Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Balakrishna J, Sharabi A.. Lipofuscin. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodeslipofuscin.html. Accessed August 27th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Common incidental finding
- Lipofuscin is a golden brown, finely granular pigment derived chiefly from the breakdown products of lipids, usually those derived from cell membranes
- Ceroid is a variant of lipofuscin that is acid fast and autofluorescent
Sites
- Portal lymph nodes and other nodes draining the liver
- Also in other lymph node groups
Pathophysiology
- Accumulation of lipofuscin in post mitotic cells by accretion of oxidized, cross linked proteins
- Conspicuous in conditions associated with atrophy of an organ
Etiology
- Various inflammatory, necrotic, neoplastic lesions, including chronic cholestatic lesions like primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis
Clinical features
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Prognostic factors
- Although previously thought to have no significance, there is increasing evidence that lipofuscin may both cause and be due to increased oxidant stress in cells and may impair proteasomal and lysosomal functions
Gross description
- Enlarged lymph nodes with brown pigment
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sinus histiocytosis with granular deposits of brown pigment in sinus macrophages
- Varying degrees of follicular hyperplasia
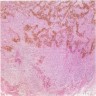
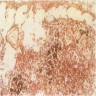
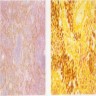
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Sudan Black B, Schmorl reaction, oil red O, carbol lipofuscin stain, periodic acid-Schiff, Ziehl-Neelsen acid fast stain, autofluorescence or the lysosomal acid phosphatase and esterase stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Membrane limited, electron dense, spherical inclusions
Differential diagnosis
- Iron / hemosiderin
- Melanin
- Tattoo pigment