Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Ahmad Z, Minhas MK, Memon A. Myxopapillary ependymoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumormyxopapillaryependymoma.html. Accessed September 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- CNS WHO grade 2 glial neoplasm with a variably papillary architecture characterized by a radial arrangement of spindled or epithelioid to cuboidal cells around blood vessels with perivascular myxoid change (intermediate layer of Alcian blue positive myxoid stroma) and mucin rich microcyst formation (Neuro Oncol 2021;23:1231)
Essential features
- Glioma with papillary architecture and perivascular myxoid change or at least focal myxoid microcysts
- Immunoreactive for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)
- For unresolved tumors, DNA methylation profile is aligned with myxopapillary ependymoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9394/1 - myxopapillary ependymoma
- ICD-11: 2A00.0Y & XH15U1 - other specified gliomas of brain & myxopapillary ependymoma
Epidemiology
- Incidence rates are 0.6 - 1.0 cases per 1 million person years
- M:F = 1.4 - 2.1:1
- Seen in all ages but most common in adults
- 2 age peaks: 25 - 29 years and 45 - 49 years (J Neurooncol 2016;129:251, Neuro Oncol 2015;17:588)
Sites
- Almost exclusively occurs in the conus medullaris and filum terminale of the spinal cord (Mod Pathol 1997;10:304, Minerva Chir 1997;52:629)
- Occasional examples in lateral and fourth ventricles, inside or outside the brain or in cervicothoracic spinal cord but most often is in a sacrococcygeal or presacral location; rarely reported in mediastinum, lung, uterine adnexae, etc. (Brain Tumor Pathol 2012;29:25, Clin Neuropathol 2004;23:53, Cancer 1985;56:883, J Neurooncol 1993;15:251, J Clin Neurosci 2018;47:202)
- When this tumor occurs at higher levels of neuroaxis, origin from conus / filum terminale should be excluded (Pathology 1996;28:373)
Pathophysiology
- Pathophysiology is unknown; various recurring chromosomal copy number abnormalities have been described
- No consistent structural variants or other driving mutations have been demonstrated (J Clin Neurosci 2018;50:144, Neuro Oncol 2018;20:1616)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Chronic lower backache
- Sciatica
