Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Virology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Screening | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Viruet-Guzmán L, Vyas M. Hepatitis B virus (HBV). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverhepb.html. Accessed September 10th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Hepatitis B is a vaccine preventable disease that causes acute and chronic liver inflammation and is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV)
- Hepatitis B has several serological markers
- HBsAg and anti-HBs
- HBeAg and anti-HBe
- Anti-HBc IgM and IgG
Essential features
- Hepatitis B is a virus induced disease that causes acute hepatitis, chronic hepatitis and is associated with an increase in risk for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Hepatitis B is caused by HBV, a partly double stranded DNA virus
- Constitutes a major global health problem that can be prevented by vaccination
- Diagnosis is based on the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and IgM hepatitis B core antibody; HBV DNA is present in the initial phase of the infection (MMWR Recomm Rep 2023;72:1)
ICD coding
- ICD-10
- ICD-11
Epidemiology
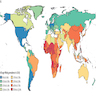
- HBV infection is a major public health problem in most countries with ~2 billion people worldwide showing exposure to the virus and nearly 300 million people carrying an HBV chronic infection (J Clin Virol 2005;34:S1)
- According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), HBV caused 257,000 chronic infections and 887,000 deaths in 2015
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates there were 2,157 new cases of acute hepatitis B and 5 new cases reported of chronic hepatitis B per 100,000 people during 2020 in the United States
- Virus induced hepatitis is one of the most common causes of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer (J Hepatol 2013;58:593)
Sites
- Liver
- Acute hepatitis
- Chronic hepatitis
- Asymptomatic to chronic liver disease stigmata (jaundice, splenomegaly, ascites, peripheral edema, encephalopathy)
- Extrahepatic manifestations (complications of chronic hepatitis B)
- Polyarteritis nodosa (Medicine (Baltimore) 1995;74:238)
- Glomerular disease (N Engl J Med 1979;300:814)
Pathophysiology
- Immune mediated and direct cytopathic liver injury
- Innate and adaptive immune responses contribute to immune control of HBV infection (World J Gastroenterol 2022;28:881, Front Immunol 2022;13:970938, Annu Rev Pathol 2006;1:23)
