Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Dai M, Yeh YA. Inverted urothelial papilloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderinvertedpapilloma.html. Accessed September 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Inverted urothelial papilloma is a benign urothelial neoplasm with an endophytic growth of complex and interconnecting trabeculae
Essential features
- Endophytic proliferation of normal thickness urothelium forming anastomosing cords, islands and trabeculae (Mod Pathol 2015;28:612)
- Consists of uniformly bland urothelial cells with preserved polarity and peripheral palisading lacking cytologic atypia
Terminology
- Inverted urothelial papilloma
- Inverted papilloma of the urinary bladder
- Brunnian adenoma (Hum Pathol 1978;9:229)
ICD coding
- ICD-O
- ICD-10: D30.3 - benign neoplasm of bladder
- ICD-11
- 2F35 & XH5A08 - benign neoplasm of urinary organs & urothelial papilloma, inverted
- XH3HQ8 - transitional papilloma, inverted, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare; < 1% of all urothelial neoplasms of the bladder
- Broad age range (8 - 88 years), commonly 50 - 60 years (Urol Oncol 2013;31:1584, Urol Case Rep 2020;35:101543)
- More common in men; M:F = 5.8:1 (Urol Oncol 2013;31:1584)
Sites
- Urinary bladder: bladder neck (most common, 41%), trigone, lateral wall, posterior wall, some tumors multifocal (Urol Oncol 2013;31:1584)