- Sensory or motor deficits leading to impotence, urinary and fecal incontinence, myelopathy
Diagnosis
- Tissue biopsy with immunohistochemistry
- Morphology (see Microscopic (histologic) description)
- Immunophenotype (see Positive stains)
- Diagnostic molecular pathology: unique DNA methylation profile (Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:305, Cancer Cell 2015;27:728, Neuro Oncol 2018;20:1616)
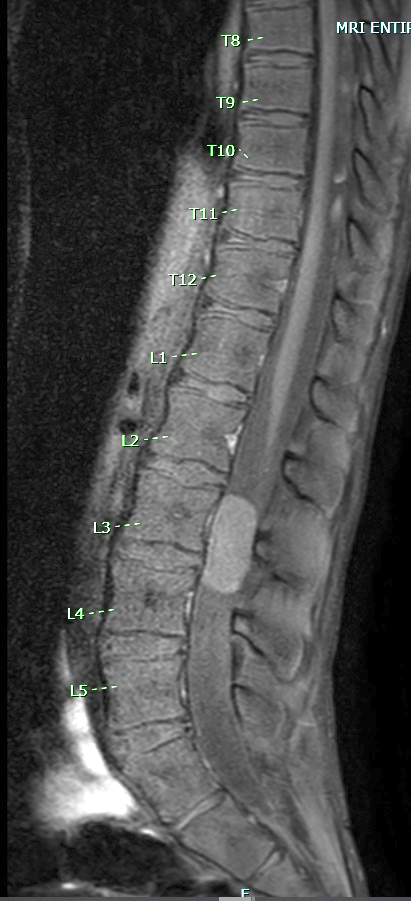
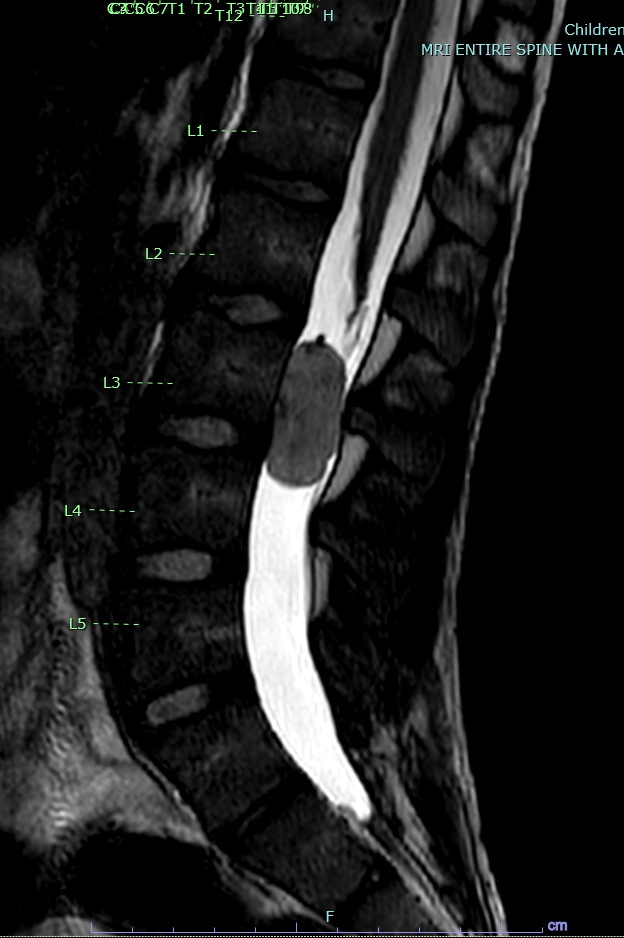
Radiology description
- Well circumscribed, sharply demarcated, ovoid, contrast enhancing mass in the cauda equina / conus / filum terminale region
- Hyperintense on T1 and T2 weighted MRI with intense contrast enhancement
Prognostic factors
- Relatively favorable prognosis with 10 year survival rates > 90.6% (J Neurooncol 2016;126:165, Neuro Oncol 2015;17:588)
- Often resistant to complete removal due to locally advanced growth or cerebrospinal fluid borne seeding of the thecal sac or more rostral neuroaxis; this may be seen in > 50% of pediatric cases (World Neurosurg 2020;136:e245, J Neurooncol 2016;126:165)
- Many patients live with this disease but require repeated operations and adjuvant therapy