- Host's immune response to the virus mediates the hepatocellular damage observed in acute and chronic infections (Annu Rev Immunol 1995;13:29, Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023;13:1206720)
- Cytotoxic T cell mediated lysis of infected hepatocytes is thought to cause HBV related liver disease (Med Microbiol Immunol 2015;204:11)
- Viral variants
- Mutations in HBV have been identified and can potentially modulate the severity of the liver disease, affecting the level of HBV replication or the expression of immunogenic epitopes; for example, lack of detectable HBsAg in the serum has been correlated to deletions of the pre-S region, allowing viral persistence by eliminating human leukocyte antigen (HLA) restricted B cell and T cell epitopes (World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:126)
- Development of chronic infection
- Patients with weak immune systems or who are immunocompromised have an increased risk of progressing to chronic HBV infection (J Hepatol 2003;39:115)
Virology
- HBV is a partly double stranded DNA virus belonging to the family Hepadnaviridae (World J Gastroenterol 2009;15:5761)
- Infectious virion (the envelope of the Dane particle) is made of a cell originated membrane containing HBsAg
- Core contains the viral DNA genome, viral polymerase / reverse transcriptase (originating from infected cells), hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)
Diagrams / tables
Images hosted on other servers:
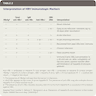
Immunohistochemical expression of HBsAg / HBcAg in various phases of hepatitis B infection (Hepatology 2009;49:S61, Liver Transpl 2006;12:S50)
| HBsAg IHC expression | HBcAg IHC expression | |
| Acute hepatitis | Negative | Nuclear (rare) |
| Chronic hepatitis B | Cytoplasmic / membranous | Nuclear / cytoplasmic |
| Active viral replication | Diffuse membranous | Nuclear |
| Immunotolerant (or immunosuppressed) | Membranous | Diffuse nuclear |
| Inactive carrier | Clusters of positive cells | Negative |
Clinical features
- Acute hepatitis B infection
- Variable course ranging from asymptomatic to fulminant hepatitis
- 70% of patients have subclinical course / 30% develop icteric hepatitis (J Infect Dis 1985;151:599)
- Variable course ranging from asymptomatic to fulminant hepatitis
- Chronic hepatitis B infection
- Asymptomatic, fatigue, hepatic failure, cirrhosis, decompensated cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, extrahepatic manifestations (Hepatology 1988;8:493, Gastroenterology 1992;103:1630, Hepatology 1995;21:77)