- Upper urinary tract and urethra
Pathophysiology
- RAS-ERK pathway activation
- Mutations of HRAS or KRAS activating nuclear transcription of proteins and promoting cell growth, cell cycle progression and proliferation (J Pathol 2019;249:3)
- No TERT promotor or FGFR3 mutations
Etiology
- HRAS mutation (10 of 11 tumors) and KRAS (1 of 11 tumors) (J Pathol 2019;248:260)
Clinical features
- Hematuria, dysuria, irritative voiding symptoms, lower urinary tract obstructive symptoms (Cancer 2006;107:2622)
- Flank pain in upper urinary tract lesions (Oncol Lett 2012;4:71)
Diagnosis
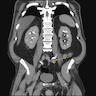
- Tumor mass on computerized tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
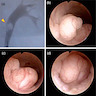
- Sessile or pedunculated mass with smooth contour on cystoscopy
- Histopathological exam (see Microscopic (histologic) description) (Mod Pathol 2015;28:612)
Radiology description
- CT scan with contrast: filling defect
- MRI: polypoid lesion with nonpapillary surface and thin stalk (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015;205:311)
Prognostic factors
- Low recurrence rate (< 2%) (Urol Oncol 2013;31:1584)
Case reports
- 8 year old girl presented with painless gross hematuria (Urol Case Rep 2020;35:101543)
- 27 year old man presented with hematuria (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2020;63:96)
