroma (desmoplastic fibroblastoma).
Differential diagnosis
- Desmoid type fibromatosis:
- Predominantly affects young adults (mean age: 41)
- Deep seated soft tissue tumors, subdivided into extra-abdominal, abdominal and intra-abdominal
- May be associated with Gardner syndrome
- Locally aggressive, nonmetastasizing
- Long fascicles of bland fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
- Usually more cellular than collagenous fibroma, except for the hypocellular variant
- Conspicuous thin walled blood vessels with perivascular edema and lymphoid aggregates
- Beta catenin nuclear staining
- Mutations CTNNB1 (sporadic) and APC (familial)
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma:
- Predominantly affects young adults (mean age: 35 - 45)
- Deep seated soft tissue tumors of proximal extremities and trunk
- Protracted clinical course with high risk of local recurrence and late metastasis
- Short fascicles of bland spindle fibroblasts in alternating myxoid and collagenous stroma
- Curvilinear blood vessels (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11:5860)
- MUC4 positive
- FUS::CREB3L2, FUS::CREB3L1 and rarely EWSR1::CREB3L1 fusions
- Fibroma of tendon sheath:
- Predominantly affects young to middle aged adults (median age: 31)
- Arises from synovium of tendon sheath in small distal joints
- 5 - 10% risk of recurrence
- Well circumscribed paucicellular tumor with bland fibroblasts, collagenous stroma and slit-like vessels
- SMA positive; may be focal
- Desmin and nuclear beta catenin negative
- USP6 gene rearrangement by FISH
Additional references
Practice question #1
What molecular findings are associated with collagenous fibroma?
- t(2;11)(q31;q12)
- t(7;16)(q32-34;p11) FUS::CREB3L2 fusion
- t(17;22)
- USP6 gene rearrangement
Practice answer #1
A. t(2;11)(q31;q12). Collagenous fibromas (desmoplastic fibroblastomas) have been reported to have translocations involving 11q12, including t(2;11)(q31;q12) and t(11;17)(q12;p11.2). Answer D is incorrect because USP6 gene rearrangement is associated with fibroma of tendon sheath. Answer C is incorrect because t(17;22) is associated with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Answer B is incorrect because t(7;16)(q32-34;p11) FUS::CREB3L2 fusion is associated with low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous fibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous fibroma
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
A. Collagenous fibroma. Collagenous fibroma is a hypocellular tumor with bland spindled to stellate shaped fibroblasts and a fibromyxoid to collagenous background. Answer C is incorrect because fibroma of tendon sheath shows bland fibroblasts and collagenous stroma with slit-like vessels. Answer B is incorrect because desmoid type fibromatosis shows long fascicles of bland fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, conspicuous thin walled blood vessels with perivascular edema, lymphoid aggregates and more cellularity. Answer D is incorrect because low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma shows short fascicles of bland spindled fibroblasts in alternating myxoid and collagenous stroma as well as curvilinear blood vessels.
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous fibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Collagenous fibroma