Screening
- Presence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs) and total hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) (MMWR Recomm Rep 2023;72:1)
Diagnosis
- Acute HBV infection diagnosis
- HBsAg and IgM to HBcAg
- Markers of HBV replication: HBeAg and HBV DNA are present (MMWR Recomm Rep 2023;72:1)
- Chronic hepatitis B is defined as the persistence of HBsAg for > 6 months
- HBcAg can be detected throughout the course of the infection and stays in the blood after recovery
- Detection of anti-HBc indicates current or past infection (Hepatology 2018;67:1560)
- Other tests for HBV replication, HBeAg and alanine transaminase (ALT) should be performed to determine if the patient should start antiviral therapy
Laboratory
- See Diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- Per the CDC, the lifetime risk for hepatocellular carcinoma is 40% for men and 15% for women
- Risk of chronic infection is related to age at infection; ~90% of infants with hepatitis B will develop chronic infection, whereas < 5% of immunocompetent adult patients with acute hepatitis B progress to chronic infection (Hepatology 1989;9:452, CDC: Hepatitis B [Accessed 5 February 2024])
- Chronic HBV infection has been associated with increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 2012;100:1)
- CDC reported that 25% of chronic hepatitis B infections progress to liver cancer
- Prognosis is worse in HBV infected patients from endemic areas and patients with chronic hepatitis B (Hepatology 1995;21:77)
- Reduction in inflammation (biopsy determined) is associated with less fibrosis progression (Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1388)
Case reports
- 25 year old woman with end stage renal disease of unknown cause received a living donor kidney transplant 6 years prior (Exp Clin Transplant 2019;17:408)
- 41 year old previously healthy woman presented with asthenia, jaundice and upper abdominal pain at palpation (BMJ Case Rep 2017;2017:bcr2017221763)
- 63 year old Vietnamese woman with IgG kappa myeloma and positive for anti-HBcAb (Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:1271)
Treatment
- Treatment for most patients with acute hepatitis B is mainly supportive; for patients who require treatment, tenofovir or entecavir are preferred as a monotherapy (Hepatology 2016;63:261)