- Tumors arising in the conus have a poorer prognosis than tumors in the cauda equina as the former adhere strongly to the spinal cord and are less amenable to resection
- Radiotherapy improves progression free survival (Neuro Oncol 2015;17:588)
- Anaplastic histology may increase risk of aggressive behavior (Brain Pathol 2019;29:75)
Case reports
- 6 year old girl with 1 week history of progressive upper and lower extremity weakness and bilateral upper extremity dysesthesia (Childs Nerv Syst 2022;38:223)
- 9 year old girl with slow growing painless mass in the sacrococcygeal region (Am J Dermatopathol 2021;43:e273)
- 22 year old man with acute exacerbation of chronic back pain shooting down both thighs secondary to preoperative intracranial dissemination of spinal myxopapillary ependymoma (World Neurosurg 2021;145:13)
- 32 year old man with primary seeding of myxopapillary ependymoma into multiple lumbosacral areas (World Neurosurg 2017;99:812.e21)
- 34 year old man with multifocal lumbosacral mass presenting with drop metastasis (Spinal Cord Ser Cases 2022;8:43)
- 36 year old woman with spinal cord myxopapillary ependymoma who refused surgery and presented 5 years later with paraparesis (World Neurosurg 2019;121:239)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is the mainstay of treatment
- Often lifted cleanly from the operative bed; others dissected piecemeal but still in toto
- Low risk of recurrence in either of the above scenarios
- Radiotherapy reserved for subtotally resected tumors
- Some authors recommend radiotherapy for tumors excised completely but piecemeal (Mod Pathol 1997;10:304, Neurosurgery 1992;30:202, Cancer 1985;56:883)
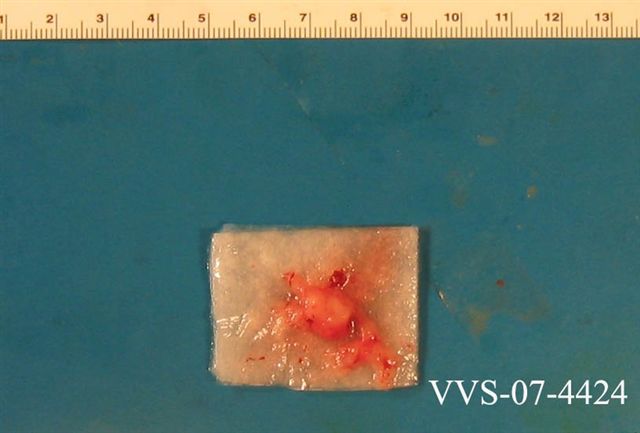
Gross description
- Often encapsulated, soft in consistency, pink to tan-gray
- May be grossly gelatinous or show hemorrhage and cystic changes
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Intraoperative squash / smear preparation and frozen section reveals epithelioid to spindled tumor cells arranged around microcysts and forming papillary structures with perivascular myxoid change; these features are diagnostic in the appropriate clinical setting
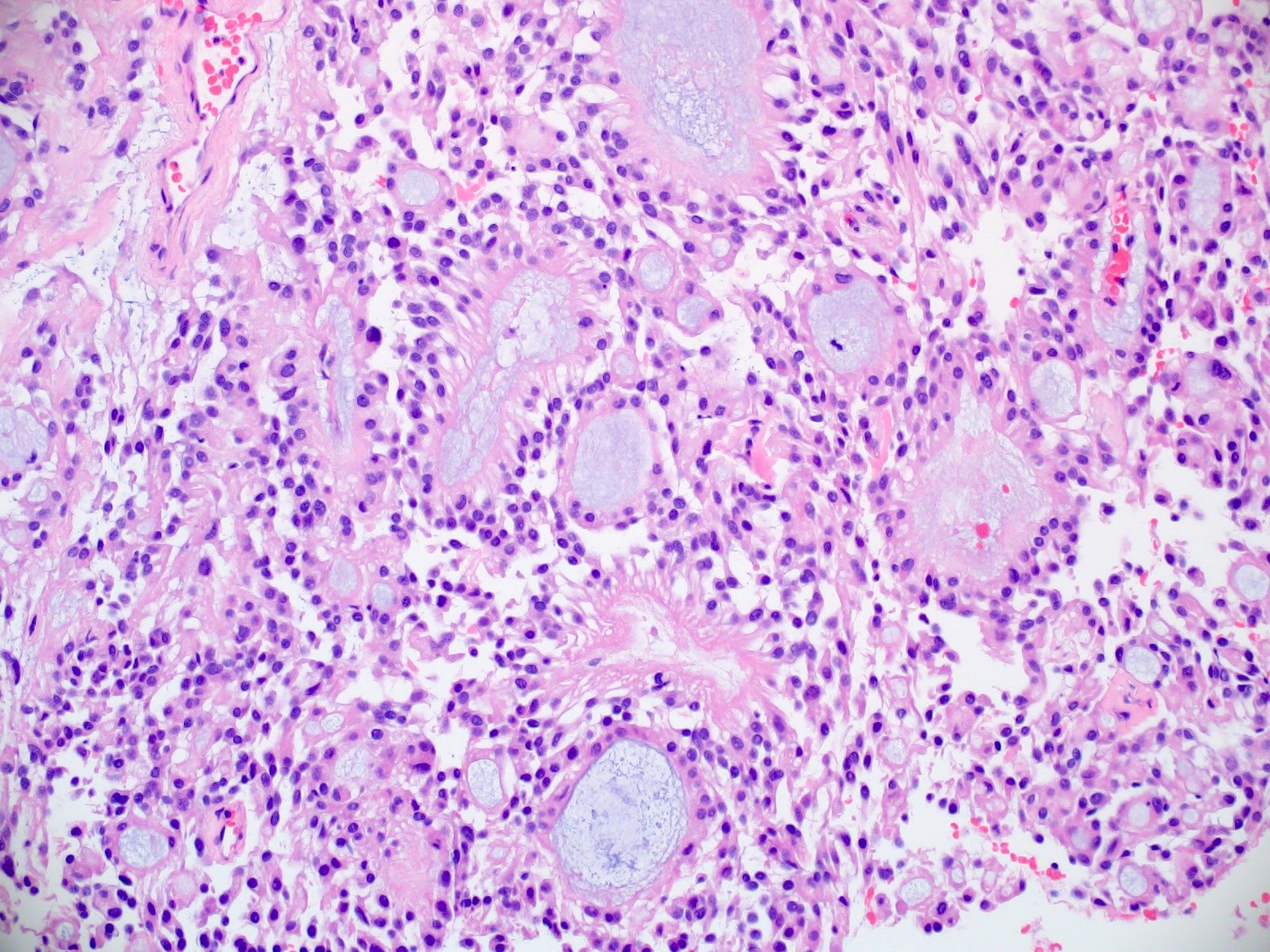
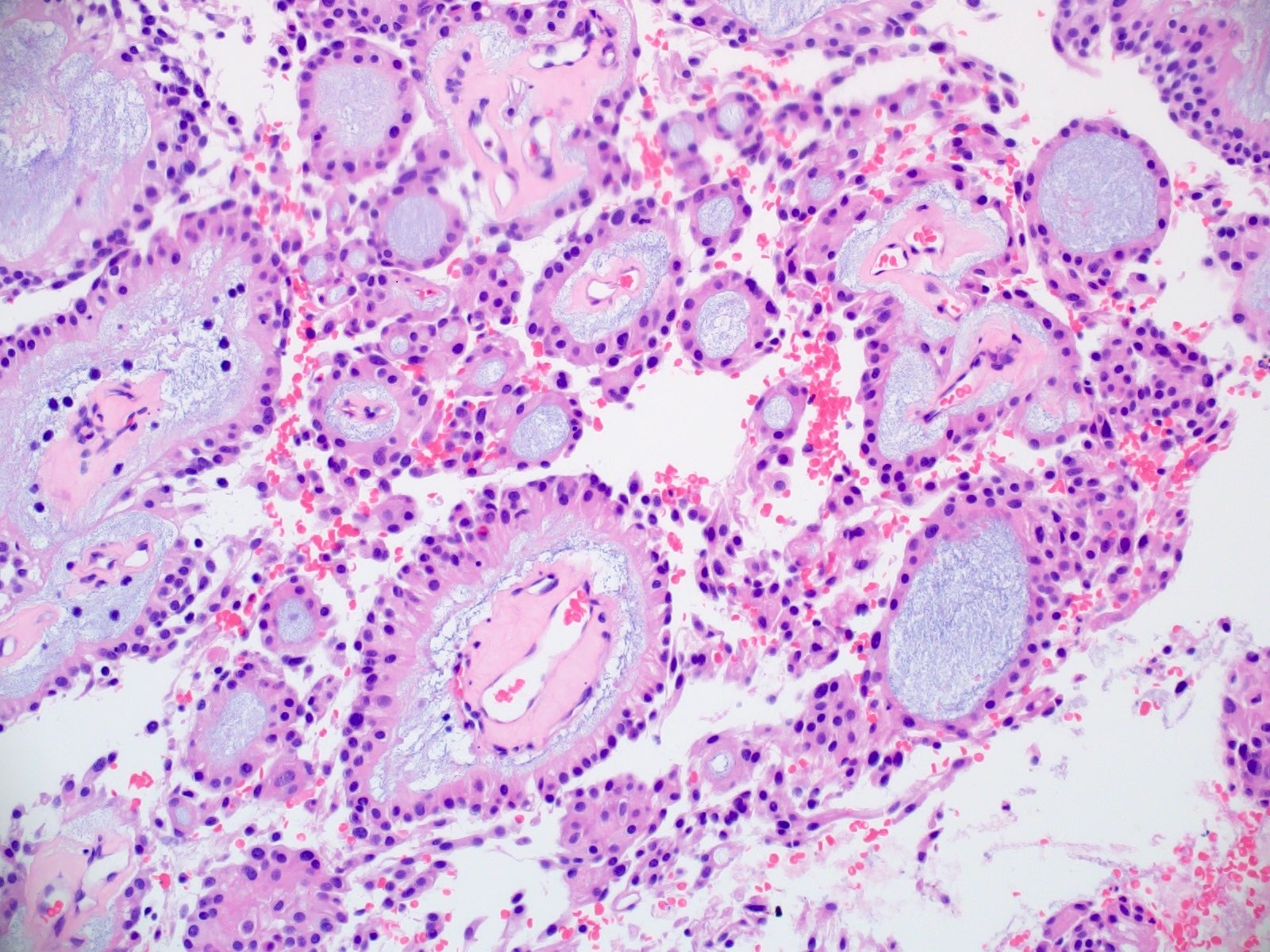
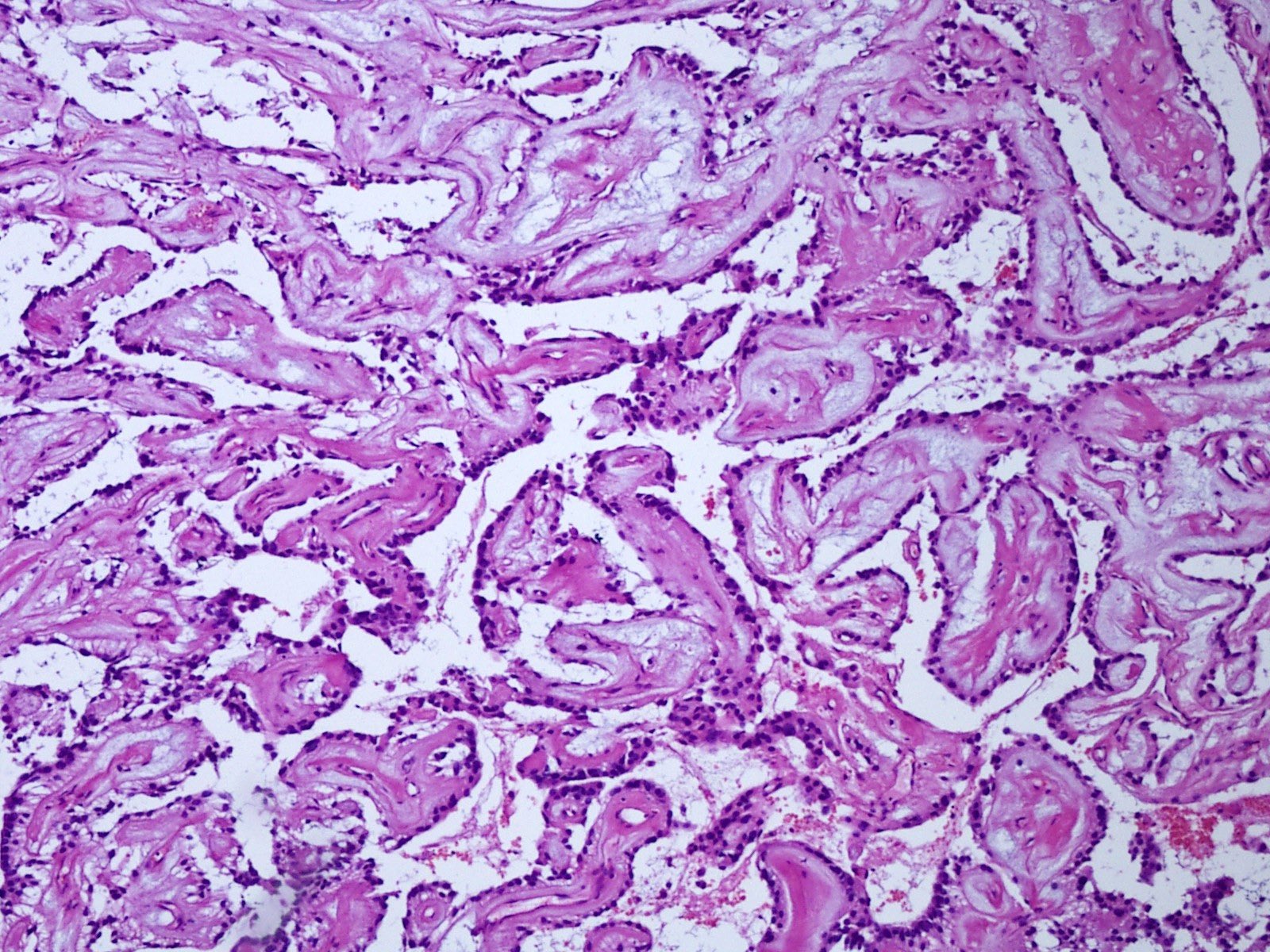