- 54 year old man presented with painless intermittent gross hematuria (Urol Case Rep 2021;40:101926)
- 56 year old woman, 63 year old man and 78 year old man presented with hematuria (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:766)
- 71 year old man presented with hematuria and dysuria (Rare Tumors 2012;4:e45)
Treatment
- Complete transurethral resection (Cancer 2006;107:2622)
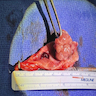
Gross description
- Raised, sessile, pedunculated or polypoid mass with smooth contour
- Single or multiple (1.3 - 4.4%) (J Urol 1996;155:1391)
- Size ranges from 1 to 50 mm (mean of 12.8 mm), measured up to 8 cm (BJU Int 2011;107:532)
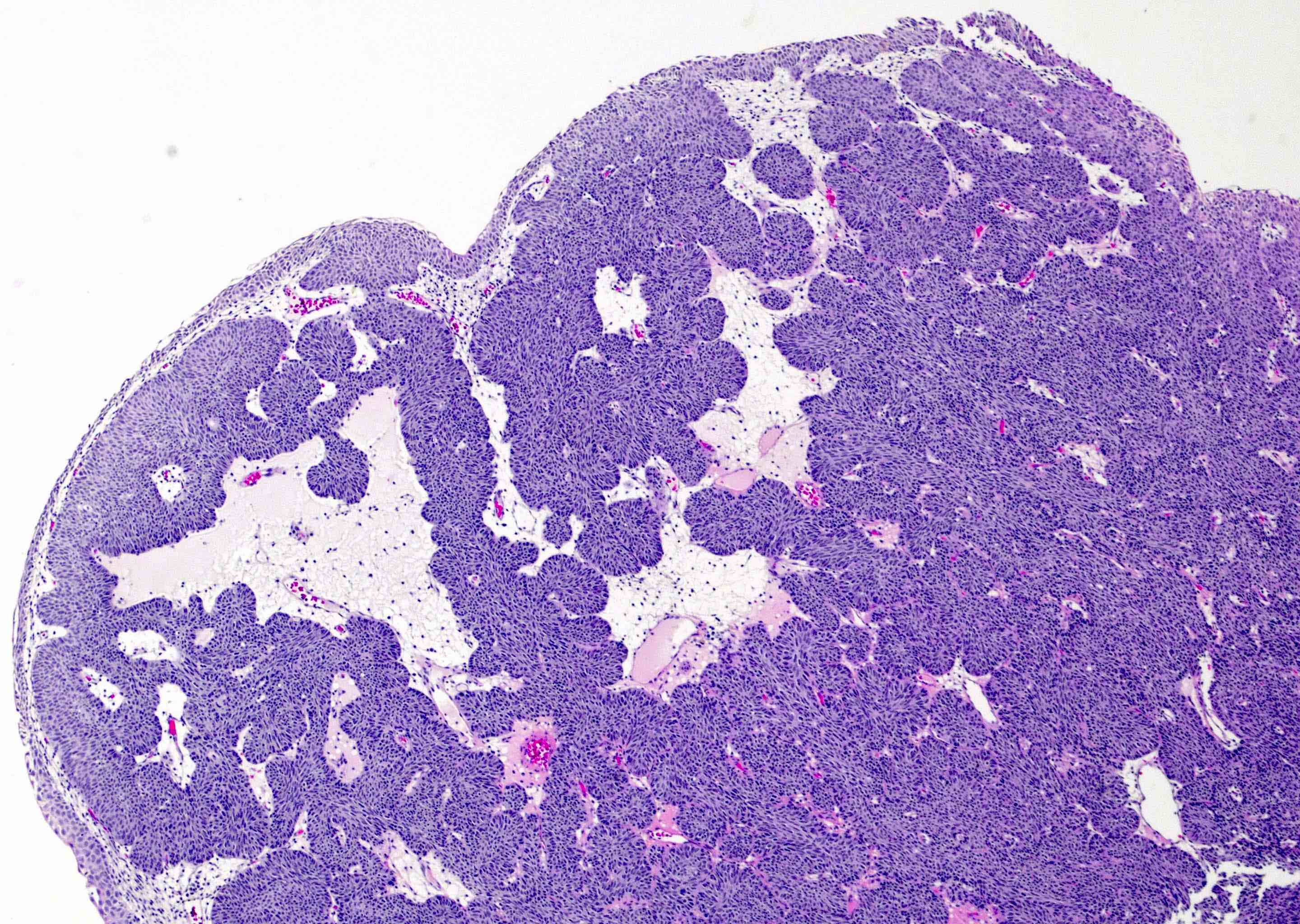
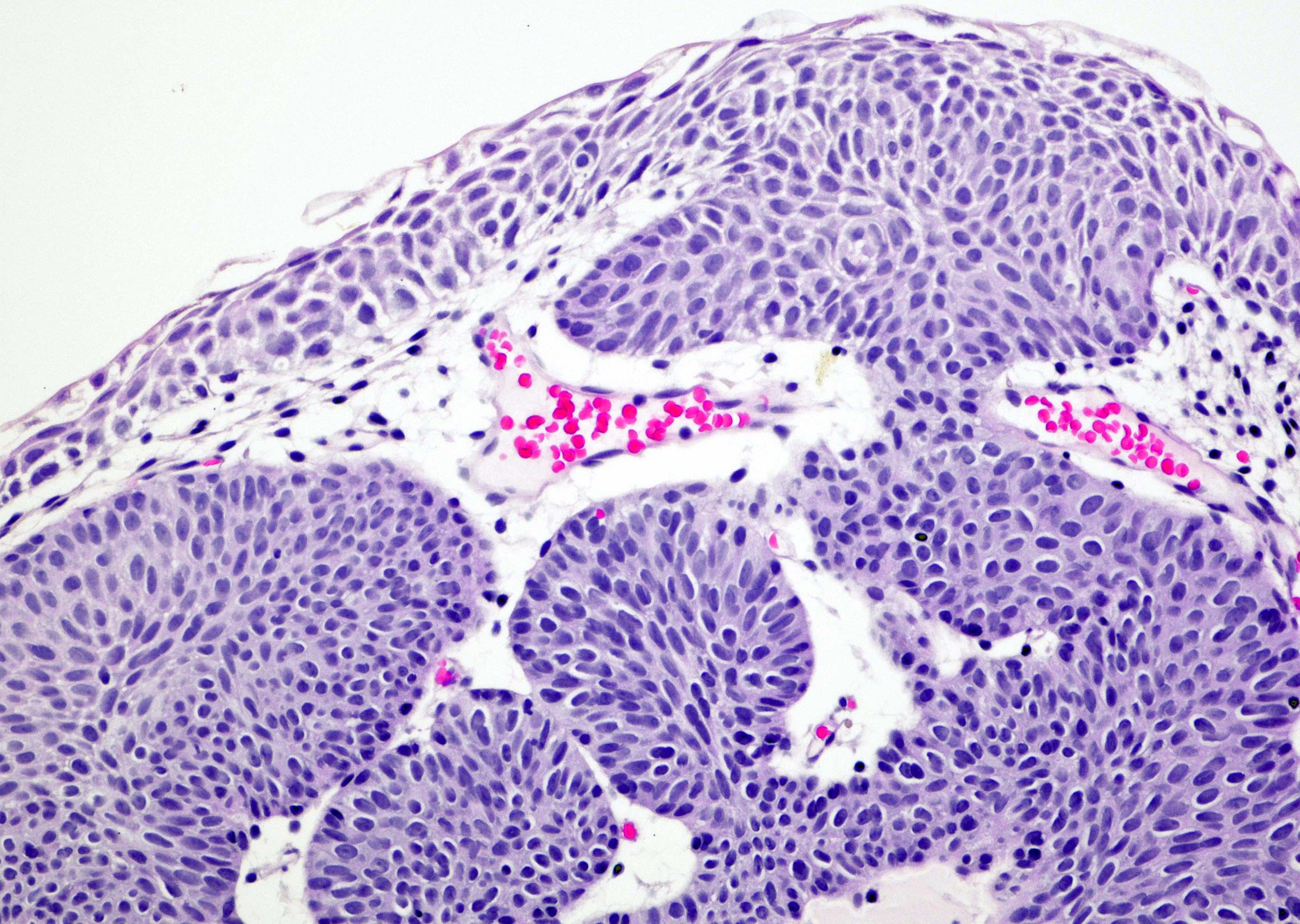
Microscopic (histologic) description
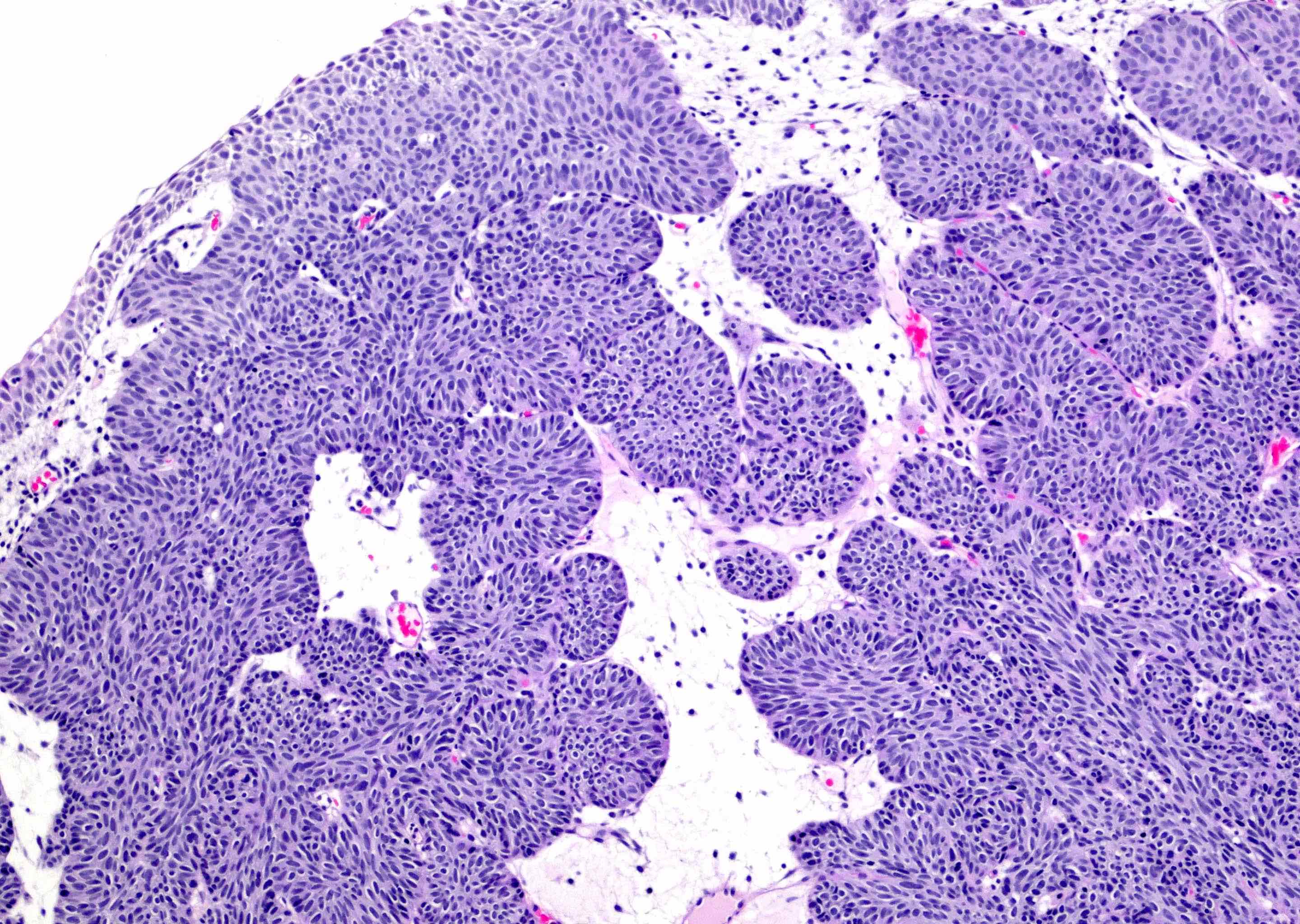
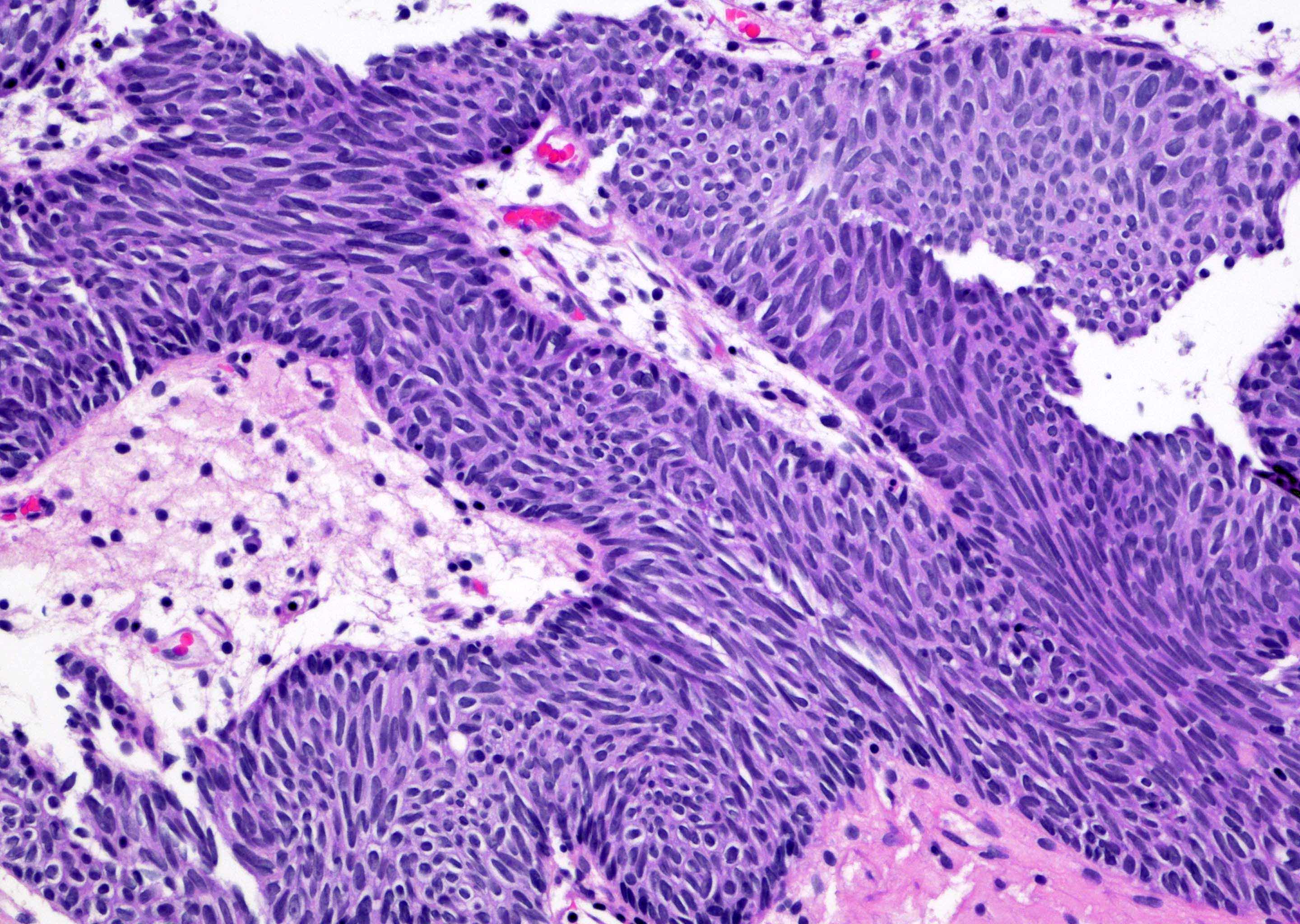
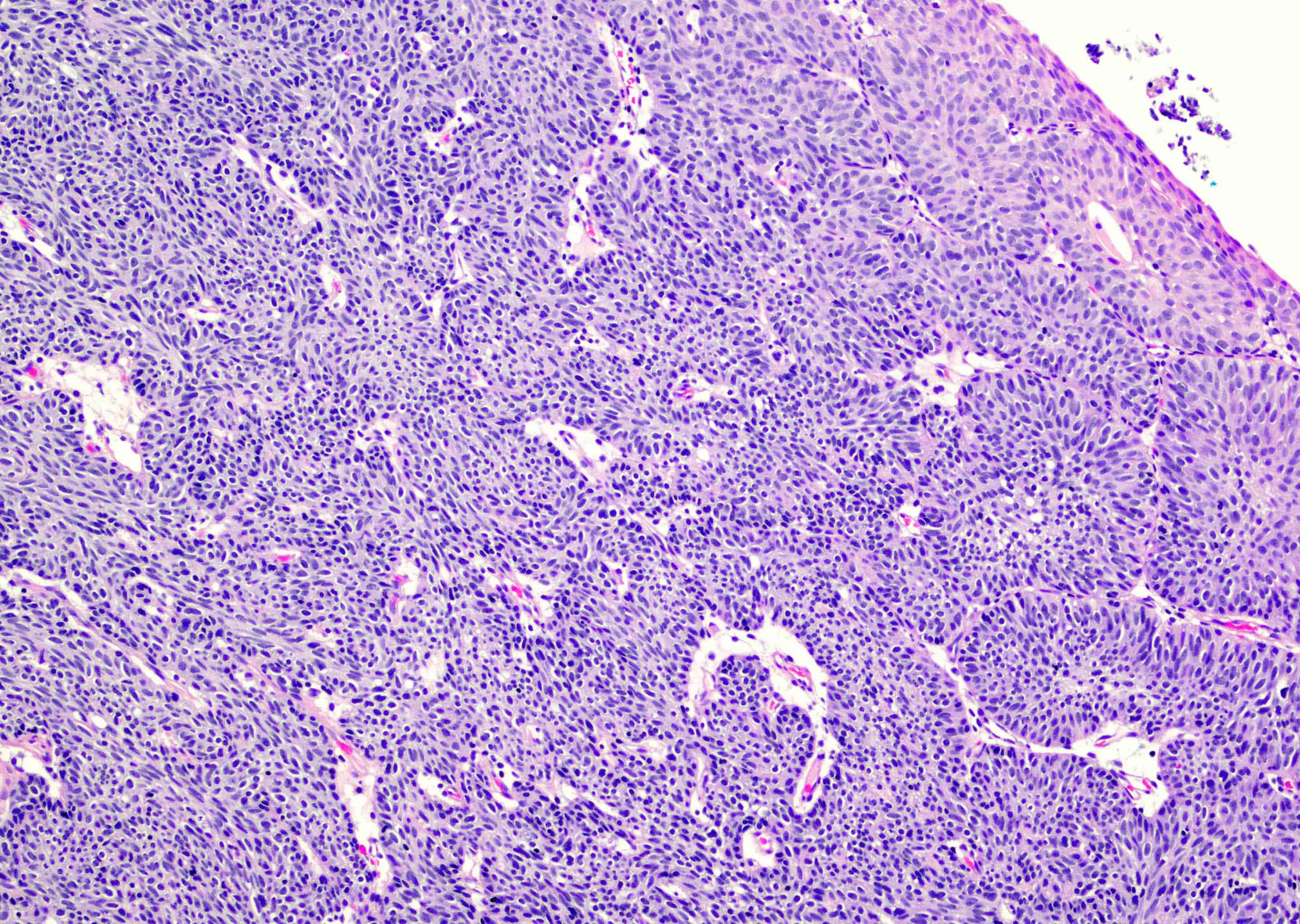
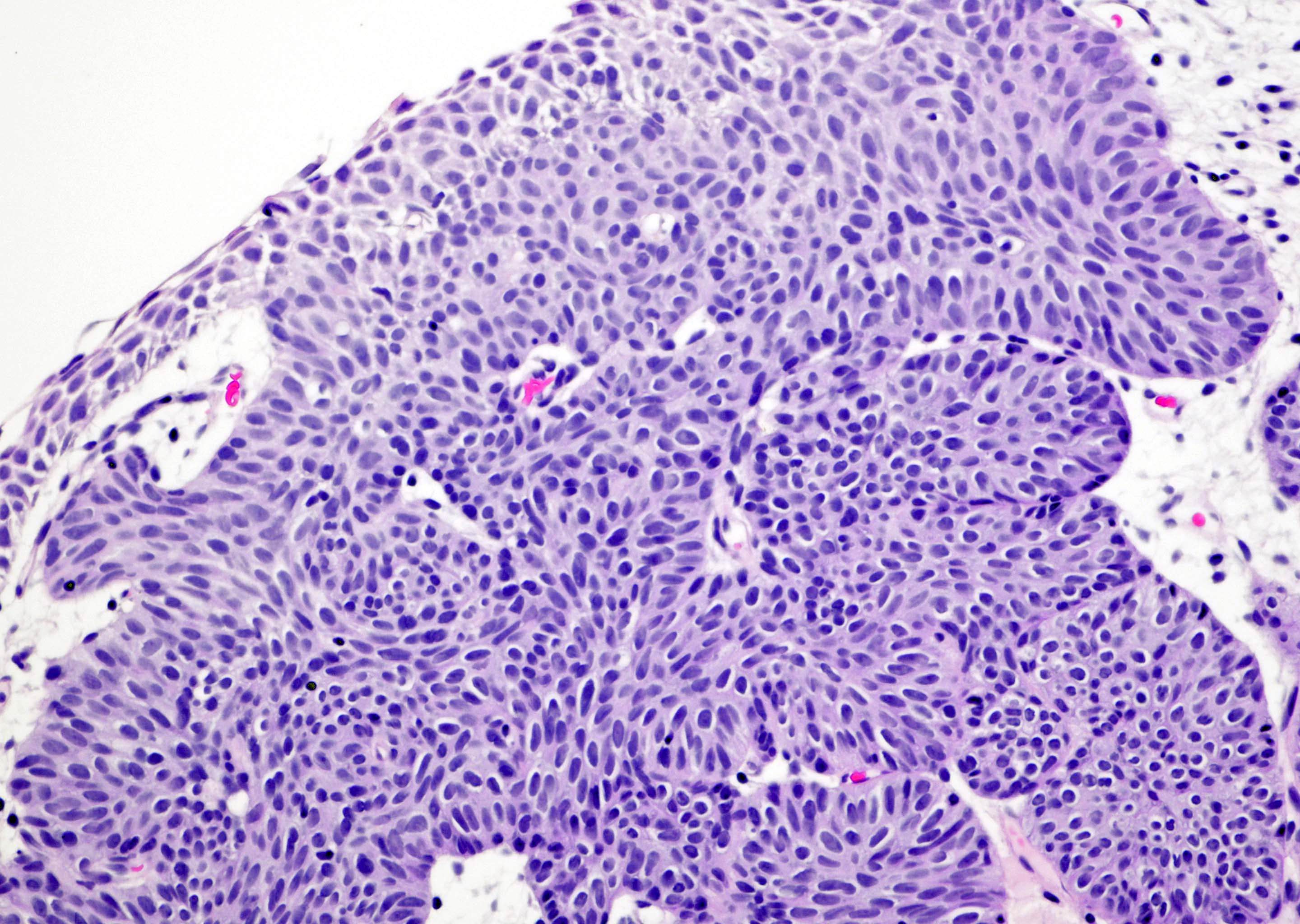
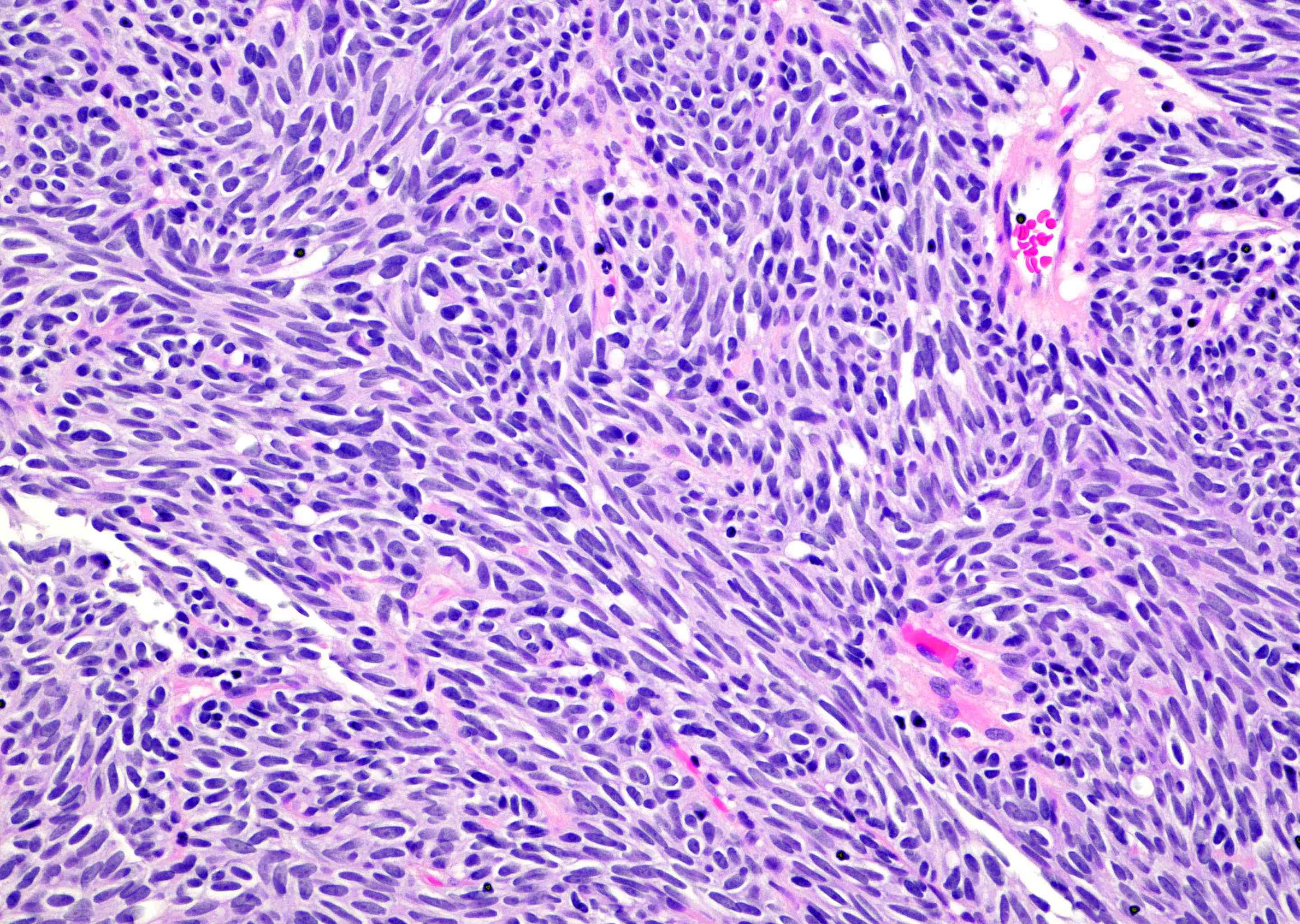
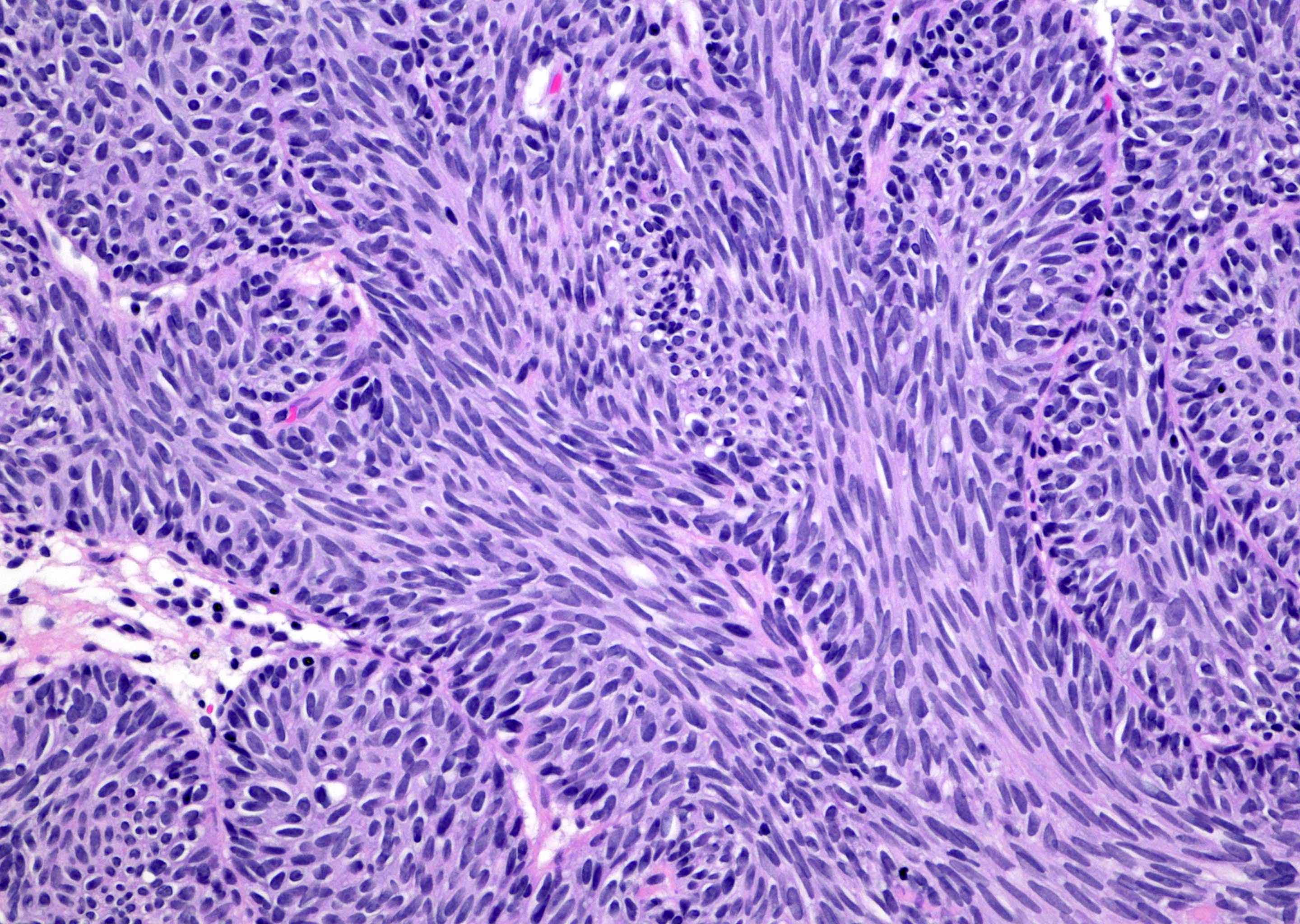
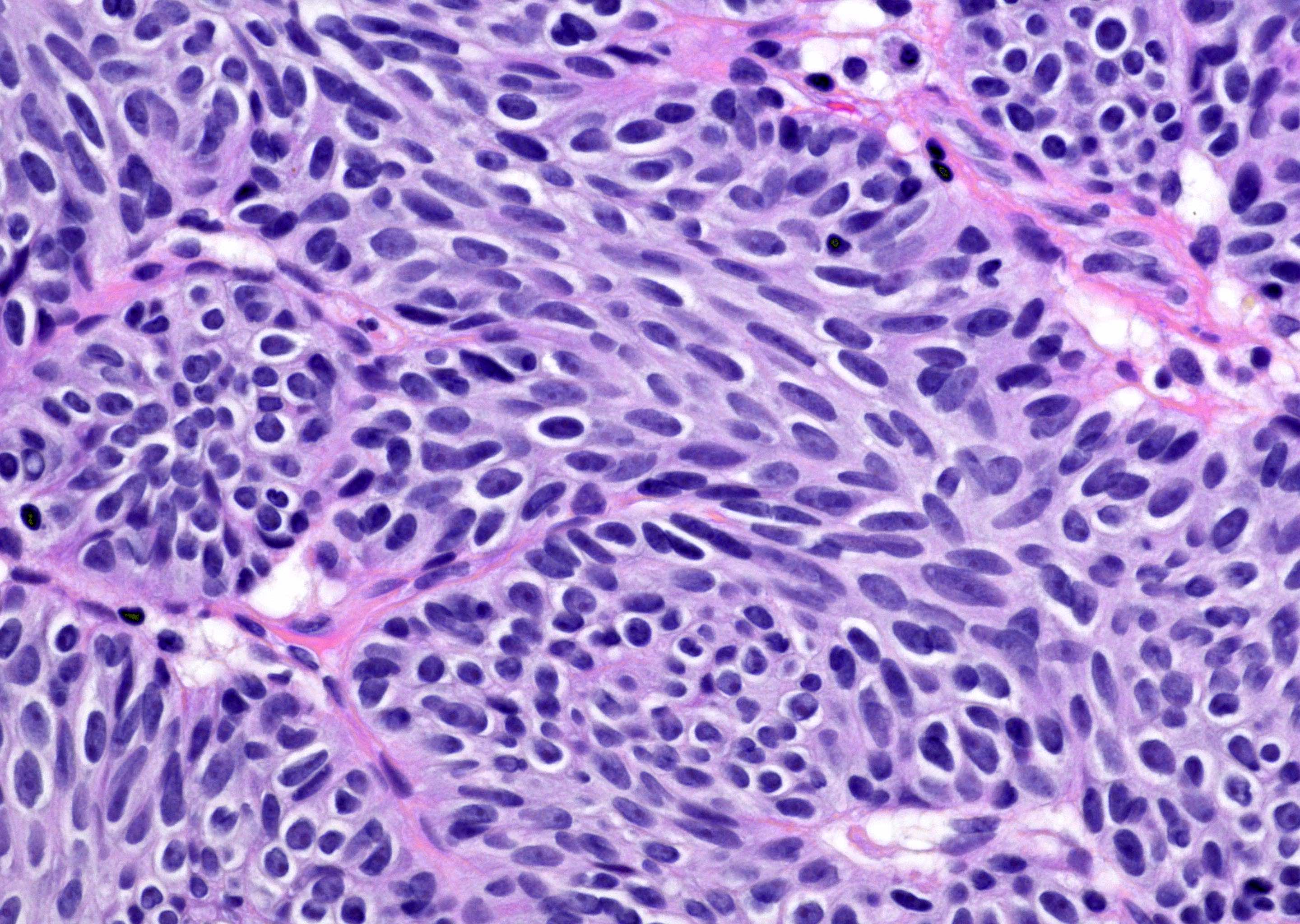
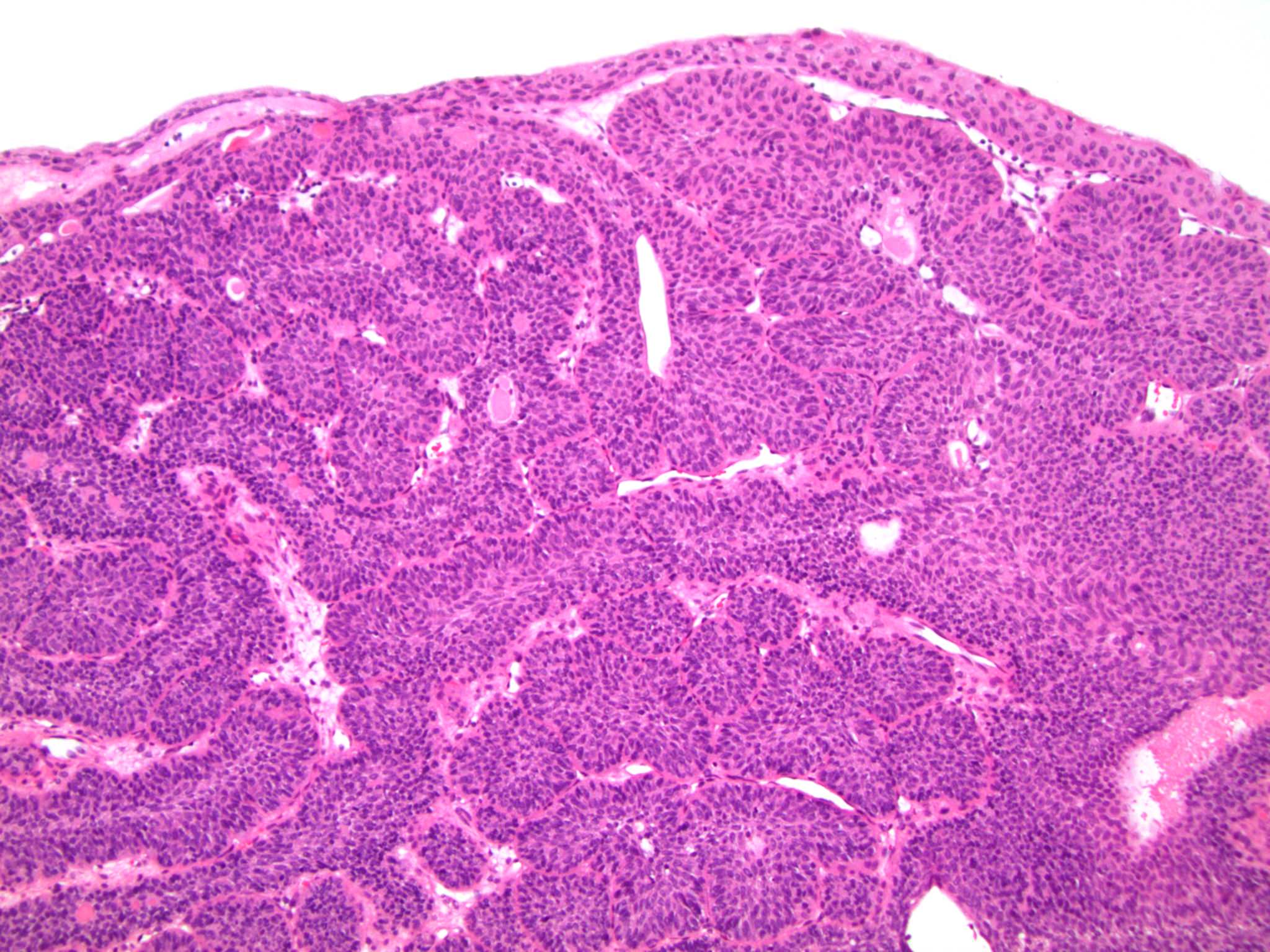
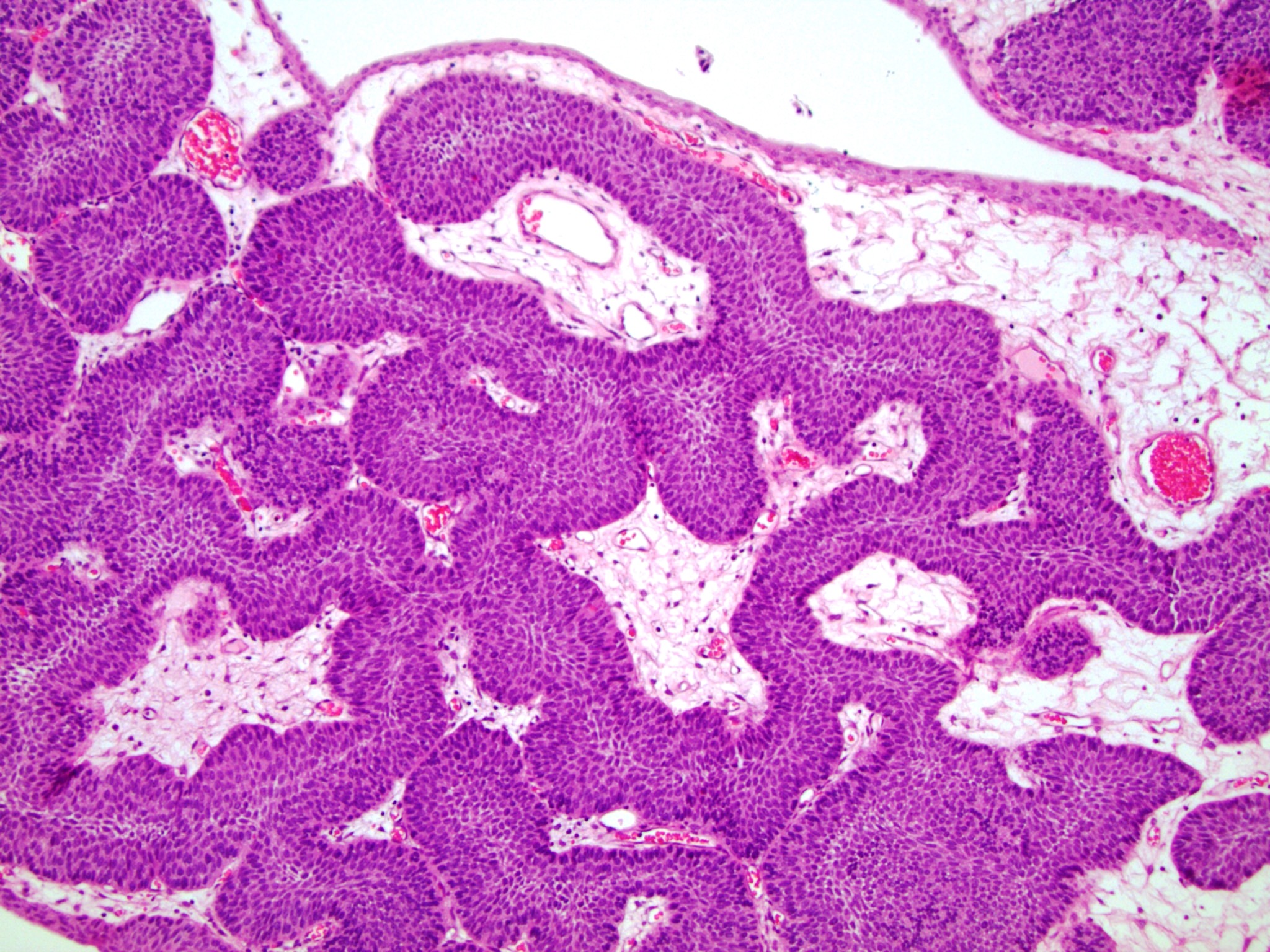
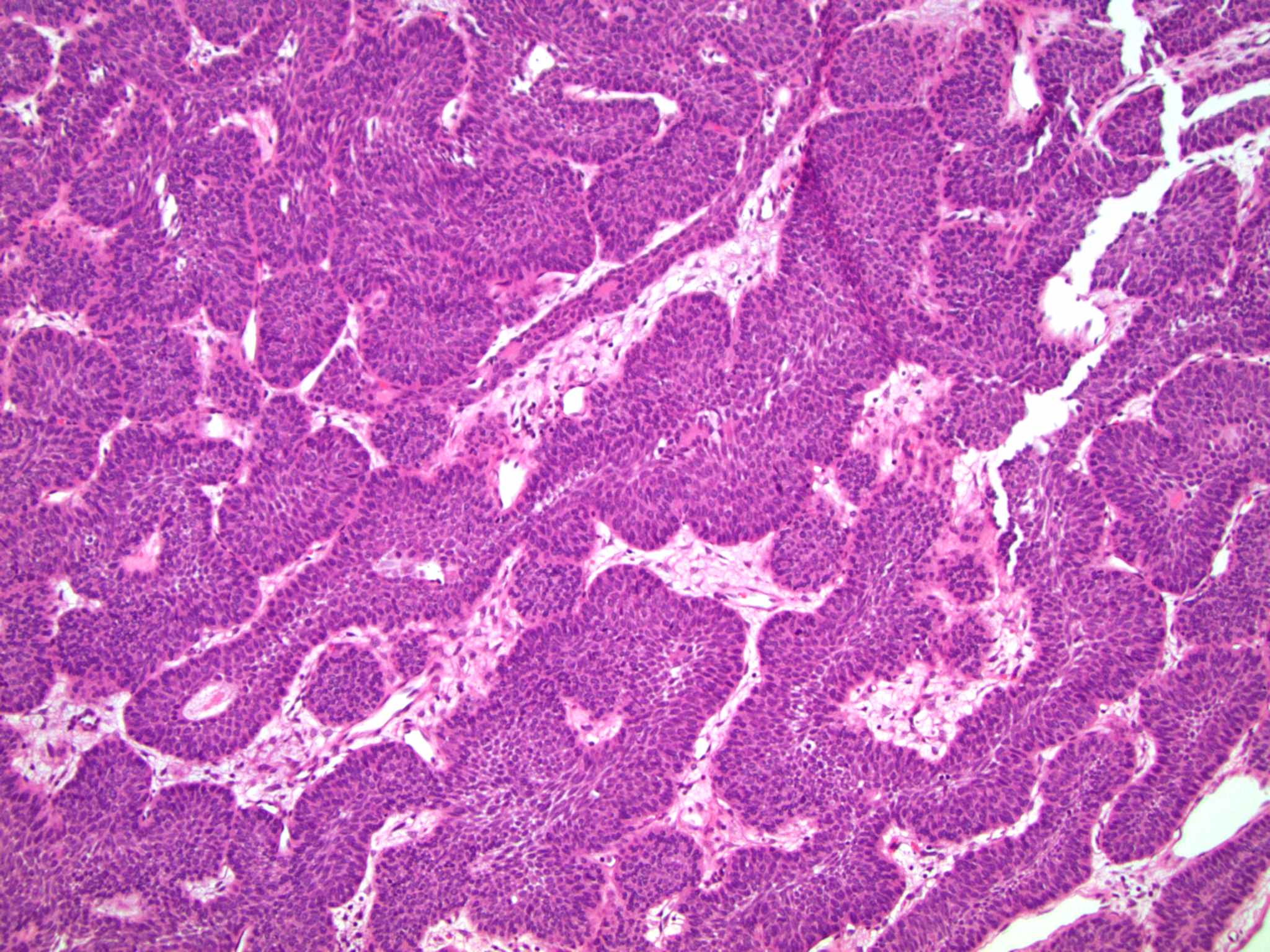
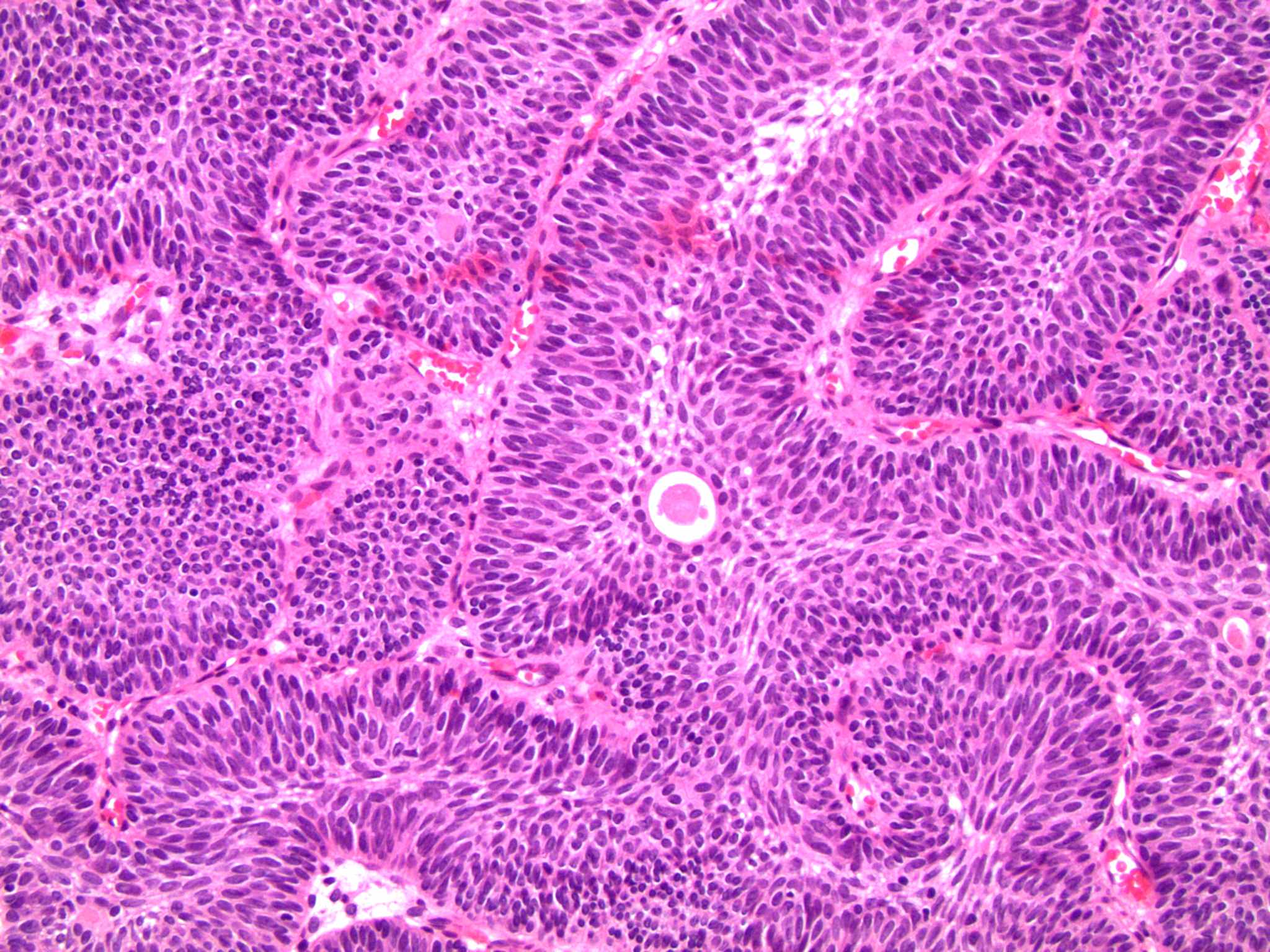
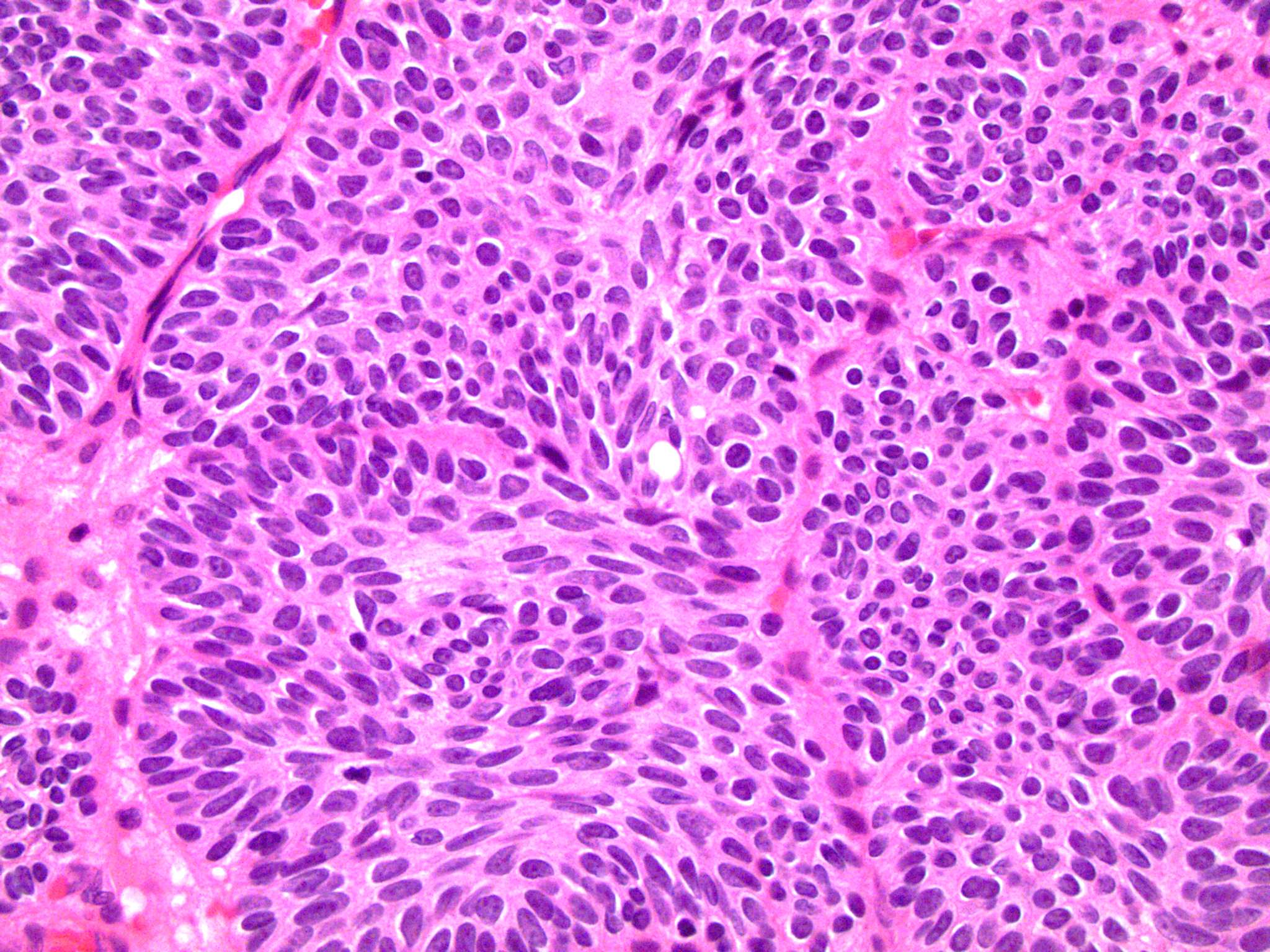
- Sharply circumscribed, endophytic proliferation of thin and complex anastomosing cords, islands and trabeculae of cytologically bland urothelial cells with virtually no nuclear atypia (Mod Pathol 2015;28:612)