- Therapeutic agents approved for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis B in the U.S. are peginterferon 2a, nucleos(t)ide analogs, lamivudine, telbivudine, entecavir and adefovir (Hepatology 2016;63:261)
- HBeAg positive children (ages 2 - 18) with elevated ALT and measurable HBV DNA levels should be in antiviral therapy to achieve sustained HBeAg seroconversion (Hepatology 2016;63:261)
- Pregnant women with HBV DNA > 2 x 105 IU/mL treatment should be based on recommendations for nonpregnant women (Hepatology 2016;63:261)
- Combination of antiviral therapy targeting multiple steps in the HBV lifecycle can be used to restore immune response to HBV (J Clin Med 2020;9:3187)
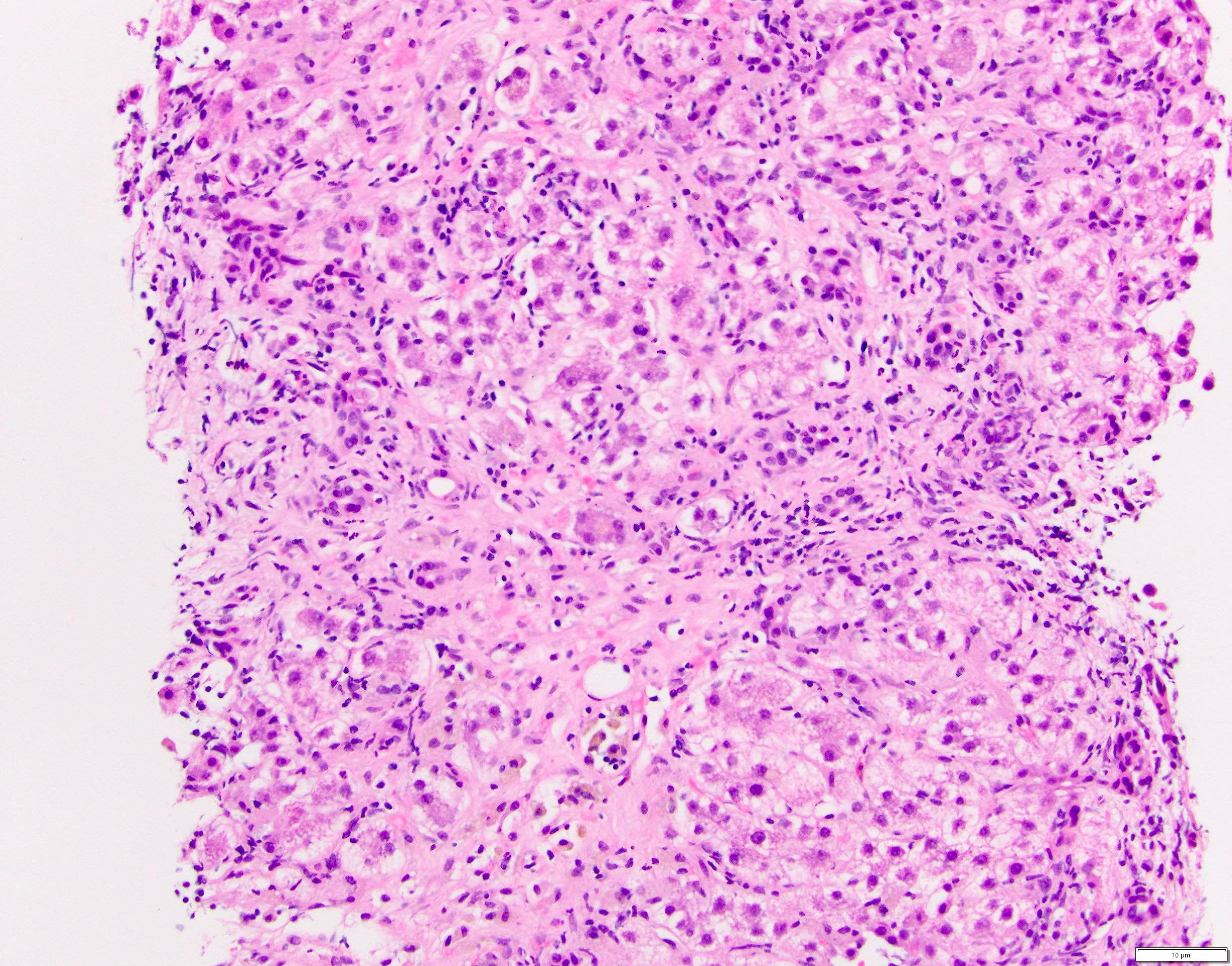
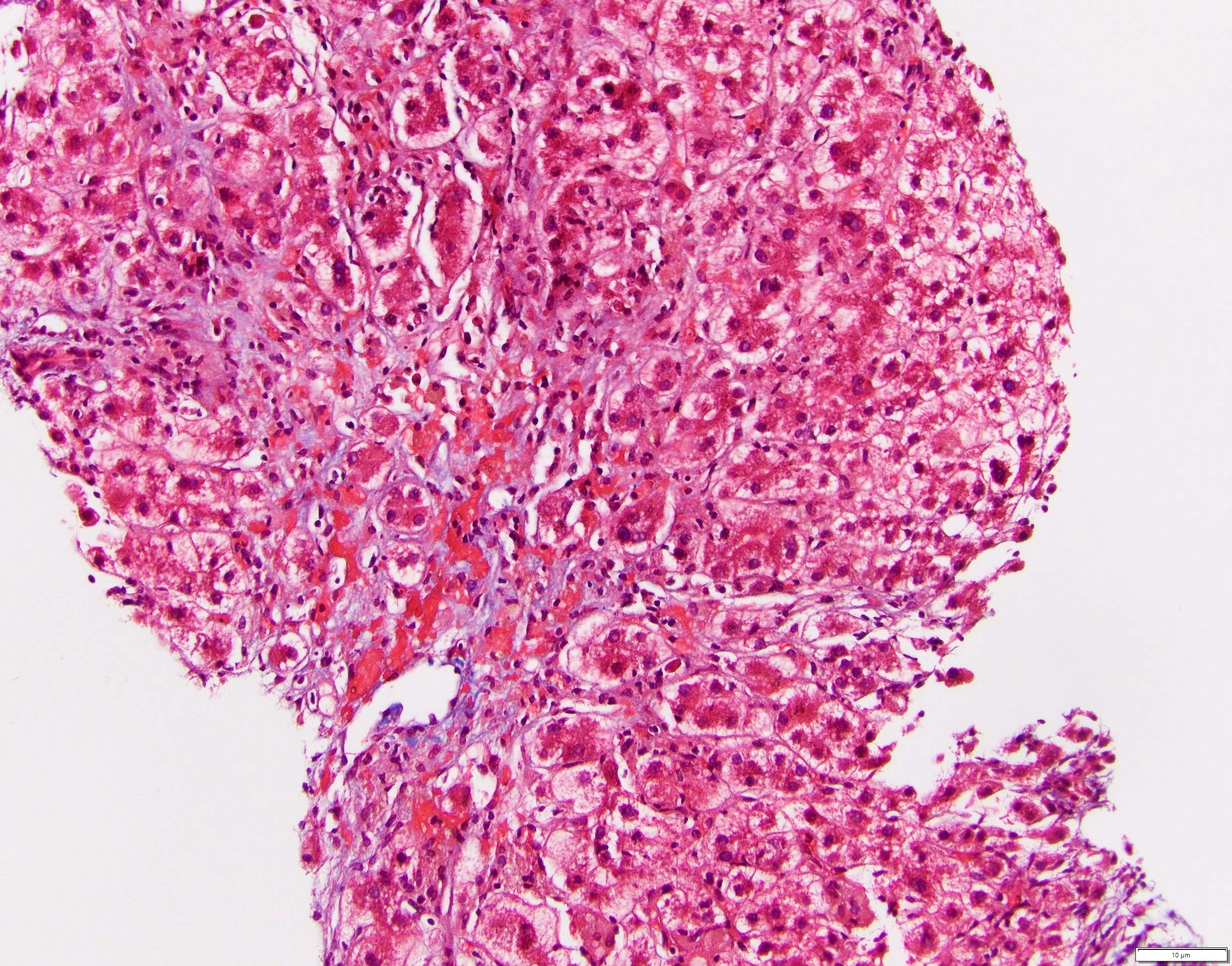
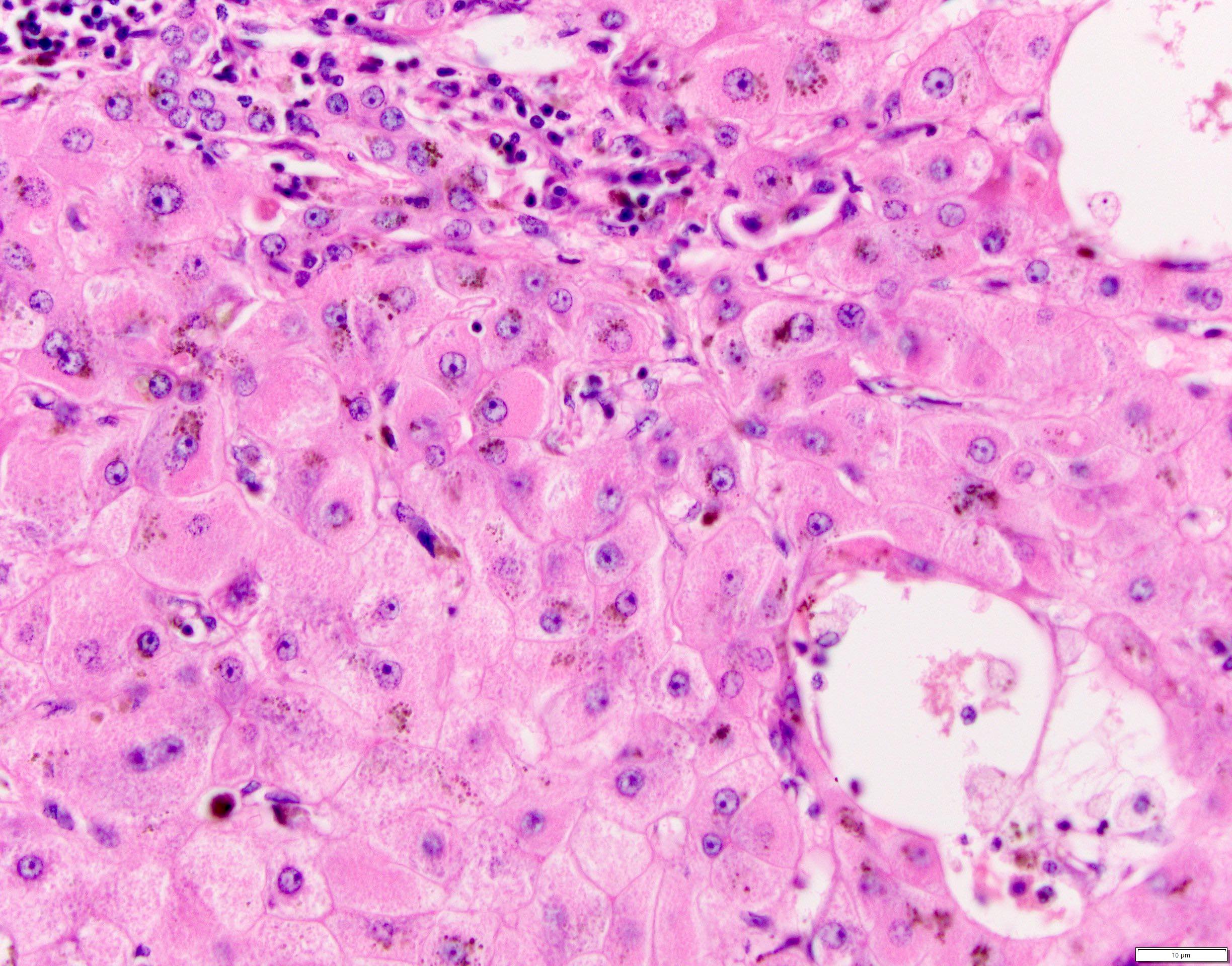
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Acute phase of hepatitis B
- Inflammatory cell infiltration
- Predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate within the parenchyma and portal tracts (usually perivenular distribution)
- Involvement of portal inflammation is variable
- Plasma cells may also be prominent and few neutrophils and eosinophils may be present (Liver 1985;5:84)
- Compared to acute hepatitis C, acute hepatitis B has periportal inflammation (J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001;16:209)
- Occult infection and mild portal inflammation, focal necrosis, apoptosis and fibrosis may persist following clinical recovery of acute hepatitis B (Hepatology 2003;37:1172)
- Predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate within the parenchyma and portal tracts (usually perivenular distribution)
- Hepatocellular damage
- Hepatocyte nuclei show prominent nucleoli and a moderate degree of pleomorphism; may show multiple nucleoli
- Changes ranging from a minor degree of cell swelling to cell death, most severe in perivenular areas
- Ballooning degeneration is seen as more severe degrees of cell swelling
- Acidophil bodies or Councilman bodies
- Eosinophilic globule or fragments of apoptotic hepatocytes where deposits of HBsAg are found (Leber Magen Darm 1982;12:146)
- Granular or vacuolated cytoplasm might be present
- Other features: cholestasis, Kupffer cell activation, endotheliitis, bile duct damage, ductular reaction and mild hepatocellular siderosis (Am J Clin Pathol 1984;81:162)
- Inflammatory cell infiltration
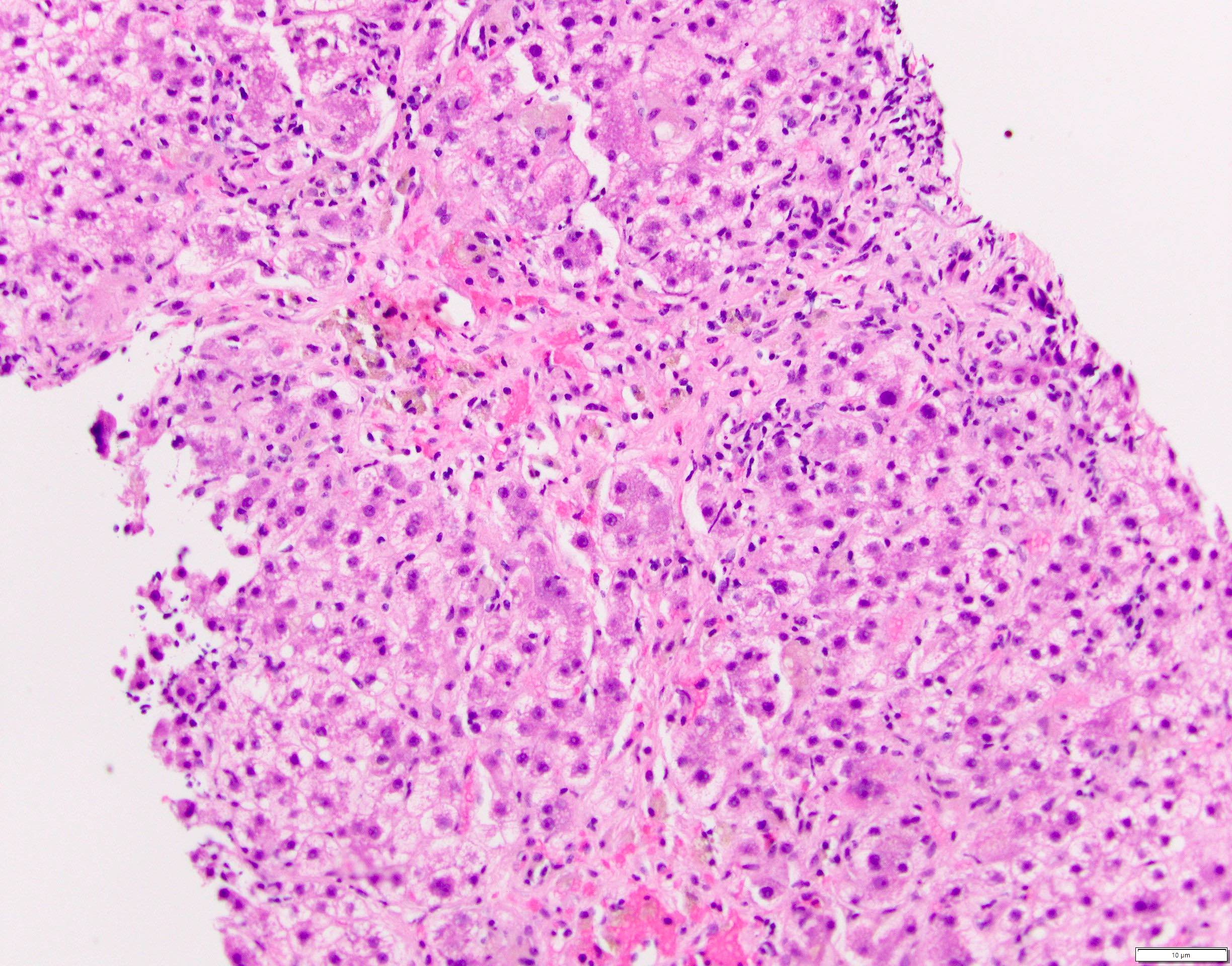
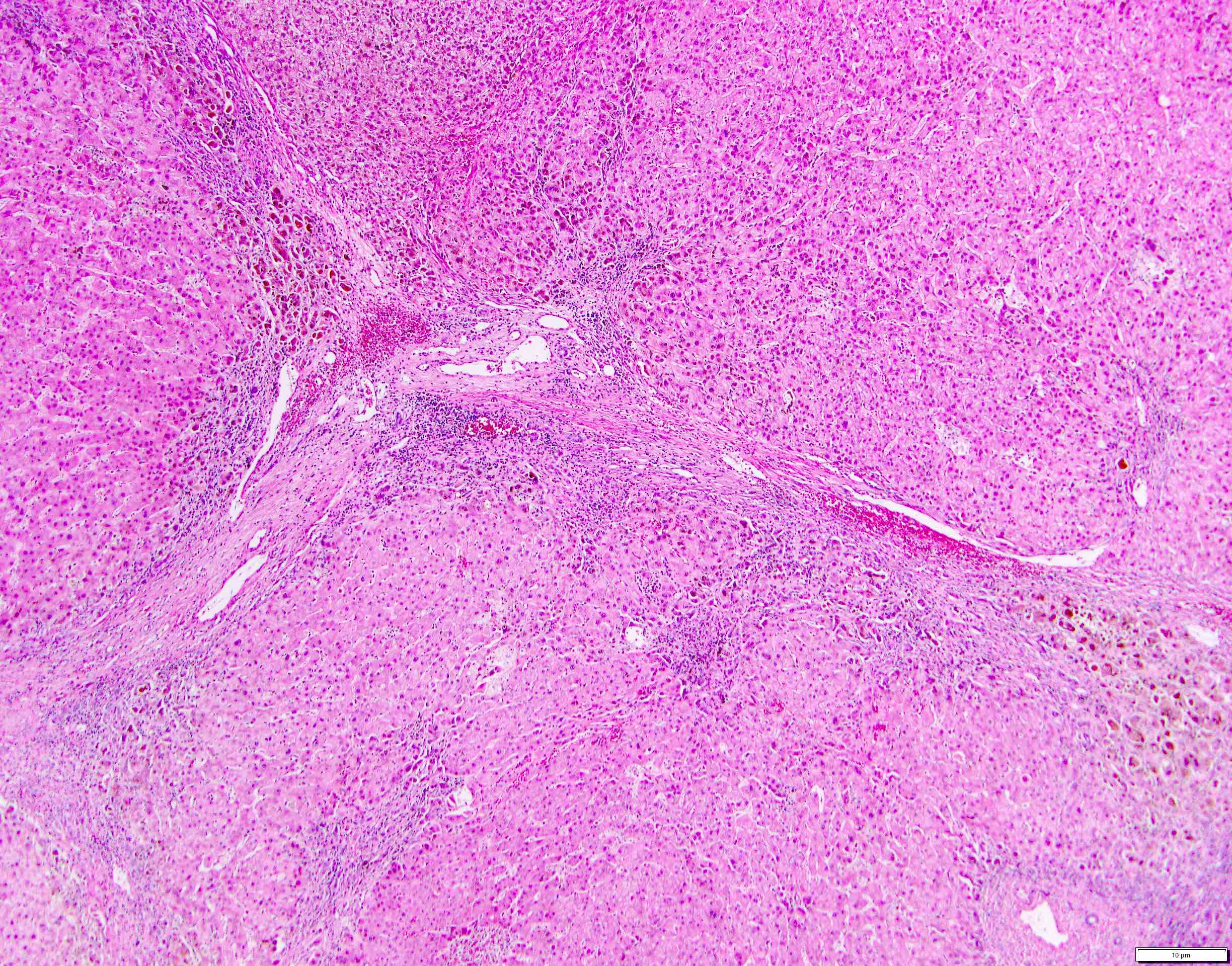
- Chronic hepatitis B
- Inflammatory cell infiltration
- Mononuclear infiltration of portal tracts