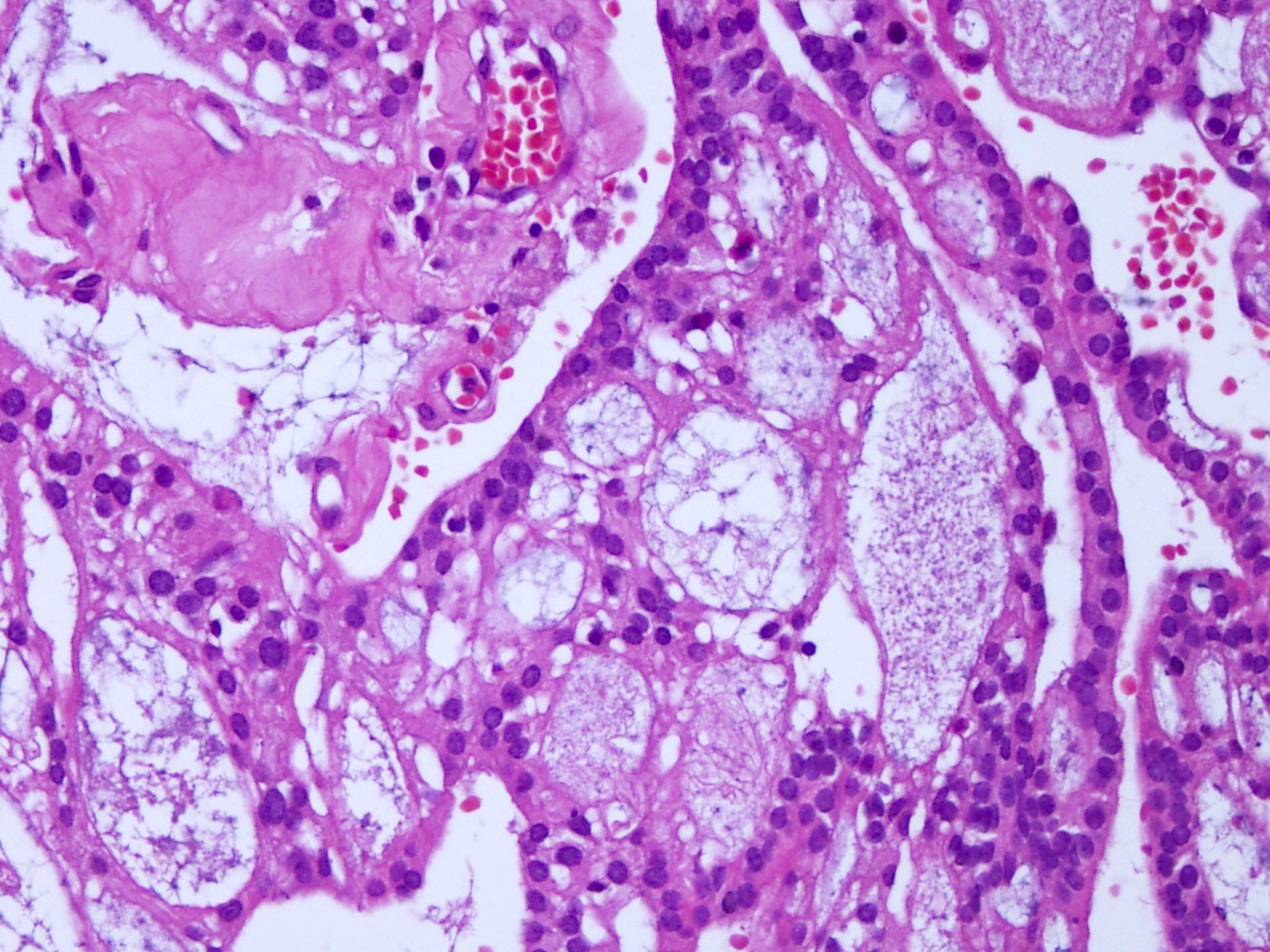
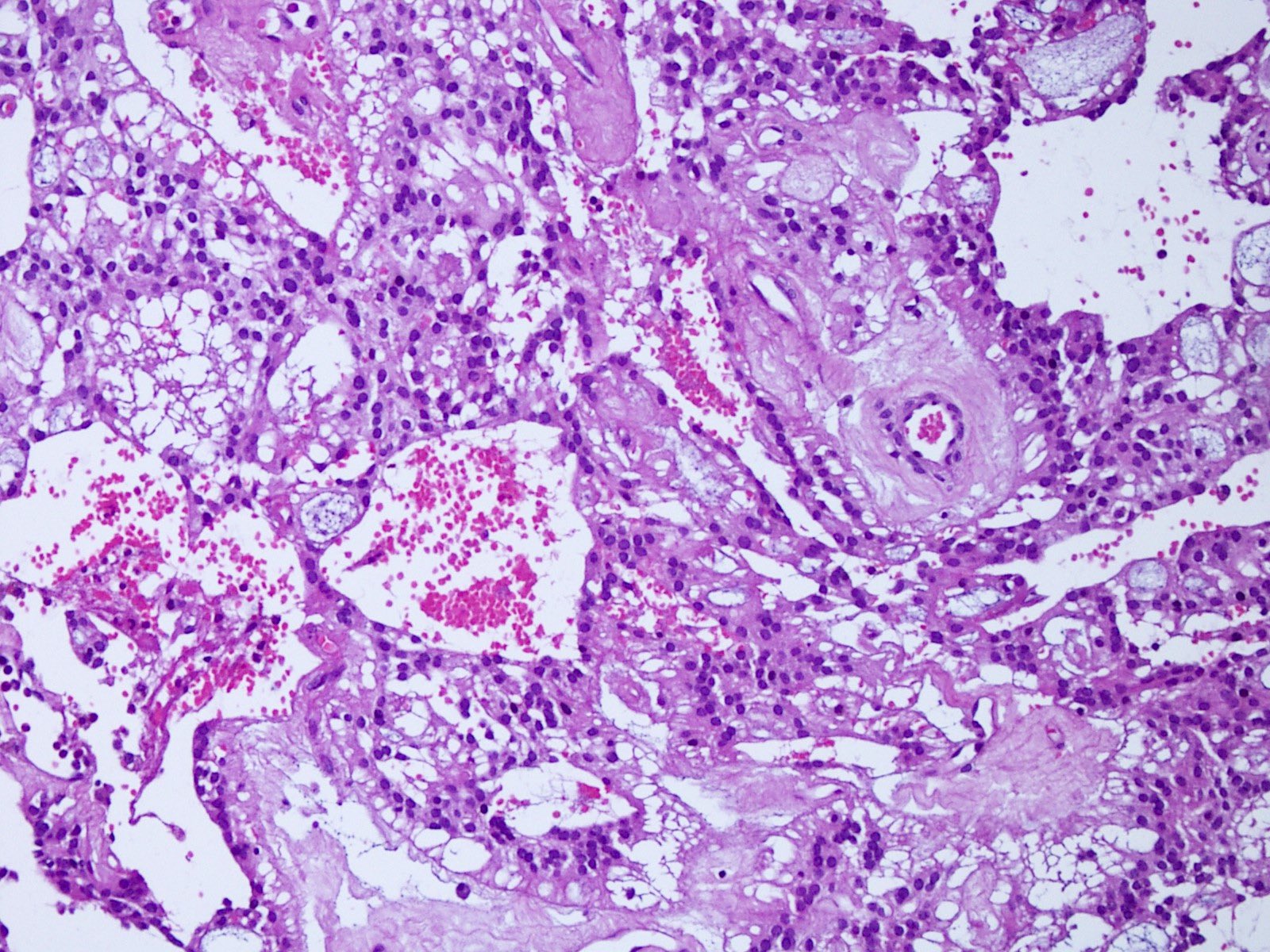
Microscopic (histologic) description
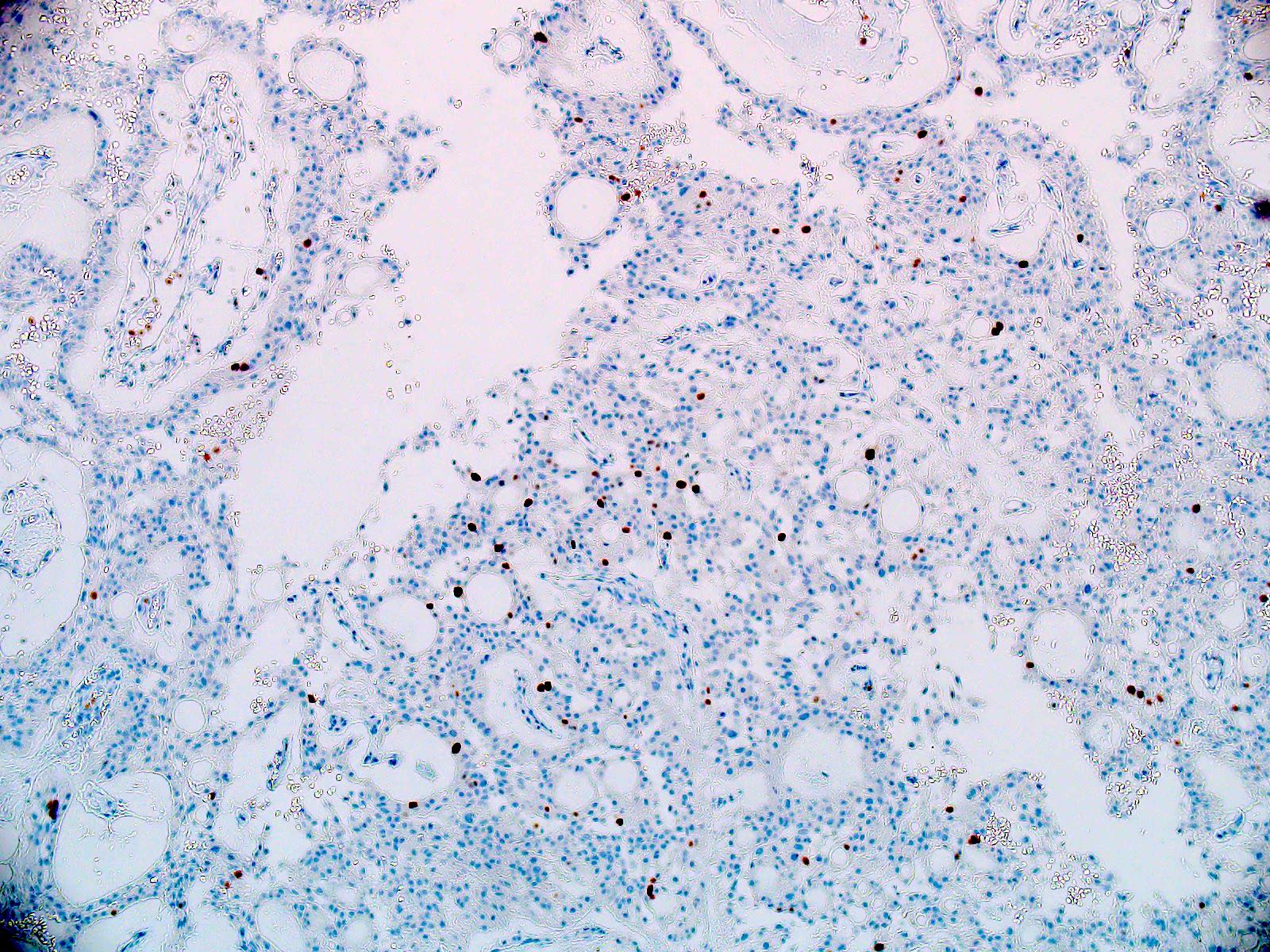
- Most common pattern is radial arrangement of cuboidal to epithelioid elongated glial tumor cells around hyalinized fibrovascular (central, often hyalinized blood vessels) cores in a papillary configuration
- Accumulation of basophilic myxoid material around blood vessels (myxoid stroma) and in microcysts
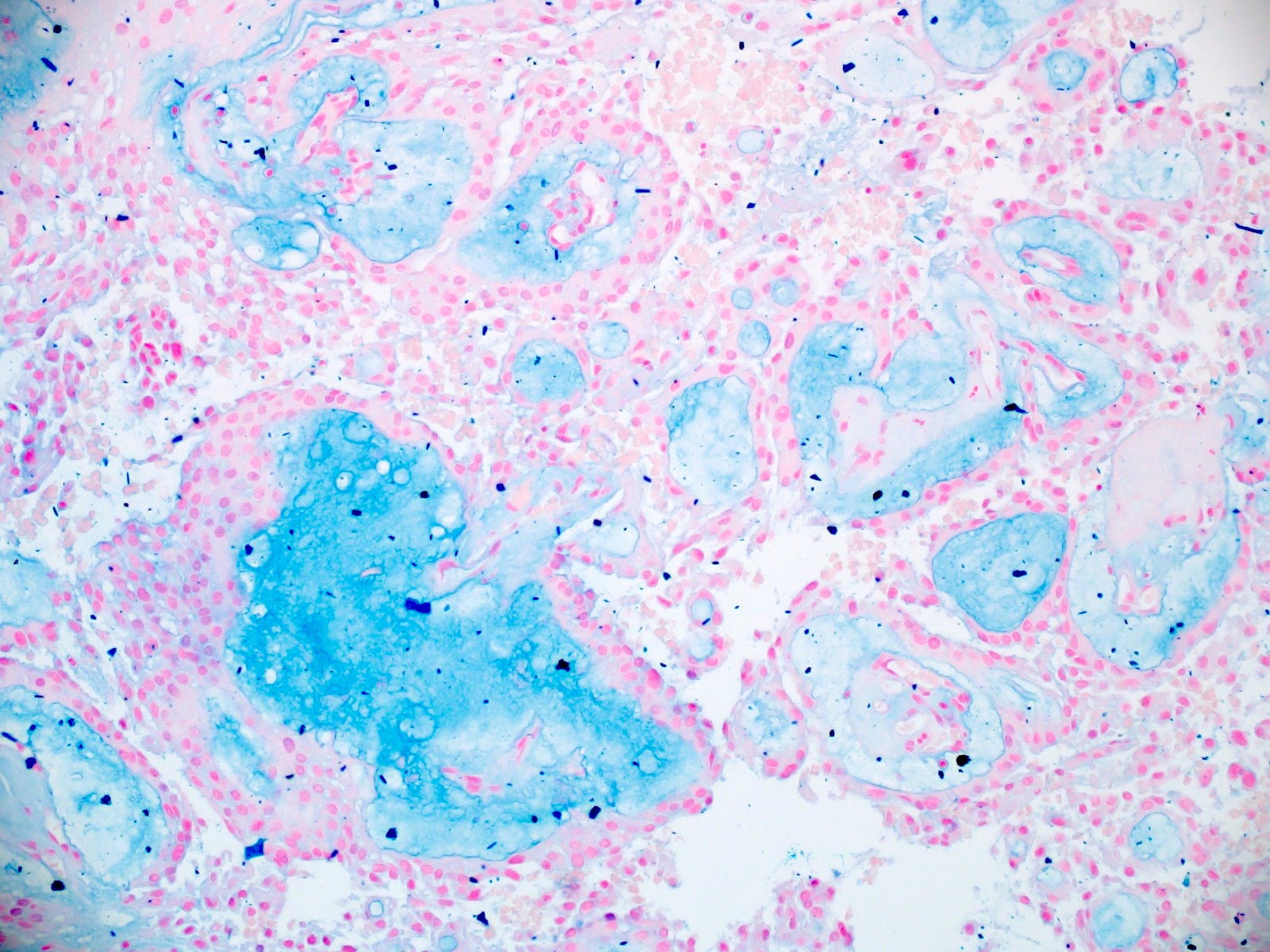
- Myxoid material is highlighted by PAS and Alcian blue positive staining
- In cases composed of confluent sheets of epithelioid cells with little or no papillary structures, PAS and Alcian blue positivity is useful in reaching a correct diagnosis
- Fascicular growth and spindle cells are common
- Pleomorphic tumor giant cells can be seen
- Occasionally tumor cells show distinctive eosinophilic balloons; these are PAS positive spherules that demonstrate spiculated reticulin staining (Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:1091)