- Invaginating trabeculae composed of 5 - 10 layers of urothelial cells with central streaming and peripheral palisading cells, embedded in lamina propria
- Surface is lined by the normal urothelium with no or minimal exophytic papillary component
- Urothelial cells with vacuolation and foamy xanthomatous cytoplasmic changes may be seen (Hum Pathol 2006;37:1577)
- Mild degenerative cytologic atypia may be seen
- Mitotic figures are absent or extremely rare
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Y. Albert Yeh, M.D., Ph.D., Daniel Athanazio, M.D., Ph.D. and Debra Zynger, M.D.
Immunofluorescence description
- UroVysion FISH
- Negative (0%) for gain of chromosomes 3, 7, 17 or loss of 9p21 in inverted urothelial papilloma versus positive (72%) in inverted pattern urothelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1861)
Positive stains
- CD44 (50%) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;44:151433)
Negative stains
- Ki67, CK20, p53 (6.7% positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1861)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Microsatellite instability (1.8%), 9p deletions (3.9%), 9q deletions (13.2%), 17p deletions (5.1%), nuclear p53 accumulation (18.9%) and abnormal immunostaining pattern for MSH2 (5.8%), MLH1 (11.8%) and MSH6 (3.8%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:938)
- FGFR3 mutations (45%) (Mod Pathol 2009;22:627)
- HRAS mutations (60%) (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1957)
- Absence of APOBEC (apolipoprotein B mRNA editing catalytic polypeptide-like) mutational signature (J Pathol 2019;248:260)
- HRAS / KRAS mutations and no mutated FGFR3, TERT, TP53 and chromatin modifying gene (J Pathol 2020;250:464)
Sample pathology report
- Urinary bladder, neck, biopsy:
- Inverted urothelial papilloma (see comment)
- Comment: The bladder lesion shows an invaginating polypoid proliferation of anastomosing cords and trabeculae with peripheral palisading of cells. There is central streaming of urothelial cells. No exophytic components are noted. The tumor cells are characterized by small, uniform and cytologically bland nuclei. Mitotic figure is not seen. These features are consistent with an inverted urothelial papilloma.
Differential diagnosis
- Endophytic growth of papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:3):
- Uniformly thickened, expanded cords and nests of cytologically bland urothelial cells
- Absence of central streaming or peripheral palisading
- Endophytic growth of low grade to high grade urothelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1861):
- Endophytic growth with thick irregular columns to solid nests of tumor cells with low grade or high grade nuclei