- Both interface hepatitis and lobular hepatitis can be seen
- Mononuclear infiltration of portal tracts
- Hepatocellular changes
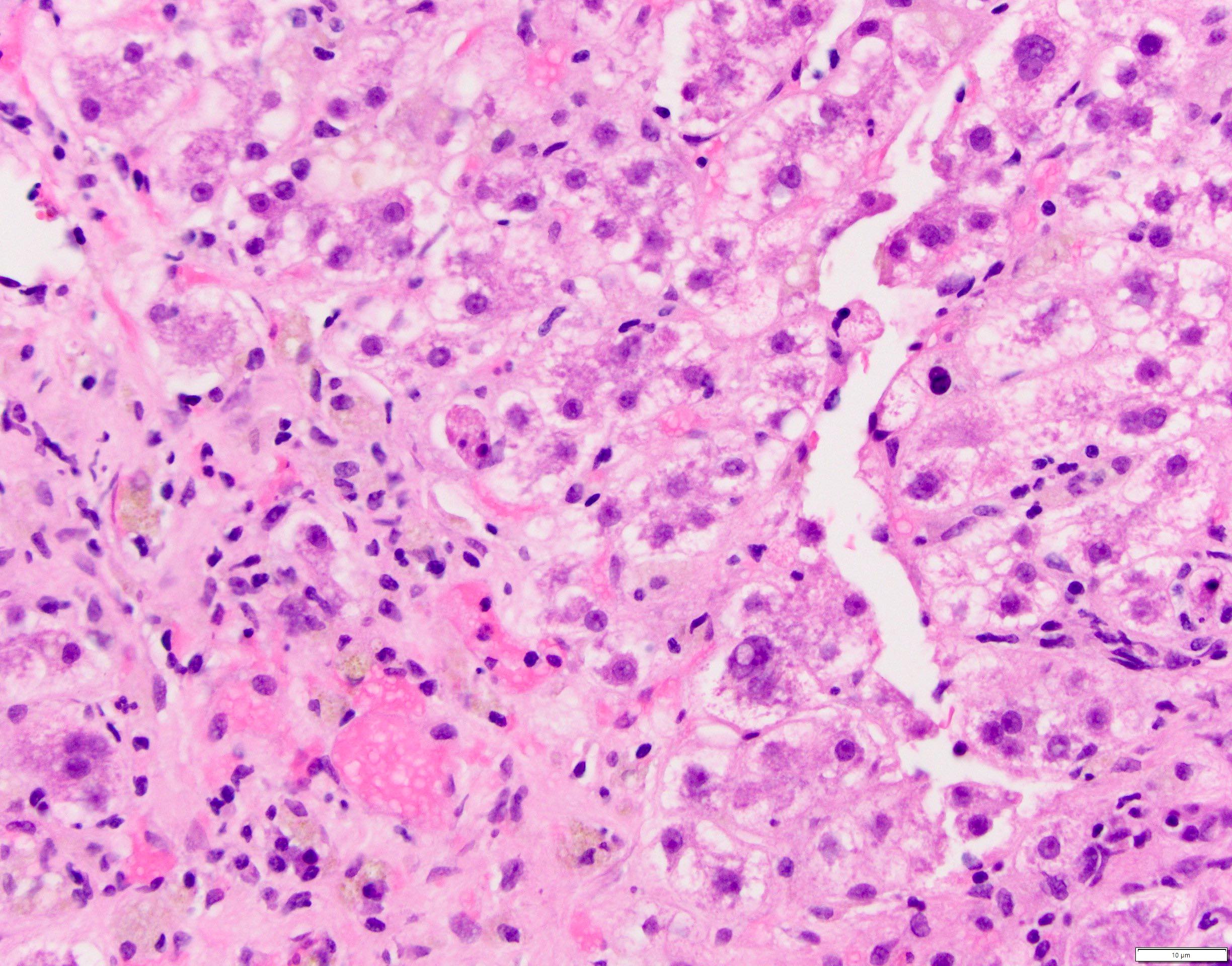
- Hallmark of chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- Ground glass appearance (of the central part of the cytoplasm) of hepatocytes when HBsAg is elevated or in active viral replication (Viruses 2019;11:386)
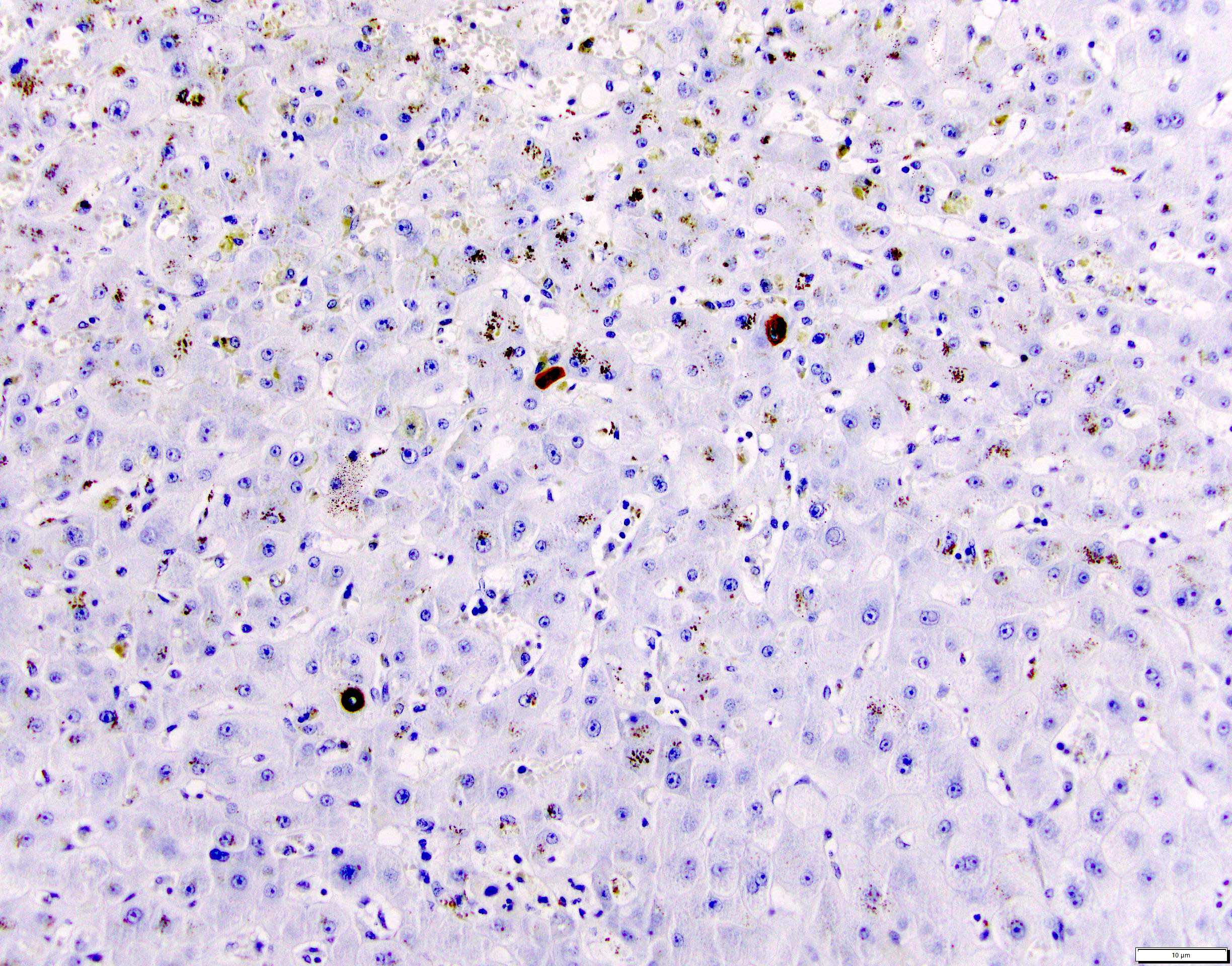
- Active viral replication can also be demonstrated by hepatocyte nuclei or cytoplasmic stain of HBcAg
- Nuclei of hepatocytes may contain large amounts of core protein and have a pale, homogenous appearance on H&E sections, described as sanded
- Marked variation in size and appearance of hepatocyte nuclei and close contact between hepatocytes and lymphocytes might be seen
- Enlargement of portal tracts due to infiltration of mononuclear cells (J R Soc Med 1985;78:391)
- Lobular spotty necrosis (J R Soc Med 1985;78:391)
- Hepatocyte death, atrophy, regeneration and fibrosis
- Hallmark of chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- Inflammatory cell infiltration
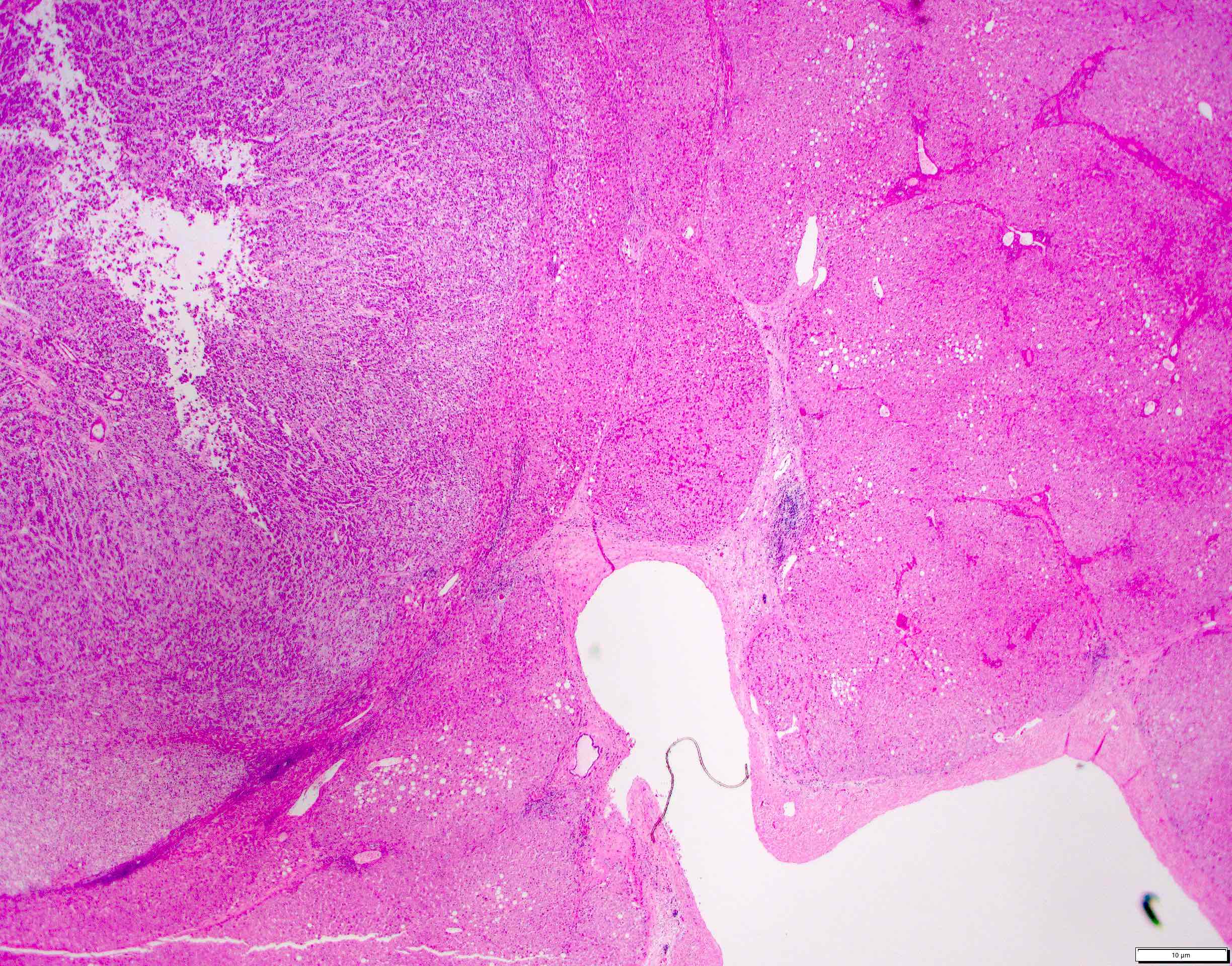
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
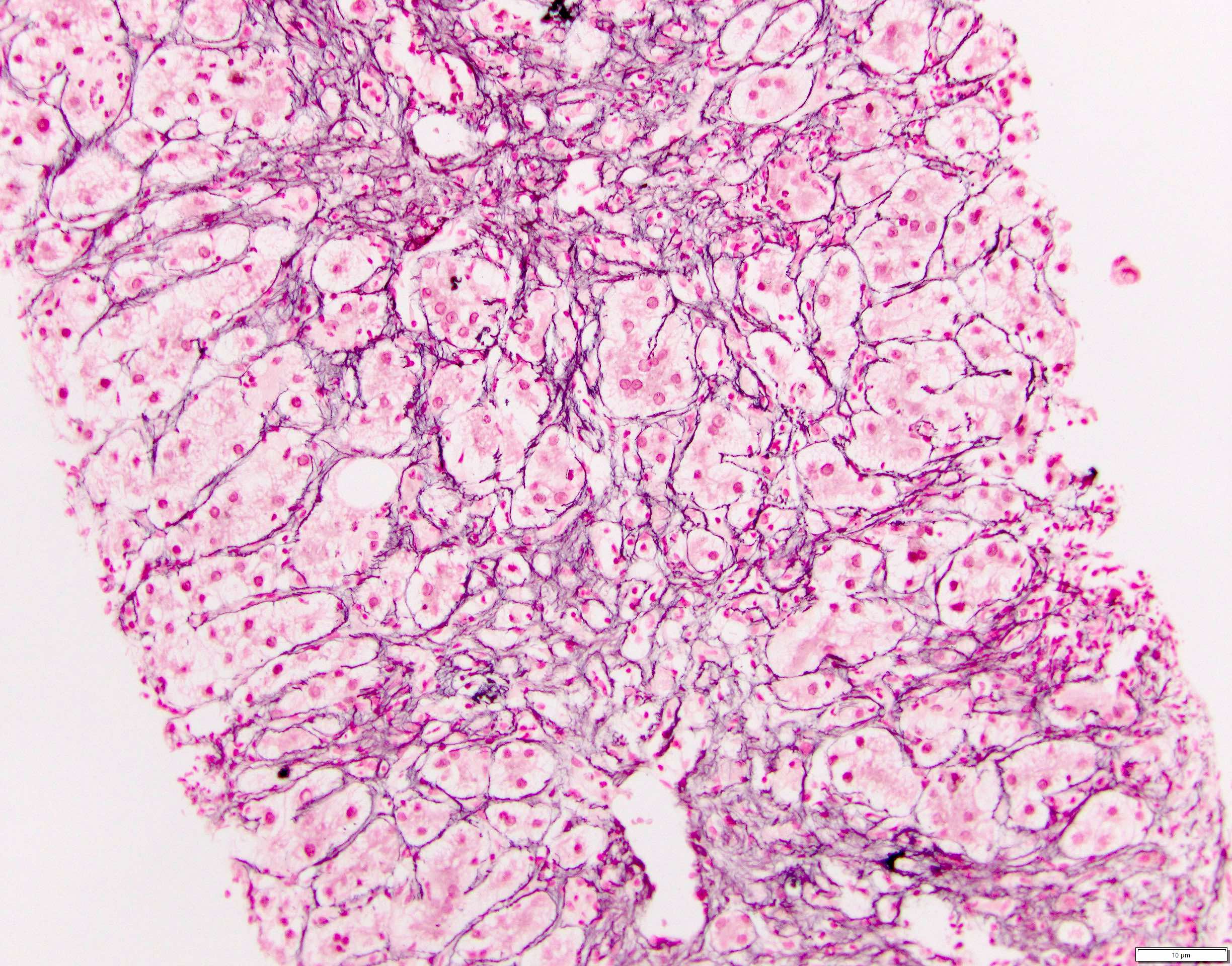
- Reticulin stain is useful in the early stage to evaluate for parenchymal loss (J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1989;27:345)
- HBsAG / HBcAG: double staining technology staining infected cells showing colocalization of the 2 antibodies
- Macrophages contain diastase periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive material (J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1989;27:345)
- Iron stain highlighting iron deposits within hepatocytes or macrophages
- Masson trichrome stain: stains increased collagen accumulation and is an indicator of fibrosis (Semin Diagn Pathol 2006;23:190, Coll Relat Res 1982;2:151)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, nontargeted, core needle biopsy:
- Moderate portal and lobular mononuclear inflammation comprised predominantly of lymphocytes and plasma cells (grade 2) compatible with hepatitis B infection (see comment)
- No steatosis, ballooning degeneration or intracytoplasmic hyaline seen
- Iron stain shows minimal iron deposition in hepatocytes
- Trichrome stain shows no fibrosis
- Reticulin stain highlights unremarkable hepatic cell plates