- Uncommon examples reported as anaplastic myxopapillary ependymomas show hypercellularity and reduced mucin in association with at least 2 of the following features: ≥ 5 mitoses / 10 high power field, Ki67 labeling index ≥ 10%, microvascular proliferation, spontaneous necrosis (Brain Pathol 2019;29:75)
Microscopic (histologic) images
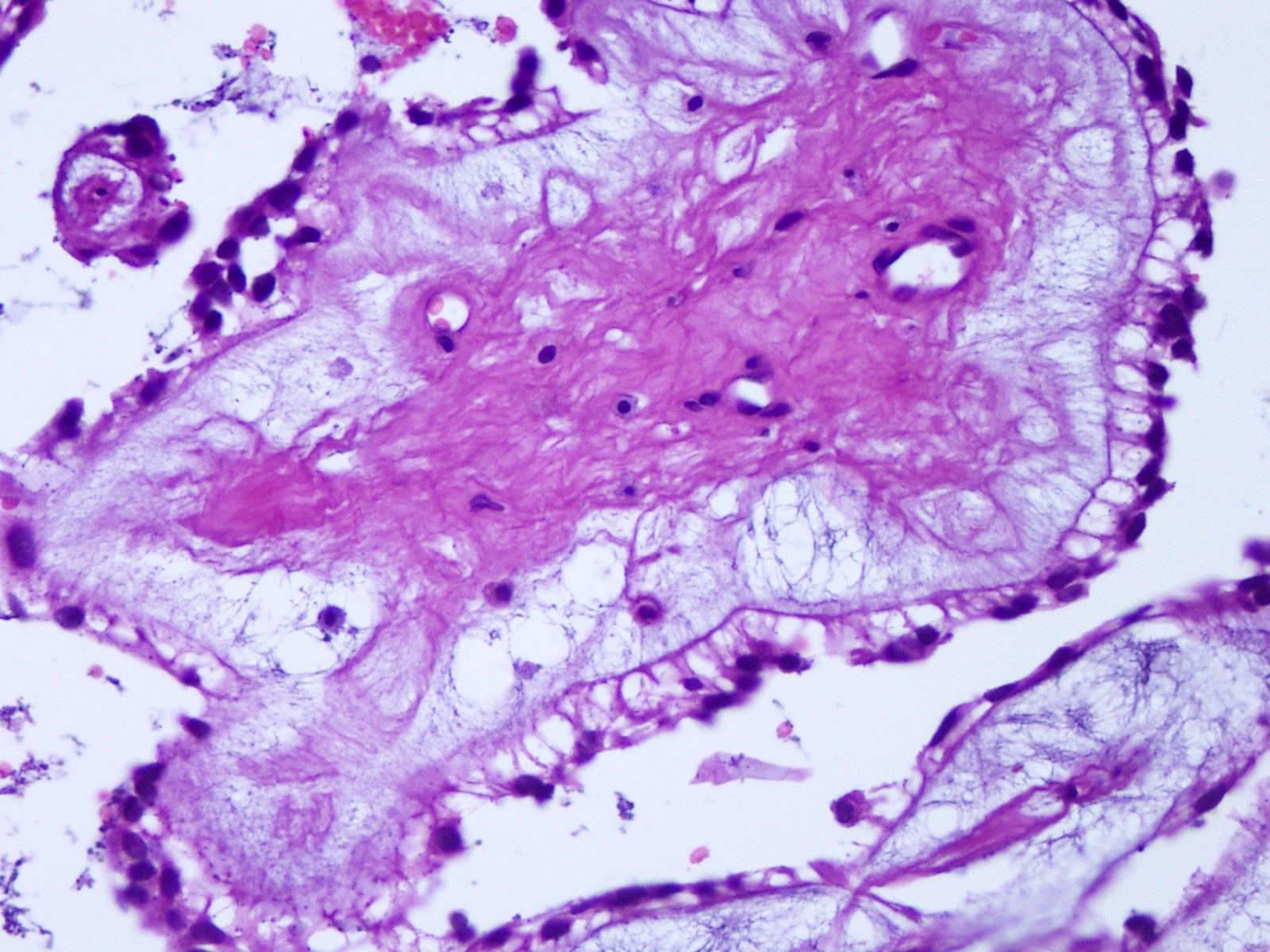
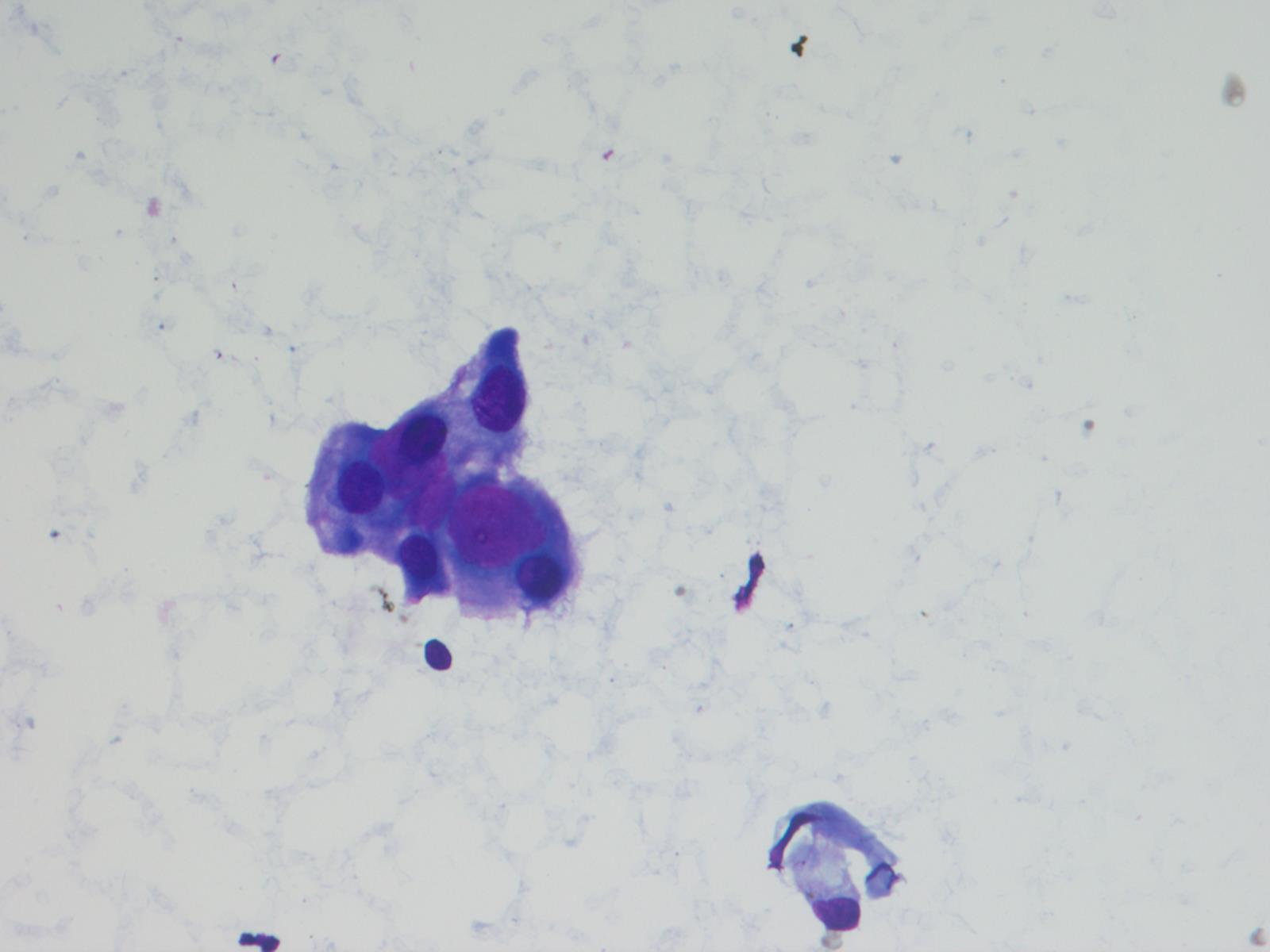
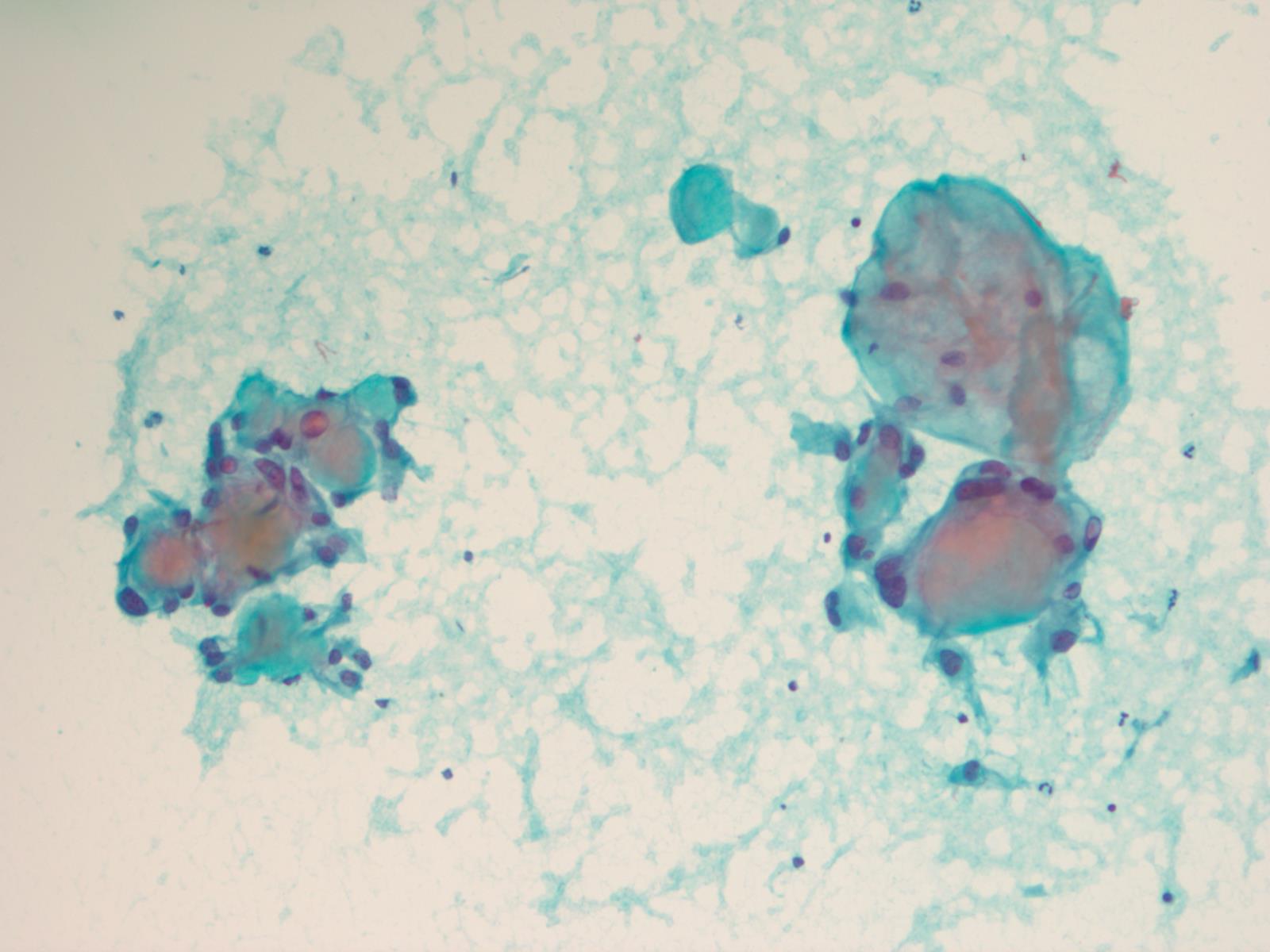
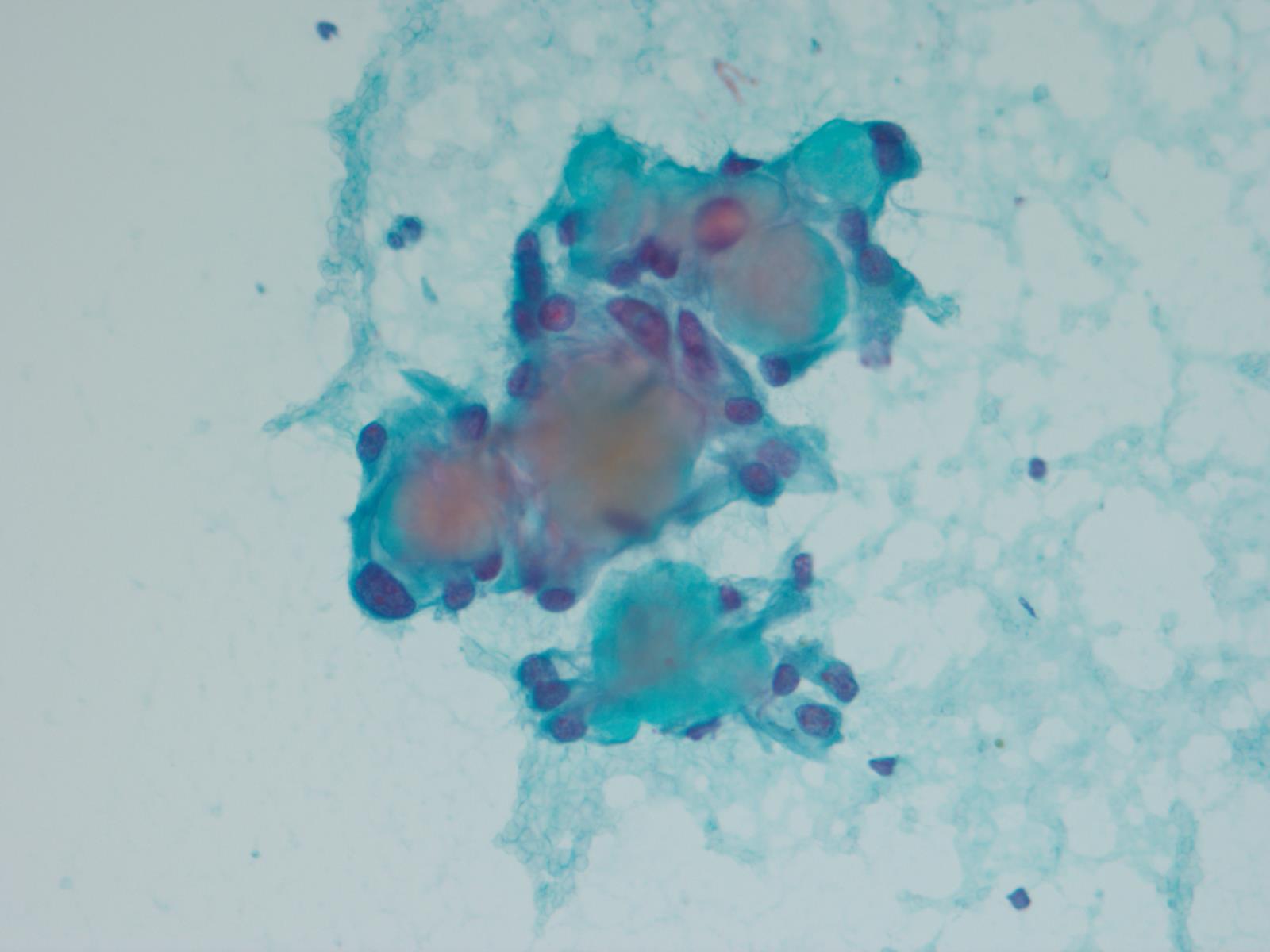
Cytology description
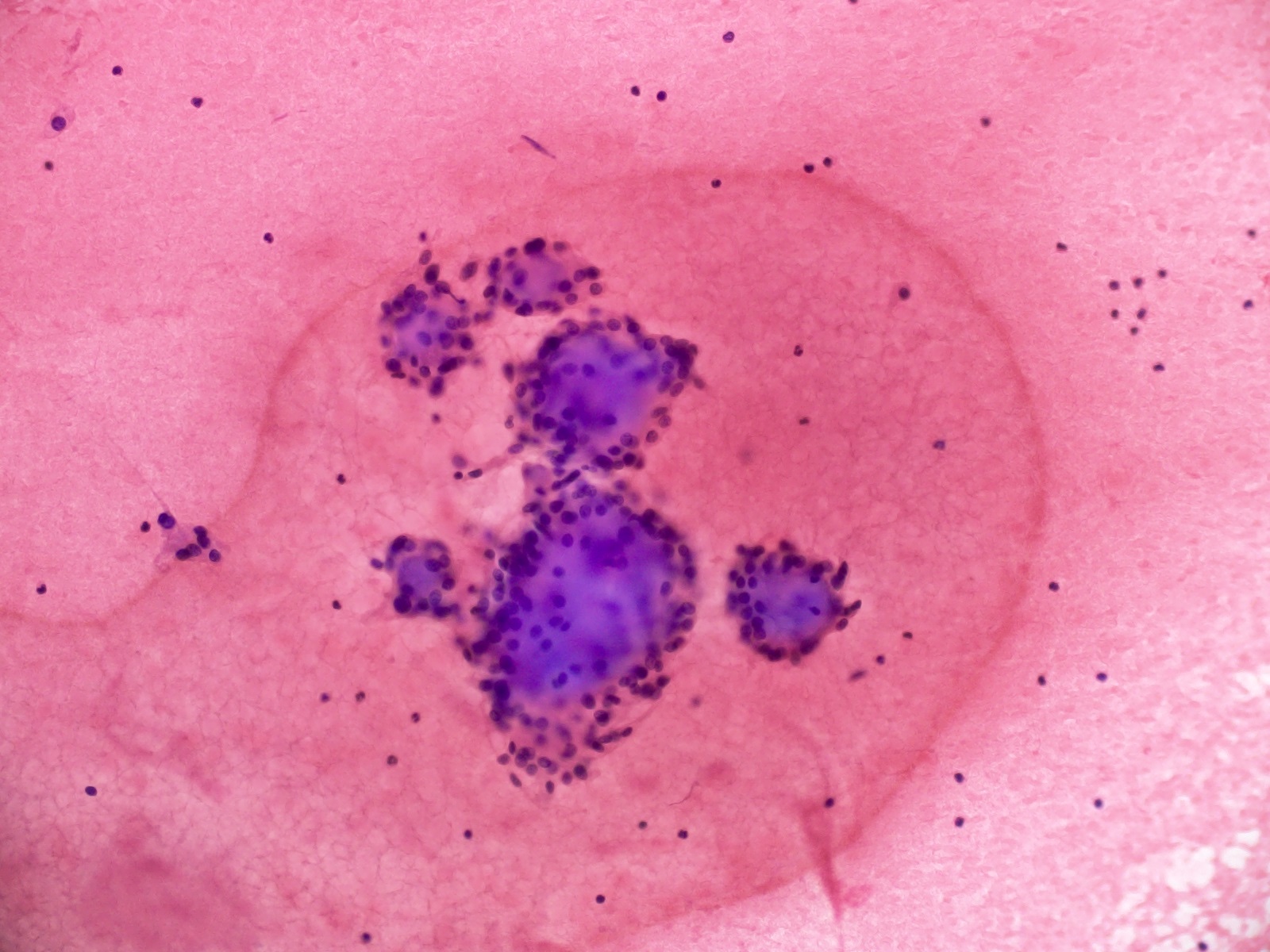
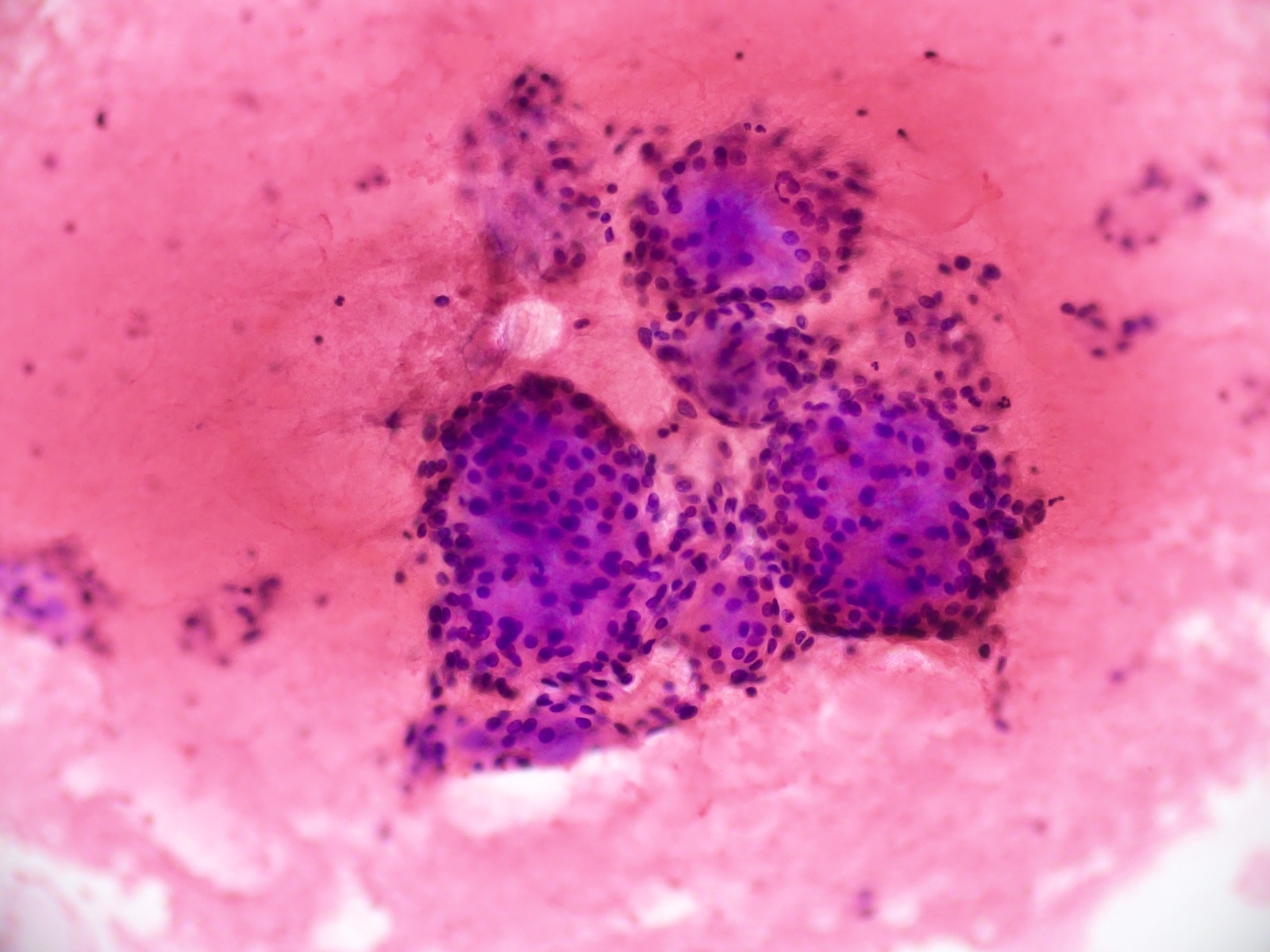
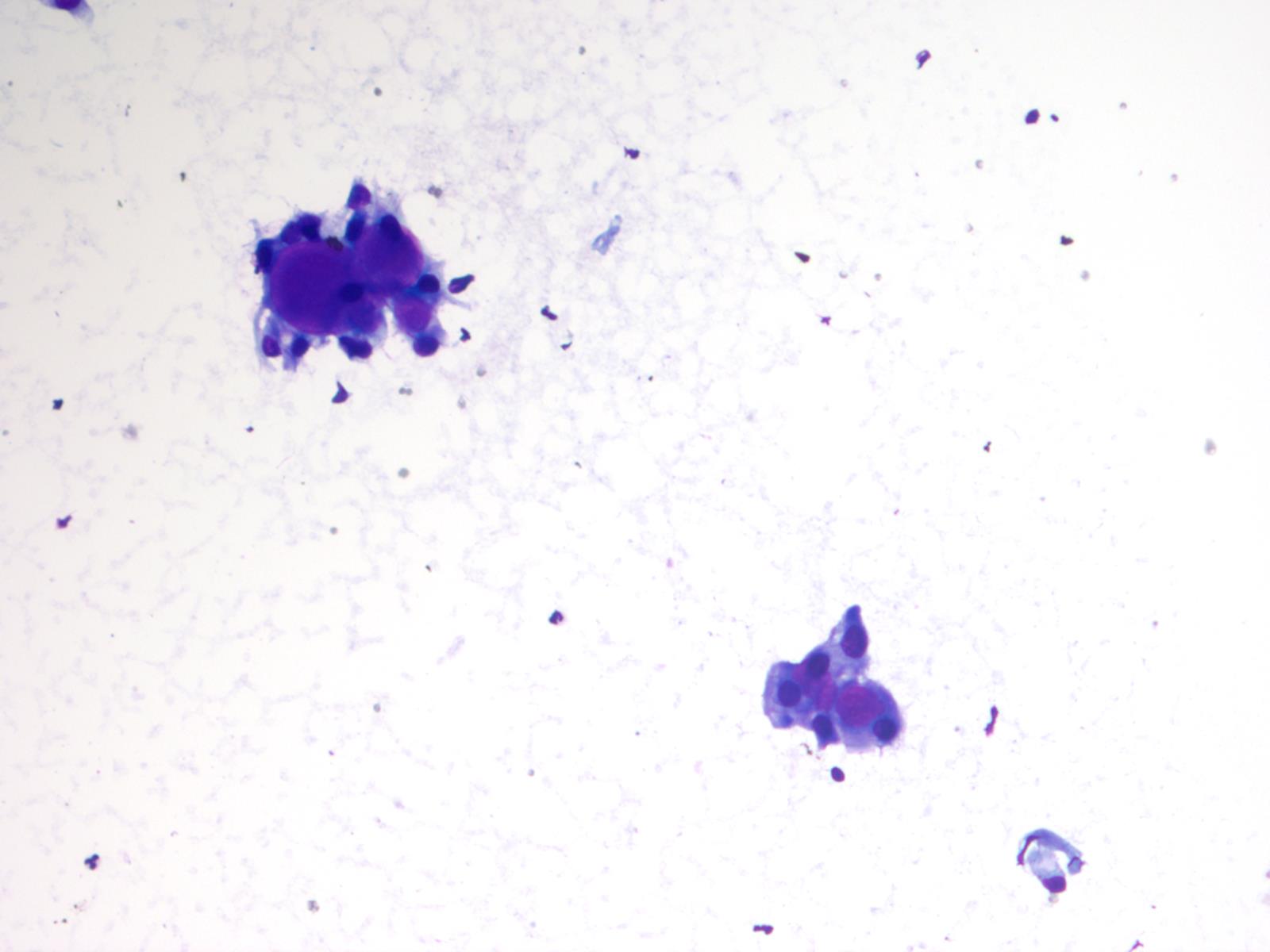
- Cytology usually recapitulates the histologic findings; myxoid matrix and cells show nuclear uniformity and process formation
- Epithelioid to spindle cells
- Arrangement of tumor cells around blood vessels forms papillary structures with perivascular myxoid change
- Tumor cells are arranged around myxoid microcysts
Cytology images
Positive stains
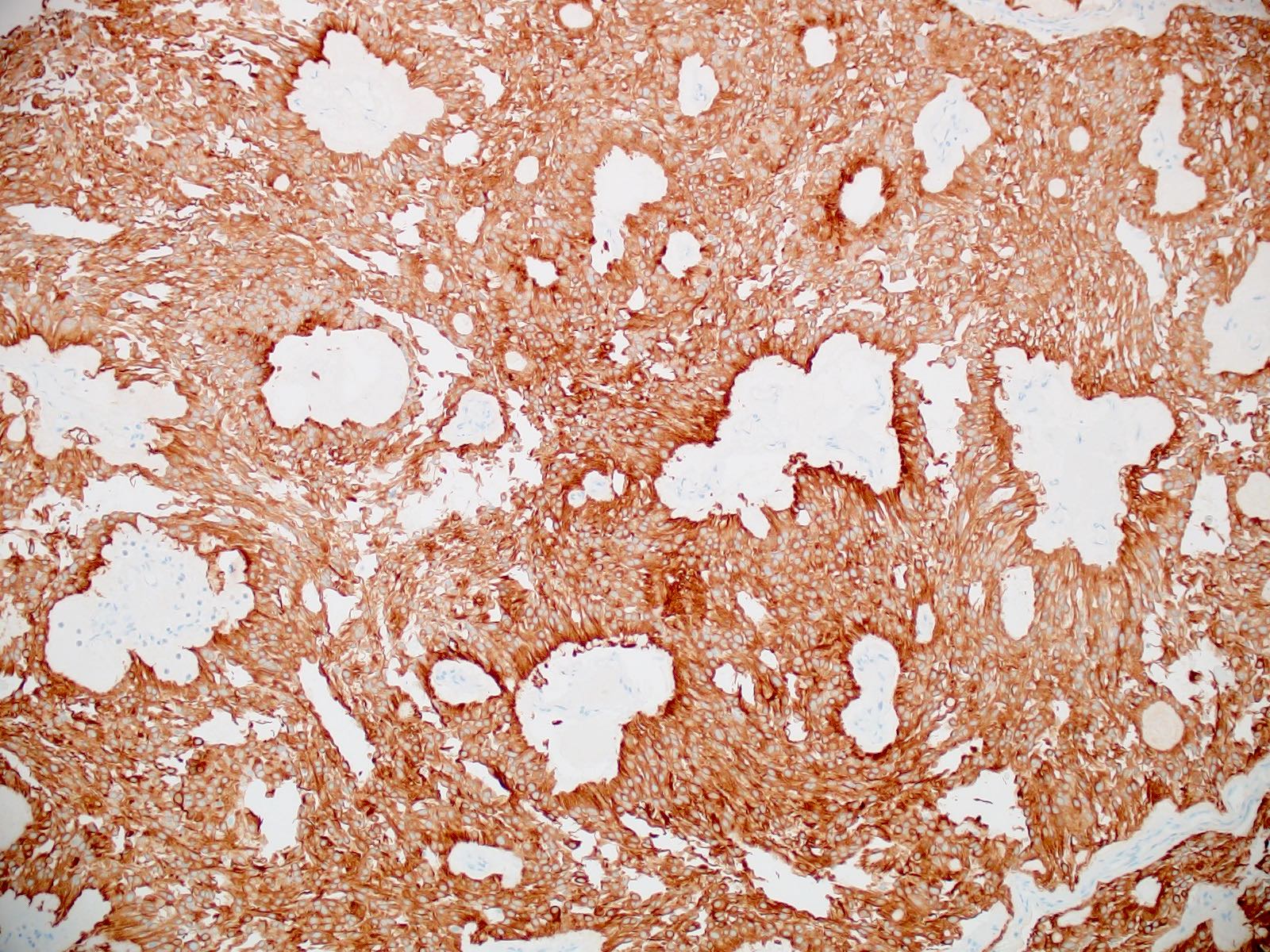
- Positive for GFAP (diffuse expression of GFAP distinguishes myxopapillary ependymomas from other tumors in the differential diagnosis, such as metastatic carcinomas, chordomas, paragangliomas, myxoid chondrosarcomas, schwannomas, etc.)