- Exophytic papillary structures or muscularis propria invasion
- Nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, abundant mitotic figures
- Lamina propria or muscularis propria invasion in high grade urothelial carcinoma may occur
- Invasive nested urothelial carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2003;16:1289):
- Irregular distribution of urothelial nests
- May not have trabecular pattern
- Lamina propria or muscularis propria invasion is common
- Paraganglioma (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2014;57:19):
- Zellballen nested growth pattern
- Variation in nuclear size
- Positive for synaptophysin or chromogranin A; positive for GATA3 (potential pitfall) and S100 in sustentacular cells
- Negative for p63 and cytokeratins
- Florid von Brunn nest proliferation / cystitis cystica (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;38:11):
- Lobular pattern and no trabeculae
- Large nests with regular spacing
- Carcinoid tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1754):
- Similar nested or trabecular distribution
- Endocrine tumor cells with coarse and stippled (salt and pepper) chromatin
- Positive for synaptophysin or chromogranin A
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 74 year old man presented to the urology clinic with hematuria and dysuria. Cystoscopic examination showed a polypoid mass with smooth surface in the bladder neck. A transurethral bladder tumor resection was performed. An image of the histopathological examination is shown above. What is the diagnosis?
- Florid cystitis cystica proliferation
- Florid von Brunn nest proliferation
- Inverted high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
- Inverted urothelial papilloma
- Paraganglioma
Practice answer #1
D. Inverted urothelial papilloma. This image shows an inverted urothelial papilloma characterized by invaginating growth of anastomosing trabeculae with central streaming of bland urothelial cells. Answers B and A are incorrect because florid von Brunn nests and cystitis cystica are composed of large nests of urothelial cells arranged in a lobular pattern with regular spacing. There is no trabecular formation. Answer C is incorrect because inverted high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma is composed of irregular and complex anastomosing cords and trabeculae with disorganized, pleomorphic and hyperchromatic urothelial cells. Answer E is incorrect because no zellballen pattern of cells is seen.
Comment Here
Reference: Inverted urothelial papilloma
Comment Here
Reference: Inverted urothelial papilloma
Practice question #2