- Comment: The findings are consistent with the patient's known viral (hepatitis B) infection with grade 2 inflammatory activity and stage 0 fibrosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Histologic findings in both acute and chronic hepatitis B may be essentially indistinguishable from other etiologies of acute and chronic hepatitis listed in this section; serologic studies are generally required to establish the diagnosis
- Also, IHC for HBs and HBc can be helpful when the patient has known HBV but it is not clear if the current liver injury is due primarily to active HBV or to another etiology like autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) or drug injury
- Hepatitis C:
- Dense portal lymphocytic infiltrate, including lymphoid follicles with germinal centers (Hepatology 1992;15:572)
- Lobular inflammation is seen in chronic infection
- Steatosis (predominantly macrovesicular with patchy pattern) and bile duct damage (Hepatology 1992;15:572)
- Autoimmune hepatitis:
- Plasma cells in clusters at limiting plate and in areas of interface hepatitis (nonspecific but suggestive) (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:255)
- Piecemeal necrosis (Hepatology 1992;15:572)
- Hepatocellular rosettes (nonspecific) (Histopathology 2015;66:351)
- Syncytial multinucleated hepatocyte giant cells (Ann Hepatol 2009;8:68)
- Drug induced hepatotoxicity:
- Hepatotoxicity can mimic almost every other type of liver disease
- Dense interface / lobular lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and hepatocellular injury
- Prominent eosinophilic infiltrate
- Centrizonal necrosis is highly suggestive of drug induced liver injury
- Wilson disease:
- Steatosis and periportal glycogenated nuclei (Am J Clin Pathol 1994;102:443)
- Perinuclear and intracytoplasmic Mallory-Denk bodies in periportal liver cells (Lancet 1979;1:1205)
- Copper storage within periportal hepatocytes
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency:
- Predominantly lymphocytic portal inflammation
- Eosinophilic ground glass globules, negative / weakly positive on PASD (Hum Pathol 2000;31:575)
- Cirrhosis is usually present at diagnosis
- Steatosis and mild cholestasis may be present
Additional references
Practice question #1
Hepatitis B has the strongest association with development of which of the following malignancies?
- Angiosarcoma of the liver
- Hepatoblastoma
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Practice answer #1
C. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus has been established as a major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma and there is a strong correlation between the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and endemic hepatitis B virus infection worldwide (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1986;83:8338, J Hepatol 2012;57:69, J Clin Gastroenterol 2013;47:S2, J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97:265).
Answer D is incorrect because although recent studies suggest that hepatitis B virus infection plays an important etiological role in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) development, ICC is much less common than hepatocellular carcinoma (World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:5721, J Hepatol 2020;72:95). Answer A is incorrect because angiosarcoma of the liver is a rare type of liver cancer predominantly associated with arsenic and vinyl chloride monomer as causal agents (BMC Gastroenterol 2011;11:142). Answer B is incorrect because although hepatoblastoma should be considered among the differential diagnoses in young patients presenting with HBV infection without cirrhosis, HBV is not a risk factor for hepatoblastoma (World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:3980, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2005;6:213).
Comment Here
Reference: Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Answer D is incorrect because although recent studies suggest that hepatitis B virus infection plays an important etiological role in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) development, ICC is much less common than hepatocellular carcinoma (World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:5721, J Hepatol 2020;72:95). Answer A is incorrect because angiosarcoma of the liver is a rare type of liver cancer predominantly associated with arsenic and vinyl chloride monomer as causal agents (BMC Gastroenterol 2011;11:142). Answer B is incorrect because although hepatoblastoma should be considered among the differential diagnoses in young patients presenting with HBV infection without cirrhosis, HBV is not a risk factor for hepatoblastoma (World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:3980, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2005;6:213).
Comment Here
Reference: Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Practice question #2
A 63 year old man with a longstanding history of hepatitis B presents with FibroScan results consistent with moderate liver fibrosis. A liver biopsy is performed and is shown above. Which of the following is true regarding this patient's histologic evaluation for hepatitis B infected hepatocytes?