- Positivity for S100 is typical; CD99, vimentin and CD56 positivity is seen frequently
- Positivity for cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) is seen in the majority of cases (60%) (Neuropathology 2006;26:422)
- Often positive for keratin AE1 / AE3 cocktail (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2013;21:485, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:25)
Negative stains
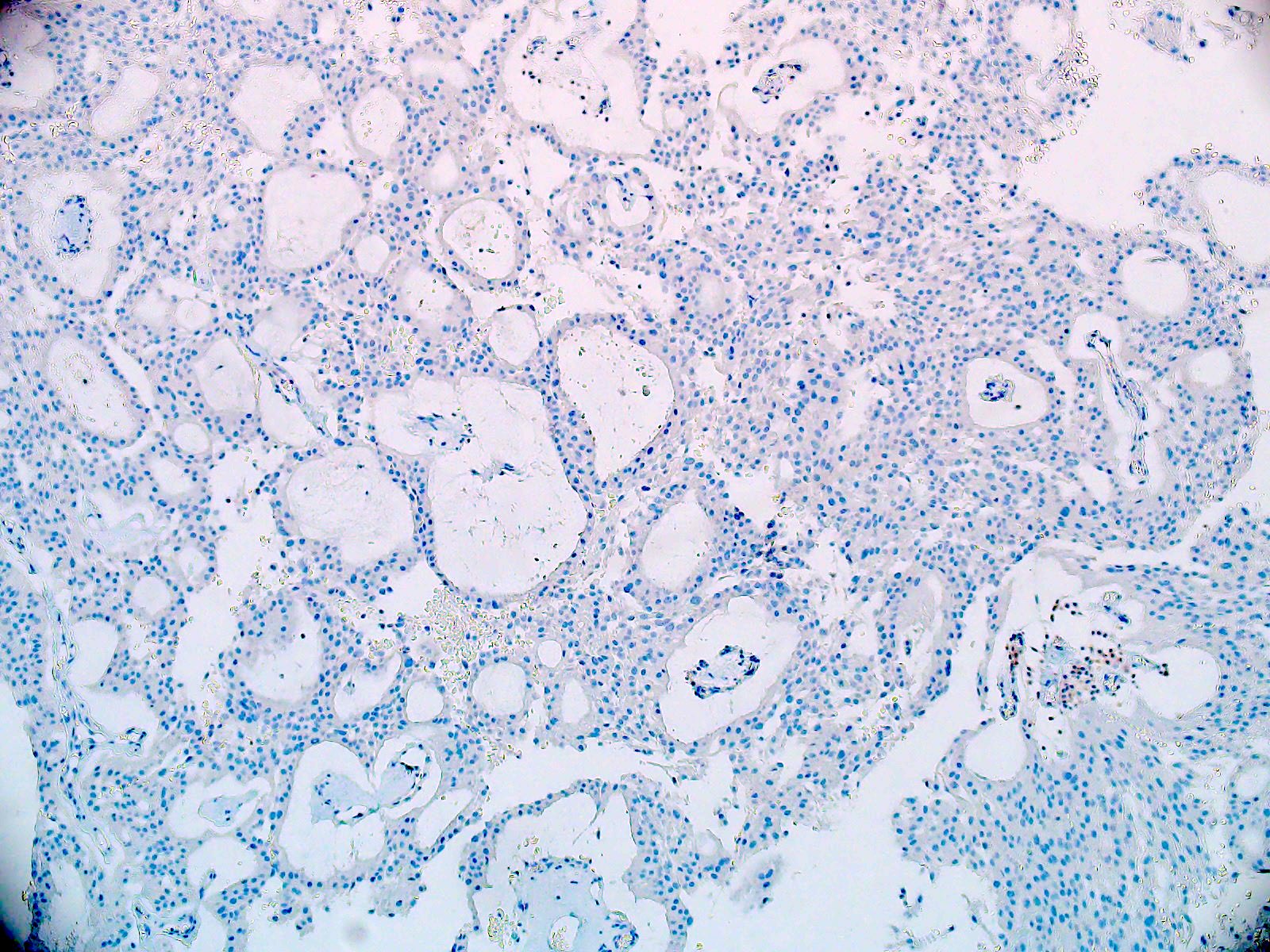
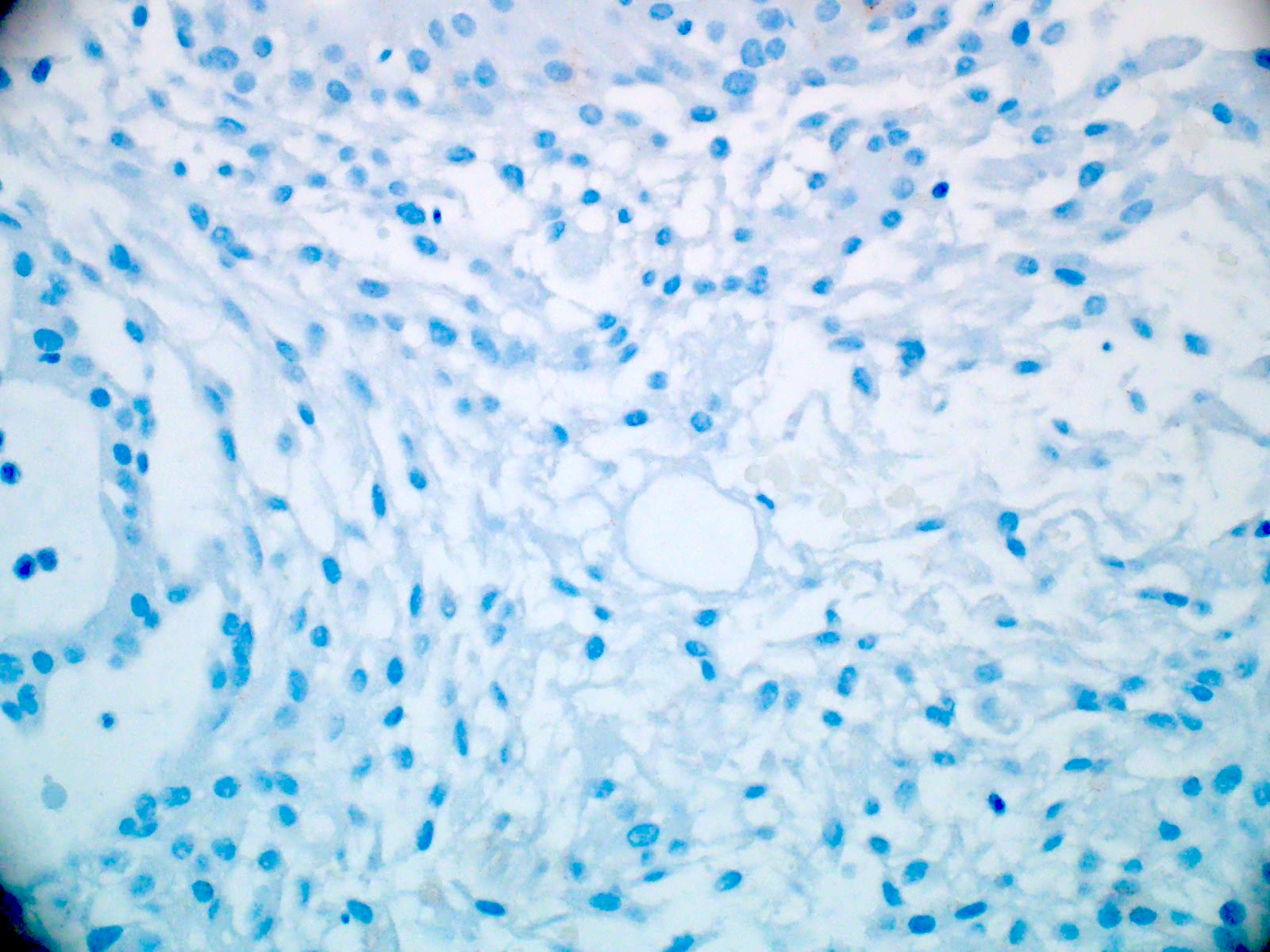
- Olig2 (tumor nuclei are negative), EMA (dot-like cytokeratin expression seen in other ependymoma variants is often absent)
- Negative for cytokeratin CAM 5.2, CK5/6, CK7 and CK20 (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2013;21:485, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:25)
Electron microscopy description
- Zipper-like intercellular junctional complexes, occasional cilia, surface and intraluminal microvilli are typical features of ependymal differentiation
- In addition, interdigitating cell processes and microtubular aggregates bond by endoplasmic reticulum
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Unique DNA methylation profile (however, histologically classic ependymomas may also cluster on DNA methylation with myxopapillary ependymomas)
- Prognostic significance of DNA methylation profile of myxopapillary ependymomas in context of uncharacteristic histological features (little myxoid change, pseudorosetting, spindle cells or tanycytic features) is not known
- Recurrent gain of chromosome 16 and losses of chromosome 10 have been noted (Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:305, Cancer Cell 2015;27:728, Neuro Oncol 2018;20:1616)
Sample pathology report
- Lower spinal mass, resection specimen:
- Myxopapillary ependymoma, CNS WHO grade 2
Differential diagnosis
- Schwannoma:
- Arises from nerve roots (myxopapillary ependymomas usually arise in the filum terminale)
- Usually, distinctive histological appearance from ependymoma; however, a paucicellular ependymoma with fascicular architecture may simulate schwannoma
- No Antoni A or B areas are present in ependymomas
- There are no nuclear or cytoplasmic inclusions in ependymomas
- Myxopapillary ependymomas have a delicate rather than densely collagenized capsule seen in schwannomas
- Schwannomas show pericellular reticulin and extensive immunostaining for laminin and type IV collagen
- Both tumors are S100 and GFAP positive
- Schwannomas show more intense staining for S100 compared with GFAP; the reverse is true for myxopapillary ependymomas
- Paraganglioma:
- More often arises from nerve roots than ependymomas
- Presence of zellballen pattern or ganglion cells confirms the diagnosis of paraganglioma
- Chromogranin positive (myxopapillary ependymomas are negative)
- Chordoma:
- Mostly extradural
- Mucinous matrix of myxopapillary ependymoma may simulate chordoma; however, mucin distribution in chordoma is diffuse and tends not to be confined in perivascular spaces
- Chordomas are strongly immunoreactive for low molecular weight keratins and EMA; negative for GFAP
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma:
- Myxoid chondrosarcoma:
- Myxoid or chondroid matrix with lacunar-like spaces supports the diagnosis of myxoid chondrosarcoma
- Myxoid chondrosarcoma cells would be negative for GFAP
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 22 year old man was diagnosed with a myxopapillary ependymoma in the filum terminale of the spinal cord. The diagnosis was confirmed by histological examination and immunohistochemical staining. What is the most important IHC stain expressed by this tumor that distinguishes it from the other lesions included in the differential diagnosis?
- CD99
- GFAP
- Keratin
- Olig2
- S100
Practice answer #1
B. GFAP. Diffuse immunoreactivity for GFAP distinguishes myxopapillary ependymoma from metastatic carcinoma, paraganglioma, schwannoma, chordoma and myxoid chondrosarcoma (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2013;21:485).
Comment Here
Reference: Myxopapillary ependymoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myxopapillary ependymoma
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
B. Grade 2. The Consortium to Inform Molecular and Practical Approaches to CNS Tumor Taxonomy update 6 recommends that spinal myxopapillary ependymomas be diagnosed based on histological criteria but notes that these tumors have a clinical outcome similar to classic ependymoma and should be assigned WHO grade 2 rather than grade 1 assigned in 2016 WHO CNS (Brain Pathol 2020;30:844).
Comment Here
Reference: Myxopapillary ependymoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myxopapillary ependymoma