A 68 year old man presented to the urology clinic with lower urinary tract obstructive symptoms. Cystoscopic examination showed a polypoid mass with smooth contour in the posterior wall of the bladder. A transurethral bladder tumor resection was performed. An image of the histopathological examination showed an endophytic growth with tumor cells stained positive for immunomarkers GATA3 and p63. A histopathological image is shown above. What is the diagnosis?
- Carcinoid tumor
- Inverted high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
- Inverted low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
- Inverted urothelial papilloma
- Leiomyoma
Practice answer #2
D. Inverted urothelial papilloma. The tumor is composed of trabeculae of urothelial cells (positive for GATA3 and p63) with central streaming and peripheral palisading of cells. Answer E is incorrect because is incorrect because leiomyoma is negative for GATA3 and has very focal and weak cytoplasmic staining for p63. Answers B and C are incorrect because the urothelial cells in both inverted low grade and high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma show marked dispolarity of cells with moderate to severe nuclear pleomorphism and hyperchromasia. Answer A is incorrect because carcinoid tumor cells do not have fine and coarse chromatin. Neuroendocrine cells are stained negative for GATA3, although p63 may be weakly or focally positive.
Comment Here
Reference: Inverted urothelial papilloma
Comment Here
Reference: Inverted urothelial papilloma