- Diffuse nuclear expression of HBsAg suggests active viral replication
- Finely granular intranuclear eosinophilic inclusions known as sanded nuclei correspond to HBsAg accumulation in hepatitis B infected hepatocytes
- Ground glass hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B infection consist of endoplasmic reticulum hyperplasia HBsAg in chronic carriers
- Variation in size and cytology of hepatocyte nuclei can be present and the chronic intralobular inflammatory infiltrate associated with chronic hepatitis B consists of CD4+ lymphocytes
Practice answer #2
C. Ground glass hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B infection consist of endoplasmic reticulum hyperplasia HBsAg in chronic carriers, which can be highlighted with Victoria blue special stain (Hepatology 2009;49:S61, Jpn J Exp Med 1974;44:25).
Answer B is incorrect because sanded nuclei in a persistent hepatitis B virus infection indicate excessive core formation and can be seen on H&E stain (Lab Invest 1976;35:1). Answer A is incorrect because while HBsAg expression can be membranous or cytoplasmic, HBcAg expression may be nuclear or cytoplasmic (Hepatology 2009;49:S61). Extensive nuclear membranous expression of HBcAg is associated with active viral replication and viral load (J Clin Gastroenterol 2003;36:269). Answer D is incorrect because the portal inflammatory infiltrate seen in hepatitis B is usually composed of CD4+ lymphocytes, B lymphocytes and dendritic cells. The intralobular inflammatory infiltrate is usually CD8+ (J Viral Hepat 2019;26:727).
Comment Here
Reference: Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Answer B is incorrect because sanded nuclei in a persistent hepatitis B virus infection indicate excessive core formation and can be seen on H&E stain (Lab Invest 1976;35:1). Answer A is incorrect because while HBsAg expression can be membranous or cytoplasmic, HBcAg expression may be nuclear or cytoplasmic (Hepatology 2009;49:S61). Extensive nuclear membranous expression of HBcAg is associated with active viral replication and viral load (J Clin Gastroenterol 2003;36:269). Answer D is incorrect because the portal inflammatory infiltrate seen in hepatitis B is usually composed of CD4+ lymphocytes, B lymphocytes and dendritic cells. The intralobular inflammatory infiltrate is usually CD8+ (J Viral Hepat 2019;26:727).
Comment Here
Reference: Hepatitis B virus (HBV)